CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON. Instructor: Rahul Nayar TAs: Mohit Verma, Annie Lin
|
|
|
- Avice Bates
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Instructor: Rahul Nayar TAs: Mohit Verma, Annie Lin Examination 4 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday, May 3rd, 2017 Weight: 17.5% NO BOOK(S), NOTE(S), CALCULATORS OR ELECTRONIC DEVICES OF ANY SORT. The exam has eleven pages. You must turn in the pages 1-9. Circle your final answers. Plan your time carefully since some problems are longer than others. Use the blank sides of the exam for scratch work. LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: ID#: 1
2 Problem Maximum Points Points Earned Total 32 2
3 1. The following LC-3 assembly code contains assembly syntax errors. Identify and fix at least 4 errors. (4 points).orig x3000 ADD R3, R3, ONE LD R5, STRING LOOP ADD R1, R1, #32 BRz LOOP MAIN LD R4, MAIN SUB R3, R3, #1 ST R3, STRING LOOP HALT ONE.FILL #1.BLKW 4.BLKW 3 STRING.STRINGZ "ABC".END.ORIG x3000 ADD R3, R3, ONE LD R5, STRING LOOP ADD R1, R1, #32 BRz LOOP MAIN LD R4, MAIN SUB R3, R3, #1 ST R3, STRING LOOP HALT ONE.FILL #1.BLKW 4.BLKW 3 STRING.STRINGZ "ABC".END 3
4 2. a) Fill in the symbol table for following LC-3 assembly code. You may not need to fill all rows. (5 points).orig x3000 AND R3, R3, #0 LD R4, VAL1 LOOP BRz EXIT JSR INC JSR DEC EXIT ST R3, ANS PUTS HALT INC ADD R3, R3, #1 RET DEC ADD R4, R4, #-1 RET ; Storage area for variables below: ANS.BLKW #5 VAL0.STRINGZ "252" VAL1.STRINGZ "CS".END SYMBOL LOOP EXIT INC DEC ANS VAL0 VAL1 Value (in hex) 0x3002 0x3005 0x3008 0x300A 0x300C 0x3011 0x3015 b) Convert the instruction stored at memory location 0x3006 into binary. 0xF022 (TRAP x22) 4
5 3. An LC-3 assembly code is given below: (5 points).orig x3000 AND R0, R0, #0 LD R0, DATA ADD R0, R0, #11 PRINT1 OUT AND R0, R0, #0 ADD R0, R7, R0 PRINT2 OUT HALT DATA.FILL 0xFFFF a. What is the output (in hex) after the OUT statement at the symbol PRINT1 finishes execution? 0x000A b. What is the output (in hex) after the OUT statement at the symbol PRINT2 finishes execution? Explain your answer. 0x3004 c. Complete the following incomplete code snippet that uses the memory-mapped LC-3 registers KBSR and KBDR to take input from the keyboard instead of the GETC instruction. Your code should store the value entered from keyboard in register R3. (Assume KBSR is mapped to address xfe00 and KBDR is mapped to address xfe02.) ECHO:,, KBSR, R3, KBDR KBSR KBDR.FILL xfe00.fill xfe02 ECHO: LDI, R0, KBSR BRnp ECHO LDI, R2, KBDR KBSR.FILL xfe00 KBDR.FILL xfe02 5
6 4. Short answer questions (5 points) a. Briefly describe what happens in the linking phase of an assembly program. Linking is resolving symbols between independent object files. b. How are the Display Data Register (DDR) and Display Status Register (DSR) used when TRAP x21 (OUT) is called? When the monitor is ready to display another character, DSR[15] is set to 1. DSR[7:0] is displayed and DSR[15] is set to 1. Any other data written to DDR is ignored while DSR[15] is zero. c. What is a service routine in LC-3? Give an example. A service routine is a function that performs a specific operation (optionally as part of the operating system). In LC-3, traps are service routines. Any trap will work here as an example. d. Briefly describe the difference between synchronous and asynchronous I/O. Synchronous I/O events occur at fixed, predictable rates. CPU reads every X seconds. Asynchronous I/O is unpredictable. Can use flag to achieve I/O. Example is keyboard input. 6
7 5. The following LC-3 assembly code implements a subroutine. After taking input, it outputs a lowercase letter (a-z) if the input was uppercase (A-Z), and a N otherwise. (5 points) SUBR GETC ADD R5, R0, 0 NOT R5, R5 ADD R5, R5, 1 LD R1, LBOUND LD R2, UBOUND ADD R3, R5, R2 BRn PNOT ADD R3, R5, R1 BRp PNOT LD R3, DIFF ADD R0, R0, R3 OUT BRnzp FINISH PNOT LD R0, N OUT FINISH RET UBOUND.FILL x5a ;ASCII value of "Z" LBOUND.FILL x41 ;ASCII value of "A" N.FILL x4e ;ASCII value of "N" DIFF.FILL x20 a. Is this code able to successfully return? Explain why or why not. No. R7 is overwritten by GETC and OUT. b. Add lines to the code above to make this subroutine callee-saved. You should not modify any existing lines. Clearly indicate which lines you have added and where. Before GETC: ST R0, SAVE0 ST R1, SAVE1 ST R2, SAVE2 7
8 ST R3, SAVE3 ST R5, SAVE5 ST R7, SAVE7 Before FINISH: LD R0, SAVE0 LD R1, SAVE1 LD R2, SAVE2 LD R3, SAVE3 LD R5, SAVE5 LD R7, SAVE7 After DIFF SAVE0.FILL x0 SAVE1.FILL x0 SAVE2.FILL x0 SAVE3.FILL x0 SAVE5.FILL x0 SAVE7.FILL x0 8
9 6. Examine the code below. You may assume that at the start of the program, all registers are set to 0. (4 points).orig x3000 GETC AND R3, R3, 0 ADD R3, R3, R0 LD R1, ONE NOT R1, R1 ADD R1, R1, 1 PRINT LD R0, C OUT LD R0, A OUT LD R0, T OUT ADD R0, R3, R1 BRz FINISH LD R0, S OUT FINISH HALT C.FILL x63 ; ASCII 'c' A.FILL x61 ; ASCII 'a' T.FILL x74 ; ASCII 't' S.FILL x73 ; ASCII 's' ONE.FILL x31 ; ASCII '1' a. If the input is the decimal number "3", what is output on the screen at the end of the program? cats b. OUT only prints out one character at a time. Instead of printing individually, we decide to replace the code stored at memory locations x3006 to x300b with the following, much shorter block of code: PRINT LD R0, C PUTS Will this output the same result as a)? Why or why not? You must explain your answer for credit. No. It'll output a bunch of garbage (whatever is stored at memory location x63 until it hits a null terminator). This is because PUTS uses the register value as an address, not as a value. 9
10 7. Multiple choice questions. Circle one answer for each question. (4 points) (i) Which of the following can not be used multiple times in a single assembly program? a).blkw b).fill c).orig d).stringz (ii) Assume that a LC-3 processor receives interrupts from 3 I/O devices (A, B and C) simultaneously. The priority levels for the interrupts are given below: A) PL0 B) PL7 C) PL6 Assuming that no other interrupts come in, which of the above interrupts is serviced last? a) A b) B c) C d) Any selected at random (iii) Our program begins at memory location x4000. We want to load the value x4020 into R3. Which LC-3 instruction can we use to accomplish this in a single line? a) LD b) LEA c) LDI d) ST (iv) Which register is used to store input data after IN is called? a) R7 b) R4 c) R1 d) R0 10
