Semantic Multicast for Content-based Stream Dissemination
|
|
|
- Tobias Sparks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Semantic Multicast for Content-based Stream Dissemination Olga Papaemmanouil Brown University Uğur Çetintemel Brown University
2 Stream Dissemination Applications Clients Data Providers Push-based applications Environmental monitoring Real-time financial services Characteristics High data volume Fast stream rates Highly dispersed sources & destinations 2
3 Content-based Dissemination Centralized filtering Single node gathers profiles Unicast to destinations e.g., XFilter [Altinel et al., 2000] Distributed content-based routing Interest-based routing Predefined acyclic overlay network e.g. SIENA [Carzaniga et al., 2001] Predicate-based filtering network Upstream profile aggregation Content filtering of each message at each hop x>10 A x<20 B x>10 C 1 S 1 x<5 D x<5 C 2 C 1 x>10 C 2 x<5 3
4 Content-based routing overhead Processing cost Local filtering of each message Compression/decompression for XML streams Bandwidth consumption Missed tree optimization opportunities Different client sets request different sub-streams One spanning tree of the whole network is not the best solution for low cost 4
5 Our approach: Semantic Multicast Constructs content-based (a.k.a. semantic) multicast channels Independent overlay dissemination trees Channels characterized by their content Advantages Decreases processing cost Eliminates local filtering at interior brokers Decreases overall bandwidth requirements Allows QoS-aware multicast trees 5
6 Content-based Channelization SemCast decides: Number of channels Content of channels Clients subscriptions to channels Channel implementation Operational goals No false exclusion Low run-time cost : Overall bandwidth consumption Minimize redundancy among channels content Create efficient multicast trees 6
7 System Model Publishers Source brokers (S) Receive XML streams from publishers Gateway brokers (GB) Receive XPath profiles from subscribers Rendezvous points (RP) Roots of channels Interior brokers (I) Forward incoming messages Coordinator Identifies content of channels Coordinator S S S RP RP RP I GB GB GB GB I GB Subscribers I 7
8 SemCast Overview Membership Management Syntactical analysis of profiles Dynamic Channelization Exploit statistical information Reorganize channels 8
9 Membership Management Adding subscriptions Gateway broker forwards unsatisfied subscriptions to coordinator Coordinator creates a new channel for any subscription not covered by existing channels Removing subscriptions Gateway broker forwards request to upstream brokers Interior brokers remove channel entries from routing tables Coordinator removes channel if there are no more remaining clients 9
10 Profile Containment Hierarchies Identify channels covering a profile based on profile syntax Containment algorithms for XPath expressions. e.g. [Wood, 2003] Maintain syntax-based containment hierarchies Parent profile covers children Root is the channel s content expression Channel1 Channel 2 a//* d//* a/b a/c d/*/g d/f/g 10
11 Dynamic Channelization Syntactic analysis might cause high data redundancy Undiscovered full/partial overlapping profiles Assign similar profiles to different channels Forward matching messages to more than one channel Use statistics to re-evaluate channelization Profile overlap Run-time stream rate 11
12 Profile Overlapping Relations SemCast exploits also partial overlap among profiles Partial overlap P i k-overlaps with P j : Containment match( PP ) k i j Pi! Pj, k = match( P) Special case of partial overlap, k=1 P j covers P i :messages matching P i are subset of those matching P j i 12
13 Rate-based Hierarchies P j is parent of P i if { k }! P # P and k = max k r P # P 1 i j j i j i P, i" j j r = rate of non-overlapping part between P and P j! i j i P j is more general than P i If multiple candidate parents exist Maximum overlap Low stream rate of redundant messages 13
14 Hierarchy Merging Highly diverse profiles may increase cost High message replication Large number of channels Large routing tables at interior brokers Merging hierarchies with partial overlap reduces cost Use a cost-based model Merge pairs with maximum benefit in bandwidth High profile overlap Efficient single multicast tree 14
15 Multicast Tree Construction Base low cost heuristic Request channel s destinations from RP Find min-cost path to all destinations in the channel Connect to closest one C 2 RP S C 1 C 3 15
16 Simulation Metrics Processing cost Eliminate need for local filtering (not in this paper) Bandwidth efficiency Approaches Unicast approach SPT: Shortest Path Tree approach Distributed pub-sub system [Carzaniga et al., 2001] SemCast: Distributed content-based channelization Optimal: Centralized Steiner tree construction Simulation environment Random graph generated by GT-ITM Up to 700 nodes and 7000 profiles 16
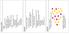
17 Bandwidth efficiency % cost degradation over Optimal Unicast SPT SemCas t Heuris tic profile selectivity percentage Network size =700 #profiles =
18 Scalability % cost degradation over Optimal Unicast SPT SemCast Heuristic netw ork size (profile selectivity factor = 0.7%) 18
19 Related Work Publish-Subscribe Systems Centralized approaches: XML Filtering XFilter [Altinel et al., 2000], YFilter [Diao et al., 2002] XTrie [Chan et al., 2002] Distributed approaches: Content- based Routing Gryphon [Opyrchal et al., 2000] SIENA [Carzaniga et al., 2001] Application-Level Multicast SCRIBE [Castro et al., 2002] CAN-based Multicast [Ratnasamy et al., 2001] 19
20 Conclusions & Ongoing Work SemCast Performs semantic split of incoming streams Eliminates local filtering in interior brokers Improves bandwidth consumption Ongoing work SemCast prototype Demonstrate processing cost benefit Investigate affects of network topology Storage-oriented model: caching XML nodes 20
Architecture and Implementation of a Content-based Data Dissemination System
 Architecture and Implementation of a Content-based Data Dissemination System Austin Park Brown University austinp@cs.brown.edu ABSTRACT SemCast is a content-based dissemination model for large-scale data
