4/18/ Binary Search Trees (BSTs) 17.1 Adding an Element to a BST Removing an Element from a BST. 17.
|
|
|
- Janis Patterson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 17.1 Binary Search Trees (BSTs) 17.1 Adding an Element to a BST! Write the inorder traversal of this tree. What do you observe?! A search tree is a tree whose elements are organized to facilitate finding a particular element! A binary search tree is a binary tree that, for each node n n n the left subtree of n contains elements less than the element stored in n the right subtree of n contains elements greater than or equal to the element stored in n! Binary search trees must hold Comparable data. Why?! How do you search for an element? Next to add: Animation: On what does the shape of a binary search tree depends? Degenerate Tree 17.1 Removing an Element from a BST! A grossly unbalanced tree, with some long paths! When does it occur?! Removing a target in a BST is not as simple as that for linear data structures! After removing the element, the resulting tree must still be valid! What if you remove 88? 1? 60?! Why is it undesirable? 1
2 17.1 After the Root Node is Removed! Draw Tree (2 valid configurations) 17.2 BST Implementation! The BinarySearchTree interface class adds support for add, remove, find, findmin, and findmax 17.2 javafoundations.binarysearchtree * BinarySearchTree.java Java Foundations Defines the interface to a binary search tree. * public interface BinarySearchTree<T extends Comparable<T>> extends BinaryTree<T> Adds the specified element to the tree. public void add (T element); Finds and returns the element in the tree matching the specified target. Overrides the find method of BinaryTree. public T find (T target); Returns the minimum value in the binary search tree. public T findmin(); Returns the maximum value in the binary search tree. public T findmax(); BSTNode.java Java Foundations Represents a node in a binary search tree, storing Comparable elements. public class BSTNode<T extends Comparable<T>> extends BTNode<T> Creates a new tree node with the specified data. public BSTNode (T element) super(element); Removes and returns the specified element from the tree. public T remove (T target); 2
3 77 Next to add: Adds a new node containing the specified element at the appropriate place in this tree public void add (T item) if (item.compareto(element) < 0) if (left == null) left = new BSTNode (item); Add recursively ((BSTNode)left).add (item); item >= element, go right if (right == null) right = new BSTNode (item); Add recursively ((BSTNode)right).add (item); Returns the node in this subtree whose element matches the specified target. Returns null if the target is not found. Overrides the find method of BTNode to capitalize on the binary search tree characteristics. public BSTNode<T> find (T target) BSTNode<T> result = null; if (target.compareto(element) == 0) result = this; if (target.compareto(element) < 0) if (left!= null) result = ((BSTNode)left).find (target); if (right!= null) result = ((BSTNode)right).find (target); return result; Removes the specified target from this subtree. Returns a reference to the revised tree. The tree will be unchanged if the target is not found. public BSTNode<T> remove(t target) BSTNode<T> result = this; if (target.compareto(element) == 0) if (left == null && right == null) result = null; Situation 1 if (left!= null && right == null) result = (BSTNode)left; Situation 2 if (left == null && right!= null) result = (BSTNode)right; Situation 2 Situation result = getsuccessor(); result.left = left; result.right = right; if (target.compareto(element) < 0) if (left!= null) left = ((BSTNode)left).remove(target); target > element, look to the right to remove if (right!= null) right = ((BSTNode)right).remove(target); return result; Finds and returns the node containing the inorder successor of this node, and then removes the successor from its original location in the tree. protected BSTNode<T> getsuccessor() BSTNode<T> successor = (BSTNode)right; while (successor.getleft()!= null) successor = (BSTNode) successor.getleft(); ((BSTNode)right).remove (successor.getelement()); return successor;
4 LinkedBinarySearchTree.java Java Foundations Implements the binary tree using a linked representation. import javafoundations.*; import javafoundations.exceptions.*; public class LinkedBinarySearchTree<T extends Comparable<T>> extends LinkedBinaryTree<T> implements BinarySearchTree<T> Creates an empty binary search tree. public LinkedBinarySearchTree() super(); Creates a binary search tree with the specified element at its root. public LinkedBinarySearchTree (T element) root = new BSTNode<T>(element); Adds the specified element to this binary search tree. public void add (T item) if (root == null) root = new BSTNode<T>(item); ((BSTNode)root).add(item); 17. Balanced Binary Search Trees Removes and returns the element matching the specified target from this binary search tree. Throws an ElementNotFoundException if the target is not found. public T remove (T target) BSTNode<T> node = null; if (root!= null) node = ((BSTNode)root).find(target); if (node == null) throw new ElementNotFoundException ("Remove operation failed. " + "No such element in tree."); root = ((BSTNode)root).remove(target); return node.getelement(); public T findmin() public T findmax()! The find and add operations of a balanced tree of n nodes have an efficiency of O(log 2 n) [ = length of the longest path]! The more degenerate a tree becomes, the find and add operations approach O(n)! Our BST implementation does not guarantee a balanced tree n The shape of a BST is determined by the order which elements are added to the tree! Other types of trees exist to ensure that they stay balanced! They include AVL trees and red/black trees. See animation at n 4
5 17. Right Rotation (zig) 17. Left Rotation (zag) zig-zag Rotation! If the imbalance is caused by a long path in the left subtree of the right child of the root we can address it by n performing a right rotation around the offending subtree n and then performing a left rotation around the root 17. zag-zig Rotation! If the imbalance is caused by a long path in the right subtree of the left child of the root we can address it by n performing a left rotation around the offending subtree n and then performing a right rotation around the root
A grossly unbalanced tree, with some long paths. Next to add: When does it occur? Why is it undesirable?
