Functions (API) Setup Functions
|
|
|
- Esmond Holt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Functions (API) Some of the functions in the WiringPi library are designed to mimic those in the Arduino Wiring system. There are relatively easy to use and should present no problems for anyone used to the Arduino system, or C programming in-general. The main difference is that unlike the Arduino system, the main loop of the program is not provided for you you need to write it yourself. This is often desirable in a Linux system anyway as it can give you access to command-line arguments and so on. See the examples page for some simple examples and a Makefile to use. Before using the WiringPi library, you need to include its header file: #include <wiringpi.h> You may also need to add -I/usr/local/include -L/usr/local/lib -lwiringpi to the compile line of your program depending on the environment you are using. The important one is -lwiringpi Setup Functions There are three ways to initialise wiringpi. int wiringpisetup (void) ; int wiringpisetupgpio (void) ; int wiringpisetupsys (void) ; One of the setup functions must be called at the start of your program. If it returns -1 then the initialisation of the GPIO has failed, and you should consult the global errno to see why. The differences between the setup functions are as follows: wiringpisetup(void) ; This initialises the wiringpi system and assumes that the calling program is going to be using the wiringpi pin numbering scheme. This is a simplified numbering scheme which provides a mapping from virtual pin numbers 0 through 16 to the real underlying Broadcom GPIO pin numbers. See the pins page for a table which maps the wiringpi pin number to the Broadcom GPIO pin number to the physical location on the edge connector. This function needs to be called with root privileges. wiringpisetupgpio(void) ; This is identical to above, however it allows the calling programs to use the Broadcom GPIO pin numbers directly with no re-mapping. As above, this function need to be called with root priveledges wiringpisetupsys(void) This initialises the wiringpi system but uses the /sys/class/gpio interface rather than accessing the hardware directly. This can be called as a non-root user provided the GPIO pins have been exported before-hand using the gpio program. Pin number in this mode is the native Broadcom GPIO numbers. Note: In this mode you can only use the pins which have been exported via the /sys/class/gpio interface. You must export these pins before you call your program. You can do this in a separate
2 shell-script, or by using the system() function from inside your program. Also note that some functions (noted below) have no effect when using this mode as they re not currently possible to action unless called with root privileges. General wiring functions void pinmode (int pin, int mode) ; This sets the mode of a pin to either INPUT, OUTPUT, or PWM_OUTPUT. Note that only wiringpi pin 1 (BCM_GPIO 18) supports PWM output. The pin number is the number obtained from the pins table. This function has no effect when in Sys mode. void digitalwrite (int pin, int value) ; Writes the value HIGH or LOW (1 or 0) to the given pin which must have been previously set as an output. void digitalwritebyte (int value) ; This writes the 8-bit byte supplied to the 8 GPIO pins. It s the fastest way to set all 8 bits at once to a particular value, although it still takes twi write operations to the GPIO hardware. void pwmwrite (int pin, int value) ; Writes the value to the PWM register for the given pin. The value must be between 0 and (Again, note that only pin 1 (BCM_GPIO 18) supports PWM) This function has no effect when in Sys mode (see above) int digitalread (int pin) ; This function returns the value read at the given pin. It will be HIGH or LOW (1 or 0) depending on the logic level at the pin. void pullupdncontrol (int pin, int pud) ; This sets the pull-up or pull-down resistor mode on the given pin, which should be set as an input. Unlike the Arduino, the BCM2835 has both pull-up an down internal resistors. The parameter pud should be; PUD_OFF, (no pull up/down), PUD_DOWN (pull to ground) or PUD_UP (pull to 3.3v) This function has no effect when in Sys mode. If you need to activate a pull-up/pull-down, then you can do it with the gpio program in a script before you start your program. PWM Control PWM can not be controlled when running in Sys mode. pwmsetmode (int mode) ; The PWM generator can run in 2 modes balanced and mark:space. The mark:space mode is traditional, however the default mode in the Pi is balanced. You can switch modes by supplying the parameter: PWM_MODE_BAL or PWM_MODE_MS. pwmsetrange (unsigned int range) ; This sets the range register in the PWM generator. The default is pwmsetclock (int divisor) ; This sets the divisor for the PWM clock.
3 To understand more about the PWM system, you ll need to read the Broadcom ARM peripherals manual. Timing functions unsigned int millis (void) This returns a number representing the number if milliseconds since your program called one of the wiringpisetup functions. It returns an unsigned 32-bit number which wraps after 49 days. void delay (unsigned int howlong) This causes program execution to pause for at least howlong milliseconds. Due to the multi-tasking nature of Linux it could be longer. Note that the maximum delay is an unsigned 32-bit integer or approximately 49 days. void delaymicroseconds (unsigned int howlong) This causes program execution to pause for at least howlong microseconds. Due to the multitasking nature of Linux it could be longer. Note that the maximum delay is an unsigned 32-bit integer microseconds or approximately 71 minutes. Program/Thread Priority int pihipri (int priority) ; This attempts to shift your program (or thread in a multi-threaded program) to a higher priority and enables a real-time scheduling. The priority parameter should be from 0 (the default) to 99 (the maximum). This won t make your program go any faster, but it will give it a bigger slice of time when other programs are running. The priority parameter works relative to others so you can make one program priority 1 and another priority 2 and it will have the same effect as setting one to 10 and the other to 90 (as long as no other programs are running with elevated priorities) The return value is 0 for success and -1 for error. If an error is returned, the program should then consult the errno global variable, as per the usual conventions. Note: Only programs running as root can change their priority. If called from a non-root program then nothing happens. Interrupts With a newer kernel patched with the GPIO interrupt handling code, (ie. any kernel after about June 2012), you can now wait for an interrupt in your program. This frees up the processor to do other tasks while you re waiting for that interrupt. The GPIO can be set to interrupt on a rising, falling or both edges of the incoming signal. Note: Jan 2013: The waitforinterrupt() function is deprecated you should use the newer and easier to use wiringpiisr() function below. int waitforinterrupt (int pin, int timeout) ; When called, it will wait for an interrupt event to happen on that pin and your program will be stalled. The timeout parameter is given in milliseconds, or can be -1 which means to wait forever. The return value is -1 if an error occurred (and errno will be set appropriately), 0 if it timed out, or 1 on a successful interrupt event. Before you call waitforinterrupt, you must first initialise the GPIO pin and at present the only way to do this is to use the gpio program, either in a script, or using the system() call from inside your program.
