Lecture 19 Shortest Path vs Spanning Tree Max-Flow Problem. October 25, 2009
|
|
|
- Caroline Clarke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Shortest Path vs Spanning Tree Max-Flow Problem October 25, 2009
2 Outline Lecture 19 Undirected Network Illustration of the difference between the shortest path tree and the spanning tree Modeling Dilemma: Shortest path or Spanning tree? Max-Flow Problem Operations Research Methods 1
3 One-To-All Shortest Path Problem in UNDIRECTED NETWORK We are given a weighted undirected network (V, E, C) with node set V, edge set E, and the weight set C specifying weights c ij for the edges {i, j} E. We are also given a starting node s V. The problem is to determine the shortest path from s to any other node in the network. In the figure, we have s = 1 Operations Research Methods 2
4 Solution obtained by Dijkstra s algorithm The tree of the shortest paths from node 1 a a By pure chance it happen to be the same as in the directed version discussed in Lecture 18 Shortest path Length The table has paths sorted by the index of the destination node Operations Research Methods 3
5 How is the Shortest Path tree related to the Minimal Spanning Tree? These trees are NOT the same! Reason: The tree of shortest paths depends on the starting node Operations Research Methods 4
6 The tree of the shortest paths for a traveler starting a trip at node 1 The tree cost is 38 The tree of the shortest paths for a traveler starting a trip at node 3 The tree cost is 41 Operations Research Methods 5
7 Spanning tree problem over the same network In the spanning tree problem, there is no starting node The minimal spanning tree The tree cost is 33 In the spanning tree problem: The cost is incurred by one who builds the links One who builds the links sees the network with the whole structure One who travels in the network from an origin to a destination sees only the links that lead from the origin to the destination Operations Research Methods 6
8 Model Dilemma: Spanning Tree or Shortest Path Lecture 19 Confusion may arise when the problem is given in words To identify the problem type, ask yourself a question: Who incurs the cost? A user or the owner of the network? If it is a user of the network, then shortest path is the right model If it is the one who builds or owns the network, then spanning tree is the right model This helps in most of the situations BUT need not work all the time Operations Research Methods 7
9 Problem Sample The TM mobile phone company services six geographical areas. The satellite distances in thousands of miles are given in the figure below. TM needs to determine the best quality message routes that should be established between each two areas in the network QUESTION: What type of the problem are we facing here? Operations Research Methods 8
10 Max-Flow Problem: Single-Source Single-Sink We are given a directed capacitated network (V, E, C) connecting a source (origin) node with a sink (destination) node. The set V is the set of nodes in the network. The set E is the set of directed links (i, j) The set C is the set of capacities c ij 0 of the links (i, j) E. The problem is to determine the maximum amount of flow that can be sent from the source node to the sink node. This is Max-Flow Problem for single-source and single-sink Operations Research Methods 9
11 Max-Flow Problem: Multiple-Sources Multiple-Sinks We are given a directed capacitated network (V, E, C) connecting multiple source nodes with multiple sink nodes. The set V is the set of nodes and the set E is the set of directed links (i, j) The set C is the set of capacities c ij 0 of the links (i, j) E The problem is to determine the maximum amount of flow that can be sent from the source nodes to the sink nodes. cij This is Max-Flow Problem for multiple-sources and multiple-sinks Operations Research Methods 10
12 Multiple-sources multiple-links problem can be converted to a single-source and single-sink problem by Introducing a dummy source node that is connected to the original source nodes with infinite capacity links Introducing a dummy sink node that is connected with the original sink nodes with infinite capacity links Operations Research Methods 11
Lecture 18 Solving Shortest Path Problem: Dijkstra s Algorithm. October 23, 2009
 Solving Shortest Path Problem: Dijkstra s Algorithm October 23, 2009 Outline Lecture 18 Focus on Dijkstra s Algorithm Importance: Where it has been used? Algorithm s general description Algorithm steps
Solving Shortest Path Problem: Dijkstra s Algorithm October 23, 2009 Outline Lecture 18 Focus on Dijkstra s Algorithm Importance: Where it has been used? Algorithm s general description Algorithm steps
Class Overview. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence COMP 3501 / COMP Lecture 2: Search. Problem Solving Agents
 Class Overview COMP 3501 / COMP 4704-4 Lecture 2: Search Prof. 1 2 Problem Solving Agents Problem Solving Agents: Assumptions Requires a goal Assume world is: Requires actions Observable What actions?
Class Overview COMP 3501 / COMP 4704-4 Lecture 2: Search Prof. 1 2 Problem Solving Agents Problem Solving Agents: Assumptions Requires a goal Assume world is: Requires actions Observable What actions?
Network Flow Models. Chapter Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 Network Flow Models Chapter 7 7-1 Chapter Topics The Shortest Route Problem The Minimal Spanning Tree Problem The Maximal Flow Problem 7-2 Network Components A network is an arrangement of paths (branches)
Network Flow Models Chapter 7 7-1 Chapter Topics The Shortest Route Problem The Minimal Spanning Tree Problem The Maximal Flow Problem 7-2 Network Components A network is an arrangement of paths (branches)
TA: Jade Cheng ICS 241 Recitation Lecture Note #9 October 23, 2009
 TA: Jade Cheng ICS 241 Recitation Lecture Note #9 October 23, 2009 Recitation #9 Question: For each of these problems about a subway system, describe a weighted graph model that can be used to solve the
TA: Jade Cheng ICS 241 Recitation Lecture Note #9 October 23, 2009 Recitation #9 Question: For each of these problems about a subway system, describe a weighted graph model that can be used to solve the
Introduction To Graphs and Networks. Fall 2013 Carola Wenk
 Introduction To Graphs and Networks Fall 203 Carola Wenk On the Internet, links are essentially weighted by factors such as transit time, or cost. The goal is to find the shortest path from one node to
Introduction To Graphs and Networks Fall 203 Carola Wenk On the Internet, links are essentially weighted by factors such as transit time, or cost. The goal is to find the shortest path from one node to
Lecture 8 Network Flow Models
 Lecture 8 Andrew Nunekpeku / Charles Jackson Fall 2011 Outline 1 1 Assignment 4 When we ask for the solution of an LP, we typically mean tell me the values of the decision variables or what is the plan?
