CSE 373 Midterm 2 2/27/06 Sample Solution. Question 1. (6 points) (a) What is the load factor of a hash table? (Give a definition.
|
|
|
- Dylan Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Question 1. (6 points) (a) What is the load factor of a hash table? (Give a definition.) The load factor is number of items in the table / size of the table (number of buckets) (b) What is a reasonable value for the load factor of a hash table if the operations on the table are to be efficient (i.e., O(1) instead of something significantly slower)? Generally it should be less than 1.0, usually no more than 0.5 to (c) What needs to be true about a hash function if operations using that function to locate items in a hash table are to be efficient? The main requirement is if we compute hash values for many keys, they should be distributed evenly among the different buckets. Also, the hash computation itself should be efficient O(1). Question 2. (3 points) You have been asked to design a hash function for a set data structure (an unordered collection with no duplicates). There are two possibilities. One would be to calculate a polynomial using the hashcodes of the elements of the set, i.e., if the set elements are s1, s2,, sn, then use ( ((s1.hashcode()* 37 + s2.hashcode()) * 37 + ) * 37 + sn.hashcode(). The other possibility is to just add up the individual hashcodes without any additional calculations, i.e., s1.hashcode() + s2.hashcode() + + sn.hashcode(). Which of these functions would be the right hashcode to use for a set, or would either one be equally good? Give a brief reason for your answer. The sum of the individual hash codes is needed here. If we use the polynomial computation, we will get a different result if the hashcodes for the set elements are added in different orders. But a set is unordered, so we should have the same hashcode for any sets that contain the same elements, no matter what order we use the hashcodes of the individual elements to calculate the set s hashcode. Page 1 of 7
2 Question 3. (6 points) Suppose that we have the following class containing a few instance variables and an equals method. public class Thing { private Gizmo g; private int number; private Thing nextthing; private Blob b; private Whazzit w; /** return true if this Thing equals other */ public boolean equals(object other) { if (!other instanceof Thing) { return false; Thing t = (Thing) other; return this.g.equals(t.g) && this.b.equals(t.b) && this.w.equals(t.w);... Complete the definition of a suitable hashcode() method for class Thing, below. For full credit, your hashcode() function should compute a high-quality hash code, but should also be consistent with the equals() method defined above for class Thing. /** return a suitable hash code for Thing objects */ public int hashcode() { return (g.hashcode() * 37 + b.hashcode()) * 37 + w.hashcode() Key points: A polynomial computation is likely to give a better hashcode. More importantly, the hashcode computation should only involve the fields g, b, and w, since these are the only ones referenced in equals(). If other fields in a Thing object are used in the hashcode computation, we could wind up in a situation where two Things are equal, but have different hashcodes. One other note: 37 isn t the only possible prime number to use in a calculation like this, but it is one of the ones that is known to produce reasonable results in lots of cases. Page 2 of 7
3 Question 4. (6 points) Consider the following AVL tree Now suppose we insert a new node containing 4 into this tree. (a) (1 point) Show where a new node containing 4 would be inserted in the above tree before any rotations are done to rebalance the tree. (Just draw it in the correct place in the above diagram.) (b) (5 points) Assuming that the tree that results from adding a node containing 4 in part (a) is out of balance, show the results of the rotations that would be performed to restore the AVL property. If more than one rotation step is needed, draw diagrams that show the successive results of the rotations performed. (i.e., show your work) Page 3 of 7
4 Question 5. (6 points) Consider the following splay tree Show the tree that results if we search for 60 in this tree and perform the splay operations that are implied by that search. If more than one splay operation is required, please draw a sequence of diagrams showing each of the splay operations (this will help you organize your answer, and will help the grader figure out what happened if something isn t quite right.) Page 4 of 7
5 The next questions concern binary search trees whose nodes are defined as follows. class BSTNode { public Comparable item; public BSTNode left; public BSTNode right; public BSTNode parent; // item referred to by this node // left subtree; null if none // right subtree; null if none // this node s parent; null if // none (i.e., null if this is // the root node) In this representation, each node contains a reference to its parent in the tree, if there is one, in addition to its left and right subtrees. Question 6. (12 points) Complete the definition of the following Java method so that, given a reference to some node in a binary search tree (implemented with the above node data structure) the method returns a reference to the node that precedes it in an in-order traversal of the tree. The result should be null if there is no node preceding p. /* Given a non-null reference p to some node in a binary * search tree, return a reference to the node that PRECEEDES * p in an in-order traversal of the binary search tree. * Return null if p has no predecessor node. */ public BSTNode previousnode(bstnode p) { // Strategy: if p has a left child, then the previous node // is the largest one on the left. If not, then it is the // closest ancestor node whose item is less than p.item BSTNode q; if (p.left!= null) { q = p.left; while (q.right!= null) { q = q.right; else { q = p.parent; while (q!= null && q.item.compareto(p.item) > 0) { q = q.parent; return q; Another way to search for the nearest ancestor that contains a smaller value is to ascend the tree as long as the current node is the left child of its parent. q = p; while (q.parent!= null && q.parent.left == q) { q = q.parent; return q.parent; This is likely to be cheaper than the first solution, since it avoids a potentially expensive compareto computation. Page 5 of 7
6 Question 7. (12 points) When a node is inserted in a red-black tree it is initially colored red. If it is inserted as the child of another red node, a rotation must be performed to restructure the tree to preserve the red-black property. One of the possible rotations is described by the following diagrams, where x is the new node, p is initially its parent, and g is initially its grandparent. Before g After p x p b c x b g c Assuming that variable x is initialized to point to the node labeled x in the left diagram above, write a sequence of assignment statements to perform this rotation. You do not need to write a complete method, and you do not need to worry about keeping track of the colors of the nodes. Just write a sequence of statements to change the pointers in the various nodes to restructure the nodes as shown in the diagram. You should assume that the nodes are instances of the BTNode class (data structure) defined on the previous page, with links parent, left, and right referring to adjacent nodes in the tree. BSTNode x; // initialized to point to node x... // write your answer below // name the ancestor nodes (optional, but helps clarify) BSTNode p = x.parent; BSTNode g = p.parent; // fix child pointers g.left = p.right; p.right = g; // fix parent pointers p.parent = g.parent; g.parent = p; if (g.left!= null) { g.left.parent = g; Page 6 of 7
