Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
|
|
|
- Patience Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Arrays, Part 1 of 2 Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 1 / 14
2 Modeling Aggregates As you ve seen, you can get pretty far with "scalar" data. But many phenomena we wish to model computationally are aggregates, or collections, for example: scores on assignments in a class, word counts in a document, or pixel colors in a bitmap image. Today we ll learn Java s most basic facility for modeling such phenomena: arrays. CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 2 / 14
3 Arrays Java Arrays (JLS 10): are objects, are dynamically allocated (e.g., with operator new), and have a fixed number of elements of the same type. CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 3 / 14
4 Creating Arrays Consider the following array creation expression (JLS 10.3): double[] scores = new double[5]; This declaration: allocates a 5-element array, the 5 in the example above can be any expression that is unary promotable to an int (JLS 5.6.1) stores the address of this new array in scores, and initializes each value to it s default value (0 for numeric types, false for boolean types, and null for references, JLS ). CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 4 / 14
5 Array Declarations The preceding array definition double[] scores = new double[5]; could be split into a declaration and initialization: double[] scores; scores = new double[5]; Also, you can put the [] on the type or the variable name when delaring an array. These two declarations are equivalent: double[] scores; double scores[]; Generally, it s better style to put the [] on the type. CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 5 / 14
6 Mixed Declarations Note that you can mix aray declarations with declarations of variables having the same element type. The declaration line: double scores[], average; creates an array of double reference named scores, and a double variable named average What s the size of the scores array declared above? CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 6 / 14
7 Array Objects After the definition: double[] scores = new double[5]; scores points to an array object in memory that can be visualized as: The indexes of scores range from 0 to 4. The size of arrays are stored in a public final instance variable named length scores.length == 5; What is the type and value of the expression above? CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 7 / 14
8 Accessing Array Elements Array elements are accessed with an int-promotable expression enclosed in square brackets ([]) double[] scores = new double[5]; scores[0] = 89; scores[1] = 100; scores[2] = 95.6; scores[3] = 84.5; scores[4] = 91; scores[scores.length - 1] = 99.2; Will this line compile? If so, what will happen at runtime? scores[scores.length] = 100; CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 8 / 14
9 Initializing Arrays You can provide initial values for (small) arrays String[] validsuits = {"diamonds", "clubs", "hearts","spades"; What is validsuits.length? What is validsuits[1]? You can also use a loop to initialize the values of an array: int[] squares = new int[5]; for (int i = 0; i < squares.length; ++i) { squares[i] = i*i; What is squares[4]? CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 9 / 14
10 Traversing Arrays Arrays and for statements go hand-in-hand: double[] scores = new double[5]; for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) { System.out.printf("scores[%d] = %.2f%n", i, scores[i]); You can also use the enhanced for loop: for (double score: scores) { System.out.println(score); Read the enhanced for loop as for each element of the array.... Why use for-each instead of traditional for?... CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 10 / 14
11 Traditional for Versus for-each In cases where you don t need the index, use the enhanced for loop. Consider: double sum = 0.0; for (int i = 0; i < scores.length; ++i) { sum += scores[i]; In the code above, scores.length is used only for bounding the array traversal, and the index i is only used for sequential array access. Those are two things we can mess up. The enhanced for loop is cleaner: double sum = 0.0; for (double score: scores) { sum += score; Also note how our naming conventions help to make the code clear. You can read the loop above as for each score in scores. CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 11 / 14
12 Array Initialization and Access Gotchas Because arrays are allocated dynamically, this will compile: double[] scores = new double[-5]; but will produce an error at run-time: Exception in thread "main" java.lang.negativearraysizeexception at ArrayBasics.main(ArrayBasics.java:4) Also, array access expressions are evaluated and checked at run-time. So, in the same way that accessing an array with an index the size of the array produces a run-time error, negative indexes like: scores[-1] = 100; produce: Exception in thread "main" java.lang.arrayindexoutofboundsexception: -1 at ArrayBasics.main(ArrayBasics.java:23) CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 12 / 14
13 Arrays as Method Parameters - main We ve already seen an array parameter: public static void main(string[] args) We can use this array just like we use any other array. public class Shout { public static void main(string[] args) { for (String arg: args) { System.out.print(arg.toUpperCase() + " "); System.out.println(); See also CourseAverage.java CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 13 / 14
14 Closing Thoughts Arrays are our first collection classes (but are not Java Collection classes). Arrays are objects, so array objects are created with operator new and array variables can have the value null. Arrays have sugar to add convenience and make them syntactically similar to C s arrays. CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 14 / 14
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
 Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Arrays, Part 2 of 2 Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu Chris Simpkins (Georgia Tech) CS 1331 Arrays, Part 2 of 2 1 / 16 A few more array topics Variable