4 e.g. We want to wait for a falling-edge interrupt on GPIO pin 0, so to setup the hardware, we need to run: gpio edge 0 falling before running the program. int wiringpiisr (int pin, int edgetype, void (*function)(void)) ; This function registers a function to received interrupts on the specified pin. The edgetype parameter is either INT_EDGE_FALLING, INT_EDGE_RISING, INT_EDGE_BOTH or INT_EDGE_SETUP. If it is INT_EDGE_SETUP then no initialisation of the pin will happen it s assumed that you have already setup the pin elsewhere (e.g. with the gpio program), but if you specify one of the other types, then the pin will be exported and initialised as specified. This is accomplished via a suitable call to the gpio utility program, so it need to be available. The pin number is supplied in the current mode native wiringpi, BCM_GPIO or Sys modes. This function will work in any mode, and does not need root privileges to work. The function will be called when the interrupt triggers. When it is triggered, it s cleared in the dispatcher before calling your function, so if a subsequent interrupt fires before you finish your handler, then it won t be missed. (However it can only track one more interrupt, if more than one interrupt fires while one is being handled then they will be ignored) This function is run at a high priority (if the program is run using sudo, or as root) and executes concurrently with the main program. It has full access to all the global variables, open file handles and so on. See the isr.c example program for more details on how to use this feature. Concurrent Processing (multi-threading) wiringpi has a simplified interface to the Linux implementation of Posix threads, as well as a (simplified) mechanisms to access mutex s (Mutual exclusions) Using these functions you can create a new process (a function inside your main program) which runs concurrently with your main program and using the mutex mechanisms, safely pass variables between them. int pithreadcreate (name) ; This function creates a thread which is another function in your program previously declared using the PI_THREAD declaration. This function is then run concurrently with your main program. An example may be to have this function wait for an interrupt while your program carries on doing other tasks. The thread can indicate an event, or action by using global variables to communicate back to the main program, or other threads. Thread functions are declared as follows: PI_THREAD (mythread) {.. code here to run concurrently with the main program, probably in an infinite loop } and would be started in the main program with: x = pithreadcreate (mythread) ; if (x!= 0) printf ("it didn't start\n")
5 This is really nothing more than a simplified interface to the Posix threads mechanism that Linux supports. See the manual pages on Posix threads (man pthread) if you need more control over them. pilock (int keynum) ; piunlock (int keynum) ; These allow you to synchronise variable updates from your main program to any threads running in your program. keynum is a number from 0 to 3 and represents a key. When another process tries to lock the same key, it will be stalled until the first process has unlocked the same key. You may need to use these functions to ensure that you get valid data when exchanging data between your main program and a thread otherwise it s possible that the thread could wake-up halfway during your data copy and change the data so the data you end up copying is incomplete, or invalid. See the wfi.c program in the examples directory for an example. Misc. Functions piboardrev (void) ; This returns the board revision of the Raspberry Pi. It will be either 1 or 2. Some of the BCM_GPIO pins changed number and function when moving from board revision 1 to 2, so if you are using BCM_GPIO pin numbers, then you need to be aware of the differences. wpipintogpio (int wpipin) ; This returns the BCM_GPIO pin number of the supplied wiringpi pin. It takes the board revision into account. setpaddrive (int group, int value) ; This sets the strength of the pad drivers for a particular group of pins. There are 3 groups of pins and the drive strength is from 0 to 7. Do not use this unless you know what you are doing.
RPi General Purpose IO (GPIO) Pins
 GPIO RPi Setup for Today Because the cobbler connector has a notch, you can only put the cable in the right way But, it is possible to put the cable in upside down on the Raspberry Pi The colored wire
GPIO RPi Setup for Today Because the cobbler connector has a notch, you can only put the cable in the right way But, it is possible to put the cable in upside down on the Raspberry Pi The colored wire
6 GPIO 84. Date: 29/09/2016 Name: ID: This laboratory session discusses about writing program to interact with GPIO of Reapberry Pi.
 6 GPIO 84 Date: 29/09/2016 Name: ID: Name: ID: 6 GPIO This laboratory session discusses about writing program to interact with GPIO of Reapberry Pi. GPIO programming with Assembly Code:block installation
6 GPIO 84 Date: 29/09/2016 Name: ID: Name: ID: 6 GPIO This laboratory session discusses about writing program to interact with GPIO of Reapberry Pi. GPIO programming with Assembly Code:block installation
ArdOS The Arduino Operating System Quick Start Guide and Examples
 ArdOS The Arduino Operating System Quick Start Guide and Examples Contents 1. Introduction... 1 2. Obtaining ArdOS... 2 3. Installing ArdOS... 2 a. Arduino IDE Versions 1.0.4 and Prior... 2 b. Arduino
ArdOS The Arduino Operating System Quick Start Guide and Examples Contents 1. Introduction... 1 2. Obtaining ArdOS... 2 3. Installing ArdOS... 2 a. Arduino IDE Versions 1.0.4 and Prior... 2 b. Arduino
Microcontrollers and Interfacing week 8 exercises
 2 HARDWARE DEBOUNCING Microcontrollers and Interfacing week 8 exercises 1 More digital input When using a switch for digital input we always need a pull-up resistor. For convenience, the microcontroller
2 HARDWARE DEBOUNCING Microcontrollers and Interfacing week 8 exercises 1 More digital input When using a switch for digital input we always need a pull-up resistor. For convenience, the microcontroller
Arduino Prof. Dr. Magdy M. Abdelhameed
 Course Code: MDP 454, Course Name:, Second Semester 2014 Arduino What is Arduino? Microcontroller Platform Okay but what s a Microcontroller? Tiny, self-contained computers in an IC Often contain peripherals
Course Code: MDP 454, Course Name:, Second Semester 2014 Arduino What is Arduino? Microcontroller Platform Okay but what s a Microcontroller? Tiny, self-contained computers in an IC Often contain peripherals
The OMNI Thread Abstraction
 The OMNI Thread Abstraction Tristan Richardson AT&T Laboratories Cambridge Revised November 2001 1 Introduction The OMNI thread abstraction is designed to provide a common set of thread operations for
The OMNI Thread Abstraction Tristan Richardson AT&T Laboratories Cambridge Revised November 2001 1 Introduction The OMNI thread abstraction is designed to provide a common set of thread operations for
Lesson6_7segments digital LED score board
 Lesson6_7segments digital LED score board 7 segments digital LED score board is a digital LED display, and made by 7 LED lights, there are share a common ground pin, so we can control each pin to show
Lesson6_7segments digital LED score board 7 segments digital LED score board is a digital LED display, and made by 7 LED lights, there are share a common ground pin, so we can control each pin to show
tm1640-rpi Documentation
 tm1640-rpi Documentation Release 0.1 Michael Farrell October 20, 2015 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Resources................................................. 3 2 Building the software 5 3 Wiring the
tm1640-rpi Documentation Release 0.1 Michael Farrell October 20, 2015 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Resources................................................. 3 2 Building the software 5 3 Wiring the
Digital Design and Computer Architecture
 Digital Design and Computer Architecture Lab 6: C Programming Introduction In this lab, you will learn to program an ARM processor on the Raspberry Pi in C by following a tutorial and then writing several
Digital Design and Computer Architecture Lab 6: C Programming Introduction In this lab, you will learn to program an ARM processor on the Raspberry Pi in C by following a tutorial and then writing several
Ideas to improve glibc and Kernel interaction. Adhemerval Zanella
 Ideas to improve glibc and Kernel interaction Adhemerval Zanella Overview This is RFC session to check kernel features glibc lacks (such as termios2), some features glibc
Ideas to improve glibc and Kernel interaction Adhemerval Zanella Overview This is RFC session to check kernel features glibc lacks (such as termios2), some features glibc
ECE 574 Cluster Computing Lecture 8
 ECE 574 Cluster Computing Lecture 8 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 16 February 2017 Announcements Too many snow days Posted a video with HW#4 Review HW#5 will
ECE 574 Cluster Computing Lecture 8 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 16 February 2017 Announcements Too many snow days Posted a video with HW#4 Review HW#5 will
Programming Assignment #4 Writing a simple parallel port device driver
 Programming Assignment #4 Writing a simple parallel port device driver Value: (See the Grading section of the Syllabus.) Due Date and Time: (See the Course Calendar.) Summary: This is your second exercise
Programming Assignment #4 Writing a simple parallel port device driver Value: (See the Grading section of the Syllabus.) Due Date and Time: (See the Course Calendar.) Summary: This is your second exercise
Arduino Uno. Arduino Uno R3 Front. Arduino Uno R2 Front
 Arduino Uno Arduino Uno R3 Front Arduino Uno R2 Front Arduino Uno SMD Arduino Uno R3 Back Arduino Uno Front Arduino Uno Back Overview The Arduino Uno is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328 (datasheet).