Architecture and Implementation of a Content-based Data Dissemination System Austin Park Brown University austinp@cs.brown.edu ABSTRACT SemCast is a content-based dissemination model for large-scale data
XFlow: Dynamic Dissemination Trees for Extensible In-Network Stream Processing
 XFlow: Dynamic Dissemination Trees for Extensible In-Network Stream Processing Olga Papaemmanouil, Uğur Çetintemel, John Jannotti Department of Computer Science, Brown University {olga, ugur, jj}@cs.brown.edu
XFlow: Dynamic Dissemination Trees for Extensible In-Network Stream Processing Olga Papaemmanouil, Uğur Çetintemel, John Jannotti Department of Computer Science, Brown University {olga, ugur, jj}@cs.brown.edu
Extensible Optimization in Overlay Dissemination Trees
 Extensible Optimization in Overlay Dissemination Trees Olga Papaemmanouil, Yanif Ahmad, Uğur Çetintemel, John Jannotti, Yenel Yildirim Department of Computer Science Brown University {olga, yna, ugur,
Extensible Optimization in Overlay Dissemination Trees Olga Papaemmanouil, Yanif Ahmad, Uğur Çetintemel, John Jannotti, Yenel Yildirim Department of Computer Science Brown University {olga, yna, ugur,
Application-aware Overlay Networks for Data Dissemination
 Application-aware Overlay Networks for Data Dissemination Olga Papaemmanouil Yanif Ahmad Uğur Çetintemel John Jannotti Brown University, Department of Computer Science, Providence, RI USA E-mail: {olga,yna,ugur,jj}@cs.brown.edu
Application-aware Overlay Networks for Data Dissemination Olga Papaemmanouil Yanif Ahmad Uğur Çetintemel John Jannotti Brown University, Department of Computer Science, Providence, RI USA E-mail: {olga,yna,ugur,jj}@cs.brown.edu
IP Multicast Technology Overview
 IP multicast is a bandwidth-conserving technology that reduces traffic by delivering a single stream of information simultaneously to potentially thousands of businesses and homes. Applications that take
IP multicast is a bandwidth-conserving technology that reduces traffic by delivering a single stream of information simultaneously to potentially thousands of businesses and homes. Applications that take
IP Multicast. Overview. Casts. Tarik Čičić University of Oslo December 2001
 IP Multicast Tarik Čičić University of Oslo December 00 Overview One-to-many communication, why and how Algorithmic approach (IP) multicast protocols: host-router intra-domain (router-router) inter-domain
IP Multicast Tarik Čičić University of Oslo December 00 Overview One-to-many communication, why and how Algorithmic approach (IP) multicast protocols: host-router intra-domain (router-router) inter-domain
Adaptive In-Network Query Deployment for Shared Stream Processing Environments
 Adaptive In-Network Query Deployment for Shared Stream Processing Environments Olga Papaemmanouil Brown University olga@cs.brown.edu Sujoy Basu HP Labs basus@hpl.hp.com Sujata Banerjee HP Labs sujata@hpl.hp.com
Adaptive In-Network Query Deployment for Shared Stream Processing Environments Olga Papaemmanouil Brown University olga@cs.brown.edu Sujoy Basu HP Labs basus@hpl.hp.com Sujata Banerjee HP Labs sujata@hpl.hp.com
Multicast Communications. Tarik Čičić, 4. March. 2016
 Multicast Communications Tarik Čičić, 4. March. 06 Overview One-to-many communication, why and how Algorithmic approach: Steiner trees Practical algorithms Multicast tree types Basic concepts in multicast
Multicast Communications Tarik Čičić, 4. March. 06 Overview One-to-many communication, why and how Algorithmic approach: Steiner trees Practical algorithms Multicast tree types Basic concepts in multicast
Multicast Communications
 Multicast Communications Multicast communications refers to one-to-many or many-tomany communications. Unicast Broadcast Multicast Dragkedja IP Multicasting refers to the implementation of multicast communication
Multicast Communications Multicast communications refers to one-to-many or many-tomany communications. Unicast Broadcast Multicast Dragkedja IP Multicasting refers to the implementation of multicast communication
XML Filtering Technologies
 XML Filtering Technologies Introduction Data exchange between applications: use XML Messages processed by an XML Message Broker Examples Publish/subscribe systems [Altinel 00] XML message routing [Snoeren
XML Filtering Technologies Introduction Data exchange between applications: use XML Messages processed by an XML Message Broker Examples Publish/subscribe systems [Altinel 00] XML message routing [Snoeren
! Naive n-way unicast does not scale. ! IP multicast to the rescue. ! Extends IP architecture for efficient multi-point delivery. !
 Bayeux: An Architecture for Scalable and Fault-tolerant Wide-area Data Dissemination ACM NOSSDAV 001 Shelley Q. Zhuang, Ben Y. Zhao, Anthony D. Joseph, Randy H. Katz, John D. Kubiatowicz {shelleyz, ravenben,
Bayeux: An Architecture for Scalable and Fault-tolerant Wide-area Data Dissemination ACM NOSSDAV 001 Shelley Q. Zhuang, Ben Y. Zhao, Anthony D. Joseph, Randy H. Katz, John D. Kubiatowicz {shelleyz, ravenben,
Overlay Multicast. Application Layer Multicast. Structured Overlays Unstructured Overlays. CAN Flooding Centralised. Scribe/SplitStream Distributed
 Overlay Multicast Application Layer Multicast Structured Overlays Unstructured Overlays CAN Flooding Centralised Scribe/SplitStream Distributed PeerCast 1 Prof. Dr. Thomas Schmidt http:/www.informatik.haw-hamburg.de/~schmidt
Overlay Multicast Application Layer Multicast Structured Overlays Unstructured Overlays CAN Flooding Centralised Scribe/SplitStream Distributed PeerCast 1 Prof. Dr. Thomas Schmidt http:/www.informatik.haw-hamburg.de/~schmidt
What is Multicasting? Multicasting Fundamentals. Unicast Transmission. Agenda. L70 - Multicasting Fundamentals. L70 - Multicasting Fundamentals
 What is Multicasting? Multicasting Fundamentals Unicast transmission transmitting a packet to one receiver point-to-point transmission used by most applications today Multicast transmission transmitting
What is Multicasting? Multicasting Fundamentals Unicast transmission transmitting a packet to one receiver point-to-point transmission used by most applications today Multicast transmission transmitting
Bayeux: An Architecture for Scalable and Fault Tolerant Wide area Data Dissemination