7 Question 8. (9 points) We ve now seen many possible ways to implement collections of data. For each of the following applications, explain which data structure from the given list you would choose and give your reasons for doing so. There may not be a single right answer to some of the questions. Your choices will be evaluated on whether they are appropriate for the given application and the quality of the (brief) reason(s) that you give in support of your choice. Choose from the following list of data structures: Array-based list Linked list Binary tree, not a binary search tree Unbalanced binary search tree AVL tree Splay tree Hash table (a) List of names of all UW students. Lookup operations tend to be random and are much more frequent than additions and deletions. Additions often arrive in large batches and are initially in alphabetical order. The application also needs to be able to list alphabetically all names in the directory starting at a particular name and ending at another name, e.g., list all names from Jones to Ngyuen, inclusive. AVL tree. Access to any entry is reasonably fast (O(log n)), and access to a range of entries is also quick for each successive entry. The rebalancing will ensure that the height remains O(log n), even if entries are added in alphabetical order. (b) List of book titles sold by Amazon. There are hundreds of thousands of titles in the list, and access to any title needs to be relatively fast, but almost all accesses (greater than 99.5%) refer to a few dozen best sellers. Splay tree. Amortized access to any entry will be O(log n), although it may be slower for some entries. However, access to the best sellers will be quite fast since the splay operations will move those to the top of the tree. (c) Parts inventory in an automobile supply shop. There are hundreds of thousands of different parts in the inventory and, given a part number, information about the part with that number needs to be accessed quickly. Hash table. Assuming a reasonable hash function and enough buckets, access to entries will be O(1). The part number would be a suitable key for the hash function. Page 7 of 7
Data Structures and Algorithms Winter term 2016
 Page 0 German University in Cairo December 26, 2016 Media Engineering and Technology Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher Dr. Wael Abouelsaadat Data Structures and Algorithms Winter term 2016 Final Exam Bar Code
Page 0 German University in Cairo December 26, 2016 Media Engineering and Technology Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher Dr. Wael Abouelsaadat Data Structures and Algorithms Winter term 2016 Final Exam Bar Code
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the City University of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE
 BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the City University of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE CSI Section E01 AVL Trees AVL Property While BST structures have average performance of Θ(log(n))
BRONX COMMUNITY COLLEGE of the City University of New York DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE CSI Section E01 AVL Trees AVL Property While BST structures have average performance of Θ(log(n))
Algorithms. AVL Tree
 Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES. 3 8 z 4
 CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES v 6 3 8 z 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES v 6 3 8 z 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
AVL Tree Definition. An example of an AVL tree where the heights are shown next to the nodes. Adelson-Velsky and Landis
 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 0 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser
Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 0 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser
AVL Trees Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees 1
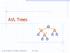 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 20 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees AVL Tree Definition Adelson-Velsky and Landis binary search tree balanced each internal node v the heights of the children of v can 2 3 7
AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 20 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees AVL Tree Definition Adelson-Velsky and Landis binary search tree balanced each internal node v the heights of the children of v can 2 3 7
CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015
 CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015 Lecture #17, Implementing Binary Search Trees John Ridgway April 2, 2015 1 Implementing Binary Search Trees Review: The BST Interface Binary search
CmpSci 187: Programming with Data Structures Spring 2015 Lecture #17, Implementing Binary Search Trees John Ridgway April 2, 2015 1 Implementing Binary Search Trees Review: The BST Interface Binary search
Section 1: True / False (1 point each, 15 pts total)
 Section : True / False ( point each, pts total) Circle the word TRUE or the word FALSE. If neither is circled, both are circled, or it impossible to tell which is circled, your answer will be considered
Section : True / False ( point each, pts total) Circle the word TRUE or the word FALSE. If neither is circled, both are circled, or it impossible to tell which is circled, your answer will be considered
1. AVL Trees (10 Points)
 CSE 373 Spring 2012 Final Exam Solution 1. AVL Trees (10 Points) Given the following AVL Tree: (a) Draw the resulting BST after 5 is removed, but before any rebalancing takes place. Label each node in
CSE 373 Spring 2012 Final Exam Solution 1. AVL Trees (10 Points) Given the following AVL Tree: (a) Draw the resulting BST after 5 is removed, but before any rebalancing takes place. Label each node in
Ch04 Balanced Search Trees
 Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 05 Ch0 Balanced Search Trees v 3 8 z Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries,
Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 05 Ch0 Balanced Search Trees v 3 8 z Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries,
Unit III - Tree TREES
 TREES Unit III - Tree Consider a scenario where you are required to represent the directory structure of your operating system. The directory structure contains various folders and files. A folder may
TREES Unit III - Tree Consider a scenario where you are required to represent the directory structure of your operating system. The directory structure contains various folders and files. A folder may
Chapter 22 Splay Trees
 Chapter 22 Splay Trees Introduction Splay trees support all the operations of binary trees. But they do not guarantee Ο(log N) worst-case performance. Instead, its bounds are amortized, meaning that although
Chapter 22 Splay Trees Introduction Splay trees support all the operations of binary trees. But they do not guarantee Ο(log N) worst-case performance. Instead, its bounds are amortized, meaning that although
9/29/2016. Chapter 4 Trees. Introduction. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology
 Introduction Chapter 4 Trees for large input, even linear access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit average running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 2 Terminology recursive
Introduction Chapter 4 Trees for large input, even linear access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit average running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 2 Terminology recursive
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees
 Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Self-Balancing Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
CS 62 Midterm 2 Practice
 CS 62 Midterm 2 Practice 2017-4-7 Please put your name on the back of the last page of the test. Problem 1: Multiple Choice [8 points] [2 points each] For each question, circle the correct answer. If you
CS 62 Midterm 2 Practice 2017-4-7 Please put your name on the back of the last page of the test. Problem 1: Multiple Choice [8 points] [2 points each] For each question, circle the correct answer. If you
Lecture 27. Binary Search Trees. Binary Search Trees
 Lecture Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees In the previous lecture, we defined the concept of binary search tree as a binary tree of nodes containing an ordered key with the following additional property.