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Arrays, Part 2 of 2 Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu Chris Simpkins (Georgia Tech) CS 1331 Arrays, Part 2 of 2 1 / 16 A few more array topics Variable
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
 Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Conditional Execution Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Conditional Execution 1 / 14 Structured Programming In reasoning
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Conditional Execution Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Conditional Execution 1 / 14 Structured Programming In reasoning
Classes Classes 2 / 35
 Classes 1 / 35 Classes Classes 2 / 35 Anatomy of a Class By the end of next lecture, you ll understand everything in this class definition. package edu. gatech. cs1331. card ; import java. util. Arrays
Classes 1 / 35 Classes Classes 2 / 35 Anatomy of a Class By the end of next lecture, you ll understand everything in this class definition. package edu. gatech. cs1331. card ; import java. util. Arrays
Java is an objet-oriented programming language providing features that support
 Java Essentials CSCI 136: Spring 2018 Handout 2 February 2 Language Basics Java is an objet-oriented programming language providing features that support Data abstraction Code reuse Modular development
Java Essentials CSCI 136: Spring 2018 Handout 2 February 2 Language Basics Java is an objet-oriented programming language providing features that support Data abstraction Code reuse Modular development
Classes Classes 2 / 36
 Classes 1 / 36 Classes Classes 2 / 36 Anatomy of a Class By the end of next lecture, you ll understand everything in this class definition. package edu. gatech. cs1331. card ; import java. util. Arrays
Classes 1 / 36 Classes Classes 2 / 36 Anatomy of a Class By the end of next lecture, you ll understand everything in this class definition. package edu. gatech. cs1331. card ; import java. util. Arrays
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
 Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Recursion Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Recursion 1 / 11 Recursion A recursive processes or data structure is defined
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Recursion Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Recursion 1 / 11 Recursion A recursive processes or data structure is defined
SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR DIPLOMA IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY; YEAR 1
 FACULTY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR DIPLOMA IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY; YEAR 1 ACADEMIC SESSION 2014; SEMESTER 3 PRG102D: BASIC PROGRAMMING CONCEPTS Section A Compulsory section Question
FACULTY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR DIPLOMA IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY; YEAR 1 ACADEMIC SESSION 2014; SEMESTER 3 PRG102D: BASIC PROGRAMMING CONCEPTS Section A Compulsory section Question
CS 2340 Objects and Design - Scala
 CS 2340 Objects and Design - Scala Objects and Operators Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu Chris Simpkins (Georgia Tech) CS 2340 Objects and Design - Scala Objects and Operators 1 / 13 Classes
CS 2340 Objects and Design - Scala Objects and Operators Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu Chris Simpkins (Georgia Tech) CS 2340 Objects and Design - Scala Objects and Operators 1 / 13 Classes
Classes and Objects 3/28/2017. How can multiple methods within a Java class read and write the same variable?
 Peer Instruction 8 Classes and Objects How can multiple methods within a Java class read and write the same variable? A. Allow one method to reference a local variable of the other B. Declare a variable
Peer Instruction 8 Classes and Objects How can multiple methods within a Java class read and write the same variable? A. Allow one method to reference a local variable of the other B. Declare a variable
Object-oriented programming. and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018
 Object-oriented programming 1 and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018 Lecture 1: Types and Control Flow http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110/2018su Lecture 1 Outline 2 Languages Overview Imperative
Object-oriented programming 1 and data-structures CS/ENGRD 2110 SUMMER 2018 Lecture 1: Types and Control Flow http://courses.cs.cornell.edu/cs2110/2018su Lecture 1 Outline 2 Languages Overview Imperative
Practice Midterm 1. Problem Points Score TOTAL 50
 CS 120 Software Design I Spring 2019 Practice Midterm 1 University of Wisconsin - La Crosse February 25 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages including the
CS 120 Software Design I Spring 2019 Practice Midterm 1 University of Wisconsin - La Crosse February 25 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages including the
Administration. Objects and Arrays. Objects. Agenda. What is an Object? What is a Class?
 Administration Objects and Arrays CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 6 Read clarified grading policies Lab 6 due tomorrow Submit.java files in a folder named Lab6 Lab 7 Posted today Upson Lab closed
Administration Objects and Arrays CS 99 Summer 2000 Michael Clarkson Lecture 6 Read clarified grading policies Lab 6 due tomorrow Submit.java files in a folder named Lab6 Lab 7 Posted today Upson Lab closed
4CCS1PRP, Programming Practice 2012 Lecture 6: Arrays - Part 1
 4CCS1PRP, Programming Practice 2012 Lecture 6: Arrays - Part 1 Martin Chapman Java for Everyone by Cay Horstmann Copyright 2009 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved. Slides by Donald W. Smith TechNeTrain.com
4CCS1PRP, Programming Practice 2012 Lecture 6: Arrays - Part 1 Martin Chapman Java for Everyone by Cay Horstmann Copyright 2009 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved. Slides by Donald W. Smith TechNeTrain.com
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
 Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Object-Oriented Programming, Part 2 of 3 Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Object-Oriented Programming, Part 2 of 3 1 / 16