 Bayeux: An Architecture for Scalable and Fault Tolerant Wide area Data Dissemination By Shelley Zhuang,Ben Zhao,Anthony Joseph, Randy Katz,John Kubiatowicz Introduction Multimedia Streaming typically involves
Bayeux: An Architecture for Scalable and Fault Tolerant Wide area Data Dissemination By Shelley Zhuang,Ben Zhao,Anthony Joseph, Randy Katz,John Kubiatowicz Introduction Multimedia Streaming typically involves
A Routing Scheme for Content-Based Networking
 A Routing Scheme for Content-Based Networking Antonio Carzaniga, Matthew J. Rutherford, and Alexander L. Wolf Department of Computer Science University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado 839-43 USA Email: {carzanig,rutherfo,alw}@cs.colorado.edu
A Routing Scheme for Content-Based Networking Antonio Carzaniga, Matthew J. Rutherford, and Alexander L. Wolf Department of Computer Science University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado 839-43 USA Email: {carzanig,rutherfo,alw}@cs.colorado.edu
DATA COMMUNICATOIN NETWORKING
 DATA COMMUNICATOIN NETWORKING Instructor: Ouldooz Baghban Karimi Course Book & Slides: Computer Networking, A Top-Down Approach By: Kurose, Ross Introduction Course Overview Basics of Computer Networks
DATA COMMUNICATOIN NETWORKING Instructor: Ouldooz Baghban Karimi Course Book & Slides: Computer Networking, A Top-Down Approach By: Kurose, Ross Introduction Course Overview Basics of Computer Networks
SFilter: A Simple and Scalable Filter for XML Streams
 SFilter: A Simple and Scalable Filter for XML Streams Abdul Nizar M., G. Suresh Babu, P. Sreenivasa Kumar Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai - 600 036 INDIA nizar@cse.iitm.ac.in, sureshbabuau@gmail.com,
SFilter: A Simple and Scalable Filter for XML Streams Abdul Nizar M., G. Suresh Babu, P. Sreenivasa Kumar Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai - 600 036 INDIA nizar@cse.iitm.ac.in, sureshbabuau@gmail.com,
Design of Next Generation Internet Based on Application-Oriented Networking
 Design of Next Generation Internet Based on Application-Oriented Networking Yu Cheng Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Illinois Institute of Technology Chicago, Illinois, USA cheng@iit.edu
Design of Next Generation Internet Based on Application-Oriented Networking Yu Cheng Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Illinois Institute of Technology Chicago, Illinois, USA cheng@iit.edu
IP Multicast Technology Overview
 IP multicast is a bandwidth-conserving technology that reduces traffic by delivering a single stream of information simultaneously to potentially thousands of businesses and homes. Applications that take
IP multicast is a bandwidth-conserving technology that reduces traffic by delivering a single stream of information simultaneously to potentially thousands of businesses and homes. Applications that take
Subscription Aggregation for Scalability and Efficiency in XPath/XML-Based Publish/Subscribe Systems
 Subscription Aggregation for Scalability and Efficiency in XPath/XML-Based Publish/Subscribe Systems Abdulbaset Gaddah, Thomas Kunz Department of Systems and Computer Engineering Carleton University, 1125
Subscription Aggregation for Scalability and Efficiency in XPath/XML-Based Publish/Subscribe Systems Abdulbaset Gaddah, Thomas Kunz Department of Systems and Computer Engineering Carleton University, 1125
Scalable Application Layer Multicast
 Scalable Application Layer Multicast Suman Banerjee Bobby Bhattacharjee Christopher Kommareddy http://www.cs.umd.edu/projects/nice Group Communication A C A C 1 2 1 2 B D B D Network-layer Multicast Replication
Scalable Application Layer Multicast Suman Banerjee Bobby Bhattacharjee Christopher Kommareddy http://www.cs.umd.edu/projects/nice Group Communication A C A C 1 2 1 2 B D B D Network-layer Multicast Replication
ASM. Engineering Workshops
 1 ASM 2 ASM Allows SPTs and RPTs RP: Matches senders with receivers Provides network source discovery Typically uses RPT to bootstrap SPT RPs can be learned via: Static configuration recommended Anycast-RP
1 ASM 2 ASM Allows SPTs and RPTs RP: Matches senders with receivers Provides network source discovery Typically uses RPT to bootstrap SPT RPs can be learned via: Static configuration recommended Anycast-RP
Architectural Approaches for Social Networks. Presenter: Qian Li
 Architectural Approaches for Social Networks Presenter: Qian Li The Gossple Anonymous Social Network Marin Bertier, Davide Frey, Rachid Guerraoui, AnneMarie Kermarrec and Vincent Leroy Gossple overview
Architectural Approaches for Social Networks Presenter: Qian Li The Gossple Anonymous Social Network Marin Bertier, Davide Frey, Rachid Guerraoui, AnneMarie Kermarrec and Vincent Leroy Gossple overview
Staying FIT: Efficient Load Shedding Techniques for Distributed Stream Processing
 Staying FIT: Efficient Load Shedding Techniques for Distributed Stream Processing Nesime Tatbul Uğur Çetintemel Stan Zdonik Talk Outline Problem Introduction Approach Overview Advance Planning with an
Staying FIT: Efficient Load Shedding Techniques for Distributed Stream Processing Nesime Tatbul Uğur Çetintemel Stan Zdonik Talk Outline Problem Introduction Approach Overview Advance Planning with an
BGP. Daniel Zappala. CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University
 Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University 2/20 Scaling Routing for the Internet scale 200 million destinations - can t store all destinations or all prefixes in routing tables
Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University 2/20 Scaling Routing for the Internet scale 200 million destinations - can t store all destinations or all prefixes in routing tables
Chapter 11 Chapter 6
 Routing Protocols References H. Karl and A. Willing. Protocols and Architectures for Wireless Sensor Networks. John Wiley & Sons, 2005. (Chapter 11) K. Sohraby, D. Minoli, and T. Znati. Wireless Sensor
Routing Protocols References H. Karl and A. Willing. Protocols and Architectures for Wireless Sensor Networks. John Wiley & Sons, 2005. (Chapter 11) K. Sohraby, D. Minoli, and T. Znati. Wireless Sensor
References. Forwarding. Introduction...