Lecture Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees In the previous lecture, we defined the concept of binary search tree as a binary tree of nodes containing an ordered key with the following additional property.
CS350: Data Structures Red-Black Trees
 Red-Black Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Red-Black Tree An alternative to AVL trees Insertion can be done in a bottom-up or
Red-Black Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Red-Black Tree An alternative to AVL trees Insertion can be done in a bottom-up or
Red-black trees (19.5), B-trees (19.8), trees
 Red-black trees (19.5), B-trees (19.8), 2-3-4 trees Red-black trees A red-black tree is a balanced BST It has a more complicated invariant than an AVL tree: Each node is coloured red or black A red node
Red-black trees (19.5), B-trees (19.8), 2-3-4 trees Red-black trees A red-black tree is a balanced BST It has a more complicated invariant than an AVL tree: Each node is coloured red or black A red node
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees
 Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming. Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2
 CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2 Last Time Binary search trees (Ch 14) The locate method Further Implementation 2 Today s Outline Binary search trees
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2 Last Time Binary search trees (Ch 14) The locate method Further Implementation 2 Today s Outline Binary search trees
Some Search Structures. Balanced Search Trees. Binary Search Trees. A Binary Search Tree. Review Binary Search Trees
 Some Search Structures Balanced Search Trees Lecture 8 CS Fall Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Some Search Structures Balanced Search Trees Lecture 8 CS Fall Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Binary Trees: Practice Problems
 Binary Trees: Practice Problems College of Computing & Information Technology King Abdulaziz University CPCS-204 Data Structures I Warmup Problem 1: Searching for a node public boolean recursivesearch(int
Binary Trees: Practice Problems College of Computing & Information Technology King Abdulaziz University CPCS-204 Data Structures I Warmup Problem 1: Searching for a node public boolean recursivesearch(int
Trees. Chapter 6. strings. 3 Both position and Enumerator are similar in concept to C++ iterators, although the details are quite different.
 Chapter 6 Trees In a hash table, the items are not stored in any particular order in the table. This is fine for implementing Sets and Maps, since for those abstract data types, the only thing that matters
Chapter 6 Trees In a hash table, the items are not stored in any particular order in the table. This is fine for implementing Sets and Maps, since for those abstract data types, the only thing that matters
Recall from Last Time: AVL Trees
 CSE 326 Lecture 8: Getting to now AVL Trees Today s Topics: Balanced Search Trees AVL Trees and Rotations Splay trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Recall from Last Time: AVL Trees AVL trees are height-balanced
CSE 326 Lecture 8: Getting to now AVL Trees Today s Topics: Balanced Search Trees AVL Trees and Rotations Splay trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Recall from Last Time: AVL Trees AVL trees are height-balanced
Module 4: Index Structures Lecture 13: Index structure. The Lecture Contains: Index structure. Binary search tree (BST) B-tree. B+-tree.
