Collections and Combinatorial Search
|
|
|
- Rodney Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Streams
2 Collections and Combinatorial Search We ve seen a number of immutable collections that provide powerful operations, in particular for combinatorial search. For instance, to find the second prime number between 1000 and 10000: ((1000 to 10000) filter isprime)(1) This is much shorter than the recursive alternative: def secondprime(from: Int, to: Int) = nthprime(from, to, 2) def nthprime(from: Int, to: Int, n: Int): Int = if (from >= to) throw new Error( no prime ) else if (isprime(from)) if (n == 1) from else nthprime(from + 1, to, n - 1) else nthprime(from + 1, to, n)
3 Performance Problem But from a standpoint of performance, ((1000 to 10000) filter isprime)(1) is pretty bad; it constructs all prime numbers between 1000 and in a list, but only ever looks at the first two elements of that list. Reducing the upper bound would speed things up, but risks that we miss the second prime number all together.
4 Delayed Evaluation However, we can make the short-code efficient by using a trick: Avoid computing the tail of a sequence until it is needed for the evaluation result (which might be never) This idea is implemented in a new class, the Stream. Streams are similar to lists, but their tail is evaluated only on demand.
5 Defining Streams Streams are defined from a constant Stream.empty and a constructor Stream.cons. For instance, val xs = Stream.cons(1, Stream.cons(2, Stream.empty)) They can also be defined like the other collections by using the object Stream as a factory. Stream(1, 2, 3) The tostream method on a collection will turn the collection into a stream: (1 to 1000).toStream > res0: Stream[Int] = Stream(1,?)
6 Stream Ranges Let s try to write a function that returns (lo until hi).tostream directly: def streamrange(lo: Int, hi: Int): Stream[Int] = if (lo >= hi) Stream.empty else Stream.cons(lo, streamrange(lo + 1, hi)) Compare to the same function that produces a list: def listrange(lo: Int, hi: Int): List[Int] = if (lo >= hi) Nil else lo :: listrange(lo + 1, hi)
7 Comparing the Two Range Functions The functions have almost identical structure yet they evaluate quite differently. listrange(start, end) will produce a list with end - start elements and return it. streamrange(start, end) returns a single object of type Stream with start as head element. The other elements are only computed when they are needed, where needed means that someone calls tail on the stream.
8 Methods on Streams Stream supports almost all methods of List. For instance, to find the second prime number between 1000 and 10000: ((1000 to 10000).toStream filter isprime)(1)
9 Stream Cons Operator The one major exception is ::. x :: xs always produces a list, never a stream. There is however an alternative operator #:: which produces a stream. x #:: xs == Stream.cons(x, xs) #:: can be used in expressions as well as patterns.
10 Implementation of Streams The implementation of streams is quite close to the one of lists. Here s the trait Stream: trait Stream[+A] extends Seq[A] { def isempty: Boolean def head: A def tail: Stream[A]... } As for lists, all other methods can be defined in terms of these three.
11 Implementation of Streams(2) Concrete implementations of streams are defined in the Stream companion object. Here s a first draft: object Stream { def cons[t](hd: T, tl: => Stream[T]) = new Stream[T] { def isempty = false def head = hd def tail = tl } val empty = new Stream[Nothing] { def isempty = true def head = throw new NoSuchElementException( empty.head ) def tail = throw new NoSuchElementException( empty.tail ) } }
12 Difference to List The only important difference between the implementations of List and Stream concern tl, the second parameter of Stream.cons. For streams, this is a by-name parameter. That s why the second argument to Stream.cons is not evaluated at the point of call. Instead, it will be evaluated each time someone calls tail on a Stream object.
13 Other Stream Methods The other stream methods are implemented analogously to their list counterparts. For instance, here s filter: class Stream[+T] {... def filter(p: T => Boolean): Stream[T] = if (isempty) this else if (p(head)) cons(head, tail.filter(p)) else tail.filter(p) }
14 Exercise Consider this modification of streamrange. def streamrange(lo: Int, hi: Int): Stream[Int] = { print(lo+ ) if (lo >= hi) Stream.empty else Stream.cons(lo, streamrange(lo + 1, hi)) } When you write streamrange(1, 10).take(3).toList what gets printed? O Nothing O 1 O O O
15 Exercise Consider this modification of streamrange. def streamrange(lo: Int, hi: Int): Stream[Int] = { print(lo+ ) if (lo >= hi) Stream.empty else Stream.cons(lo, streamrange(lo + 1, hi)) } When you write streamrange(1, 10).take(3).toList what gets printed? O Nothing O 1 O O O
Lazy Evaluation in Scala
 Lazy Evaluation Lazy Evaluation The proposed implementation suffers from a serious potential performance problem: If tail is called several times, the corresponding stream will be recomputed each time.
Lazy Evaluation Lazy Evaluation The proposed implementation suffers from a serious potential performance problem: If tail is called several times, the corresponding stream will be recomputed each time.