Arduino Uno Arduino Uno R3 Front Arduino Uno R2 Front Arduino Uno SMD Arduino Uno R3 Back Arduino Uno Front Arduino Uno Back Overview The Arduino Uno is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328 (datasheet).
How to Use an Arduino
 How to Use an Arduino By Vivian Law Introduction The first microcontroller, TMS-1802-NC, was built in 1971 by Texas Instruments. It owed its existence to the innovation and versatility of silicon and the
How to Use an Arduino By Vivian Law Introduction The first microcontroller, TMS-1802-NC, was built in 1971 by Texas Instruments. It owed its existence to the innovation and versatility of silicon and the
Arduino Uno R3 INTRODUCTION
 Arduino Uno R3 INTRODUCTION Arduino is used for building different types of electronic circuits easily using of both a physical programmable circuit board usually microcontroller and piece of code running
Arduino Uno R3 INTRODUCTION Arduino is used for building different types of electronic circuits easily using of both a physical programmable circuit board usually microcontroller and piece of code running
MEDIS Module 2. Microcontroller based systems for controlling industrial processes. Chapter 4: Timer and interrupts. M. Seyfarth, Version 0.
 MEDIS Module 2 Microcontroller based systems for controlling industrial processes Chapter 4: Timer and interrupts M. Seyfarth, Version 0.1 Steuerungstechnik 1: Speicherprogrammierbare Steuerungstechnik
MEDIS Module 2 Microcontroller based systems for controlling industrial processes Chapter 4: Timer and interrupts M. Seyfarth, Version 0.1 Steuerungstechnik 1: Speicherprogrammierbare Steuerungstechnik
ARDUINO UNO REV3 Code: A000066
 ARDUINO UNO REV3 Code: A000066 The UNO is the best board to get started with electronics and coding. If this is your first experience tinkering with the platform, the UNO is the most robust board you can
ARDUINO UNO REV3 Code: A000066 The UNO is the best board to get started with electronics and coding. If this is your first experience tinkering with the platform, the UNO is the most robust board you can
Interrupt response times on Arduino and Raspberry Pi. Tomaž Šolc
 Interrupt response times on Arduino and Raspberry Pi Tomaž Šolc tomaz.solc@ijs.si Introduction Full-featured Linux-based systems are replacing microcontrollers in some embedded applications for low volumes,
Interrupt response times on Arduino and Raspberry Pi Tomaž Šolc tomaz.solc@ijs.si Introduction Full-featured Linux-based systems are replacing microcontrollers in some embedded applications for low volumes,
ArdOS The Arduino Operating System Reference Guide Contents
 ArdOS The Arduino Operating System Reference Guide Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Error Handling... 2 3. Initialization and Startup... 2 3.1 Initializing and Starting ArdOS... 2 4. Task Creation... 3
ArdOS The Arduino Operating System Reference Guide Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Error Handling... 2 3. Initialization and Startup... 2 3.1 Initializing and Starting ArdOS... 2 4. Task Creation... 3
Chapter 3 Process Description and Control
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 3 Process Description and Control Seventh Edition By William Stallings Process Control Block Structure of Process Images in Virtual Memory How
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 3 Process Description and Control Seventh Edition By William Stallings Process Control Block Structure of Process Images in Virtual Memory How
SquareWear Programming Reference 1.0 Oct 10, 2012
 Content: 1. Overview 2. Basic Data Types 3. Pin Functions 4. main() and initsquarewear() 5. Digital Input/Output 6. Analog Input/PWM Output 7. Timing, Delay, Reset, and Sleep 8. USB Serial Functions 9.
Content: 1. Overview 2. Basic Data Types 3. Pin Functions 4. main() and initsquarewear() 5. Digital Input/Output 6. Analog Input/PWM Output 7. Timing, Delay, Reset, and Sleep 8. USB Serial Functions 9.
Lab 01 Arduino 程式設計實驗. Essential Arduino Programming and Digital Signal Process
 Lab 01 Arduino 程式設計實驗 Essential Arduino Programming and Digital Signal Process Arduino Arduino is an open-source electronics prototyping platform based on flexible, easy-to-use hardware and software. It's
Lab 01 Arduino 程式設計實驗 Essential Arduino Programming and Digital Signal Process Arduino Arduino is an open-source electronics prototyping platform based on flexible, easy-to-use hardware and software. It's
Programming Assignment #4 Writing a simple parallel port device driver
 Programming Assignment #4 Writing a simple parallel port device driver Value: (See the Grading section of the Syllabus.) Due Date and Time: (See the Course Calendar.) Summary: This programming exercise
Programming Assignment #4 Writing a simple parallel port device driver Value: (See the Grading section of the Syllabus.) Due Date and Time: (See the Course Calendar.) Summary: This programming exercise
Arduino ADK Rev.3 Board A000069
 Arduino ADK Rev.3 Board A000069 Overview The Arduino ADK is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560 (datasheet). It has a USB host interface to connect with Android based phones, based on the MAX3421e
Arduino ADK Rev.3 Board A000069 Overview The Arduino ADK is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560 (datasheet). It has a USB host interface to connect with Android based phones, based on the MAX3421e
USER MANUAL ARDUINO I/O EXPANSION SHIELD
 USER MANUAL ARDUINO I/O EXPANSION SHIELD Description: Sometimes Arduino Uno users run short of pins because there s a lot of projects that requires more than 20 signal pins. The only option they are left
USER MANUAL ARDUINO I/O EXPANSION SHIELD Description: Sometimes Arduino Uno users run short of pins because there s a lot of projects that requires more than 20 signal pins. The only option they are left
Moving Your Application on the Raspberry Pi to the UC-8100-LX Computer. 1 Background Requirement Overview System Environment...
