TETRIX Getting Started Guide FTC Extension
|
|
|
- Philomena Hart
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TeleOp Programming TETRIX Getting Started Guide FTC Extension Introduction In this guide, a TETRIX with LEGO MINDSTORMS robot with an arm and gripper extension will be programmed to be controlled by a joystick using the Remote Control Editor. The joystick will be configured so that it can make the robot move and pick up objects. Then, the remote control configuration will be generated into code and modified. This guide is for use with the ROBOTC programming language. Review: To review the basics of FTC programming in ROBOTC, review the Programming Guides and Tutorial Videos from the FTC Programming extension. These materials contain detailed information about how to use the FCS to run a FTC game and FTC templates to create FCS compatible programs. Configure the Motor and TETRIX Controllers: 1. Navigate to the Robot menu and select Motors and Sensors Setup. 2. Select the TETRIX Controllers tab and then select the Standard Configuration. One motor controller, one servo controller on sensor port S1 option. 37
2 TETRIX Getting Started Guide FTC Extension TeleOp Programming 3. Click the Motors tab. Under Type for motora, motorb, and motorc, select No Motor from the pull-down menu. Check the Reversed option for MotorD. 4. Since this is an arm and gripper bot, the servos will also have to be configured. By clicking the down arrow in the Type column, select Continuous Rotation Servo for both Servo 1 and Servo 2. 38
3 TeleOp Programming TETRIX Getting Started Guide FTC Extension Getting Started: 1. To start the program, open the TeleOp template from the FIRST Tech Challenge folder. Save the file with a new name in an appropriate directory. 2. Navigate to the initializerobot() function and place the commands that will move the arm and gripper to the initial position, where the Arm will be raised and the Gripper will be open. Set the arm servo, servo2, to an initial position of 127 and the gripper servo, servo1, to an initial position of 255. void initializerobot() Place code here to initialize servos to starting positions. Sensors are automatically configured and setup by ROBOTC. They may need a brief time to stabilize. servo[servo1] = 255; servo[servo2] = 127; Gripper opened Arm raised return; Declare the Variables: 3. Scroll down to the main() function. Inside this function, below the call to the initializerobot() function, declare two integer variables, mthreshold and athreshold. These will function as threshold values for the movement of the analog sticks so that any small, unintentional nudges will not cause the robot or any of the servos to move. Set mthreshold, the threshold for the drive motors, to a value of 15 and athreshold, the threshold for the arm servo motor, to a value of 30. int mthreshold = 15; int athreshold = 30; To avoid unnecessary movement Note: Two different thresholds have been declared because one of the analog sticks will control the motors, while the other will control the servo attached to the arm of the robot. 4. Declare two more integer variables, xval and yval. These variables will store the x and y values of the left analog stick, which controls the drive motors. It is not necessary to set initial values for these, as they will be set later in the program before they are used. int xval, yval; stores left analog stick values Note: Variables of the same type can be declared in one line of code, separated by commas. However, code will looks neater and is easier to debug later if it has been organized effectively. Any variables being initialized when they are declared should be put on a separate line. The two variables in Step 4 should be grouped together on one line because they are not being initialized at this point and because they are related to one another in how they will be used. 39
4 TETRIX Getting Started Guide FTC Extension TeleOp Programming 5. Declare two variables with a type of float, scalefactor and aposition. A float, or floating point number, stores seven decimal digits in total. Set the scalefactor variable to a value of 40.0/127, which will store the number into scalefactor. The scale factor will be used to set a maximum power for the drive motors, as well as map the range of the analog stick to the maximum power that has been set. In this case, the maximum power set is Set the aposition variable to ServoValue[servo2]. This will retrieve the arm servo s position value and store it in the aposition variable. float scalefactor = 40.0 / 127; Sets max. average motor power and maps range of analog stick to this power range float aposition = ServoValue[servo2]; Stores the current position of the arm servo 6. Once the variables have been defined, scroll down to the infinite loop found below the waitforstart() function call. The template contains a comment that says Add your robot specific tele-op code here. The rest of the code should be placed here. The first command to be placed here will be the getjoysticksettings(joystick) command, which will retrieve the data from the joystick every single time that the loop is run. Action will be taken according to the input received from the joystick through this command. while (true) getjoysticksettings(joystick); Retrieves data from the joystick 7. Set xval to the x position value and yval to the y position value retrieved from the left analog stick. xval = joystick.joy1_x1; yval = joystick.joy1_y1; 8. Use conditional statements, also referred to as if statements, to check if the values of the left analog stick are within the dead zone defined by the mthreshold variable. If either is within this dead zone, set the corresponding xval or yval variable to 0, so that the motor power will not be affected. if (abs(xval) < mthreshold) xval = 0; if (abs(yval) < mthreshold) yval = 0; Note: Because the analog stick reports values from -128 to 127, the absolute value of the position is taken to make the comparison easier. Otherwise, large negative values would be filtered out in the dead zone as well. 9. Set the drive motor power using the yval, xval and scalefactor variables. motor[motord] = ((yval) + (xval)) * scalefactor; motor[motore] = ((yval) - (xval)) * scalefactor; 40
5 TeleOp Programming TETRIX Getting Started Guide FTC Extension 10. The right analog stick will control the movement of the servo connected to the arm and will use a set of if and else if statements. The value of the analog stick needs to be compared to the value of athreshold to determine if the analog stick is within the dead zone. If the value of the analog stick is positive and within the dead zone, aposition should be decreased by a value of 0.15, to a minimum value of 0. If the value of the analog stick is negative and within the dead zone, aposition should be increased by a value of 0.15, to a maximum value of 255. if((joystick.joy1_y2 > athreshold) && (aposition > 0)) aposition -= 0.15; else if((joystick.joy1_y2 < (athreshold * -1)) && (aposition < 255)) aposition += 0.15; 11. Set the arm servo s position as defined by the aposition variable. servo[servo2] = aposition; Moves the arm servo 12. Use another set of if and else if statements to respond to the pressing of Buttons 5 and 6. The gripper should open if Button 5 is pressed, and close if Button 6 is pressed. if(joy1btn(5)) Open Gripper servo[servo1] = 255; else if(joy1btn(6)) Close Gripper servo[servo1] = 0; 41
