9.4.1 Search and Update Operations in a Skip List
|
|
|
- Leona McBride
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 400 Chapter 9. Maps and Dictionaries Search and Update Operations in a Skip List The skip list structure allows for simple dictionary search and update algorithms. In fact, all of the skip list search and update algorithms are based on an elegant SkipSearch method that takes a key k and finds the position p of the entry e in list So such that e has the largest key (which is possibly -m) less than or equal to k. Searching in a Skip List Suppose we are given a search key k. We begin the SkipSearch method by setting a position variable p to the top-most, left position in the skip list S, called the start position of S. That is, the start position is the position of $ storing the special entry with key -00. We then perform the following steps (see Figure 9.10), where key(p) denotes the key of the entry at position p: 1. If S.below(p) is null, then the search terminates-we are at the bottom and have located the largest entry in S with key less than or equal to the search key k. Otherwise, we drop down to the next lower level in the present tower by setting p + S. below(p). 2. Starting at position p, we move p forward until it is at the right-most position on the present level such that key(p) 5 k. We call this the scan forward step. Note that such a position always exists, since each level contains the keys +m and -00. In fact, after we perform the scan forward for this level, p may remain where it started. In any case, we then repeat the previous step. Figure 9.10: Example of a search in a skip list. The positions visited when searching for key 50 are highlighted in blue. We give a pseudo-code description of the skip-list search algorithm, SkipSearch, in Code Fragment Given this method, it is now easy to implement the operation find(k)-we simply perform p t SkipSearch(k) and test whether or not key(p) = k. If these two keys are equal, we return p; otherwise, we return null.
2 9.4. Skip Lists 401 Algorithm SkipSearch(k): Iizput: A search key k Output: Position p in the bottom list So such that the entry at p has the largest key less than or equal to k Pts while below(p) # null do p t below(p) {drop down) while k 1 key(next(p)) do P next(^) {scan forward) return p. Code Fragment 9.10: Search in a skip list S. Variable s holds the start position of S. As it turns out, the expected running time of algorithm Skipsearch on a skip list with n entries is O(1ogn). We postpone the justification of this fact, however, until after we discuss the implementation of the update methods for skip lists. Insertion in a Skip List The insertion algorithm for skip lists uses randomization to decide the height of the tower for the new entry. We begin the insertion of a new entry (k, v) by performing a SkipSearch(k) operation. This gives us the position p of the bottom-level entry with the largest key less than or equal to k (note that p may hold the special entry with key -w). We then insert (k, v) immediately after position p. After inserting the new entry at the bottom level, we "flip" a coin. If the flip comes up tails, then we stop here. Else (the flip comes up heads), we backtrack to the previous (next higher) level and insert (k,v) in this level at the appropriate position. We again flip a coin; if it comes up heads, we go to the next higher level and repeat. Thus, we continue to insert the new entry (k,v) in lists until we finally get a flip that comes up tails. We link together all the references to the new entry (k,v) created in this process to create the tower for the new entry. A coin flip can be simulated with Java's built-in pseudo-random number generator java. util. Random by calling nextlnt(2), which returns 0 of 1, each with probability 112. We give the insertion algorithm for a skip list S in Code Fragment and we illustrate it in Figure The algorithm uses method insertafterabove(p,q, (k, v)) that inserts a position storing the entry (k, v) after position p (on the same level as p) and above position q, returning the position r of the new entry (and setting internal references so that next, prev, above, and below methods will work correctly for p, q, and r). The expected running time of the insertion algorithm on a skip list with n entries is O(logn), which we show in Section
3 Chapter 9. Maps and Dictionaries Algorithm Skiplnsert(k, v): Input: Key k and value v Output: Entry inserted in the skip list p t SkipSearch(k) q t insertafterabove(p, null, (k,v)) {we are at the bottom level) e t q.element() i t 0 while coin Flip() = heads do iti+l if i >_ h then hthfl {add a new level to the skip list) t t next(s) s t insertafterabove(nuli,s, (-oo, null)) insertafterabove(s,t, (+m, null)) while a bove(p) = null do P + P ~ P ) {scan backward) p t above(p) {jump up to higher level) q t insertafterabove(p,q,e) {add a position to the tower of the new entry) ntn+l return e Code Fragment 9.11: Insertion in a skip list. Method coinflip() returns "heads" or "tails", each with probability 112. Variables n, h, and s hold the number of entries, the height, and the start node of the skip list. Figure 9.11: Insertion of an entry with key 42 into the skip list of Figure 9.9. We assume that the random "coin flips" for the new entry came up heads three times in a row, followed by tails. The positions visited are highlighted in blue. The positions inserted to hold the new entry are drawn with thick lines, and the positions preceding them are flagged.
4 9.4. Skip Lists Removal in a Skip List Like the search and insertion algorithms, the removal algorithm for a skip list is quite simple. In fact, it is even easier than the insertion algorithm. That is, to perform a remove(k) operation, we begin by executing method SkipSearch(k). If the position p stores an entry with key different from k, we return null. Otherwise, we remove p and all the positions above p, which are easily accessed by using above operations to climb up the tower of this entry in S starting at position p. The removal algorithm is illustrated in Figure 9.12 and a detailed description of it is left as an exercise (R-9.16). As we show in the next subsection, operation remove in a skip list with n entries has O(1ogn) expected running time. Before we give this analysis, however, there are some minor improvements to the skip list data structure we would like to discuss. First, we don't actually need to store references to entries at the levels of the skip list above the bottom level, because all that is needed at these levels are references to keys. Second, we don't actually need the above method. In fact, we don't need the prev method either. We can perform entry insertion and removal in strictly a top-down, scan-forward fashion, thus saving space for "up" and "prev" references. We explore the details of this optimization in Exercise C Neither of these optimizations improve the asymptotic performance of skip lists by more than a constant factor, but these improvements can, nevertheless, be meaningful in practice. In fact, experimental evidence suggests that optimized skip lists are faster in practice than AVL trees and other balanced search trees, which are discussed in Chapter 10. The expected running time of the removal algorithm is O(logn), which we show in Section I Figure 9.12: Removal of the entry with key 25 from the skip list of Figure The positions visited after the search for the position of 5 holding the entry are highlighted in blue. The positions removed are drawn with dashed lines.