 Write the inorder traversal of this tree. What do you observe? A search tree is a tree whose elements are organized to facilitate finding a particular element A binary search tree is a binary tree that,
Write the inorder traversal of this tree. What do you observe? A search tree is a tree whose elements are organized to facilitate finding a particular element A binary search tree is a binary tree that,
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures. Lecture #28: Binary Search Trees 21 November 2011
 CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture #28: Binary Search Trees 21 November 2011 Binary Search Trees The Idea of a Binary Search Tree The BinarySearchTreeADT Interface The LinkedBinarySearchTree
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture #28: Binary Search Trees 21 November 2011 Binary Search Trees The Idea of a Binary Search Tree The BinarySearchTreeADT Interface The LinkedBinarySearchTree
Lecture 23: Binary Search Trees
 Lecture 23: Binary Search Trees CS 62 Fall 2017 Kim Bruce & Alexandra Papoutsaki 1 BST A binary tree is a binary search tree iff it is empty or if the value of every node is both greater than or equal
Lecture 23: Binary Search Trees CS 62 Fall 2017 Kim Bruce & Alexandra Papoutsaki 1 BST A binary tree is a binary search tree iff it is empty or if the value of every node is both greater than or equal
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Balanced Binary Search Trees
 Balanced Binary Search Trees Why is our balance assumption so important? Lets look at what happens if we insert the following numbers in order without rebalancing the tree: 3 5 9 12 18 20 1-45 2010 Pearson
Balanced Binary Search Trees Why is our balance assumption so important? Lets look at what happens if we insert the following numbers in order without rebalancing the tree: 3 5 9 12 18 20 1-45 2010 Pearson
Binary Search Trees. See Section 11.1 of the text.
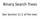 Binary Search Trees See Section 11.1 of the text. Consider the following Binary Search Tree 17 This tree has a nice property: for every node, all of the nodes in its left subtree have values less than
Binary Search Trees See Section 11.1 of the text. Consider the following Binary Search Tree 17 This tree has a nice property: for every node, all of the nodes in its left subtree have values less than
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
CS102 Binary Search Trees
 CS102 Binary Search Trees Prof Tejada 1 To speed up insertion, removal and search, modify the idea of a Binary Tree to create a Binary Search Tree (BST) Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees have one
CS102 Binary Search Trees Prof Tejada 1 To speed up insertion, removal and search, modify the idea of a Binary Tree to create a Binary Search Tree (BST) Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees have one
CS350: Data Structures Binary Search Trees
 Binary Search Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction to Binary Search Trees A binary search tree is a binary tree that
Binary Search Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction to Binary Search Trees A binary search tree is a binary tree that
Trees Chapter 19, 20. Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013
 Trees Chapter 19, 20 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 2 Scope Trees: Trees as data structures Tree terminology Tree implementations Analyzing tree efficiency Tree traversals
Trees Chapter 19, 20 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 2 Scope Trees: Trees as data structures Tree terminology Tree implementations Analyzing tree efficiency Tree traversals
Binary Search Tree: Balanced. Data Structures and Algorithms Emory University Jinho D. Choi
 Binary Search Tree: Balanced Data Structures and Algorithms Emory University Jinho D. Choi Binary Search Tree Worst-case Complexity Search Insert Delete Unbalanced O(n) O(n) O(n) + α Balanced O(log n)
Binary Search Tree: Balanced Data Structures and Algorithms Emory University Jinho D. Choi Binary Search Tree Worst-case Complexity Search Insert Delete Unbalanced O(n) O(n) O(n) + α Balanced O(log n)
Data Structures in Java
 Data Structures in Java Lecture 10: AVL Trees. 10/1/015 Daniel Bauer Balanced BSTs Balance condition: Guarantee that the BST is always close to a complete binary tree (every node has exactly two or zero
Data Structures in Java Lecture 10: AVL Trees. 10/1/015 Daniel Bauer Balanced BSTs Balance condition: Guarantee that the BST is always close to a complete binary tree (every node has exactly two or zero
Self-Balancing Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Algorithms. AVL Tree
 Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
CS 350 : Data Structures Binary Search Trees
 CS 350 : Data Structures Binary Search Trees David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction to Binary Search Trees A binary