11 LC-3 Instruction Set (Entered by Mark D. Hill on 03/14/2007; last update 03/15/2007) PC : incremented PC. setcc(): set condition codes N, Z, and P. mem[a]:memory contents at address A. SEXT(immediate): sign-extend immediate to 16 bits. ZEXT(immediate): zero-extend immediate to 16 bits ADD DR, SR1, SR2 ; Addition DR SR SR DR SR1 + SR2 also setcc() ADD DR, SR1, imm5 ; Addition with Immediate DR SR1 1 imm DR SR1 + SEXT(imm5) also setcc() AND DR, SR1, SR2 ; Bit-wise AND DR SR SR DR SR1 AND SR2 also setcc() AND DR,SR1,imm5 ; Bit-wise AND with Immediate DR SR1 1 imm DR SR1 AND SEXT(imm5) also setcc() BRx,label (where x={n,z,p,zp,np,nz,nzp}); Branch n z p PCoffset9 GO ((n and N) OR (z AND Z) OR (p AND P)) if(go is true) then PC PC + SEXT(PCoffset9) JMP BaseR ; Jump BaseR PC BaseR JSR label ; Jump to Subroutine PCoffset R7 PC, PC PC + SEXT(PCoffset11) JSRR BaseR ; Jump to Subroutine in Register BaseR temp PC, PC BaseR, R7 temp LD DR, label ; Load PC-Relative DR PCoffset DR mem[pc + SEXT(PCoffset9)] also setcc() LDI DR, label ; Load Indirect DR PCoffset DR mem[mem[pc +SEXT(PCoffset9)]] also setcc() LDR DR, BaseR, offset6 ; Load Base+Offset DR BaseR offset DR mem[baser + SEXT(offset6)] also setcc() LEA, DR, label ; Load Effective Address DR PCoffset DR PC + SEXT(PCoffset9) also setcc() NOT DR, SR ; Bit-wise Complement DR SR DR NOT(SR) also setcc() RET ; Return from Subroutine PC R RTI ; Return from Interrupt See textbook (2 nd Ed. page 537) ST SR, label ; Store PC-Relative SR PCoffset mem[pc + SEXT(PCoffset9)] SR STI, SR, label ; Store Indirect SR PCoffset mem[mem[pc + SEXT(PCoffset9)]] SR STR SR, BaseR, offset6 ; Store Base+Offset SR BaseR offset mem[baser + SEXT(offset6)] SR TRAP ; System Call trapvect R7 PC, PC mem[zext(trapvect8)] ; Unused Opcode Initiate illegal opcode exception
12 Assembler Directives Trap Codes 12
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi, Kai Zhao TAs: Yuzhe Ma, Annie Lin, Mohit Verma, Neha Mittal, Daniel Griffin, Examination 4 In Class
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi, Kai Zhao TAs: Yuzhe Ma, Annie Lin, Mohit Verma, Neha Mittal, Daniel Griffin, Examination 4 In Class
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Professor Guri Sohi TAs: Newsha Ardalani and Rebecca Lam Examination 4 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday, Dec 14, 2011 Weight:
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Professor Guri Sohi TAs: Newsha Ardalani and Rebecca Lam Examination 4 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday, Dec 14, 2011 Weight:
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON. Instructor: Rahul Nayar TAs: Annie Lin, Mohit Verma
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Instructor: Rahul Nayar TAs: Annie Lin, Mohit Verma Examination 2 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday, March 8, 207 Weight:
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Instructor: Rahul Nayar TAs: Annie Lin, Mohit Verma Examination 2 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday, March 8, 207 Weight:
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Professor Karthikeyan Sankaralingam TAs: Kamlesh Prakash, Suriyha Balaram Sankari, Rebecca Lam, Newsha Ardalani, and Yinggang
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Professor Karthikeyan Sankaralingam TAs: Kamlesh Prakash, Suriyha Balaram Sankari, Rebecca Lam, Newsha Ardalani, and Yinggang
ECE/CS 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 ECE/CS 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Mikko Lipasti & Prof. Gurindar S. Sohi TAs: Felix Loh, Daniel Chang, Philip Garcia, Sean Franey, Vignyan Kothinti
ECE/CS 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Mikko Lipasti & Prof. Gurindar S. Sohi TAs: Felix Loh, Daniel Chang, Philip Garcia, Sean Franey, Vignyan Kothinti
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Junaid Khalid and Pradip Vallathol Midterm Examination 3 In Class (50 minutes) Friday, November
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Junaid Khalid and Pradip Vallathol Midterm Examination 3 In Class (50 minutes) Friday, November
UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Lisa Ossian, Minsub Shin, Sujith Surendran Midterm Examination 3 In Class (50 minutes) Friday,
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Lisa Ossian, Minsub Shin, Sujith Surendran Midterm Examination 3 In Class (50 minutes) Friday,
ECE/CS 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 ECE/CS 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Mikko Lipasti & Prof. Gurindar S. Sohi TAs: Felix Loh, Daniel Chang, Philip Garcia, Sean Franey, Vignyan Kothinti
ECE/CS 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Mikko Lipasti & Prof. Gurindar S. Sohi TAs: Felix Loh, Daniel Chang, Philip Garcia, Sean Franey, Vignyan Kothinti
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Pradip Vallathol and Junaid Khalid Examination 4 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday, December 12,
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Pradip Vallathol and Junaid Khalid Examination 4 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday, December 12,
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Mikko Lipasti & Prof. Gurinder S. Sohi TAs: Daniel Chang, Felix Loh, Philip Garcia, Sean Franey, Vignyan Kothinti
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Mikko Lipasti & Prof. Gurinder S. Sohi TAs: Daniel Chang, Felix Loh, Philip Garcia, Sean Franey, Vignyan Kothinti
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON Prof. Mark D. Hill & Prof. Mikko H. Lipasti TAs Sanghamitra Roy, Eric Hill, Samuel Javner,
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON Prof. Mark D. Hill & Prof. Mikko H. Lipasti TAs Sanghamitra Roy, Eric Hill, Samuel Javner,