Programming Principles
 Programming Principles Final Exam Wednesday, December 18th 2013 First Name: Last Name: Your points are precious, don t let them go to waste! Your Name Work that can t be attributed to you is lost: write
Programming Principles Final Exam Wednesday, December 18th 2013 First Name: Last Name: Your points are precious, don t let them go to waste! Your Name Work that can t be attributed to you is lost: write
Exercise 1: Graph coloring (10 points)
 Exercise 1: Graph coloring (10 points) Graph coloring is the problem of assigning colors to vertices in a non-directed graph, so that no two adjacent nodes have the same color. In other words, if two vertices
Exercise 1: Graph coloring (10 points) Graph coloring is the problem of assigning colors to vertices in a non-directed graph, so that no two adjacent nodes have the same color. In other words, if two vertices
Comp 311 Functional Programming. Eric Allen, Two Sigma Investments Robert Corky Cartwright, Rice University Sağnak Taşırlar, Two Sigma Investments
 Comp 311 Functional Programming Eric Allen, Two Sigma Investments Robert Corky Cartwright, Rice University Sağnak Taşırlar, Two Sigma Investments Streams Streams a form of lazy sequence inspired by signal-processing
Comp 311 Functional Programming Eric Allen, Two Sigma Investments Robert Corky Cartwright, Rice University Sağnak Taşırlar, Two Sigma Investments Streams Streams a form of lazy sequence inspired by signal-processing
11 Parameterized Classes
 Object-Oriented Design Lecture 11 CS 3500 Fall 2010 (Pucella) Friday, Oct 22, 2010 11 Parameterized Classes Last time, we advocated subtyping from multiple types as a way to get more reuse out of client
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 11 CS 3500 Fall 2010 (Pucella) Friday, Oct 22, 2010 11 Parameterized Classes Last time, we advocated subtyping from multiple types as a way to get more reuse out of client
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Functional Programming with Lists
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with Lists CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 Lists in OCaml The basic data structure in OCaml Lists can be of arbitrary length Implemented as
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with Lists CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 Lists in OCaml The basic data structure in OCaml Lists can be of arbitrary length Implemented as
CompSci 220. Programming Methodology 12: Functional Data Structures
 CompSci 220 Programming Methodology 12: Functional Data Structures A Polymorphic Higher- Order Function def findfirst[a](as: Array[A], p: A => Boolean): Int = { def loop(n: Int): Int = if (n >= as.length)
CompSci 220 Programming Methodology 12: Functional Data Structures A Polymorphic Higher- Order Function def findfirst[a](as: Array[A], p: A => Boolean): Int = { def loop(n: Int): Int = if (n >= as.length)
Recap from last time. Programming Languages. CSE 130 : Fall Lecture 3: Data Types. Put it together: a filter function
 CSE 130 : Fall 2011 Recap from last time Programming Languages Lecture 3: Data Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 2 A shorthand for function binding Put it together: a filter function # let neg = fun f
CSE 130 : Fall 2011 Recap from last time Programming Languages Lecture 3: Data Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 2 A shorthand for function binding Put it together: a filter function # let neg = fun f
ITERATORS AND STREAMS 9
 ITERATORS AND STREAMS 9 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A November 12, 2015 1 Iterators An iterator is an object that tracks the position in a sequence of values. It can return an element at a time, and it is only
ITERATORS AND STREAMS 9 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A November 12, 2015 1 Iterators An iterator is an object that tracks the position in a sequence of values. It can return an element at a time, and it is only
List are immutable Lists have recursive structure Lists are homogeneous
 WORKING WITH LISTS val fruit = List("apples", "oranges", "pears") val nums: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3, 4) val diag3 = List( List(1, 0, 0), List(0, 1, 0), List(0, 0, 1) ) val empty = List() List are immutable
WORKING WITH LISTS val fruit = List("apples", "oranges", "pears") val nums: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3, 4) val diag3 = List( List(1, 0, 0), List(0, 1, 0), List(0, 0, 1) ) val empty = List() List are immutable
Lecture 2. 1 Immutability. 2 Case Classes
 Lecture 2 1 Immutability Consider the function incrlist in fig. 3.1, which increments all numbers in a list. We want to emphasize that incrlist produces a new list and leaves the original list unchanged.
Lecture 2 1 Immutability Consider the function incrlist in fig. 3.1, which increments all numbers in a list. We want to emphasize that incrlist produces a new list and leaves the original list unchanged.
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 13 CSU 370 Fall 2008 (Pucella) Friday, Oct 31, 2008
 Object-Oriented Design Lecture 13 CSU 370 Fall 2008 (Pucella) Friday, Oct 31, 2008 Laziness For this lecture, I want to return to something that came up during the last homework, the third homework where
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 13 CSU 370 Fall 2008 (Pucella) Friday, Oct 31, 2008 Laziness For this lecture, I want to return to something that came up during the last homework, the third homework where
Outline. Collections Arrays vs. Lists Functions using Arrays/Lists Higher order functions using Arrays/Lists
 Arrays and Lists Outline Collections Arrays vs. Lists Functions using Arrays/Lists Higher order functions using Arrays/Lists Collections We've seen tuples to store multiple objects together, but the tuple
Arrays and Lists Outline Collections Arrays vs. Lists Functions using Arrays/Lists Higher order functions using Arrays/Lists Collections We've seen tuples to store multiple objects together, but the tuple
Linked lists and the List class
 Linked lists and the List class Cheong 1 Linked lists So far, the only container object we used was the array. An array is a single object that contains references to other objects, possibly many of them.
Linked lists and the List class Cheong 1 Linked lists So far, the only container object we used was the array. An array is a single object that contains references to other objects, possibly many of them.