 Moving Your Application on the Raspberry Pi to the UC-8100-LX Computer Contents Jimmy Chen ( 陳永達 ) Field Application Engineer jimmy.chen@moxa.com 1 Background... 2 2 Requirement... 2 3 Overview... 2 4
Moving Your Application on the Raspberry Pi to the UC-8100-LX Computer Contents Jimmy Chen ( 陳永達 ) Field Application Engineer jimmy.chen@moxa.com 1 Background... 2 2 Requirement... 2 3 Overview... 2 4
For 100% Result Oriented IGNOU Coaching and Project Training Call CPD: ,
 Question 2: (15 Marks) The Sleeping-Barber Problem: A barbershop consists of a waiting room with n chairs, and the barber room containing the barber chair. If there are no customers to be served, the barber
Question 2: (15 Marks) The Sleeping-Barber Problem: A barbershop consists of a waiting room with n chairs, and the barber room containing the barber chair. If there are no customers to be served, the barber
SpiNNaker Application Programming Interface (API)
 SpiNNaker Application Programming Interface (API) Version 2.0.0 10 March 2016 Application programming interface (API) Event-driven programming model The SpiNNaker API programming model is a simple, event-driven
SpiNNaker Application Programming Interface (API) Version 2.0.0 10 March 2016 Application programming interface (API) Event-driven programming model The SpiNNaker API programming model is a simple, event-driven
Unix System Programming - Chapter 2, part a
 Unix System Programming - Chapter 2, part a Neal Nelson The Evergreen State College Mar 23, 2010 USP Chapter 2.1 to 2.6 Processes and Threads Program Storage and Linkage Library Function Calls Error Handling
Unix System Programming - Chapter 2, part a Neal Nelson The Evergreen State College Mar 23, 2010 USP Chapter 2.1 to 2.6 Processes and Threads Program Storage and Linkage Library Function Calls Error Handling
ECGR 4101/5101, Fall 2016: Lab 1 First Embedded Systems Project Learning Objectives:
 ECGR 4101/5101, Fall 2016: Lab 1 First Embedded Systems Project Learning Objectives: This lab will introduce basic embedded systems programming concepts by familiarizing the user with an embedded programming
ECGR 4101/5101, Fall 2016: Lab 1 First Embedded Systems Project Learning Objectives: This lab will introduce basic embedded systems programming concepts by familiarizing the user with an embedded programming
CS 2112 Lecture 20 Synchronization 5 April 2012 Lecturer: Andrew Myers
 CS 2112 Lecture 20 Synchronization 5 April 2012 Lecturer: Andrew Myers 1 Critical sections and atomicity We have been seeing that sharing mutable objects between different threads is tricky We need some
CS 2112 Lecture 20 Synchronization 5 April 2012 Lecturer: Andrew Myers 1 Critical sections and atomicity We have been seeing that sharing mutable objects between different threads is tricky We need some
Gooligum Electronics 2015
 The Wombat Prototyping Board for Raspberry Pi Operation and Software Guide This prototyping board is intended to make it easy to experiment and try out ideas for building electronic devices that connect
The Wombat Prototyping Board for Raspberry Pi Operation and Software Guide This prototyping board is intended to make it easy to experiment and try out ideas for building electronic devices that connect
Java Threads. Written by John Bell for CS 342, Spring 2018
 Java Threads Written by John Bell for CS 342, Spring 2018 Based on chapter 9 of Learning Java, Fourth Edition by Niemeyer and Leuck, and other sources. Processes A process is an instance of a running program.
Java Threads Written by John Bell for CS 342, Spring 2018 Based on chapter 9 of Learning Java, Fourth Edition by Niemeyer and Leuck, and other sources. Processes A process is an instance of a running program.
Semaphore. Originally called P() and V() wait (S) { while S <= 0 ; // no-op S--; } signal (S) { S++; }
 Semaphore Semaphore S integer variable Two standard operations modify S: wait() and signal() Originally called P() and V() Can only be accessed via two indivisible (atomic) operations wait (S) { while
Semaphore Semaphore S integer variable Two standard operations modify S: wait() and signal() Originally called P() and V() Can only be accessed via two indivisible (atomic) operations wait (S) { while
CSE 451 Midterm 1. Name:
 CSE 451 Midterm 1 Name: 1. [2 points] Imagine that a new CPU were built that contained multiple, complete sets of registers each set contains a PC plus all the other registers available to user programs.
CSE 451 Midterm 1 Name: 1. [2 points] Imagine that a new CPU were built that contained multiple, complete sets of registers each set contains a PC plus all the other registers available to user programs.
pthreads CS449 Fall 2017
 pthreads CS449 Fall 2017 POSIX Portable Operating System Interface Standard interface between OS and program UNIX-derived OSes mostly follow POSIX Linux, macos, Android, etc. Windows requires separate
pthreads CS449 Fall 2017 POSIX Portable Operating System Interface Standard interface between OS and program UNIX-derived OSes mostly follow POSIX Linux, macos, Android, etc. Windows requires separate
EEG 101L INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING EXPERIENCE
 EEG 101L INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING EXPERIENCE LABORATORY 1: INTRODUCTION TO ARDUINO IDE AND PROGRAMMING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA, LAS VEGAS 1. FYS KIT COMPONENTS
EEG 101L INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING EXPERIENCE LABORATORY 1: INTRODUCTION TO ARDUINO IDE AND PROGRAMMING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA, LAS VEGAS 1. FYS KIT COMPONENTS
Operating Systems, Assignment 2 Threads and Synchronization
 Operating Systems, Assignment 2 Threads and Synchronization Responsible TA's: Zohar and Matan Assignment overview The assignment consists of the following parts: 1) Kernel-level threads package 2) Synchronization
Operating Systems, Assignment 2 Threads and Synchronization Responsible TA's: Zohar and Matan Assignment overview The assignment consists of the following parts: 1) Kernel-level threads package 2) Synchronization
keyestudio Keyestudio MEGA 2560 R3 Board
 Keyestudio MEGA 2560 R3 Board Introduction: Keyestudio Mega 2560 R3 is a microcontroller board based on the ATMEGA2560-16AU, fully compatible with ARDUINO MEGA 2560 REV3. It has 54 digital input/output
Keyestudio MEGA 2560 R3 Board Introduction: Keyestudio Mega 2560 R3 is a microcontroller board based on the ATMEGA2560-16AU, fully compatible with ARDUINO MEGA 2560 REV3. It has 54 digital input/output
Lesson 8: Digital Input, If Else
 Lesson 8 Lesson 8: Digital Input, If Else Digital Input, If Else The Big Idea: This lesson adds the ability of an Arduino sketch to respond to its environment, taking different actions for different situations.