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON Prof. Mark D. Hill & Prof. Mikko H. Lipasti TAs Sanghamitra Roy, Eric Hill, Samuel Javner,
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON Prof. Mark D. Hill & Prof. Mikko H. Lipasti TAs Sanghamitra Roy, Eric Hill, Samuel Javner,
appendix a The LC-3 ISA A.1 Overview
 A.1 Overview The Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) of the LC-3 is defined as follows: Memory address space 16 bits, corresponding to 2 16 locations, each containing one word (16 bits). Addresses are numbered
A.1 Overview The Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) of the LC-3 is defined as follows: Memory address space 16 bits, corresponding to 2 16 locations, each containing one word (16 bits). Addresses are numbered
Trap Vector Table. Interrupt Vector Table. Operating System and Supervisor Stack. Available for User Programs. Device Register Addresses
 Chapter 1 The LC-3b ISA 1.1 Overview The Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) of the LC-3b is defined as follows: Memory address space 16 bits, corresponding to 2 16 locations, each containing one byte (8
Chapter 1 The LC-3b ISA 1.1 Overview The Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) of the LC-3b is defined as follows: Memory address space 16 bits, corresponding to 2 16 locations, each containing one byte (8
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof Mark D. Hill and Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Rebecca Lam, Mona Jalal, Preeti Agarwal, Pradip Vallathol Midterm Examination
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof Mark D. Hill and Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Rebecca Lam, Mona Jalal, Preeti Agarwal, Pradip Vallathol Midterm Examination
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON. Instructor: Rahul Nayar TAs: Annie Lin, Mohit Verma
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Instructor: Rahul Nayar TAs: Annie Lin, Mohit Verma Examination 3 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday, April 7, 2017 Weight:
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Instructor: Rahul Nayar TAs: Annie Lin, Mohit Verma Examination 3 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday, April 7, 2017 Weight:
UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Sujith Surendran, Lisa Ossian, Minsub Shin Midterm Examination 4 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday,
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi TAs: Sujith Surendran, Lisa Ossian, Minsub Shin Midterm Examination 4 In Class (50 minutes) Wednesday,
Register Files. Single Bus Architecture. Register Files. Single Bus Processor. Term Project: using VHDL. Accumulator based architecture
 Register Files DR 3 SelS Design and simulate the LC-3 processor using VHDL Term Project: Single Processor Decoder... R R3 R6...... mux mux S S SelDR 3 DRin Clock 3 SelS LC-3 Architecture 3 Register File
Register Files DR 3 SelS Design and simulate the LC-3 processor using VHDL Term Project: Single Processor Decoder... R R3 R6...... mux mux S S SelDR 3 DRin Clock 3 SelS LC-3 Architecture 3 Register File
LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture. Textbook Chapter 5
 LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture Textbook Chapter 5 Instruction set architecture What is an instruction set architecture (ISA)? It is all of the programmer-visible components and operations of the computer
LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture Textbook Chapter 5 Instruction set architecture What is an instruction set architecture (ISA)? It is all of the programmer-visible components and operations of the computer
LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture
 CMPE12 Notes LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture (Textbookʼs Chapter 5 and 6)# Instruction Set Architecture# ISA is all of the programmer-visible components and operations of the computer.# memory organization#
CMPE12 Notes LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture (Textbookʼs Chapter 5 and 6)# Instruction Set Architecture# ISA is all of the programmer-visible components and operations of the computer.# memory organization#
Introduction to Computer Engineering. CS/ECE 252, Spring 2017 Rahul Nayar Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Spring 2017 Rahul Nayar Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 8 & 9.1 I/O and Traps Aside Off-Topic: Memory Hierarchy 8-3
Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Spring 2017 Rahul Nayar Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 8 & 9.1 I/O and Traps Aside Off-Topic: Memory Hierarchy 8-3
CIT 593: Intro to Computer Systems Homework #4: Assembly Language Due October 18, 2012, 4:30pm. Name
 CIT 593: Intro to Computer Systems Homework #4: Assembly Language Due October 18, 2012, 4:30pm Instructions You may print this document and write your answers here, or submit solutions on a separate piece
CIT 593: Intro to Computer Systems Homework #4: Assembly Language Due October 18, 2012, 4:30pm Instructions You may print this document and write your answers here, or submit solutions on a separate piece
CS 135: Computer Architecture I
 What next? : Computer Architecture I Instructor: Prof. Bhagi Narahari Dept. of Computer Science Course URL: www.seas.gwu.edu/~bhagiweb/cs135/ Low level/machine-level Programming Assembly Language programming
What next? : Computer Architecture I Instructor: Prof. Bhagi Narahari Dept. of Computer Science Course URL: www.seas.gwu.edu/~bhagiweb/cs135/ Low level/machine-level Programming Assembly Language programming
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON Prof. Mark D. Hill & Prof. Parmesh Ramanathan TAs Kasturi Bidarkar, Ryan Johnson, Jie Liu,
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON Prof. Mark D. Hill & Prof. Parmesh Ramanathan TAs Kasturi Bidarkar, Ryan Johnson, Jie Liu,
Midterm 2 Review Chapters 4-16 LC-3
 Midterm 2 Review Chapters 4-16 LC-3 ISA You will be allowed to use the one page summary. 8-2 LC-3 Overview: Instruction Set Opcodes 15 opcodes Operate instructions: ADD, AND, NOT Data movement instructions:
Midterm 2 Review Chapters 4-16 LC-3 ISA You will be allowed to use the one page summary. 8-2 LC-3 Overview: Instruction Set Opcodes 15 opcodes Operate instructions: ADD, AND, NOT Data movement instructions:
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON Prof. Mark D. Hill & Prof. Parmesh Ramanathan TAs Kasturi Bidarkar, Ryan Johnson, Jie Liu,
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING COMPUTER SCIENCES DEPARTMENT UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MADISON Prof. Mark D. Hill & Prof. Parmesh Ramanathan TAs Kasturi Bidarkar, Ryan Johnson, Jie Liu,
LC-3 ISA - II. Lecture Topics. Lecture materials. Homework. Machine problem. Announcements. ECE 190 Lecture 10 February 17, 2011
 LC- ISA - II Lecture Topics LC- data movement instructions LC- control instructions LC- data path review Lecture materials Textbook 5. - 5.6 Textbook Appendix A. Homework HW due Wednesday February 2 at
LC- ISA - II Lecture Topics LC- data movement instructions LC- control instructions LC- data path review Lecture materials Textbook 5. - 5.6 Textbook Appendix A. Homework HW due Wednesday February 2 at
Lab 1. Warm-up : discovering the target machine, LC-3
 Lab 1 Warm-up : discovering the target machine, LC-3 Credits This sequence of compilation labs has been inspired by those designed by C. Alias and G. Iooss in 2013/14. In 2016/17 we changed the support
Lab 1 Warm-up : discovering the target machine, LC-3 Credits This sequence of compilation labs has been inspired by those designed by C. Alias and G. Iooss in 2013/14. In 2016/17 we changed the support
The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture. ISA Overview Operate instructions Data Movement instructions Control Instructions LC-3 data path
 Chapter 5 The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture ISA Overview Operate instructions Data Movement instructions Control Instructions LC-3 data path A specific ISA: The LC-3 We have: Reviewed data encoding
Chapter 5 The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture ISA Overview Operate instructions Data Movement instructions Control Instructions LC-3 data path A specific ISA: The LC-3 We have: Reviewed data encoding
Memory Usage in Programs
 Memory Usage in Programs ECE2893 Lecture 4a ECE2893 Memory Usage in Programs Spring 2011 1 / 17 The Little Computer 3 (LC3) ECE2893 Memory Usage in Programs Spring 2011 2 / 17 The LC3 Instruction Set,
Memory Usage in Programs ECE2893 Lecture 4a ECE2893 Memory Usage in Programs Spring 2011 1 / 17 The Little Computer 3 (LC3) ECE2893 Memory Usage in Programs Spring 2011 2 / 17 The LC3 Instruction Set,
20/08/14. Computer Systems 1. Instruction Processing: FETCH. Instruction Processing: DECODE
 Computer Science 210 Computer Systems 1 Lecture 11 The Instruction Cycle Ch. 5: The LC-3 ISA Credits: McGraw-Hill slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University Instruction Processing:
Computer Science 210 Computer Systems 1 Lecture 11 The Instruction Cycle Ch. 5: The LC-3 ISA Credits: McGraw-Hill slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University Instruction Processing:
CS 2461: Computer Architecture I
 Computer Architecture is... CS 2461: Computer Architecture I Instructor: Prof. Bhagi Narahari Dept. of Computer Science Course URL: www.seas.gwu.edu/~bhagiweb/cs2461/ Instruction Set Architecture Organization
Computer Architecture is... CS 2461: Computer Architecture I Instructor: Prof. Bhagi Narahari Dept. of Computer Science Course URL: www.seas.gwu.edu/~bhagiweb/cs2461/ Instruction Set Architecture Organization
Introduction to Computer Engineering. CS/ECE 252, Spring 2017 Rahul Nayar Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Spring 2017 Rahul Nayar Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 7 & 9.2 Assembly Language and Subroutines Human-Readable Machine
Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Spring 2017 Rahul Nayar Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 7 & 9.2 Assembly Language and Subroutines Human-Readable Machine
Introduction to Computer Engineering. CS/ECE 252, Fall 2012 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Fall 2012 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 8 & 9.1 I/O and Traps I/O: Connecting to Outside World So
Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Fall 2012 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 8 & 9.1 I/O and Traps I/O: Connecting to Outside World So
LC-2 Programmer s Reference and User Guide
 LC-2 Programmer s Reference and User Guide University of Michigan EECS 100 Matt Postiff Copyright (C) Matt Postiff 1995-1999. All rights reserved. Written permission of the author is required for duplication
LC-2 Programmer s Reference and User Guide University of Michigan EECS 100 Matt Postiff Copyright (C) Matt Postiff 1995-1999. All rights reserved. Written permission of the author is required for duplication
Ch. 5: The LC-3. PC-Relative Addressing Mode. Data Movement Instructions. James Goodman!
 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ADD + 0001 1 0 00 2 Computer Science 210 s1c Computer Systems 1 2012 Semester 1 Lecture Notes ADD + AND + AND + BR JMP 0001 1 1 imm5 0101 1 0 00 2 0101 1 1 imm5 0000
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ADD + 0001 1 0 00 2 Computer Science 210 s1c Computer Systems 1 2012 Semester 1 Lecture Notes ADD + AND + AND + BR JMP 0001 1 1 imm5 0101 1 0 00 2 0101 1 1 imm5 0000
10/31/2016. The LC-3 ISA Has Three Kinds of Opcodes. ECE 120: Introduction to Computing. ADD and AND Have Two Addressing Modes
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 120: Introduction to Computing The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture The LC-3 ISA Has Three Kinds of Opcodes
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 120: Introduction to Computing The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture The LC-3 ISA Has Three Kinds of Opcodes
ECE 411 Exam 1. This exam has 5 problems. Make sure you have a complete exam before you begin.