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Functional Programming with Lists
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with Lists 1 Lists in OCaml The basic data structure in OCaml Lists can be of arbitrary length Implemented as a linked data structure
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with Lists 1 Lists in OCaml The basic data structure in OCaml Lists can be of arbitrary length Implemented as a linked data structure
CS 151. Linked Lists, Recursively Implemented. Wednesday, October 3, 12
 CS 151 Linked Lists, Recursively Implemented 1 2 Linked Lists, Revisited Recall that a linked list is a structure that represents a sequence of elements that are stored non-contiguously in memory. We can
CS 151 Linked Lists, Recursively Implemented 1 2 Linked Lists, Revisited Recall that a linked list is a structure that represents a sequence of elements that are stored non-contiguously in memory. We can
Datatype declarations
 Datatype declarations datatype suit = HEARTS DIAMONDS CLUBS SPADES datatype a list = nil (* copy me NOT! *) op :: of a * a list datatype a heap = EHEAP HEAP of a * a heap * a heap type suit val HEARTS
Datatype declarations datatype suit = HEARTS DIAMONDS CLUBS SPADES datatype a list = nil (* copy me NOT! *) op :: of a * a list datatype a heap = EHEAP HEAP of a * a heap * a heap type suit val HEARTS
CS558 Programming Languages
 CS558 Programming Languages Fall 2016 Lecture 6a Andrew Tolmach Portland State University 1994-2016 Functional Programming An alternative paradigm to imperative programming First-class functions Emphasis
CS558 Programming Languages Fall 2016 Lecture 6a Andrew Tolmach Portland State University 1994-2016 Functional Programming An alternative paradigm to imperative programming First-class functions Emphasis
CSE 341, Autumn 2005, Assignment 3 ML - MiniML Interpreter
 Due: Thurs October 27, 10:00pm CSE 341, Autumn 2005, Assignment 3 ML - MiniML Interpreter Note: This is a much longer assignment than anything we ve seen up until now. You are given two weeks to complete
Due: Thurs October 27, 10:00pm CSE 341, Autumn 2005, Assignment 3 ML - MiniML Interpreter Note: This is a much longer assignment than anything we ve seen up until now. You are given two weeks to complete
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120)
 Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 3 September 5, 2018 Value-Oriented Programming (continued) Lists and Recursion CIS 120 Announcements Homework 1: OCaml Finger Exercises Due: Tuesday
Programming Languages and Techniques (CIS120) Lecture 3 September 5, 2018 Value-Oriented Programming (continued) Lists and Recursion CIS 120 Announcements Homework 1: OCaml Finger Exercises Due: Tuesday
OCaml. ML Flow. Complex types: Lists. Complex types: Lists. The PL for the discerning hacker. All elements must have same type.
 OCaml The PL for the discerning hacker. ML Flow Expressions (Syntax) Compile-time Static 1. Enter expression 2. ML infers a type Exec-time Dynamic Types 3. ML crunches expression down to a value 4. Value
OCaml The PL for the discerning hacker. ML Flow Expressions (Syntax) Compile-time Static 1. Enter expression 2. ML infers a type Exec-time Dynamic Types 3. ML crunches expression down to a value 4. Value
CS205: Scalable Software Systems
 CS205: Scalable Software Systems Lecture 3 September 5, 2016 Lecture 3 CS205: Scalable Software Systems September 5, 2016 1 / 19 Table of contents 1 Quick Recap 2 Type of recursive solutions 3 Translating
CS205: Scalable Software Systems Lecture 3 September 5, 2016 Lecture 3 CS205: Scalable Software Systems September 5, 2016 1 / 19 Table of contents 1 Quick Recap 2 Type of recursive solutions 3 Translating
Sometimes it s good to be lazy
 Chapter 8 Sometimes it s good to be lazy Typically, languages such as OCaml (SML, Lisp or Scheme) evaluate expressions by a call-by-value discipline. All variables in OCaml are bound by value, which means
Chapter 8 Sometimes it s good to be lazy Typically, languages such as OCaml (SML, Lisp or Scheme) evaluate expressions by a call-by-value discipline. All variables in OCaml are bound by value, which means
Homework 3 COSE212, Fall 2018
 Homework 3 COSE212, Fall 2018 Hakjoo Oh Due: 10/28, 24:00 Problem 1 (100pts) Let us design and implement a programming language called ML. ML is a small yet Turing-complete functional language that supports
Homework 3 COSE212, Fall 2018 Hakjoo Oh Due: 10/28, 24:00 Problem 1 (100pts) Let us design and implement a programming language called ML. ML is a small yet Turing-complete functional language that supports
// Body of shortestlists starts here y flatmap { case Nil => Nil case x :: xs => findshortest(list(x), xs)
 8 Shortest-strings Problem: Partial-Solution Dump Drew McDermott drew.mcdermott@yale.edu Lecture notes for 2016-09-19, revised 20016-09-25 Here is the state of play in solving the little puzzle about finding
8 Shortest-strings Problem: Partial-Solution Dump Drew McDermott drew.mcdermott@yale.edu Lecture notes for 2016-09-19, revised 20016-09-25 Here is the state of play in solving the little puzzle about finding
The fringe of a binary tree are the values in left-to-right order. For example, the fringe of the following tree:
 Lecture 13 The Same Fringe Problem Given a binary tree: sealed trait BinTree [+A] case class Node [A]( lhs : BinTree [A], rhs : BinTree [A]) extends BinTree [A] case class Leaf [A]( x: A) extends BinTree
Lecture 13 The Same Fringe Problem Given a binary tree: sealed trait BinTree [+A] case class Node [A]( lhs : BinTree [A], rhs : BinTree [A]) extends BinTree [A] case class Leaf [A]( x: A) extends BinTree
A Second Look At ML. Chapter Seven Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1
 A Second Look At ML Chapter Seven Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1 Outline Patterns Local variable definitions A sorting example Chapter Seven Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 2 Two Patterns
A Second Look At ML Chapter Seven Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1 Outline Patterns Local variable definitions A sorting example Chapter Seven Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 2 Two Patterns
Implementing a List in Java. CSE 143 Java. Just an Illusion? List Interface (review) Using an Array to Implement a List.
 Implementing a List in Java CSE 143 Java List Implementation Using Arrays Reading: Ch. 13 Two implementation approaches are most commonly used for simple lists: Arrays Linked list Java Interface List concrete
Implementing a List in Java CSE 143 Java List Implementation Using Arrays Reading: Ch. 13 Two implementation approaches are most commonly used for simple lists: Arrays Linked list Java Interface List concrete
Lecture 5: Implementing Lists, Version 1
 CS18 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Fisler, Nelson Lecture 5: Implementing Lists, Version 1 Contents 1 Implementing Lists 1 2 Methods 2 2.1 isempty...........................................
CS18 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Fisler, Nelson Lecture 5: Implementing Lists, Version 1 Contents 1 Implementing Lists 1 2 Methods 2 2.1 isempty...........................................