6 TETRIX Getting Started Guide FTC Extension TeleOp Programming Completed Code: #pragma config(hubs, S1, HTMotor, HTServo, none, none) #pragma config(motor, mtr_s1_c1_1, motord, tmotornormal, openloop, reversed) #pragma config(motor, mtr_s1_c1_2, motore, tmotornormal, openloop) #pragma config(servo, srvo_s1_c2_1,, tservostandard) #pragma config(servo, srvo_s1_c2_2,, tservostandard) *!!Code automatically generated by 'ROBOTC' configuration wizard!!* / Tele-Operation Mode Code Template This file contains a template for simplified creation of an tele-op program for an FTC competition. You need to customize two functions with code unique to your specific robot. / #include "JoystickDriver.c" Include file to "handle" the Bluetooth messages. / initializerobot Prior to the start of TeleOp mode, you may want to perform some initialization on your robot and the variables within your program. In most cases, you may not have to add any code to this function and it will remain "empty". / void initializerobot() servo[servo1] = 255; Gripper opened servo[servo2] = 127; Arm raised return; 42
7 TeleOp Programming TETRIX Getting Started Guide FTC Extension Completed Code (continued): / Main Task The following is the main code for the tele-op robot operation. Customize as appropriate for your specific robot. Game controller / joystick information is sent periodically (about every 50 milliseconds) from the FMS (Field Management System) to the robot. Most TeleOp programs will follow the following logic: 1. Loop forever repeating the following actions: 2. Get the latest game controller / joystick settings that have been received from the PC. 3. Perform appropriate actions based on the joystick + buttons settings. This is usually a simple action: * Joystick values are usually directly translated into power levels for a motor or position of a servo. * Buttons are usually used to start/stop a motor or cause a servo to move to a specific position. 4. Repeat the loop. Your program needs to continuously loop because you need to continuously respond to changes in the game controller settings. At the end of the TeleOp period, the FMS will automatically abort (stop) execution of the program. / task main() initializerobot(); int mthreshold = 15; Sets dead zones to avoid unnecessary movement int athreshold = 30; int xval, yval; Stores left analog stick values float scalefactor = 40.0 / 127; Sets max. power and maps range of analog stick to max. power float aposition = ServoValue[servo2]; Stores the current position of the arm servo waitforstart(); Wait for start of TeleOp phase 43
8 TETRIX Getting Started Guide FTC Extension TeleOp Programming Completed Code (continued): while (true) getjoysticksettings(joystick); Retrieves data from the joystick xval = joystick.joy1_x1; yval = joystick.joy1_y1; Checks if analog stick values are within the dead zone if (abs(xval) < mthreshold) xval = 0; if (abs(yval) < mthreshold) yval = 0; motor[motord] = ((yval) + (xval)) * scalefactor; motor[motore] = ((yval) - (xval)) * scalefactor; Sets left motor power Sets right motor power Controls arm servo position 44 if((joystick.joy1_y2 > athreshold) && (aposition > 0)) aposition -= 0.15; else if((joystick.joy1_y2 < (athreshold * -1)) && (aposition < 255)) aposition += 0.15; servo[servo2] = aposition; Moves the arm servo if(joy1btn(5)) Open Gripper servo[servo1] = 255; else if(joy1btn(6)) Close Gripper servo[servo1] = 0;
TETRIX Getting Started Guide FTC Extension. Programming Guide (ROBOTC ) Autonomous Programming
 Introduction In this guide, a TETRIX with LEGO MINDSTORMS robot with an arm and gripper extension will be programmed to move forward until it detects an object, slow down as it approaches the object, and
Introduction In this guide, a TETRIX with LEGO MINDSTORMS robot with an arm and gripper extension will be programmed to move forward until it detects an object, slow down as it approaches the object, and
TETRIX Getting Started Guide FTC Extension
 Introduction In this guide, code created with the FTC templates will be explored and then run using the Field Control Software (FCS). An FTC game begins with an autonomous period where only autonomous
Introduction In this guide, code created with the FTC templates will be explored and then run using the Field Control Software (FCS). An FTC game begins with an autonomous period where only autonomous
RobotC Basics. FTC Team 2843 SSI Robotics October 6, 2012 Capitol College FTC Workshop
 RobotC Basics FTC Team 2843 SSI Robotics October 6, 2012 Capitol College FTC Workshop Agenda The Brick Sample Setup Template Multi Click Program Cancel Configuration (Pragmas) Joystick Data (get data)
RobotC Basics FTC Team 2843 SSI Robotics October 6, 2012 Capitol College FTC Workshop Agenda The Brick Sample Setup Template Multi Click Program Cancel Configuration (Pragmas) Joystick Data (get data)
TETRIX Getting Started Guide. Harvester and Transporter Programming Guide (ROBOTC )
 Introduction: In this guide, the Ranger Bot will be programmed to follow a line, pick up an object using the harvester, and put the object into the transporter. It will also count the number of objects
Introduction: In this guide, the Ranger Bot will be programmed to follow a line, pick up an object using the harvester, and put the object into the transporter. It will also count the number of objects
TETRIX Getting Started Guide. Launcher Programming Guide (ROBOTC )
 Introduction: In this guide, the Ranger Bot will be programmed to follow a line while carrying a ball. Upon sensing a bin with its ultrasonic sensor, it will launch the ball into the bin. This guide is
Introduction: In this guide, the Ranger Bot will be programmed to follow a line while carrying a ball. Upon sensing a bin with its ultrasonic sensor, it will launch the ball into the bin. This guide is
//#define HTIRS2_DSP_MODE = 1200;
 #pragma config(hubs, S1, HTMotor, HTMotor, HTMotor, HTMotor) #pragma config(hubs, S2, HTServo, none, none, none) #pragma config(sensor, S1,, sensori2cmuxcontroller) #pragma config(sensor, S2,, sensori2cmuxcontroller)
#pragma config(hubs, S1, HTMotor, HTMotor, HTMotor, HTMotor) #pragma config(hubs, S2, HTServo, none, none, none) #pragma config(sensor, S1,, sensori2cmuxcontroller) #pragma config(sensor, S2,, sensori2cmuxcontroller)
Getting Started with FTC Using RobotC
 Oregon Robotics Tournament and Outreach Program Getting Started with FTC Using RobotC 2008 Opening doors to the worlds of science and technology for Oregon s s youth Instructors Coordinator Robot C for
Oregon Robotics Tournament and Outreach Program Getting Started with FTC Using RobotC 2008 Opening doors to the worlds of science and technology for Oregon s s youth Instructors Coordinator Robot C for
RobotC for VEX. By Willem Scholten Learning Access Institute
 RobotC for VEX By Willem Scholten Learning Access Institute 1 RobotCgetStarted.key - February 5, 2016 RobotC for VEX Section 1 - RobotC How to switch between VEX 2.0 Cortex and VEX IQ Section 2 - RobotC
RobotC for VEX By Willem Scholten Learning Access Institute 1 RobotCgetStarted.key - February 5, 2016 RobotC for VEX Section 1 - RobotC How to switch between VEX 2.0 Cortex and VEX IQ Section 2 - RobotC
RobotC. Remote Control
 RobotC Remote Control Learning Objectives: Focusing on Virtual World with Physical Examples Understand Real-Time Joystick Mapping Understand how to use timers Understand how to incorporate buttons into