 This exam has 5 problems. Make sure you have a complete exam before you begin. Write your name on every page in case pages become separated during grading. You will have three hours to complete this exam.
This exam has 5 problems. Make sure you have a complete exam before you begin. Write your name on every page in case pages become separated during grading. You will have three hours to complete this exam.
Instruction Set Architecture
 Chapter 5 The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture ISA = All of the programmer-visible components and operations of the computer memory organization address space -- how may locations can be addressed? addressibility
Chapter 5 The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture ISA = All of the programmer-visible components and operations of the computer memory organization address space -- how may locations can be addressed? addressibility
Introduction to Computer Engineering. Chapter 5 The LC-3. Instruction Set Architecture
 Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Spring 200 Prof. David A. Wood Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 5 The LC-3 Adapted from Prof. Mark Hill s slides Instruction
Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Spring 200 Prof. David A. Wood Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 5 The LC-3 Adapted from Prof. Mark Hill s slides Instruction
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign First Midterm Exam, ECE 220 Honors Section
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign First Midterm Exam, ECE 220 Honors Section Name: SOLUTION IS IN RED Thursday 15 February 2018 Net ID: Be sure that your exam booklet has ELEVEN pages. Write your
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign First Midterm Exam, ECE 220 Honors Section Name: SOLUTION IS IN RED Thursday 15 February 2018 Net ID: Be sure that your exam booklet has ELEVEN pages. Write your
Introduction to Computer Engineering. CS/ECE 252, Fall 2016 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Fall 2016 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 5 The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture ISA = All of the
Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Fall 2016 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 5 The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture ISA = All of the
LC-3. 3 bits for condition codes (more later) Fixed-length instructions, with 4-bit opcodes. IIT CS 350 S 18- Hale
 LC-3 (Little computer version 3) 16-bit address width, 16-bit addressability. (Word size is 16 bits) 65K possible memory addresses Signed integers are 2 s complement 8 General purpose registers (GPRs),
LC-3 (Little computer version 3) 16-bit address width, 16-bit addressability. (Word size is 16 bits) 65K possible memory addresses Signed integers are 2 s complement 8 General purpose registers (GPRs),
Introduction to Computer Engineering. CS/ECE 252, Spring 2017 Rahul Nayar Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Spring 2017 Rahul Nayar Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 5 The LC-3 Announcements Homework 3 due today No class on Monday
Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Spring 2017 Rahul Nayar Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 5 The LC-3 Announcements Homework 3 due today No class on Monday
LC-3 Subroutines and Traps. (Textbook Chapter 9)"
 LC-3 Subroutines and Traps (Textbook Chapter 9)" Subroutines" Blocks can be encoded as subroutines" A subroutine is a program fragment that:" lives in user space" performs a well-defined task" is invoked
LC-3 Subroutines and Traps (Textbook Chapter 9)" Subroutines" Blocks can be encoded as subroutines" A subroutine is a program fragment that:" lives in user space" performs a well-defined task" is invoked
Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines
 Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines System Calls Certain operations require specialized knowledge and protection: specific knowledge of I/O device registers and the sequence of operations needed to
Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines System Calls Certain operations require specialized knowledge and protection: specific knowledge of I/O device registers and the sequence of operations needed to
Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines
 Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines System Calls Certain operations require specialized knowledge and protection: specific knowledge of I/O device registers and the sequence of operations needed to
Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines System Calls Certain operations require specialized knowledge and protection: specific knowledge of I/O device registers and the sequence of operations needed to
Logistics. IIT CS 350 S '17 - Hale
 Logistics Remember: Lab 5 due next week not this week. Finish it early though so you can move on to Lab 6! Lab 2 grades in BB Required reading posted (Patt & Patel Ch. 5) First exam during class next Wednesday
Logistics Remember: Lab 5 due next week not this week. Finish it early though so you can move on to Lab 6! Lab 2 grades in BB Required reading posted (Patt & Patel Ch. 5) First exam during class next Wednesday
Intro. to Computer Architecture Homework 4 CSE 240 Autumn 2005 DUE: Mon. 10 October 2005
 Name: 1 Intro. to Computer Architecture Homework 4 CSE 24 Autumn 25 DUE: Mon. 1 October 25 Write your answers on these pages. Additional pages may be attached (with staple) if necessary. Please ensure
Name: 1 Intro. to Computer Architecture Homework 4 CSE 24 Autumn 25 DUE: Mon. 1 October 25 Write your answers on these pages. Additional pages may be attached (with staple) if necessary. Please ensure
Introduction to Computer Engineering. CS/ECE 252, Fall 2016 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Fall 2016 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 7 & 9.2 Assembly Language and Subroutines Human-Readable
Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Fall 2016 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 7 & 9.2 Assembly Language and Subroutines Human-Readable
Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines
 Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 5-2 System Calls Certain operations require specialized knowledge
Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 5-2 System Calls Certain operations require specialized knowledge
Subroutines & Traps. Announcements. New due date for assignment 2 5pm Wednesday, 5May
 Computer Science 210 s1c Computer Systems 1 2010 Semester 1 Lecture Notes Lecture 19, 26Apr10: Subroutines & Traps James Goodman! Announcements New due date for assignment 2 5pm Wednesday, 5May Test is
Computer Science 210 s1c Computer Systems 1 2010 Semester 1 Lecture Notes Lecture 19, 26Apr10: Subroutines & Traps James Goodman! Announcements New due date for assignment 2 5pm Wednesday, 5May Test is