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Object-Oriented Programming, Part 2 of 3 Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Object-Oriented Programming, Part 2 of 3 1 / 16
Java Programming: from the Beginning
 CSc 2310: Principle of Programming g( (Java) Spring 2013 Java Programming: from the Beginning Chapter 5 Arrays 1 Copyright 2000 W. W. Norton & Company. All rights reserved. Outline 5.1 Creating and Using
CSc 2310: Principle of Programming g( (Java) Spring 2013 Java Programming: from the Beginning Chapter 5 Arrays 1 Copyright 2000 W. W. Norton & Company. All rights reserved. Outline 5.1 Creating and Using
(A) 99 ** (B) 100 (C) 101 (D) 100 initial integers plus any additional integers required during program execution
 Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice Test 01. An array is a ** (A) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. (B) data structure with LIFO access. (C) data structure, which allows transfer between
Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice Test 01. An array is a ** (A) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. (B) data structure with LIFO access. (C) data structure, which allows transfer between
BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I
![BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I](/thumbs/81/83968367.jpg) BASIC COMPUTATION x public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Using Eclipse Data Types Variables Primitive and Class Data Types Expressions Declaration Assignment
BASIC COMPUTATION x public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Using Eclipse Data Types Variables Primitive and Class Data Types Expressions Declaration Assignment
CSSE 220 Day 8. Arrays, ArrayLists, Wrapper Classes, Auto-boxing, Enhanced for loop. Check out ArraysAndLists from SVN
 CSSE 220 Day 8 Arrays, ArrayLists, Wrapper Classes, Auto-boxing, Enhanced for loop Check out ArraysAndLists from SVN Questions? Exam 1 is October 1, 7-9 PM! Over chapters 1-7 You'll have a chance to ask
CSSE 220 Day 8 Arrays, ArrayLists, Wrapper Classes, Auto-boxing, Enhanced for loop Check out ArraysAndLists from SVN Questions? Exam 1 is October 1, 7-9 PM! Over chapters 1-7 You'll have a chance to ask
Method OverLoading printf method Arrays Declaring and Using Arrays Arrays of Objects Array as Parameters
 Outline Method OverLoading printf method Arrays Declaring and Using Arrays Arrays of Objects Array as Parameters Variable Length Parameter Lists split() Method from String Class Integer & Double Wrapper
Outline Method OverLoading printf method Arrays Declaring and Using Arrays Arrays of Objects Array as Parameters Variable Length Parameter Lists split() Method from String Class Integer & Double Wrapper
CSSE 220. Arrays, ArrayLists, Wrapper Classes, Auto-boxing, Enhanced for loop. Check out ArraysListPractice from SVN
 CSSE 220 Arrays, ArrayLists, Wrapper Classes, Auto-boxing, Enhanced for loop Check out ArraysListPractice from SVN Help with Peers Having a peer help you with some strange bug or specific problem Great
CSSE 220 Arrays, ArrayLists, Wrapper Classes, Auto-boxing, Enhanced for loop Check out ArraysListPractice from SVN Help with Peers Having a peer help you with some strange bug or specific problem Great
CS/B.TECH/CSE(New)/SEM-5/CS-504D/ OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING. Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 GROUP A. (Multiple Choice Type Question)
 CS/B.TECH/CSE(New)/SEM-5/CS-504D/2013-14 2013 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
CS/B.TECH/CSE(New)/SEM-5/CS-504D/2013-14 2013 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
CIS133J. Working with Numbers in Java
 CIS133J Working with Numbers in Java Contents: Using variables with integral numbers Using variables with floating point numbers How to declare integral variables How to declare floating point variables
CIS133J Working with Numbers in Java Contents: Using variables with integral numbers Using variables with floating point numbers How to declare integral variables How to declare floating point variables
Java How to Program, 10/e. Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Java How to Program, 10/e Copyright 1992-2015 by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Data structures Collections of related data items. Discussed in depth in Chapters 16 21. Array objects Data
Java How to Program, 10/e Copyright 1992-2015 by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Data structures Collections of related data items. Discussed in depth in Chapters 16 21. Array objects Data
egrapher Language Reference Manual
 egrapher Language Reference Manual Long Long: ll3078@columbia.edu Xinli Jia: xj2191@columbia.edu Jiefu Ying: jy2799@columbia.edu Linnan Wang: lw2645@columbia.edu Darren Chen: dsc2155@columbia.edu 1. Introduction
egrapher Language Reference Manual Long Long: ll3078@columbia.edu Xinli Jia: xj2191@columbia.edu Jiefu Ying: jy2799@columbia.edu Linnan Wang: lw2645@columbia.edu Darren Chen: dsc2155@columbia.edu 1. Introduction
Arrays. Eng. Mohammed Abdualal
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 9 Arrays
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 9 Arrays
Arrays. COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science. Christopher Conway 10 June 2003
 Arrays COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science Christopher Conway 10 June 2003 Arrays An array is a list of values. In Java, the components of an array can be of any type, basic or object. An array
Arrays COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science Christopher Conway 10 June 2003 Arrays An array is a list of values. In Java, the components of an array can be of any type, basic or object. An array
Handout 4 Conditionals. Boolean Expressions.
 Handout 4 cs180 - Programming Fundamentals Fall 17 Page 1 of 8 Handout 4 Conditionals. Boolean Expressions. Example Problem. Write a program that will calculate and print bills for the city power company.
Handout 4 cs180 - Programming Fundamentals Fall 17 Page 1 of 8 Handout 4 Conditionals. Boolean Expressions. Example Problem. Write a program that will calculate and print bills for the city power company.