RobotC Remote Control Learning Objectives: Focusing on Virtual World with Physical Examples Understand Real-Time Joystick Mapping Understand how to use timers Understand how to incorporate buttons into
Advanced RobotC. Sensors and Autonomous Coding Teams 5233 Vector and 5293 Rexbotics
 Advanced RobotC Sensors and Autonomous Coding Teams 5233 Vector and 5293 Rexbotics jcagle@chapelgateacademy.org Setup Select platform NXT + TETRIX/MATRIX Create New Autonomous Configure Robot with your
Advanced RobotC Sensors and Autonomous Coding Teams 5233 Vector and 5293 Rexbotics jcagle@chapelgateacademy.org Setup Select platform NXT + TETRIX/MATRIX Create New Autonomous Configure Robot with your
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Robot C Settings for Programming in VEX IQ Text Mode Setup the software for Vex IQ: Platform Tab: Platform Type [Vex Robotics] [VEX IQ] Quick
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Robot C Settings for Programming in VEX IQ Text Mode Setup the software for Vex IQ: Platform Tab: Platform Type [Vex Robotics] [VEX IQ] Quick
Getting Started in RobotC. // Comment task main() motor[] {} wait1msec() ; = Header Code Compile Download Run
![Getting Started in RobotC. // Comment task main() motor[] {} wait1msec() ; = Header Code Compile Download Run Getting Started in RobotC. // Comment task main() motor[] {} wait1msec() ; = Header Code Compile Download Run](/thumbs/74/70117328.jpg) Getting Started in RobotC // Comment task main() motor[] {} wait1msec() ; = Header Code Compile Download Run Understand Motion Learning Objectives Motors: How they work and respond. Fuses: Understand why
Getting Started in RobotC // Comment task main() motor[] {} wait1msec() ; = Header Code Compile Download Run Understand Motion Learning Objectives Motors: How they work and respond. Fuses: Understand why
LabVIEW for FTC Release Notes
 LabVIEW for FTC Release Notes FTC 2010 Contents These release notes contain system requirements and installation instructions for LabVIEW for FTC. LabVIEW for FTC includes LabVIEW 2009 Student Edition
LabVIEW for FTC Release Notes FTC 2010 Contents These release notes contain system requirements and installation instructions for LabVIEW for FTC. LabVIEW for FTC includes LabVIEW 2009 Student Edition
16-311: Getting Started with ROBOTC and the. LEGO Mindstorms NXT. Aurora Qian, Billy Zhu
 16-311: Getting Started with ROBOTC and the LEGO Mindstorms NXT Aurora Qian, Billy Zhu May, 2016 Table of Contents 1. Download and Install 2. License Activation 3. Wireless Connection 4. Running Programs
16-311: Getting Started with ROBOTC and the LEGO Mindstorms NXT Aurora Qian, Billy Zhu May, 2016 Table of Contents 1. Download and Install 2. License Activation 3. Wireless Connection 4. Running Programs
G. Tardiani RoboCup Rescue. EV3 Workshop Part 1 Introduction to RobotC
 RoboCup Rescue EV3 Workshop Part 1 Introduction to RobotC Why use RobotC? RobotC is a more traditional text based programming language The more compact coding editor allows for large programs to be easily
RoboCup Rescue EV3 Workshop Part 1 Introduction to RobotC Why use RobotC? RobotC is a more traditional text based programming language The more compact coding editor allows for large programs to be easily
Getting Started with the FTC SDK. Jaxon Brown August 5, 2017
 Getting Started with the FTC SDK Jaxon Brown August 5, 2017 Goals Install the Software Development Kit (SDK) Learn the Java basics How is the FTC SDK structured? Creating a basic Teleop Program Creating
Getting Started with the FTC SDK Jaxon Brown August 5, 2017 Goals Install the Software Development Kit (SDK) Learn the Java basics How is the FTC SDK structured? Creating a basic Teleop Program Creating
Getting Started in RobotC. // Comment task main() motor[] {} wait1msec() ; = Header Code Compile Download Run
![Getting Started in RobotC. // Comment task main() motor[] {} wait1msec() ; = Header Code Compile Download Run Getting Started in RobotC. // Comment task main() motor[] {} wait1msec() ; = Header Code Compile Download Run](/thumbs/76/73855663.jpg) Getting Started in RobotC // Comment task main() motor[] {} wait1msec() ; = Header Code Compile Download Run Learning Objectives Explore Computer Programming using by controlling a virtual robot. Understand
Getting Started in RobotC // Comment task main() motor[] {} wait1msec() ; = Header Code Compile Download Run Learning Objectives Explore Computer Programming using by controlling a virtual robot. Understand
These instructions use a standard Robot Configuration based on the PushBot tutorial from FIRST. The Robot setup is as follows:
 Introduction to Robotics and Engineering Marist School Resource: FTC_Android_Programming Description: These instructions will take you through downloading and setting up the Android Studio and FTC Robot
Introduction to Robotics and Engineering Marist School Resource: FTC_Android_Programming Description: These instructions will take you through downloading and setting up the Android Studio and FTC Robot
! Before you start, make sure you have the right parts available. Set these parts on a table, and put all other parts away for now.
 Tank Tread Drivetrain Before you start, make sure you have the right parts available. Set these parts on a table, and put all other parts away for now. Brain & Battery 4 1x standoffs 4 2x2 black connectors
Tank Tread Drivetrain Before you start, make sure you have the right parts available. Set these parts on a table, and put all other parts away for now. Brain & Battery 4 1x standoffs 4 2x2 black connectors
K Force The Kristin Robotics Team Introductory Programming Tutorial 2014 For use with the teams squarebot training robots.
 K Force The Kristin Robotics Team Introductory Programming Tutorial 2014 For use with the teams squarebot training robots. K Force Squarebot Programming Course - 2014 Robot moves forward for two seconds
K Force The Kristin Robotics Team Introductory Programming Tutorial 2014 For use with the teams squarebot training robots. K Force Squarebot Programming Course - 2014 Robot moves forward for two seconds
Programming Preset Heights in ROBOTC for VEX Robotics By George Gillard
 Programming Preset Heights in ROBOTC for VEX Robotics By George Gillard Introduction Programming a button that lifts an arm (or other mechanism for that matter) to a specific preprogrammed point can be
Programming Preset Heights in ROBOTC for VEX Robotics By George Gillard Introduction Programming a button that lifts an arm (or other mechanism for that matter) to a specific preprogrammed point can be
Chapter 19 Assembly Modeling with the TETRIX by Pitsco Building System Autodesk Inventor
 Tools for Design Using AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor 19-1 Chapter 19 Assembly Modeling with the TETRIX by Pitsco Building System Autodesk Inventor Create and Use Subassemblies in Assemblies Creating an
Tools for Design Using AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor 19-1 Chapter 19 Assembly Modeling with the TETRIX by Pitsco Building System Autodesk Inventor Create and Use Subassemblies in Assemblies Creating an
Next Gen Platform: Team & Mentor Guide
 Next Gen Platform: Team & Mentor Guide 1 Introduction For the 2015-2016 season, the FIRST Tech Challenge (FTC) will be adopting a new controller for its robot competitions. The new platform, which will
