CCNP SWITCH Portable Command Guide Scott Empson Hans Roth Warning and Disclaimer Trademark Acknowledgments
|
|
|
- Bridget Fox
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 ii CCNP SWITCH Portable Command Guide Scott Empson Hans Roth Copyright 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. Published by: Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN USA All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without written permission from the publisher, except for the inclusion of brief quotations in a review. Printed in the United States of America First Printing March 2010 Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication data is on file. ISBN-13: ISBN-10: Warning and Disclaimer This book is designed to provide information about the CCNP SWITCH exam ( ). Every effort has been made to make this book as complete and as accurate as possible, but no warranty or fitness is implied. The information is provided on an as is basis. The authors, Cisco Press, and Cisco Systems, Inc. shall have neither liability nor responsibility to any person or entity with respect to any loss or damages arising from the information contained in this book or from the use of the discs or programs that may accompany it. The opinions expressed in this book belong to the author and are not necessarily those of Cisco Systems, Inc. Trademark Acknowledgments All terms mentioned in this book that are known to be trademarks or service marks have been appropriately capitalized. Cisco Press or Cisco Systems, Inc., cannot attest to the accuracy of this information. Use of a term in this book should not be regarded as affecting the validity of any trademark or service mark.
3 xiii Introduction Welcome to CCNP SWITCH Portable Command Guide. When Cisco Press approached me about updating the four-volume CCNP Portable Command Guides, two thoughts immediately jumped into my head: Is it time for revisions already? and Yikes! I am in the middle of pursuing my master s degree. Where will I find the time? Because of those thoughts, two more soon followed: I wonder what Hans is up to? and I hope Carol is in a good mood, as I am about to ask to take Hans away again. The result is what you now have before you: a new Portable Command Guide for the latest version of the CCNP exam that focuses on switching: CCNP SWITCH. For those of you who have worked with my books before, thank you for looking at this one. I hope that it will help you as you prepare for the vendor exam, or assist you in your daily activities as a Cisco network administrator/manager. For those of you who are new to my books, you are reading what is essentially a cleanedup version of my own personal engineering journals a small notebook that I carry around with me that contains little nuggets of information; commands that I use but then forget; IP address schemes for the parts of the network I work with only occasionally; and quick refreshers for those concepts that I work with only once or twice a year. Although I teach these topics to postsecondary students, the classes I teach sometimes occur only once a year; as you can attest to, it is extremely difficult to remember all those commands all the time. Having a journal of commands at your fingertips, without having to search the Cisco website, can be a real time-saver (or a job-saver if the network is down and you are responsible for getting it back online). With the creation of the new CCNP exam objectives, there is always something new to read, or a new podcast to listen to, or another slideshow from CiscoLive that you missed or want to review. The engineering journal can be that central repository of information that won t weigh you down as you carry it from the office or cubicle to the server and infrastructure rooms in some remote part of the building or some branch office. To make this guide a more realistic one for you to use, the folks at Cisco Press have decided to continue with an appendix of blank pages pages on which you can write your own personal notes, such as your own configurations, commands that are not in this book but are needed in your world, and so on. That way, this book will look less like the authors journals and more like your own. Networking Devices Used in the Preparation of This Book To verify the commands that are in this new series of CCNP Portable Command Guides, many different devices were used. The following is a list of the equipment used in the preparation of these books: C2620 router running Cisco IOS Release 12.3(7)T, with a fixed Fast Ethernet interface, a WIC 2A/S serial interface card, and an NM-1E Ethernet interface C2811 ISR bundle with PVDM2, CMME, a WIC-2T, FXS and FXO VICs, running Cisco IOS Release 12.4(3g) C2821 ISR bundle with HWICD 9ESW, a WIC 2A/S, running 12.4(16) Advanced Security IOS
4 xiv WS-C EMI Catalyst Switch, running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)SE WS-C EMI Catalyst Switch, running Cisco IOS Release 12.1(9)EA1c WS TT-L Catalyst Switch, running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(25)SE WS Catalyst Switch, running version C2950-C3.0(5.3)WC(1) Enterprise Edition Software WS-C TS Catalyst Switches, running ipservicesk9 release 12.2(52)SE C1760-V Voice Router with PVDM-256K-20, WIC-4ESW, VIC-2FXO, VIC-2FXS running ENTSERVICESK9 release 12.4(11)T2 You might notice that some of the devices were not running the latest and greatest IOS. Some of them are running code that is quite old. Those of you familiar with Cisco devices will recognize that a majority of these commands work across the entire range of the Cisco product line. These commands are not limited to the platforms and IOS versions listed. In fact, in most cases, these devices are adequate for someone to continue their studies beyond the CCNP level as well. We have endeavored to identify throughout the book commands that are specific to a platform and/or IOS version. Who Should Read This Book? This book is for those people preparing for the CCNP SWITCH exam, whether through self-study, on-the-job training and practice, study within the Cisco Academy Program, or study through the use of a Cisco Training Partner. This book includes some handy hints and tips along the way to make life a bit easier for you in this endeavor. It is small enough that you will find it easy to carry around with you. Big, heavy textbooks might look impressive on your bookshelf in your office, but can you really carry them all around with you when you are working in a server room or equipment closet somewhere? Strategies for Exam Preparation The strategy that you use for CCNP SWITCH might be slightly different from strategies that other readers use, mainly based on the skills, knowledge, and experience you already have obtained. For example, if you have attended the SWITCH course, you might take a different approach than someone who learned routing via on-the-job training. Regardless of the strategy you use or the background you have, the book is designed to help you get to the point where you can pass the exam with the least amount of time required. For instance, there is no need for you to practice or read about VLANs or Spanning Tree if you fully understand it already. However, many people like to make sure they truly know a topic, and thus read over material they already know. Several book features help you gain the confidence you need to be convinced that you know some material already, and determine which topics you need to study more.
5 xv Organization of This Book Although this book could be read cover to cover, we strongly advise against it. The book is designed to be a simple listing of those commands that you need to understand to pass the SWITCH exam. Very little theory is included in the Portable Command Guides; they are designed to list commands needed at this level of study. This book roughly follows the list of objectives for the CCNP SWITCH exam: Chapter 1: Analyzing Campus Network Designs This chapter shows the Cisco Hierarchical Model of Network Design; the Cisco Enterprise Composite Network Model, the Cisco Service-Oriented Network Architecture (SONA), and the PPDIOO network lifecycle. Chapter 2: Implementing VLANs in a Campus Network This chapter provides information on creating, verifying, and troubleshooting Virtual LANs, along with private VLANs and EtherChannel. Chapter 3: Implementing Spanning Tree This chapter provides information on the configuration of Spanning Tree, along with commands used to verify the protocol and to configure enhancements to Spanning Tree, such as Rapid Spanning Tree and Multiple Spanning Tree. Chapter 4: Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing This chapter shows the different ways to enable inter-vlan communication using an external router or using SVIs on a multilayer switch. DHCP and CEF are also covered in this chapter. Chapter 5: Implementing a Highly Available Network This chapter covers topics such as network logging and syslog, SNMP managed nodes, and Cisco IOS Service Level Agreements. Chapter 6: Implementing a First Hop Redundancy Protocols Solution This chapter provides information needed to ensure you have first hop redundancy HSRO, VRRP, and GLBP are covered here. Chapter 7: Minimizing Service Loss and Data Theft in a Campus Network Security is the focus of this chapter. Topics covered include port security, 802.1x authentication, mitigating VLAN hopping, DHCP snooping, DAI, CDP security issues, LLDP configuration, SSH, restricting access to telnet as web interface sessions with ACLs, how to disable unneeded ports, and securing end-device access ports. Chapter 8: Accommodating Voice and Video in Campus Networks This chapter covers topics such as configuring and verifying voice VLANs, Power over Ethernet (POE), High Availability for Voice and Video, and configuring and verifying AutoQoS. Chapter 9: Integrating Wireless LANs into a Campus Network This chapter provides information on topics such as switch configuration for standalone APs and HREAPs as well as controller-based APs; configuration for a WLAN controller; configuration for WiSM controllers; and configuring a wireless client.