5 404 Chapter 9. Maps and Dictionaries Maintaining the ~o~-most Level A skip-list S must maintain a reference to the start position (the top-most, left position in S) as an instance variable, and must have a policy for any insertion that wishes to continue inserting a new entry past the top level of S. There are two possible courses of action we can take, both of which have their merits. One possibility is to restrict the top level, h, to be kept at some fixed value that is a function of n, the number of entries currently in the dictionary (from the analysis we will see that h = maxi l0,2 [log nl ) is a reasonable choice, and picking h = 3 [lognl is even safer). Implementing this choice means that we must modify the insertion algorithm to stop inserting a new position once we reach the top-most level (unless [log nl < [log(. + I)], in which case we can now go at least one more level, since the bound on the height is increasing). The other possibility is to let an insertion continue inserting a new position as long as heads keeps getting returned from the random number generator. This is the approach taken in Algorithm Skiplnsert of Code Fragment As we show in the analysis of skip lists, the probability that an insertion will go to a level that is more than O(1ogn) is very low, so this design choice should also work. Either choice will still result in the expected O(1ogn) time to perform search, insertion, and removal, however, which we show in the next section A Probabilistic Analysis of Skip Lists * As we have shown above, skip lists provide a simple implementation of an ordered dictionary. In terms of worst-case performance, however, skip lists are not a superior data structure. In fact, if we don't officially prevent an insertion from continuing significantly past the current highest level, then the insertion algorithm can go into what is almost an infinite loop (it is not actually an infinite loop, however, since the probability of having a fair coin repeatedly come up heads forever is 0). Moreover, we cannot infinitely add positions to a list without eventually running out of memory. In any case, if we terminate position insertion at the highest level h, then the worst-case running time for performing the find, insert, and remove operations in a skip list S with n entries and height h is O(n + h). This worst-case performance occurs when the tower of every entry reaches level h - 1, where h is the height of S. However, this event has very low probability. Judging from this worst case, we might conclude that the skip list structure is strictly inferior to the other dictionary implementations discussed earlier in this chapter. But this would not be a fair analysis, for this worst-case behavior is a gross overestimate. *We use a star (*) to indicate sections containing material more advanced than the material in the rest of the chapter; this material can be considered optional in a first reading.
COSC 2011 Section N Data structure for efficient Thursday, April
 Skip Lists - Description: (1) COSC 2011 Data structure for efficient Thursday, April 26 2001 Overview Skip Lists Description, Definition ADT Searching Insertion Removal realization of the Ordered Dictionary.
Skip Lists - Description: (1) COSC 2011 Data structure for efficient Thursday, April 26 2001 Overview Skip Lists Description, Definition ADT Searching Insertion Removal realization of the Ordered Dictionary.
Skip Lists S 3 S 2 S 1. Skip Lists Goodrich, Tamassia
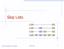 Skip Lists S 3 15 15 23 10 15 23 36 Skip Lists 1 What is a Skip List A skip list for a set S of distinct (key, element) items is a series of lists,,, S h such that Each list S i contains the special keys
Skip Lists S 3 15 15 23 10 15 23 36 Skip Lists 1 What is a Skip List A skip list for a set S of distinct (key, element) items is a series of lists,,, S h such that Each list S i contains the special keys
Using Randomization in the Teaching of Data Structures and Algorithms
 Using Randomization in the Teaching of Data Structures and Algorithms Michael T. Goodrich* Dept. of Computer Science Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, MD 21218 goodrichqcs.jhu.edu Roberto Tamassiat Dept.
Using Randomization in the Teaching of Data Structures and Algorithms Michael T. Goodrich* Dept. of Computer Science Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, MD 21218 goodrichqcs.jhu.edu Roberto Tamassiat Dept.
CS 561, Lecture 2 : Randomization in Data Structures. Jared Saia University of New Mexico
 CS 561, Lecture 2 : Randomization in Data Structures Jared Saia University of New Mexico Outline Hash Tables Bloom Filters Skip Lists 1 Dictionary ADT A dictionary ADT implements the following operations
CS 561, Lecture 2 : Randomization in Data Structures Jared Saia University of New Mexico Outline Hash Tables Bloom Filters Skip Lists 1 Dictionary ADT A dictionary ADT implements the following operations
Skip Lists: Motivation
 CSE 100: SKIP LISTS Announcements Please fill out the end of year survey and CAPEs https://wwwsurveymonkeycom/s/qfzpmt2 Please remove print statements to standard output when submitting your PA4 assignment
CSE 100: SKIP LISTS Announcements Please fill out the end of year survey and CAPEs https://wwwsurveymonkeycom/s/qfzpmt2 Please remove print statements to standard output when submitting your PA4 assignment
CHAPTER 9 HASH TABLES, MAPS, AND SKIP LISTS
 0 1 2 025-612-0001 981-101-0002 3 4 451-229-0004 CHAPTER 9 HASH TABLES, MAPS, AND SKIP LISTS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH,
0 1 2 025-612-0001 981-101-0002 3 4 451-229-0004 CHAPTER 9 HASH TABLES, MAPS, AND SKIP LISTS ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH,
Treaps. 1 Binary Search Trees (BSTs) CSE341T/CSE549T 11/05/2014. Lecture 19
 CSE34T/CSE549T /05/04 Lecture 9 Treaps Binary Search Trees (BSTs) Search trees are tree-based data structures that can be used to store and search for items that satisfy a total order. There are many types
CSE34T/CSE549T /05/04 Lecture 9 Treaps Binary Search Trees (BSTs) Search trees are tree-based data structures that can be used to store and search for items that satisfy a total order. There are many types
CSED233: Data Structures (2017F) Lecture10:Hash Tables, Maps, and Skip Lists
 (2017F) Lecture10:Hash Tables, Maps, and Skip Lists Daijin Kim CSE, POSTECH dkim@postech.ac.kr Maps A map models a searchable collection of key-value entries The main operations of a map are for searching,
(2017F) Lecture10:Hash Tables, Maps, and Skip Lists Daijin Kim CSE, POSTECH dkim@postech.ac.kr Maps A map models a searchable collection of key-value entries The main operations of a map are for searching,