Next Gen Platform: Team & Mentor Guide 1 Introduction For the 2015-2016 season, the FIRST Tech Challenge (FTC) will be adopting a new controller for its robot competitions. The new platform, which will
Autonomous Parking. LEGOeducation.com/MINDSTORMS. Duration Minutes. Learning Objectives Students will: Di culty Beginner
 Autonomous Parking Design cars that can park themselves safely without driver intervention. Learning Objectives Students will: Understand that algorithms are capable of carrying out a series of instructions
Autonomous Parking Design cars that can park themselves safely without driver intervention. Learning Objectives Students will: Understand that algorithms are capable of carrying out a series of instructions
WIZ-PRO2 CURRICULUM HIGHLIGHTS
 WIZ-PRO2 CURRICULUM HIGHLIGHTS STEM Learning and Advanced Robotics (ages 9-11) Develop more advanced programming skills, create programs using lines of code in Scratch, use more powerful robotics components
WIZ-PRO2 CURRICULUM HIGHLIGHTS STEM Learning and Advanced Robotics (ages 9-11) Develop more advanced programming skills, create programs using lines of code in Scratch, use more powerful robotics components
Variables and Functions. ROBOTC Software
 Variables and Functions ROBOTC Software Variables A variable is a space in your robots memory where data can be stored, including whole numbers, decimal numbers, and words Variable names follow the same
Variables and Functions ROBOTC Software Variables A variable is a space in your robots memory where data can be stored, including whole numbers, decimal numbers, and words Variable names follow the same
Intro to Android Studio
 Intro to Android Studio Presenters Knut Peterson, Project Manager, Robo Raiders Jamari Morrison, Programming Lead, Robo Raiders Learning Goals How component mapping works Combining flow charting with programming
Intro to Android Studio Presenters Knut Peterson, Project Manager, Robo Raiders Jamari Morrison, Programming Lead, Robo Raiders Learning Goals How component mapping works Combining flow charting with programming
Introduction to Robotics using Lego Mindstorms EV3
 Introduction to Robotics using Lego Mindstorms EV3 Facebook.com/roboticsgateway @roboticsgateway Robotics using EV3 Are we ready to go Roboticists? Does each group have at least one laptop? Do you have
Introduction to Robotics using Lego Mindstorms EV3 Facebook.com/roboticsgateway @roboticsgateway Robotics using EV3 Are we ready to go Roboticists? Does each group have at least one laptop? Do you have
26 27 //m8 (6u, two values, 127 for released button and +127 for pressed button, was m7) (suggest servo only)
 1 //ReadMe.txt 2 3 //BEST WarpXX (2012 Game) 4 5 //Default code, jg revision 7/16/2012 6 7 //Motor (control) Description 8 9 //Port (joystick or buttons) 10 11 //m2 (+j3) m2 and m9 are opposing analog
1 //ReadMe.txt 2 3 //BEST WarpXX (2012 Game) 4 5 //Default code, jg revision 7/16/2012 6 7 //Motor (control) Description 8 9 //Port (joystick or buttons) 10 11 //m2 (+j3) m2 and m9 are opposing analog
Movement using Shaft Encoders
 Movement using Shaft Encoders Configure (Motors and Sensors Setup) We will look at the following in this section SensorValue[] while Conditions (, =,!=, ==) Quadrature/Shaft/Rotation Encoder 360
Movement using Shaft Encoders Configure (Motors and Sensors Setup) We will look at the following in this section SensorValue[] while Conditions (, =,!=, ==) Quadrature/Shaft/Rotation Encoder 360
Six Omni Wheel Chain Drivetrain
 Six Omni Wheel Chain Drivetrain Before you start, make sure you have the right parts available. Set these parts on a table, and put all other parts away for now. [Note, this can be built with only 4 omni
Six Omni Wheel Chain Drivetrain Before you start, make sure you have the right parts available. Set these parts on a table, and put all other parts away for now. [Note, this can be built with only 4 omni
The Power Turtle Drivetrain
 The Power Turtle Drivetrain Before you start, make sure you have the right parts available. Set these parts on a table, and put all other parts away for now. Brain & Battery 4 small gears 1 4x8 plate 4
The Power Turtle Drivetrain Before you start, make sure you have the right parts available. Set these parts on a table, and put all other parts away for now. Brain & Battery 4 small gears 1 4x8 plate 4
Command and Control Tutorial
 Command and Control Tutorial Introduction Command and Control is a new LabVIEW template added for the 2016 season which organizes robot code into commands and controllers for a collection of robot-specific
Command and Control Tutorial Introduction Command and Control is a new LabVIEW template added for the 2016 season which organizes robot code into commands and controllers for a collection of robot-specific
FTC Control Systems + Java The Gifted Gears
 FTC Control Systems + Java 101 Outline Control Systems REV Modern Robotics Phones and Phone Setup Programming Options and Setup Navigating Android Studios Java! OpModes Basics Actuators Teleop What Am
FTC Control Systems + Java 101 Outline Control Systems REV Modern Robotics Phones and Phone Setup Programming Options and Setup Navigating Android Studios Java! OpModes Basics Actuators Teleop What Am
Creating a robot project
 Creating a robot project Liquid error: No route matches {:action=>"show", :controller=>"spaces/chapters", :space_id=>"3120", :manual_id=>"7952", :id=>nil} Launching WindRiver Workbench WindRiver Workbench
Creating a robot project Liquid error: No route matches {:action=>"show", :controller=>"spaces/chapters", :space_id=>"3120", :manual_id=>"7952", :id=>nil} Launching WindRiver Workbench WindRiver Workbench
General Syntax. Operators. Variables. Arithmetic. Comparison. Assignment. Boolean. Types. Syntax int i; float j = 1.35; int k = (int) j;
 General Syntax Statements are the basic building block of any C program. They can assign a value to a variable, or make a comparison, or make a function call. They must be terminated by a semicolon. Every
General Syntax Statements are the basic building block of any C program. They can assign a value to a variable, or make a comparison, or make a function call. They must be terminated by a semicolon. Every
Electronics Workshop. Jessie Liu
 Electronics Workshop Jessie Liu 1 Return Kit Servos Servo Extensions Controller Analog USB/Tether Serial WiFi key (2) (2) Digital i/o Servo Power Adaptor AAA Battery Charger motors/ servos (4) Servo Mounting
Electronics Workshop Jessie Liu 1 Return Kit Servos Servo Extensions Controller Analog USB/Tether Serial WiFi key (2) (2) Digital i/o Servo Power Adaptor AAA Battery Charger motors/ servos (4) Servo Mounting
Download Program. Setup ROBOTC. task main() { motor[motorc] = 100; wait1msec(3000);
![Download Program. Setup ROBOTC. task main() { motor[motorc] = 100; wait1msec(3000); Download Program. Setup ROBOTC. task main() { motor[motorc] = 100; wait1msec(3000);](/thumbs/73/68136870.jpg) Your robot is ready to go! All that s left is for you to tell it what to do by sending it a program. A program is a set of commands that tell the robot what to do and how to react to its environment. Once
Your robot is ready to go! All that s left is for you to tell it what to do by sending it a program. A program is a set of commands that tell the robot what to do and how to react to its environment. Once
FTC 2017 Control System