6 xvi Did We Miss Anything? As educators, we are always interested in hearing how our students, and now readers of our books, do on both vendor exams and future studies. If you would like to contact either of us and let us know how this book helped you in your certification goals, please do so. Did we miss anything? Let us know. Contact us at or through the Cisco Press website,
7 CHAPTER 4 Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Inter-VLAN communication Inter-VLAN communication using an external router: router-on-a-stick Inter-VLAN communication tips Inter-VLAN communication on a multilayer switch through a switch virtual interface Removing L2 switchport capability of a switch port Configuring SVI Autostate Configuring a Layer 3 EtherChannel Configuring inter-vlan communication Configuration example: inter-vlan communication DHCP Configuring DHCP server on a Router or Layer 3 Switch Verifying and troubleshooting DHCP configuration Configuring a DHCP helper address DHCP client on a Cisco IOS Software Ethernet interface Configuration example: DHCP CEF Configuring Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) Verifying CEF Troubleshooting CEF Inter-VLAN Communication Using an External Router: Routeron-a-Stick Router(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 Router(config-if)#duplex full Router(config-if)#no shutdown Router(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/0.1 Moves to interface configuration Sets interface to full duplex. Enables interface. Creates subinterface 0/0.1 and moves to subinterface configuration
8 56 Inter-VLAN Communication Tips Router(config-subif)#description Management VLAN 1 Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 1 native Router(config-subif)#ip address Router(config-subif)#interface fastethernet 0/0.10 Router(config-subif)#description Accounting VLAN 10 Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 10 Router(config-subif)#ip address Router(config-subif)#exit Router(config-if)#exit (Optional) Sets locally significant descriptor of the subinterface. Assigns VLAN 1 to this subinterface. VLAN 1 is the native VLAN. This subinterface uses the 802.1Q trunking protocol. Assigns IP address and netmask. Creates subinterface 0/0.10 and moves to subinterface configuration (Optional) Sets locally significant descriptor of the subinterface. Assigns VLAN 10 to this subinterface. This subinterface uses the 802.1Q trunking protocol. Assigns IP address and netmask. Returns to interface configuration Router(config)# NOTE: The subnets of the VLANs are directly connected to the router. Routing between these subnets does not require a dynamic routing protocol. In a more complex topology, these routes need to either be advertised with whatever dynamic routing protocol is used, or be redistributed into whatever dynamic routing protocol is used. NOTE: Routes to the subnets associated with these VLANs appear in the routing table as directly connected networks. Inter-VLAN Communication Tips Although most routers support both Inter-Switch Link (ISL) and Dot1Q encapsulation, some switch models support only Dot1Q, such as the 2950 and 2960 series. If you need to use ISL as your trunking protocol, use the command encapsulation isl x, where x is the number of the VLAN to be assigned to that subinterface.
9 Inter-VLAN Communication on a Multilayer Switch Through a Switch Virtual Interface 57 Recommended best practice is to use the same number of the VLAN number for the subinterface number. It is easier to troubleshoot VLAN 10 on subinterface fastethernet0/0.10 than on fastethernet0/0.2. The native VLAN (usually VLAN 1) cannot be configured on a subinterface for Cisco IOS releases that are earlier than 12.1(3)T. Native VLAN IP addresses will, therefore, need to be configured on the physical interface. Other VLAN traffic will be configured on subinterfaces: Router(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 Router(config-if)#encapsulation dot1q 1 native Router(config-if)#ip address Router(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/0.10 Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 10 Router(config-subif)#ip address Inter-VLAN Communication on a Multilayer Switch Through a Switch Virtual Interface Rather than using an external router to provide inter-vlan communication, a multilayer switch can perform the same task through the use of a switched virtual interface (SVI). Removing L2 Switchport Capability of a Switch Port 3750Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1 Moves to interface configuration 3750Switch(config-if)#no switchport Creates a Layer 3 port on the switch. NOTE: The no switchport command can be used on physical ports only on a Layer 3 capable switch. Configuring SVI Autostate 3750Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1 3750Switch(config-if)#switchport auto-state exclude Moves to interface configuration Excludes the access port/trunk in defining the status of an SVI as up or down. NOTE: This command is commonly used for ports that are used for monitoring, for example, so that a monitoring port does not cause the SVI to remain up when no other ports are active in the VLAN.
10 58 Inter-VLAN Communication on a Multilayer Switch Through a Switch Virtual Interface NOTE: For the SVI line state to be up, at least one port in the VLAN must be up and forwarding. The switchport auto-state exclude command excludes a port from the SVI interface line-state up-or-down calculation. Configuring a Layer 3 EtherChannel Switch(config)#interface portchannel 1 Switch(config-if)#no switchport Switch(config-if)#ip address Switch(config)#interface range fastethernet 5/4-5 Switch(config-if-range)#no switchport Switch(config-if-range)#channelprotocol pagp Switch(config-if-range)#channelgroup 1 mode desirable Creates a virtual Layer 2 interface. Changes interface to Layer 3 to enable the use of the IP address command. Assigns an IP address to the Layer 3 port-channel interface. Moves to interface range configuration Creates Layer 3 ports on a switch. Configures port aggregation protocol. Assigns the physical interfaces in the range to the EtherChannel group. Configuring Inter-VLAN Communication 3550Switch(config)#interface vlan 1 Creates a virtual interface for VLAN 1 and enters interface configuration 3550Switch(config-if)#ip address Switch(config-if)#no shutdown Assigns IP address and netmask. 3550Switch(config)#interface vlan 10 Creates a virtual interface for VLAN 10 and enters interface configuration 3550Switch(config-if)#ip address Switch(config-if)#no shutdown Assigns IP address and netmask. 3550Switch(config)#interface vlan 20 Creates a virtual interface for VLAN 20 and enters interface configuration
11 Configuration Example: Inter-VLAN Communication Switch(config-if)#ip address Switch(config-if)#no shutdown 3550Switch(config-if)#exit 3550Switch(config)#ip routing Assigns IP address and netmask. Enables routing on the switch. Configuration Example: Inter-VLAN Communication Figure 4-1 shows the network topology for the configuration that follows, which shows how to configure inter-vlan communication using commands covered in this chapter. Some commands used in this configuration are from previous chapters. Figure 4-1 Network Topology for Inter-VLAN Communication Configuration s 0/0/ /30 s 0/0/0 DCE /30 ISP Lo /24 Internet fa 0/ /30 Gi0/1 fa 0/ / L3Switch1 CORP fa 0/0 no IP address fa 0/0.1 VLAN 1 (Native) /24 fa 0/0.10 VLAN /24 fa 0/0.20 VLAN /24 fa 0/0.30 VLAN /24 IEEE 802.1q Trunk fa0/1 L2Switch Gi0/1 L2Switch1 IEEE 802.1q Gigabit Trunk 2950 Native VLAN /24 Sales VLAN 10 fa 0/ /24 Engineering VLAN 20 fa 0/ /24 Marketing VLAN 30 fa 0/ /24 WS3 WS4 WS5 Native VLAN /24 Accounting VLAN 10 fa 0/ /24 Marketing VLAN 20 fa 0/ / / / /24 WS1 WS / /24
12 60 Configuration Example: Inter-VLAN Communication ISP Router Router>enable Router>#configure terminal Router(config)#hostname ISP ISP(config)#interface loopback 0 ISP(config-if)#description simulated address representing remote website ISP(config-if)#ip address ISP(config-if)#interface serial 0/0/0 ISP(config-if)#description WAN link to the Corporate Router ISP(config-if)#ip address ISP(config-if)#clock rate ISP(config-if)#no shutdown ISP(config-if)#exit ISP(config-if)#router eigrp 10 ISP(config-router)#network ISP(config-router)#network ISP(config-router)#no auto-summary ISP(config-router)#exit Moves to privileged Moves to global configuration Sets the host name. Moves to interface configuration Sets the locally significant interface description. Assigns IP address and netmask. Moves to interface configuration Sets the locally significant interface description. Assigns IP address and netmask. Assigns a clock rate to the interface DCE cable is plugged in to this interface. Creates Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) routing process 10. Advertises directly connected networks (classful address only). Advertises directly connected networks (classful address only). Disables auto summarization.