CS 350 : Data Structures Skip Lists
 CS 350 : Data Structures Skip Lists David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Skip List Introduction A data structure used for
CS 350 : Data Structures Skip Lists David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Skip List Introduction A data structure used for
10.2 AVL Trees. Definition of an AVL Tree. 438 Chapter 10. Search Trees
 438 Chapter 10. Search Trees 10. AVL Trees In theprevioussection,wediscussedwhatshouldbeanefficientmapdatastructure, but the worst-case performance it achieves for the various operations is linear time,
438 Chapter 10. Search Trees 10. AVL Trees In theprevioussection,wediscussedwhatshouldbeanefficientmapdatastructure, but the worst-case performance it achieves for the various operations is linear time,
Decision-Making and Repetition
 2.2 Recursion Introduction A recursive method is a method that call itself. You may already be familiar with the factorial function (N!) in mathematics. For any positive integer N, N! is defined to be
2.2 Recursion Introduction A recursive method is a method that call itself. You may already be familiar with the factorial function (N!) in mathematics. For any positive integer N, N! is defined to be
CS 561, Lecture 2 : Hash Tables, Skip Lists, Bloom Filters, Count-Min sketch. Jared Saia University of New Mexico
 CS 561, Lecture 2 : Hash Tables, Skip Lists, Bloom Filters, Count-Min sketch Jared Saia University of New Mexico Outline Hash Tables Skip Lists Count-Min Sketch 1 Dictionary ADT A dictionary ADT implements
CS 561, Lecture 2 : Hash Tables, Skip Lists, Bloom Filters, Count-Min sketch Jared Saia University of New Mexico Outline Hash Tables Skip Lists Count-Min Sketch 1 Dictionary ADT A dictionary ADT implements
Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees
 Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2016) Frank Pfenning 1 Introduction Binary search trees are an excellent data structure to implement associative arrays,
Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2016) Frank Pfenning 1 Introduction Binary search trees are an excellent data structure to implement associative arrays,
1 Probability Review. CS 124 Section #8 Hashing, Skip Lists 3/20/17. Expectation (weighted average): the expectation of a random quantity X is:
 CS 124 Section #8 Hashing, Skip Lists 3/20/17 1 Probability Review Expectation (weighted average): the expectation of a random quantity X is: x= x P (X = x) For each value x that X can take on, we look
CS 124 Section #8 Hashing, Skip Lists 3/20/17 1 Probability Review Expectation (weighted average): the expectation of a random quantity X is: x= x P (X = x) For each value x that X can take on, we look
infix expressions (review)
 Outline infix, prefix, and postfix expressions queues queue interface queue applications queue implementation: array queue queue implementation: linked queue application of queues and stacks: data structure
Outline infix, prefix, and postfix expressions queues queue interface queue applications queue implementation: array queue queue implementation: linked queue application of queues and stacks: data structure
Fractional Cascading
 C.S. 252 Prof. Roberto Tamassia Computational Geometry Sem. II, 1992 1993 Lecture 11 Scribe: Darren Erik Vengroff Date: March 15, 1993 Fractional Cascading 1 Introduction Fractional cascading is a data
C.S. 252 Prof. Roberto Tamassia Computational Geometry Sem. II, 1992 1993 Lecture 11 Scribe: Darren Erik Vengroff Date: March 15, 1993 Fractional Cascading 1 Introduction Fractional cascading is a data
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Algorithm Analysis Page 1 - Algorithm Analysis Dr. Fall 2008 Algorithm Analysis Page 2 Outline Textbook Overview Analysis of Algorithm Pseudo-Code and Primitive Operations Growth Rate and Big-Oh Notation
Algorithm Analysis Page 1 - Algorithm Analysis Dr. Fall 2008 Algorithm Analysis Page 2 Outline Textbook Overview Analysis of Algorithm Pseudo-Code and Primitive Operations Growth Rate and Big-Oh Notation
Linked List Implementation of Queues
 Outline queue implementation: linked queue application of queues and stacks: data structure traversal double-ended queues application of queues: simulation of an airline counter random numbers recursion
Outline queue implementation: linked queue application of queues and stacks: data structure traversal double-ended queues application of queues: simulation of an airline counter random numbers recursion
Statistics: Interpreting Data and Making Predictions. Visual Displays of Data 1/31
 Statistics: Interpreting Data and Making Predictions Visual Displays of Data 1/31 Last Time Last time we discussed central tendency; that is, notions of the middle of data. More specifically we discussed
Statistics: Interpreting Data and Making Predictions Visual Displays of Data 1/31 Last Time Last time we discussed central tendency; that is, notions of the middle of data. More specifically we discussed
Motivation for B-Trees
 1 Motivation for Assume that we use an AVL tree to store about 20 million records We end up with a very deep binary tree with lots of different disk accesses; log2 20,000,000 is about 24, so this takes
1 Motivation for Assume that we use an AVL tree to store about 20 million records We end up with a very deep binary tree with lots of different disk accesses; log2 20,000,000 is about 24, so this takes
Computer Programming. Basic Control Flow - Loops. Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons
 Computer Programming Basic Control Flow - Loops Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons Objectives To learn about the three types of loops: while for do To avoid infinite
Computer Programming Basic Control Flow - Loops Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons Objectives To learn about the three types of loops: while for do To avoid infinite
Lecture 7. Random number generation More randomized data structures Skip lists: ideas and implementation Skip list time costs
 Lecture 7 Random number generation More randomized data structures Skip lists: ideas and implementation Skip list time costs Reading: Skip Lists: A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees paper (Pugh);
Lecture 7 Random number generation More randomized data structures Skip lists: ideas and implementation Skip list time costs Reading: Skip Lists: A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees paper (Pugh);
CSE 613: Parallel Programming. Lecture 6 ( Basic Parallel Algorithmic Techniques )
 CSE 613: Parallel Programming Lecture 6 ( Basic Parallel Algorithmic Techniques ) Rezaul A. Chowdhury Department of Computer Science SUNY Stony Brook Spring 2017 Some Basic Techniques 1. Divide-and-Conquer