 FTC 2017 Control System Common Pitfalls & Text Based Java September 9, 2017 Ranger Robotics 1 Modern Robotics : Buy More Fuses Always have a few spare 20A automotive fuses Burnout often caused by the following
FTC 2017 Control System Common Pitfalls & Text Based Java September 9, 2017 Ranger Robotics 1 Modern Robotics : Buy More Fuses Always have a few spare 20A automotive fuses Burnout often caused by the following
Activity Basic Inputs Programming - VEX Clawbot
 Activity 3.1.3 Basic Inputs Programming - VEX Clawbot Introduction Inputs are devices which provide a processor with environmental information to make decisions. These devices have the capacity to sense
Activity 3.1.3 Basic Inputs Programming - VEX Clawbot Introduction Inputs are devices which provide a processor with environmental information to make decisions. These devices have the capacity to sense
Activity Basic Inputs Programming VEX
 Activity 3.1.3 Basic Inputs Programming VEX Introduction Inputs are devices which provide a processor with environmental information to make decisions. These devices have the capacity to sense the environment
Activity 3.1.3 Basic Inputs Programming VEX Introduction Inputs are devices which provide a processor with environmental information to make decisions. These devices have the capacity to sense the environment
Activity Basic Inputs Programming VEX
 Activity 3.1.3 Basic Inputs Programming VEX Introduction Inputs are devices which provide a processor with environmental information to make decisions. These devices have the capacity to sense the environment
Activity 3.1.3 Basic Inputs Programming VEX Introduction Inputs are devices which provide a processor with environmental information to make decisions. These devices have the capacity to sense the environment
Choosing a Base Class
 Choosing a Base Class There a number of base classes (starting points) for your robot program. Each base class sets the style and structure of your program. Be sure to read through this section before
Choosing a Base Class There a number of base classes (starting points) for your robot program. Each base class sets the style and structure of your program. Be sure to read through this section before
FIRST Tech Challenge 8/31/2016
 FTC Training Manual Using the FTC SDK FIRST Tech Challenge 8/31/2016 This document contains training material to introduce students and mentors how to write programs for the FIRST Tech Challenge Robot
FTC Training Manual Using the FTC SDK FIRST Tech Challenge 8/31/2016 This document contains training material to introduce students and mentors how to write programs for the FIRST Tech Challenge Robot
Introduction to Lab 2
 Introduction to Lab 2 Programming LEGO Mindstorms NXT using Ada Jakaria Abdullah 12 September 2016 Jakaria Abdullah Lab 2: LEGO 12 September 2016 1 / 25 Lab 2: Programming LEGO Mindstorms using Ada Lab
Introduction to Lab 2 Programming LEGO Mindstorms NXT using Ada Jakaria Abdullah 12 September 2016 Jakaria Abdullah Lab 2: LEGO 12 September 2016 1 / 25 Lab 2: Programming LEGO Mindstorms using Ada Lab
2. Within your four student group, form a two student team known as Team A and a two student team known as Team B.
 Introduction Inputs are devices which provide a processor with environmental information to make decisions. These devices have the capacity to sense the environment in a variety of ways such as physical
Introduction Inputs are devices which provide a processor with environmental information to make decisions. These devices have the capacity to sense the environment in a variety of ways such as physical
the robot not only to go forward, backwards, and turn, but also to straffe from side to side.
 Programming This will be the second year for FTC to have the new Android control system. Our team loves it. Java was very similar to RobotC, but also opens up a lot of possibilities for us to stretch further
Programming This will be the second year for FTC to have the new Android control system. Our team loves it. Java was very similar to RobotC, but also opens up a lot of possibilities for us to stretch further
Autonomous Programming FTC Challenge Workshops VCU School of Engineering September 24, 2016 Presented by: Team 8297 Geared UP!
 Autonomous Programming 2016-2017 FTC Challenge Workshops VCU School of Engineering September 24, 2016 Presented by: Team 8297 Geared UP! Autonomous in VELOCITY VORTEX The Match starts with a 30 second
Autonomous Programming 2016-2017 FTC Challenge Workshops VCU School of Engineering September 24, 2016 Presented by: Team 8297 Geared UP! Autonomous in VELOCITY VORTEX The Match starts with a 30 second
Activity Basic Inputs Programming Answer Key (VEX)
 Activity 1.2.4 Basic Inputs Programming Answer Key (VEX) Introduction Inputs are devices which provide a processor with environmental information to make decisions. These devices have the capacity to sense
Activity 1.2.4 Basic Inputs Programming Answer Key (VEX) Introduction Inputs are devices which provide a processor with environmental information to make decisions. These devices have the capacity to sense
The Beginners Guide to ROBOTC. Volume 2, 3 rd Edition Written by George Gillard Published: 18-July-2016
 The Beginners Guide to ROBOTC Volume 2, 3 rd Edition Written by George Gillard Published: 18-July-2016 Introduction ROBOTC is an application used for programming robots. There are many different versions
The Beginners Guide to ROBOTC Volume 2, 3 rd Edition Written by George Gillard Published: 18-July-2016 Introduction ROBOTC is an application used for programming robots. There are many different versions
W I T H EAGLE ROBOTICS TEAM 7373
 P R O G R A M M I N G W I T H A N D R O I D EAGLE ROBOTICS TEAM 7373 DISCLAIMER This is only an overview We cannot cover every aspect of Android Studio If you have questions, contact us using the information
P R O G R A M M I N G W I T H A N D R O I D EAGLE ROBOTICS TEAM 7373 DISCLAIMER This is only an overview We cannot cover every aspect of Android Studio If you have questions, contact us using the information
Activity Variables and Functions VEX
 Activity 3.1.5 Variables and Functions VEX Introduction A program can accomplish a given task in any number of ways. Programs can quickly grow to an unmanageable size so variables and functions provide
Activity 3.1.5 Variables and Functions VEX Introduction A program can accomplish a given task in any number of ways. Programs can quickly grow to an unmanageable size so variables and functions provide
INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
 DATA15001 INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE THE FINAL EPISODE (11): ROBOTICS TODAY S MENU 1. "GRAND CHALLENGE" 2. LEGO MIND- STORMS 3. ROBO WORKSHOPS ROBOTICS AS A "GRAND CHALLENGE" OF AI actuators:
DATA15001 INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE THE FINAL EPISODE (11): ROBOTICS TODAY S MENU 1. "GRAND CHALLENGE" 2. LEGO MIND- STORMS 3. ROBO WORKSHOPS ROBOTICS AS A "GRAND CHALLENGE" OF AI actuators:
Robotics Study Material School Level 1 Semester 2
 Robotics Study Material School Level 1 Semester 2 Contents UNIT-3... 4 NXT-PROGRAMMING... 4 CHAPTER-1... 5 NXT- PROGRAMMING... 5 CHAPTER-2... 6 NXT-BRICK PROGRAMMING... 6 A. Multiple choice questions:...
Robotics Study Material School Level 1 Semester 2 Contents UNIT-3... 4 NXT-PROGRAMMING... 4 CHAPTER-1... 5 NXT- PROGRAMMING... 5 CHAPTER-2... 6 NXT-BRICK PROGRAMMING... 6 A. Multiple choice questions:...