13 Configuration Example: Inter-VLAN Communication 61 ISP(config)#exit ISP#copy running-config startup-config Returns to privileged Saves the configuration to NVRAM. CORP Router Router>enable Router>#configure terminal Router(config)#hostname CORP ISP(config)#interface serial 0/0/0 CORP(config-if)#description link to ISP CORP(config-if)#ip address CORP(config-if)#no shutdown CORP(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1 CORP(config-if)#description link to 3560 Switch CORP(config-if)#ip address CORP(config-if)#no shutdown CORP(config-if)#exit CORP(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 CORP(config-if)#duplex full CORP(config-if)#no shutdown Moves to privileged Moves to global configuration Sets the host name. Moves to interface configuration Sets the locally significant interface description. Assigns IP address and netmask. Moves to interface configuration Sets the locally significant interface description. Assigns the IP address and netmask. Enters interface configuration Enables full-duplex operation to ensure trunking will take effect between here and L2Switch2.
14 62 Configuration Example: Inter-VLAN Communication CORP(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/0.1 CORP(config-subif)#description Management VLAN 1 Native VLAN CORP(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 1 native CORP(config-subif)#ip address CORP(config-subif)#interface fastethernet 0/0.10 CORP(config-subif)#description Sales VLAN 10 CORP(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 10 CORP(config-subif)#ip address CORP(config-subif)#interface fastethernet 0/0.20 CORP(config-subif)#description Engineering VLAN 20 CORP(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 20 CORP(config-subif)#ip address CORP(config-subif)#interface fastethernet 0/0.30 Creates a virtual subinterface and moves to subinterface configuration Sets the locally significant interface description. Assigns VLAN 1 to this subinterface. VLAN 1 is the native VLAN. This subinterface uses the 802.1Q trunking protocol. Assigns the IP address and netmask. Creates a virtual subinterface and moves to subinterface configuration Sets the locally significant interface description. Assigns VLAN 10 to this subinterface. This subinterface uses the 802.1Q trunking protocol. Assigns the IP address and netmask. Creates a virtual subinterface and moves to subinterface configuration Sets the locally significant interface description. Assigns VLAN 20 to this subinterface. This subinterface uses the 802.1Q trunking protocol. Assigns the IP address and netmask. Creates a virtual subinterface and moves to subinterface configuration
15 Configuration Example: Inter-VLAN Communication 63 CORP(config-subif)#description Marketing VLAN 30 CORP(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 30 CORP(config-subif)#ip add CORP(config-subif)#exit CORP(config-if)#exit Sets the locally significant interface description. Assigns VLAN 30 to this subinterface. This subinterface uses the 802.1Q trunking protocol. Assigns the IP address and netmask. Returns to interface configuration CORP(config)#router eigrp 10 Creates EIGRP routing process 10 and moves to router configuration CORP(config-router)#network Advertises the network. CORP(config-router)#network CORP(config-router)#network CORP(config-router)#network CORP(config-router)#network CORP(config-router)#network CORP(config-router)#no auto-summary CORP(config-router)#exit CORP(config)#exit CORP#copy running-config startup-config Advertises the network. Advertises the network. Advertises the network. Advertises the network. Advertises the network. Turns off automatic summarization at classful boundary. Returns to privileged Saves the configuration in NVRAM.
16 64 Configuration Example: Inter-VLAN Communication L2Switch2 (Catalyst 2960) Switch>enable Switch#configure terminal Switch(config)#hostname L2Switch2 L2Switch2(config)#vlan 10 L2Switch2(config-vlan)#name Sales L2Switch2(config-vlan)#exit L2Switch2(config)#vlan 20 L2Switch2(config-vlan)#name Engineering L2Switch2(config-vlan)#vlan 30 L2Switch2(config-vlan)#name Marketing L2Switch2(config-vlan)#exit L2Switch2(config)#interface range fastethernet 0/2-4 L2Switch2(config-if-range)#switchport mode access L2Switch2(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 10 L2Switch2(config-if-range)#interface range fastethernet 0/5-8 L2Switch2(config-if-range)#switchport mode access Moves to privileged Moves to global configuration Sets the host name. Creates VLAN 10 and enters VLAN-configuration Assigns a name to the VLAN. Creates VLAN 20 and enters VLAN-configuration Assigns a name to the VLAN. Creates VLAN 30 and enters VLAN-configuration Note that you do not have to exit back to global configuration mode to execute this command. Assigns a name to the VLAN. Enables you to set the same configuration parameters on multiple ports at the same time. Sets ports 2 4 as access ports. Assigns ports 2 4 to VLAN 10. Enables you to set the same configuration parameters on multiple ports at the same time. Sets ports 5 8 as access ports.
17 Configuration Example: Inter-VLAN Communication 65 L2Switch2(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 20 L2Switch2(config-if-range)#interface range fastethernet 0/9-12 L2Switch2(config-if-range)#switchport mode access L2Switch2(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 30 L2Switch2(config-if-range)#exit L2Switch2(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1 L2Switch2(config)#description Trunk Link to CORP Router L2Switch2(config-if)#switchport mode trunk L2Switch2(config-if)#exit L2Switch2(config)#interface vlan 1 L2Switch2(config-if)#ip address L2Switch2(config-if)#no shutdown L2Switch2(config-if)#exit L2Switch2(config)#ip default-gateway L2Switch2(config)#exit L2Switch2#copy running-config startupconfig Assigns ports 5 8 to VLAN 20. Enables you to set the same configuration parameters on multiple ports at the same time. Sets ports 9 12 as access ports. Assigns ports 9 12 to VLAN 30. Moves to interface configuration Sets locally significant interface description. Puts the interface into trunking mode and negotiates to convert the link into a trunk link. Creates virtual interface for VLAN 1 and enters interface configuration Assigns the IP address and netmask. Assigns the default gateway address. Returns to privileged Saves the configuration in NVRAM.
18 66 Configuration Example: Inter-VLAN Communication L3Switch1 (Catalyst 3560) Switch>enable Switch#configure terminal Switch(config)#hostname L3Switch1 L3Switch1(config)#vtp mode sever L3Switch1(config)#vtp domain testdomain L3Switch1(config)#vlan 10 L3Switch1(config-vlan)#name Accounting L3Switch1(config-vlan)#exit L3Switch1(config)#vlan 20 L3Switch1(config-vlan)#name Marketing L3Switch1(config-vlan)#exit L3Switch1(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/1 L3Switch1(config-if)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q L3Switch1(config-if)#switchport mode trunk L3Switch1(config-if)#exit L3Switch1(config)#ip routing L3Switch1(config)#interface vlan 1 Moves to privileged Moves to global configuration Sets the host name. Changes the switch to VTP server Configures the VTP domain name to testdomain. Creates VLAN 10 and enters VLAN-configuration Assigns a name to the VLAN. Creates VLAN 20 and enters VLAN-configuration Assigns a name to the VLAN. Moves to interface configuration Specifies 802.1Q encapsulation on the trunk link. Puts the interface into trunking mode and negotiates to convert the link into a trunk link. Enables IP routing on this device. Creates a virtual interface for VLAN 1 and enters interface configuration
19 Configuration Example: Inter-VLAN Communication 67 L3Switch1(config-if)#ip address L3Switch1(config-if)#no shutdown L3Switch1(config-if)#interface vlan 10 L3Switch1(config-if)#ip address L3Switch1(config-if)#no shutdown L3Switch1(config-if)#interface vlan 20 L3Switch1(config-if)#ip address L3Switch1(config-if)#no shutdown L3Switch1(config-if)#exit L3Switch1(config)#interface fastethernet 0/24 L3Switch1(config-if)#no switchport L3Switch1(config-if)#ip address L3Switch1(config-if)#exit Assigns the IP address and netmask. Creates a virtual interface for VLAN 10 and enters interface configuration Assigns the IP address and mask. Creates a virtual interface for VLAN 20 and enters interface configuration Assigns the IP address and mask. Enters interface configuration Creates a Layer 3 port on the switch. Assigns the IP address and netmask. L3Switch1(config)#router eigrp 10 Creates EIGRP routing process 10 and moves to router config L3Switch1(config-router)#network L3Switch1(config-router)#network Advertises the classful network. Advertises the classful network.