CS 350 : Data Structures Binary Search Trees David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Introduction to Binary Search Trees A binary
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures. Lecture #26: Binary Search Trees David Mix Barrington 9 November 2012
 CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture #26: Binary Search Trees David Mix Barrington 9 November 2012 Binary Search Trees Why Binary Search Trees? Trees, Binary Trees and Vocabulary The BST
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture #26: Binary Search Trees David Mix Barrington 9 November 2012 Binary Search Trees Why Binary Search Trees? Trees, Binary Trees and Vocabulary The BST
The Binary Search Tree ADT
 The Binary Search Tree ADT Binary Search Tree A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree with an ordering property of its elements, such that the data in any internal node is Greater than the data in
The Binary Search Tree ADT Binary Search Tree A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree with an ordering property of its elements, such that the data in any internal node is Greater than the data in
Priority Queues. 04/10/03 Lecture 22 1
 Priority Queues It is a variant of queues Each item has an associated priority value. When inserting an item in the queue, the priority value is also provided for it. The data structure provides a method
Priority Queues It is a variant of queues Each item has an associated priority value. When inserting an item in the queue, the priority value is also provided for it. The data structure provides a method
Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers
 04-630 Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers David Vernon Carnegie Mellon University Africa vernon@cmu.edu www.vernon.eu Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers 1 Carnegie Mellon University
04-630 Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers David Vernon Carnegie Mellon University Africa vernon@cmu.edu www.vernon.eu Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers 1 Carnegie Mellon University
Module 4: Index Structures Lecture 13: Index structure. The Lecture Contains: Index structure. Binary search tree (BST) B-tree. B+-tree.
 The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
Analysis of Algorithms
 Analysis of Algorithms Trees-I Prof. Muhammad Saeed Tree Representation.. Analysis Of Algorithms 2 .. Tree Representation Analysis Of Algorithms 3 Nomenclature Nodes (13) Size (13) Degree of a node Depth
Analysis of Algorithms Trees-I Prof. Muhammad Saeed Tree Representation.. Analysis Of Algorithms 2 .. Tree Representation Analysis Of Algorithms 3 Nomenclature Nodes (13) Size (13) Degree of a node Depth
Draw the resulting binary search tree. Be sure to show intermediate steps for partial credit (in case your final tree is incorrect).
 Problem 1. Binary Search Trees (36 points) a) (12 points) Assume that the following numbers are inserted into an (initially empty) binary search tree in the order shown below (from left to right): 42 36
Problem 1. Binary Search Trees (36 points) a) (12 points) Assume that the following numbers are inserted into an (initially empty) binary search tree in the order shown below (from left to right): 42 36
Motivation Computer Information Systems Storage Retrieval Updates. Binary Search Trees. OrderedStructures. Binary Search Tree
 Binary Search Trees CMPUT 115 - Lecture Department of Computing Science University of Alberta Revised 21-Mar-05 In this lecture we study an important data structure: Binary Search Tree (BST) Motivation
Binary Search Trees CMPUT 115 - Lecture Department of Computing Science University of Alberta Revised 21-Mar-05 In this lecture we study an important data structure: Binary Search Tree (BST) Motivation
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
COMP 250. Lecture 22. binary search trees. Oct. 30, 2017
 COMP 250 Lecture 22 binary search trees Oct. 30, 2017 1 (binary search) tree binary (search tree) 2 class BSTNode< K >{ K BSTNode< K > BSTNode< K > : } key; leftchild; rightchild; The keys are comparable
COMP 250 Lecture 22 binary search trees Oct. 30, 2017 1 (binary search) tree binary (search tree) 2 class BSTNode< K >{ K BSTNode< K > BSTNode< K > : } key; leftchild; rightchild; The keys are comparable
Data Structures. Giri Narasimhan Office: ECS 254A Phone: x-3748
 Data Structures Giri Narasimhan Office: ECS 254A Phone: x-3748 giri@cs.fiu.edu Search Tree Structures Binary Tree Operations u Tree Traversals u Search O(n) calls to visit() Why? Every recursive has one
Data Structures Giri Narasimhan Office: ECS 254A Phone: x-3748 giri@cs.fiu.edu Search Tree Structures Binary Tree Operations u Tree Traversals u Search O(n) calls to visit() Why? Every recursive has one
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees
 Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms. Trees IV. Lecture 21. Prof.