Lesson 8 Lesson 8: Digital Input, If Else Digital Input, If Else The Big Idea: This lesson adds the ability of an Arduino sketch to respond to its environment, taking different actions for different situations.
Button Input: On/off state change
 Button Input: On/off state change Living with the Lab Gerald Recktenwald Portland State University gerry@pdx.edu User input features of the fan Potentiometer for speed control Continually variable input
Button Input: On/off state change Living with the Lab Gerald Recktenwald Portland State University gerry@pdx.edu User input features of the fan Potentiometer for speed control Continually variable input
ECE 471 Embedded Systems Lecture 20
 ECE 471 Embedded Systems Lecture 20 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 20 October 2017 Announcements Project coming Only one person was in class Wednesday due to Career
ECE 471 Embedded Systems Lecture 20 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 20 October 2017 Announcements Project coming Only one person was in class Wednesday due to Career
IME-100 Interdisciplinary Design and Manufacturing
 IME-100 Interdisciplinary Design and Manufacturing Introduction Arduino and Programming Topics: 1. Introduction to Microprocessors/Microcontrollers 2. Introduction to Arduino 3. Arduino Programming Basics
IME-100 Interdisciplinary Design and Manufacturing Introduction Arduino and Programming Topics: 1. Introduction to Microprocessors/Microcontrollers 2. Introduction to Arduino 3. Arduino Programming Basics
Micrium OS Kernel Labs
 Micrium OS Kernel Labs 2018.04.16 Micrium OS is a flexible, highly configurable collection of software components that provides a powerful embedded software framework for developers to build their application
Micrium OS Kernel Labs 2018.04.16 Micrium OS is a flexible, highly configurable collection of software components that provides a powerful embedded software framework for developers to build their application
OPTO32A 24 Input Bit, 8 Output Bit Optical Isolator Board
 OPTO32A 24 Input Bit, 8 Output Bit Optical Isolator Board PMC-OPTO32A Linux Device Driver User Manual Manual Revision: July 15, 2005 General Standards Corporation 8302A Whitesburg Drive Huntsville, AL
OPTO32A 24 Input Bit, 8 Output Bit Optical Isolator Board PMC-OPTO32A Linux Device Driver User Manual Manual Revision: July 15, 2005 General Standards Corporation 8302A Whitesburg Drive Huntsville, AL
ARDUINO YÚN Code: A000008
 ARDUINO YÚN Code: A000008 Arduino YÚN is the perfect board to use when designing connected devices and, more in general, Internet of Things projects. It combines the power of Linux with the ease of use
ARDUINO YÚN Code: A000008 Arduino YÚN is the perfect board to use when designing connected devices and, more in general, Internet of Things projects. It combines the power of Linux with the ease of use
COSC 2P95 Lab 9 Signals, Mutexes, and Threads
 COSC 2P95 Lab 9 Signals, Mutexes, and Threads Sometimes, we can't achieve what we want via a single execution pipeline. Whether it's for responsiveness, or to process more data simultaneously, we rely
COSC 2P95 Lab 9 Signals, Mutexes, and Threads Sometimes, we can't achieve what we want via a single execution pipeline. Whether it's for responsiveness, or to process more data simultaneously, we rely
Laboratory Assignment #3. Extending scull, a char pseudo-device
 Laboratory Assignment #3 Extending scull, a char pseudo-device Value: (See the Grading section of the Syllabus.) Due Date and Time: (See the Course Calendar.) Summary: This is your first exercise that
Laboratory Assignment #3 Extending scull, a char pseudo-device Value: (See the Grading section of the Syllabus.) Due Date and Time: (See the Course Calendar.) Summary: This is your first exercise that
Outline. Overview. Linux-specific, since kernel 2.6.0
 Outline 25 Alternative I/O Models 25-1 25.1 Overview 25-3 25.2 Signal-driven I/O 25-9 25.3 I/O multiplexing: poll() 25-12 25.4 Problems with poll() and select() 25-29 25.5 The epoll API 25-32 25.6 epoll
Outline 25 Alternative I/O Models 25-1 25.1 Overview 25-3 25.2 Signal-driven I/O 25-9 25.3 I/O multiplexing: poll() 25-12 25.4 Problems with poll() and select() 25-29 25.5 The epoll API 25-32 25.6 epoll
CS444 1/28/05. Lab 03
 CS444 1/28/05 Lab 03 Note All the code that is found in this lab guide can be found at the following web address: www.clarkson.edu/class/cs444/cs444.sp2005/labs/lab03/code/ Threading A thread is an independent
CS444 1/28/05 Lab 03 Note All the code that is found in this lab guide can be found at the following web address: www.clarkson.edu/class/cs444/cs444.sp2005/labs/lab03/code/ Threading A thread is an independent
Project 2: Part 1: RPC and Locks
 Project 2: Part 1: RPC and Locks Due: 11:59PM Thursday, October 14, 2010 1 Introduction In this series of labs, you will implement a fully functional distributed file server with the Frangipani architecture
Project 2: Part 1: RPC and Locks Due: 11:59PM Thursday, October 14, 2010 1 Introduction In this series of labs, you will implement a fully functional distributed file server with the Frangipani architecture
Table 1: Cross Reference of Applicable Products. INTERNAL PIC NUMBER Arm Cortex M0+ UT32M0R GPIO Module QS30
 Standard Product Enable the GPIO Module UT32M0R500 32-bit Arm Cortex M0+ Microcontroller Application Note December 21, 2017 The most important thing we build is trust PRODUCT NAME Table 1: Cross Reference
Standard Product Enable the GPIO Module UT32M0R500 32-bit Arm Cortex M0+ Microcontroller Application Note December 21, 2017 The most important thing we build is trust PRODUCT NAME Table 1: Cross Reference
Locks. Dongkun Shin, SKKU
 Locks 1 Locks: The Basic Idea To implement a critical section A lock variable must be declared A lock variable holds the state of the lock Available (unlocked, free) Acquired (locked, held) Exactly one
Locks 1 Locks: The Basic Idea To implement a critical section A lock variable must be declared A lock variable holds the state of the lock Available (unlocked, free) Acquired (locked, held) Exactly one
CPS221 Lecture: Operating System Functions
 CPS221 Lecture: Operating System Functions Objectives last revised 6/23/10 1. To overview key hardware concepts 2. To iintroduce the process concept 3. To discuss the various kinds of functionality of