Last Updated: ROBOTBUILDER
 Last Updated: 12-01-2016 ROBOTBUILDER Table of Contents The basic steps to create a robot program...4 Overview of RobotBuilder...5 Starting RobotBuilder... 12 The RobotBuilder user interface... 14 Setting
Last Updated: 12-01-2016 ROBOTBUILDER Table of Contents The basic steps to create a robot program...4 Overview of RobotBuilder...5 Starting RobotBuilder... 12 The RobotBuilder user interface... 14 Setting
Block Programming Guide
 f Block Programming Guide FIRST Global Block Programming Guide - Rev 1 Copyright 2018 REV Robotics, LLC TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Getting Started... 1 1.1 Prerequisites... 1 2 Introduction... 2 2.1 What is an
f Block Programming Guide FIRST Global Block Programming Guide - Rev 1 Copyright 2018 REV Robotics, LLC TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Getting Started... 1 1.1 Prerequisites... 1 2 Introduction... 2 2.1 What is an
Application Note 44. Controlling a Lynx6 Robotic Arm. Introduction
 Introduction Application Note 44 Controlling a Lynx6 Robotic Arm This application note describes the control of a Lynx6 robotic arm (www.lynxmotion.com) using an embedded microcontroller and the um-fpu
Introduction Application Note 44 Controlling a Lynx6 Robotic Arm This application note describes the control of a Lynx6 robotic arm (www.lynxmotion.com) using an embedded microcontroller and the um-fpu
Activity Inputs and Outputs VEX
 Activity 3.1.1 Inputs and Outputs VEX Introduction Robots are similar to humans if you consider that both use inputs and outputs to sense and react to the world. Most humans use five senses to perceive
Activity 3.1.1 Inputs and Outputs VEX Introduction Robots are similar to humans if you consider that both use inputs and outputs to sense and react to the world. Most humans use five senses to perceive
Controlling the Robotic Arm using the BBC micro:bit
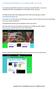 Controlling the Robotic Arm using the BBC micro:bit You need to plug the BBC micro:bit into a computer using a USB cable or sync to it using Bluetooth after downloading the correct app from your app store.
Controlling the Robotic Arm using the BBC micro:bit You need to plug the BBC micro:bit into a computer using a USB cable or sync to it using Bluetooth after downloading the correct app from your app store.
Activity Inputs and Outputs VEX
 Activity 3.1.1 Inputs and Outputs VEX Introduction Robots are similar to humans if you consider that both use inputs and outputs to sense and react to the world. Most humans use five senses to perceive
Activity 3.1.1 Inputs and Outputs VEX Introduction Robots are similar to humans if you consider that both use inputs and outputs to sense and react to the world. Most humans use five senses to perceive
AndyMark Arduino Tutorial
 AndyMark Arduino Tutorial Tank Drive June 2014 Required: Required Software List: - Kit Arduino IDE - Robot Power Cable Kit (am-0975) RobotOpen Arduino Shield Software - Battery Base Package (am-0477) RobotOpen
AndyMark Arduino Tutorial Tank Drive June 2014 Required: Required Software List: - Kit Arduino IDE - Robot Power Cable Kit (am-0975) RobotOpen Arduino Shield Software - Battery Base Package (am-0477) RobotOpen
EV3 Programming Workshop for FLL Coaches
 EV3 Programming Workshop for FLL Coaches Tony Ayad 2017 Outline This workshop is intended for FLL coaches who are interested in learning about Mindstorms EV3 programming language. Programming EV3 Controller
EV3 Programming Workshop for FLL Coaches Tony Ayad 2017 Outline This workshop is intended for FLL coaches who are interested in learning about Mindstorms EV3 programming language. Programming EV3 Controller
Robot Code Review. Welcome!
 Robot Code Review Welcome! Basic robot code knowledge review Two phases in each game: Autonomous The robot runs on preprogrammed instructions Teleoperated The robot runs on commands as given by a driver
Robot Code Review Welcome! Basic robot code knowledge review Two phases in each game: Autonomous The robot runs on preprogrammed instructions Teleoperated The robot runs on commands as given by a driver
Introduction to Lab 2
 Introduction to Lab 2 Programming LEGO Mindstorms NXT using Ada Jakaria Abdullah 19 September 2017 Jakaria Abdullah Lab 2: LEGO 19 September 2017 1 / 24 Lab 2: Programming LEGO NXTs using Ada Lab goals:
Introduction to Lab 2 Programming LEGO Mindstorms NXT using Ada Jakaria Abdullah 19 September 2017 Jakaria Abdullah Lab 2: LEGO 19 September 2017 1 / 24 Lab 2: Programming LEGO NXTs using Ada Lab goals:
Robotics with Lego EV3 + MS Makecode. Andrea Sterbini
 Robotics with Lego Andrea Sterbini sterbini@di.uniroma1.it Microsoft Makecode.com Many development systems supported (embedded/robotics/game) micro:bit Adafruit Minecraft Lego EV3 Cue Arcade Chibi chip
Robotics with Lego Andrea Sterbini sterbini@di.uniroma1.it Microsoft Makecode.com Many development systems supported (embedded/robotics/game) micro:bit Adafruit Minecraft Lego EV3 Cue Arcade Chibi chip
BROWNCOATS Team 7842 Engineering Notebook - FIRST Relic Recovery
 Code Teleop Hardware package org.firstinspires.ftc.teamcode; import com.qualcomm.robotcore.hardware.crservo; import com.qualcomm.robotcore.hardware.dcmotor; import com.qualcomm.robotcore.hardware.dcmotorsimple;
Code Teleop Hardware package org.firstinspires.ftc.teamcode; import com.qualcomm.robotcore.hardware.crservo; import com.qualcomm.robotcore.hardware.dcmotor; import com.qualcomm.robotcore.hardware.dcmotorsimple;
RCX Tutorial. Commands Sensor Watchers Stack Controllers My Commands
 RCX Tutorial Commands Sensor Watchers Stack Controllers My Commands The following is a list of commands available to you for programming the robot (See advanced below) On Turns motors (connected to ports
RCX Tutorial Commands Sensor Watchers Stack Controllers My Commands The following is a list of commands available to you for programming the robot (See advanced below) On Turns motors (connected to ports
Activity Basic Outputs Programming VEX
 Activity 3.1.2 Basic Outputs Programming VEX Introduction Computer programs are used in many applications in our daily life. Devices that are controlled by a processor are called outputs. These devices
Activity 3.1.2 Basic Outputs Programming VEX Introduction Computer programs are used in many applications in our daily life. Devices that are controlled by a processor are called outputs. These devices
RobotC primer. Alexander Kirillov
 RobotC primer version 1.1, September 2013 Alexander Kirillov IslandBots robotic club URL: http://islandbots.org/robotc/ E-mail address: shurik179@gmail.com This work is licensed under the Creative Commons
RobotC primer version 1.1, September 2013 Alexander Kirillov IslandBots robotic club URL: http://islandbots.org/robotc/ E-mail address: shurik179@gmail.com This work is licensed under the Creative Commons
VEX ARM Cortex -based Microcontroller and VEXnet Joystick User Guide
 1. VEX ARM Cortex -based Microcontroller and VEXnet Joystick Pairing Procedure: a. The Joystick must first be paired to the VEX ARM Cortex -based Microcontroller before they will work using VEXnet Keys.
1. VEX ARM Cortex -based Microcontroller and VEXnet Joystick Pairing Procedure: a. The Joystick must first be paired to the VEX ARM Cortex -based Microcontroller before they will work using VEXnet Keys.