Class 2 Recursion on Lists
 Class 2 Recursion on Lists The list data type Recursive methods on lists 2014-15 MSc Workshop S.Kamin, U.S.Reddy 1B - Lists - 1 Data structures Contain large amounts of data Allow for access to that data
Class 2 Recursion on Lists The list data type Recursive methods on lists 2014-15 MSc Workshop S.Kamin, U.S.Reddy 1B - Lists - 1 Data structures Contain large amounts of data Allow for access to that data
G Programming Languages - Fall 2012
 G22.2110-003 Programming Languages - Fall 2012 Week 13 - Part 1 Thomas Wies New York University Review Last lecture Object Oriented Programming Outline Today: Scala Sources: Programming in Scala, Second
G22.2110-003 Programming Languages - Fall 2012 Week 13 - Part 1 Thomas Wies New York University Review Last lecture Object Oriented Programming Outline Today: Scala Sources: Programming in Scala, Second
Arne Brüsch Philipp Wille. Pattern Matching Syntax
 Scala Enthusiasts BS Arne Brüsch Philipp Wille Pattern Matching Syntax Scala Modular programming language Some used to call it objectfunctional 2 Scala Modular programming language Some used to call it
Scala Enthusiasts BS Arne Brüsch Philipp Wille Pattern Matching Syntax Scala Modular programming language Some used to call it objectfunctional 2 Scala Modular programming language Some used to call it
Functional Programming
 Functional Programming Final Exam Friday, December 18 2015 First Name: Last Name: Your points are precious, don t let them go to waste! Your Name Work that can t be attributed to you is lost: write your
Functional Programming Final Exam Friday, December 18 2015 First Name: Last Name: Your points are precious, don t let them go to waste! Your Name Work that can t be attributed to you is lost: write your
Scala Style Guide Spring 2018
 CS18 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Fisler, Nelson Scala Style Guide Spring 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Naming 1 3 Formatting 2 4 Class Declarations 3 5 Functional Paradigms 4 6 Comments
CS18 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Fisler, Nelson Scala Style Guide Spring 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Naming 1 3 Formatting 2 4 Class Declarations 3 5 Functional Paradigms 4 6 Comments
News. Programming Languages. Recap. Recap: Environments. Functions. of functions: Closures. CSE 130 : Fall Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes
 CSE 130 : Fall 2007 Programming Languages News PA deadlines shifted PA #2 now due 10/24 (next Wed) Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables
CSE 130 : Fall 2007 Programming Languages News PA deadlines shifted PA #2 now due 10/24 (next Wed) Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables
News. Programming Languages. Complex types: Lists. Recap: ML s Holy Trinity. CSE 130: Spring 2012
 News CSE 130: Spring 2012 Programming Languages On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 4/13) Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Please post questions to Piazza Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today: A
News CSE 130: Spring 2012 Programming Languages On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 4/13) Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Please post questions to Piazza Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Today: A
Finally, all fields are public by default, so you can easily write simple functions, such as this one, without writing getters:
 Lecture 2 Case Classes Scala classes tend to be shorter than their Java counterparts. For example, fig. 3.1a shows a Point class in Java and fig. 3.1b shows the equivalent class in Scala, which is much
Lecture 2 Case Classes Scala classes tend to be shorter than their Java counterparts. For example, fig. 3.1a shows a Point class in Java and fig. 3.1b shows the equivalent class in Scala, which is much
High Wizardry in the Land of Scala. Daniel Spiewak
 High Wizardry in the Land of Scala Daniel Spiewak Agenda Higher-Kinds Typeclasses Type-Level Encodings Continuations Higher-Kinds What is a kind system? Higher-Kinds What is a kind system? What is a type
High Wizardry in the Land of Scala Daniel Spiewak Agenda Higher-Kinds Typeclasses Type-Level Encodings Continuations Higher-Kinds What is a kind system? Higher-Kinds What is a kind system? What is a type
Summer 2017 Discussion 10: July 25, Introduction. 2 Primitives and Define
 CS 6A Scheme Summer 207 Discussion 0: July 25, 207 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
CS 6A Scheme Summer 207 Discussion 0: July 25, 207 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Winter 2009 Programming Languages News PA 2 out, and due Mon 1/26 5pm Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes t UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables = names Values = phone number
CSE 130 : Winter 2009 Programming Languages News PA 2 out, and due Mon 1/26 5pm Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes t UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables = names Values = phone number
CS 2340 Objects and Design - Scala
 CS 2340 Objects and Design - Scala Objects and Operators Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu Chris Simpkins (Georgia Tech) CS 2340 Objects and Design - Scala Objects and Operators 1 / 13 Classes
CS 2340 Objects and Design - Scala Objects and Operators Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu Chris Simpkins (Georgia Tech) CS 2340 Objects and Design - Scala Objects and Operators 1 / 13 Classes
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course Ctd, Expressions and Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A shorthand for function binding # let neg = fun f -> fun x -> not (f x); # let
CSE 130 : Spring 2011 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course Ctd, Expressions and Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego A shorthand for function binding # let neg = fun f -> fun x -> not (f x); # let
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 11 CS 3500 Spring 2010 (Pucella) Tuesday, Feb 16, 2010
 Object-Oriented Design Lecture 11 CS 3500 Spring 2010 (Pucella) Tuesday, Feb 16, 2010 11 Polymorphism The functional iterator interface we have defined last lecture is nice, but it is not very general.
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 11 CS 3500 Spring 2010 (Pucella) Tuesday, Feb 16, 2010 11 Polymorphism The functional iterator interface we have defined last lecture is nice, but it is not very general.
Begin at the beginning
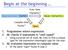 Begin at the beginning Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set of
Begin at the beginning Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set of
Functional Programming in Scheme
 Cristian Giumale / Lecture Notes 1 Functional Programming in Scheme Functional programming languages - or applicative languages - follow closely the Lambda calculus model. Their strengths and weaknesses
Cristian Giumale / Lecture Notes 1 Functional Programming in Scheme Functional programming languages - or applicative languages - follow closely the Lambda calculus model. Their strengths and weaknesses
Classical Themes of Computer Science
 Functional Programming (Part 1/2) Bernhard K. Aichernig Institute for Software Technology Graz University of Technology Austria Winter Term 2017/18 Version: November 22, 2017 1/49 Agenda I Functional Programming?
