Functions. x y z. f (x, y, z) Take in input arguments (zero or more) Perform some computation - May have side-effects (such as drawing)
|
|
|
- Dwight Andrews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2.1 Functions
2 Functions Take in input arguments (zero or more) Perform some computation - May have side-effects (such as drawing) Return one output value Input Arguments x y z f Return Value f (x, y, z)
3 Functions (Static Methods) Applications: - Use mathematical functions to calculate formulas - Use functions to build modular programs Examples: - Built-in functions: Math.random(), Math.abs(), Integer.parseInt() These methods return, respectively, a double, double, and int value. - I/O libraries: PennDraw.circle(x,y,halfRadius), PennDraw.line(x0,y0,x1,y1) - User-defined functions: main() 4
4 Why do we need functions? Break code down into logical sub-steps Readability of the code improves Testability - focus on getting each individual function correct 5
5 Method Signatures We need some way to uniquely identify a method The name of the method alone isn t enough - PennDraw.square(0.5, 0.5, 0.25) - PennDraw.square(0.5, 0.5, 0.25, 45) The methods have the same name, but do different things! 6
6 In Class Poll Which of these sets of elements are part of the method signature? 1) Method name, return type, name of parameters 2) Method name, return type, type of parameters 3) Method name, number of parameters 4) Method name, type of parameters 7
7 Anatomy of a Java Function Java functions It is easy to write your own - Example: double sqrt(double c) input sqrt(c) = c output return type method name arguments public static double sqrt(double c) {... method signature (excludes return type) Please note that the method signature is defined incorrectly in the figure on pg 188 of your textbook 8
8 Anatomy of a Java Function Java functions It is easy to write your own - Example: double sqrt(double c) input sqrt(c) = c output public static double sqrt(double c) 9
9 Flow of Control Functions provide a new way to control the flow of execution implicit return statement at end of void function 10
10 Flow of Control What happens when a function is called: - Control transfers to the function - Argument variables are assigned the values given in the call - Function code is executed - Return value is substituted in place of the function call in the calling code - Control transfers back to the calling code Note: This is known as "pass by value" 11
11 Example Function to reverse a word Apply this word reversal function to reverse a sentence that is entered via command line arguments. Live coding time.. 12
12 Organizing Your Program Functions help you organize your program by breaking it down into a series of steps - Each function represents some abstract step or calculation - Arguments let you make the function have different behaviors Key Idea: write something ONCE as a function then reuse it many times 13
13 Scope Scope: the code that can refer to a particular variable - A variable's scope is the entire code block (any any nested blocks) after its declaration Simple example: int count = 1; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { count *= 2; // using 'i' here generates // a compiler error Best practice: declare variables to limit their scope 15
14 Function Challenge 1 Q. What happens when you compile and run the following code? public class Cubes1 { public static int cube(int i) { int j = i * i * i; return j; public static void main(string[] args) { int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) System.out.println(i + " " + cube(i)); 16
15 Scope with Functions 17
16 Tracing Functions public class Cubes1 { public static int cube(int i) { int j = i * i * i; return j; public static void main(string[] args) { int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) System.out.println(i + " " + cube(i)); % javac Cubes1.java % java Cubes
17 Last In First Out (LIFO) Stack of Plates
18 Method Overloading 20 Two or more methods in the same class may also have the same name This is called method overloading
19 Method Signature 21 A method is uniquely identified by - its name and - its parameter list (parameter types and their order) This is known as its signature Examples: static int min(int a, int b) static double min(double a, double b) static float min(float a, float b)
20 22 Return Type is Not Enough Suppose we attempt to create an overloaded circle(double x, double y, double r) method by using different return types: static void circle(double x, double y, double r) {... //returns true if circle is entirely onscreen, false otherwise static boolean circle(double x, double y, double r) {... This is NOT valid method overloading because the code that calls the function can ignore the return value circle(50, 50, 10); - The compiler can t tell which circle() method to invoke - Just because a method returns a value doesn t mean the calling code has to use it
21 23 Too Much of a Good Thing Automatic type promotion and overloading can sometimes interact in ways that confuse the compiler For example: // version 1 static void printaverage(int a, double b) {... // version 2 static void printaverage(double a, int b) {... Why might this be problematic?