BEST Control System. Dave Wilkerson. September 12, 2015
 BEST Control System BEST Robotics, Inc. Dave Wilkerson September 12, 2015 Copyright 2012 BEST Robotics, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Servos Joystick Return Kit AAA Battery Charger Analog WiFi key USB/Tether
BEST Control System BEST Robotics, Inc. Dave Wilkerson September 12, 2015 Copyright 2012 BEST Robotics, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Servos Joystick Return Kit AAA Battery Charger Analog WiFi key USB/Tether
LCP-USB Inclinometer sensor DLL Interface library description Page 1 of 5
 LCP-USB Inclinometer sensor DLL Interface library description Page 1 of 5 Description The LCP-USB sensor connects to a USB host (PC) with a standard 4 pin USB A connector. It is USB 2.0 compatible. The
LCP-USB Inclinometer sensor DLL Interface library description Page 1 of 5 Description The LCP-USB sensor connects to a USB host (PC) with a standard 4 pin USB A connector. It is USB 2.0 compatible. The
ROBOTC Basic Programming
 ROBOTC Basic Programming Open ROBOTC and create a new file Check Compiler Target If you plan to download code to a robot, select the Physical Robot opbon. If you plan to download code to a virtual robot,
ROBOTC Basic Programming Open ROBOTC and create a new file Check Compiler Target If you plan to download code to a robot, select the Physical Robot opbon. If you plan to download code to a virtual robot,
Tutorial: Making Legobot Move Steering Command Brighton H.S Engineering By: Matthew Jourden
 Tutorial: Making Legobot Move Steering Command Brighton H.S Engineering By: Matthew Jourden 1. Build Bas Robot. See Build Manual in the Lego Core Set Kit for details or Build Instructions Base Robot File
Tutorial: Making Legobot Move Steering Command Brighton H.S Engineering By: Matthew Jourden 1. Build Bas Robot. See Build Manual in the Lego Core Set Kit for details or Build Instructions Base Robot File
Robot Design Workshop: VEX Hardware & Robot Building Basics
 Robot Design Workshop: VEX Hardware & Robot Building Basics Nik Kukert Bison BEST Robotics 1 Basics Only use parts supplied in the consumable and returnable kits (or approved optional items) Robots containing
Robot Design Workshop: VEX Hardware & Robot Building Basics Nik Kukert Bison BEST Robotics 1 Basics Only use parts supplied in the consumable and returnable kits (or approved optional items) Robots containing
Activity Basic Outputs Programming VEX
 Activity 3.1.2 Basic Outputs Programming VEX Introduction Computer programs are used in many applications in our daily life. Devices that are controlled by a processor are called outputs. These devices
Activity 3.1.2 Basic Outputs Programming VEX Introduction Computer programs are used in many applications in our daily life. Devices that are controlled by a processor are called outputs. These devices
Arduino 101 AN INTRODUCTION TO ARDUINO BY WOMEN IN ENGINEERING FT T I NA A ND AW E S O ME ME NTO R S
 Arduino 101 AN INTRODUCTION TO ARDUINO BY WOMEN IN ENGINEERING FT T I NA A ND AW E S O ME ME NTO R S Overview Motivation Circuit Design and Arduino Architecture Projects Blink the LED Switch Night Lamp
Arduino 101 AN INTRODUCTION TO ARDUINO BY WOMEN IN ENGINEERING FT T I NA A ND AW E S O ME ME NTO R S Overview Motivation Circuit Design and Arduino Architecture Projects Blink the LED Switch Night Lamp
1 Overview Sequencer PS2 Control...26 C O N T E N T S INTRODUCTION...5 USER INTERFACE...6 CONNECTING...7 SIMULATOR...
 AL5 ARM GUIDE C O N T E N T S CHAPTER 1 1 Overview...4 INTRODUCTION...5 USER INTERFACE...6 CONNECTING...7 CONNECTING VIA USB (FOR SSC-32U, RB-LYN-850)...7 CONNECTING VIA SERIAL CABLE (FOR DISCONTINUED
AL5 ARM GUIDE C O N T E N T S CHAPTER 1 1 Overview...4 INTRODUCTION...5 USER INTERFACE...6 CONNECTING...7 CONNECTING VIA USB (FOR SSC-32U, RB-LYN-850)...7 CONNECTING VIA SERIAL CABLE (FOR DISCONTINUED
Unit 03 Tutorial 3: Sensors: Touch Sensor Brighton H.S Engineering By: Matthew Jourden
 Unit 03 Tutorial 3: Sensors: Touch Sensor Brighton H.S Engineering By: Matthew Jourden Robots have a variety of sensors that help the machine sense the world around it. We will be looking at four different
Unit 03 Tutorial 3: Sensors: Touch Sensor Brighton H.S Engineering By: Matthew Jourden Robots have a variety of sensors that help the machine sense the world around it. We will be looking at four different
Objectives. Part 1: forward kinematics. Physical Dimension
 ME 446 Laboratory #1 Kinematic Transformations Report is due at the beginning of your lab time the week of February 20 th. One report per group. Lab sessions will be held the weeks of January 23 rd, January
ME 446 Laboratory #1 Kinematic Transformations Report is due at the beginning of your lab time the week of February 20 th. One report per group. Lab sessions will be held the weeks of January 23 rd, January
MS4SSA Robotics Module:
 MS4SSA Robotics Module: Programming and Sensors Brad Miller and Kim Hollan What are we doing today? Talk about why to program robots Learn about basic RobotC programming Learn how to make the robot move
MS4SSA Robotics Module: Programming and Sensors Brad Miller and Kim Hollan What are we doing today? Talk about why to program robots Learn about basic RobotC programming Learn how to make the robot move
Troubleshooting ROBOTC with Cortex
 This guide is to designed to be used by a student or teacher as a reference for help troubleshooting ROBOTC software issues. Troubleshooting Topics Computer will not Recognize the VEX Cortex Not able to
This guide is to designed to be used by a student or teacher as a reference for help troubleshooting ROBOTC software issues. Troubleshooting Topics Computer will not Recognize the VEX Cortex Not able to
Importing the Vernier Sensor Block into LEGO MINDSTORMS 2
 Using the Vernier Adapter and Vernier Block with LEGO s MINDSTORMS Edu NXT V2.0 software (Updated April 14, 2011) Introduction The Vernier NXT Adapter allows many of our analog ( -BTA ) sensors to work
Using the Vernier Adapter and Vernier Block with LEGO s MINDSTORMS Edu NXT V2.0 software (Updated April 14, 2011) Introduction The Vernier NXT Adapter allows many of our analog ( -BTA ) sensors to work
VEX Startup and Configuration Procedures
 VEX Startup and Configuration Procedures Power Up Open RobotC Step 2 Plug battery into the Cortex power port. The plug is keyed to only install one way. Black wire will face to the outside of the Cortex.
VEX Startup and Configuration Procedures Power Up Open RobotC Step 2 Plug battery into the Cortex power port. The plug is keyed to only install one way. Black wire will face to the outside of the Cortex.