Lecture 8 Andrew Nunekpeku / Charles Jackson Fall 2011 Outline 1 1 Assignment 4 When we ask for the solution of an LP, we typically mean tell me the values of the decision variables or what is the plan?
Class Overview. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence COMP 3501 / COMP Lecture 2. Problem Solving Agents. Problem Solving Agents: Assumptions
 Class Overview COMP 3501 / COMP 4704-4 Lecture 2 Prof. JGH 318 Problem Solving Agents Problem Solving Agents: Assumptions Requires a goal Assume world is: Requires actions Observable What actions? Discrete
Class Overview COMP 3501 / COMP 4704-4 Lecture 2 Prof. JGH 318 Problem Solving Agents Problem Solving Agents: Assumptions Requires a goal Assume world is: Requires actions Observable What actions? Discrete
Dynamic modelling and network optimization
 Dynamic modelling and network optimization Risto Lahdelma Aalto University Energy Technology Otakaari 4, 25 Espoo, Finland risto.lahdelma@aalto.fi Risto Lahdelma Feb 4, 26 Outline Dynamic systems Dynamic
Dynamic modelling and network optimization Risto Lahdelma Aalto University Energy Technology Otakaari 4, 25 Espoo, Finland risto.lahdelma@aalto.fi Risto Lahdelma Feb 4, 26 Outline Dynamic systems Dynamic
Introduction to Management Science (8th Edition, Bernard W. Taylor III) Chapter 12 Network Flow Models. Chapter 12 - Network Flow Models 1
 Introduction to Management Science (8th Edition, Bernard W. Taylor III) Chapter 12 Network Flow Models Chapter 12 - Network Flow Models 1 Chapter Topics The Shortest Route Problem The Minimal Spanning
Introduction to Management Science (8th Edition, Bernard W. Taylor III) Chapter 12 Network Flow Models Chapter 12 - Network Flow Models 1 Chapter Topics The Shortest Route Problem The Minimal Spanning
Math 381 Discrete Mathematical Modeling
 Math 381 Discrete Mathematical Modeling Sean Griffin Today: -Equipment Replacement Problem -Min Spanning Tree Problem -Clustering Friday s Plan Intro to LPSolve software Download before class (link on
Math 381 Discrete Mathematical Modeling Sean Griffin Today: -Equipment Replacement Problem -Min Spanning Tree Problem -Clustering Friday s Plan Intro to LPSolve software Download before class (link on
Graph Data Processing with MapReduce
 Distributed data processing on the Cloud Lecture 5 Graph Data Processing with MapReduce Satish Srirama Some material adapted from slides by Jimmy Lin, 2015 (licensed under Creation Commons Attribution
Distributed data processing on the Cloud Lecture 5 Graph Data Processing with MapReduce Satish Srirama Some material adapted from slides by Jimmy Lin, 2015 (licensed under Creation Commons Attribution
Solutions to Math 381 Quiz 2
 Solutions to Math 381 Quiz 2 November 7, 2018 (1) In one sentence, what is the goal of your class project? Each team has a different answer here. (2) Write a function in Python which computes a linear
Solutions to Math 381 Quiz 2 November 7, 2018 (1) In one sentence, what is the goal of your class project? Each team has a different answer here. (2) Write a function in Python which computes a linear
Overview. H. R. Alvarez A., Ph. D.
 Network Modeling Overview Networks arise in numerous settings: transportation, electrical, and communication networks, for example. Network representations also are widely used for problems in such diverse
Network Modeling Overview Networks arise in numerous settings: transportation, electrical, and communication networks, for example. Network representations also are widely used for problems in such diverse
Algorithms after Dijkstra and Kruskal for Big Data. User Manual
 Algorithms after Dijkstra and Kruskal for Big Data User Manual Ovak Technologies 2016 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1. Definition and Acronyms... 3 1.2. Purpose... 3 1.3. Overview... 3 2. Algorithms...
Algorithms after Dijkstra and Kruskal for Big Data User Manual Ovak Technologies 2016 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1. Definition and Acronyms... 3 1.2. Purpose... 3 1.3. Overview... 3 2. Algorithms...
Routing Algorithms. CS158a Chris Pollett Apr 4, 2007.