Functional Programming (Part 1/2) Bernhard K. Aichernig Institute for Software Technology Graz University of Technology Austria Winter Term 2017/18 Version: November 22, 2017 1/49 Agenda I Functional Programming?
COSE212: Programming Languages. Lecture 4 Recursive and Higher-Order Programming
 COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 4 Recursive and Higher-Order Programming Hakjoo Oh 2016 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2016 Fall, Lecture 4 September 27, 2016 1 / 21 Recursive and Higher-Order Programming
COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 4 Recursive and Higher-Order Programming Hakjoo Oh 2016 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2016 Fall, Lecture 4 September 27, 2016 1 / 21 Recursive and Higher-Order Programming
GADTs. Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano. Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences]
![GADTs. Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano. Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences] GADTs. Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano. Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences]](/thumbs/78/76904283.jpg) GADTs Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7 Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano 1 Today s lecture Generalized algebraic data types (GADTs) 2 A datatype data Tree a = Leaf Node (Tree a) a (Tree
GADTs Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7 Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano 1 Today s lecture Generalized algebraic data types (GADTs) 2 A datatype data Tree a = Leaf Node (Tree a) a (Tree
Logic - CM0845 Introduction to Haskell
 Logic - CM0845 Introduction to Haskell Diego Alejandro Montoya-Zapata EAFIT University Semester 2016-1 Diego Alejandro Montoya-Zapata (EAFIT University) Logic - CM0845 Introduction to Haskell Semester
Logic - CM0845 Introduction to Haskell Diego Alejandro Montoya-Zapata EAFIT University Semester 2016-1 Diego Alejandro Montoya-Zapata (EAFIT University) Logic - CM0845 Introduction to Haskell Semester
Implementing a List in Java. CSC 143 Java. List Interface (review) Just an Illusion? Using an Array to Implement a List CSC
 Implementing a List in Java CSC 143 Java List Implementation Using Arrays Updated with Java 5.0 Generics Reading: Ch. 13 Two implementation approaches are most commonly used for simple lists: Arrays Linked
Implementing a List in Java CSC 143 Java List Implementation Using Arrays Updated with Java 5.0 Generics Reading: Ch. 13 Two implementation approaches are most commonly used for simple lists: Arrays Linked
8 Hiding Implementation Details
 Object-Oriented Design Lecture 8 CS 3500 Spring 2011 (Pucella) Friday, Feb 4, 2011 8 Hiding Implementation Details Last time we saw the Interpreter Design Pattern as a rather mechanical way to get an implementation
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 8 CS 3500 Spring 2011 (Pucella) Friday, Feb 4, 2011 8 Hiding Implementation Details Last time we saw the Interpreter Design Pattern as a rather mechanical way to get an implementation
CS 457/557: Functional Languages
 CS 457/557: Functional Languages Lists and Algebraic Datatypes Mark P Jones Portland State University 1 Why Lists? Lists are a heavily used data structure in many functional programs Special syntax is
CS 457/557: Functional Languages Lists and Algebraic Datatypes Mark P Jones Portland State University 1 Why Lists? Lists are a heavily used data structure in many functional programs Special syntax is
GADTs. Alejandro Serrano. AFP Summer School. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences]
![GADTs. Alejandro Serrano. AFP Summer School. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences] GADTs. Alejandro Serrano. AFP Summer School. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences]](/thumbs/95/124893351.jpg) GADTs AFP Summer School Alejandro Serrano 1 Today s lecture Generalized algebraic data types (GADTs) 2 A datatype data Tree a = Leaf Node (Tree a) a (Tree a) This definition introduces: 3 A datatype data
GADTs AFP Summer School Alejandro Serrano 1 Today s lecture Generalized algebraic data types (GADTs) 2 A datatype data Tree a = Leaf Node (Tree a) a (Tree a) This definition introduces: 3 A datatype data
ITI Introduction to Computing II
 ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Recursive list processing (part I) Version of March 24, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes are
ITI 1121. Introduction to Computing II Marcel Turcotte School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Recursive list processing (part I) Version of March 24, 2013 Abstract These lecture notes are
CS205: Scalable Software Systems
 CS205: Scalable Software Systems Lecture 4 September 14, 2016 Lecture 4 CS205: Scalable Software Systems September 14, 2016 1 / 16 Quick Recap Things covered so far Problem solving by recursive decomposition
CS205: Scalable Software Systems Lecture 4 September 14, 2016 Lecture 4 CS205: Scalable Software Systems September 14, 2016 1 / 16 Quick Recap Things covered so far Problem solving by recursive decomposition
CSE341 Spring 2016, Final Examination June 6, 2016
 CSE341 Spring 2016, Final Examination June 6, 2016 Please do not turn the page until 8:30. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note, etc. except for both sides of one 8.5x11in piece of paper. Please
CSE341 Spring 2016, Final Examination June 6, 2016 Please do not turn the page until 8:30. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note, etc. except for both sides of one 8.5x11in piece of paper. Please
Lecture: Functional Programming
 Lecture: Functional Programming This course is an introduction to the mathematical foundations of programming languages and the implementation of programming languages and language-based tools. We use
Lecture: Functional Programming This course is an introduction to the mathematical foundations of programming languages and the implementation of programming languages and language-based tools. We use
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Winter 2013 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course, Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 Story So Far... Simple Expressions Branches Let-Bindings... Today: Finish Crash Course Datatypes
CSE 130 : Winter 2013 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course, Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 Story So Far... Simple Expressions Branches Let-Bindings... Today: Finish Crash Course Datatypes
Principles of Programming Languages 2017W, Functional Programming
 Principles of Programming Languages 2017W, Functional Programming Assignment 3: Lisp Machine (16 points) Lisp is a language based on the lambda calculus with strict execution semantics and dynamic typing.