CSE 613: Parallel Programming Lecture 6 ( Basic Parallel Algorithmic Techniques ) Rezaul A. Chowdhury Department of Computer Science SUNY Stony Brook Spring 2017 Some Basic Techniques 1. Divide-and-Conquer
The while Loop 4/6/16 4
 Chapter 4: Loops Chapter Goals To implement while and for loops To hand-trace the execution of a program To become familiar with common loop algorithms To understand nested loops To implement programs
Chapter 4: Loops Chapter Goals To implement while and for loops To hand-trace the execution of a program To become familiar with common loop algorithms To understand nested loops To implement programs
UAB CIS High School Programming Contest. March 18, 2017 OFFICIAL HIGH SCHOOL CONTEST QUESTIONS
 UAB CIS High School Programming Contest March 18, 2017 OFFICIAL HIGH SCHOOL CONTEST QUESTIONS Each problem in this packet contains a brief description, followed by three example test cases of a successful
UAB CIS High School Programming Contest March 18, 2017 OFFICIAL HIGH SCHOOL CONTEST QUESTIONS Each problem in this packet contains a brief description, followed by three example test cases of a successful
Lecture 16 AVL Trees
 Lecture 16 AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning Binary search trees are an excellent data structure to implement associative arrays, maps, sets, and similar
Lecture 16 AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning Binary search trees are an excellent data structure to implement associative arrays, maps, sets, and similar
Vertex Cover Approximations
 CS124 Lecture 20 Heuristics can be useful in practice, but sometimes we would like to have guarantees. Approximation algorithms give guarantees. It is worth keeping in mind that sometimes approximation
CS124 Lecture 20 Heuristics can be useful in practice, but sometimes we would like to have guarantees. Approximation algorithms give guarantees. It is worth keeping in mind that sometimes approximation
15.4 Longest common subsequence
 15.4 Longest common subsequence Biological applications often need to compare the DNA of two (or more) different organisms A strand of DNA consists of a string of molecules called bases, where the possible
15.4 Longest common subsequence Biological applications often need to compare the DNA of two (or more) different organisms A strand of DNA consists of a string of molecules called bases, where the possible
Problem Set 4 Solutions
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms March 5, 205 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/8.40J Profs. Erik Demaine, Srini Devadas, and Nancy Lynch Problem Set 4 Solutions Problem Set 4 Solutions This
Design and Analysis of Algorithms March 5, 205 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/8.40J Profs. Erik Demaine, Srini Devadas, and Nancy Lynch Problem Set 4 Solutions Problem Set 4 Solutions This
CS2351 Data Structures. Lecture 1: Getting Started
 CS2351 Data Structures Lecture 1: Getting Started About this lecture Study some sorting algorithms Insertion Sort Selection Sort Merge Sort Show why these algorithms are correct Analyze the efficiency
CS2351 Data Structures Lecture 1: Getting Started About this lecture Study some sorting algorithms Insertion Sort Selection Sort Merge Sort Show why these algorithms are correct Analyze the efficiency
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Berner Fachhochschule - Technik und Informatik Data Structures and Algorithms Topic 1: Algorithm Analysis Philipp Locher FS 2018 Outline Course and Textbook Overview Analysis of Algorithm Pseudo-Code and
Berner Fachhochschule - Technik und Informatik Data Structures and Algorithms Topic 1: Algorithm Analysis Philipp Locher FS 2018 Outline Course and Textbook Overview Analysis of Algorithm Pseudo-Code and
Repetition, Looping. While Loop
 Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
Repetition, Looping Last time we looked at how to use if-then statements to control the flow of a program. In this section we will look at different ways to repeat blocks of statements. Such repetitions
LinkedList Implementation Mini-project intro
 LinkedList Implementation Mini-project intro Turn in your written problems Mini-project Partner Survey: Do it by 4:00 today Reminder: Exam #2 is this Thursday In order to reduce time pressure, you optionally
LinkedList Implementation Mini-project intro Turn in your written problems Mini-project Partner Survey: Do it by 4:00 today Reminder: Exam #2 is this Thursday In order to reduce time pressure, you optionally
CSE373 Fall 2013, Midterm Examination October 18, 2013
 CSE373 Fall 2013, Midterm Examination October 18, 2013 Please do not turn the page until the bell rings. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note, closed calculator, closed electronics. Please stop
CSE373 Fall 2013, Midterm Examination October 18, 2013 Please do not turn the page until the bell rings. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note, closed calculator, closed electronics. Please stop
2010 SMT Power Round
 Definitions 2010 SMT Power Round A graph is a collection of points (vertices) connected by line segments (edges). In this test, all graphs will be simple any two vertices will be connected by at most one
Definitions 2010 SMT Power Round A graph is a collection of points (vertices) connected by line segments (edges). In this test, all graphs will be simple any two vertices will be connected by at most one
Lecture 17 Notes Priority Queues
 Lecture 17 Notes Priority Queues 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Summer 1 2015) Frank Pfenning, Rob Simmons 1 Introduction In this lecture we will look at priority queues as an abstract type
Lecture 17 Notes Priority Queues 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Summer 1 2015) Frank Pfenning, Rob Simmons 1 Introduction In this lecture we will look at priority queues as an abstract type
4.1 COMPUTATIONAL THINKING AND PROBLEM-SOLVING
 4.1 COMPUTATIONAL THINKING AND PROBLEM-SOLVING 4.1.2 ALGORITHMS ALGORITHM An Algorithm is a procedure or formula for solving a problem. It is a step-by-step set of operations to be performed. It is almost
4.1 COMPUTATIONAL THINKING AND PROBLEM-SOLVING 4.1.2 ALGORITHMS ALGORITHM An Algorithm is a procedure or formula for solving a problem. It is a step-by-step set of operations to be performed. It is almost
Recitation 11. Graph Contraction and MSTs Announcements. SegmentLab has been released, and is due Friday, April 14. It s worth 135 points.
 Recitation Graph Contraction and MSTs. Announcements SegmentLab has been released, and is due Friday, April. It s worth 5 points. Midterm is on Friday, April. 5 RECITATION. GRAPH CONTRACTION AND MSTS.