 The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
UNIT III BALANCED SEARCH TREES AND INDEXING
 UNIT III BALANCED SEARCH TREES AND INDEXING OBJECTIVE The implementation of hash tables is frequently called hashing. Hashing is a technique used for performing insertions, deletions and finds in constant
UNIT III BALANCED SEARCH TREES AND INDEXING OBJECTIVE The implementation of hash tables is frequently called hashing. Hashing is a technique used for performing insertions, deletions and finds in constant
AVL Trees (10.2) AVL Trees
 AVL Trees (0.) CSE 0 Winter 0 8 February 0 AVL Trees AVL trees are balanced. An AVL Tree is a binary search tree such that for every internal node v of T, the heights of the children of v can differ by
AVL Trees (0.) CSE 0 Winter 0 8 February 0 AVL Trees AVL trees are balanced. An AVL Tree is a binary search tree such that for every internal node v of T, the heights of the children of v can differ by
Binary Search Trees. Analysis of Algorithms
 Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees. Eric McCreath
 Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms. Fall 2017 TuTh 3:25 pm 4:40 pm Aug 30- Dec 22 Hoyt Auditorium
 CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2017 TuTh 3:25 pm 4:40 pm Aug 30- Dec 22 Hoyt Auditorium Announcement Coming week: Nov 19 Nov 25 No Quiz No Workshop No New Lab Monday and Tuesday: regular Lab
CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2017 TuTh 3:25 pm 4:40 pm Aug 30- Dec 22 Hoyt Auditorium Announcement Coming week: Nov 19 Nov 25 No Quiz No Workshop No New Lab Monday and Tuesday: regular Lab
AVL Trees. (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 17
 AVL Trees (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 17 Balanced Binary Tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time
AVL Trees (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 17 Balanced Binary Tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time
12 July, Red-Black Trees. Red-Black Trees
 1 BST work well if the data is inserted into the tree in random order. They work much slower if the data is inserted in already sorted order. When the values to be inserted are already ordered, a binary
1 BST work well if the data is inserted into the tree in random order. They work much slower if the data is inserted in already sorted order. When the values to be inserted are already ordered, a binary
Trees, Part 1: Unbalanced Trees
 Trees, Part 1: Unbalanced Trees The first part of this chapter takes a look at trees in general and unbalanced binary trees. The second part looks at various schemes to balance trees and/or make them more
Trees, Part 1: Unbalanced Trees The first part of this chapter takes a look at trees in general and unbalanced binary trees. The second part looks at various schemes to balance trees and/or make them more
COMP : Trees. COMP20012 Trees 219
 COMP20012 3: Trees COMP20012 Trees 219 Trees Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees Search Trees Family Trees Hierarchical Structures Management Directories COMP20012 Trees 220 Trees have natural
COMP20012 3: Trees COMP20012 Trees 219 Trees Seen lots of examples. Parse Trees Decision Trees Search Trees Family Trees Hierarchical Structures Management Directories COMP20012 Trees 220 Trees have natural
Data Structure - Advanced Topics in Tree -
 Data Structure - Advanced Topics in Tree - AVL, Red-Black, B-tree Hanyang University Jong-Il Park AVL TREE Division of Computer Science and Engineering, Hanyang University Balanced binary trees Non-random
Data Structure - Advanced Topics in Tree - AVL, Red-Black, B-tree Hanyang University Jong-Il Park AVL TREE Division of Computer Science and Engineering, Hanyang University Balanced binary trees Non-random
Week 2. TA Lab Consulting - See schedule (cs400 home pages) Peer Mentoring available - Friday 8am-12pm, 12:15-1:30pm in 1289CS
 ASSIGNMENTS h0 available and due before 10pm on Monday 1/28 h1 available and due before 10pm on Monday 2/4 p1 available and due before 10pm on Thursday 2/7 Week 2 TA Lab Consulting - See schedule (cs400
ASSIGNMENTS h0 available and due before 10pm on Monday 1/28 h1 available and due before 10pm on Monday 2/4 p1 available and due before 10pm on Thursday 2/7 Week 2 TA Lab Consulting - See schedule (cs400
Sorted Arrays. Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min
 Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Note that this is a rep invariant! The type system doesn t enforce this but you need it to be true. Should use repok to check in debug version.
 Announcements: Prelim tonight! 7:30-9:00 in Thurston 203/205 o Handed back in section tomorrow o If you have a conflict you can take the exam at 5:45 but can t leave early. Please email me so we have a
Announcements: Prelim tonight! 7:30-9:00 in Thurston 203/205 o Handed back in section tomorrow o If you have a conflict you can take the exam at 5:45 but can t leave early. Please email me so we have a
Algorithms. Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees
 Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
10.2 AVL Trees. Definition of an AVL Tree. 438 Chapter 10. Search Trees
 438 Chapter 10. Search Trees 10. AVL Trees In theprevioussection,wediscussedwhatshouldbeanefficientmapdatastructure, but the worst-case performance it achieves for the various operations is linear time,
438 Chapter 10. Search Trees 10. AVL Trees In theprevioussection,wediscussedwhatshouldbeanefficientmapdatastructure, but the worst-case performance it achieves for the various operations is linear time,
Balanced Search Trees. CS 3110 Fall 2010
 Balanced Search Trees CS 3110 Fall 2010 Some Search Structures Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Balanced Search Trees CS 3110 Fall 2010 Some Search Structures Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Introduction. for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit times closer to O(log N) binary search tree
 Chapter 4 Trees 2 Introduction for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 3 Terminology recursive definition
Chapter 4 Trees 2 Introduction for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 3 Terminology recursive definition
Name Section Number. CS210 Exam #3 *** PLEASE TURN OFF ALL CELL PHONES*** Practice
 Name Section Number CS210 Exam #3 *** PLEASE TURN OFF ALL CELL PHONES*** Practice All Sections Bob Wilson OPEN BOOK / OPEN NOTES: You will have all 90 minutes until the start of the next class period.
Name Section Number CS210 Exam #3 *** PLEASE TURN OFF ALL CELL PHONES*** Practice All Sections Bob Wilson OPEN BOOK / OPEN NOTES: You will have all 90 minutes until the start of the next class period.