CPS221 Lecture: Operating System Functions Objectives last revised 6/23/10 1. To overview key hardware concepts 2. To iintroduce the process concept 3. To discuss the various kinds of functionality of
SmartHeap for Multi-Core
 SmartHeap for Multi-Core Getting Started and Platform Guide for Linux Version 11.2 SmartHeap and HeapAgent are trademarks of Compuware Corporation. All other trademarks are the property of their respective
SmartHeap for Multi-Core Getting Started and Platform Guide for Linux Version 11.2 SmartHeap and HeapAgent are trademarks of Compuware Corporation. All other trademarks are the property of their respective
ADWGC C library User's Guide Revision February /20
 Revision 1.09-13 February 2015 1/20 Byte Paradigm info@byteparadigm.com Table of Content 1 Introduction... 4 2 GP Series device ADWGC C Library... 5 2.1 Functions quick Reference Table... 5 2.2 Functions
Revision 1.09-13 February 2015 1/20 Byte Paradigm info@byteparadigm.com Table of Content 1 Introduction... 4 2 GP Series device ADWGC C Library... 5 2.1 Functions quick Reference Table... 5 2.2 Functions
ARDUINO MEGA 2560 REV3 Code: A000067
 ARDUINO MEGA 2560 REV3 Code: A000067 The MEGA 2560 is designed for more complex projects. With 54 digital I/O pins, 16 analog inputs and a larger space for your sketch it is the recommended board for 3D
ARDUINO MEGA 2560 REV3 Code: A000067 The MEGA 2560 is designed for more complex projects. With 54 digital I/O pins, 16 analog inputs and a larger space for your sketch it is the recommended board for 3D
Installation of RedHawk 6.5-r24.2 on the Jetson TX1 Development Board Release Notes. September 19 th, 2017
 Installation of RedHawk 6.5-r24.2 on the Jetson TX1 Development Board Release Notes September 19 th, 2017 This page intentionally left blank 1. Introduction This document describes the process of installing
Installation of RedHawk 6.5-r24.2 on the Jetson TX1 Development Board Release Notes September 19 th, 2017 This page intentionally left blank 1. Introduction This document describes the process of installing
Linux Driver and Embedded Developer
 Linux Driver and Embedded Developer Course Highlights The flagship training program from Veda Solutions, successfully being conducted from the past 10 years A comprehensive expert level course covering
Linux Driver and Embedded Developer Course Highlights The flagship training program from Veda Solutions, successfully being conducted from the past 10 years A comprehensive expert level course covering
Specification. 1.Power Supply direct from Microcontroller Board. 2.The circuit can be used with Microcontroller Board such as Arduino UNO R3.
 Part Number : Product Name : FK-FA1410 12-LED AND 3-BOTTON SHIELD This is the experimental board for receiving and transmitting data from the port of microcontroller. The function of FK-FA1401 is fundamental
Part Number : Product Name : FK-FA1410 12-LED AND 3-BOTTON SHIELD This is the experimental board for receiving and transmitting data from the port of microcontroller. The function of FK-FA1401 is fundamental
ARDUINO YÚN MINI Code: A000108
 ARDUINO YÚN MINI Code: A000108 The Arduino Yún Mini is a compact version of the Arduino YUN OVERVIEW: Arduino Yún Mini is a breadboard PCB developed with ATmega 32u4 MCU and QCA MIPS 24K SoC CPU operating
ARDUINO YÚN MINI Code: A000108 The Arduino Yún Mini is a compact version of the Arduino YUN OVERVIEW: Arduino Yún Mini is a breadboard PCB developed with ATmega 32u4 MCU and QCA MIPS 24K SoC CPU operating
Task Based Programming Revisited Real Time Operating Systems
 ECE3411 Fall 2016 Lecture 6a. Task Based Programming Revisited Real Time Operating Systems Marten van Dijk, Syed Kamran Haider Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
ECE3411 Fall 2016 Lecture 6a. Task Based Programming Revisited Real Time Operating Systems Marten van Dijk, Syed Kamran Haider Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
OPi.GPIO Documentation
 OPi.GPIO Documentation Release 0.3.1 Richard Hull and contributors Jan 01, 2018 Contents 1 Installation 3 2 API Documentation 5 2.1 Importing the module.......................................... 5 2.2
OPi.GPIO Documentation Release 0.3.1 Richard Hull and contributors Jan 01, 2018 Contents 1 Installation 3 2 API Documentation 5 2.1 Importing the module.......................................... 5 2.2
Lesson 6 Programming Arduino Example 9.7. Chapter-9 L06: "Internet of Things ", Raj Kamal, Publs.: McGraw-Hill Education
 Lesson 6 Programming Arduino Example 9.7 1 Multitasking Environment A multitasking environment consists of multiple processes, tasks or threads. Consider Example 9.1. A set of Functions void north_south_green
Lesson 6 Programming Arduino Example 9.7 1 Multitasking Environment A multitasking environment consists of multiple processes, tasks or threads. Consider Example 9.1. A set of Functions void north_south_green
Today: Synchronization. Recap: Synchronization
 Today: Synchronization Synchronization Mutual exclusion Critical sections Example: Too Much Milk Locks Synchronization primitives are required to ensure that only one thread executes in a critical section
Today: Synchronization Synchronization Mutual exclusion Critical sections Example: Too Much Milk Locks Synchronization primitives are required to ensure that only one thread executes in a critical section
1.8inch LCD Module USER MANUAL
 1.8inch LCD Module USER MANUAL OVERVIEW This product is 1.8inch resistive screen module with resolution 128x160. It has internal controller and uses SPI interface for communication. It has already basic
1.8inch LCD Module USER MANUAL OVERVIEW This product is 1.8inch resistive screen module with resolution 128x160. It has internal controller and uses SPI interface for communication. It has already basic
ECE 598 Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 4
 ECE 598 Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 4 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 28 January 2016 Announcements HW#1 was due HW#2 was posted, will be tricky Let me know
ECE 598 Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 4 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 28 January 2016 Announcements HW#1 was due HW#2 was posted, will be tricky Let me know
ARDUINO UNO REV3 SMD Code: A The board everybody gets started with, based on the ATmega328 (SMD).