20 68 Configuration Example: Inter-VLAN Communication L3Switch1(config-router)#no auto-summary L3Switch1(config-router)#exit L3Switch1(config)#exit L3Switch1#copy running-config startupconfig Turns off automatic summarization at classful boundary. Applies changes and returns to global configuration Returns to privileged Saves configuration in NVRAM. L2Switch1 (Catalyst 2960) Switch>enable Switch#configure terminal Switch(config)#hostname L2Switch1 L2Switch1(config)#vtp domain testdomain L2Switch1(config)#vtp mode client L2Switch1(config)#interface range fastethernet 0/1-4 L2Switch1(config-if-range)#switchport mode access L2Switch1(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 10 L2Switch1(config-if-range)#interface range fastethernet 0/5-8 L2Switch1(config-if-range)#switchport mode access L2Switch1(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 20 L2Switch1(config-if-range)#exit Moves to privileged Moves to global configuration Sets the host name. Configures the VTP domain name to testdomain. Changes the switch to VTP client Enables you to set the same configuration parameters on multiple ports at the same time. Sets ports 1 4 as access ports. Assigns ports 1 4 to VLAN 10. Enables you to set the same configuration parameters on multiple ports at the same time. Sets ports 5 8 as access ports. Assigns ports 5 8 to VLAN 20.
21 Configuring DHCP Server on a Router or Layer 3 Switch 69 L2Switch1(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/1 L2Switch1(config-if)#switchport mode trunk L2Switch1(config-if)#exit L2Switch1(config)#interface vlan 1 L2Switch1(config-if)#ip address L2Switch1(config-if)#no shutdown L2Switch1(config-if)#exit L2Switch1(config)#ip default-gateway L2Switch1(config)#exit L2Switch1#copy running-config startupconfig Moves to interface configuration Puts the interface into trunking mode and negotiates to convert the link into a trunk link. Creates a virtual interface for VLAN 1 and enters interface configuration Assigns the IP address and netmask. Assigns the default gateway address. Returns to privileged Saves the configuration in NVRAM. Configuring DHCP Server on a Router or Layer 3 Switch Router(config)#ip dhcp pool internal Router(dhcp-config)#network Router(dhcp-config)#default-router Router(dhcp-config)#dns-server Creates a DHCP pool called internal. Defines the range of addresses to be leased. Defines the address of the default router for the client. Defines the address of the Domain Name System (DNS) server for the client.
22 70 Verifying and Troubleshooting DHCP Configuration Router(dhcp-config)#netbios-nameserver Router(dhcp-config)#domain-name fakedomainname.ca Router(dhcp-config)# lease Router(dhcp-config)#lease infinite Router(dhcp-config)#exit Router(config)#ip dhcp excluded-address Router(config)#service dhcp Router(config)#no service dhcp Defines the address of the NetBIOS server for the client. Defines the domain name for the client. Defines the lease time to be 14 days, 12 hours, 23 minutes. Sets the lease time to infinity; the default time is 1 day. Specifies the range of addresses not to be leased out to clients. Enables the DHCP service and relay features on a Cisco IOS router. Turns off the DHCP service. DHCP service is enabled by default in Cisco IOS Software. Verifying and Troubleshooting DHCP Configuration Router#show ip dhcp binding Router#show ip dhcp binding w.x.y.z Router#clear ip dhcp binding a.b.c.d Router#clear ip dhcp binding * Router#show ip dhcp conflict Router#clear ip dhcp conflict a.b.c.d Router#clear ip dhcp conflict * Displays a list of all bindings created. Displays the bindings for a specific DHCP client with an IP address of w.x.y.z. Clears an automatic address binding from the DHCP server database. Clears all automatic DHCP bindings. Displays a list of all address conflicts recorded by the DHCP server. Clears address conflict from the database. Clears conflicts for all addresses.
23 Configuring a DHCP Helper Address 71 Router#show ip dhcp database Router#show ip dhcp server statistics Router#clear ip dhcp server statistics Router#debug ip dhcp server {events packets linkage class} Displays recent activity on the DHCP database. Displays a list of the number of messages sent and received by the DHCP server. Resets all DHCP server counters to 0. Displays the DHCP process of addresses being leased and returned. Configuring a DHCP Helper Address NOTE: For the SVI line state to be up, at least one port in the VLAN must be up and forwarding. The switchport auto-state exclude command excludes a port from the SVI interface line-state up-or-down calculation. Router Router(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 Router(config-if)#ip helperaddress Moves to interface configuration DHCP broadcasts will be forwarded as a unicast to this specific address rather than be dropped by the router. Layer 3 Switch Switch(config)#interface vlan 10 Switch(config-if)#ip helperaddress Moves to SVI configuration DHCP broadcasts will be forwarded as a unicast to this specific address rather than be dropped by the router. NOTE: The ip helper-address command forwards broadcast packets as a unicast to eight different UDP ports by default: TFTP (port 69) DNS (port 53) Time service (port 37)
24 72 Configuration Example: DHCP NetBIOS name server (port 137) NetBIOS datagram server (port 138) Boot Protocol (BOOTP) client and server datagrams (ports 67 and 68) TACACS service (port 49) Host Name Service (port 42) To close some of these ports, use the no ip forward-protocol udp x command at the global configuration prompt, where x is the port number you want to close. The following command stops the forwarding of broadcasts to port 49: Router(config)#no ip forward-protocol udp 49 To open other UDP ports, use the ip forward-helper udp x command, where x is the port number you want to open: Router(config)#ip forward-protocol udp 517 DHCP Client on a Cisco IOS Software Ethernet Interface Router(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 Router(config-if)#ip address dhcp Moves to interface configuration Specifies that the interface acquire an IP address through DHCP. NOTE: The ip address dhcp command can also be applied on an L3 switch at the SVI as well as any port where the no switchport command has been used. Configuration Example: DHCP Figure 4-2 illustrates the network topology for the configuration that follows, which shows how to configure DHCP services on a Cisco IOS router using the commands covered in this chapter. Figure 4-2 Network Topology for DHCP Configuration Fa0/ /24 NetBIOS Server /8 DNS Server /8 DHCP Client Edmonton Edmonton Is an IOS DHCP Server S0/0/ /30 s0/0/ /30 DHCP Client Gibbons Fa0/ /24
25 Configuration Example: DHCP 73 Edmonton Router router>enable router#configure terminal router(config)#host Edmonton Edmonton(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 Edmonton(config-if)#description LAN Interface Edmonton(config-if)#ip address Edmonton(config-if)#no shutdown Edmonton(config-if)#interface serial 0/0/0 Edmonton(config-if)#description Link to Gibbons Router Edmonton(config-if)#ip address Edmonton(config-if)#clock rate Edmonton(config-if)#no shutdown Edmonton(config-if)#exit Edmonton(config)#router eigrp 10 Edmonton(config-router)#network Edmonton(config-router)#network Edmonton(config-router)#exit Edmonton(config)#service dhcp Edmonton(config)#ip dhcp excludedaddress Moves to privileged Moves to global configuration Sets the host name. Moves to interface configuration Sets the local description of the interface. Assigns an IP address and netmask. Moves to interface configuration Sets the local description of the interface. Assigns an IP address and netmask. Assigns the clock rate to the DCE cable on this side of link. Enables the EIGRP routing process for autonomous system 10. Advertises the network. Advertises the network. Verifies that the router can use DHCP services and that DHCP is enabled. Specifies the range of addresses not to be leased out to clients.