22 24 Too Much of a Good Thing static void average(int a, double b) { /*code*/ static void average(double a, int b) { /*code*/ Consider if we do this public static void main (String[] args) {... average(4, 8);... The Java compiler can t decide whether to: - promote 7 to 7.0 and invoke the first version of average(), or - promote 5 to 5.0 and invoke the second version Take-home lesson: don t be too clever with method overloading
23 Function Examples overloading multiple arguments 30
24 Function Challenge 2 Q. What happens when you compile and run the following code? public class Cubes2 { public static int cube(int i) { int i = i * i * i; return i; public static void main(string[] args) { int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) System.out.println(i + " " + cube(i)); 31
25 Function Challenge 3 Q. What happens when you compile and run the following code? public class Cubes3 { public static int cube(int i) { i = i * i * i; public static void main(string[] args) { int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) System.out.println(i + " " + cube(i)); 32
26 Function Challenge 4 Q. What happens when you compile and run the following code? public class Cubes4 { public static int cube(int i) { i = i * i * i; return i; public static void main(string[] args) { int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) System.out.println(i + " " + cube(i)); 33
27 Function Challenge 5 Q. What happens when you compile and run the following code? public class Cubes5 { public static int cube(int i) { return i * i * i; public static void main(string[] args) { int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) System.out.println(i + " " + cube(i)); 34
A Foundation for Programming
 2.1 Functions A Foundation for Programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build bigger programs and reuse code graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and
2.1 Functions A Foundation for Programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build bigger programs and reuse code graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and
Lecture 5: Methods CS2301
 Lecture 5: Methods NADA ALZAHRANI CS2301 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Solution public static int sum(int i1, int i2) { int
Lecture 5: Methods NADA ALZAHRANI CS2301 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Solution public static int sum(int i1, int i2) { int
CS110D: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I
 CS110D: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science department Lecture 7&8: Methods Lecture Contents What is a method? Static methods Declaring and using methods Parameters Scope of declaration Overloading
CS110D: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science department Lecture 7&8: Methods Lecture Contents What is a method? Static methods Declaring and using methods Parameters Scope of declaration Overloading
Inf1-OOP. Functions aka Static Methods. Perdita Stevens, adapting earlier version by Ewan Klein. January 11, School of Informatics
 Inf1-OOP Functions aka Static Methods Perdita Stevens, adapting earlier version by Ewan Klein School of Informatics January 11, 2015 Overview Static Methods in Java Modularity Summary/Admin Functions /
Inf1-OOP Functions aka Static Methods Perdita Stevens, adapting earlier version by Ewan Klein School of Informatics January 11, 2015 Overview Static Methods in Java Modularity Summary/Admin Functions /
Announcements. PS 3 is due Thursday, 10/6. Midterm Exam 1: 10/14 (Fri), 9:00am-10:53am
 Announcements PS 3 is due Thursday, 10/6 Midterm Exam 1: 10/14 (Fri), 9:00am-10:53am Room TBD Scope: Lecture 1 to Lecture 9 (Chapters 1 to 6 of text) You may bring a sheet of paper (A4, both sides) Tutoring
Announcements PS 3 is due Thursday, 10/6 Midterm Exam 1: 10/14 (Fri), 9:00am-10:53am Room TBD Scope: Lecture 1 to Lecture 9 (Chapters 1 to 6 of text) You may bring a sheet of paper (A4, both sides) Tutoring
Functions / Static Methods. Inf1-OP. What s this static method business? Functions / Static Methods. Haskell function: type declaration
 Functions / Static Methods Inf1-OP Functions aka Static Methods Timothy Hospedales, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein School of Informatics February 6, 2017 Java functions: Take
Functions / Static Methods Inf1-OP Functions aka Static Methods Timothy Hospedales, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein School of Informatics February 6, 2017 Java functions: Take
2.1 Functions. f (x, y, z)
 2.1 Functions x y z f f (x, y, z) 1 A Foundation for Programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build bigger programs and reuse code graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays
2.1 Functions x y z f f (x, y, z) 1 A Foundation for Programming any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build bigger programs and reuse code graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013
 CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388)
 Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I
 CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science Department Lecture 8: Methods Lecture Contents: 2 Introduction Program modules in java Defining Methods Calling Methods Scope of local variables Passing Parameters
CS110: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE I Computer Science Department Lecture 8: Methods Lecture Contents: 2 Introduction Program modules in java Defining Methods Calling Methods Scope of local variables Passing Parameters
Review. Primitive Data Types & Variables. String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > <= >= == int, long float, double boolean char
 Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #12: Functions & Libraries Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements:
CS 112 Introduction to Programming (Spring 2012) Lecture #12: Functions & Libraries Zhong Shao Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson http://flint.cs.yale.edu/cs112 Acknowledgements:
Functions (or Static Methods) (Spring 2012)
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Functions (or Static Methods) (Spring 2012) Lecture #12: Functions & Libraries Zhong Shao x y Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson z f f
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Functions (or Static Methods) (Spring 2012) Lecture #12: Functions & Libraries Zhong Shao x y Department of Computer Science Yale University Office: 314 Watson z f f
Chapter 5 Methods. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
JAVA PROGRAMMING LAB. ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) ABSTRACT In this Lab you will learn to define and invoke void and return java methods JAVA
Static methods. Not actually a valid Java static method. Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen
 Static methods http://xkcd.com/221/ Not actually a valid Java static method Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen One big main(): Programs thus far public class DiceRolling public static void
Static methods http://xkcd.com/221/ Not actually a valid Java static method Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen One big main(): Programs thus far public class DiceRolling public static void
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming. February 29, 2012 Midterm
 CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming February 29, 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming February 29, 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
Opening Problem. Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively.