Principles of Programming Languages 2017W, Functional Programming Assignment 3: Lisp Machine (16 points) Lisp is a language based on the lambda calculus with strict execution semantics and dynamic typing.
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1, sample for Quiz #1 on Thu PA #1 (due next Fri 10/10) No make-up quizzes
CSE 130 : Fall 2008 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1, sample for Quiz #1 on Thu PA #1 (due next Fri 10/10) No make-up quizzes
Data Structures G5029
 Data Structures G5029 Lecture 2 Kingsley Sage Room 5C16, Pevensey III khs20@sussex.ac.uk University of Sussex 2006 Lecture 2 Stacks The usual analogy is the stack of plates. A way of buffering a stream
Data Structures G5029 Lecture 2 Kingsley Sage Room 5C16, Pevensey III khs20@sussex.ac.uk University of Sussex 2006 Lecture 2 Stacks The usual analogy is the stack of plates. A way of buffering a stream
Typed Racket: Racket with Static Types
 Typed Racket: Racket with Static Types Version 5.0.2 Sam Tobin-Hochstadt November 6, 2010 Typed Racket is a family of languages, each of which enforce that programs written in the language obey a type
Typed Racket: Racket with Static Types Version 5.0.2 Sam Tobin-Hochstadt November 6, 2010 Typed Racket is a family of languages, each of which enforce that programs written in the language obey a type
Lecture #13: Type Inference and Unification. Typing In the Language ML. Type Inference. Doing Type Inference
 Lecture #13: Type Inference and Unification Typing In the Language ML Examples from the language ML: fun map f [] = [] map f (a :: y) = (f a) :: (map f y) fun reduce f init [] = init reduce f init (a ::
Lecture #13: Type Inference and Unification Typing In the Language ML Examples from the language ML: fun map f [] = [] map f (a :: y) = (f a) :: (map f y) fun reduce f init [] = init reduce f init (a ::
Lab 10: OCaml sequences, comparators, stable sorting 12:00 PM, Nov 12, 2017
 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Hughes Lab 10: OCaml sequences, comparators, stable sorting 12:00 PM, Nov 12, 2017 Contents 1 A last OCaml type, and its utility 1 1.1 Sequences in OCaml....................................
Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Hughes Lab 10: OCaml sequences, comparators, stable sorting 12:00 PM, Nov 12, 2017 Contents 1 A last OCaml type, and its utility 1 1.1 Sequences in OCaml....................................
15 Multiple Inheritance and Traits
 Object-Oriented Design Lecture 15 CS 3500 Fall 2010 (Pucella) Tuesday, Nov 9, 2010 15 Multiple Inheritance and Traits Recall our code for MList from last time. We defined MList to be a subtype of List,
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 15 CS 3500 Fall 2010 (Pucella) Tuesday, Nov 9, 2010 15 Multiple Inheritance and Traits Recall our code for MList from last time. We defined MList to be a subtype of List,
Implementing a List in Java. CSE 143 Java. List Interface (review) Just an Illusion? Using an Array to Implement a List.
 Implementing a List in Java CSE 143 Java List Implementation Using Arrays Reading: Ch. 22 Two implementation approaches are most commonly used for simple lists: Arrays Linked list Java Interface List concrete
Implementing a List in Java CSE 143 Java List Implementation Using Arrays Reading: Ch. 22 Two implementation approaches are most commonly used for simple lists: Arrays Linked list Java Interface List concrete
A First Look at ML. Chapter Five Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1
 A First Look at ML Chapter Five Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1 ML Meta Language One of the more popular functional languages (which, admittedly, isn t saying much) Edinburgh, 1974, Robin Milner
A First Look at ML Chapter Five Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1 ML Meta Language One of the more popular functional languages (which, admittedly, isn t saying much) Edinburgh, 1974, Robin Milner
Programming Languages
 CSE 130: Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Wed 4/9) Please post questions to WebCT Today: A crash
CSE 130: Spring 2010 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Wed 4/9) Please post questions to WebCT Today: A crash
Functional Programming. Pure Functional Programming
 Functional Programming Pure Functional Programming Computation is largely performed by applying functions to values. The value of an expression depends only on the values of its sub-expressions (if any).
Functional Programming Pure Functional Programming Computation is largely performed by applying functions to values. The value of an expression depends only on the values of its sub-expressions (if any).
Tail Recursion: Factorial. Begin at the beginning. How does it execute? Tail recursion. Tail recursive factorial. Tail recursive factorial
 Begin at the beginning Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types Values (Semantics) 1. Programmer enters epression 2. ML checks if epression is well-typed Using a precise set of rules,
Begin at the beginning Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types Values (Semantics) 1. Programmer enters epression 2. ML checks if epression is well-typed Using a precise set of rules,
Programming Languages. Next: Building datatypes. Suppose I wanted. Next: Building datatypes 10/4/2017. Review so far. Datatypes.