 ECE 22 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece22/ Trees IV Lecture 2 Prof. Eric Polizzi Summary previous lectures Implementations BST 5 5 7 null 8 null null 7 null
ECE 22 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece22/ Trees IV Lecture 2 Prof. Eric Polizzi Summary previous lectures Implementations BST 5 5 7 null 8 null null 7 null
Tree traversals and binary trees
 Tree traversals and binary trees Comp Sci 1575 Data Structures Valgrind Execute valgrind followed by any flags you might want, and then your typical way to launch at the command line in Linux. Assuming
Tree traversals and binary trees Comp Sci 1575 Data Structures Valgrind Execute valgrind followed by any flags you might want, and then your typical way to launch at the command line in Linux. Assuming
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS
 LECTURE 13 Babeş - Bolyai University Computer Science and Mathematics Faculty 2017-2018 In Lecture 12... Binary Search Trees Binary Tree Traversals Huffman coding Binary Search Tree Today Binary Search
LECTURE 13 Babeş - Bolyai University Computer Science and Mathematics Faculty 2017-2018 In Lecture 12... Binary Search Trees Binary Tree Traversals Huffman coding Binary Search Tree Today Binary Search
Binary Tree Applications
 Binary Tree Applications Lecture 30 Section 19.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 15, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Binary Tree Applications Wed, Apr 15, 2015 1 / 56 1 Binary
Binary Tree Applications Lecture 30 Section 19.2 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 15, 2015 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Binary Tree Applications Wed, Apr 15, 2015 1 / 56 1 Binary
Chapter 11.!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1
 Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-12-01 09:30:53 1/54 Chapter-11.pdf (#13) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or
Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-12-01 09:30:53 1/54 Chapter-11.pdf (#13) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or
Chapter 11.!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1
 Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-03-25 21:47:41 1/53 Chapter-11.pdf (#4) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or more
Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-03-25 21:47:41 1/53 Chapter-11.pdf (#4) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or more
Chapter 22 Splay Trees
 Chapter 22 Splay Trees Introduction Splay trees support all the operations of binary trees. But they do not guarantee Ο(log N) worst-case performance. Instead, its bounds are amortized, meaning that although
Chapter 22 Splay Trees Introduction Splay trees support all the operations of binary trees. But they do not guarantee Ο(log N) worst-case performance. Instead, its bounds are amortized, meaning that although
Some Search Structures. Balanced Search Trees. Binary Search Trees. A Binary Search Tree. Review Binary Search Trees
 Some Search Structures Balanced Search Trees Lecture 8 CS Fall Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Some Search Structures Balanced Search Trees Lecture 8 CS Fall Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
CS2110 Assignment 3 Inheritance and Trees, Summer 2008
 CS2110 Assignment 3 Inheritance and Trees, Summer 2008 Due Sunday July 13, 2008, 6:00PM 0 Introduction 0.1 Goals This assignment will help you get comfortable with basic tree operations and algorithms.
CS2110 Assignment 3 Inheritance and Trees, Summer 2008 Due Sunday July 13, 2008, 6:00PM 0 Introduction 0.1 Goals This assignment will help you get comfortable with basic tree operations and algorithms.
COMP171. AVL-Trees (Part 1)
 COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
Binary Search Trees 1
 Binary Search Trees 1 The Problem with Linked Lists 8Accessing a item from a linked list takes O(N) time for an arbitrary element 8Binary trees can improve upon this and reduce access to O( log N ) time
Binary Search Trees 1 The Problem with Linked Lists 8Accessing a item from a linked list takes O(N) time for an arbitrary element 8Binary trees can improve upon this and reduce access to O( log N ) time
IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10)
 IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) -1- A. Introduction: Searching a linked list. 1. Linear Search /* To linear search a list for a particular Item */ 1. Set Loc = 0; 2. Repeat the following: a. If Loc >= length
IX. Binary Trees (Chapter 10) -1- A. Introduction: Searching a linked list. 1. Linear Search /* To linear search a list for a particular Item */ 1. Set Loc = 0; 2. Repeat the following: a. If Loc >= length
Sorted Arrays. Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min
 Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Spring 2018 Mentoring 8: March 14, Binary Trees
 CSM 6B Binary Trees Spring 08 Mentoring 8: March 4, 08 Binary Trees. Define a procedure, height, which takes in a Node and outputs the height of the tree. Recall that the height of a leaf node is 0. private
CSM 6B Binary Trees Spring 08 Mentoring 8: March 4, 08 Binary Trees. Define a procedure, height, which takes in a Node and outputs the height of the tree. Recall that the height of a leaf node is 0. private
9/29/2016. Chapter 4 Trees. Introduction. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology
 Introduction Chapter 4 Trees for large input, even linear access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit average running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 2 Terminology recursive
Introduction Chapter 4 Trees for large input, even linear access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit average running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 2 Terminology recursive
TREES. Trees - Introduction
 TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES. 3 8 z 4
 CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES v 6 3 8 z 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES v 6 3 8 z 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