 References Routing Protocols H. Karl and A. Willing. Protocols and Architectures for Wireless Sensor Networks. John Wiley & Sons, 005. (Chapter 11) K. Sohraby, D. Minoli, and T. Znati. Wireless Sensor
References Routing Protocols H. Karl and A. Willing. Protocols and Architectures for Wireless Sensor Networks. John Wiley & Sons, 005. (Chapter 11) K. Sohraby, D. Minoli, and T. Znati. Wireless Sensor
Delaunay Triangulation Overlays
 HighPerf or mance Swi tchi ng and Routi ng Tele com Cent erw orksh op: Sept 4, 1 97. Delaunay Triangulation Overlays Jörg Liebeherr 2003 1 HyperCast Project HyperCast is a set of protocols for large-scale
HighPerf or mance Swi tchi ng and Routi ng Tele com Cent erw orksh op: Sept 4, 1 97. Delaunay Triangulation Overlays Jörg Liebeherr 2003 1 HyperCast Project HyperCast is a set of protocols for large-scale
IPv6 PIM. Based on the forwarding mechanism, IPv6 PIM falls into two modes:
 Overview Protocol Independent Multicast for IPv6 () provides IPv6 multicast forwarding by leveraging static routes or IPv6 unicast routing tables generated by any IPv6 unicast routing protocol, such as
Overview Protocol Independent Multicast for IPv6 () provides IPv6 multicast forwarding by leveraging static routes or IPv6 unicast routing tables generated by any IPv6 unicast routing protocol, such as
Indirect Communication
 Indirect Communication To do q Today q q Space and time (un)coupling Common techniques q Next time: Overlay networks xkdc Direct coupling communication With R-R, RPC, RMI Space coupled Sender knows the
Indirect Communication To do q Today q q Space and time (un)coupling Common techniques q Next time: Overlay networks xkdc Direct coupling communication With R-R, RPC, RMI Space coupled Sender knows the
Arvind Krishnamurthy Fall 2003
 Overlay Networks Arvind Krishnamurthy Fall 003 Internet Routing Internet routing is inefficient: Does not always pick the lowest latency paths Does not always pick paths with low drop rates Experimental
Overlay Networks Arvind Krishnamurthy Fall 003 Internet Routing Internet routing is inefficient: Does not always pick the lowest latency paths Does not always pick paths with low drop rates Experimental
On Minimizing Packet Loss Rate and Delay for Mesh-based P2P Streaming Services
 On Minimizing Packet Loss Rate and Delay for Mesh-based P2P Streaming Services Zhiyong Liu, CATR Prof. Zhili Sun, UniS Dr. Dan He, UniS Denian Shi, CATR Agenda Introduction Background Problem Statement
On Minimizing Packet Loss Rate and Delay for Mesh-based P2P Streaming Services Zhiyong Liu, CATR Prof. Zhili Sun, UniS Dr. Dan He, UniS Denian Shi, CATR Agenda Introduction Background Problem Statement
Implementing Multicast Service Reflection
 Implementing Multicast Service Reflection First Published: September 22, 2006 Last Updated: June 4, 2010 The Cisco Multicast Service Reflection feature provides the capability for users to translate externally
Implementing Multicast Service Reflection First Published: September 22, 2006 Last Updated: June 4, 2010 The Cisco Multicast Service Reflection feature provides the capability for users to translate externally
Distributed Core Multicast (DCM): a multicast routing protocol for many groups with few receivers
 Distributed Core Multicast (DCM): a multicast routing protocol for many groups with few receivers Ljubica Blazević Jean-Yves Le Boudec Institute for computer Communications and Applications (ICA) Swiss
Distributed Core Multicast (DCM): a multicast routing protocol for many groups with few receivers Ljubica Blazević Jean-Yves Le Boudec Institute for computer Communications and Applications (ICA) Swiss
Distributed Conditional Multicast Access for IP TV in High-Speed Wireless Networks (Destination Specific Multicast)
 137 Distributed Conditional Multicast Access for IP TV in High-Speed Wireless Networks (Destination Specific Multicast) 1, 2 Jan Fesl, 1 Richard Klee, 1 Marie Dolezalova 1 Institute of Applied Informatics,
137 Distributed Conditional Multicast Access for IP TV in High-Speed Wireless Networks (Destination Specific Multicast) 1, 2 Jan Fesl, 1 Richard Klee, 1 Marie Dolezalova 1 Institute of Applied Informatics,
Distributed Core Multicast (DCM): a multicast routing protocol for many groups with few receivers
 Distributed Core Multicast (DCM): a multicast routing protocol for many groups with few receivers Ljubica Blazević Jean-Yves Le Boudec Institute for computer Communications and Applications (ICA) Swiss
Distributed Core Multicast (DCM): a multicast routing protocol for many groups with few receivers Ljubica Blazević Jean-Yves Le Boudec Institute for computer Communications and Applications (ICA) Swiss
Contents. Overview Multicast = Send to a group of hosts. Overview. Overview. Implementation Issues. Motivation: ISPs charge by bandwidth
 EECS Contents Motivation Overview Implementation Issues Ethernet Multicast IGMP Routing Approaches Reliability Application Layer Multicast Summary Motivation: ISPs charge by bandwidth Broadcast Center
EECS Contents Motivation Overview Implementation Issues Ethernet Multicast IGMP Routing Approaches Reliability Application Layer Multicast Summary Motivation: ISPs charge by bandwidth Broadcast Center
Table of Contents 1 PIM Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 PIM Configuration 1-1 PIM Overview 1-1 Introduction to PIM-DM 1-2 How PIM-DM Works 1-2 Introduction to PIM-SM 1-4 How PIM-SM Works 1-5 Introduction to Administrative Scoping in PIM-SM
Table of Contents 1 PIM Configuration 1-1 PIM Overview 1-1 Introduction to PIM-DM 1-2 How PIM-DM Works 1-2 Introduction to PIM-SM 1-4 How PIM-SM Works 1-5 Introduction to Administrative Scoping in PIM-SM
Overlay Multicast/Broadcast
 Overlay Multicast/Broadcast Broadcast/Multicast Introduction Structured Overlays Application Layer Multicast Flooding: CAN & Prefix Flood. Unstructured Overlays Centralised Distributed Tree-based: Scribe/
Overlay Multicast/Broadcast Broadcast/Multicast Introduction Structured Overlays Application Layer Multicast Flooding: CAN & Prefix Flood. Unstructured Overlays Centralised Distributed Tree-based: Scribe/
Enhancement of the CBT Multicast Routing Protocol
 Enhancement of the CBT Multicast Routing Protocol Seok Joo Koh and Shin Gak Kang Protocol Engineering Center, ETRI, Korea E-mail: sjkoh@pec.etri.re.kr Abstract In this paper, we propose a simple practical
Enhancement of the CBT Multicast Routing Protocol Seok Joo Koh and Shin Gak Kang Protocol Engineering Center, ETRI, Korea E-mail: sjkoh@pec.etri.re.kr Abstract In this paper, we propose a simple practical