 Review so far Programming Languages Expressions Values Datatypes Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions Review so far We ve seen some base types and values: Integers, Floats,
Review so far Programming Languages Expressions Values Datatypes Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions Review so far We ve seen some base types and values: Integers, Floats,
Programming Languages. Datatypes
 Programming Languages Datatypes Review so far Expressions Values Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions Review so far We ve seen some base types and values: Integers, Floats,
Programming Languages Datatypes Review so far Expressions Values Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions Review so far We ve seen some base types and values: Integers, Floats,
The SCAlable LAnguage
 The SCAlable LAnguage The Scala Language: Object Oriented Functional Programming Gabor Szokoli Overview Introduction Everything is an Object Inheritance and mixins For comprehensions Generic Types: Covariance,
The SCAlable LAnguage The Scala Language: Object Oriented Functional Programming Gabor Szokoli Overview Introduction Everything is an Object Inheritance and mixins For comprehensions Generic Types: Covariance,
Advanced Type System Features Tom Schrijvers. Leuven Haskell User Group
 Advanced Type System Features Tom Schrijvers Leuven Haskell User Group Data Recursion Genericity Schemes Expression Problem Monads GADTs DSLs Type Type Families Classes Lists and Effect Free Other Handlers
Advanced Type System Features Tom Schrijvers Leuven Haskell User Group Data Recursion Genericity Schemes Expression Problem Monads GADTs DSLs Type Type Families Classes Lists and Effect Free Other Handlers
Recap: ML s Holy Trinity
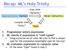 Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set
Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set
Programming Languages
 CSE 130: Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 10/9) Technical issues installing Ocaml - should be resolved soon! Ranjit Jhala
CSE 130: Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 10/9) Technical issues installing Ocaml - should be resolved soon! Ranjit Jhala
CS171 Midterm Exam. October 29, Name:
 CS171 Midterm Exam October 29, 2012 Name: You are to honor the Emory Honor Code. This is a closed-book and closed-notes exam. You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. Read each problem carefully, and
CS171 Midterm Exam October 29, 2012 Name: You are to honor the Emory Honor Code. This is a closed-book and closed-notes exam. You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. Read each problem carefully, and
Chapter 3 Linear Structures: Lists
 Plan Chapter 3 Linear Structures: Lists 1. Lists... 3.2 2. Basic operations... 3.4 3. Constructors and pattern matching... 3.5 4. Polymorphism... 3.8 5. Simple operations on lists... 3.11 6. Application:
Plan Chapter 3 Linear Structures: Lists 1. Lists... 3.2 2. Basic operations... 3.4 3. Constructors and pattern matching... 3.5 4. Polymorphism... 3.8 5. Simple operations on lists... 3.11 6. Application:
Delayed Expressions Fall 2017 Discussion 9: November 8, Iterables and Iterators. For Loops. Other Iterable Uses
 CS 6A Delayed Expressions Fall 07 Discussion 9: November 8, 07 Iterables and Iterators An iterable is any container that can be processed sequentially. Examples include lists, tuples, strings, and dictionaries.
CS 6A Delayed Expressions Fall 07 Discussion 9: November 8, 07 Iterables and Iterators An iterable is any container that can be processed sequentially. Examples include lists, tuples, strings, and dictionaries.
Using Scala in CS241
 Using Scala in CS241 Winter 2018 Contents 1 Purpose 1 2 Scala 1 3 Basic Syntax 2 4 Tuples, Arrays, Lists and Vectors in Scala 3 5 Binary output in Scala 5 6 Maps 5 7 Option types 5 8 Objects and Classes
Using Scala in CS241 Winter 2018 Contents 1 Purpose 1 2 Scala 1 3 Basic Syntax 2 4 Tuples, Arrays, Lists and Vectors in Scala 3 5 Binary output in Scala 5 6 Maps 5 7 Option types 5 8 Objects and Classes
More Functions on Lists
 More Functions on Lists List Methods (1) Sublists and element access: xs.length xs.last xs.init xs take n xs drop n xs(n) The number of elements of xs. The list s last element, exception if xs is empty.
More Functions on Lists List Methods (1) Sublists and element access: xs.length xs.last xs.init xs take n xs drop n xs(n) The number of elements of xs. The list s last element, exception if xs is empty.
Introduction to Functional Programming: Lecture 7 2 Functions as innite data structures Ordinary ML data structures are always nite. We can, however,
 Introduction to Functional Programming: Lecture 7 1 Introduction to Functional Programming John Harrison University of Cambridge Lecture 7 Innite data structures Topics covered: Functions as innite data
Introduction to Functional Programming: Lecture 7 1 Introduction to Functional Programming John Harrison University of Cambridge Lecture 7 Innite data structures Topics covered: Functions as innite data
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists. Zach Tatlock Winter 2018
 CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists Zach Tatlock Winter 2018 Function definitions Functions: the most important building block in the whole course Like Java methods, have arguments
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists Zach Tatlock Winter 2018 Function definitions Functions: the most important building block in the whole course Like Java methods, have arguments
Function definitions. CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists. Example, extended. Some gotchas. Zach Tatlock Winter 2018
 Function definitions CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists Zach Tatlock Winter 2018 Functions: the most important building block in the whole course Like Java methods, have arguments
Function definitions CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 2 Functions, Pairs, Lists Zach Tatlock Winter 2018 Functions: the most important building block in the whole course Like Java methods, have arguments
Queues. CITS2200 Data Structures and Algorithms. Topic 5
 CITS2200 Data Structures and Algorithms Topic 5 Queues Implementations of the Queue ADT Queue specification Queue interface Block (array) representations of queues Recursive (linked) representations of
CITS2200 Data Structures and Algorithms Topic 5 Queues Implementations of the Queue ADT Queue specification Queue interface Block (array) representations of queues Recursive (linked) representations of
Sorting: Given a list A with n elements possessing a total order, return a list with the same elements in non-decreasing order.