Recitation Graph Contraction and MSTs. Announcements SegmentLab has been released, and is due Friday, April. It s worth 5 points. Midterm is on Friday, April. 5 RECITATION. GRAPH CONTRACTION AND MSTS.
 www.thestudycampus.com Recursion Recursion is a process for solving problems by subdividing a larger problem into smaller cases of the problem itself and then solving the smaller, more trivial parts. Recursion
www.thestudycampus.com Recursion Recursion is a process for solving problems by subdividing a larger problem into smaller cases of the problem itself and then solving the smaller, more trivial parts. Recursion
Arrays. myints = new int[15];
![Arrays. myints = new int[15]; Arrays. myints = new int[15];](/thumbs/72/66387724.jpg) Arrays As you know from COMP 202 (or equivalent), an array is a data structure that holds a set of elements that are of the same type. Each element in the array can be accessed or indexed by a unique number
Arrays As you know from COMP 202 (or equivalent), an array is a data structure that holds a set of elements that are of the same type. Each element in the array can be accessed or indexed by a unique number
Unit-2 Divide and conquer 2016
 2 Divide and conquer Overview, Structure of divide-and-conquer algorithms, binary search, quick sort, Strassen multiplication. 13% 05 Divide-and- conquer The Divide and Conquer Paradigm, is a method of
2 Divide and conquer Overview, Structure of divide-and-conquer algorithms, binary search, quick sort, Strassen multiplication. 13% 05 Divide-and- conquer The Divide and Conquer Paradigm, is a method of
Lecture Notes on Priority Queues
 Lecture Notes on Priority Queues 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 16 October 18, 2012 1 Introduction In this lecture we will look at priority queues as an abstract type
Lecture Notes on Priority Queues 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 16 October 18, 2012 1 Introduction In this lecture we will look at priority queues as an abstract type
Balanced Search Trees
 Balanced Search Trees Computer Science E-22 Harvard Extension School David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Review: Balanced Trees A tree is balanced if, for each node, the node s subtrees have the same height or have
Balanced Search Trees Computer Science E-22 Harvard Extension School David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Review: Balanced Trees A tree is balanced if, for each node, the node s subtrees have the same height or have
Trees, Part 1: Unbalanced Trees
 Trees, Part 1: Unbalanced Trees The first part of this chapter takes a look at trees in general and unbalanced binary trees. The second part looks at various schemes to balance trees and/or make them more
Trees, Part 1: Unbalanced Trees The first part of this chapter takes a look at trees in general and unbalanced binary trees. The second part looks at various schemes to balance trees and/or make them more
ECE 122. Engineering Problem Solving Using Java
 ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving Using Java Lecture 27 Linear and Binary Search Overview Problem: How can I efficiently locate data within a data structure Searching for data is a fundamental function
ECE 122 Engineering Problem Solving Using Java Lecture 27 Linear and Binary Search Overview Problem: How can I efficiently locate data within a data structure Searching for data is a fundamental function
L10: Dictionary & Skip List
 Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India भ रत य व ज ञ न स स थ न ब गल र, भ रत Department of Computational and Data Sciences DS286 2016-09-14 L10: Dictionary & Skip List Yogesh Simmhan s i m m h a n
Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India भ रत य व ज ञ न स स थ न ब गल र, भ रत Department of Computational and Data Sciences DS286 2016-09-14 L10: Dictionary & Skip List Yogesh Simmhan s i m m h a n
Balanced Binary Search Trees. Victor Gao
 Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
Assume you are given a Simple Linked List (i.e. not a doubly linked list) containing an even number of elements. For example L = [A B C D E F].
![Assume you are given a Simple Linked List (i.e. not a doubly linked list) containing an even number of elements. For example L = [A B C D E F]. Assume you are given a Simple Linked List (i.e. not a doubly linked list) containing an even number of elements. For example L = [A B C D E F].](/thumbs/79/79282263.jpg) Question Assume you are given a Simple Linked List (i.e. not a doubly linked list) containing an even number of elements. For example L = [A B C D E F]. a) Draw the linked node structure of L, including
Question Assume you are given a Simple Linked List (i.e. not a doubly linked list) containing an even number of elements. For example L = [A B C D E F]. a) Draw the linked node structure of L, including
A Reduction of Conway s Thrackle Conjecture
 A Reduction of Conway s Thrackle Conjecture Wei Li, Karen Daniels, and Konstantin Rybnikov Department of Computer Science and Department of Mathematical Sciences University of Massachusetts, Lowell 01854
A Reduction of Conway s Thrackle Conjecture Wei Li, Karen Daniels, and Konstantin Rybnikov Department of Computer Science and Department of Mathematical Sciences University of Massachusetts, Lowell 01854
Tutorial for Algorithm s Theory Problem Set 5. January 17, 2013
 Tutorial for Algorithm s Theory Problem Set 5 January 17, 2013 Exercise 1: Maximum Flow Algorithms Consider the following flow network: a) Solve the maximum flow problem on the above network by using the
Tutorial for Algorithm s Theory Problem Set 5 January 17, 2013 Exercise 1: Maximum Flow Algorithms Consider the following flow network: a) Solve the maximum flow problem on the above network by using the
Problem Set 5 Solutions
 Introduction to Algorithms November 4, 2005 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/18.410J Professors Erik D. Demaine and Charles E. Leiserson Handout 21 Problem Set 5 Solutions Problem 5-1. Skip
Introduction to Algorithms November 4, 2005 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/18.410J Professors Erik D. Demaine and Charles E. Leiserson Handout 21 Problem Set 5 Solutions Problem 5-1. Skip
CS127: B-Trees. B-Trees
 CS127: B-Trees B-Trees 1 Data Layout on Disk Track: one ring Sector: one pie-shaped piece. Block: intersection of a track and a sector. Disk Based Dictionary Structures Use a disk-based method when the
CS127: B-Trees B-Trees 1 Data Layout on Disk Track: one ring Sector: one pie-shaped piece. Block: intersection of a track and a sector. Disk Based Dictionary Structures Use a disk-based method when the
Insertion Sort: an algorithm for sorting an array
 Insertion Sort: an algorithm for sorting an array Let s use arrays to solve a problem that comes up often in programming, namely sorting. Suppose we have an array of objects that is in no particular order