Many-to-Many Communications in HyperCast
 Many-to-Many Communications in HyperCast Jorg Liebeherr University of Virginia Jörg Liebeherr, 2001 HyperCast Project HyperCast is a set of protocols for large-scale overlay multicasting and peer-to-peer
Many-to-Many Communications in HyperCast Jorg Liebeherr University of Virginia Jörg Liebeherr, 2001 HyperCast Project HyperCast is a set of protocols for large-scale overlay multicasting and peer-to-peer
CCD: Efficient Customized Content Dissemination in Distributed Publish/Subscribe
 Dissemination in Distributed Publish/Subscribe H. Jafarpour, B. Hore, S. Mehrotra and N. Venkatasubramanian Information Systems Group Dept. of Computer Science UC Irvine 1 Customized content dissemination
Dissemination in Distributed Publish/Subscribe H. Jafarpour, B. Hore, S. Mehrotra and N. Venkatasubramanian Information Systems Group Dept. of Computer Science UC Irvine 1 Customized content dissemination
A Self-Organizing Crash-Resilient Topology Management System for Content-Based Publish/Subscribe
 A Self-Organizing Crash-Resilient Topology Management System for Content-Based Publish/Subscribe R. Baldoni, R. Beraldi, L. Querzoni and A. Virgillito Dipartimento di Informatica e Sistemistica Università
A Self-Organizing Crash-Resilient Topology Management System for Content-Based Publish/Subscribe R. Baldoni, R. Beraldi, L. Querzoni and A. Virgillito Dipartimento di Informatica e Sistemistica Università
Overlay Networks for Multimedia Contents Distribution
 Overlay Networks for Multimedia Contents Distribution Vittorio Palmisano vpalmisano@gmail.com 26 gennaio 2007 Outline 1 Mesh-based Multicast Networks 2 Tree-based Multicast Networks Overcast (Cisco, 2000)
Overlay Networks for Multimedia Contents Distribution Vittorio Palmisano vpalmisano@gmail.com 26 gennaio 2007 Outline 1 Mesh-based Multicast Networks 2 Tree-based Multicast Networks Overcast (Cisco, 2000)
Broadcast Routing. Multicast. Flooding. In-network duplication. deliver packets from source to all other nodes source duplication is inefficient:
 Broadcast Routing Multicast deliver packets from source to all other nodes source duplication is inefficient: duplicate duplicate creation/transmission duplicate source duplication in-network duplication
Broadcast Routing Multicast deliver packets from source to all other nodes source duplication is inefficient: duplicate duplicate creation/transmission duplicate source duplication in-network duplication
Top-Down Network Design, Ch. 7: Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols. Top-Down Network Design. Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
Data Communication. Guaranteed Delivery Based on Memorization
 Data Communication Guaranteed Delivery Based on Memorization Motivation Many greedy routing schemes perform well in dense networks Greedy routing has a small communication overhead Desirable to run Greedy
Data Communication Guaranteed Delivery Based on Memorization Motivation Many greedy routing schemes perform well in dense networks Greedy routing has a small communication overhead Desirable to run Greedy
Adaptive Content-Based Routing in General Overlay Topologies
 Adaptive Content-Based Routing in General Overlay Topologies Guoli Li, Vinod Muthusamy, and Hans-Arno Jacobsen University of Toronto gli@cs.toronto.edu, {vinod,jacobsen}@eecg.toronto.edu http://padres.msrg.toronto.edu
Adaptive Content-Based Routing in General Overlay Topologies Guoli Li, Vinod Muthusamy, and Hans-Arno Jacobsen University of Toronto gli@cs.toronto.edu, {vinod,jacobsen}@eecg.toronto.edu http://padres.msrg.toronto.edu
Configuring IP Multicast Routing
 CHAPTER 46 This chapter describes how to configure IP multicast routing on the Catalyst 3750-E or 3560-E switch. IP multicasting is a more efficient way to use network resources, especially for bandwidth-intensive
CHAPTER 46 This chapter describes how to configure IP multicast routing on the Catalyst 3750-E or 3560-E switch. IP multicasting is a more efficient way to use network resources, especially for bandwidth-intensive
CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018
 CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018 Network Layer V Dmitri Loguinov Texas A&M University April 17, 2018 Original slides copyright 1996-2004 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross Chapter 4:
CSCE 463/612 Networks and Distributed Processing Spring 2018 Network Layer V Dmitri Loguinov Texas A&M University April 17, 2018 Original slides copyright 1996-2004 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross Chapter 4:
Configuring a Rendezvous Point
 Version History Version Number Date Notes 1 03/15/2002 This document was created. The purpose of this document is to outline four recommended methods for configuring a rendezvous point (RP) in a Protocol
Version History Version Number Date Notes 1 03/15/2002 This document was created. The purpose of this document is to outline four recommended methods for configuring a rendezvous point (RP) in a Protocol
IP Multicast. What is multicast?
 IP Multicast 1 What is multicast? IP(v4) allows a host to send packets to a single host (unicast), or to all hosts (broadcast). Multicast allows a host to send packets to a subset of all host called a
IP Multicast 1 What is multicast? IP(v4) allows a host to send packets to a single host (unicast), or to all hosts (broadcast). Multicast allows a host to send packets to a subset of all host called a
Configuring IP Multicast Routing
 CHAPTER 45 This chapter describes how to configure IP multicast routing on the Catalyst 3750 Metro switch. IP multicasting is a more efficient way to use network resources, especially for bandwidth-intensive
CHAPTER 45 This chapter describes how to configure IP multicast routing on the Catalyst 3750 Metro switch. IP multicasting is a more efficient way to use network resources, especially for bandwidth-intensive
Peer-to-Peer Overlay Broker Networks in an Event-Based Middleware
 Peer-to-Peer Overlay Broker Networks in an Event-Based Middleware Peter R. Pietzuch Peter.Pietzuch@cl.cam.ac.uk University of Cambridge Computer Laboratory JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 FD, United Kingdom
Peer-to-Peer Overlay Broker Networks in an Event-Based Middleware Peter R. Pietzuch Peter.Pietzuch@cl.cam.ac.uk University of Cambridge Computer Laboratory JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 FD, United Kingdom
Content. 1. Introduction. 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm. 3. Simulation and Results. 4. Future Work. 5.