10/23/2013. AVL Trees. Height of an AVL Tree. Height of an AVL Tree. AVL Trees
 // AVL Trees AVL Trees An AVL tree is a binary search tree with a balance condition. AVL is named for its inventors: Adel son-vel skii and Landis AVL tree approximates the ideal tree (completely balanced
// AVL Trees AVL Trees An AVL tree is a binary search tree with a balance condition. AVL is named for its inventors: Adel son-vel skii and Landis AVL tree approximates the ideal tree (completely balanced
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Computer Science. Second Examination
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Computer Science Second Examination CS 225 Data Structures and Software Principles Spring 2014 7-10p, Tuesday, April 8 Name: NetID: Lab Section
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Computer Science Second Examination CS 225 Data Structures and Software Principles Spring 2014 7-10p, Tuesday, April 8 Name: NetID: Lab Section
Quiz 1 Solutions. (a) f(n) = n g(n) = log n Circle all that apply: f = O(g) f = Θ(g) f = Ω(g)
 Introduction to Algorithms March 11, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Spring 2009 Professors Sivan Toledo and Alan Edelman Quiz 1 Solutions Problem 1. Quiz 1 Solutions Asymptotic orders
Introduction to Algorithms March 11, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Spring 2009 Professors Sivan Toledo and Alan Edelman Quiz 1 Solutions Problem 1. Quiz 1 Solutions Asymptotic orders
Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises
 Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises A Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will
Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises A Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will
Search Trees - 1 Venkatanatha Sarma Y
 Search Trees - 1 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Search Trees - 1 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
CISC 235: Topic 4. Balanced Binary Search Trees
 CISC 235: Topic 4 Balanced Binary Search Trees Outline Rationale and definitions Rotations AVL Trees, Red-Black, and AA-Trees Algorithms for searching, insertion, and deletion Analysis of complexity CISC
CISC 235: Topic 4 Balanced Binary Search Trees Outline Rationale and definitions Rotations AVL Trees, Red-Black, and AA-Trees Algorithms for searching, insertion, and deletion Analysis of complexity CISC
ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms. Trees IV. Lecture 21. Prof.
 ECE 22 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece22/ Trees IV Lecture 2 Prof. Eric Polizzi Summary previous lectures Implementations BST 5 5 7 null 8 null null 7 null
ECE 22 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece22/ Trees IV Lecture 2 Prof. Eric Polizzi Summary previous lectures Implementations BST 5 5 7 null 8 null null 7 null
More Binary Search Trees AVL Trees. CS300 Data Structures (Fall 2013)
 More Binary Search Trees AVL Trees bstdelete if (key not found) return else if (either subtree is empty) { delete the node replacing the parents link with the ptr to the nonempty subtree or NULL if both
More Binary Search Trees AVL Trees bstdelete if (key not found) return else if (either subtree is empty) { delete the node replacing the parents link with the ptr to the nonempty subtree or NULL if both
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS
 LECTURE 13 Babeş - Bolyai University Computer Science and Mathematics Faculty 2017-2018 In Lecture 12... Binary Search Trees Binary Tree Traversals Huffman coding Binary Search Tree Today Binary Search
LECTURE 13 Babeş - Bolyai University Computer Science and Mathematics Faculty 2017-2018 In Lecture 12... Binary Search Trees Binary Tree Traversals Huffman coding Binary Search Tree Today Binary Search
COMP171. AVL-Trees (Part 1)
 COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
CS Transform-and-Conquer
 CS483-11 Transform-and-Conquer Instructor: Fei Li Room 443 ST II Office hours: Tue. & Thur. 1:30pm - 2:30pm or by appointments lifei@cs.gmu.edu with subject: CS483 http://www.cs.gmu.edu/ lifei/teaching/cs483_fall07/
CS483-11 Transform-and-Conquer Instructor: Fei Li Room 443 ST II Office hours: Tue. & Thur. 1:30pm - 2:30pm or by appointments lifei@cs.gmu.edu with subject: CS483 http://www.cs.gmu.edu/ lifei/teaching/cs483_fall07/
Prelim 2 Solution. CS 2110, April 26, 2016, 7:30 PM
 Prelim Solution CS 110, April 6, 016, 7:0 PM 1 5 Total Question True/False Complexity Heaps Trees Graphs Max 10 0 0 0 0 100 Score Grader The exam is closed book and closed notes. Do not begin until instructed.
Prelim Solution CS 110, April 6, 016, 7:0 PM 1 5 Total Question True/False Complexity Heaps Trees Graphs Max 10 0 0 0 0 100 Score Grader The exam is closed book and closed notes. Do not begin until instructed.
CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning. Sourangshu Bhattacharya
 CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Binary Search Tree - Best Time All BST operations are O(d), where d is tree depth minimum d is d = ëlog for a binary tree
CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Binary Search Tree - Best Time All BST operations are O(d), where d is tree depth minimum d is d = ëlog for a binary tree
More BSTs & AVL Trees bstdelete
 More BSTs & AVL Trees bstdelete if (key not found) return else if (either subtree is empty) { delete the node replacing the parents link with the ptr to the nonempty subtree or NULL if both subtrees are
More BSTs & AVL Trees bstdelete if (key not found) return else if (either subtree is empty) { delete the node replacing the parents link with the ptr to the nonempty subtree or NULL if both subtrees are
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Total
 Name: SSN: Computer Science Foundation Exam May 5, 006 Computer Science Section 1A Q1 Q Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Total KNW KNW KNW ANL,DSN KNW DSN You have to do all the 6 problems in this section of the exam. Partial
Name: SSN: Computer Science Foundation Exam May 5, 006 Computer Science Section 1A Q1 Q Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Total KNW KNW KNW ANL,DSN KNW DSN You have to do all the 6 problems in this section of the exam. Partial
Part 2: Balanced Trees
 Part 2: Balanced Trees 1 AVL Trees We could dene a perfectly balanced binary search tree with N nodes to be a complete binary search tree, one in which every level except the last is completely full. A
Part 2: Balanced Trees 1 AVL Trees We could dene a perfectly balanced binary search tree with N nodes to be a complete binary search tree, one in which every level except the last is completely full. A
CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning. Sourangshu Bhattacharya
 CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Balanced search trees Balanced search tree: A search-tree data structure for which a height of O(lg n) is guaranteed when
CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Balanced search trees Balanced search tree: A search-tree data structure for which a height of O(lg n) is guaranteed when
Splay Trees. (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 27
 Splay Trees (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 27 Basic Idea Invented by Sleator and Tarjan (1985) Blind rebalancing no height info kept! Worst-case time per operation is O(n)
Splay Trees (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 27 Basic Idea Invented by Sleator and Tarjan (1985) Blind rebalancing no height info kept! Worst-case time per operation is O(n)
An AVL tree with N nodes is an excellent data. The Big-Oh analysis shows that most operations finish within O(log N) time
 B + -TREES MOTIVATION An AVL tree with N nodes is an excellent data structure for searching, indexing, etc. The Big-Oh analysis shows that most operations finish within O(log N) time The theoretical conclusion
B + -TREES MOTIVATION An AVL tree with N nodes is an excellent data structure for searching, indexing, etc. The Big-Oh analysis shows that most operations finish within O(log N) time The theoretical conclusion
Data Structures in Java
 Data Structures in Java Lecture 10: AVL Trees. 10/1/015 Daniel Bauer Balanced BSTs Balance condition: Guarantee that the BST is always close to a complete binary tree (every node has exactly two or zero
Data Structures in Java Lecture 10: AVL Trees. 10/1/015 Daniel Bauer Balanced BSTs Balance condition: Guarantee that the BST is always close to a complete binary tree (every node has exactly two or zero
Instructions. Definitions. Name: CMSC 341 Fall Question Points I. /12 II. /30 III. /10 IV. /12 V. /12 VI. /12 VII.
 CMSC 341 Fall 2013 Data Structures Final Exam B Name: Question Points I. /12 II. /30 III. /10 IV. /12 V. /12 VI. /12 VII. /12 TOTAL: /100 Instructions 1. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. 2. You
CMSC 341 Fall 2013 Data Structures Final Exam B Name: Question Points I. /12 II. /30 III. /10 IV. /12 V. /12 VI. /12 VII. /12 TOTAL: /100 Instructions 1. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. 2. You
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall Topic Notes: Binary Search Trees
 Computer Science 10 Data Structures Siena College Fall 018 Topic Notes: Binary Search Trees Possibly the most common usage of a binary tree is to store data for quick retrieval. Definition: A binary tree
Computer Science 10 Data Structures Siena College Fall 018 Topic Notes: Binary Search Trees Possibly the most common usage of a binary tree is to store data for quick retrieval. Definition: A binary tree
CSC 421: Algorithm Design Analysis. Spring 2013
 CSC 421: Algorithm Design Analysis Spring 2013 Transform & conquer transform-and-conquer approach presorting balanced search trees, heaps Horner's Rule problem reduction 1 Transform & conquer the idea
CSC 421: Algorithm Design Analysis Spring 2013 Transform & conquer transform-and-conquer approach presorting balanced search trees, heaps Horner's Rule problem reduction 1 Transform & conquer the idea
CS 112 Introduction to Computing II. Wayne Snyder Computer Science Department Boston University
 CS 112 Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today: Efficiency of binary trees; Balanced Trees 2-3 Trees Next Time: 2-3 Trees continued B-Trees and External Search Efficiency
CS 112 Introduction to Computing II Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Today: Efficiency of binary trees; Balanced Trees 2-3 Trees Next Time: 2-3 Trees continued B-Trees and External Search Efficiency
Hash Tables. CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides. Wednesday, April 22, Glenn G. Chappell
 Hash Tables CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Wednesday, April 22, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005
Hash Tables CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Wednesday, April 22, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005
Consider the search operation FindKey (): find an element of a particular key value in a binary tree. This operation takes O(n) time in a binary
 1 Consider the search operation FindKey (): find an element of a particular key value in a binary tree. This operation takes O(n) time in a binary tree. In a binary tree of 10 6 nodes 10 6 steps required
1 Consider the search operation FindKey (): find an element of a particular key value in a binary tree. This operation takes O(n) time in a binary tree. In a binary tree of 10 6 nodes 10 6 steps required
Advanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises
 dvanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will focus
dvanced Java Concepts Unit 5: Trees. Notes and Exercises Tree is a data structure like the figure shown below. We don t usually care about unordered trees but that s where we ll start. Later we will focus
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Searching Red-Black and Other Dynamically BalancedTrees PLSD210 Searching - Re-visited Binary tree O(log n) if it stays balanced Simple binary tree good for static collections
Data Structures and Algorithms Searching Red-Black and Other Dynamically BalancedTrees PLSD210 Searching - Re-visited Binary tree O(log n) if it stays balanced Simple binary tree good for static collections
Balanced Binary Search Trees
 Balanced Binary Search Trees Why is our balance assumption so important? Lets look at what happens if we insert the following numbers in order without rebalancing the tree: 3 5 9 12 18 20 1-45 2010 Pearson
Balanced Binary Search Trees Why is our balance assumption so important? Lets look at what happens if we insert the following numbers in order without rebalancing the tree: 3 5 9 12 18 20 1-45 2010 Pearson
Prelim 2. CS 2110, November 20, 2014, 7:30 PM Extra Total Question True/False Short Answer
 Prelim 2 CS 2110, November 20, 2014, 7:30 PM 1 2 3 4 5 Extra Total Question True/False Short Answer Complexity Induction Trees Graphs Extra Credit Max 20 10 15 25 30 5 100 Score Grader The exam is closed
Prelim 2 CS 2110, November 20, 2014, 7:30 PM 1 2 3 4 5 Extra Total Question True/False Short Answer Complexity Induction Trees Graphs Extra Credit Max 20 10 15 25 30 5 100 Score Grader The exam is closed
CMPE 160: Introduction to Object Oriented Programming
 CMPE 6: Introduction to Object Oriented Programming General Tree Concepts Binary Trees Trees Definitions Representation Binary trees Traversals Expression trees These are the slides of the textbook by
CMPE 6: Introduction to Object Oriented Programming General Tree Concepts Binary Trees Trees Definitions Representation Binary trees Traversals Expression trees These are the slides of the textbook by
Operations on Heap Tree The major operations required to be performed on a heap tree are Insertion, Deletion, and Merging.