 Routing Algorithms CS158a Chris Pollett Apr 4, 2007. Outline Routing Algorithms Adaptive/non-adaptive algorithms The Optimality Principle Shortest Path Routing Flooding Distance Vector Routing Routing
Routing Algorithms CS158a Chris Pollett Apr 4, 2007. Outline Routing Algorithms Adaptive/non-adaptive algorithms The Optimality Principle Shortest Path Routing Flooding Distance Vector Routing Routing
Greedy Algorithms. COMP 215 Lecture 6
 Greedy Algorithms COMP 215 Lecture 6 Wrapping Up DP A few words on traveling salesperson problem. The problem. Brute force algorithm. Dynamic programming algorithm. Greedy Algorithms If we can view our
Greedy Algorithms COMP 215 Lecture 6 Wrapping Up DP A few words on traveling salesperson problem. The problem. Brute force algorithm. Dynamic programming algorithm. Greedy Algorithms If we can view our
University of Maryland. Tuesday, March 2, 2010
 Data-Intensive Information Processing Applications Session #5 Graph Algorithms Jimmy Lin University of Maryland Tuesday, March 2, 2010 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share
Data-Intensive Information Processing Applications Session #5 Graph Algorithms Jimmy Lin University of Maryland Tuesday, March 2, 2010 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share
CSE 101. Algorithm Design and Analysis Miles Jones Office 4208 CSE Building Lecture 5: SCC/BFS
 CSE 101 Algorithm Design and Analysis Miles Jones mej016@eng.ucsd.edu Office 4208 CSE Building Lecture 5: SCC/BFS DECOMPOSITION There is a linear time algorithm that decomposes a directed graph into its
CSE 101 Algorithm Design and Analysis Miles Jones mej016@eng.ucsd.edu Office 4208 CSE Building Lecture 5: SCC/BFS DECOMPOSITION There is a linear time algorithm that decomposes a directed graph into its
OVERVIEW OF THE NETWORK OPTIMIZATION PROGRAM (NOP) A. INTRODUCTION
 OVERVIEW OF THE NETWORK OPTIMIZATION PROGRAM (NOP) A. INTRODUCTION NOP is a 32-bit GUI application. This helps the user to use and understand the system quickly. Opening and saving input files have become
OVERVIEW OF THE NETWORK OPTIMIZATION PROGRAM (NOP) A. INTRODUCTION NOP is a 32-bit GUI application. This helps the user to use and understand the system quickly. Opening and saving input files have become
Ch.07 Shortest Route, Minimal Spanning Tree, and Maximal Flow Models. Management Science / Prof. Bonghyun Ahn
 Ch.07 Shortest Route, Minimal Spanning Tree, and Maximal Flow Models Management Science / Prof. Bonghyun Ahn Chapter Topics Network Components The Shortest Route Problem The Minimal Spanning Tree Problem
Ch.07 Shortest Route, Minimal Spanning Tree, and Maximal Flow Models Management Science / Prof. Bonghyun Ahn Chapter Topics Network Components The Shortest Route Problem The Minimal Spanning Tree Problem
Graph Algorithms. Revised based on the slides by Ruoming Kent State
 Graph Algorithms Adapted from UMD Jimmy Lin s slides, which is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 United States. See http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/us/
Graph Algorithms Adapted from UMD Jimmy Lin s slides, which is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 United States. See http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/us/
Purchasing Calling Card Services
 Purchasing Calling Card Services Courtesy of Main Resource, Inc. Visit us at www.mainresource.com or call 800 362-6740 for all your telecom needs. PURCHASING CALLING CARD SERVICES Many times when a company
Purchasing Calling Card Services Courtesy of Main Resource, Inc. Visit us at www.mainresource.com or call 800 362-6740 for all your telecom needs. PURCHASING CALLING CARD SERVICES Many times when a company
of optimization problems. In this chapter, it is explained that what network design
 CHAPTER 2 Network Design Network design is one of the most important and most frequently encountered classes of optimization problems. In this chapter, it is explained that what network design is? The
CHAPTER 2 Network Design Network design is one of the most important and most frequently encountered classes of optimization problems. In this chapter, it is explained that what network design is? The
Algorithm Circle Extra Lecture: Solving the Assignment Problem with Network Flow
 The Network Flow Minimum-Cost Maximum Flow Shameless Plug Algorithm Circle Extra Lecture: Solving the with Network Flow 17 September 2012 The Network Flow Minimum-Cost Maximum Flow Shameless Plug Outline
The Network Flow Minimum-Cost Maximum Flow Shameless Plug Algorithm Circle Extra Lecture: Solving the with Network Flow 17 September 2012 The Network Flow Minimum-Cost Maximum Flow Shameless Plug Outline
GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014
 GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014 These are not Graphs 2...not the kind we mean, anyway These are Graphs 3 K 5 K 3,3 = Applications of Graphs 4 Communication networks The internet is a huge graph Routing
GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014 These are not Graphs 2...not the kind we mean, anyway These are Graphs 3 K 5 K 3,3 = Applications of Graphs 4 Communication networks The internet is a huge graph Routing
Networks: Lecture 1. General Comments
 Networks: Lecture 1 Amedeo R. Odoni November 1, 200 * Thanks to Prof. R.. Larson for some of the slides General omments From continuous to a more discretized travel environment Enormous literature and
Networks: Lecture 1 Amedeo R. Odoni November 1, 200 * Thanks to Prof. R.. Larson for some of the slides General omments From continuous to a more discretized travel environment Enormous literature and
CSE 101 Final Exam. Spring 2017
 CSE 101 Final Exam Spring 2017 Instructions: Do not open until the exam starts. The exam will run for 180 minutes. The problems are roughly sorted in increasing order of difficulty. Answer all questions
CSE 101 Final Exam Spring 2017 Instructions: Do not open until the exam starts. The exam will run for 180 minutes. The problems are roughly sorted in increasing order of difficulty. Answer all questions
6.854J / J Advanced Algorithms Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.854J / 18.415J Advanced Algorithms Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.415/6.854 Advanced
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.854J / 18.415J Advanced Algorithms Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.415/6.854 Advanced
Graphs. 04/01/03 Lecture 20 1
 Graphs Graphs model networks of various kinds: roads, highways, oil pipelines, airline routes, dependency relationships, etc. Graph G(V,E) VVertices or Nodes EEdges or Links: pairs of vertices Directed
Graphs Graphs model networks of various kinds: roads, highways, oil pipelines, airline routes, dependency relationships, etc. Graph G(V,E) VVertices or Nodes EEdges or Links: pairs of vertices Directed
CS 491 CAP Introduction to Graphs and Search
 CS 491 CAP Introduction to Graphs and Search Jingbo Shang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Sep 9, 2016 Outline Graphs Adjacency Matrix vs. Adjacency List Special Graphs Depth-first and Breadth-first
CS 491 CAP Introduction to Graphs and Search Jingbo Shang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Sep 9, 2016 Outline Graphs Adjacency Matrix vs. Adjacency List Special Graphs Depth-first and Breadth-first