26 74 Configuration Example: DHCP Edmonton(config)#ip dhcp pool 10 network Edmonton(dhcp-config)#network Edmonton(dhcp-config)#defaultrouter Edmonton(dhcp-config)#netbiosname-server Edmonton(dhcp-config)#dns-server Edmonton(dhcp-config)#domain-name fakedomainname.ca Edmonton(dhcp-config)#lease Edmonton(dhcp-config)#exit Edmonton(config)#ip dhcp pool network Edmonton(dhcp-config)#network Edmonton(dhcp-config)#defaultrouter Edmonton(dhcp-config)#netbiosname-server Edmonton(dhcp-config)#dns-server Edmonton(dhcp-config)#domain-name fakedomainname.ca Edmonton(dhcp-config)#lease Edmonton(dhcp-config)#exit Edmonton(config)#exit Edmonton#copy running-config startup-config Creates a DHCP pool called 10network. Defines the range of addresses to be leased. Defines the address of the default router for clients. Defines the address of the NetBIOS server for clients. Defines the address of the DNS server for clients. Defines the domain name for clients. Sets the lease time to be 12 days, 14 hours, 30 minutes. Creates a DHCP pool called the network. Defines the range of addresses to be leased. Defines the address of the default router for clients. Defines the address of the NetBIOS server for clients. Defines the address of the DNS server for clients. Defines the domain name for clients. Sets the lease time to be 12 days, 14 hours, 30 minutes. Returns to privileged Saves the configuration to NVRAM.
27 Configuration Example: DHCP 75 Gibbons Router router>enable router#configure terminal router(config)#host Gibbons Gibbons(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 Gibbons(config-if)#description LAN Interface Gibbons(config-if)#ip address Gibbons(config-if)#ip helperaddress Gibbons(config-if)#no shutdown Gibbons(config-if)#interface serial 0/0/1 Gibbons(config-if)#description Link to Edmonton Router Gibbons(config-if)#ip address Gibbons(config-if)#no shutdown Gibbons(config-if)#exit Gibbons(config)#router eigrp 10 Gibbons(config-router)#network Gibbons(config-router)#network Gibbons(config-router)#exit Gibbons(config)#exit Gibbons#copy running-config startup-config Enters privileged Enters global configuration Sets the host name. Enters interface configuration Sets the local description of the interface. Assigns an IP address and netmask. DHCP broadcasts will be forwarded as a unicast to this address rather than be dropped. Enters interface configuration Sets the local description of the interface. Assigns an IP address and netmask. Enables the EIGRP routing process for autonomous system 10. Advertises the network. Advertises the network. Returns to privileged Saves the configuration to NVRAM.
28 76 Verifying CEF NOTE: The subnets of the VLANs are directly connected to the switch. Routing between these subnets does not require a dynamic routing protocol. If the switch is to be connected to a router and remote communication is desired, a routing protocol must be enabled and networks advertised: 3750Switch(config)#router eigrp Switch(config-router)#network Switch(config-router)#exit 3750Switch(config)# Configuring Cisco Express Forwarding Switch(config)#ip cef Switch(config)#ip cef distributed Switch(config)#no ip cef Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1 Switch(config-if)#ip route-cache cef Enables standard CEF. Enables distributed CEF (dcef). Disables CEF globally. Moves to interface configuration Enables CEF on the interface. Verifying CEF Switch#show ip cef Switch#show ip cef summary Switch#show ip cef unresolved Switch#show ip cef fastethernet 0/1 Switch#show ip cef fastethernet 0/1 detail Switch#show interface fastethernet 0/1 begin L3 Displays entries in the Forwarding Information Base (FIB). Displays a summary of the FIB. Displays unresolved FIB entries. Displays the FIB entry for the specified interface. Displays detailed information about the FIB for the interface. Displays switching statistics for the interface beginning at the section for L3.
29 Troubleshooting CEF 77 Switch#show interface gigabitethernet 1/1 include switched Switch#show adjacency fastethernet 0/20 detail Displays switching statistics that show statistics for each layer. Displays the content of the information to be used during L2 encapsulation. NOTE: When using the show adjacency interface xx detail command, both the next hop-hop and local MAC addresses are displayed as well as the well-known Ethertype value of the encapsulation protocol (0x0800 for IP). Switch#show cef drop Switch#show ip interface vlan10 Displays packets that are dropped because adjacencies are incomplete or nonexistent. Verifies whether CEF is enabled on an interface. Troubleshooting CEF Switch#debug ip cef Switch#debug ip cef drops Switch#debug ip cef drops x Switch#debug ip cef receive Switch#debug ip cef events Switch#debug ip cef prefix-ipc Switch#debug ip cef table Switch#ping ip Displays debug information for CEF. Displays debug information about dropped packets. Records CEF dropped packets that match access-list x. Displays packets that are not switched using information from the FIB but that are received and sent to the next switching layer. Displays general CEF events. Displays updates related to IP prefix information. Produces a table showing events related to the FIB table. Performs an extended ping.
Interconnecting networks with switches. Virtual Local Area Networks (VLAN)
 1 Interconnecting networks with switches. Virtual Local Area Networks (VLAN) Experimental Development Exercise 1: Creating VLANs and trunk links using the 802.1Q protocol The aims of this exercise are:
1 Interconnecting networks with switches. Virtual Local Area Networks (VLAN) Experimental Development Exercise 1: Creating VLANs and trunk links using the 802.1Q protocol The aims of this exercise are:
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing
 Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Internetwork Communications C:>ping 172.16.30.100 Can two hosts on different subnets communicate without a router? No
Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Internetwork Communications C:>ping 172.16.30.100 Can two hosts on different subnets communicate without a router? No
Lab 6.4.1: Basic Inter-VLAN Routing
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1
Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing
 Internetwork Communications C:>ping 72.6.30.00 Implementing Inter-VLN Routing Can two hosts on different subnets communicate without a router? No What would happen if a host tried to ping another host?
Internetwork Communications C:>ping 72.6.30.00 Implementing Inter-VLN Routing Can two hosts on different subnets communicate without a router? No What would happen if a host tried to ping another host?
The following graphic shows a single switch VLAN configuration.
 7.1. VLAN A Virtual LAN (VLAN) can be defined as: Broadcast domains defined by switch port rather than network address. A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria rather than
7.1. VLAN A Virtual LAN (VLAN) can be defined as: Broadcast domains defined by switch port rather than network address. A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria rather than
Ch. 9 VTP (Trunking, VTP, Inter-VLAN Routing) CCNA 3 version 3.0
 Ch. 9 VTP (Trunking, VTP, Inter-VLAN Routing) CCNA 3 version 3.0 Overview Explain the origins and functions of VLAN trunking Describe how trunking enables the implementation of VLANs in a large network
Ch. 9 VTP (Trunking, VTP, Inter-VLAN Routing) CCNA 3 version 3.0 Overview Explain the origins and functions of VLAN trunking Describe how trunking enables the implementation of VLANs in a large network
the larger the number of users and devices, the more broadcasts and packets each switch must handle.