 ARDUINO UNO REV3 SMD Code: A000073 The board everybody gets started with, based on the ATmega328 (SMD). The Arduino Uno SMD R3 is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328. It has 14 digital input/output
ARDUINO UNO REV3 SMD Code: A000073 The board everybody gets started with, based on the ATmega328 (SMD). The Arduino Uno SMD R3 is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328. It has 14 digital input/output
Robotics and Electronics Unit 5
 Robotics and Electronics Unit 5 Objectives. Students will work with mechanical push buttons understand the shortcomings of the delay function and how to use the millis function. In this unit we will use
Robotics and Electronics Unit 5 Objectives. Students will work with mechanical push buttons understand the shortcomings of the delay function and how to use the millis function. In this unit we will use
Threads Cannot Be Implemented As a Library
 Threads Cannot Be Implemented As a Library Authored by Hans J. Boehm Presented by Sarah Sharp February 18, 2008 Outline POSIX Thread Library Operation Vocab Problems with pthreads POSIX Thread Library
Threads Cannot Be Implemented As a Library Authored by Hans J. Boehm Presented by Sarah Sharp February 18, 2008 Outline POSIX Thread Library Operation Vocab Problems with pthreads POSIX Thread Library
The Kernel Abstraction
 The Kernel Abstraction Debugging as Engineering Much of your time in this course will be spent debugging In industry, 50% of software dev is debugging Even more for kernel development How do you reduce
The Kernel Abstraction Debugging as Engineering Much of your time in this course will be spent debugging In industry, 50% of software dev is debugging Even more for kernel development How do you reduce
Introduction to PThreads and Basic Synchronization
 Introduction to PThreads and Basic Synchronization Michael Jantz, Dr. Prasad Kulkarni Dr. Douglas Niehaus EECS 678 Pthreads Introduction Lab 1 Introduction In this lab, we will learn about some basic synchronization
Introduction to PThreads and Basic Synchronization Michael Jantz, Dr. Prasad Kulkarni Dr. Douglas Niehaus EECS 678 Pthreads Introduction Lab 1 Introduction In this lab, we will learn about some basic synchronization
User Space Multithreading. Computer Science, University of Warwick
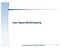 User Space Multithreading 1 Threads Thread short for thread of execution/control B efore create Global During create Global Data Data Executing Code Code Stack Stack Stack A fter create Global Data Executing
User Space Multithreading 1 Threads Thread short for thread of execution/control B efore create Global During create Global Data Data Executing Code Code Stack Stack Stack A fter create Global Data Executing
Procedure: Determine the polarity of the LED. Use the following image to help:
 Section 2: Lab Activity Section 2.1 Getting started: LED Blink Purpose: To understand how to upload a program to the Arduino and to understand the function of each line of code in a simple program. This
Section 2: Lab Activity Section 2.1 Getting started: LED Blink Purpose: To understand how to upload a program to the Arduino and to understand the function of each line of code in a simple program. This
Synchronising Threads
 Synchronising Threads David Chisnall March 1, 2011 First Rule for Maintainable Concurrent Code No data may be both mutable and aliased Harder Problems Data is shared and mutable Access to it must be protected
Synchronising Threads David Chisnall March 1, 2011 First Rule for Maintainable Concurrent Code No data may be both mutable and aliased Harder Problems Data is shared and mutable Access to it must be protected
Raspberry PI 'How-To' Series
 Raspberry PI 'How-To' Series AOSONG AM2315 Temperature Sensor Implementation Guide Update Written by: Sopwith Revision 3.0 February 1, 2019 sopwith@ismellsmoke.net 1 Introduction Here we are in February
Raspberry PI 'How-To' Series AOSONG AM2315 Temperature Sensor Implementation Guide Update Written by: Sopwith Revision 3.0 February 1, 2019 sopwith@ismellsmoke.net 1 Introduction Here we are in February
FUNCTIONS For controlling the Arduino board and performing computations.
 d i g i t a l R e a d ( ) [Digital I/O] Reads the value from a specified digital pin, either HIGH or LOW. digitalread(pin) pin: the number of the digital pin you want to read HIGH or LOW Sets pin 13 to
d i g i t a l R e a d ( ) [Digital I/O] Reads the value from a specified digital pin, either HIGH or LOW. digitalread(pin) pin: the number of the digital pin you want to read HIGH or LOW Sets pin 13 to
ARDUINO MEGA ADK REV3 Code: A000069
 ARDUINO MEGA ADK REV3 Code: A000069 OVERVIEW The Arduino MEGA ADK is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560. It has a USB host interface to connect with Android based phones, based on the MAX3421e
ARDUINO MEGA ADK REV3 Code: A000069 OVERVIEW The Arduino MEGA ADK is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560. It has a USB host interface to connect with Android based phones, based on the MAX3421e
Operating System Architecture. CS3026 Operating Systems Lecture 03
 Operating System Architecture CS3026 Operating Systems Lecture 03 The Role of an Operating System Service provider Provide a set of services to system users Resource allocator Exploit the hardware resources
Operating System Architecture CS3026 Operating Systems Lecture 03 The Role of an Operating System Service provider Provide a set of services to system users Resource allocator Exploit the hardware resources
Installation of RedHawk on Jetson TX1, TX2 and TX2i Development Boards Release Notes
 Installation of RedHawk 7.3.2 on Jetson TX1, TX2 and TX2i Development Boards Release Notes July 20 th, 2018 0898003-7.3.2-TX-REV-A This page intentionally left blank 1. Introduction This document describes
Installation of RedHawk 7.3.2 on Jetson TX1, TX2 and TX2i Development Boards Release Notes July 20 th, 2018 0898003-7.3.2-TX-REV-A This page intentionally left blank 1. Introduction This document describes
New APIs and Hacks. Servo API. Chapter 4. The Theory versus Practice
 Chapter 4 New APIs and Hacks The challenge when Intel Galileo was designed was to create a board that would be compatible with Arduino headers and reference language using only the Quark microprocessor,
Chapter 4 New APIs and Hacks The challenge when Intel Galileo was designed was to create a board that would be compatible with Arduino headers and reference language using only the Quark microprocessor,
More Arduino Programming
 Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Arduino Part 2, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota More Arduino Programming Digital I/O (Read/Write) Analog
Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Arduino Part 2, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota More Arduino Programming Digital I/O (Read/Write) Analog
Laboratory 1 Introduction to the Arduino boards
 Laboratory 1 Introduction to the Arduino boards The set of Arduino development tools include µc (microcontroller) boards, accessories (peripheral modules, components etc.) and open source software tools
Laboratory 1 Introduction to the Arduino boards The set of Arduino development tools include µc (microcontroller) boards, accessories (peripheral modules, components etc.) and open source software tools
CPS221 Lecture: Operating System Protection
 Objectives CPS221 Lecture: Operating System Protection last revised 9/5/12 1. To explain the use of two CPU modes as the basis for protecting privileged instructions and memory 2. To introduce basic protection
Objectives CPS221 Lecture: Operating System Protection last revised 9/5/12 1. To explain the use of two CPU modes as the basis for protecting privileged instructions and memory 2. To introduce basic protection
IoT with Intel Galileo Gerardo Carmona. makerobots.tk
 IoT with Intel Galileo Gerardo Carmona Outline What is Intel Galileo? Hello world! In Arduino Arduino and Linux Linux via SSH Playing around in Linux Programming flexibility How GPIOs works Challenge 1:
IoT with Intel Galileo Gerardo Carmona Outline What is Intel Galileo? Hello world! In Arduino Arduino and Linux Linux via SSH Playing around in Linux Programming flexibility How GPIOs works Challenge 1:
User Manual & Reference
 DreamCity Innovations M177v2 Reduced Human Interface Device User Manual & Reference Version 1C113 Applicable Devices: M177v2 M177v2-T M177v2-H M177v2-HT Applicable Firmware: M177v2 FW 1C114 Copyright 2015
DreamCity Innovations M177v2 Reduced Human Interface Device User Manual & Reference Version 1C113 Applicable Devices: M177v2 M177v2-T M177v2-H M177v2-HT Applicable Firmware: M177v2 FW 1C114 Copyright 2015
My first Raspberry Pi tutorial in C. Christophe Delord
 My first Raspberry Pi tutorial in C Christophe Delord Sunday 22 October 2017 2 Contents 1 Availability 7 1.1 COPYRIGHT............................. 7 1.2 This book is now freely available..................