Data and Variables. Data Types Expressions. String Concatenation Variables Declaration Assignment Shorthand operators. Operators Precedence
 Data and Variables Data Types Expressions Operators Precedence String Concatenation Variables Declaration Assignment Shorthand operators Review class All code in a java file is written in a class public
Data and Variables Data Types Expressions Operators Precedence String Concatenation Variables Declaration Assignment Shorthand operators Review class All code in a java file is written in a class public
CSE 214 Computer Science II Java Classes and Information Hiding
 CSE 214 Computer Science II Java Classes and Information Hiding Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Java
CSE 214 Computer Science II Java Classes and Information Hiding Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Java
CIS*2430 (Fall 2012) Miterm Exam (I) Solutions
 CIS*2430 (Fall 2012) Miterm Exam (I) Solutions Instructor: F. Song Part I: Multiple Choice (4 marks each): circle the choice for the right answer. 1. An object-oriented programming language (a) uses structured
CIS*2430 (Fall 2012) Miterm Exam (I) Solutions Instructor: F. Song Part I: Multiple Choice (4 marks each): circle the choice for the right answer. 1. An object-oriented programming language (a) uses structured
CONTENTS: Array Usage Multi-Dimensional Arrays Reference Types. COMP-202 Unit 6: Arrays
 CONTENTS: Array Usage Multi-Dimensional Arrays Reference Types COMP-202 Unit 6: Arrays Introduction (1) Suppose you want to write a program that asks the user to enter the numeric final grades of 350 COMP-202
CONTENTS: Array Usage Multi-Dimensional Arrays Reference Types COMP-202 Unit 6: Arrays Introduction (1) Suppose you want to write a program that asks the user to enter the numeric final grades of 350 COMP-202
(A) 99 (B) 100 (C) 101 (D) 100 initial integers plus any additional integers required during program execution
 Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice 01. An array is a (A) (B) (C) (D) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. data structure with LIFO access. data structure, which allows transfer between
Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice 01. An array is a (A) (B) (C) (D) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. data structure with LIFO access. data structure, which allows transfer between
Array Basics: Outline. Creating and Accessing Arrays. Creating and Accessing Arrays. Arrays (Savitch, Chapter 7)
 Array Basics: Outline Arrays (Savitch, Chapter 7) TOPICS Array Basics Arrays in Classes and Methods Programming with Arrays Searching and Sorting Arrays Multi-Dimensional Arrays Static Variables and Constants
Array Basics: Outline Arrays (Savitch, Chapter 7) TOPICS Array Basics Arrays in Classes and Methods Programming with Arrays Searching and Sorting Arrays Multi-Dimensional Arrays Static Variables and Constants
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
 Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Iterators and Streams Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Iterators and Streams 1 / 20 The Collections Framework A collection
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Iterators and Streams Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Iterators and Streams 1 / 20 The Collections Framework A collection
*Java has included a feature that simplifies the creation of
 Java has included a feature that simplifies the creation of methods that need to take a variable number of arguments. This feature is called as varargs (short for variable-length arguments). A method that
Java has included a feature that simplifies the creation of methods that need to take a variable number of arguments. This feature is called as varargs (short for variable-length arguments). A method that
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming. Fall 2018 Instructors Bill Lenhart & Bill Jannen
 CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Fall 2018 Instructors Bill Lenhart & Bill Jannen Administrative Details Lab 1 handout is online Prelab (should be completed before lab): Lab 1 design doc
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Fall 2018 Instructors Bill Lenhart & Bill Jannen Administrative Details Lab 1 handout is online Prelab (should be completed before lab): Lab 1 design doc
Array. Lecture 12. Based on Slides of Dr. Norazah Yusof
 Array Lecture 12 Based on Slides of Dr. Norazah Yusof 1 Introducing Arrays Array is a data structure that represents a collection of the same types of data. In Java, array is an object that can store a
Array Lecture 12 Based on Slides of Dr. Norazah Yusof 1 Introducing Arrays Array is a data structure that represents a collection of the same types of data. In Java, array is an object that can store a
CS 112 Introduction to Computing II. Wayne Snyder Computer Science Department Boston University
 9/5/6 CS Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today: Arrays (D and D) Methods Program structure Fields vs local variables Next time: Program structure continued: Classes
9/5/6 CS Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today: Arrays (D and D) Methods Program structure Fields vs local variables Next time: Program structure continued: Classes
News and information! Review: Java Programs! Feedback after Lecture 2! Dead-lines for the first two lab assignment have been posted.!