Insertion Sort: an algorithm for sorting an array Let s use arrays to solve a problem that comes up often in programming, namely sorting. Suppose we have an array of objects that is in no particular order
Algorithms. AVL Tree
 Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Recursion: The Beginning
 Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland This lecture is the inception of a powerful technique called recursion. If used judiciously, this technique can simplify the design of an algorithm significantly,
Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland This lecture is the inception of a powerful technique called recursion. If used judiciously, this technique can simplify the design of an algorithm significantly,
p 2<1 x+y A B C D E G H L M P Q R S V X x--y
 Skip List Skip List Marko Berezovský PAL 2015 p 2
Skip List Skip List Marko Berezovský PAL 2015 p 2
Ch04 Balanced Search Trees
 Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 05 Ch0 Balanced Search Trees v 3 8 z Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries,
Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 05 Ch0 Balanced Search Trees v 3 8 z Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries,
- Wikipedia Commons. Intro Problem Solving in Computer Science 2011 McQuain
 Recursion Recursion 1 Around the year 1900 the illustration of the "nurse" appeared on Droste's cocoa tins. This is most probably invented by the commercial artist Jan (Johannes) Musset, who had been inspired
Recursion Recursion 1 Around the year 1900 the illustration of the "nurse" appeared on Droste's cocoa tins. This is most probably invented by the commercial artist Jan (Johannes) Musset, who had been inspired
p 2<1 x+y A A C E E G H I L M N P R S X x--y
 Skip List Skip List ACM ICPC Maraton Prague 2015 p 2
Skip List Skip List ACM ICPC Maraton Prague 2015 p 2
Financial Statement Generator Script
 Financial Statement Generator Script Clip Link: http://www.eshbel.com/movie_search/financial_statement_generator.htm. instructions Note: Yellow highlights indicate action Introduction (00:00-01:12) This
Financial Statement Generator Script Clip Link: http://www.eshbel.com/movie_search/financial_statement_generator.htm. instructions Note: Yellow highlights indicate action Introduction (00:00-01:12) This
Problem Set 4 Solutions
 Introduction to Algorithms October 24, 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/18.410J Professors Shafi Goldwasser and Silvio Micali Handout 18 Problem 4-1. Problem Set 4 Solutions Reconstructing
Introduction to Algorithms October 24, 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/18.410J Professors Shafi Goldwasser and Silvio Micali Handout 18 Problem 4-1. Problem Set 4 Solutions Reconstructing
ECE608 - Chapter 16 answers
 ¼ À ÈÌ Ê ½ ÈÊÇ Ä ÅË ½µ ½ º½¹ ¾µ ½ º½¹ µ ½ º¾¹½ µ ½ º¾¹¾ µ ½ º¾¹ µ ½ º ¹ µ ½ º ¹ µ ½ ¹½ ½ ECE68 - Chapter 6 answers () CLR 6.-4 Let S be the set of n activities. The obvious solution of using Greedy-Activity-
¼ À ÈÌ Ê ½ ÈÊÇ Ä ÅË ½µ ½ º½¹ ¾µ ½ º½¹ µ ½ º¾¹½ µ ½ º¾¹¾ µ ½ º¾¹ µ ½ º ¹ µ ½ º ¹ µ ½ ¹½ ½ ECE68 - Chapter 6 answers () CLR 6.-4 Let S be the set of n activities. The obvious solution of using Greedy-Activity-
(Refer Slide Time: 1:27)
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 1 Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms Welcome to data
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture 1 Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms Welcome to data
Conditionals and Loops
 Conditionals and Loops Conditionals and Loops Now we will examine programming statements that allow us to: make decisions repeat processing steps in a loop Chapter 5 focuses on: boolean expressions conditional
Conditionals and Loops Conditionals and Loops Now we will examine programming statements that allow us to: make decisions repeat processing steps in a loop Chapter 5 focuses on: boolean expressions conditional
III Data Structures. Dynamic sets
 III Data Structures Elementary Data Structures Hash Tables Binary Search Trees Red-Black Trees Dynamic sets Sets are fundamental to computer science Algorithms may require several different types of operations
III Data Structures Elementary Data Structures Hash Tables Binary Search Trees Red-Black Trees Dynamic sets Sets are fundamental to computer science Algorithms may require several different types of operations
CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6
 CS Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6 Priority Queues and Heaps In this lecture, we will discuss another important ADT: PriorityQueue. Like stacks and queues, priority queues store arbitrary collections
CS Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6 Priority Queues and Heaps In this lecture, we will discuss another important ADT: PriorityQueue. Like stacks and queues, priority queues store arbitrary collections
Recursion. notes Chapter 8
 Recursion notes Chapter 8 1 Tower of Hanoi A B C move the stack of n disks from A to C can move one disk at a time from the top of one stack onto another stack cannot move a larger disk onto a smaller
Recursion notes Chapter 8 1 Tower of Hanoi A B C move the stack of n disks from A to C can move one disk at a time from the top of one stack onto another stack cannot move a larger disk onto a smaller
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science University of Southern Denmark, Odense. Exercises for Week 47 on. Online Algorithms
 Department of Mathematics and Computer Science University of Southern Denmark, Odense November 7, 06 KSL Exercises for Week 7 on Online Algorithms a topic in DM5 Introduction to Computer Science Kim Skak
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science University of Southern Denmark, Odense November 7, 06 KSL Exercises for Week 7 on Online Algorithms a topic in DM5 Introduction to Computer Science Kim Skak
Recursive Thinking. Chapter 8: Recursion. Recursive Definitions. Recursion. Java Software Solutions for AP* Computer Science A 2nd Edition
 Chapter 8: Recursion Presentation slides for Recursive Thinking Recursion is a programming technique in which a method can call itself to solve a problem Java Software Solutions for AP* Computer Science
Chapter 8: Recursion Presentation slides for Recursive Thinking Recursion is a programming technique in which a method can call itself to solve a problem Java Software Solutions for AP* Computer Science
Lecture Notes on Tries
 Lecture Notes on Tries 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Thomas Cortina, Frank Pfenning, Rob Simmons, Penny Anderson Lecture 22 June 20, 2014 1 Introduction In the data structures implementing
Lecture Notes on Tries 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Thomas Cortina, Frank Pfenning, Rob Simmons, Penny Anderson Lecture 22 June 20, 2014 1 Introduction In the data structures implementing
We have used both of the last two claims in previous algorithms and therefore their proof is omitted.