 Sorting The sorting problem is defined as follows: Sorting: Given a list A with n elements possessing a total order, return a list with the same elements in non-decreasing order. Remember that total order
Sorting The sorting problem is defined as follows: Sorting: Given a list A with n elements possessing a total order, return a list with the same elements in non-decreasing order. Remember that total order
High-level Parallel Programming: Scala on the JVM
 High-level Parallel Programming: Scala on the JVM Contents of Lecture 4 The Scala programming language Parallel programming using actors Jonas Skeppstedt (jonasskeppstedt.net) Lecture 4 2017 1 / 40 Purpose
High-level Parallel Programming: Scala on the JVM Contents of Lecture 4 The Scala programming language Parallel programming using actors Jonas Skeppstedt (jonasskeppstedt.net) Lecture 4 2017 1 / 40 Purpose
Intro. Scheme Basics. scm> 5 5. scm>
 Intro Let s take some time to talk about LISP. It stands for LISt Processing a way of coding using only lists! It sounds pretty radical, and it is. There are lots of cool things to know about LISP; if
Intro Let s take some time to talk about LISP. It stands for LISt Processing a way of coding using only lists! It sounds pretty radical, and it is. There are lots of cool things to know about LISP; if
COSE212: Programming Languages. Lecture 3 Functional Programming in OCaml
 COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 3 Functional Programming in OCaml Hakjoo Oh 2017 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2017 Fall, Lecture 3 September 18, 2017 1 / 44 Why learn ML? Learning ML is a good way of
COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 3 Functional Programming in OCaml Hakjoo Oh 2017 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2017 Fall, Lecture 3 September 18, 2017 1 / 44 Why learn ML? Learning ML is a good way of
SML A F unctional Functional Language Language Lecture 19
 SML A Functional Language Lecture 19 Introduction to SML SML is a functional programming language and acronym for Standard d Meta Language. SML has basic data objects as expressions, functions and list
SML A Functional Language Lecture 19 Introduction to SML SML is a functional programming language and acronym for Standard d Meta Language. SML has basic data objects as expressions, functions and list
Chapter 3 Linear Structures: Lists
 Plan Chapter 3 Linear Structures: Lists 1. Two constructors for lists... 3.2 2. Lists... 3.3 3. Basic operations... 3.5 4. Constructors and pattern matching... 3.6 5. Simple operations on lists... 3.9
Plan Chapter 3 Linear Structures: Lists 1. Two constructors for lists... 3.2 2. Lists... 3.3 3. Basic operations... 3.5 4. Constructors and pattern matching... 3.6 5. Simple operations on lists... 3.9
GADTs. Wouter Swierstra. Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7. Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences
 GADTs Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7 Wouter Swierstra 1 Today s lecture Generalized algebraic data types (GADTs) 2 A datatype data Tree a = Leaf Node (Tree a) a (Tree a) This definition introduces:
GADTs Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7 Wouter Swierstra 1 Today s lecture Generalized algebraic data types (GADTs) 2 A datatype data Tree a = Leaf Node (Tree a) a (Tree a) This definition introduces:
Haskell: From Basic to Advanced. Part 2 Type Classes, Laziness, IO, Modules
 Haskell: From Basic to Advanced Part 2 Type Classes, Laziness, IO, Modules Qualified types In the types schemes we have seen, the type variables were universally quantified, e.g. ++ :: [a] -> [a] -> [a]
Haskell: From Basic to Advanced Part 2 Type Classes, Laziness, IO, Modules Qualified types In the types schemes we have seen, the type variables were universally quantified, e.g. ++ :: [a] -> [a] -> [a]
Computer Science CS221 Test 2 Name. 1. Give a definition of the following terms, and include a brief example. a) Big Oh
 Computer Science CS221 Test 2 Name 1. Give a definition of the following terms, and include a brief example. a) Big Oh b) abstract class c) overriding d) implementing an interface 10/21/1999 Page 1 of
Computer Science CS221 Test 2 Name 1. Give a definition of the following terms, and include a brief example. a) Big Oh b) abstract class c) overriding d) implementing an interface 10/21/1999 Page 1 of
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 6 Nested Patterns Exceptions Tail Recursion. Zach Tatlock Winter 2018
 CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 6 Nested Patterns Exceptions Tail Recursion Zach Tatlock Winter 2018 Nested patterns We can nest patterns as deep as we want Just like we can nest expressions as deep
CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 6 Nested Patterns Exceptions Tail Recursion Zach Tatlock Winter 2018 Nested patterns We can nest patterns as deep as we want Just like we can nest expressions as deep
Shell CSCE 314 TAMU. Functions continued
 1 CSCE 314: Programming Languages Dr. Dylan Shell Functions continued 2 Outline Defining Functions List Comprehensions Recursion 3 A Function without Recursion Many functions can naturally be defined in
1 CSCE 314: Programming Languages Dr. Dylan Shell Functions continued 2 Outline Defining Functions List Comprehensions Recursion 3 A Function without Recursion Many functions can naturally be defined in
Exercises on ML. Programming Languages. Chanseok Oh
 Exercises on ML Programming Languages Chanseok Oh chanseok@cs.nyu.edu Dejected by an arcane type error? - foldr; val it = fn : ('a * 'b -> 'b) -> 'b -> 'a list -> 'b - foldr (fn x=> fn y => fn z => (max
Exercises on ML Programming Languages Chanseok Oh chanseok@cs.nyu.edu Dejected by an arcane type error? - foldr; val it = fn : ('a * 'b -> 'b) -> 'b -> 'a list -> 'b - foldr (fn x=> fn y => fn z => (max
Lecture 09: Introduction to Scala
 Lecture 09: Introduction to Scala Computer Science Department, University of Crete Multicore Processor Programming Based on slides by D. Malayeri, S.D. Vick, P. Haller, and M. Madsen Pratikakis (CSD) Scala
Lecture 09: Introduction to Scala Computer Science Department, University of Crete Multicore Processor Programming Based on slides by D. Malayeri, S.D. Vick, P. Haller, and M. Madsen Pratikakis (CSD) Scala
Lists. Michael P. Fourman. February 2, 2010
 Lists Michael P. Fourman February 2, 2010 1 Introduction The list is a fundamental datatype in most functional languages. ML is no exception; list is a built-in ML type constructor. However, to introduce
Lists Michael P. Fourman February 2, 2010 1 Introduction The list is a fundamental datatype in most functional languages. ML is no exception; list is a built-in ML type constructor. However, to introduce
Recap: ML s Holy Trinity. Story So Far... CSE 130 Programming Languages. Datatypes. A function is a value! Next: functions, but remember.
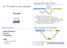 CSE 130 Programming Languages Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Datatypes Compile-time Static Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1. Programmer enters expression
CSE 130 Programming Languages Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Datatypes Compile-time Static Types Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1. Programmer enters expression