 True object-oriented programming: Dynamic Objects Reference Variables D0010E Object-Oriented Programming and Design Lecture 3 Static Object-Oriented Programming UML" knows-about Eckel: 30-31, 41-46, 107-111,
True object-oriented programming: Dynamic Objects Reference Variables D0010E Object-Oriented Programming and Design Lecture 3 Static Object-Oriented Programming UML" knows-about Eckel: 30-31, 41-46, 107-111,
COSC 123 Computer Creativity. Java Lists and Arrays. Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan
 COSC 123 Computer Creativity Java Lists and Arrays Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Objectives 1) Create and use arrays of base types and objects. 2) Create
COSC 123 Computer Creativity Java Lists and Arrays Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Objectives 1) Create and use arrays of base types and objects. 2) Create
Java Programming Language. 0 A history
 Java Programming Language 0 A history How java works What you ll do in Java JVM API Java Features 0Platform Independence. 0Object Oriented. 0Compiler/Interpreter 0 Good Performance 0Robust. 0Security 0
Java Programming Language 0 A history How java works What you ll do in Java JVM API Java Features 0Platform Independence. 0Object Oriented. 0Compiler/Interpreter 0 Good Performance 0Robust. 0Security 0
CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall Office hours:
 CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall alphonce@buffalo.edu Office hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM 12:00 PM * Wednesday 4:00 PM 5:00 PM Friday 11:00 AM 12:00 PM OR
CSE115 / CSE503 Introduction to Computer Science I Dr. Carl Alphonce 343 Davis Hall alphonce@buffalo.edu Office hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM 12:00 PM * Wednesday 4:00 PM 5:00 PM Friday 11:00 AM 12:00 PM OR
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388)
 Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
CS 1316 Exam 1 Summer 2009
 1 / 8 Your Name: I commit to uphold the ideals of honor and integrity by refusing to betray the trust bestowed upon me as a member of the Georgia Tech community. CS 1316 Exam 1 Summer 2009 Section/Problem
1 / 8 Your Name: I commit to uphold the ideals of honor and integrity by refusing to betray the trust bestowed upon me as a member of the Georgia Tech community. CS 1316 Exam 1 Summer 2009 Section/Problem
Flow of Control: Loops. Chapter 4
 Flow of Control: Loops Chapter 4 Java Loop Statements: Outline The while statement The do-while statement The for Statement Java Loop Statements A portion of a program that repeats a statement or a group
Flow of Control: Loops Chapter 4 Java Loop Statements: Outline The while statement The do-while statement The for Statement Java Loop Statements A portion of a program that repeats a statement or a group
Give one example where you might wish to use a three dimensional array
 CS 110: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE SAMPLE TEST 3 TIME ALLOWED: 60 MINUTES Student s Name: MAXIMUM MARK 100 NOTE: Unless otherwise stated, the questions are with reference to the Java Programming
CS 110: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE SAMPLE TEST 3 TIME ALLOWED: 60 MINUTES Student s Name: MAXIMUM MARK 100 NOTE: Unless otherwise stated, the questions are with reference to the Java Programming
Chapter 5: Arrays. Chapter 5. Arrays. Java Programming FROM THE BEGINNING. Copyright 2000 W. W. Norton & Company. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Arrays 1 5.1 Creating and Using Arrays A collection of data items stored under a single name is known as a data structure. An object is one kind of data structure, because it can store multiple
Chapter 5 Arrays 1 5.1 Creating and Using Arrays A collection of data items stored under a single name is known as a data structure. An object is one kind of data structure, because it can store multiple
Arrays in Java Using Arrays
 Recall Length of an Array Arrays in Java Using Arrays Once an array has been created in memory, its size is fixed for the duration of its existence. Every array object has a length field whose value can
Recall Length of an Array Arrays in Java Using Arrays Once an array has been created in memory, its size is fixed for the duration of its existence. Every array object has a length field whose value can
Arrays. Weather Problem Array Declaration Accessing Elements Arrays and for Loops Array length field Quick Array Initialization Array Traversals
 Arrays Weather Problem Array Declaration Accessing Elements Arrays and for Loops Array length field Quick Array Initialization Array Traversals Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program
Arrays Weather Problem Array Declaration Accessing Elements Arrays and for Loops Array length field Quick Array Initialization Array Traversals Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program
CS 2340 Objects and Design
 CS 2340 Objects and Design Structural Patterns Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu Chris Simpkins (Georgia Tech) CS 2340 Objects and Design Structural Patterns 1 / 10 Structural Design Patterns
CS 2340 Objects and Design Structural Patterns Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu Chris Simpkins (Georgia Tech) CS 2340 Objects and Design Structural Patterns 1 / 10 Structural Design Patterns
CSE 142 Su01 Final Exam Sample Solution page 1 of 7
 CSE 142 Su01 Final Exam Sample Solution page 1 of 7 Answer all of the following questions. READ EACH QUESTION CAREFULLY. Answer each question in the space provided on these pages. Budget your time so you
CSE 142 Su01 Final Exam Sample Solution page 1 of 7 Answer all of the following questions. READ EACH QUESTION CAREFULLY. Answer each question in the space provided on these pages. Budget your time so you
Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal
 Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand the basic constructs of a Java Program Understand how to use basic identifiers Understand simple Java data types
Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand the basic constructs of a Java Program Understand how to use basic identifiers Understand simple Java data types
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Full file at
 Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
Java Identifiers, Data Types & Variables
 Java Identifiers, Data Types & Variables 1. Java Identifiers: Identifiers are name given to a class, variable or a method. public class TestingShastra { //TestingShastra is an identifier for class char