 Rahem Abri Content 1. Introduction 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm Path Discovery Reverse Path Setup Forward Path Setup Route Table Management Path Management Local Connectivity Management
Rahem Abri Content 1. Introduction 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm Path Discovery Reverse Path Setup Forward Path Setup Route Table Management Path Management Local Connectivity Management
Lab 7-3 Routing IP Multicast with PIM Sparse Mode
 Lab 7-3 Routing IP Multicast with PIM Sparse Mode Learning Objectives Implement and verify PIM-SM operation and adjacencies Implement and verify the use of a static rendezvous point Observe the shared
Lab 7-3 Routing IP Multicast with PIM Sparse Mode Learning Objectives Implement and verify PIM-SM operation and adjacencies Implement and verify the use of a static rendezvous point Observe the shared
Adaptive Content-based Routing In General Overlay Topologies
 Adaptive Content-based Routing In General Overlay Topologies Guoli Li, Vinod Muthusamy, and Hans-Arno Jacobsen University of Toronto gli@cs.toronto.edu, vinod@eecg.toronto.edu, jacobsen@eecg.toronto.edu
Adaptive Content-based Routing In General Overlay Topologies Guoli Li, Vinod Muthusamy, and Hans-Arno Jacobsen University of Toronto gli@cs.toronto.edu, vinod@eecg.toronto.edu, jacobsen@eecg.toronto.edu
FSOS Multicast Configuration Guide
 FSOS Multicast Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Multicast-Routing...6 1.1 Overview...6 1.2 Configuration... 6 1.3 Validation... 6 2 Configuring IGMP... 8 2.1 Overview...8 2.2 References...9
FSOS Multicast Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Multicast-Routing...6 1.1 Overview...6 1.2 Configuration... 6 1.3 Validation... 6 2 Configuring IGMP... 8 2.1 Overview...8 2.2 References...9
Multicast Technology White Paper
 Multicast Technology White Paper Keywords: Multicast, IGMP, IGMP Snooping, PIM, MBGP, MSDP, and SSM Mapping Abstract: The multicast technology implements high-efficiency point-to-multipoint data transmission
Multicast Technology White Paper Keywords: Multicast, IGMP, IGMP Snooping, PIM, MBGP, MSDP, and SSM Mapping Abstract: The multicast technology implements high-efficiency point-to-multipoint data transmission
Configuring Bidirectional PIM
 Configuring Bidirectional PIM This chapter describes how to configure the Bidirectional PIM (bidir-pim) feature. Bidir-PIM is a variant of the Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) suite of routing protocols
Configuring Bidirectional PIM This chapter describes how to configure the Bidirectional PIM (bidir-pim) feature. Bidir-PIM is a variant of the Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) suite of routing protocols
PUBLISHER Subscriber system is an event notification service
 A Bandwidth Aware Topology Generation Mechanism for Peer-to-Peer based Publish-Subscribe Systems Abhigyan, Joydeep Chandra, Niloy Ganguly Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Indian Institute
A Bandwidth Aware Topology Generation Mechanism for Peer-to-Peer based Publish-Subscribe Systems Abhigyan, Joydeep Chandra, Niloy Ganguly Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Indian Institute
Multicast routing Draft
 Multicast routing Draft Lucia Tudose Nokia Research Center E-mail: tudose@research.nokia.com Abstract Multicast routing is establishing a tree which is routed from the source node and contains all the
Multicast routing Draft Lucia Tudose Nokia Research Center E-mail: tudose@research.nokia.com Abstract Multicast routing is establishing a tree which is routed from the source node and contains all the
Configuring multicast VPN
 Contents Configuring multicast VPN 1 Multicast VPN overview 1 Multicast VPN overview 1 MD-VPN overview 3 Protocols and standards 6 How MD-VPN works 6 Share-MDT establishment 6 Share-MDT-based delivery
Contents Configuring multicast VPN 1 Multicast VPN overview 1 Multicast VPN overview 1 MD-VPN overview 3 Protocols and standards 6 How MD-VPN works 6 Share-MDT establishment 6 Share-MDT-based delivery
Financial Services Design for High Availability
 Financial Services Design for High Availability Version History Version Number Date Notes 1 March 28, 2003 This document was created. This document describes the best practice for building a multicast
Financial Services Design for High Availability Version History Version Number Date Notes 1 March 28, 2003 This document was created. This document describes the best practice for building a multicast
Rethinking the Design of Distributed Stream Processing Systems
 Rethinking the Design of Distributed Stream Processing Systems Yongluan Zhou Karl Aberer Ali Salehi Kian-Lee Tan EPFL, Switzerland National University of Singapore Abstract In this paper, we present a
Rethinking the Design of Distributed Stream Processing Systems Yongluan Zhou Karl Aberer Ali Salehi Kian-Lee Tan EPFL, Switzerland National University of Singapore Abstract In this paper, we present a
Multicast EECS 122: Lecture 16
 Multicast EECS 1: Lecture 16 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California Berkeley Broadcasting to Groups Many applications are not one-one Broadcast Group collaboration
Multicast EECS 1: Lecture 16 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California Berkeley Broadcasting to Groups Many applications are not one-one Broadcast Group collaboration
Configuring SSM. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for Configuring SSM
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 1 Restrictions for, page 2 Information About SSM, page 3 How to Configure SSM, page 7 Monitoring SSM, page 15 Configuration Examples for Source
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 1 Restrictions for, page 2 Information About SSM, page 3 How to Configure SSM, page 7 Monitoring SSM, page 15 Configuration Examples for Source
Abstract In this paper we describe a new network service called Speccast. Speccast offers a generalized addressing and
 Speccast Leonid Poutievski, Kenneth L. Calvert, and James N. Griffioen Laboratory for Advanced Networking University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506-0046 Abstract In this paper we describe a new network
Speccast Leonid Poutievski, Kenneth L. Calvert, and James N. Griffioen Laboratory for Advanced Networking University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506-0046 Abstract In this paper we describe a new network
Tag Switching. Background. Tag-Switching Architecture. Forwarding Component CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 23 Tag Switching Background Rapid changes in the type (and quantity) of traffic handled by the Internet and the explosion in the number of Internet users is putting an unprecedented strain on the
CHAPTER 23 Tag Switching Background Rapid changes in the type (and quantity) of traffic handled by the Internet and the explosion in the number of Internet users is putting an unprecedented strain on the
Multicast VPN C H A P T E R. Introduction to IP Multicast
 C H A P T E R 7 Multicast VPN Multicast is a popular feature used mainly by IP-networks of Enterprise customers. Multicast allows the efficient distribution of information between a single multicast source
C H A P T E R 7 Multicast VPN Multicast is a popular feature used mainly by IP-networks of Enterprise customers. Multicast allows the efficient distribution of information between a single multicast source
05 Indirect Communication
 05 Indirect Communication Group Communication Publish-Subscribe Coulouris 6 Message Queus Point-to-point communication Participants need to exist at the same time Establish communication Participants need
05 Indirect Communication Group Communication Publish-Subscribe Coulouris 6 Message Queus Point-to-point communication Participants need to exist at the same time Establish communication Participants need
Top-Down Network Design
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Original slides by Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Selection Criteria for Switching and Routing Protocols Network traffic
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Original slides by Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Selection Criteria for Switching and Routing Protocols Network traffic
Hierarchical Routing. Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat not true in practice
 Hierarchical Routing Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat not true in practice scale: with 200 million destinations: can t store all destinations in routing tables!