 Chapter 6 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 A Solution int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 6 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 A Solution int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1
 McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1 Midterm Exam Thursday, October 26, 2006, 18:00-20:00 (6:00 8:00 PM) Instructors: Mathieu Petitpas, Shah Asaduzzaman, Sherif
McGill University School of Computer Science COMP-202A Introduction to Computing 1 Midterm Exam Thursday, October 26, 2006, 18:00-20:00 (6:00 8:00 PM) Instructors: Mathieu Petitpas, Shah Asaduzzaman, Sherif
Opening Problem. Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively.
 Chapter 6 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 A Solution int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 6 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 A Solution int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Lecture #6-7 Methods
 Lecture #6-7 s 1. a. group of statements designed to perform a specific function b. may be reused many times i. in a particular program or ii. in multiple programs 2. Examples from the Java Library a.
Lecture #6-7 s 1. a. group of statements designed to perform a specific function b. may be reused many times i. in a particular program or ii. in multiple programs 2. Examples from the Java Library a.
All classes in a package can be imported by using only one import statement. If the postcondition of a method is not met, blame its implementer
 Java By Abstraction ANSWERS O ES-A GROUP - A For each question, give +0.5 if correct, -0.5 if wrong, and 0 if blank. If the overall total is negative, record it (on the test's cover sheet)
Java By Abstraction ANSWERS O ES-A GROUP - A For each question, give +0.5 if correct, -0.5 if wrong, and 0 if blank. If the overall total is negative, record it (on the test's cover sheet)
DATA TYPES AND EXPRESSIONS
 DATA TYPES AND EXPRESSIONS Outline Variables Naming Conventions Data Types Primitive Data Types Review: int, double New: boolean, char The String Class Type Conversion Expressions Assignment Mathematical
DATA TYPES AND EXPRESSIONS Outline Variables Naming Conventions Data Types Primitive Data Types Review: int, double New: boolean, char The String Class Type Conversion Expressions Assignment Mathematical
Chapter 5 Methods. Modifier returnvaluetype methodname(list of parameters) { // method body; }
 Chapter 5 Methods 5.1 Introduction A method is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation. You will learn how to: o create your own mthods with or without return values,
Chapter 5 Methods 5.1 Introduction A method is a collection of statements that are grouped together to perform an operation. You will learn how to: o create your own mthods with or without return values,
Chapter 5 Methods. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (c) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Methods rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. rights reserved. 0132130807 2 1 Problem int sum =
Chapter 5 Methods rights reserved. 0132130807 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. rights reserved. 0132130807 2 1 Problem int sum =
Chapter 5 Methods. public class FirstMethod { public static void main(string[] args) { double x= -2.0, y; for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++ ) { y = f( x );
![Chapter 5 Methods. public class FirstMethod { public static void main(string[] args) { double x= -2.0, y; for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++ ) { y = f( x ); Chapter 5 Methods. public class FirstMethod { public static void main(string[] args) { double x= -2.0, y; for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++ ) { y = f( x );](/thumbs/82/85488895.jpg) Chapter 5 Methods Sections Pages Review Questions Programming Exercises 5.1 5.11 142 166 1 18 2 22 (evens), 30 Method Example 1. This is of a main() method using a another method, f. public class FirstMethod
Chapter 5 Methods Sections Pages Review Questions Programming Exercises 5.1 5.11 142 166 1 18 2 22 (evens), 30 Method Example 1. This is of a main() method using a another method, f. public class FirstMethod
Inf1-OP. Functions aka Static Methods. Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein. School of Informatics
 Inf1-OP Functions aka Static Methods Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein School of Informatics February 26, 2018 Functions / Static Methods Why are functions so helpful?
Inf1-OP Functions aka Static Methods Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein School of Informatics February 26, 2018 Functions / Static Methods Why are functions so helpful?