 Priority Queue, Heap and Heap Sort In this time, we will study Priority queue, heap and heap sort. Heap is a data structure, which permits one to insert elements into a set and also to find the largest
Priority Queue, Heap and Heap Sort In this time, we will study Priority queue, heap and heap sort. Heap is a data structure, which permits one to insert elements into a set and also to find the largest
COSC 2007 Data Structures II Final Exam. Part 1: multiple choice (1 mark each, total 30 marks, circle the correct answer)
 COSC 2007 Data Structures II Final Exam Thursday, April 13 th, 2006 This is a closed book and closed notes exam. There are total 3 parts. Please answer the questions in the provided space and use back
COSC 2007 Data Structures II Final Exam Thursday, April 13 th, 2006 This is a closed book and closed notes exam. There are total 3 parts. Please answer the questions in the provided space and use back
Section 05: Solutions
 Section 05: Solutions 1. Asymptotic Analysis (a) Applying definitions For each of the following, choose a c and n 0 which show f(n) O(g(n)). Explain why your values of c and n 0 work. (i) f(n) = 5000n
Section 05: Solutions 1. Asymptotic Analysis (a) Applying definitions For each of the following, choose a c and n 0 which show f(n) O(g(n)). Explain why your values of c and n 0 work. (i) f(n) = 5000n
CS251-SE1. Midterm 2. Tuesday 11/1 8:00pm 9:00pm. There are 16 multiple-choice questions and 6 essay questions.
 CS251-SE1 Midterm 2 Tuesday 11/1 8:00pm 9:00pm There are 16 multiple-choice questions and 6 essay questions. Answer the multiple choice questions on your bubble sheet. Answer the essay questions in the
CS251-SE1 Midterm 2 Tuesday 11/1 8:00pm 9:00pm There are 16 multiple-choice questions and 6 essay questions. Answer the multiple choice questions on your bubble sheet. Answer the essay questions in the
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees
 Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
CSE 332 Autumn 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators)
 Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Autumn 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Autumn 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
CS102 Binary Search Trees
 CS102 Binary Search Trees Prof Tejada 1 To speed up insertion, removal and search, modify the idea of a Binary Tree to create a Binary Search Tree (BST) Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees have one
CS102 Binary Search Trees Prof Tejada 1 To speed up insertion, removal and search, modify the idea of a Binary Tree to create a Binary Search Tree (BST) Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees have one
Prelim 2 Solution. CS 2110, April 26, 2016, 5:30 PM
 Prelim Solution CS 110, April 6, 016, 5:0 PM 1 5 Total Question True/False Complexity Heaps Trees Graphs Max 10 0 0 0 0 100 Score Grader The exam is closed book and closed notes. Do not begin until instructed.
Prelim Solution CS 110, April 6, 016, 5:0 PM 1 5 Total Question True/False Complexity Heaps Trees Graphs Max 10 0 0 0 0 100 Score Grader The exam is closed book and closed notes. Do not begin until instructed.
Trees. Reading: Weiss, Chapter 4. Cpt S 223, Fall 2007 Copyright: Washington State University
 Trees Reading: Weiss, Chapter 4 1 Generic Rooted Trees 2 Terms Node, Edge Internal node Root Leaf Child Sibling Descendant Ancestor 3 Tree Representations n-ary trees Each internal node can have at most
Trees Reading: Weiss, Chapter 4 1 Generic Rooted Trees 2 Terms Node, Edge Internal node Root Leaf Child Sibling Descendant Ancestor 3 Tree Representations n-ary trees Each internal node can have at most
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 21, 2018 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement 1.3: Balanced Binary Search Trees Balanced Binary Search Trees Outline
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 21, 2018 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement 1.3: Balanced Binary Search Trees Balanced Binary Search Trees Outline
CSE 502 Class 16. Jeremy Buhler Steve Cole. March A while back, we introduced the idea of collections to put hash tables in context.