Hierarchical Routing Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat not true in practice scale: with 200 million destinations: can t store all destinations in routing tables!
Exercises to Communication Systems
 Exercises to Communication Systems IP Multicast Additional Slides Dr.-Ing. Falko Dressler Department of Computer Science 7 University of Erlangen ÜKS, WS 05/06 1 IP Multicast Introduction Internet Group
Exercises to Communication Systems IP Multicast Additional Slides Dr.-Ing. Falko Dressler Department of Computer Science 7 University of Erlangen ÜKS, WS 05/06 1 IP Multicast Introduction Internet Group
Multicast. Presented by Hakim Weatherspoon. Slides borrowed from Qi Huang 2009 and Tom Ternquist 2010
 Multicast Presented by Hakim Weatherspoon Slides borrowed from Qi Huang 2009 and Tom Ternquist 2010 Midterm report abstract, introduction, background, related work, and design section. These sections should
Multicast Presented by Hakim Weatherspoon Slides borrowed from Qi Huang 2009 and Tom Ternquist 2010 Midterm report abstract, introduction, background, related work, and design section. These sections should
Network Configuration Example
 Network Configuration Example Release NCE0051 Modified: 2016-09-08 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net All rights reserved. Juniper Networks,
Network Configuration Example Release NCE0051 Modified: 2016-09-08 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net All rights reserved. Juniper Networks,
Application Layer Multicast For Efficient Peer-to-Peer Applications
 Application Layer Multicast For Efficient Peer-to-Peer Applications Adam Wierzbicki 1 e-mail: adamw@icm.edu.pl Robert Szczepaniak 1 Marcin Buszka 1 1 Polish-Japanese Institute of Information Technology
Application Layer Multicast For Efficient Peer-to-Peer Applications Adam Wierzbicki 1 e-mail: adamw@icm.edu.pl Robert Szczepaniak 1 Marcin Buszka 1 1 Polish-Japanese Institute of Information Technology
YFilter: an XML Stream Filtering Engine. Weiwei SUN University of Konstanz
 YFilter: an XML Stream Filtering Engine Weiwei SUN University of Konstanz 1 Introduction Data exchange between applications: use XML Messages processed by an XML Message Broker Examples Publish/subscribe
YFilter: an XML Stream Filtering Engine Weiwei SUN University of Konstanz 1 Introduction Data exchange between applications: use XML Messages processed by an XML Message Broker Examples Publish/subscribe
Multicast overview. Introduction to multicast. Information transmission techniques. Unicast
 Contents Multicast overview 1 Introduction to multicast 1 Information transmission techniques 1 Multicast features 3 Common notations in multicast 4 Multicast advantages and applications 4 Multicast models
Contents Multicast overview 1 Introduction to multicast 1 Information transmission techniques 1 Multicast features 3 Common notations in multicast 4 Multicast advantages and applications 4 Multicast models
Routing over Low Power and Lossy Networks
 outing over Low Power and Lossy Networks Analysis and possible enhancements of the IETF PL routing protocol Enzo Mingozzi Associate Professor @ University of Pisa e.mingozzi@iet.unipi.it outing over LLNs
outing over Low Power and Lossy Networks Analysis and possible enhancements of the IETF PL routing protocol Enzo Mingozzi Associate Professor @ University of Pisa e.mingozzi@iet.unipi.it outing over LLNs
List of groups known at each router. Router gets those using IGMP. And where they are in use Where members are located. Enhancement to OSPF
 Multicast OSPF OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link State Protocol Use Dijkstra s algorithm (SPF) Calculate shortest path from the router to every possible destination Areas Limit the information volume
Multicast OSPF OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link State Protocol Use Dijkstra s algorithm (SPF) Calculate shortest path from the router to every possible destination Areas Limit the information volume
ICS 351: Today's plan. distance-vector routing game link-state routing OSPF
 ICS 351: Today's plan distance-vector routing game link-state routing OSPF distance-vector routing game 1. prepare a list of all neighbors and the links to them, and the metric for each link 2. create
ICS 351: Today's plan distance-vector routing game link-state routing OSPF distance-vector routing game 1. prepare a list of all neighbors and the links to them, and the metric for each link 2. create
ROUTING ALGORITHMS Part 1: Data centric and hierarchical protocols
 ROUTING ALGORITHMS Part 1: Data centric and hierarchical protocols 1 Why can t we use conventional routing algorithms here?? A sensor node does not have an identity (address) Content based and data centric
ROUTING ALGORITHMS Part 1: Data centric and hierarchical protocols 1 Why can t we use conventional routing algorithms here?? A sensor node does not have an identity (address) Content based and data centric
Scalable Overlay Multicast Tree Construction for Media Streaming
 Scalable Overlay Multicast Tree Construction for Media Streaming Gabriel Parmer, Richard West, Gerald Fry Computer Science Department Boston University Boston, MA 02215 {gabep1,richwest,gfry}@cs.bu.edu
Scalable Overlay Multicast Tree Construction for Media Streaming Gabriel Parmer, Richard West, Gerald Fry Computer Science Department Boston University Boston, MA 02215 {gabep1,richwest,gfry}@cs.bu.edu
Network Configuration Example
 Network Configuration Example Configuring Protocol Independent Multicast Join Load Balancing Release NCE0054 Modified: 2017-01-20 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089
Network Configuration Example Configuring Protocol Independent Multicast Join Load Balancing Release NCE0054 Modified: 2017-01-20 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089
Recent Advances and Challenges in XML Document Routing
 Recent Advances and Challenges in XML Document Routing Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS), Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK University of California, Riverside,
Recent Advances and Challenges in XML Document Routing Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS), Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil Microsoft Research, Cambridge, UK University of California, Riverside,
SCAN: Scalable Content routing for
 ICC 2011@kyoto SCAN: Scalable routing for content-aware Networking Munyoung Lee, Kideok Cho, Kunwoo Park, Td T Ted Taekyoung Kwon, Yanghee Choi (mylee@mmlab.snu.ac.kr) Seoul National University 2011. 6.