LC-3 TRAP Routines. Textbook Chapter 9
 LC-3 TRAP Routines Textbook Chapter 9 System Calls Certain operations require specialized knowledge and protection: specific knowledge of I/O device registers and the sequence of operations needed to use
LC-3 TRAP Routines Textbook Chapter 9 System Calls Certain operations require specialized knowledge and protection: specific knowledge of I/O device registers and the sequence of operations needed to use
COSC121: Computer Systems: Review
 COSC121: Computer Systems: Review Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Constructed using materials: - Patt and Patel Introduction to Computing Systems (2nd) - Patterson and Hennessy Computer
COSC121: Computer Systems: Review Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Constructed using materials: - Patt and Patel Introduction to Computing Systems (2nd) - Patterson and Hennessy Computer
System Calls. Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines
 System Calls Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Certain operations require
System Calls Chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Certain operations require
TRAPs and Subroutines. University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell
 TRAPs and Subroutines University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell System Calls Certain operations require specialized knowledge and protection: specific knowledge
TRAPs and Subroutines University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell System Calls Certain operations require specialized knowledge and protection: specific knowledge
EEL 5722C Field-Programmable Gate Array Design
 EEL 5722C Field-Programmable Gate Array Design Lecture 12: Pipelined Processor Design and Implementation Prof. Mingjie Lin Patt and Patel: Intro. to Computing System * Stanford EE271 notes 1 Instruction
EEL 5722C Field-Programmable Gate Array Design Lecture 12: Pipelined Processor Design and Implementation Prof. Mingjie Lin Patt and Patel: Intro. to Computing System * Stanford EE271 notes 1 Instruction
Introduction to Computer. Chapter 5 The LC-3. Instruction Set Architecture
 Introduction to Computer Engineering ECE/CS 252, Fall 2010 Prof. Mikko Lipasti Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 5 The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture
Introduction to Computer Engineering ECE/CS 252, Fall 2010 Prof. Mikko Lipasti Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 5 The LC-3 Instruction Set Architecture
ECE 109 Sections 602 to 605 Final exam Fall December, 2007
 ECE 109 Sections 602 to 605 Final exam Fall 2007 13 December, 2007 This is a closed book and closed notes exam. Calculators, PDA's, cell phones, and any other electronic or communication devices may not
ECE 109 Sections 602 to 605 Final exam Fall 2007 13 December, 2007 This is a closed book and closed notes exam. Calculators, PDA's, cell phones, and any other electronic or communication devices may not
Chapter 5 - ISA. 1.The Von Neumann Model. The Stored Program Computer. Von Neumann Model. Memory
 Chapter 5 - ISA 1.The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atanasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program
Chapter 5 - ISA 1.The Von Neumann Model The Stored Program Computer 1943: ENIAC Presper Eckert and John Mauchly -- first general electronic computer. (or was it John V. Atanasoff in 1939?) Hard-wired program
Input & Output. Lecture 16. James Goodman (revised by Robert Sheehan) Computer Science 210 s1c Computer Systems 1 Lecture Notes
 Computer Science 210 s1c Computer Systems 1 Lecture Notes Lecture 16 Input & Output James Goodman (revised by Robert Sheehan) Credits: Slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University
Computer Science 210 s1c Computer Systems 1 Lecture Notes Lecture 16 Input & Output James Goodman (revised by Robert Sheehan) Credits: Slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University
Chapter 5 The LC-3. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 5-2
 Chapter 5 The LC-3 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 5-2 Instruction Set Architecture ISA = All of the programmer-visible components
Chapter 5 The LC-3 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 5-2 Instruction Set Architecture ISA = All of the programmer-visible components
ECE Homework 8
 ECE 252 - Homework 8 Written (problems 1 & 2) Due in Discussion Wed Dec. 7 th Code (problem 3) Due Thurs. Dec 8 th at Midnight (11:59 PM) Instructions: You should do this homework in your group assigned
ECE 252 - Homework 8 Written (problems 1 & 2) Due in Discussion Wed Dec. 7 th Code (problem 3) Due Thurs. Dec 8 th at Midnight (11:59 PM) Instructions: You should do this homework in your group assigned
Chapter 6 Programming the LC-3
 Chapter 6 Programming the LC-3 Based on slides McGraw-Hill Additional material 4/5 Lewis/Martin Aside: Booting the Computer How does it all begin? We have LC-3 hardware and a program, but what next? Initial
Chapter 6 Programming the LC-3 Based on slides McGraw-Hill Additional material 4/5 Lewis/Martin Aside: Booting the Computer How does it all begin? We have LC-3 hardware and a program, but what next? Initial
Load -- read data from memory to register. Store -- write data from register to memory. Load effective address -- compute address, save in register
 Data Movement Instructions Load -- read data from memory to register LD: PC-relative mode LDR: base+offset mode LDI: indirect mode Store -- write data from register to memory ST: PC-relative mode STR:
Data Movement Instructions Load -- read data from memory to register LD: PC-relative mode LDR: base+offset mode LDI: indirect mode Store -- write data from register to memory ST: PC-relative mode STR:
Computing Layers. Chapter 5 The LC-3
 Computing Layers Problems Chapter 5 The LC-3 Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Algorithms Language Instruction
Computing Layers Problems Chapter 5 The LC-3 Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Algorithms Language Instruction
ECE 206, Fall 2001: Lab 3
 ECE 206, : Lab 3 Data Movement Instructions Learning Objectives This lab will give you practice with a number of LC-2 programming constructs. In particular you will cover the following topics: - Load/store
ECE 206, : Lab 3 Data Movement Instructions Learning Objectives This lab will give you practice with a number of LC-2 programming constructs. In particular you will cover the following topics: - Load/store
Chapter 8 I/O. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. But where does data in memory come from?
 Chapter 8 I/O I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory to registers store data from registers to memory But where does data
Chapter 8 I/O I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory to registers store data from registers to memory But where does data
Fill in your name, section, and username. DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO.