 CSE 502 Class 16 Jeremy Buhler Steve Cole March 17 2015 Onwards to trees! 1 Collection Types Revisited A while back, we introduced the idea of collections to put hash tables in context. abstract data types
CSE 502 Class 16 Jeremy Buhler Steve Cole March 17 2015 Onwards to trees! 1 Collection Types Revisited A while back, we introduced the idea of collections to put hash tables in context. abstract data types
Balanced Binary Search Trees
 Balanced Binary Search Trees Pedro Ribeiro DCC/FCUP 2017/2018 Pedro Ribeiro (DCC/FCUP) Balanced Binary Search Trees 2017/2018 1 / 48 Motivation Let S be a set of comparable objects/items: Let a and b be
Balanced Binary Search Trees Pedro Ribeiro DCC/FCUP 2017/2018 Pedro Ribeiro (DCC/FCUP) Balanced Binary Search Trees 2017/2018 1 / 48 Motivation Let S be a set of comparable objects/items: Let a and b be
AVL Trees. See Section 19.4of the text, p
 AVL Trees See Section 19.4of the text, p. 706-714. AVL trees are self-balancing Binary Search Trees. When you either insert or remove a node the tree adjusts its structure so that the remains a logarithm
AVL Trees See Section 19.4of the text, p. 706-714. AVL trees are self-balancing Binary Search Trees. When you either insert or remove a node the tree adjusts its structure so that the remains a logarithm
Section 05: Solutions
 Section 05: Solutions 1. Memory and B-Tree (a) Based on your understanding of how computers access and store memory, why might it be faster to access all the elements of an array-based queue than to access
Section 05: Solutions 1. Memory and B-Tree (a) Based on your understanding of how computers access and store memory, why might it be faster to access all the elements of an array-based queue than to access
Solution to CSE 250 Final Exam
 Solution to CSE 250 Final Exam Fall 2013 Time: 3 hours. December 13, 2013 Total points: 100 14 pages Please use the space provided for each question, and the back of the page if you need to. Please do
Solution to CSE 250 Final Exam Fall 2013 Time: 3 hours. December 13, 2013 Total points: 100 14 pages Please use the space provided for each question, and the back of the page if you need to. Please do
1.00/1.001 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving. Final Exam
 1.00/1.001 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving Final Exam Name: Email Address: TA: Section: You have three hours to complete this exam. For coding questions, you do not need to include
1.00/1.001 Introduction to Computers and Engineering Problem Solving Final Exam Name: Email Address: TA: Section: You have three hours to complete this exam. For coding questions, you do not need to include
Final Examination CSE 100 UCSD (Practice)
 Final Examination UCSD (Practice) RULES: 1. Don t start the exam until the instructor says to. 2. This is a closed-book, closed-notes, no-calculator exam. Don t refer to any materials other than the exam
Final Examination UCSD (Practice) RULES: 1. Don t start the exam until the instructor says to. 2. This is a closed-book, closed-notes, no-calculator exam. Don t refer to any materials other than the exam
CSE100 Practice Final Exam Section C Fall 2015: Dec 10 th, Problem Topic Points Possible Points Earned Grader
 CSE100 Practice Final Exam Section C Fall 2015: Dec 10 th, 2015 Problem Topic Points Possible Points Earned Grader 1 The Basics 40 2 Application and Comparison 20 3 Run Time Analysis 20 4 C++ and Programming
CSE100 Practice Final Exam Section C Fall 2015: Dec 10 th, 2015 Problem Topic Points Possible Points Earned Grader 1 The Basics 40 2 Application and Comparison 20 3 Run Time Analysis 20 4 C++ and Programming
SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES. Chapter 11
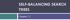 SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES Chapter 11 Tree Balance and Rotation Section 11.1 Algorithm for Rotation BTNode root = left right = data = 10 BTNode = left right = data = 20 BTNode NULL = left right = NULL
SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES Chapter 11 Tree Balance and Rotation Section 11.1 Algorithm for Rotation BTNode root = left right = data = 10 BTNode = left right = data = 20 BTNode NULL = left right = NULL
CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees
 CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees Irwin King king@cse.cuhk.edu.hk http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~king Department of Computer Science & Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong Introduction General Tree
CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees Irwin King king@cse.cuhk.edu.hk http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~king Department of Computer Science & Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong Introduction General Tree
CSE 332 Spring 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators)
 Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Spring 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Spring 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Multi-way Search Trees. (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 25
 Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
Laboratory Module X B TREES
 Purpose: Purpose 1... Purpose 2 Purpose 3. Laboratory Module X B TREES 1. Preparation Before Lab When working with large sets of data, it is often not possible or desirable to maintain the entire structure
Purpose: Purpose 1... Purpose 2 Purpose 3. Laboratory Module X B TREES 1. Preparation Before Lab When working with large sets of data, it is often not possible or desirable to maintain the entire structure
Week 2. CS 400 Programming III. Read: Module 2 readings before lecture
 Week 2 Waitlisted Students: please come to front of class and sign by your name on waitlist. TopHat Join Code for my lecture: Announcements and Course Policies: https://pages.cs.wisc.edu/~deppeler/cs400/
Week 2 Waitlisted Students: please come to front of class and sign by your name on waitlist. TopHat Join Code for my lecture: Announcements and Course Policies: https://pages.cs.wisc.edu/~deppeler/cs400/