Introduction to Mathematical Programming IE406. Lecture 16. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Introduction to Mathematical Programming IE406 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs IE406 Lecture 16 1 Reading for This Lecture Bertsimas 7.1-7.3 IE406 Lecture 16 2 Network Flow Problems Networks are used to model
Introduction to Mathematical Programming IE406 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs IE406 Lecture 16 1 Reading for This Lecture Bertsimas 7.1-7.3 IE406 Lecture 16 2 Network Flow Problems Networks are used to model
Temporally Adaptive A* Algorithm on Time Dependent Transportation Network
 Temporally Adaptive A* Algorithm on Time Dependent Transportation Network Nianbo Zheng, Feng Lu Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research Chinese Academy of Sciences Beijing, 100101,
Temporally Adaptive A* Algorithm on Time Dependent Transportation Network Nianbo Zheng, Feng Lu Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research Chinese Academy of Sciences Beijing, 100101,
Algorithms for Data Science
 Algorithms for Data Science CSOR W4246 Eleni Drinea Computer Science Department Columbia University Thursday, October 1, 2015 Outline 1 Recap 2 Shortest paths in graphs with non-negative edge weights (Dijkstra
Algorithms for Data Science CSOR W4246 Eleni Drinea Computer Science Department Columbia University Thursday, October 1, 2015 Outline 1 Recap 2 Shortest paths in graphs with non-negative edge weights (Dijkstra
Material handling and Transportation in Logistics. Paolo Detti Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Informazione e Scienze Matematiche Università di Siena
 Material handling and Transportation in Logistics Paolo Detti Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Informazione e Scienze Matematiche Università di Siena Introduction to Graph Theory Graph Theory As Mathematical
Material handling and Transportation in Logistics Paolo Detti Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell Informazione e Scienze Matematiche Università di Siena Introduction to Graph Theory Graph Theory As Mathematical
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Shortest Path Problem G. Guérard Department of Nouvelles Energies Ecole Supérieur d Ingénieurs Léonard de Vinci Lecture 3 GG A.I. 1/42 Outline 1 The Shortest Path Problem Introduction
Artificial Intelligence Shortest Path Problem G. Guérard Department of Nouvelles Energies Ecole Supérieur d Ingénieurs Léonard de Vinci Lecture 3 GG A.I. 1/42 Outline 1 The Shortest Path Problem Introduction
The Shortest Path Problem. The Shortest Path Problem. Mathematical Model. Integer Programming Formulation
 The Shortest Path Problem jla,jc@imm.dtu.dk Department of Management Engineering Technical University of Denmark The Shortest Path Problem Given a directed network G = (V,E,w) for which the underlying
The Shortest Path Problem jla,jc@imm.dtu.dk Department of Management Engineering Technical University of Denmark The Shortest Path Problem Given a directed network G = (V,E,w) for which the underlying
5.2 Routing Algorithms
 CEN445 Network Protocols and Algorithms Chapter 5 Network Layer 5. Routing Algorithms Dr. Mostafa Hassan Dahshan Department of Computer Engineering College of Computer and Information Sciences King Saud
CEN445 Network Protocols and Algorithms Chapter 5 Network Layer 5. Routing Algorithms Dr. Mostafa Hassan Dahshan Department of Computer Engineering College of Computer and Information Sciences King Saud
Graphs. Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale Room - Faner 3131
 Graphs Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale tessema.mengistu@siu.edu Room - Faner 3131 1 Outline Introduction to Graphs Graph Traversals Finding a
Graphs Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale tessema.mengistu@siu.edu Room - Faner 3131 1 Outline Introduction to Graphs Graph Traversals Finding a
Introduction to Algorithms
 Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401 Lecture 21 Prof. Piotr Indyk P vs NP (interconnectedness of all things) A whole course by itself We ll do just two lectures More in 6.045, 6.840J, etc. Introduction
Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401 Lecture 21 Prof. Piotr Indyk P vs NP (interconnectedness of all things) A whole course by itself We ll do just two lectures More in 6.045, 6.840J, etc. Introduction
COMP/ELEC 429/556 Introduction to Computer Networks
 OMP/ELE 49/6 Introduction to omputer Networks Intra-domain routing Some slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica, Hui Zhang T. S. Eugene Ng eugeneng at cs.rice.edu
OMP/ELE 49/6 Introduction to omputer Networks Intra-domain routing Some slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica, Hui Zhang T. S. Eugene Ng eugeneng at cs.rice.edu
CSE 101 Winter 2018 Programming Assignment (PA) Two
 CSE 101 Winter 2018 Programming Assignment (PA) Two Due: Friday February 9, 11:59 PM PST Link to starter code: https://github.com/ucsd-cse101/w18-pa2 PLEASE READ THE FAQ BEFORE POSTING ON PIAZZA https://docs.google.com/document/d/1zjgcrhbtzatpb9gs3xtt50tfw5xxeh_x1
CSE 101 Winter 2018 Programming Assignment (PA) Two Due: Friday February 9, 11:59 PM PST Link to starter code: https://github.com/ucsd-cse101/w18-pa2 PLEASE READ THE FAQ BEFORE POSTING ON PIAZZA https://docs.google.com/document/d/1zjgcrhbtzatpb9gs3xtt50tfw5xxeh_x1
Routing Algorithms McGraw-Hill The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2001
 Routing Algorithms Main issue is how the routers that constitute the network layer of a network cooperate to find the best routes between all pairs of stations. Routing algorithm at a router decides which
Routing Algorithms Main issue is how the routers that constitute the network layer of a network cooperate to find the best routes between all pairs of stations. Routing algorithm at a router decides which
TIE Graph algorithms
 TIE-20106 1 1 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
TIE-20106 1 1 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
Outline: Finish uncapacitated simplex method Negative cost cycle algorithm The max-flow problem Max-flow min-cut theorem
 Outline: Finish uncapacitated simplex method Negative cost cycle algorithm The max-flow problem Max-flow min-cut theorem Uncapacitated Networks: Basic primal and dual solutions Flow conservation constraints
Outline: Finish uncapacitated simplex method Negative cost cycle algorithm The max-flow problem Max-flow min-cut theorem Uncapacitated Networks: Basic primal and dual solutions Flow conservation constraints
CS 4407 Algorithms Lecture 5: Graphs an Introduction
 CS 4407 Algorithms Lecture 5: Graphs an Introduction Prof. Gregory Provan Department of Computer Science University College Cork 1 Outline Motivation Importance of graphs for algorithm design applications
CS 4407 Algorithms Lecture 5: Graphs an Introduction Prof. Gregory Provan Department of Computer Science University College Cork 1 Outline Motivation Importance of graphs for algorithm design applications
ECE 242 HOMEWORK 5. In the figure below, one can go from node B to A but not from A to B.