 VLANs Introduction By default, routers allow broadcasts to occur only within the originating network, while switches forward broadcasts to all segments. Flat network = one broadcast domain. that the largest
VLANs Introduction By default, routers allow broadcasts to occur only within the originating network, while switches forward broadcasts to all segments. Flat network = one broadcast domain. that the largest
Lab Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test
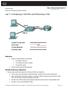 Lab 7.1.6 Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test Objectives Analyze a sample test plan to determine: The subject of the test The methods and tools for testing The potential results Perform the test
Lab 7.1.6 Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test Objectives Analyze a sample test plan to determine: The subject of the test The methods and tools for testing The potential results Perform the test
CCNP SWITCH Portable Command Guide
 CCNP SWITCH Portable Command Guide Scott Empson Hans Roth Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 USA ii CCNP SWITCH Portable Command Guide Scott Empson Hans Roth Copyright 2010 Cisco Systems,
CCNP SWITCH Portable Command Guide Scott Empson Hans Roth Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 USA ii CCNP SWITCH Portable Command Guide Scott Empson Hans Roth Copyright 2010 Cisco Systems,
SWITCH Lab Guide Labs powered by
 SWITCH Lab Guide 300-115 ii SWITCH 300-115 Lab Guide LM20170908/BV1.0 iii 25 C e n tur y Blvd., S te. 5 0 0, N a s hvill e, T N 37214 B o s o n.c o m To perform the labs referenced in this book, please
SWITCH Lab Guide 300-115 ii SWITCH 300-115 Lab Guide LM20170908/BV1.0 iii 25 C e n tur y Blvd., S te. 5 0 0, N a s hvill e, T N 37214 B o s o n.c o m To perform the labs referenced in this book, please
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Advance Networks Laboratory Exp.4 Inter-VLAN Routing
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Advance Networks Laboratory 0907529 Exp.4 Inter-VLAN Routing Objectives 1. Describe the three primary options for
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Advance Networks Laboratory 0907529 Exp.4 Inter-VLAN Routing Objectives 1. Describe the three primary options for
CCENT Study Guide. Chapter 11 VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing
 CCENT Study Guide Chapter 11 VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing Chapter 11 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: 2.0 LAN Switching Technologies 2.4 Configure, verify, and troubleshoot
CCENT Study Guide Chapter 11 VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing Chapter 11 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: 2.0 LAN Switching Technologies 2.4 Configure, verify, and troubleshoot
Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing
 Internetwork Communications C:>ping 172.16.30.100 Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing Can two hosts on different subnets communicate without a router? No What would happen if a host tried to ping another host?
Internetwork Communications C:>ping 172.16.30.100 Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing Can two hosts on different subnets communicate without a router? No What would happen if a host tried to ping another host?
Sybex CCENT Chapter 11: VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing. Instructor & Todd Lammle
 Sybex CCENT 100-101 Chapter 11: VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 11 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: LAN Switching Technologies Describe how VLANs
Sybex CCENT 100-101 Chapter 11: VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 11 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: LAN Switching Technologies Describe how VLANs
Describing the STP. Enhancements to STP. Configuring PortFast. Describing PortFast. Configuring. Verifying
 Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0)
 CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Cisco 200-125 Dumps Available Here at: /cisco-exam/200-125-dumps.html Enrolling now you will get access to 455 questions in a unique set of 200-125 dumps
CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Cisco 200-125 Dumps Available Here at: /cisco-exam/200-125-dumps.html Enrolling now you will get access to 455 questions in a unique set of 200-125 dumps
Lab Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
VLANs. Traditional Campus Networks. Performance Issues. Broadcast Issues. Bridges terminate collision domains
 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example
 EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example Document ID: 82288 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions EtherSwitch Modules Concepts Configure
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example Document ID: 82288 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions EtherSwitch Modules Concepts Configure
CCNP SWITCH (22 Hours)
 CCNP SWITCH 642-813 (22 Hours) Chapter-1 Enterprise Campus Network Design 1.1 IIN & SONA 1.2 Campus Network 1.3 Enterprise Model 1.4 Nonhierarchical Network Devices Layer-2 Switching, Layer-3 Routing Multilayer
CCNP SWITCH 642-813 (22 Hours) Chapter-1 Enterprise Campus Network Design 1.1 IIN & SONA 1.2 Campus Network 1.3 Enterprise Model 1.4 Nonhierarchical Network Devices Layer-2 Switching, Layer-3 Routing Multilayer
BraindumpsIT. BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf!
 BraindumpsIT http://www.braindumpsit.com BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf! Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
BraindumpsIT http://www.braindumpsit.com BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf! Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks (BCMSN)
 Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks (BCMSN) Table of Contents Module 1 Defining VLANs Implementing Best Practices for VLAN Topologies Describing Issues in a Poorly Designed Network Grouping Business
Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks (BCMSN) Table of Contents Module 1 Defining VLANs Implementing Best Practices for VLAN Topologies Describing Issues in a Poorly Designed Network Grouping Business
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup
 Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy
 Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1
Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1
Configuring Private VLANs
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Configuring a Management IP Address on Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000, 6500/6000, and Catalyst Fixed Configuration Switches
 Configuring a Management IP Address on Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000, 6500/6000, and Catalyst Fixed Configuration Switches Document ID: 10594 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your
Configuring a Management IP Address on Catalyst 4500/4000, 5500/5000, 6500/6000, and Catalyst Fixed Configuration Switches Document ID: 10594 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your
SWITCH Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks
 Hands-On SWITCH Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks CCNP Course 2 Course Description Revised CCNP Curriculum and Exams Cisco has redesigned the CCNP courses and exams to reflect the evolving job tasks
Hands-On SWITCH Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks CCNP Course 2 Course Description Revised CCNP Curriculum and Exams Cisco has redesigned the CCNP courses and exams to reflect the evolving job tasks
Configuring Interface Characteristics
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the switch and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack. The
CHAPTER 10 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the switch and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack. The
Configuring Network Access to the GGSN
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure access from the gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) to a serving GPRS support node (SGSN), public data network (PDN), and optionally to a Virtual Private
CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure access from the gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) to a serving GPRS support node (SGSN), public data network (PDN), and optionally to a Virtual Private
Integrated IS-IS CHAPTER 4. ISO Network Entity Title (NET)
 CHAPTER 4 Integrated IS-IS This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) topics: ISO Network Entity Title (NET) Rules for creating
CHAPTER 4 Integrated IS-IS This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) topics: ISO Network Entity Title (NET) Rules for creating
SOHO. A Case Study. Case Study: SOHO
 SOHO A Case Study Authors: Mary Hawkins & Patrick Neff - 2006 Page 1 of 21 Core Area These routers connect to the various offices and to the core router to ensure that all offices are able to connect to
SOHO A Case Study Authors: Mary Hawkins & Patrick Neff - 2006 Page 1 of 21 Core Area These routers connect to the various offices and to the core router to ensure that all offices are able to connect to
Lab Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.1 Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure Inter-VLAN routing using a switch with an internal route processor. The network
Lab 5.3.4.1 Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure Inter-VLAN routing using a switch with an internal route processor. The network
CCENT Study Guide. Chapter 7 Managing a Cisco Internetwork
 CCENT Study Guide Chapter 7 Managing a Cisco Internetwork Chapter 7 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: 2.0 LAN Switching Technologies 2.6 Configure and verify Layer 2 protocols.
CCENT Study Guide Chapter 7 Managing a Cisco Internetwork Chapter 7 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: 2.0 LAN Switching Technologies 2.6 Configure and verify Layer 2 protocols.
Implement Inter-VLAN Routing. LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 6 Modified by Tony Chen 11/01/2008
 Implement Inter-VLAN Routing LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 6 Modified by Tony Chen 11/01/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you see any mistake
Implement Inter-VLAN Routing LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 6 Modified by Tony Chen 11/01/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you see any mistake
Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP)
 Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) MSIT106 / 120 Hours / 12 Months / Self-Paced / Materials Included Course Overview: This CCNP Routing & Switching, Troubleshooting & Maintaining, and Implementing
Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) MSIT106 / 120 Hours / 12 Months / Self-Paced / Materials Included Course Overview: This CCNP Routing & Switching, Troubleshooting & Maintaining, and Implementing
Lab 5: Basic VLAN Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
TestOut Routing and Switching Pro - English 6.0.x COURSE OUTLINE. Modified
 TestOut Routing and Switching Pro - English 6.0.x COURSE OUTLINE Modified 2017-07-10 TestOut Routing and Switching Pro Outline- English 6.0.x Videos: 133 (15:42:34) Demonstrations: 78 (7:22:19) Simulations:
TestOut Routing and Switching Pro - English 6.0.x COURSE OUTLINE Modified 2017-07-10 TestOut Routing and Switching Pro Outline- English 6.0.x Videos: 133 (15:42:34) Demonstrations: 78 (7:22:19) Simulations:
Actual4Test. Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams
 Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 200-125 Title : CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 200-125 Title : CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
Chapter 3: VLANs. Routing & Switching
 Chapter 3: VLANs Routing & Switching VLAN Definitions A VLAN is a logical partition of a Layer 2 network. VLANs logically group hosts, regardless of physical location. Multiple partitions can be created,
Chapter 3: VLANs Routing & Switching VLAN Definitions A VLAN is a logical partition of a Layer 2 network. VLANs logically group hosts, regardless of physical location. Multiple partitions can be created,
Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF).
 Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
CCNA Routing and Switching (NI )
 CCNA Routing and Switching (NI400+401) 150 Hours ` Outline The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) Routing and Switching composite exam (200-125) is a 90-minute, 50 60 question assessment that is
CCNA Routing and Switching (NI400+401) 150 Hours ` Outline The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) Routing and Switching composite exam (200-125) is a 90-minute, 50 60 question assessment that is
Chapter 7. IP Addressing Services. IP Addressing Services. Part I
 Chapter 7 IP Addressing Services Part I CCNA4-1 Chapter 7-1 IP Addressing Services Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) CCNA4-2 Chapter 7-1 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Every device
Chapter 7 IP Addressing Services Part I CCNA4-1 Chapter 7-1 IP Addressing Services Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) CCNA4-2 Chapter 7-1 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Every device
Cisco Certified Network Associate ( )
 Cisco Certified Network Associate (200-125) Exam Description: The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) Routing and Switching composite exam (200-125) is a 90-minute, 50 60 question assessment that
Cisco Certified Network Associate (200-125) Exam Description: The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) Routing and Switching composite exam (200-125) is a 90-minute, 50 60 question assessment that
Configuring HSRP. Global Knowledge Training LLC L5-1
 L5 Configuring HSRP Global Knowledge Training LLC L5-1 Objectives In this lab you will examine the hot standby router protocol (HSRP). First you will configure PxR2 similar to PxR1, so they are both possible
L5 Configuring HSRP Global Knowledge Training LLC L5-1 Objectives In this lab you will examine the hot standby router protocol (HSRP). First you will configure PxR2 similar to PxR1, so they are both possible
CCNP TSHOOT. Quick Reference Sheet Exam
 CCNP TSHOOT Quick Reference Sheet Exam 300-135 Chapter 1. Network Principles Troubleshooting Steps Problem Identification Collection of Information Examination and Action Plan Verification Basic Troubleshooting
CCNP TSHOOT Quick Reference Sheet Exam 300-135 Chapter 1. Network Principles Troubleshooting Steps Problem Identification Collection of Information Examination and Action Plan Verification Basic Troubleshooting
CCNA. Murlisona App. Hiralal Lane, Ravivar Karanja, Near Pethe High-School, ,
 CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate (200-125) Exam DescrIPtion: The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) Routing and Switching composite exam (200-125) is a 90-minute, 50 60 question assessment
CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate (200-125) Exam DescrIPtion: The Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) Routing and Switching composite exam (200-125) is a 90-minute, 50 60 question assessment
EIGRP CHAPTER 9. Configuring Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
 CHAPTER 9 EIGRP This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) EIGRP auto-summarization Load balancing: variance
CHAPTER 9 EIGRP This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) EIGRP auto-summarization Load balancing: variance
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Layer 3 Switch Processing. CEF-Based Multilayer Switches. Layer 3 Switch Processing (Cont.)
 Layer 3 Switch Processing In Layer 3 switches, the control path and data path are relatively independent. The control path code, such as routing protocols, runs on the route processor. Data packets are
Layer 3 Switch Processing In Layer 3 switches, the control path and data path are relatively independent. The control path code, such as routing protocols, runs on the route processor. Data packets are
PT Activity 8.6.1: CCNA Skills Integration Challenge Topology Diagram
 Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 7 Addressing Table for HQ Device Interface IP Address Subnet
Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 7 Addressing Table for HQ Device Interface IP Address Subnet
Table of Contents. Cisco Using One DHCP Server for Voice and Data Networks
 Table of Contents Using One DHCP Server for Voice and Data Networks1 Document ID: 19580..1 Introduction.1 Prerequisites1 Requirements1 Components Used..1 Conventions..1 Problem.2 Solution.2 The Network
Table of Contents Using One DHCP Server for Voice and Data Networks1 Document ID: 19580..1 Introduction.1 Prerequisites1 Requirements1 Components Used..1 Conventions..1 Problem.2 Solution.2 The Network
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
12.1. IPv6 Feature. The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) assigns IPv6 addresses based on the following strategy:
 12.1. IPv6 Feature The current IP addressing standard, version 4, will eventually run out of unique addresses, so a new system is being developed. It is named IP version 6 or IPv6. You should know about
12.1. IPv6 Feature The current IP addressing standard, version 4, will eventually run out of unique addresses, so a new system is being developed. It is named IP version 6 or IPv6. You should know about
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2
 Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Configuring and Deploying DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) on a Cisco Router
 Technical Brief Configuring and Deploying DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) on a Cisco Router Prepared by Don R. Crawley, MCSE, CCNA-certified President, soundtraining.net Email: don@soundtraining.net
Technical Brief Configuring and Deploying DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) on a Cisco Router Prepared by Don R. Crawley, MCSE, CCNA-certified President, soundtraining.net Email: don@soundtraining.net
Laboration 1 Examine the Topology and Basic Troubleshooting Commands
 Laboration 1 Examine the Topology and Basic Troubleshooting Commands Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page
Laboration 1 Examine the Topology and Basic Troubleshooting Commands Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page
LAN Switching and Wireless
 LAN Switching and Wireless CCNA Exploration Labs and Study Guide Allan Johnson ii LAN Switching and Wireless, CCNA Exploration Labs and Study Guide LAN Switching and Wireless CCNA Exploration Labs and
LAN Switching and Wireless CCNA Exploration Labs and Study Guide Allan Johnson ii LAN Switching and Wireless, CCNA Exploration Labs and Study Guide LAN Switching and Wireless CCNA Exploration Labs and
DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II. DOiT-200v6 Lab 3 Multi-Topic CCIE-Level Scenario. For CCIE Candidates
 Revision 7.0 (10/20/2005) DOiT-200v6-SCENARIO 3 Page 1 NETMASTERCLASS ROUTING AND SWITCHING CCIE TRACK DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II DOiT-200v6 Lab 3 Multi-Topic CCIE-Level Scenario For CCIE Candidates Revision
Revision 7.0 (10/20/2005) DOiT-200v6-SCENARIO 3 Page 1 NETMASTERCLASS ROUTING AND SWITCHING CCIE TRACK DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II DOiT-200v6 Lab 3 Multi-Topic CCIE-Level Scenario For CCIE Candidates Revision
CCNP BCMSN Portable Command Guide
 CCNP BCMSN Portable Command Guide Scott Empson Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 USA ii CCNP BCMSN Portable Command Guide Scott Empson Copyright 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. Published
CCNP BCMSN Portable Command Guide Scott Empson Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 USA ii CCNP BCMSN Portable Command Guide Scott Empson Copyright 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. Published
PT Activity 4.4.1: Basic VTP Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13 255.255.255.0
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13 255.255.255.0
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 9, Issue 9, September ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 9, Issue 9, September-2018 10 The Importance of VLANs and Trunk Links in Network Communication Areas Dlnya Abdulahad Aziz Computer Technical
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 9, Issue 9, September-2018 10 The Importance of VLANs and Trunk Links in Network Communication Areas Dlnya Abdulahad Aziz Computer Technical
Configuring Interface Characteristics
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Catalyst 3750 switch and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and a switch
CHAPTER 11 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Catalyst 3750 switch and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and a switch
CISCO EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
 CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Number: 100-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 35.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Exam Name: CCNA Interconnecting
CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Number: 100-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 35.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Exam Name: CCNA Interconnecting
CCNA Practice Questions Exam Cram 2. Copyright 2004 by Que Publishing. International Standard Book Number: Warning and Disclaimer