Java Identifiers, Data Types & Variables 1. Java Identifiers: Identifiers are name given to a class, variable or a method. public class TestingShastra { //TestingShastra is an identifier for class char
Getting started with Java
 Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools
 CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools Hal Perkins Fall 2017 Lecture 8 C: Miscellanea Control, Declarations, Preprocessor, printf/scanf 1 The story so far The low-level execution model of a process (one
CSE 374 Programming Concepts & Tools Hal Perkins Fall 2017 Lecture 8 C: Miscellanea Control, Declarations, Preprocessor, printf/scanf 1 The story so far The low-level execution model of a process (one
Pace University. Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1
 Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II
 CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
CS111: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE II Computer Science Department Lecture 1(c): Java Basics (II) Lecture Contents Java basics (part II) Conditions Loops Methods Conditions & Branching Conditional Statements A
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Arrays
 CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Arrays Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs Opening Problem Read one hundred numbers, compute their
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Arrays Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs Opening Problem Read one hundred numbers, compute their
AP Computer Science Chapter 10 Implementing and Using Classes Study Guide
 AP Computer Science Chapter 10 Implementing and Using Classes Study Guide 1. A class that uses a given class X is called a client of X. 2. Private features of a class can be directly accessed only within
AP Computer Science Chapter 10 Implementing and Using Classes Study Guide 1. A class that uses a given class X is called a client of X. 2. Private features of a class can be directly accessed only within
Values and Variables 1 / 30
 Values and Variables 1 / 30 Values 2 / 30 Computing Computing is any purposeful activity that marries the representation of some dynamic domain with the representation of some dynamic machine that provides
Values and Variables 1 / 30 Values 2 / 30 Computing Computing is any purposeful activity that marries the representation of some dynamic domain with the representation of some dynamic machine that provides
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
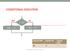 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CHAPTER 7 OBJECTS AND CLASSES
 CHAPTER 7 OBJECTS AND CLASSES OBJECTIVES After completing Objects and Classes, you will be able to: Explain the use of classes in Java for representing structured data. Distinguish between objects and
CHAPTER 7 OBJECTS AND CLASSES OBJECTIVES After completing Objects and Classes, you will be able to: Explain the use of classes in Java for representing structured data. Distinguish between objects and
CSC 1214: Object-Oriented Programming
 CSC 1214: Object-Oriented Programming J. Kizito Makerere University e-mail: jkizito@cis.mak.ac.ug www: http://serval.ug/~jona materials: http://serval.ug/~jona/materials/csc1214 e-learning environment:
CSC 1214: Object-Oriented Programming J. Kizito Makerere University e-mail: jkizito@cis.mak.ac.ug www: http://serval.ug/~jona materials: http://serval.ug/~jona/materials/csc1214 e-learning environment:
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
 Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Linked Lists Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Linked Lists 1 / 13 Linked Lists Dynamic data structures Singly linked lists
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Linked Lists Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Linked Lists 1 / 13 Linked Lists Dynamic data structures Singly linked lists
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below.
 C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
C212 Early Evaluation Exam Mon Feb 10 2014 Name: Please provide brief (common sense) justifications with your answers below. 1. What is the type (and value) of this expression: 5 * (7 + 4 / 2) 2. What
Classes. 1 Data Abstraction. 2 A Complex Number ADT
 Classes 1 Data Abstraction An abstraction of a concept attempts to capture the essence of the concept its essential properties and behaviors by ignoring irrelevant details. Process abstraction - group
Classes 1 Data Abstraction An abstraction of a concept attempts to capture the essence of the concept its essential properties and behaviors by ignoring irrelevant details. Process abstraction - group
CIS 110 Fall 2016 Introduction to Computer Programming 13 Oct 2016 Midterm Exam Answer Key
 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Midterm 1 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Introduction to Computer Programming 13 Oct 2016 Midterm Exam Answer Key 1.) The Easy One (1 point total) Check cover sheet for name, recitation #, PennKey,
CIS 110 Fall 2016 Midterm 1 CIS 110 Fall 2016 Introduction to Computer Programming 13 Oct 2016 Midterm Exam Answer Key 1.) The Easy One (1 point total) Check cover sheet for name, recitation #, PennKey,
17 Hello world 18 Type: String: literal 19 Standard API: System: out.println() 20 Hello world 21 Statement 22 Statement: simple statements are ended w
 List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 2: Sequential execution and program errors 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Hello world 5 Aim 6 Class: programs are divided into classes 7 Class: public class 8 Class:
List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 2: Sequential execution and program errors 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Hello world 5 Aim 6 Class: programs are divided into classes 7 Class: public class 8 Class:
CP122 CS I. Iteration
 CP122 CS I Iteration Tech News! Pix2Pix: machine learning translation of images https://affinelayer.com/pixsrv/ Tech News! Pix2Pix: machine learning translation of images https://affinelayer.com/pixsrv/
CP122 CS I Iteration Tech News! Pix2Pix: machine learning translation of images https://affinelayer.com/pixsrv/ Tech News! Pix2Pix: machine learning translation of images https://affinelayer.com/pixsrv/
BIT Java Programming. Sem 1 Session 2011/12. Chapter 2 JAVA. basic