 ECE 242 HOMEWORK 5 Question 1: Define the following terms. For lines with multiple terms,differentiate between the terms. Also draw a figure illustrating each term. (a) Directed graph and undirected graph
ECE 242 HOMEWORK 5 Question 1: Define the following terms. For lines with multiple terms,differentiate between the terms. Also draw a figure illustrating each term. (a) Directed graph and undirected graph
Homework Assignment #3 Graph
 CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
Classic Graph Theory Problems
 Classic Graph Theory Problems Hiroki Sayama sayama@binghamton.edu The Origin Königsberg bridge problem Pregel River (Solved negatively by Euler in 176) Representation in a graph Can all the seven edges
Classic Graph Theory Problems Hiroki Sayama sayama@binghamton.edu The Origin Königsberg bridge problem Pregel River (Solved negatively by Euler in 176) Representation in a graph Can all the seven edges
Link Analysis in the Cloud
 Cloud Computing Link Analysis in the Cloud Dell Zhang Birkbeck, University of London 2017/18 Graph Problems & Representations What is a Graph? G = (V,E), where V represents the set of vertices (nodes)
Cloud Computing Link Analysis in the Cloud Dell Zhang Birkbeck, University of London 2017/18 Graph Problems & Representations What is a Graph? G = (V,E), where V represents the set of vertices (nodes)
Computer Networking. Intra-Domain Routing. RIP (Routing Information Protocol) & OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
 Computer Networking Intra-Domain Routing RIP (Routing Information Protocol) & OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) IP Forwarding The Story So Far IP addresses are structured to reflect Internet structure IP
Computer Networking Intra-Domain Routing RIP (Routing Information Protocol) & OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) IP Forwarding The Story So Far IP addresses are structured to reflect Internet structure IP
Module 2: NETWORKS AND DECISION MATHEMATICS
 Further Mathematics 2017 Module 2: NETWORKS AND DECISION MATHEMATICS Chapter 9 Undirected Graphs and Networks Key knowledge the conventions, terminology, properties and types of graphs; edge, face, loop,
Further Mathematics 2017 Module 2: NETWORKS AND DECISION MATHEMATICS Chapter 9 Undirected Graphs and Networks Key knowledge the conventions, terminology, properties and types of graphs; edge, face, loop,
U.C. Berkeley CS170 : Algorithms Midterm 1 Lecturers: Alessandro Chiesa and Satish Rao September 18, Midterm 1
 U.C. Berkeley CS170 : Algorithms Lecturers: Alessandro Chiesa and Satish Rao September 18, 2018 1 Connectivity in Graphs No justification is required on this problem. A B C D E F G H I J (a) (2 points)
U.C. Berkeley CS170 : Algorithms Lecturers: Alessandro Chiesa and Satish Rao September 18, 2018 1 Connectivity in Graphs No justification is required on this problem. A B C D E F G H I J (a) (2 points)
Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 15/15 Hua Lu
 Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 15/15 Hua Lu Department of Computer Science Aalborg University Fall 2007 This Lecture Minimum spanning trees Definitions Kruskal s algorithm Prim s algorithm
Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 15/15 Hua Lu Department of Computer Science Aalborg University Fall 2007 This Lecture Minimum spanning trees Definitions Kruskal s algorithm Prim s algorithm
CS Algorithms and Complexity
 CS 350 - Algorithms and Complexity Graph Theory, Midterm Review Sean Anderson 2/6/18 Portland State University Table of contents 1. Graph Theory 2. Graph Problems 3. Uninformed Exhaustive Search 4. Informed
CS 350 - Algorithms and Complexity Graph Theory, Midterm Review Sean Anderson 2/6/18 Portland State University Table of contents 1. Graph Theory 2. Graph Problems 3. Uninformed Exhaustive Search 4. Informed
Practical Use of ADUS for Real- Time Routing and Travel Time Prediction
 Practical Use of ADUS for Real- Time Routing and Travel Time Prediction Dr. Jaimyoung Kwon Statistics, Cal State East Bay, Hayward, CA, USA Dr. Karl Petty, Bill Morris, Eric Shieh Berkeley Transportation
Practical Use of ADUS for Real- Time Routing and Travel Time Prediction Dr. Jaimyoung Kwon Statistics, Cal State East Bay, Hayward, CA, USA Dr. Karl Petty, Bill Morris, Eric Shieh Berkeley Transportation
Optimization Problems. Optimization Problems
 Optimization Problems Optimization Problems We have been looking at problems such as selection and sorting. These problems don t really involve the notion of making a choice, or more specifically, the
Optimization Problems Optimization Problems We have been looking at problems such as selection and sorting. These problems don t really involve the notion of making a choice, or more specifically, the
We have already seen the transportation problem and the assignment problem. Let us take the transportation problem, first.
 Advanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 19 Network Models In this lecture, we will discuss network models. (Refer
Advanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 19 Network Models In this lecture, we will discuss network models. (Refer
Graph Theoretic Models for Ad hoc Wireless Networks
 Graph Theoretic Models for Ad hoc Wireless Networks Prof. Srikrishnan Divakaran DA-IICT 10/4/2009 DA-IICT 1 Talk Outline Overview of Ad hoc Networks Design Issues in Modeling Ad hoc Networks Graph Theoretic
Graph Theoretic Models for Ad hoc Wireless Networks Prof. Srikrishnan Divakaran DA-IICT 10/4/2009 DA-IICT 1 Talk Outline Overview of Ad hoc Networks Design Issues in Modeling Ad hoc Networks Graph Theoretic
Chalmers University of Technology. Network Models. April 11, Birgit Grohe
 Chalmers University of Technology Applied Optimisation lp 4 VT08 Network Models April 11, 2008 Birgit Grohe Network Models - Examples Many different problems can be formulated as graph/network models:
Chalmers University of Technology Applied Optimisation lp 4 VT08 Network Models April 11, 2008 Birgit Grohe Network Models - Examples Many different problems can be formulated as graph/network models:
Network Models - Examples. Network Models. Definition and Terminology. The Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) Problem
 Chalmers University of Technology Applied Optimisa- Network Models - Examples tion lp 4 VT08 Network Models April 11, 2008 Birgit Grohe Many different problems can be formulated as graph/network models:
Chalmers University of Technology Applied Optimisa- Network Models - Examples tion lp 4 VT08 Network Models April 11, 2008 Birgit Grohe Many different problems can be formulated as graph/network models:
56:272 Integer Programming & Network Flows Final Exam -- December 16, 1997
 56:272 Integer Programming & Network Flows Final Exam -- December 16, 1997 Answer #1 and any five of the remaining six problems! possible score 1. Multiple Choice 25 2. Traveling Salesman Problem 15 3.