 CCNA Practice Questions Exam Cram 2 Copyright 2004 by Que Publishing International Standard Book Number: 0789731789 Warning and Disclaimer Every effort has been made to make this book as complete and as
CCNA Practice Questions Exam Cram 2 Copyright 2004 by Que Publishing International Standard Book Number: 0789731789 Warning and Disclaimer Every effort has been made to make this book as complete and as
LAB 3 Basic Switch Configuration Commands
 LAB 3 Basic Switch Configuration Commands This lab explains basic switch configuration commands in detail with examples. Configuration and commands explained in this tutorial are essential commands to
LAB 3 Basic Switch Configuration Commands This lab explains basic switch configuration commands in detail with examples. Configuration and commands explained in this tutorial are essential commands to
Lab 7.5.3: Troubleshooting the Wireless WRT300N
 Lab 7.5.3: Troubleshooting the Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/1.5 5.5.5.10 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/1.10 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 7.5.3: Troubleshooting the Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/1.5 5.5.5.10 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/1.10 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
TEXTBOOK MAPPING CISCO COMPANION GUIDES
 TestOut Routing and Switching Pro - English 6.0.x TEXTBOOK MAPPING CISCO COMPANION GUIDES Modified 2018-08-20 Objective Mapping: Cisco 100-105 ICND1 Objective to LabSim Section # Exam Objective TestOut
TestOut Routing and Switching Pro - English 6.0.x TEXTBOOK MAPPING CISCO COMPANION GUIDES Modified 2018-08-20 Objective Mapping: Cisco 100-105 ICND1 Objective to LabSim Section # Exam Objective TestOut
IEEE 802.1Q Configuration
 CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
Wireless LAN Controller Module Configuration Examples
 Wireless LAN Controller Module Configuration Examples Document ID: 70530 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Basic Configuration Example 1 Basic Configuration with
Wireless LAN Controller Module Configuration Examples Document ID: 70530 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Basic Configuration Example 1 Basic Configuration with
Exam Topics Cross Reference
 Appendix R Exam Topics Cross Reference This appendix lists the exam topics associated with the ICND1 100-105 exam and the CCNA 200-125 exam. Cisco lists the exam topics on its website. Even though changes
Appendix R Exam Topics Cross Reference This appendix lists the exam topics associated with the ICND1 100-105 exam and the CCNA 200-125 exam. Cisco lists the exam topics on its website. Even though changes
VLANs and Trunking C H A P T E R. 6-1: VLAN Configuration. Section 6-1
 C H A P T E R 6 Section 6-1 VLANs and Trunking See the following sections for configuration information about these topics: 6-1: VLAN Configuration Describes the method for configuring, creating, and configuring
C H A P T E R 6 Section 6-1 VLANs and Trunking See the following sections for configuration information about these topics: 6-1: VLAN Configuration Describes the method for configuring, creating, and configuring
Configuring VLANs. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller
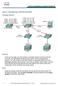 Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller Topology Diagram Scenario Step 1 In the next two labs, you will configure a wireless solution involving a WLAN controller, two lightweight wireless access points,
Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller Topology Diagram Scenario Step 1 In the next two labs, you will configure a wireless solution involving a WLAN controller, two lightweight wireless access points,
Configuring the Cisco IOS XE DHCP Server
 Configuring the Cisco IOS XE DHCP Server Last Updated: December 20, 2011 Cisco routers running Cisco IOS XE software include Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server and relay agent software.
Configuring the Cisco IOS XE DHCP Server Last Updated: December 20, 2011 Cisco routers running Cisco IOS XE software include Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server and relay agent software.
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses
 Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
Smart Serial. Show interfaces. Shut down. logging synchronous
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 2 Static Networking V 4.0 2.1.1 What are the primary responsibilities of the router? 2.1.3 What is the first serial connector described called at the router end? What is the first serial
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 2 Static Networking V 4.0 2.1.1 What are the primary responsibilities of the router? 2.1.3 What is the first serial connector described called at the router end? What is the first serial
RealCiscoLAB.com. Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions Topology Objective Background Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions Topology Objective Background Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route
Lab Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration
 Lab 1.1.5 Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration Objective Configure a router for Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) Test the configuration and verify NAT/PAT statistics
Lab 1.1.5 Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration Objective Configure a router for Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) Test the configuration and verify NAT/PAT statistics
CCNA Explorer 1 Chapter 11 Configuring & Testing Your Network
 CCNA Explorer 1 Chapter 11 Configuring & Testing Your Network 11.1.1 What is the system software in Cisco devices? The Cisco IOS provides devices with what network services? How is the IOS generally accessed?
CCNA Explorer 1 Chapter 11 Configuring & Testing Your Network 11.1.1 What is the system software in Cisco devices? The Cisco IOS provides devices with what network services? How is the IOS generally accessed?
Cisco CCNA (ICND1, ICND2) Bootcamp
 Cisco CCNA (ICND1, ICND2) Bootcamp Course Duration: 5 Days Course Overview This five-day course covers the essential topics of ICND1 and ICND2 in an intensive Bootcamp format. It teaches students the skills
Cisco CCNA (ICND1, ICND2) Bootcamp Course Duration: 5 Days Course Overview This five-day course covers the essential topics of ICND1 and ICND2 in an intensive Bootcamp format. It teaches students the skills
CCNA( ) Dumps V2.0( ) CCNA
 CCNA(200-125) Dumps V2.0(2018.1.3) CCNA 200-125 QUESTION 1 Which technology supports the stateless assignment of IPv6 addresses?(choose two.) A. DNS B. DHCPv6 C. DHCP D. autoconfiguration Correct Answer:
CCNA(200-125) Dumps V2.0(2018.1.3) CCNA 200-125 QUESTION 1 Which technology supports the stateless assignment of IPv6 addresses?(choose two.) A. DNS B. DHCPv6 C. DHCP D. autoconfiguration Correct Answer:
Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller
 Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller Topology Diagram Scenario In the next two labs, you will configure a wireless solution involving a router with a built-in WLAN controller, two lightweight wireless
Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller Topology Diagram Scenario In the next two labs, you will configure a wireless solution involving a router with a built-in WLAN controller, two lightweight wireless
VLAN Configuration. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
Actual4Test. Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams
 Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid
Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid
Switches running the LAN Base feature set support only static routing on SVIs.
 Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, on page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, on page 2 Information About VLANs, on page 2 How to Configure VLANs, on page 6 Monitoring VLANs, on page
Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, on page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, on page 2 Information About VLANs, on page 2 How to Configure VLANs, on page 6 Monitoring VLANs, on page
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Payload Types At Different OSI Layers: Layer 2 - Frame Layer 3 - Packet Layer 4 - Datagram
 Payload Types At Different OSI Layers: Layer 2 - Frame Layer 3 - Packet Layer 4 - Datagram Default Cisco Terminal Options: 9600 bits/second No hardware flow control 8-bit ASCII No parity 1 stop bit Setting
Payload Types At Different OSI Layers: Layer 2 - Frame Layer 3 - Packet Layer 4 - Datagram Default Cisco Terminal Options: 9600 bits/second No hardware flow control 8-bit ASCII No parity 1 stop bit Setting
Lab Configuring and Testing the Rapid Spanning Tree Prototype
 Lab 7.3.3 Configuring and Testing the Rapid Spanning Tree Prototype Device Designation Device Name IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0.1 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 R1 BR4 Fa0/0.10 10.10.10.254 255.255.255.0
Lab 7.3.3 Configuring and Testing the Rapid Spanning Tree Prototype Device Designation Device Name IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0.1 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 R1 BR4 Fa0/0.10 10.10.10.254 255.255.255.0