 BIT 3383 Java Programming Sem 1 Session 2011/12 Chapter 2 JAVA basic Objective: After this lesson, you should be able to: declare, initialize and use variables according to Java programming language guidelines
BIT 3383 Java Programming Sem 1 Session 2011/12 Chapter 2 JAVA basic Objective: After this lesson, you should be able to: declare, initialize and use variables according to Java programming language guidelines
EXERCISES SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT I. 04 Arrays & Methods 2018W
 EXERCISES SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT I 04 Arrays & Methods 2018W Solution First Test DATA TYPES, BRANCHING AND LOOPS Complete the following program, which calculates the price for a car rental. First, the program
EXERCISES SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT I 04 Arrays & Methods 2018W Solution First Test DATA TYPES, BRANCHING AND LOOPS Complete the following program, which calculates the price for a car rental. First, the program
Lecture 3. Lecture
 True Object-Oriented programming: Dynamic Objects Static Object-Oriented Programming Reference Variables Eckel: 30-31, 41-46, 107-111, 114-115 Riley: 5.1, 5.2 D0010E Object-Oriented Programming and Design
True Object-Oriented programming: Dynamic Objects Static Object-Oriented Programming Reference Variables Eckel: 30-31, 41-46, 107-111, 114-115 Riley: 5.1, 5.2 D0010E Object-Oriented Programming and Design
Controls Structure for Repetition
 Controls Structure for Repetition So far we have looked at the if statement, a control structure that allows us to execute different pieces of code based on certain conditions. However, the true power
Controls Structure for Repetition So far we have looked at the if statement, a control structure that allows us to execute different pieces of code based on certain conditions. However, the true power
CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE
 CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE Instructor: Joel Castellanos e-mail: joel.unm.edu Web: http://cs.unm.edu/~joel/ Office: Electrical and Computer Engineering building
CS 152: Data Structures with Java Hello World with the IntelliJ IDE Instructor: Joel Castellanos e-mail: joel.unm.edu Web: http://cs.unm.edu/~joel/ Office: Electrical and Computer Engineering building
Arrays: Higher Dimensional Arrays. CS0007: Introduction to Computer Programming
 Arrays: Higher Dimensional Arrays CS0007: Introduction to Computer Programming Review If the == operator has two array variable operands, what is being compared? The reference variables held in the variables.
Arrays: Higher Dimensional Arrays CS0007: Introduction to Computer Programming Review If the == operator has two array variable operands, what is being compared? The reference variables held in the variables.
Arrays. Chapter 7 (Done right after 4 arrays and loops go together, especially for loops)
 Arrays Chapter 7 (Done right after 4 arrays and loops go together, especially for loops) Object Quick Primer A large subset of Java s features are for OOP Object- Oriented Programming We ll get to that
Arrays Chapter 7 (Done right after 4 arrays and loops go together, especially for loops) Object Quick Primer A large subset of Java s features are for OOP Object- Oriented Programming We ll get to that
CS260 Intro to Java & Android 03.Java Language Basics
 03.Java Language Basics http://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/index.htm CS260 - Intro to Java & Android 1 What is the distinction between fields and variables? Java has the following kinds of variables: Instance
03.Java Language Basics http://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/index.htm CS260 - Intro to Java & Android 1 What is the distinction between fields and variables? Java has the following kinds of variables: Instance
V2 3/5/2012. Programming in C. Introduction to Arrays. 111 Ch 07 A 1. Introduction to Arrays
 Programming in C 1 Introduction to Arrays A collection of variable data Same name Same type Contiguous block of memory Can manipulate or use Individual variables or List as one entity 2 Celsius temperatures:
Programming in C 1 Introduction to Arrays A collection of variable data Same name Same type Contiguous block of memory Can manipulate or use Individual variables or List as one entity 2 Celsius temperatures:
CS 1331 Exam 1. Fall Failure to properly fill in the information on this page will result in a deduction of up to 5 points from your exam score.
 CS 1331 Exam 1 Fall 2016 Name (print clearly): GT account (gpburdell1, msmith3, etc): Section (e.g., B1): Signature: Failure to properly fill in the information on this page will result in a deduction
CS 1331 Exam 1 Fall 2016 Name (print clearly): GT account (gpburdell1, msmith3, etc): Section (e.g., B1): Signature: Failure to properly fill in the information on this page will result in a deduction
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL
 JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 2: Sequential execution and program errors 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Hello world 5 Aim 6 Class: programs ar
 List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 2: Sequential execution and program errors 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Hello world 5 Aim 6 Class: programs are divided into classes 7 Class: public class 8 Class:
List of Slides 1 Title 2 Chapter 2: Sequential execution and program errors 3 Chapter aims 4 Section 2: Example:Hello world 5 Aim 6 Class: programs are divided into classes 7 Class: public class 8 Class:
School of Computer Science CPS109 Course Notes 5 Alexander Ferworn Updated Fall 15
 Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 IF... 1 2.1 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS... 3 2.2 BLOCKS... 3 2.3 IF-ELSE... 4 2.4 NESTING... 5 3 SWITCH (SOMETIMES KNOWN AS CASE )... 6 3.1 A BIT ABOUT BREAK... 7 4 CONDITIONAL
Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 IF... 1 2.1 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS... 3 2.2 BLOCKS... 3 2.3 IF-ELSE... 4 2.4 NESTING... 5 3 SWITCH (SOMETIMES KNOWN AS CASE )... 6 3.1 A BIT ABOUT BREAK... 7 4 CONDITIONAL
Computer Programming, I. Laboratory Manual. Experiment #2. Elementary Programming
 Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #2
Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #2
COMP 110 Introduction to Programming. What did we discuss?