56:272 Integer Programming & Network Flows Final Exam -- December 16, 1997 Answer #1 and any five of the remaining six problems! possible score 1. Multiple Choice 25 2. Traveling Salesman Problem 15 3.
NETWORK OPTIMIZATION MODELS
 NETWORK OPTIMIZATION MODELS Network models Transportation, electrical and communication networks pervade our daily lives. Network representation are widely used in: Production, distribution, project planning,
NETWORK OPTIMIZATION MODELS Network models Transportation, electrical and communication networks pervade our daily lives. Network representation are widely used in: Production, distribution, project planning,
Further Mathematics 2016 Module 2: NETWORKS AND DECISION MATHEMATICS Chapter 9 Undirected Graphs and Networks
 Further Mathematics 2016 Module 2: NETWORKS AND DECISION MATHEMATICS Chapter 9 Undirected Graphs and Networks Key knowledge the conventions, terminology, properties and types of graphs; edge, face, loop,
Further Mathematics 2016 Module 2: NETWORKS AND DECISION MATHEMATICS Chapter 9 Undirected Graphs and Networks Key knowledge the conventions, terminology, properties and types of graphs; edge, face, loop,
4/8/11. Single-Source Shortest Path. Shortest Paths. Shortest Paths. Chapter 24
 /8/11 Single-Source Shortest Path Chapter 1 Shortest Paths Finding the shortest path between two nodes comes up in many applications o Transportation problems o Motion planning o Communication problems
/8/11 Single-Source Shortest Path Chapter 1 Shortest Paths Finding the shortest path between two nodes comes up in many applications o Transportation problems o Motion planning o Communication problems
Introduction to Computer Science
 Introduction to Computer Science CSCI 09 Readings St. Amant, Ch. China nhe- Andrew Goodney Fall 08 An algorithm (pronounced AL-go-rithum) is a procedure or formula for solving a problem. The word derives
Introduction to Computer Science CSCI 09 Readings St. Amant, Ch. China nhe- Andrew Goodney Fall 08 An algorithm (pronounced AL-go-rithum) is a procedure or formula for solving a problem. The word derives
Jordan Boyd-Graber University of Maryland. Thursday, March 3, 2011
 Data-Intensive Information Processing Applications! Session #5 Graph Algorithms Jordan Boyd-Graber University of Maryland Thursday, March 3, 2011 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share
Data-Intensive Information Processing Applications! Session #5 Graph Algorithms Jordan Boyd-Graber University of Maryland Thursday, March 3, 2011 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share
CAD Algorithms. Categorizing Algorithms
 CAD Algorithms Categorizing Algorithms Mohammad Tehranipoor ECE Department 2 September 2008 1 Categorizing Algorithms Greedy Algorithms Prim s Algorithm (Minimum Spanning Tree) A subgraph that is a tree
CAD Algorithms Categorizing Algorithms Mohammad Tehranipoor ECE Department 2 September 2008 1 Categorizing Algorithms Greedy Algorithms Prim s Algorithm (Minimum Spanning Tree) A subgraph that is a tree
The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm
 The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm Lecture 31 Sections 6.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Apr 6, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman
The Traveling Salesman Problem Nearest-Neighbor Algorithm Lecture 31 Sections 6.4 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Apr 6, 2018 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College)The Traveling Salesman
PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research. Unit 3. Network Modelling
 PBW 54 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research Unit 3 Network Modelling Background So far, we treated urban space as a continuum, where an entity could travel from any point to any other point
PBW 54 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research Unit 3 Network Modelling Background So far, we treated urban space as a continuum, where an entity could travel from any point to any other point
Computer Networks 1 (Mạng Máy Tính 1) Lectured by: Dr. Phạm Trần Vũ
 Computer Networks 1 (Mạng Máy Tính 1) Lectured by: Dr. Phạm Trần Vũ Lecture 5: Network Layer Reference: Chapter 5 - Computer Networks, Andrew S. Tanenbaum, 4th Edition, Prentice Hall, 2003. Contents The
Computer Networks 1 (Mạng Máy Tính 1) Lectured by: Dr. Phạm Trần Vũ Lecture 5: Network Layer Reference: Chapter 5 - Computer Networks, Andrew S. Tanenbaum, 4th Edition, Prentice Hall, 2003. Contents The
Department of Mathematics Oleg Burdakov of 30 October Consider the following linear programming problem (LP):
 Linköping University Optimization TAOP3(0) Department of Mathematics Examination Oleg Burdakov of 30 October 03 Assignment Consider the following linear programming problem (LP): max z = x + x s.t. x x
Linköping University Optimization TAOP3(0) Department of Mathematics Examination Oleg Burdakov of 30 October 03 Assignment Consider the following linear programming problem (LP): max z = x + x s.t. x x
GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013
 GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013 Announcements 2 Prelim 2: Two and a half weeks from now Tuesday, April16, 7:30-9pm, Statler Exam conflicts? We need to hear about them and can arrange a makeup It would
GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013 Announcements 2 Prelim 2: Two and a half weeks from now Tuesday, April16, 7:30-9pm, Statler Exam conflicts? We need to hear about them and can arrange a makeup It would
1. Let n and m be positive integers with n m. a. Write the inclusion/exclusion formula for the number S(n, m) of surjections from {1, 2,...