 Homework 3 Question 1 The algorithm will be based on the following logic: If an edge ( ) is deleted from the spanning tree, let and be the trees that were created, rooted at and respectively Adding any
Homework 3 Question 1 The algorithm will be based on the following logic: If an edge ( ) is deleted from the spanning tree, let and be the trees that were created, rooted at and respectively Adding any
Operations on Heap Tree The major operations required to be performed on a heap tree are Insertion, Deletion, and Merging.
 Priority Queue, Heap and Heap Sort In this time, we will study Priority queue, heap and heap sort. Heap is a data structure, which permits one to insert elements into a set and also to find the largest
Priority Queue, Heap and Heap Sort In this time, we will study Priority queue, heap and heap sort. Heap is a data structure, which permits one to insert elements into a set and also to find the largest
EECS 311 Data Structures Midterm Exam Don t Panic!
 April 5, 7 EECS Data Structures Midterm Exam Don t Panic!. ( pts) In each box below, show the AVL trees that result from the successive addition of the given elements. Show the nodes, links and balance
April 5, 7 EECS Data Structures Midterm Exam Don t Panic!. ( pts) In each box below, show the AVL trees that result from the successive addition of the given elements. Show the nodes, links and balance
Photoshop tutorial: Final Product in Photoshop:
 Disclaimer: There are many, many ways to approach web design. This tutorial is neither the most cutting-edge nor most efficient. Instead, this tutorial is set-up to show you as many functions in Photoshop
Disclaimer: There are many, many ways to approach web design. This tutorial is neither the most cutting-edge nor most efficient. Instead, this tutorial is set-up to show you as many functions in Photoshop
CS4311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Lecture 1: Getting Started
 CS4311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 1: Getting Started 1 Study a few simple algorithms for sorting Insertion Sort Selection Sort Merge Sort About this lecture Show why these algorithms are
CS4311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 1: Getting Started 1 Study a few simple algorithms for sorting Insertion Sort Selection Sort Merge Sort About this lecture Show why these algorithms are
Introduction to Internet of Things Prof. Sudip Misra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Introduction to Internet of Things Prof. Sudip Misra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 23 Introduction to Arduino- II Hi. Now, we will continue
Introduction to Internet of Things Prof. Sudip Misra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 23 Introduction to Arduino- II Hi. Now, we will continue
Lecture 4: Inter-Process Communication (Jan 27, 2005)
 Lecture 4: Inter-Process Communication (Jan 27, 2005) February 17, 2005 1 Review Q: What is the other command that seems to go hand-in-hand with fork()? A: exec* (6 variants of this command) Q: Suppose
Lecture 4: Inter-Process Communication (Jan 27, 2005) February 17, 2005 1 Review Q: What is the other command that seems to go hand-in-hand with fork()? A: exec* (6 variants of this command) Q: Suppose
1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1
![1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1](/thumbs/85/92778785.jpg) Asymptotics, Recurrence and Basic Algorithms 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 2. O(n) 2. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = T(n/2) + n, T(1)
Asymptotics, Recurrence and Basic Algorithms 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 2. O(n) 2. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = T(n/2) + n, T(1)
APCS-AB: Java. Recursion in Java December 12, week14 1
 APCS-AB: Java Recursion in Java December 12, 2005 week14 1 Check point Double Linked List - extra project grade Must turn in today MBCS - Chapter 1 Installation Exercises Analysis Questions week14 2 Scheme
APCS-AB: Java Recursion in Java December 12, 2005 week14 1 Check point Double Linked List - extra project grade Must turn in today MBCS - Chapter 1 Installation Exercises Analysis Questions week14 2 Scheme
Sankalchand Patel College of Engineering - Visnagar Department of Computer Engineering and Information Technology. Assignment
 Class: V - CE Sankalchand Patel College of Engineering - Visnagar Department of Computer Engineering and Information Technology Sub: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Analysis of Algorithm: Assignment
Class: V - CE Sankalchand Patel College of Engineering - Visnagar Department of Computer Engineering and Information Technology Sub: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Analysis of Algorithm: Assignment
The Probabilistic Method
 The Probabilistic Method Po-Shen Loh June 2010 1 Warm-up 1. (Russia 1996/4 In the Duma there are 1600 delegates, who have formed 16000 committees of 80 persons each. Prove that one can find two committees
The Probabilistic Method Po-Shen Loh June 2010 1 Warm-up 1. (Russia 1996/4 In the Duma there are 1600 delegates, who have formed 16000 committees of 80 persons each. Prove that one can find two committees
NAME: c. (true or false) The median is always stored at the root of a binary search tree.
 EE 322C Spring 2009 (Chase) Exam 2: READ THIS FIRST. Please use the back side of each page for scratch paper. For some of the questions you may need to think quite a bit before you write down an answer.
EE 322C Spring 2009 (Chase) Exam 2: READ THIS FIRST. Please use the back side of each page for scratch paper. For some of the questions you may need to think quite a bit before you write down an answer.