1 Binary trees. 1 Binary search trees. 1 Traversal. 1 Insertion. 1 An empty structure is an empty tree.
 Unit 6: Binary Trees Part 1 Engineering 4892: Data Structures Faculty of Engineering & Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland July 11, 2011 1 Binary trees 1 Binary search trees Analysis of
Unit 6: Binary Trees Part 1 Engineering 4892: Data Structures Faculty of Engineering & Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland July 11, 2011 1 Binary trees 1 Binary search trees Analysis of
Binary Search Trees. Analysis of Algorithms
 Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Cpt S 122 Data Structures. Data Structures Trees
 Cpt S 122 Data Structures Data Structures Trees Nirmalya Roy School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Motivation Trees are one of the most important and extensively
Cpt S 122 Data Structures Data Structures Trees Nirmalya Roy School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Motivation Trees are one of the most important and extensively
Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees
 COMP171 Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees 2 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
COMP171 Trees, Binary Trees, and Binary Search Trees 2 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
The Problem with Linked Lists. Topic 18. Attendance Question 1. Binary Search Trees. -Monty Python and The Holy Grail
 Topic 18 Binary Search Trees "Yes. Shrubberies are my trade. I am a shrubber. My name is 'Roger the Shrubber'. I arrange, design, and sell shrubberies." -Monty Python and The Holy Grail The Problem with
Topic 18 Binary Search Trees "Yes. Shrubberies are my trade. I am a shrubber. My name is 'Roger the Shrubber'. I arrange, design, and sell shrubberies." -Monty Python and The Holy Grail The Problem with
Introduction. for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit times closer to O(log N) binary search tree
 Chapter 4 Trees 2 Introduction for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 3 Terminology recursive definition
Chapter 4 Trees 2 Introduction for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 3 Terminology recursive definition
3 Trees: traversal and analysis of standard search trees
 3 Trees: traversal and analysis of standard search trees Binary search trees Binary trees for storing sets of keys, such that the operations are supported: - find - insert - delete Search tree property:
3 Trees: traversal and analysis of standard search trees Binary search trees Binary trees for storing sets of keys, such that the operations are supported: - find - insert - delete Search tree property:
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees
 Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
CS 261 Data Structures. AVL Trees
 CS 261 Data Structures AVL Trees 1 Binary Search Tree Complexity of BST operations: proportional to the length of the path from a node to the root Unbalanced tree: operations may be O(n) E.g.: adding elements
CS 261 Data Structures AVL Trees 1 Binary Search Tree Complexity of BST operations: proportional to the length of the path from a node to the root Unbalanced tree: operations may be O(n) E.g.: adding elements
AVL Tree Definition. An example of an AVL tree where the heights are shown next to the nodes. Adelson-Velsky and Landis
 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 0 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser
Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 0 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser
CS350: Data Structures AVL Trees
 S35: Data Structures VL Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & omputer Science York ollege of Pennsylvania S35: Data Structures James Moscola Balanced Search Trees Binary search trees are not
S35: Data Structures VL Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & omputer Science York ollege of Pennsylvania S35: Data Structures James Moscola Balanced Search Trees Binary search trees are not
CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees
 CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees Irwin King king@cse.cuhk.edu.hk http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~king Department of Computer Science & Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong Introduction General Tree
CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees Irwin King king@cse.cuhk.edu.hk http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~king Department of Computer Science & Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong Introduction General Tree
Why Do We Need Trees?
 CSE 373 Lecture 6: Trees Today s agenda: Trees: Definition and terminology Traversing trees Binary search trees Inserting into and deleting from trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Why Do We Need Trees?
CSE 373 Lecture 6: Trees Today s agenda: Trees: Definition and terminology Traversing trees Binary search trees Inserting into and deleting from trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Why Do We Need Trees?