2.1 Functions. 2.1 Functions. A Foundation for Programming. Functions (Static Methods) x y. f (x, y, z)
 A Foundation for Programming 2.1 Functions any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build bigger programs and reuse code graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and
A Foundation for Programming 2.1 Functions any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build bigger programs and reuse code graphics, sound, and image I/O arrays conditionals and
Chapter 3 Function Overloading
 Chapter 3 Function Overloading Function Overloading. Calling Overloaded Function. Function Overloading When Several Function declaration are specified for a single function name in the same scope, the
Chapter 3 Function Overloading Function Overloading. Calling Overloaded Function. Function Overloading When Several Function declaration are specified for a single function name in the same scope, the
Lecture 05: Methods. AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos.
 Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose
Lecture 05: Methods AITI Nigeria Summer 2012 University of Lagos. Agenda What a method is Why we use methods How to declare a method The four parts of a method How to use (invoke) a method The purpose
To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( ). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug,
 1 To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( 5.2-5.5). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug, and easy-to-maintain. ( 5.6). To use method overloading
1 To define methods, invoke methods, and pass arguments to a method ( 5.2-5.5). To develop reusable code that is modular, easy-toread, easy-to-debug, and easy-to-maintain. ( 5.6). To use method overloading
M e t h o d s a n d P a r a m e t e r s
 M e t h o d s a n d P a r a m e t e r s Objective #1: Call methods. Methods are reusable sections of code that perform actions. Many methods come from classes that are built into the Java language. For
M e t h o d s a n d P a r a m e t e r s Objective #1: Call methods. Methods are reusable sections of code that perform actions. Many methods come from classes that are built into the Java language. For
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes
 AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
Activity 4: Methods. Content Learning Objectives. Process Skill Goals
 Activity 4: Methods Java programs are organized into classes, each of which has one or more methods, each of which has one or more statements. Writing methods allows you to break down a complex program
Activity 4: Methods Java programs are organized into classes, each of which has one or more methods, each of which has one or more statements. Writing methods allows you to break down a complex program
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
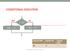 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal
 Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
Repe$$on CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition methods, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when using them: while do-while
COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2011
 NAME: login id: Precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2011 This test has 8 questions, weighted as indicated. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet. No
NAME: login id: Precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2011 This test has 8 questions, weighted as indicated. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet. No
Loops. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Loops CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Motivation Suppose that you need to print a string (e.g., "Welcome to Java!") a user-defined times N: N?
Loops CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Motivation Suppose that you need to print a string (e.g., "Welcome to Java!") a user-defined times N: N?
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals
 CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals 1 Recall From Last Time: Java Program import java.util.scanner; public class EggBasketEnhanced { public static void main(string[]
CSE 1223: Introduction to Computer Programming in Java Chapter 2 Java Fundamentals 1 Recall From Last Time: Java Program import java.util.scanner; public class EggBasketEnhanced { public static void main(string[]
Java Methods. Lecture 8 COP 3252 Summer May 23, 2017
 Java Methods Lecture 8 COP 3252 Summer 2017 May 23, 2017 Java Methods In Java, the word method refers to the same kind of thing that the word function is used for in other languages. Specifically, a method
Java Methods Lecture 8 COP 3252 Summer 2017 May 23, 2017 Java Methods In Java, the word method refers to the same kind of thing that the word function is used for in other languages. Specifically, a method
CS171:Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS171:Introduction to Computer Science II Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Li Xiong 9/7/2012 1 Announcement Introductory/Eclipse Lab, Friday, Sep 7, 2-3pm (today) Hw1 to be assigned Monday,
CS171:Introduction to Computer Science II Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Li Xiong 9/7/2012 1 Announcement Introductory/Eclipse Lab, Friday, Sep 7, 2-3pm (today) Hw1 to be assigned Monday,
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java
 CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture X: Methods II Passing Arguments Passing Arguments methods can accept outside information
CS-201 Introduction to Programming with Java California State University, Los Angeles Computer Science Department Lecture X: Methods II Passing Arguments Passing Arguments methods can accept outside information
2.1 Functions. x y. f (x, y, z) A Foundation for Programming. Functions (Static Methods)
 2.1 Functions x y z f f (x, y, z) 1 A Foundation for Programming Functions (Static Methods) any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build bigger programs and reuse code Java function.
2.1 Functions x y z f f (x, y, z) 1 A Foundation for Programming Functions (Static Methods) any program you might want to write objects functions and modules build bigger programs and reuse code Java function.
Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal
 Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition structures in Java, their syntax, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when
Repe$$on CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the following three repetition structures in Java, their syntax, their similarities and differences, and how to avoid common errors when
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012
 CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 135 Exam #0 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012 Name: This exam consists of 7 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
(A) 99 ** (B) 100 (C) 101 (D) 100 initial integers plus any additional integers required during program execution
 Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice Test 01. An array is a ** (A) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. (B) data structure with LIFO access. (C) data structure, which allows transfer between
Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice Test 01. An array is a ** (A) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. (B) data structure with LIFO access. (C) data structure, which allows transfer between
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Methods. CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University
 Methods CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Opening Problem Find multiple sums of integers: - from 1 to 10, - from 20 to 30, - from 35 to 45,... 2
Methods CSE 114, Computer Science 1 Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse114 1 Opening Problem Find multiple sums of integers: - from 1 to 10, - from 20 to 30, - from 35 to 45,... 2
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Chapter 5 Methods / Functions
 Chapter 5 Methods / Functions 1 Motivations A method is a construct for grouping statements together to perform a function. Using a method, you can write the code once for performing the function in a
Chapter 5 Methods / Functions 1 Motivations A method is a construct for grouping statements together to perform a function. Using a method, you can write the code once for performing the function in a
Programming Language Concepts: Lecture 2
 Programming Language Concepts: Lecture 2 Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute madhavan@cmi.ac.in http://www.cmi.ac.in/~madhavan/courses/pl2011 PLC 2011, Lecture 2, 6 January 2011 Classes and
Programming Language Concepts: Lecture 2 Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute madhavan@cmi.ac.in http://www.cmi.ac.in/~madhavan/courses/pl2011 PLC 2011, Lecture 2, 6 January 2011 Classes and
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Loops (Part II)
 CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Loops (Part II) Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs Review Is this an infinite loop? Why (not)?
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Loops (Part II) Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs Review Is this an infinite loop? Why (not)?
CS115 Principles of Computer Science
 CS115 Principles of Computer Science Chapter 5 Methods Prof. Joe X. Zhou Department of Computer Science CS115 Methods.1 Re: Objectives in Loops Sequence and selection aside, we need repetition (loops)
CS115 Principles of Computer Science Chapter 5 Methods Prof. Joe X. Zhou Department of Computer Science CS115 Methods.1 Re: Objectives in Loops Sequence and selection aside, we need repetition (loops)
Interpreted vs Compiled. Java Compile. Classes, Objects, and Methods. Hello World 10/6/2016. Python Interpreted. Java Compiled
 Interpreted vs Compiled Python 1 Java Interpreted Easy to run and test Quicker prototyping Program runs slower Compiled Execution time faster Virtual Machine compiled code portable Java Compile > javac
Interpreted vs Compiled Python 1 Java Interpreted Easy to run and test Quicker prototyping Program runs slower Compiled Execution time faster Virtual Machine compiled code portable Java Compile > javac
Chapter 6 Methods. Dr. Hikmat Jaber
 Chapter 6 Methods Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 6 Methods Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Object- Oriented Analysis, Design and Programming
 Object- Oriented Analysis, Design and Programming Medialogy, Semester 4 Monday 19 April 2010 9.00 12.00 You have 3 hours to complete this examination. Neither written material nor electronic equipment
Object- Oriented Analysis, Design and Programming Medialogy, Semester 4 Monday 19 April 2010 9.00 12.00 You have 3 hours to complete this examination. Neither written material nor electronic equipment
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 4: Methods Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 4: Methods Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Announcements Quiz 1 postponed: Due Jan 26 at 11:59pm Assignment 1 postponed: Due on Feb 1 at 11:59pm 2 Review What is
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 4: Methods Jackie Cheung, Winter 2016 Announcements Quiz 1 postponed: Due Jan 26 at 11:59pm Assignment 1 postponed: Due on Feb 1 at 11:59pm 2 Review What is
false, import, new 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
Object Oriented Programming in C#
 Introduction to Object Oriented Programming in C# Class and Object 1 You will be able to: Objectives 1. Write a simple class definition in C#. 2. Control access to the methods and data in a class. 3. Create
Introduction to Object Oriented Programming in C# Class and Object 1 You will be able to: Objectives 1. Write a simple class definition in C#. 2. Control access to the methods and data in a class. 3. Create
Condi(onals and Loops
 Condi(onals and Loops 1 Review Primi(ve Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathema(cal operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 2 A Founda(on for Programming any program
Condi(onals and Loops 1 Review Primi(ve Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathema(cal operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 2 A Founda(on for Programming any program
COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2014!