ICC 2011@kyoto SCAN: Scalable routing for content-aware Networking Munyoung Lee, Kideok Cho, Kunwoo Park, Td T Ted Taekyoung Kwon, Yanghee Choi (mylee@mmlab.snu.ac.kr) Seoul National University 2011. 6.
Broadcast and Multicast Routing
 Broadcast and Multicast Routing Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Group Communication 2/34 How can the Internet provide efficient group communication? send the same copy
Broadcast and Multicast Routing Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Group Communication 2/34 How can the Internet provide efficient group communication? send the same copy
Routing protocols in WSN
 Routing protocols in WSN 1.1 WSN Routing Scheme Data collected by sensor nodes in a WSN is typically propagated toward a base station (gateway) that links the WSN with other networks where the data can
Routing protocols in WSN 1.1 WSN Routing Scheme Data collected by sensor nodes in a WSN is typically propagated toward a base station (gateway) that links the WSN with other networks where the data can
QoS-Aware Hierarchical Multicast Routing on Next Generation Internetworks
 QoS-Aware Hierarchical Multicast Routing on Next Generation Internetworks by Satyabrata Pradhan A thesis Submitted to the Faculty of Graduate Studies in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the
QoS-Aware Hierarchical Multicast Routing on Next Generation Internetworks by Satyabrata Pradhan A thesis Submitted to the Faculty of Graduate Studies in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the
Enhanced Cores Based Tree for Many-to-Many IP Multicasting
 Enhanced Cores Based Tree for Many-to-Many IP Multicasting In this paper, we propose a simple and practical scheme for many-to-many IP multicasting. The proposed scheme is based on the core based tree
Enhanced Cores Based Tree for Many-to-Many IP Multicasting In this paper, we propose a simple and practical scheme for many-to-many IP multicasting. The proposed scheme is based on the core based tree
ITEC310 Computer Networks II
 ITEC310 Computer Networks II Chapter 22 Network Layer:, and Routing Department of Information Technology Eastern Mediterranean University Objectives 2/131 After completing this chapter you should be able
ITEC310 Computer Networks II Chapter 22 Network Layer:, and Routing Department of Information Technology Eastern Mediterranean University Objectives 2/131 After completing this chapter you should be able
Configuring IP Multicast Routing
 34 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure IP multicast routing on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. IP multicasting is a more efficient way to use network resources, especially for bandwidth-intensive
34 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure IP multicast routing on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. IP multicasting is a more efficient way to use network resources, especially for bandwidth-intensive
Path Sharing and Predicate Evaluation for High- Performance XML Filtering
 Path Sharing and Predicate Evaluation for High- Performance XML Filtering YANLEI DIAO University of California, Berkeley MEHMET ALTINEL IBM Almaden Research Center MICHAEL J. FRANKLIN, HAO ZHANG University
Path Sharing and Predicate Evaluation for High- Performance XML Filtering YANLEI DIAO University of California, Berkeley MEHMET ALTINEL IBM Almaden Research Center MICHAEL J. FRANKLIN, HAO ZHANG University
Rendezvous Point Engineering
 Rendezvous Point Engineering Last updated: November 2008 Introduction A Rendezvous Point (RP) is a router in a multicast network domain that acts as a shared root for a multicast shared tree. Any number
Rendezvous Point Engineering Last updated: November 2008 Introduction A Rendezvous Point (RP) is a router in a multicast network domain that acts as a shared root for a multicast shared tree. Any number
PIM Configuration. Page 1 of 9
 PIM Configuration Page 1 of 9 Contents Contents...2 Chapter 1 PIM Configuration...3 1.1 PIM Description...3 1.1.1 Principles of PIM-DM...3 1.1.2 Principles of PIM-SM...4 1.1.3 Principles of PIM-SSM...5
PIM Configuration Page 1 of 9 Contents Contents...2 Chapter 1 PIM Configuration...3 1.1 PIM Description...3 1.1.1 Principles of PIM-DM...3 1.1.2 Principles of PIM-SM...4 1.1.3 Principles of PIM-SSM...5
Table of Contents 1 Multicast VPN Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 Multicast VPN Configuration 1-1 Multicast VPN Overview 1-1 Introduction to MPLS L3VPN 1-1 Introduction to Multicast VPN 1-2 Introduction to MD-VPN 1-4 Protocols and Standards 1-7 How
Table of Contents 1 Multicast VPN Configuration 1-1 Multicast VPN Overview 1-1 Introduction to MPLS L3VPN 1-1 Introduction to Multicast VPN 1-2 Introduction to MD-VPN 1-4 Protocols and Standards 1-7 How
Chapter 7 CONCLUSION
 97 Chapter 7 CONCLUSION 7.1. Introduction A Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) could be considered as network of mobile nodes which communicate with each other without any fixed infrastructure. The nodes in
97 Chapter 7 CONCLUSION 7.1. Introduction A Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) could be considered as network of mobile nodes which communicate with each other without any fixed infrastructure. The nodes in
Why multicast? The concept of multicast Multicast groups Multicast addressing Multicast routing protocols MBONE Multicast applications Conclusions
 Tuomo Karhapää tuomo.karhapaa@otaverkko.fi Otaverkko Oy Why multicast? The concept of multicast Multicast groups Multicast addressing Multicast routing protocols MBONE Multicast applications Conclusions
Tuomo Karhapää tuomo.karhapaa@otaverkko.fi Otaverkko Oy Why multicast? The concept of multicast Multicast groups Multicast addressing Multicast routing protocols MBONE Multicast applications Conclusions
Indirect Communication
 Indirect Communication Today l Space and time (un)coupling l Group communication, pub/sub, message queues and shared memory Next time l Distributed file systems xkdc Indirect communication " Indirect communication
Indirect Communication Today l Space and time (un)coupling l Group communication, pub/sub, message queues and shared memory Next time l Distributed file systems xkdc Indirect communication " Indirect communication