Data Structures Lesson 7
 Data Structures Lesson 7 BSc in Computer Science University of New York, Tirana Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba 1-1 Binary Search Trees For large amounts of input, the linear access time of linked lists
Data Structures Lesson 7 BSc in Computer Science University of New York, Tirana Assoc. Prof. Dr. Marenglen Biba 1-1 Binary Search Trees For large amounts of input, the linear access time of linked lists
Search Trees - 1 Venkatanatha Sarma Y
 Search Trees - 1 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Search Trees - 1 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Data Structures in Java
 Data Structures in Java Lecture 9: Binary Search Trees. 10/7/015 Daniel Bauer 1 Contents 1. Binary Search Trees. Implementing Maps with BSTs Map ADT A map is collection of (key, value) pairs. Keys are
Data Structures in Java Lecture 9: Binary Search Trees. 10/7/015 Daniel Bauer 1 Contents 1. Binary Search Trees. Implementing Maps with BSTs Map ADT A map is collection of (key, value) pairs. Keys are
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees
 Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 02 / 24 / 2017 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Trees binary trees two ideas for representing them in code traversals start binary
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 02 / 24 / 2017 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Trees binary trees two ideas for representing them in code traversals start binary
CIS265/ Trees Red-Black Trees. Some of the following material is from:
 CIS265/506 2-3-4 Trees Red-Black Trees Some of the following material is from: Data Structures for Java William H. Ford William R. Topp ISBN 0-13-047724-9 Chapter 27 Balanced Search Trees Bret Ford 2005,
CIS265/506 2-3-4 Trees Red-Black Trees Some of the following material is from: Data Structures for Java William H. Ford William R. Topp ISBN 0-13-047724-9 Chapter 27 Balanced Search Trees Bret Ford 2005,
Multi-Way Search Tree
 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two and at most d children and stores d -1 data items (k i, D i ) Rule: Number of children = 1
Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two and at most d children and stores d -1 data items (k i, D i ) Rule: Number of children = 1
(2,4) Trees Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
Outline. Preliminaries. Binary Trees Binary Search Trees. What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications
 Trees 1 Outline Preliminaries What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Structure and operations Analysis 2 What is a Tree? A tree
Trees 1 Outline Preliminaries What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Structure and operations Analysis 2 What is a Tree? A tree
Week 2. TA Lab Consulting - See schedule (cs400 home pages) Peer Mentoring available - Friday 8am-12pm, 12:15-1:30pm in 1289CS
 ASSIGNMENTS h0 available and due before 10pm on Monday 1/28 h1 available and due before 10pm on Monday 2/4 p1 available and due before 10pm on Thursday 2/7 Week 2 TA Lab Consulting - See schedule (cs400
ASSIGNMENTS h0 available and due before 10pm on Monday 1/28 h1 available and due before 10pm on Monday 2/4 p1 available and due before 10pm on Thursday 2/7 Week 2 TA Lab Consulting - See schedule (cs400
Unit III - Tree TREES
 TREES Unit III - Tree Consider a scenario where you are required to represent the directory structure of your operating system. The directory structure contains various folders and files. A folder may
TREES Unit III - Tree Consider a scenario where you are required to represent the directory structure of your operating system. The directory structure contains various folders and files. A folder may
Announcements. Midterm exam 2, Thursday, May 18. Today s topic: Binary trees (Ch. 8) Next topic: Priority queues and heaps. Break around 11:45am
 Announcements Midterm exam 2, Thursday, May 18 Closed book/notes but one sheet of paper allowed Covers up to stacks and queues Today s topic: Binary trees (Ch. 8) Next topic: Priority queues and heaps
Announcements Midterm exam 2, Thursday, May 18 Closed book/notes but one sheet of paper allowed Covers up to stacks and queues Today s topic: Binary trees (Ch. 8) Next topic: Priority queues and heaps
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees
 Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2
 CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2 1) Shown below is an AVL tree T. Nov 14, 2012 Solutions to OPEN BOOK section. (a) Suggest a key whose insertion does not require any rotation. 18 (b) Suggest a key, if
CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2 1) Shown below is an AVL tree T. Nov 14, 2012 Solutions to OPEN BOOK section. (a) Suggest a key whose insertion does not require any rotation. 18 (b) Suggest a key, if
Binary search trees (chapters )
 Binary search trees (chapters 18.1 18.3) Binary search trees In a binary search tree (BST), every node is greater than all its left descendants, and less than all its right descendants (recall that this
Binary search trees (chapters 18.1 18.3) Binary search trees In a binary search tree (BST), every node is greater than all its left descendants, and less than all its right descendants (recall that this
Trees. Dr. Ronaldo Menezes Hugo Serrano Ronaldo Menezes, Florida Tech
 Trees Dr. Ronaldo Menezes Hugo Serrano (hbarbosafilh2011@my.fit.edu) Introduction to Trees Trees are very common in computer science They come in different variations They are used as data representation
Trees Dr. Ronaldo Menezes Hugo Serrano (hbarbosafilh2011@my.fit.edu) Introduction to Trees Trees are very common in computer science They come in different variations They are used as data representation