 NAME: login id: Precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2014 This test has 9 questions, weighted as indicated. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet. No
NAME: login id: Precept: COS 126 Midterm 1 Written Exam Fall 2014 This test has 9 questions, weighted as indicated. The exam is closed book, except that you are allowed to use a one page cheatsheet. No
The life and death of objects, sta2cs. CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen
 The life and death of objects, sta2cs CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Overview Where Java stores stuff The Heap The Stack Breaking both Java Garbage Collector (GC) CreaAng
The life and death of objects, sta2cs CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Overview Where Java stores stuff The Heap The Stack Breaking both Java Garbage Collector (GC) CreaAng
Inheritance and Polymorphism
 Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. M. G. Abbas Malik Assistant Professor Faculty of Computing and IT (North Jeddah Branch) King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, KSA mgmalik@kau.edu.sa www.sanlp.org/malik/cpit305/ap.html
Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. M. G. Abbas Malik Assistant Professor Faculty of Computing and IT (North Jeddah Branch) King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, KSA mgmalik@kau.edu.sa www.sanlp.org/malik/cpit305/ap.html
Functions / Static Methods. Why are functions so helpful? Inf1-OP. Find Nearest Neighbour to a Central Point
 Inf1-OP Functions aka Static Methods Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein Functions / Static Methods School of Informatics February 26, 2018 Find Nearest Neighbour
Inf1-OP Functions aka Static Methods Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein Functions / Static Methods School of Informatics February 26, 2018 Find Nearest Neighbour
JAVA Programming Concepts
 JAVA Programming Concepts M. G. Abbas Malik Assistant Professor Faculty of Computing and Information Technology University of Jeddah, Jeddah, KSA mgmalik@uj.edu.sa Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10,
JAVA Programming Concepts M. G. Abbas Malik Assistant Professor Faculty of Computing and Information Technology University of Jeddah, Jeddah, KSA mgmalik@uj.edu.sa Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10,
Chapter 5 Methods. Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Ninth Edition, (c) 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Chapter 5 Methods 1 Opening Problem Find the sum of integers from 1 to 10, from 20 to 30, and from 35 to 45, respectively. 2 Problem int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i
Data Abstraction and Specification of ADTs
 CITS2200 Data Structures and Algorithms Topic 4 Data Abstraction and Specification of ADTs Example The Reversal Problem and a non-adt solution Data abstraction Specifying ADTs Interfaces javadoc documentation
CITS2200 Data Structures and Algorithms Topic 4 Data Abstraction and Specification of ADTs Example The Reversal Problem and a non-adt solution Data abstraction Specifying ADTs Interfaces javadoc documentation
Total Score /15 /20 /30 /10 /5 /20 Grader
 NAME: NETID: CS2110 Fall 2009 Prelim 2 November 17, 2009 Write your name and Cornell netid. There are 6 questions on 8 numbered pages. Check now that you have all the pages. Write your answers in the boxes
NAME: NETID: CS2110 Fall 2009 Prelim 2 November 17, 2009 Write your name and Cornell netid. There are 6 questions on 8 numbered pages. Check now that you have all the pages. Write your answers in the boxes
COMP 110/L Lecture 6. Kyle Dewey
 COMP 110/L Lecture 6 Kyle Dewey Outline Methods Variable scope Call-by-value Testing with JUnit Variable Scope Question Does this compile? public class Test { public static void main(string[] args) { int
COMP 110/L Lecture 6 Kyle Dewey Outline Methods Variable scope Call-by-value Testing with JUnit Variable Scope Question Does this compile? public class Test { public static void main(string[] args) { int
false, import, new 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
Welcome Back. CSCI 262 Data Structures. Hello, Let s Review. Hello, Let s Review. How to Review 8/19/ Review. Here s a simple C++ program:
 Welcome Back CSCI 262 Data Structures 2 - Review What you learned in CSCI 261 (or equivalent): Variables Types Arrays Expressions Conditionals Branches & Loops Functions Recursion Classes & Objects Streams
Welcome Back CSCI 262 Data Structures 2 - Review What you learned in CSCI 261 (or equivalent): Variables Types Arrays Expressions Conditionals Branches & Loops Functions Recursion Classes & Objects Streams
(A) 99 (B) 100 (C) 101 (D) 100 initial integers plus any additional integers required during program execution
 Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice 01. An array is a (A) (B) (C) (D) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. data structure with LIFO access. data structure, which allows transfer between
Ch 5 Arrays Multiple Choice 01. An array is a (A) (B) (C) (D) data structure with one, or more, elements of the same type. data structure with LIFO access. data structure, which allows transfer between
Pull Lecture Materials and Open PollEv. Poll Everywhere: pollev.com/comp110. Lecture 12. else-if and while loops. Once in a while
 Pull Lecture Materials and Open PollEv Poll Everywhere: pollev.com/comp110 Lecture 12 else-if and while loops Once in a while Fall 2016 if-then-else Statements General form of an if-then-else statement:
Pull Lecture Materials and Open PollEv Poll Everywhere: pollev.com/comp110 Lecture 12 else-if and while loops Once in a while Fall 2016 if-then-else Statements General form of an if-then-else statement:
false, import, new 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
CSC207H: Software Design. Java + OOP. CSC207 Winter 2018
 Java + OOP CSC207 Winter 2018 1 Why OOP? Modularity: code can be written and maintained separately, and easily passed around the system Information-hiding: internal representation hidden from the outside
Java + OOP CSC207 Winter 2018 1 Why OOP? Modularity: code can be written and maintained separately, and easily passed around the system Information-hiding: internal representation hidden from the outside
We have written lots of code so far It has all been inside of the main() method What about a big program? The main() method is going to get really
 Week 9: Methods 1 We have written lots of code so far It has all been inside of the main() method What about a big program? The main() method is going to get really long and hard to read Sometimes you
Week 9: Methods 1 We have written lots of code so far It has all been inside of the main() method What about a big program? The main() method is going to get really long and hard to read Sometimes you
Tools : The Java Compiler. The Java Interpreter. The Java Debugger
 Tools : The Java Compiler javac [ options ] filename.java... -depend: Causes recompilation of class files on which the source files given as command line arguments recursively depend. -O: Optimizes code,
Tools : The Java Compiler javac [ options ] filename.java... -depend: Causes recompilation of class files on which the source files given as command line arguments recursively depend. -O: Optimizes code,
Java Fundamentals (II)
 Chair of Software Engineering Languages in Depth Series: Java Programming Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer Java Fundamentals (II) Marco Piccioni static imports Introduced in 5.0 Imported static members of a class
Chair of Software Engineering Languages in Depth Series: Java Programming Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer Java Fundamentals (II) Marco Piccioni static imports Introduced in 5.0 Imported static members of a class
Lecture Set 4: More About Methods and More About Operators
 Lecture Set 4: More About Methods and More About Operators Methods Definitions Invocations More arithmetic operators Operator Side effects Operator Precedence Short-circuiting main method public static
Lecture Set 4: More About Methods and More About Operators Methods Definitions Invocations More arithmetic operators Operator Side effects Operator Precedence Short-circuiting main method public static
CSCI 135 Midterm Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2011
 CSCI 135 Midterm Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2011 Name: This exam consists of 12 problems on the following 11 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CSCI 135 Midterm Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2011 Name: This exam consists of 12 problems on the following 11 pages. You may use your single- side hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the
CS321 Languages and Compiler Design I. Winter 2012 Lecture 2
 CS321 Languages and Compiler Design I Winter 2012 Lecture 2 1 A (RE-)INTRODUCTION TO JAVA FOR C++/C PROGRAMMERS Why Java? Developed by Sun Microsystems (now Oracle) beginning in 1995. Conceived as a better,
CS321 Languages and Compiler Design I Winter 2012 Lecture 2 1 A (RE-)INTRODUCTION TO JAVA FOR C++/C PROGRAMMERS Why Java? Developed by Sun Microsystems (now Oracle) beginning in 1995. Conceived as a better,
Object Oriented Methods : Deeper Look Lecture Three
 University of Babylon Collage of Computer Assistant Lecturer : Wadhah R. Baiee Experience has shown that the best way to develop and maintain a large program is to construct it from small, simple pieces,
University of Babylon Collage of Computer Assistant Lecturer : Wadhah R. Baiee Experience has shown that the best way to develop and maintain a large program is to construct it from small, simple pieces,
EECS1710. Announcements. Labtests have been returned Term Test #01 marking is in progress. Next Labtest: Thu Oct 23/Fri Oct 24
 EECS1710 Click to edit Master Week text 05, styles Lecture 10 Second level Third level Fourth level Fifth level Fall 2014! Thursday, Oct 09, 2014 1 Announcements Labtests have been returned Term Test #01
EECS1710 Click to edit Master Week text 05, styles Lecture 10 Second level Third level Fourth level Fifth level Fall 2014! Thursday, Oct 09, 2014 1 Announcements Labtests have been returned Term Test #01
Lec 3. Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables
 Lec 3 Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables Announcements First book reading due tonight at midnight Complete 80% of all activities to get 100% HW1 due Saturday at midnight Lab hours posted
Lec 3 Compilers, Debugging, Hello World, and Variables Announcements First book reading due tonight at midnight Complete 80% of all activities to get 100% HW1 due Saturday at midnight Lab hours posted
Total Score /15 /20 /30 /10 /5 /20 Grader
 NAME: NETID: CS2110 Fall 2009 Prelim 2 November 17, 2009 Write your name and Cornell netid. There are 6 questions on 8 numbered pages. Check now that you have all the pages. Write your answers in the boxes
NAME: NETID: CS2110 Fall 2009 Prelim 2 November 17, 2009 Write your name and Cornell netid. There are 6 questions on 8 numbered pages. Check now that you have all the pages. Write your answers in the boxes