 NAME: SECTION: USENAME: CS 20 Exam 2 D-Term 2006 Question : (5) Question 2: (5) Question 3: (20) Question 4: (20) Question 5: (0) Question 6: (0) Question 7: (0) TOTAL: (00) Fill in your name, section,
NAME: SECTION: USENAME: CS 20 Exam 2 D-Term 2006 Question : (5) Question 2: (5) Question 3: (20) Question 4: (20) Question 5: (0) Question 6: (0) Question 7: (0) TOTAL: (00) Fill in your name, section,
Our Simulation Equivalent: -- readmemb( "os.bin" ) -- PC <== x0200
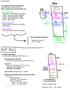 LC3 OS basics LC3 System Start-Up Assumptions We will write an OS for the LC3. What would a real LC3 do at start up? 1. BIOS execution --- PC points to BIOS (Basic IO System). --- POST: Test and initialize
LC3 OS basics LC3 System Start-Up Assumptions We will write an OS for the LC3. What would a real LC3 do at start up? 1. BIOS execution --- PC points to BIOS (Basic IO System). --- POST: Test and initialize
Fortunately not. In LC-3, there are a variety of addressing modes that deal with these concerns.
 CIT 593 Intro to Computer Systems Lecture #8 (10/2/12) Now let's see how an LC-3 program can read data from ( load ) and write data to ( store ) memory. Whenever we load/read from memory, we always have
CIT 593 Intro to Computer Systems Lecture #8 (10/2/12) Now let's see how an LC-3 program can read data from ( load ) and write data to ( store ) memory. Whenever we load/read from memory, we always have
COSC121: Computer Systems: Review
 COSC121: Computer Systems: Review Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Constructed using materials: - Patt and Patel Introduction to Computing Systems (2nd) - Patterson and Hennessy Computer
COSC121: Computer Systems: Review Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Constructed using materials: - Patt and Patel Introduction to Computing Systems (2nd) - Patterson and Hennessy Computer
11/10/2016. Review the Problem to Be Solved. ECE 120: Introduction to Computing. What Shall We Keep in the Registers? Where Are the Pieces in Memory?
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 120: Introduction to Computing Letter Frequency Coding Review the Problem to Be Solved The task: given an ASCII
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 120: Introduction to Computing Letter Frequency Coding Review the Problem to Be Solved The task: given an ASCII
Lec-memMapIOtrapJSR SYS_BUS
 Lec-memMapIOtrapJSR Memory Mapped I/O: I/O Devices have read/write access via device registers. To send a word of data to a device, write to its memory-mapped address: ST R1, To receive a word
Lec-memMapIOtrapJSR Memory Mapped I/O: I/O Devices have read/write access via device registers. To send a word of data to a device, write to its memory-mapped address: ST R1, To receive a word
LC-3 Input and Output
 LC-3 Input and Output I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory to registers store data from registers to memory use the TRAP
LC-3 Input and Output I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory to registers store data from registers to memory use the TRAP
CS 2461: Computer Architecture I
 Protecting System space : Computer Architecture I Instructor: Prof. Bhagi Narahari Dept. of Computer Science Course URL: www.seas.gwu.edu/~bhagiweb/cs2461/ System calls go to specific locations in memory
Protecting System space : Computer Architecture I Instructor: Prof. Bhagi Narahari Dept. of Computer Science Course URL: www.seas.gwu.edu/~bhagiweb/cs2461/ System calls go to specific locations in memory
LC-3 Input and Output
 LC-3 Input and Output I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory to registers store data from registers to memory use the TRAP
LC-3 Input and Output I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory to registers store data from registers to memory use the TRAP
That is, we branch to JUMP_HERE, do whatever we need to do, and then branch to JUMP_BACK, which is where we started.
 CIT 593 Intro to Computer Systems Lecture #11 (10/11/12) Previously we saw the JMP and BR instructions. Both are one-way jumps : there is no way back to the code from where you jumped, so you just go in
CIT 593 Intro to Computer Systems Lecture #11 (10/11/12) Previously we saw the JMP and BR instructions. Both are one-way jumps : there is no way back to the code from where you jumped, so you just go in
Binghamton University. CS-120 Summer LC3 Memory. Text: Introduction to Computer Systems : Sections 5.1.1, 5.3
 LC3 Memory Text: Introduction to Computer Systems : Sections 5.1.1, 5.3 John Von Neumann (1903-1957) Princeton / Institute for Advanced Studies Need to compute particle interactions during a nuclear reaction
LC3 Memory Text: Introduction to Computer Systems : Sections 5.1.1, 5.3 John Von Neumann (1903-1957) Princeton / Institute for Advanced Studies Need to compute particle interactions during a nuclear reaction
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Computing Layers
 Chapter 5 The LC-3 Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms Language
Chapter 5 The LC-3 Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms Language
11/16/2016. Review Our Process for Programming. ECE 120: Introduction to Computing. A Typical Programming Process. Can a Computer Help Us Program?