Terminology. The ADT Binary Tree. The ADT Binary Search Tree
 Terminology The ADT Binary Tree The ADT Binary Search Tree 1 Terminology 3 A general tree A general tree T is a set of one or more nodes such that T is partitioned into disjoint subsets: o A single node
Terminology The ADT Binary Tree The ADT Binary Search Tree 1 Terminology 3 A general tree A general tree T is a set of one or more nodes such that T is partitioned into disjoint subsets: o A single node
! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges. ! Parent: source node of directed edge. ! Child: terminal node of directed edge
 Trees & Heaps Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman!1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every
Trees & Heaps Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman!1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every
Tree Structures. Definitions: o A tree is a connected acyclic graph. o A disconnected acyclic graph is called a forest
 Tree Structures Definitions: o A tree is a connected acyclic graph. o A disconnected acyclic graph is called a forest o A tree is a connected digraph with these properties: There is exactly one node (Root)
Tree Structures Definitions: o A tree is a connected acyclic graph. o A disconnected acyclic graph is called a forest o A tree is a connected digraph with these properties: There is exactly one node (Root)
4. Trees. 4.1 Preliminaries. 4.2 Binary trees. 4.3 Binary search trees. 4.4 AVL trees. 4.5 Splay trees. 4.6 B-trees. 4. Trees
 4. Trees 4.1 Preliminaries 4.2 Binary trees 4.3 Binary search trees 4.4 AVL trees 4.5 Splay trees 4.6 B-trees Malek Mouhoub, CS340 Fall 2002 1 4.1 Preliminaries A Root B C D E F G Height=3 Leaves H I J
4. Trees 4.1 Preliminaries 4.2 Binary trees 4.3 Binary search trees 4.4 AVL trees 4.5 Splay trees 4.6 B-trees Malek Mouhoub, CS340 Fall 2002 1 4.1 Preliminaries A Root B C D E F G Height=3 Leaves H I J
AVL Trees / Slide 2. AVL Trees / Slide 4. Let N h be the minimum number of nodes in an AVL tree of height h. AVL Trees / Slide 6
 COMP11 Spring 008 AVL Trees / Slide Balanced Binary Search Tree AVL-Trees Worst case height of binary search tree: N-1 Insertion, deletion can be O(N) in the worst case We want a binary search tree with
COMP11 Spring 008 AVL Trees / Slide Balanced Binary Search Tree AVL-Trees Worst case height of binary search tree: N-1 Insertion, deletion can be O(N) in the worst case We want a binary search tree with
CS200: Balanced Search Trees
 Value Oriented Data Structures CS200: Balanced Search Trees Walls & Mirrors Chapters 12,13 Homework 4 extension Next week: Programming quiz during recit Midterm 2 April 8 th (in class) New partners and
Value Oriented Data Structures CS200: Balanced Search Trees Walls & Mirrors Chapters 12,13 Homework 4 extension Next week: Programming quiz during recit Midterm 2 April 8 th (in class) New partners and
AVL Trees Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees 1
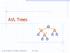 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 20 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees AVL Tree Definition Adelson-Velsky and Landis binary search tree balanced each internal node v the heights of the children of v can 2 3 7
AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 20 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees AVL Tree Definition Adelson-Velsky and Landis binary search tree balanced each internal node v the heights of the children of v can 2 3 7
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1
 CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
Search Trees (Ch. 9) > = Binary Search Trees 1
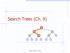 Search Trees (Ch. 9) < 6 > = 1 4 8 9 Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionaries Keys are assumed to come from a total order. New operations: closestbefore(k) closestafter(k) Binary Search Trees Binary
Search Trees (Ch. 9) < 6 > = 1 4 8 9 Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionaries Keys are assumed to come from a total order. New operations: closestbefore(k) closestafter(k) Binary Search Trees Binary
CSE 326: Data Structures Lecture #8 Binary Search Trees
 CSE 6: Data Structures Lecture #8 Binary Search Trees Alon Halevy Spring Quarter Binary Trees Many algorithms are efficient and easy to program for the special case of binary trees B A C Binary tree is
CSE 6: Data Structures Lecture #8 Binary Search Trees Alon Halevy Spring Quarter Binary Trees Many algorithms are efficient and easy to program for the special case of binary trees B A C Binary tree is
CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015
 CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015 Lecture #17, Implementing Binary Search Trees John Ridgway April 2, 2015 1 Implementing Binary Search Trees Review: The BST Interface Binary search
CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015 Lecture #17, Implementing Binary Search Trees John Ridgway April 2, 2015 1 Implementing Binary Search Trees Review: The BST Interface Binary search
CS350: Data Structures Red-Black Trees
 Red-Black Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Red-Black Tree An alternative to AVL trees Insertion can be done in a bottom-up or
Red-Black Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Red-Black Tree An alternative to AVL trees Insertion can be done in a bottom-up or
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees
 Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
Trees. Estruturas de Dados / Programação 2 Árvores. Márcio Ribeiro twitter.com/marciomribeiro. Introduc)on. Hierarchical structure