Chapter 10 Inheritance and Polymorphism. Dr. Hikmat Jaber
 Chapter 10 Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Motivations Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the
Chapter 10 Inheritance and Polymorphism Dr. Hikmat Jaber 1 Motivations Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the
CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013
 CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2013 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CS 112 Introduction to Computing II. Wayne Snyder Computer Science Department Boston University
 9/5/6 CS Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today: Arrays (D and D) Methods Program structure Fields vs local variables Next time: Program structure continued: Classes
9/5/6 CS Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today: Arrays (D and D) Methods Program structure Fields vs local variables Next time: Program structure continued: Classes
CLASSES AND OBJECTS. Fundamentals of Computer Science I
 CLASSES AND OBJECTS Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Primitive types Creating your own data types Classes Objects Instance variables Instance methods Constructors Arrays of objects A Foundation
CLASSES AND OBJECTS Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Primitive types Creating your own data types Classes Objects Instance variables Instance methods Constructors Arrays of objects A Foundation
Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79 Example Given a radius
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79 Example Given a radius
INDEX. A SIMPLE JAVA PROGRAM Class Declaration The Main Line. The Line Contains Three Keywords The Output Line
 A SIMPLE JAVA PROGRAM Class Declaration The Main Line INDEX The Line Contains Three Keywords The Output Line COMMENTS Single Line Comment Multiline Comment Documentation Comment TYPE CASTING Implicit Type
A SIMPLE JAVA PROGRAM Class Declaration The Main Line INDEX The Line Contains Three Keywords The Output Line COMMENTS Single Line Comment Multiline Comment Documentation Comment TYPE CASTING Implicit Type
COP3502 Programming Fundamentals for CIS Majors 1. Instructor: Parisa Rashidi
 COP3502 Programming Fundamentals for CIS Majors 1 Instructor: Parisa Rashidi Chapter 4 Loops for while do-while Last Week Chapter 5 Methods Input arguments Output Overloading Code reusability Scope of
COP3502 Programming Fundamentals for CIS Majors 1 Instructor: Parisa Rashidi Chapter 4 Loops for while do-while Last Week Chapter 5 Methods Input arguments Output Overloading Code reusability Scope of
Methods. Bok, Jong Soon
 Methods Bok, Jong Soon javaexpert@nate.com www.javaexpert.co.kr Methods Enable you to separate statements into code blocks. Can be called whenever appropriate. Can invoke each other. Can call themselves(recursion)
Methods Bok, Jong Soon javaexpert@nate.com www.javaexpert.co.kr Methods Enable you to separate statements into code blocks. Can be called whenever appropriate. Can invoke each other. Can call themselves(recursion)
Outline. Parts 1 to 3 introduce and sketch out the ideas of OOP. Part 5 deals with these ideas in closer detail.
 OOP in Java 1 Outline 1. Getting started, primitive data types and control structures 2. Classes and objects 3. Extending classes 4. Using some standard packages 5. OOP revisited Parts 1 to 3 introduce
OOP in Java 1 Outline 1. Getting started, primitive data types and control structures 2. Classes and objects 3. Extending classes 4. Using some standard packages 5. OOP revisited Parts 1 to 3 introduce
Chapter 5 Control Statements: Part 2 Section 5.2 Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition
 Chapter 5 Control Statements: Part 2 Section 5.2 Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition 5.2 Q1: Counter-controlled repetition requires a. A control variable and initial value. b. A control variable
Chapter 5 Control Statements: Part 2 Section 5.2 Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition 5.2 Q1: Counter-controlled repetition requires a. A control variable and initial value. b. A control variable
COS 126 General Computer Science Fall Written Exam 1
 COS 26 General Computer Science Fall 27 Written Exam This exam has 7 questions (including question ) worth a total of 7 points. You have 5 minutes. Write all answers inside the designated spaces. Policies.
COS 26 General Computer Science Fall 27 Written Exam This exam has 7 questions (including question ) worth a total of 7 points. You have 5 minutes. Write all answers inside the designated spaces. Policies.
false, import, new 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45
Lecture 10 Declarations and Scope
 Lecture 10 Declarations and Scope Declarations and Scope We have seen numerous qualifiers when defining methods and variables public private static final (we'll talk about protected when formally addressing
Lecture 10 Declarations and Scope Declarations and Scope We have seen numerous qualifiers when defining methods and variables public private static final (we'll talk about protected when formally addressing
Chapter 11 Inheritance and Polymorphism. Motivations. Suppose you will define classes to model circles,
 Chapter 11 Inheritance and Polymorphism 1 Motivations Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the best way to design
Chapter 11 Inheritance and Polymorphism 1 Motivations Suppose you will define classes to model circles, rectangles, and triangles. These classes have many common features. What is the best way to design