Module Testing. Improve FTC Hardware/Software Cooperation Presented by: Team ToborTech
 Module Testing Improve FTC Hardware/Software Cooperation Presented by: Team ToborTech Team 8610 Tobortech Veteran team, this is our 5th season Went to worlds last year So we ll be excited to share some
Module Testing Improve FTC Hardware/Software Cooperation Presented by: Team ToborTech Team 8610 Tobortech Veteran team, this is our 5th season Went to worlds last year So we ll be excited to share some
Software Design Objectives
 Team 2228 CougarTech 1 Software Design Objectives Part I Understand Software design process Part II Understand FIRST Code Development Environment Understand FIRST program structure Understand FIRST I/O
Team 2228 CougarTech 1 Software Design Objectives Part I Understand Software design process Part II Understand FIRST Code Development Environment Understand FIRST program structure Understand FIRST I/O
The "Hello world" of FRC robot programming
 The "Hello world" of FRC robot programming Here's how to create the shortest possible robot program that actually does something useful. In this case, it provides tank steering in teleop mode and drives
The "Hello world" of FRC robot programming Here's how to create the shortest possible robot program that actually does something useful. In this case, it provides tank steering in teleop mode and drives
Activity Basic Outputs Programming Answer Key (VEX) Introduction
 Activity 1.2.3 Basic Outputs Programming Answer Key (VEX) Introduction Computer programs are used in many applications in our daily life. Devices that are controlled by a processor are called outputs.
Activity 1.2.3 Basic Outputs Programming Answer Key (VEX) Introduction Computer programs are used in many applications in our daily life. Devices that are controlled by a processor are called outputs.
User Defined Functions
 User Defined Functions CS 141 Lecture 4 Chapter 5 By Ziad Kobti 27/01/2003 (c) 2003 by Ziad Kobti 1 Outline Functions in C: Definition Function Prototype (signature) Function Definition (body/implementation)
User Defined Functions CS 141 Lecture 4 Chapter 5 By Ziad Kobti 27/01/2003 (c) 2003 by Ziad Kobti 1 Outline Functions in C: Definition Function Prototype (signature) Function Definition (body/implementation)
CORTEX Microcontroller and Joystick User Guide
 This is a User Guide for using the VEX CORTEX Microcontroller and VEX Joystick. Refer to the VEX Wiki (http://www.vexforum.com/wiki/index.php/vex_cortex_microcontroller) for updates to this document. 1.
This is a User Guide for using the VEX CORTEX Microcontroller and VEX Joystick. Refer to the VEX Wiki (http://www.vexforum.com/wiki/index.php/vex_cortex_microcontroller) for updates to this document. 1.
The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce you to the Construct 2 program. First, you will be told where the software is located on the computer
 Learning Targets: Students will be introduced to industry recognized game development software Students will learn how to navigate within the software Students will learn the basics on how to use Construct
Learning Targets: Students will be introduced to industry recognized game development software Students will learn how to navigate within the software Students will learn the basics on how to use Construct
BİL200 TUTORIAL-EXERCISES Objective:
 Objective: The purpose of this tutorial is learning the usage of -preprocessors -header files -printf(), scanf(), gets() functions -logic operators and conditional cases A preprocessor is a program that
Objective: The purpose of this tutorial is learning the usage of -preprocessors -header files -printf(), scanf(), gets() functions -logic operators and conditional cases A preprocessor is a program that
FRC LABVIEW PROGRAMMING
 FRC LABVIEW PROGRAMMING Last Updated: 01-07-2017 Table of Contents Setting up the Development Environment...3 Installing LabVIEW for FRC 2017 (LabVIEW only)...4 Installing the FRC 2017 Update Suite (All
FRC LABVIEW PROGRAMMING Last Updated: 01-07-2017 Table of Contents Setting up the Development Environment...3 Installing LabVIEW for FRC 2017 (LabVIEW only)...4 Installing the FRC 2017 Update Suite (All
Wireless Networked Autonomous Mobile Robot with HAWK Animated Head System. Sputnik 3. Quick Start Guide
 Wireless Networked Autonomous Mobile Robot with HAWK Animated Head System Sputnik 3 Quick Start Guide Copyright 2009, WARNINGS Do NOT power on the robot before reading and fully understanding the operation
Wireless Networked Autonomous Mobile Robot with HAWK Animated Head System Sputnik 3 Quick Start Guide Copyright 2009, WARNINGS Do NOT power on the robot before reading and fully understanding the operation
Microsoft Word - Templates
 Microsoft Word - Templates Templates & Styles. Microsoft Word come will a large amount of predefined templates designed for you to use, it is also possible to download additional templates from web sites
Microsoft Word - Templates Templates & Styles. Microsoft Word come will a large amount of predefined templates designed for you to use, it is also possible to download additional templates from web sites
PS2 Wireless Owners Manual. By Robosoft Systems
 PS2 Wireless Owners Manual By Robosoft Systems Know your Board Symbol Device U1 P89V51RD2 Microcontroller U2 L298 Motor Driver 1 U3 L298 Motor Driver 2 U4 74HCT2400 Inverting buffer PS2 PS2 connector BATTRY
PS2 Wireless Owners Manual By Robosoft Systems Know your Board Symbol Device U1 P89V51RD2 Microcontroller U2 L298 Motor Driver 1 U3 L298 Motor Driver 2 U4 74HCT2400 Inverting buffer PS2 PS2 connector BATTRY
Last Updated: ROBOTBUILDER
 Last Updated: 06-11-2016 ROBOTBUILDER Table of Contents The basic steps to create a robot program...4 Overview of RobotBuilder...5 Starting RobotBuilder... 12 The RobotBuilder user interface... 14 Setting
Last Updated: 06-11-2016 ROBOTBUILDER Table of Contents The basic steps to create a robot program...4 Overview of RobotBuilder...5 Starting RobotBuilder... 12 The RobotBuilder user interface... 14 Setting
Chapter 7 Human Interface Devices. asyrani.com
 Chapter 7 Human Interface Devices asyrani.com Types of Human Interface Devices Magnavox Odyssey, released in 1972, was the first video game console. Interfacing with a HID Some simple devices, like game
Chapter 7 Human Interface Devices asyrani.com Types of Human Interface Devices Magnavox Odyssey, released in 1972, was the first video game console. Interfacing with a HID Some simple devices, like game
An Introduction to MATLAB
 An Introduction to MATLAB Day 1 Simon Mitchell Simon.Mitchell@ucla.edu High level language Programing language and development environment Built-in development tools Numerical manipulation Plotting of
An Introduction to MATLAB Day 1 Simon Mitchell Simon.Mitchell@ucla.edu High level language Programing language and development environment Built-in development tools Numerical manipulation Plotting of
Robotics Education & Competition Foundation
 Robotics Education & Competition Foundation VRC Event Troubleshooting Guide When Things Go Wrong NOW What? BEFORE YOU START YOUR EVENT Always set up the night before an event if possible. Always test the
Robotics Education & Competition Foundation VRC Event Troubleshooting Guide When Things Go Wrong NOW What? BEFORE YOU START YOUR EVENT Always set up the night before an event if possible. Always test the