 Introduc)on Linear structures Removing this idea, treasure of applicaons Estruturas de Dados / Programação 2 Árvores Márcio Ribeiro marcio@ic.ufal.br twitter.com/marciomribeiro Hierarchical structure Companies
Introduc)on Linear structures Removing this idea, treasure of applicaons Estruturas de Dados / Programação 2 Árvores Márcio Ribeiro marcio@ic.ufal.br twitter.com/marciomribeiro Hierarchical structure Companies
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS. Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap Summary of the previous lecture TREE is hierarchical (non linear) data structure Binary trees Definitions Full tree,
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap Summary of the previous lecture TREE is hierarchical (non linear) data structure Binary trees Definitions Full tree,
Balanced Binary Search Trees. Victor Gao
 Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
Hierarchical data structures. Announcements. Motivation for trees. Tree overview
 Announcements Midterm exam 2, Thursday, May 18 Closed book/notes but one sheet of paper allowed Covers up to stacks and queues Today s topic: Binary trees (Ch. 8) Next topic: Priority queues and heaps
Announcements Midterm exam 2, Thursday, May 18 Closed book/notes but one sheet of paper allowed Covers up to stacks and queues Today s topic: Binary trees (Ch. 8) Next topic: Priority queues and heaps
! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges. ! Parent: source node of directed edge. ! Child: terminal node of directed edge
 Trees (& Heaps) Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root -
Trees (& Heaps) Week 12 Gaddis: 20 Weiss: 21.1-3 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Tree: non-recursive definition! Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root -
a graph is a data structure made up of nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges
 1 Trees Graphs a graph is a data structure made up of nodes each node stores data each node has links to zero or more nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges graphs occur frequently in
1 Trees Graphs a graph is a data structure made up of nodes each node stores data each node has links to zero or more nodes in graph theory the links are normally called edges graphs occur frequently in
If you took your exam home last time, I will still regrade it if you want.
 Some Comments about HW2: 1. You should have used a generic node in your structure one that expected an Object, and not some other type. 2. Main is still too long for some people 3. braces in wrong place,
Some Comments about HW2: 1. You should have used a generic node in your structure one that expected an Object, and not some other type. 2. Main is still too long for some people 3. braces in wrong place,
Binary search trees (chapters )
 Binary search trees (chapters 18.1 18.3) Binary search trees In a binary search tree (BST), every node is greater than all its left descendants, and less than all its right descendants (recall that this
Binary search trees (chapters 18.1 18.3) Binary search trees In a binary search tree (BST), every node is greater than all its left descendants, and less than all its right descendants (recall that this
Trees 11/15/16. Chapter 11. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology
 Chapter 11 Trees Definition of a general tree A general tree T is a set of one or more nodes such that T is partitioned into disjoint subsets: A single node r, the root Sets that are general trees, called
Chapter 11 Trees Definition of a general tree A general tree T is a set of one or more nodes such that T is partitioned into disjoint subsets: A single node r, the root Sets that are general trees, called
Tree: non-recursive definition. Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps. Tree: recursive definition. Tree: example.
 Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
Trees, Binary Search Trees, and Heaps CS 5301 Fall 2013 Jill Seaman Tree: non-recursive definition Tree: set of nodes and directed edges - root: one node is distinguished as the root - Every node (except
COMP : Trees. COMP20012 Trees 219
 COMP20012 3: Trees COMP20012 Trees 219 Trees Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees Search Trees Family Trees Hierarchical Structures Management Directories COMP20012 Trees 220 Trees have natural
COMP20012 3: Trees COMP20012 Trees 219 Trees Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees Search Trees Family Trees Hierarchical Structures Management Directories COMP20012 Trees 220 Trees have natural
Splay Trees. (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 27
 Splay Trees (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 27 Basic Idea Invented by Sleator and Tarjan (1985) Blind rebalancing no height info kept! Worst-case time per operation is O(n)
Splay Trees (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 27 Basic Idea Invented by Sleator and Tarjan (1985) Blind rebalancing no height info kept! Worst-case time per operation is O(n)
Binary Search Tree (3A) Young Won Lim 6/2/18
 Binary Search Tree (A) /2/1 Copyright (c) 2015-201 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
Binary Search Tree (A) /2/1 Copyright (c) 2015-201 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
Friday Four Square! 4:15PM, Outside Gates
 Binary Search Trees Friday Four Square! 4:15PM, Outside Gates Implementing Set On Monday and Wednesday, we saw how to implement the Map and Lexicon, respectively. Let's now turn our attention to the Set.
Binary Search Trees Friday Four Square! 4:15PM, Outside Gates Implementing Set On Monday and Wednesday, we saw how to implement the Map and Lexicon, respectively. Let's now turn our attention to the Set.