My first Raspberry Pi tutorial in C Christophe Delord Sunday 22 October 2017 2 Contents 1 Availability 7 1.1 COPYRIGHT............................. 7 1.2 This book is now freely available..................
SX1509 I/O Expander Breakout Hookup Guide
 Page 1 of 16 SX1509 I/O Expander Breakout Hookup Guide Introduction Is your Arduino running low on GPIO? Looking to control the brightness of 16 LEDs individually? Maybe blink or breathe a few autonomously?
Page 1 of 16 SX1509 I/O Expander Breakout Hookup Guide Introduction Is your Arduino running low on GPIO? Looking to control the brightness of 16 LEDs individually? Maybe blink or breathe a few autonomously?
3 Threadsafe Bounded List Wrapper Library Monitor
 CS 453: Operating Systems Project 4 (100/110 points) Thread-safe Monitor Library Due Date (on class home page) 1 Introduction In this project, we will create a thread-safe bounded version of the linked-list
CS 453: Operating Systems Project 4 (100/110 points) Thread-safe Monitor Library Due Date (on class home page) 1 Introduction In this project, we will create a thread-safe bounded version of the linked-list
Installation & Reference Guide
 Installation & Reference Guide DOC. REV. 7/31/2015 VersaAPI VersaLogic Application Programming Interface WWW.VERSALOGIC.COM 12100 SW Tualatin Road Tualatin, OR 97062-7341 (503) 747-2261 Fax (971) 224-4708
Installation & Reference Guide DOC. REV. 7/31/2015 VersaAPI VersaLogic Application Programming Interface WWW.VERSALOGIC.COM 12100 SW Tualatin Road Tualatin, OR 97062-7341 (503) 747-2261 Fax (971) 224-4708
PROCESS CONTROL BLOCK TWO-STATE MODEL (CONT D)
 MANAGEMENT OF APPLICATION EXECUTION PROCESS CONTROL BLOCK Resources (processor, I/O devices, etc.) are made available to multiple applications The processor in particular is switched among multiple applications
MANAGEMENT OF APPLICATION EXECUTION PROCESS CONTROL BLOCK Resources (processor, I/O devices, etc.) are made available to multiple applications The processor in particular is switched among multiple applications
Arduino Part 2. Introductory Medical Device Prototyping
 Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Arduino Part 2, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota More Arduino Programming Digital I/O (Read/Write) Analog
Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Arduino Part 2, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota More Arduino Programming Digital I/O (Read/Write) Analog
Developing Real-Time Applications
 Developing Real-Time Applications Real Time Operating Systems and Middleware Luca Abeni luca.abeni@unitn.it Characterised by temporal constraints deadlines Concurrent (application: set of real-time tasks)
Developing Real-Time Applications Real Time Operating Systems and Middleware Luca Abeni luca.abeni@unitn.it Characterised by temporal constraints deadlines Concurrent (application: set of real-time tasks)
Arduino Programming Part 4: Flow Control
 Arduino Programming Part 4: Flow Control EAS 199B, Winter 2010 Gerald Recktenwald Portland State University gerry@me.pdx.edu Goal Make choices based on conditions in the environment Logical expressions:
Arduino Programming Part 4: Flow Control EAS 199B, Winter 2010 Gerald Recktenwald Portland State University gerry@me.pdx.edu Goal Make choices based on conditions in the environment Logical expressions:
ECE 598 Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 23
 ECE 598 Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 23 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 21 April 2016 Don t forget HW#9 Midterm next Thursday Announcements 1 Process States
ECE 598 Advanced Operating Systems Lecture 23 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 21 April 2016 Don t forget HW#9 Midterm next Thursday Announcements 1 Process States
Note. The above image and many others are courtesy of - this is a wonderful resource for designing circuits.
 Robotics and Electronics Unit 2. Arduino Objectives. Students will understand the basic characteristics of an Arduino Uno microcontroller. understand the basic structure of an Arduino program. know how
Robotics and Electronics Unit 2. Arduino Objectives. Students will understand the basic characteristics of an Arduino Uno microcontroller. understand the basic structure of an Arduino program. know how
Project 1 System Calls
 Project 1 System Calls Introduction In this project, you will become familiar with: 1. Using the xv6 Makefile 2. Using conditional compilation. 3. The xv6 system call invocation path. 4. Implementing a
Project 1 System Calls Introduction In this project, you will become familiar with: 1. Using the xv6 Makefile 2. Using conditional compilation. 3. The xv6 system call invocation path. 4. Implementing a
Installation and operation manual PCIe-CAN-01 / PCIe-CAN-02
 Installation and operation manual PCIe-CAN-01 / PCIe-CAN-02 Table of Contents Compliance information...3 FCC Compliance...3 EN 55022 Class A Warning...3 CE declaration of conformity...3 Safety note...3
Installation and operation manual PCIe-CAN-01 / PCIe-CAN-02 Table of Contents Compliance information...3 FCC Compliance...3 EN 55022 Class A Warning...3 CE declaration of conformity...3 Safety note...3
Adapted from a lab originally written by Simon Hastings and Bill Ashmanskas
 Physics 364 Arduino Lab 1 Adapted from a lab originally written by Simon Hastings and Bill Ashmanskas Vithayathil/Kroll Introduction Last revised: 2014-11-12 This lab introduces you to an electronic development
Physics 364 Arduino Lab 1 Adapted from a lab originally written by Simon Hastings and Bill Ashmanskas Vithayathil/Kroll Introduction Last revised: 2014-11-12 This lab introduces you to an electronic development
High Performance Computing Course Notes Shared Memory Parallel Programming
 High Performance Computing Course Notes 2009-2010 2010 Shared Memory Parallel Programming Techniques Multiprocessing User space multithreading Operating system-supported (or kernel) multithreading Distributed
High Performance Computing Course Notes 2009-2010 2010 Shared Memory Parallel Programming Techniques Multiprocessing User space multithreading Operating system-supported (or kernel) multithreading Distributed