 MATH 3012, Quiz 3, November 24, 2015, WTT Student Name and ID Number 1. Let n and m be positive integers with n m. a. Write the inclusion/exclusion formula for the number S(n, m) of surjections from {1,
MATH 3012, Quiz 3, November 24, 2015, WTT Student Name and ID Number 1. Let n and m be positive integers with n m. a. Write the inclusion/exclusion formula for the number S(n, m) of surjections from {1,
ME/CS 132: Advanced Robotics: Navigation and Vision
 ME/CS 132: Advanced Robotics: Navigation and Vision Lecture #5: Search Algorithm 1 Yoshiaki Kuwata 4/12/2011 Lecture Overview Introduction Label Correcting Algorithm Core idea Depth-first search Breadth-first
ME/CS 132: Advanced Robotics: Navigation and Vision Lecture #5: Search Algorithm 1 Yoshiaki Kuwata 4/12/2011 Lecture Overview Introduction Label Correcting Algorithm Core idea Depth-first search Breadth-first
Dijkstra s Algorithm and Priority Queue Implementations. CSE 101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 5
 Dijkstra s Algorithm and Priority Queue Implementations CSE 101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 5 CSE 101: Design and analysis of algorithms Dijkstra s algorithm and priority queue implementations
Dijkstra s Algorithm and Priority Queue Implementations CSE 101: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 5 CSE 101: Design and analysis of algorithms Dijkstra s algorithm and priority queue implementations
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007
 Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Introduction to Algorithms
 Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401J Lecture 24 Prof. Piotr Indyk Dealing with Hard Problems What to do if: Divide and conquer Dynamic programming Greedy Linear Programming/Network Flows does not
Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401J Lecture 24 Prof. Piotr Indyk Dealing with Hard Problems What to do if: Divide and conquer Dynamic programming Greedy Linear Programming/Network Flows does not
Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Karen Daniels
 UMass Lowell Computer Science 91.503 Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Karen Daniels Spring, 2010 Lecture 2 Tuesday, 2/2/10 Design Patterns for Optimization Problems Greedy Algorithms Algorithmic Paradigm Context
UMass Lowell Computer Science 91.503 Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Karen Daniels Spring, 2010 Lecture 2 Tuesday, 2/2/10 Design Patterns for Optimization Problems Greedy Algorithms Algorithmic Paradigm Context
Routing in Delay Tolerant Networks (2)
 Routing in Delay Tolerant Networks (2) Primary Reference: E. P. C. Jones, L. Li and P. A. S. Ward, Practical Routing in Delay-Tolerant Networks, SIGCOMM 05, Workshop on DTN, August 22-26, 2005, Philadelphia,
Routing in Delay Tolerant Networks (2) Primary Reference: E. P. C. Jones, L. Li and P. A. S. Ward, Practical Routing in Delay-Tolerant Networks, SIGCOMM 05, Workshop on DTN, August 22-26, 2005, Philadelphia,
CS261: Problem Set #2
 CS261: Problem Set #2 Due by 11:59 PM on Tuesday, February 9, 2016 Instructions: (1) Form a group of 1-3 students. You should turn in only one write-up for your entire group. (2) Submission instructions:
CS261: Problem Set #2 Due by 11:59 PM on Tuesday, February 9, 2016 Instructions: (1) Form a group of 1-3 students. You should turn in only one write-up for your entire group. (2) Submission instructions:
Outline. Graphs. Divide and Conquer.
 GRAPHS COMP 321 McGill University These slides are mainly compiled from the following resources. - Professor Jaehyun Park slides CS 97SI - Top-coder tutorials. - Programming Challenges books. Outline Graphs.
GRAPHS COMP 321 McGill University These slides are mainly compiled from the following resources. - Professor Jaehyun Park slides CS 97SI - Top-coder tutorials. - Programming Challenges books. Outline Graphs.
CS170 Discussion Section 4: 9/18
 CS170 Discussion Section 4: 9/18 1. Alien alphabet. Suppose you have a dictionary of an alien language which lists words in some sorted lexicographical ordering. For example, given the following list of
CS170 Discussion Section 4: 9/18 1. Alien alphabet. Suppose you have a dictionary of an alien language which lists words in some sorted lexicographical ordering. For example, given the following list of
Dynamic Programming II
 Lecture 11 Dynamic Programming II 11.1 Overview In this lecture we continue our discussion of dynamic programming, focusing on using it for a variety of path-finding problems in graphs. Topics in this
Lecture 11 Dynamic Programming II 11.1 Overview In this lecture we continue our discussion of dynamic programming, focusing on using it for a variety of path-finding problems in graphs. Topics in this
CSE 417 Network Flows (pt 4) Min Cost Flows
 CSE 417 Network Flows (pt 4) Min Cost Flows Reminders > HW6 is due Monday Review of last three lectures > Defined the maximum flow problem find the feasible flow of maximum value flow is feasible if it
CSE 417 Network Flows (pt 4) Min Cost Flows Reminders > HW6 is due Monday Review of last three lectures > Defined the maximum flow problem find the feasible flow of maximum value flow is feasible if it
CSE 100: B+ TREE, 2-3 TREE, NP- COMPLETNESS
 CSE 100: B+ TREE, 2-3 TREE, NP- COMPLETNESS Analyzing find in B-trees Since the B-tree is perfectly height-balanced, the worst case time cost for find is O(logN) Best case: If every internal node is completely
CSE 100: B+ TREE, 2-3 TREE, NP- COMPLETNESS Analyzing find in B-trees Since the B-tree is perfectly height-balanced, the worst case time cost for find is O(logN) Best case: If every internal node is completely
ME 391Q Network Flow Programming
 ME 9Q Network Flow Programming Final Exam, Summer 00. ( Points) The figure below shows an undirected network. The parameters on the edges are the edge lengths. Find the shortest path tree using Dijkstra
ME 9Q Network Flow Programming Final Exam, Summer 00. ( Points) The figure below shows an undirected network. The parameters on the edges are the edge lengths. Find the shortest path tree using Dijkstra
CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman
 CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman Lecture 11: Graphs Graph Traversals: BFS Feb 16, 2018 What s Next What s Next Graph Algorithms: Graphs: Key Definitions, Properties, Representations Exploring
CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman Lecture 11: Graphs Graph Traversals: BFS Feb 16, 2018 What s Next What s Next Graph Algorithms: Graphs: Key Definitions, Properties, Representations Exploring