CSE 332 Spring 2014: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators)
 Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Spring 2014: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Spring 2014: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Lecture Notes on Tries
 Lecture Notes on Tries 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Thomas Cortina, Frank Pfenning, Rob Simmons, Penny Anderson Lecture 21 November 10, 2014 1 Introduction In the data structures implementing
Lecture Notes on Tries 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Thomas Cortina, Frank Pfenning, Rob Simmons, Penny Anderson Lecture 21 November 10, 2014 1 Introduction In the data structures implementing
Fall 09, Homework 5
 5-38 Fall 09, Homework 5 Due: Wednesday, November 8th, beginning of the class You can work in a group of up to two people. This group does not need to be the same group as for the other homeworks. You
5-38 Fall 09, Homework 5 Due: Wednesday, November 8th, beginning of the class You can work in a group of up to two people. This group does not need to be the same group as for the other homeworks. You
LECTURE NOTES ON PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTAL USING C++ LANGUAGE
 Department of Software The University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES ON PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTAL USING C++ LANGUAGE By Collage of Information Technology, University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher_hussein@yahoo.com
Department of Software The University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES ON PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTAL USING C++ LANGUAGE By Collage of Information Technology, University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher_hussein@yahoo.com
CSE638: Advanced Algorithms, Spring 2013 Date: March 26. Homework #2. ( Due: April 16 )
 CSE638: Advanced Algorithms, Spring 2013 Date: March 26 Homework #2 ( Due: April 16 ) Task 1. [ 40 Points ] Parallel BFS with Cilk s Work Stealing. (a) [ 20 Points ] In homework 1 we analyzed and implemented
CSE638: Advanced Algorithms, Spring 2013 Date: March 26 Homework #2 ( Due: April 16 ) Task 1. [ 40 Points ] Parallel BFS with Cilk s Work Stealing. (a) [ 20 Points ] In homework 1 we analyzed and implemented
Jump Statements. The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls.
 Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Data structures are often needed to provide organization for large sets of data.
 Motivation Data structures are often needed to provide organization for large sets of data. Skip Lists However, traditional approaches offer a tradeoff between insertion/deletion and search performance:
Motivation Data structures are often needed to provide organization for large sets of data. Skip Lists However, traditional approaches offer a tradeoff between insertion/deletion and search performance:
Solutions. Suppose we insert all elements of U into the table, and let n(b) be the number of elements of U that hash to bucket b. Then.
 Assignment 3 1. Exercise [11.2-3 on p. 229] Modify hashing by chaining (i.e., bucketvector with BucketType = List) so that BucketType = OrderedList. How is the runtime of search, insert, and remove affected?
Assignment 3 1. Exercise [11.2-3 on p. 229] Modify hashing by chaining (i.e., bucketvector with BucketType = List) so that BucketType = OrderedList. How is the runtime of search, insert, and remove affected?
BST Deletion. First, we need to find the value which is easy because we can just use the method we developed for BST_Search.
 BST Deletion Deleting a value from a Binary Search Tree is a bit more complicated than inserting a value, but we will deal with the steps one at a time. First, we need to find the value which is easy because
BST Deletion Deleting a value from a Binary Search Tree is a bit more complicated than inserting a value, but we will deal with the steps one at a time. First, we need to find the value which is easy because
Search Trees (Ch. 9) > = Binary Search Trees 1
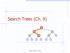 Search Trees (Ch. 9) < 6 > = 1 4 8 9 Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionaries Keys are assumed to come from a total order. New operations: closestbefore(k) closestafter(k) Binary Search Trees Binary
Search Trees (Ch. 9) < 6 > = 1 4 8 9 Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionaries Keys are assumed to come from a total order. New operations: closestbefore(k) closestafter(k) Binary Search Trees Binary
Transform & Conquer. Presorting
 Transform & Conquer Definition Transform & Conquer is a general algorithm design technique which works in two stages. STAGE : (Transformation stage): The problem s instance is modified, more amenable to
Transform & Conquer Definition Transform & Conquer is a general algorithm design technique which works in two stages. STAGE : (Transformation stage): The problem s instance is modified, more amenable to
Splay Trees. (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 27
 Splay Trees (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 27 Basic Idea Invented by Sleator and Tarjan (1985) Blind rebalancing no height info kept! Worst-case time per operation is O(n)
Splay Trees (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 27 Basic Idea Invented by Sleator and Tarjan (1985) Blind rebalancing no height info kept! Worst-case time per operation is O(n)
CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6
 CS Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6 Priority Queues and Heaps In this lecture, we will discuss priority queues, another important ADT. As stacks and queues, priority queues store arbitrary collections
CS Algorithms and Data Structures Note 6 Priority Queues and Heaps In this lecture, we will discuss priority queues, another important ADT. As stacks and queues, priority queues store arbitrary collections
Skip Lists in Julia. Drew Minnear. Massachusetts Institute of Technology. December 8, 2013
 in Julia Drew Minnear Massachusetts Institute of Technology December 8, 2013 Drew Minnear (MIT) in Julia December 8, 2013 1 / 14 What are? Introduction Randomized data structure invented by William Pugh
in Julia Drew Minnear Massachusetts Institute of Technology December 8, 2013 Drew Minnear (MIT) in Julia December 8, 2013 1 / 14 What are? Introduction Randomized data structure invented by William Pugh
Lecture 17 Priority Queues
 Lecture 17 Priority Queues 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2018) Frank Pfenning, Rob Simmons In this lecture we will look at priority queues as an abstract type and discuss several
Lecture 17 Priority Queues 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2018) Frank Pfenning, Rob Simmons In this lecture we will look at priority queues as an abstract type and discuss several
Recursion: The Beginning
 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong This lecture will introduce a useful technique called recursion. If used judiciously, this technique often leads to elegant
Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong This lecture will introduce a useful technique called recursion. If used judiciously, this technique often leads to elegant
[ DATA STRUCTURES ] Fig. (1) : A Tree
![[ DATA STRUCTURES ] Fig. (1) : A Tree [ DATA STRUCTURES ] Fig. (1) : A Tree](/thumbs/80/82537139.jpg) [ DATA STRUCTURES ] Chapter - 07 : Trees A Tree is a non-linear data structure in which items are arranged in a sorted sequence. It is used to represent hierarchical relationship existing amongst several
[ DATA STRUCTURES ] Chapter - 07 : Trees A Tree is a non-linear data structure in which items are arranged in a sorted sequence. It is used to represent hierarchical relationship existing amongst several
8. Binary Search Tree
 8 Binary Search Tree Searching Basic Search Sequential Search : Unordered Lists Binary Search : Ordered Lists Tree Search Binary Search Tree Balanced Search Trees (Skipped) Sequential Search int Seq-Search
8 Binary Search Tree Searching Basic Search Sequential Search : Unordered Lists Binary Search : Ordered Lists Tree Search Binary Search Tree Balanced Search Trees (Skipped) Sequential Search int Seq-Search