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 120: Introduction to Computing Assembly Language Review Our Process for Programming Step 1: Figure out the instruction
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 120: Introduction to Computing Assembly Language Review Our Process for Programming Step 1: Figure out the instruction
I/O. University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell
 I/O University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory
I/O University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell I/O: Connecting to Outside World So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values in registers load data from memory
Chapter 8 Input/Output
 Lecture on Introduction to Computing Systems Chapter 8 Input/Output An Hong han@ustc.edu.cn 0 Fall School of Computer Science and Technology 0/11/3 1 Review So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values
Lecture on Introduction to Computing Systems Chapter 8 Input/Output An Hong han@ustc.edu.cn 0 Fall School of Computer Science and Technology 0/11/3 1 Review So far, we ve learned how to: compute with values
컴퓨터개념및실습. 기말고사 review
 컴퓨터개념및실습 기말고사 review Sorting results Sort Size Compare count Insert O(n 2 ) Select O(n 2 ) Bubble O(n 2 ) Merge O(n log n) Quick O(n log n) 5 4 (lucky data set) 9 24 5 10 9 36 5 15 9 40 14 39 15 45 (unlucky
컴퓨터개념및실습 기말고사 review Sorting results Sort Size Compare count Insert O(n 2 ) Select O(n 2 ) Bubble O(n 2 ) Merge O(n log n) Quick O(n log n) 5 4 (lucky data set) 9 24 5 10 9 36 5 15 9 40 14 39 15 45 (unlucky
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi, Kai Zhao TAs: Annie Lin, Mohit Verma, Neha Mittal, Daniel Griffin, Yuzhe Ma Examination 1 In Class
CS/ECE 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar Sohi, Kai Zhao TAs: Annie Lin, Mohit Verma, Neha Mittal, Daniel Griffin, Yuzhe Ma Examination 1 In Class
Routines and Subroutines
 chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines 9.1 LC-3 TRAP Routines 9.1.1 Introduction Recall Figure 8.5 of the previous chapter. In order to have the program successfully obtain input from the keyboard, it
chapter 9 TRAP Routines and Subroutines 9.1 LC-3 TRAP Routines 9.1.1 Introduction Recall Figure 8.5 of the previous chapter. In order to have the program successfully obtain input from the keyboard, it
8.1 I/O Basics Device Registers. chapter
 chapter 8 Up to now, we have paid little attention to input/output (I/O). We did note (in Chapter 4) that input/output is an important component of the von Neumann model. There must be a way to get information
chapter 8 Up to now, we have paid little attention to input/output (I/O). We did note (in Chapter 4) that input/output is an important component of the von Neumann model. There must be a way to get information
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Review Topics
 Second Midterm Review Slides Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Review Topics LC-3 Programming /Stack Execution
Second Midterm Review Slides Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University Review Topics LC-3 Programming /Stack Execution
ADD R3, R4, #5 LDR R3, R4, #5
 ECE 109 Sections 602 to 605 Exam 2 Fall 2007 Solution 6 November, 2007 Problem 1 (15 points) Data Path In the table below, the columns correspond to two LC/3 instructions and the rows to the six phases
ECE 109 Sections 602 to 605 Exam 2 Fall 2007 Solution 6 November, 2007 Problem 1 (15 points) Data Path In the table below, the columns correspond to two LC/3 instructions and the rows to the six phases
Chapter 7 Assembly Language
 Chapter 7 Assembly Language Computing Layers Problems Algorithms Language Instruction Set Architecture Microarchitecture Circuits Devices 2 Human-Readable Machine Language Computers like ones and zeros
Chapter 7 Assembly Language Computing Layers Problems Algorithms Language Instruction Set Architecture Microarchitecture Circuits Devices 2 Human-Readable Machine Language Computers like ones and zeros
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 306, Fall 013 Yale Patt, Instructor Ben Lin, Mochamad Asri, Ameya Chaudhari, Nikhil Garg, Lauren Guckert, Jack Koenig,
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin EE 306, Fall 013 Yale Patt, Instructor Ben Lin, Mochamad Asri, Ameya Chaudhari, Nikhil Garg, Lauren Guckert, Jack Koenig,
Programming Studio #4 ECE 190
 Programming Studio #4 ECE 190 Programming Studio #4 Topics this week: Systematic Decomposition Memory Addressing Modes In Studio Assignment LC-3 Programming Assignment Announcements MP1 Due Wednesday,
Programming Studio #4 ECE 190 Programming Studio #4 Topics this week: Systematic Decomposition Memory Addressing Modes In Studio Assignment LC-3 Programming Assignment Announcements MP1 Due Wednesday,
Homework 06. Push Z Push Y Pop Y Push X Pop X Push W Push V Pop V Push U Pop U Pop W Pop Z Push T Push S
 Homework 06 1. How many TRAP service routines can be implemented in the LC-3? Why? Since the trap vector is 8 bits wide, 256 trap routines can be implemented in the LC-3. Why must a instruction be used
Homework 06 1. How many TRAP service routines can be implemented in the LC-3? Why? Since the trap vector is 8 bits wide, 256 trap routines can be implemented in the LC-3. Why must a instruction be used
Assembly Language. 7.1 Assembly Language Programming Moving Up o Level. chapter
 chapter 7 Assembly Language By now, you are probably a little tired of Is and Os and keeping track of 0001 meaning ADD and 1001 meaning NOT. Also, wouldn'titbe nice if we could refer to a memory location
chapter 7 Assembly Language By now, you are probably a little tired of Is and Os and keeping track of 0001 meaning ADD and 1001 meaning NOT. Also, wouldn'titbe nice if we could refer to a memory location
11/6/2016. Let s Solve a Problem. ECE 120: Introduction to Computing. Overview of Our Task. Programs are Finite State Machines
 University of Illinot Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 120: Introduction to Computing Typing in a Number Let s Solve a Problem Let s see how we can translate a task in
University of Illinot Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 120: Introduction to Computing Typing in a Number Let s Solve a Problem Let s see how we can translate a task in
Chapter 7 Assembly Language. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University
 Chapter 7 Assembly Language ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 2 Human-Readable Machine Language Computers like ones and zeros 0001110010000110
Chapter 7 Assembly Language ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 2 Human-Readable Machine Language Computers like ones and zeros 0001110010000110
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Computing Layers
 Chapter 8 I/O Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms Language Instruction
Chapter 8 I/O Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by C. Wilcox, S. Rajopadhye Colorado State University Computing Layers Problems Algorithms Language Instruction
ECE/CS 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON
 ECE/CS 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar S. Sohi TAs: Newsha Ardalani and Rebecca Lam Midterm Eamination 3 In Class (5 minutes) Friday, November 8,
ECE/CS 252: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN MADISON Prof. Gurindar S. Sohi TAs: Newsha Ardalani and Rebecca Lam Midterm Eamination 3 In Class (5 minutes) Friday, November 8,
Assembly Language. University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell
 Assembly Language University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell Human-Readable Machine Language Computers like ones and zeros 0001110010000110 Humans like symbols
Assembly Language University of Texas at Austin CS310H - Computer Organization Spring 2010 Don Fussell Human-Readable Machine Language Computers like ones and zeros 0001110010000110 Humans like symbols
Chapter 10 And, Finally... The Stack. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University
 Chapter 10 And, Finally... The Stack ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 2 Stack: An Abstract Data Type An important abstraction that
Chapter 10 And, Finally... The Stack ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: This lecture uses slides prepared by Gregory T. Byrd, North Carolina State University 2 Stack: An Abstract Data Type An important abstraction that