The State of the American Traveler TM
 The State of the American Traveler TM MOBILE EDITION Fall 2018 Volume 30 The Mobile Edition THIS FALL EDITION of The State of the American Traveler TM continues our ongoing exploration of travelers use
The State of the American Traveler TM MOBILE EDITION Fall 2018 Volume 30 The Mobile Edition THIS FALL EDITION of The State of the American Traveler TM continues our ongoing exploration of travelers use
Shortest Paths. CSE 373 Data Structures Lecture 21
 Shortest Paths CSE 7 Data Structures Lecture Readings and References Reading Section 9., Section 0.. Some slides based on: CSE 6 by S. Wolfman, 000 //0 Shortest Paths - Lecture Path A path is a list of
Shortest Paths CSE 7 Data Structures Lecture Readings and References Reading Section 9., Section 0.. Some slides based on: CSE 6 by S. Wolfman, 000 //0 Shortest Paths - Lecture Path A path is a list of
CS61B Lecture #35. Today: A* search, Minimum spanning trees, union-find. Last modified: Fri Nov 25 20:16: CS61B: Lecture #35 1
 CS61B Lecture #35 Today: A* search, Minimum spanning trees, union-find. Last modified: Fri Nov 5 0:16:54 016 CS61B: Lecture #35 1 Point-to-Point Shortest Path Dijkstra s algorithm gives you shortest paths
CS61B Lecture #35 Today: A* search, Minimum spanning trees, union-find. Last modified: Fri Nov 5 0:16:54 016 CS61B: Lecture #35 1 Point-to-Point Shortest Path Dijkstra s algorithm gives you shortest paths
Spatial Analysis (Vector) II
 Spatial Analysis (Vector) II GEOG 300, Lecture 9 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 A Spatial Network is a set of geographic locations interconnected in a system by a number of routes is a system of linear features
Spatial Analysis (Vector) II GEOG 300, Lecture 9 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 A Spatial Network is a set of geographic locations interconnected in a system by a number of routes is a system of linear features
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Applications, Volume XII, Special Issue, July 18, ISSN
 International Journal of Computer Engineering and Applications, Volume XII, Special Issue, July 18, www.ijcea.com ISSN 2321-3469 MULTICAST ROUTING: CONVENTIONAL ALGORITHMS VS ANT COLONY SYSTEM ABSTRACT
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Applications, Volume XII, Special Issue, July 18, www.ijcea.com ISSN 2321-3469 MULTICAST ROUTING: CONVENTIONAL ALGORITHMS VS ANT COLONY SYSTEM ABSTRACT
ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 11
 ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 11 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 5 October 2017 Announcements Back from Memsys. Related things: fast memories for network
ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 11 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 5 October 2017 Announcements Back from Memsys. Related things: fast memories for network
Static Interconnection Networks Prof. Kasim M. Al-Aubidy Computer Eng. Dept.
 Advanced Computer Architecture (0630561) Lecture 17 Static Interconnection Networks Prof. Kasim M. Al-Aubidy Computer Eng. Dept. INs Taxonomy: An IN could be either static or dynamic. Connections in a
Advanced Computer Architecture (0630561) Lecture 17 Static Interconnection Networks Prof. Kasim M. Al-Aubidy Computer Eng. Dept. INs Taxonomy: An IN could be either static or dynamic. Connections in a
LECTURE 26 PRIM S ALGORITHM
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 26 IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD STRATEGY Suppose we take a vertex Given a single vertex v 1, it forms a minimum spanning tree on one
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 26 IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD STRATEGY Suppose we take a vertex Given a single vertex v 1, it forms a minimum spanning tree on one
Spatio-Temporal Routing Algorithms Panel on Space-Time Research in GIScience Intl. Conference on Geographic Information Science 2012
 Spatio-Temporal Routing Algorithms Panel on Space-Time Research in GIScience Intl. Conference on Geographic Information Science 0 Shashi Shekhar McKnight Distinguished University Professor Department of
Spatio-Temporal Routing Algorithms Panel on Space-Time Research in GIScience Intl. Conference on Geographic Information Science 0 Shashi Shekhar McKnight Distinguished University Professor Department of
Computer Science 501 Data Structures & Algorithms The College of Saint Rose Fall 2014
 Computer Science 501 Data Structures & Algorithms The College of Saint Rose Fall 2014 Lab 11: Dijkstra s Road Trip Due: 6:00 PM, Tuesday, December 2, 2014 This lab, your last, and spread over 2 weeks,
Computer Science 501 Data Structures & Algorithms The College of Saint Rose Fall 2014 Lab 11: Dijkstra s Road Trip Due: 6:00 PM, Tuesday, December 2, 2014 This lab, your last, and spread over 2 weeks,
Math/Stat 2300 Modeling using Graph Theory (March 23/25) from text A First Course in Mathematical Modeling, Giordano, Fox, Horton, Weir, 2009.
 Math/Stat 2300 Modeling using Graph Theory (March 23/25) from text A First Course in Mathematical Modeling, Giordano, Fox, Horton, Weir, 2009. Describing Graphs (8.2) A graph is a mathematical way of describing
Math/Stat 2300 Modeling using Graph Theory (March 23/25) from text A First Course in Mathematical Modeling, Giordano, Fox, Horton, Weir, 2009. Describing Graphs (8.2) A graph is a mathematical way of describing
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CSE 101, Winter 2018 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 6: BFS, SPs, Dijkstra Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse101-w18/ Distance in a Graph The distance between two nodes is the length
CSE 101, Winter 2018 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 6: BFS, SPs, Dijkstra Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse101-w18/ Distance in a Graph The distance between two nodes is the length
TRIP Instructions for DAY TRIP
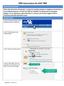 PROCESS/PROCEDURE TRIP is the University of Kentucky s system for reimbursements to employees for business travel related expenses. Use the Day TRIP for Monthly Travel that does not include lodging. For
PROCESS/PROCEDURE TRIP is the University of Kentucky s system for reimbursements to employees for business travel related expenses. Use the Day TRIP for Monthly Travel that does not include lodging. For