 COMP 110 Introduction to Programming Fall 2015 Time: TR 9:30 10:45 Room: AR 121 (Hanes Art Center) Jay Aikat FB 314, aikat@cs.unc.edu Previous Class What did we discuss? 1 Today Announcements Assignment
COMP 110 Introduction to Programming Fall 2015 Time: TR 9:30 10:45 Room: AR 121 (Hanes Art Center) Jay Aikat FB 314, aikat@cs.unc.edu Previous Class What did we discuss? 1 Today Announcements Assignment
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016 Dr. Bruce A. Maxwell Department of Computer Science Colby College Course Description Focuses on the common structures used to store data and the standard
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms, Fall 2016 Dr. Bruce A. Maxwell Department of Computer Science Colby College Course Description Focuses on the common structures used to store data and the standard
CS5000: Foundations of Programming. Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University
 CS5000: Foundations of Programming Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Overview of Source Code Components Comments Library declaration Classes Functions Variables Comments Can
CS5000: Foundations of Programming Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Overview of Source Code Components Comments Library declaration Classes Functions Variables Comments Can
Every language has its own scoping rules. For example, what is the scope of variable j in this Java program?
 Lexical Binding There are two ways a variable can be used in a program: As a declaration As a "reference" or use of the variable Scheme has two kinds of variable "declarations" -- the bindings of a let-expression
Lexical Binding There are two ways a variable can be used in a program: As a declaration As a "reference" or use of the variable Scheme has two kinds of variable "declarations" -- the bindings of a let-expression
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 4: Flow Control Loops Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 4: Flow Control Loops Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Check the calendar on the course webpage regularly for updates on tutorials and office hours.
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 4: Flow Control Loops Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Check the calendar on the course webpage regularly for updates on tutorials and office hours.
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
 Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Review 2: Object-Oriented Programming Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Review 2: Object-Oriented Programming 1 / 14 Topics
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Review 2: Object-Oriented Programming Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Review 2: Object-Oriented Programming 1 / 14 Topics
Clean Formatting. Christopher Simpkins Chris Simpkins (Georgia Tech) CS 2340 Objects and Design CS / 1
 Clean Formatting Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu Chris Simpkins (Georgia Tech) CS 2340 Objects and Design CS 1331 1 / 1 Formatting Code should be written for human beings to understand,
Clean Formatting Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu Chris Simpkins (Georgia Tech) CS 2340 Objects and Design CS 1331 1 / 1 Formatting Code should be written for human beings to understand,
5/3/2006. Today! HelloWorld in BlueJ. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont.
 Today! Build HelloWorld yourself in BlueJ and Eclipse. Look at all the Java keywords. Primitive Types. HelloWorld in BlueJ 1. Find BlueJ in the start menu, but start the Select VM program instead (you
Today! Build HelloWorld yourself in BlueJ and Eclipse. Look at all the Java keywords. Primitive Types. HelloWorld in BlueJ 1. Find BlueJ in the start menu, but start the Select VM program instead (you
Last Class. Introduction to arrays Array indices Initializer lists Making an array when you don't know how many values are in it
 Last Class Introduction to arrays Array indices Initializer lists Making an array when you don't know how many values are in it public class February4{ public static void main(string[] args) { String[]
Last Class Introduction to arrays Array indices Initializer lists Making an array when you don't know how many values are in it public class February4{ public static void main(string[] args) { String[]
CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013
 CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
In Java, data type boolean is used to represent Boolean data. Each boolean constant or variable can contain one of two values: true or false.
 CS101, Mock Boolean Conditions, If-Then Boolean Expressions and Conditions The physical order of a program is the order in which the statements are listed. The logical order of a program is the order in
CS101, Mock Boolean Conditions, If-Then Boolean Expressions and Conditions The physical order of a program is the order in which the statements are listed. The logical order of a program is the order in
CMPT 125: Lecture 3 Data and Expressions
 CMPT 125: Lecture 3 Data and Expressions Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 1 Character Strings A character string is an object in Java,
CMPT 125: Lecture 3 Data and Expressions Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 1 Character Strings A character string is an object in Java,
1 Lexical Considerations
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Spring 2013 Handout Decaf Language Thursday, Feb 7 The project for the course is to write a compiler
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.035, Spring 2013 Handout Decaf Language Thursday, Feb 7 The project for the course is to write a compiler
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I
 CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 05 / 31 / 2017 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions / Comments? recap and some more details about variables, and if / else statements do lab work
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 05 / 31 / 2017 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions / Comments? recap and some more details about variables, and if / else statements do lab work
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 7 Arrays reading: 7.1 2 Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program (input underlined): How many days' temperatures? 7 Day 1's high temp: 45 Day 2's high temp:
Building Java Programs Chapter 7 Arrays reading: 7.1 2 Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program (input underlined): How many days' temperatures? 7 Day 1's high temp: 45 Day 2's high temp:
