STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 6
|
|
|
- Anthony Osborne
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 6 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Popular audio and media players include itunes, Windows Media Player, and open source offerings such as QuickAudio and Audacity. 2. Using speech recognition software, you can "voice surf" the Web by speaking commands instead of using your mouse. 3. A(n) on-and-off connection can have a static or dynamic IP address. 4. A domain name ends with an extension that indicates its top-level domain. 5. Downstream speed is the rate of data transmitted from your computer to the Internet. 6. Mobile Internet access allows you to easily move your access device, as in the case of vehicle-mounted satellite dishes that can be deployed when the vehicle is parked. 7. Current dial-up technology can transport data at speeds up to 6 MB downstream for a distance of about 1.25 miles. 8. DSL is digital, so data doesn't need to be changed into analog signals and then back to digital. 9. Wi-Fi handoffs from one Wi-Fi network to another are clumsy and prone to packet loss. 10. The big bonus of portable WiMAX is that you use the same Internet service provider whether you are at home or on the road. 11. Some cell phones can act as a Wi-Fi hotspot by becoming the router for a wireless network. 12. Google Apps provides a glimpse of what grid computing has to offer for productivity applications. 13. Most messaging is based on a client/server technology. 14. Distributed grids tap into thousands of PCs and Macs with Internet connections whose owners rent their computer s idle hours to a grid processing task. 15. In the context of networking, a(n) virus-protector is software or hardware designed to filter out suspicious packets attempting to enter or leave a computer. 16. NATs are intended to work within LANs to monitor and direct packets being transported from one device to another. 17. Setting up a secure VPN is easy. 18. The octets in an IP address correspond to the parts of a Web site address. 19. All IP addresses are static. 20. All IP addresses are dynamic. 21. The www in a URL is part of a domain name. 22. You must pay for a domain name.
2 23. You may use an analog modem even if your phone service is digital. 24. With a voiceband modem, actual data transfer speeds are affected by factors such as the quality of your phone line and connection. 25. Cable signals are not particularly vulnerable to environmental interference. 26. Most of today s notebooks are not equipped for Wi-Fi. 27. You can use a hotspot for mobile Internet access. 28. To use portable satellite technology you must take your satellite with you. 29. The disadvantages of WAP-enabled devices include their high price. 30. Some cell phones connect to your computer and act as a wireless modem. 31. Cloud computing is the term given to analyzing cloud patterns and, with the help of the computer, predicting the weather. 32. Cell phones that offer Wi-Fi are not capable of making VoIP calls. 33. FTP is a protocol used by Internet phone companies for free long distance. 34. P2P file sharing allows users to obtain files from other users on the Internet. 35. BitTorrent protocols dissect files into small chunks that might reside on different computers. 36. One of the most common ways of gaining unauthorized access to a network is by looking for open ports. 37. Most firewall software is preconfigured to block only unnecessarily open ports targeted by hackers. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 38. MPEG, H.264, DivX, and Windows Media Video are examples of. a. video codecs c. file compression utilities b. audio codecs d. temporal compression 39. Suppose you want to send a photo to a friend. You plan to attach it to an message, but when you look at the file, you notice it is almost 4 megabytes. To quickly store the photo in a small file without any loss in quality, you can. a. use a file compression utility like PKZIP c. use an MPEG codec b. convert the image into a RAW file d. resave it using ripper software 40. The use of to identify human speakers is an emerging part of law enforcement and homeland security. Not only can digitized samples of voices be analyzed to confirm identity, but real-time voice print identification can be used to match speakers with known recordings of their voices. a. audio codecs c. MIDI sequences b. digital spectrographic analysis d. Audio Interchange formats 41. Manufacturers sometimes express the resolution of digital cameras as. a. terapixels c. gigabytes b. megapixels d. megabytes
3 42. Pixel interpolation causes some images, especially those that contain strong curved or diagonal lines, to develop an undesirable "bitmappy" or appearance. a. digitized c. reverse pixel b. pixelated d. cropped 43. Which of the following filename extensions is NOT a vector graphics file? a..wmf c..png b..ai d..eps 44. The Internet began with a project called. a. NSF c. ARPANET b. AOL d. WWW 45. There are estimated to be more than users of the Internet. a. 2 million c. 2 trillion b. 2 billion d. 100 million 46. Network service providers include. a. AT&T c. British Telecom b. Deutsche Telekom d. all answers are correct 47. ISPs can maintain servers for. a. music file sharing c. instant messaging b. online discussions d. all answers are correct 48. The octets in an IP address correspond to a. a. network class c. network configuration b. network location d. no answers are correct 49. Most Internet servers have an easy to remember name that is known as a(n). a. domain address c. FQDN b. ISP d. NAP address 50. is a valid top-level domain. a..ca c..gog b..can d..aol 51. Every domain name corresponds to a unique IP address that has been entered into the. a. domain database c. name server b. Domain Name System d. Internet Name Server 52. Until domain names are added to the DNS database, new sites can only be accessed by entering their numeric. a. ports c. protocols b. domain names d. IP addresses 53. DNS cache has been used by governments to keep citizens away from Web sites that supply politically or culturally inflammatory information. a. diversion c. poisoning b. rerouting d. distraction 54. You need your own domain name if. a. you use the Internet c. you have your own Web site b. you have an always-on connection d. you have a router
4 55. Technical management of the Internet's Domain Name System is coordinated by. a. the government c. CANN b. ICANN d. the Internet 56. The elapsed time for data to make a round trip from point A to point B and back is called. a. speed c. mhz b. latency d. access time 57. The rate of data that is transmitted from your computer to the Internet is. a. downstream speed c. download speed b. upstream speed d. upload speed 58. The rate of data arriving at your computer is. a. downstream speed c. download speed b. upstream speed d. upload speed 59. A fixed Internet connection that uses a voiceband modem and telephone lines is a(n) connection. a. dial-up c. DSL b. fixed d. ISDN 60. Digital telephone systems open up the possibilities for digital data transport options such as. a. cable Internet service c. WiMAX b. DSL d. Both B and C 61. service offered slightly faster service than dial-up but has today been replaced by DSL. a. ISDN c. Cable Internet b. WiMAX d. Satellite Internet 62. DSL uses to transmit data. a. phone lines c. T1 lines b. cable connections d. no answers are correct 63. A is a device that connects a computer to a telephone line and converts computer data signals into signals compatible with DSL. a. DSL filter c. DSL modem b. DSL converter d. DSL adapter 64. currently offers the fastest Internet access speeds. a. ISDN c. Satellite b. DSL d. Cable 65. Cable Internet service needs. a. circuitry to handle Ethernet protocols and a cable modem b. a cable modem and router c. Internet protocols and a cable modem d. a cable modem and phone lines 66. Satellite data transport is subject to delays of one second or more, which occur as your data is routed between your computer and a satellite that orbits 22,200 miles above the Earth. a. latency c. frequency b. conditional d. concatenation 67. Satellite Internet service and TV service requires. a. two satellite dishes c. two satellites dishes and two modems b. a satellite dish and a modem d. one satellite dish and two modems
5 68. wireless Internet service is designed to offer Internet access to homes and businesses by broadcasting data signals over areas large enough to cover most cities and outlying areas. a. Mobile c. WiFi b. Cellular d. Fixed 69. An Ethernet-compatible network standard designated as IEEE is. a. WiFi c. WiMAX b. WiLAN d. WiMAN 70. Portable Internet access includes all of the following EXCEPT. a. WiFi c. portable WiMAX b. portable satellite d. cellular 71. The ability to easily move your Internet service from one location to another is considered Internet service. a. mobile c. moving b. portable d. cellular 72. is an up-and-coming standard destined to be deployed by ISPs and cell phone carriers to allow seamless handoff between one tower and another. a. WiMAX c. Portable WiMAX b. Mobile WiMAX d. Mobile WiFi 73. Data transport rates depend on the technology of the cellular system. The generation of cellular technology associated with analog voice service is. a. 1G c. 2.5G b. 2G d. 3G 74. Sending computer data over a system requires a voiceband modem to convert digital data into audible signals. a. 1G c. 3G b. 2G d. 1G and 2G 75. replaced analog technology with digital technology and added support for text messages. a. 1G c. 3G b. 2G d. 4G 76. technologies support digital transmission for both voice and data. a. 1G c. 3G b. 2G d. no answers are correct 77. 3G technologies have speeds ranging from 200 Kbps to. a. 500 Kbps c. 2 Mbps b. 1 Mbps d. 5 Mbps 78. Examples of 3G technologies include. a. EDGE c. HSUPA b. EV-DO d. all answers are correct 79. Interim 4G technologies such as have been deployed since a. LTE c. EV-DO b. ITE d. no answers are correct 80. A communications protocol that provides Internet access from handheld devices is. a. WAP c. HAP b. WIP d. HIP
6 81. The disadvantage of WAP-enabled devices is their. a. access speed c. portability b. screen size d. all answers are correct 82. With you can easily assemble a small network just about anywhere. a. RF c. EVDO b. MiFi d. all answers are correct 83. computing depends on a grid of servers, storage devices, and protocols that offer Internet-accessible computing services ranging from consumer-level media sharing to office productivity applications and complex corporate data processing. a. Cloud c. Ambient b. Disperse d. Client 84. Most messaging is based on a(n) model. a. P2P c. LAN b. client/server d. Internet 85. Messaging and chat protocols include all of the following EXCEPT. a. IRC c. Jabber b. MSNP d. Talkie 86. VoIP software is sometimes referred to as a(n) client. a. ISP c. HTTP b. SIP d. no answers are correct 87. VoIP systems are offered by companies such as. a. AT&T c. Vonage b. magicjack d. all answers are correct 88. To set up free VoIP, you and the people you communicate with can install free VoIP clients such as. a. SysIP c. Presto b. Blink d. no answers are correct 89. The protocol allows the transfer of files from one computer to another over any TCP/IP network. a. ftp c. P2P b. http d. GRID 90. is a file sharing protocol that distributes the role of the file server across a collection of dispersed computers. a. ftp c. P2P b. http d. BitTorrent 91. With BitTorrent, as more computers request the file, they become part of a that uses peer-to-peer technology to exchange file pieces with each other. a. swarm c. leech b. seed d. choker 92. BitTorrent can be used to distribute. a. spyware c. malicious code b. adware d. all answers are correct 93. Network services such as the Web, ftp, and operate from. a. routers c. ports b. gateways d. portals
7 94. The use of automated software to locate computers that are vulnerable to unauthorized access is a port. a. search c. dig b. probe d. pry 95. The average survival time for an unprotected computer to remain uncompromised is only. a. nine seconds c. nine hours b. nine minutes d. nine days 96. Sharing files on a LAN or the Internet requires open. a. ports c. sources b. domains d. channels 97. are intended to work within LANs to monitor and direct packets being transported from one device to another. a. Routers c. Filters b. Gateways d. Firewalls 98. A IP address is one which can be accessed by packets on the Internet. a. static c. routable b. dynamic d. private 99. You can install personal VPN software such as. a. WiTopia c. HotSpotVPN b. StrongVPN d. all answers are correct 100. One important security precaution when connecting your computer to public networks is to install a(n). a. router c. office suite b. repeater d. remote PC
Chapter 6 The Internet
 Chapter The Internet Computer Concepts 2014 Chapter Contents Section A: Internet Technology Section B: Fixed Internet Access Section C: Portable and Mobile Internet Access Section D: Internet Services
Chapter The Internet Computer Concepts 2014 Chapter Contents Section A: Internet Technology Section B: Fixed Internet Access Section C: Portable and Mobile Internet Access Section D: Internet Services
NOS 116, 118, 218, 222. Lecture Internet
 NOS 116, 118, 218, 222 Lecture Internet BACKGROUND 1957 Soviet Union s Sputnik satellite 1969 APRA (Advanced Research Project Agency) created APRANET 1985 National Science Foundation (NSF) created a larger
NOS 116, 118, 218, 222 Lecture Internet BACKGROUND 1957 Soviet Union s Sputnik satellite 1969 APRA (Advanced Research Project Agency) created APRANET 1985 National Science Foundation (NSF) created a larger
Discovering Computers Chapter 9 Communications and Networks
 Discovering Computers 2009 Chapter 9 Communications and Networks Chapter 9 Objectives Discuss the components required for successful communications Identify various sending and receiving devices Describe
Discovering Computers 2009 Chapter 9 Communications and Networks Chapter 9 Objectives Discuss the components required for successful communications Identify various sending and receiving devices Describe
CSC Introduction to Computers and Their Applications. Background
 CSC 170 - Introduction to Computers and Their Applications Lecture 7 The Internet Background The history of the Internet begins in 1957. In a response to the Soviet Union launching Sputnik, the first man-made
CSC 170 - Introduction to Computers and Their Applications Lecture 7 The Internet Background The history of the Internet begins in 1957. In a response to the Soviet Union launching Sputnik, the first man-made
Chapter 7. Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology
 Chapter 7 Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology LEARNING OBJECTIVES What are the principal components of telecommunications networks and key networking technologies? What are the different
Chapter 7 Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology LEARNING OBJECTIVES What are the principal components of telecommunications networks and key networking technologies? What are the different
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 10 Networking Essentials
 A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
Component 4: Introduction to Information and Computer Science
 Component 4: Introduction to Information and Computer Science Unit 2: Internet and the World Wide Web Lecture 1 This material was developed by Oregon Health & Science University, funded by the Department
Component 4: Introduction to Information and Computer Science Unit 2: Internet and the World Wide Web Lecture 1 This material was developed by Oregon Health & Science University, funded by the Department
Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet
 Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet Don Mason Associate Director Copyright 2011 National Center for Justice and the Rule of Law All Rights Reserved Inside vs. Outside Inside the Box What the computer
Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet Don Mason Associate Director Copyright 2011 National Center for Justice and the Rule of Law All Rights Reserved Inside vs. Outside Inside the Box What the computer
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 10 Networking Essentials
 A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
Inside vs. Outside. Inside the Box What the computer owner actually has possession of 1/18/2011
 Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet Don Mason Associate Director Copyright 2011 National Center for Justice and the Rule of Law All Rights Reserved Inside vs. Outside Inside the Box What the computer
Outside the Box: Networks and The Internet Don Mason Associate Director Copyright 2011 National Center for Justice and the Rule of Law All Rights Reserved Inside vs. Outside Inside the Box What the computer
Communications and Networks
 Information Technology Skills (DUT 122) CHAPTER 6: Communications and Networks Miss Wan Nor Ashiqin Wan Ali School of Human Development and Technocommunication Objectives Overview Discuss the purpose of
Information Technology Skills (DUT 122) CHAPTER 6: Communications and Networks Miss Wan Nor Ashiqin Wan Ali School of Human Development and Technocommunication Objectives Overview Discuss the purpose of
VISUAL SUMMARY COMMUNICATION CHANNELS COMMUNICATIONS. Communications and Networks
 Rev.Confirming Pages VISUAL SUMMARY Communications and Networks COMMUNICATIONS COMMUNICATION CHANNELS Communications is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers.
Rev.Confirming Pages VISUAL SUMMARY Communications and Networks COMMUNICATIONS COMMUNICATION CHANNELS Communications is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers.
Chapter 5 Local Area Networks. Computer Concepts 2013
 Chapter 5 Local Area Networks Computer Concepts 2013 5 Chapter Contents Section A: Network Building Blocks Section B: Wired and Wireless Technologies Section C: Network Setup Section D: Sharing Files Section
Chapter 5 Local Area Networks Computer Concepts 2013 5 Chapter Contents Section A: Network Building Blocks Section B: Wired and Wireless Technologies Section C: Network Setup Section D: Sharing Files Section
It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers.
 1 Communications It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers. Numerous applications depend on communication systems: E-mail Instant messaging (IM) Internet
1 Communications It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers. Numerous applications depend on communication systems: E-mail Instant messaging (IM) Internet
Objectives Overview. Chapter 9 Networks and Communications. Discovering Computers Instructor: Imran Khalil MSc-IT 1 st semester Fall 2016
 Chapter 9 Networks and Communications Instructor: Imran Khalil MSc-IT 1 st semester Fall 2016 Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Discuss the purpose
Chapter 9 Networks and Communications Instructor: Imran Khalil MSc-IT 1 st semester Fall 2016 Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Discuss the purpose
Management Information Systems
 Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology Lecturer: Richard Boateng, PhD. Lecturer in Information Systems, University of Ghana Business School Executive Director, PearlRichards Foundation,
Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology Lecturer: Richard Boateng, PhD. Lecturer in Information Systems, University of Ghana Business School Executive Director, PearlRichards Foundation,
Discovering Computers Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World
 Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Discuss the evolution of the Internet Identify and briefly describe various broadband Internet connections and
Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Discuss the evolution of the Internet Identify and briefly describe various broadband Internet connections and
Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright 2005
 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright 2005 Network and Telecommunications Basics Chapter Outline The telecommunications system Network services
Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright 2005 Network and Telecommunications Basics Chapter Outline The telecommunications system Network services
Pengantar Teknologi Informasi dan Teknologi Hijau. Suryo Widiantoro, ST, MMSI, M.Com(IS)
 Pengantar Teknologi Informasi dan Teknologi Hijau Suryo Widiantoro, ST, MMSI, M.Com(IS) 1 Topics covered 1. From analog to digital age 2. Networks 3. Wired-communication data 4. Wireless-communication
Pengantar Teknologi Informasi dan Teknologi Hijau Suryo Widiantoro, ST, MMSI, M.Com(IS) 1 Topics covered 1. From analog to digital age 2. Networks 3. Wired-communication data 4. Wireless-communication
Naveen Kumar. 1 Wi-Fi Technology
 Naveen Kumar 1 Contents 2 Introduction Need of Purpose History How a Wi-Fi Network Works Topologies & Configurations Applications Wi-Fi Security Advantages & Limitations Innovations Introduction 3 Wireless
Naveen Kumar 1 Contents 2 Introduction Need of Purpose History How a Wi-Fi Network Works Topologies & Configurations Applications Wi-Fi Security Advantages & Limitations Innovations Introduction 3 Wireless
end systems, access networks, links circuit switching, packet switching, network structure
 Introduction Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge end systems, access networks, links 1.3 Network core circuit switching, packet switching, network structure 1.4 Delay, loss and
Introduction Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge end systems, access networks, links 1.3 Network core circuit switching, packet switching, network structure 1.4 Delay, loss and
Telephone. Basic Telephone. A telephone is an electronic device used for two- way talking with other people. EE1D01 Electrical Science for Everyone
 Telephone A telephone is an electronic device used for two- way talking with other people. 1 Basic Telephone Telephone Subscriber Line CO (Local Exchange) T dial switch cradle switch tip (+) ear R mouth
Telephone A telephone is an electronic device used for two- way talking with other people. 1 Basic Telephone Telephone Subscriber Line CO (Local Exchange) T dial switch cradle switch tip (+) ear R mouth
Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web
 Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web Chapter 2 Objectives Explain how to access and connect to the Internet Explain how to view pages and search for information on the Web Describe the types of Web
Chapter 2 The Internet and World Wide Web Chapter 2 Objectives Explain how to access and connect to the Internet Explain how to view pages and search for information on the Web Describe the types of Web
ACE Chapter 4 review. Name: Class: Date: True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 Name: Class: Date: ACE Chapter 4 review True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Today s Internet joins together networks of over 300 million computers, or Internet hosts, to create
Name: Class: Date: ACE Chapter 4 review True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Today s Internet joins together networks of over 300 million computers, or Internet hosts, to create
09-Jan-17. Objectives Overview. The Internet. Objectives Overview. Evolution of the Internet. Evolution of the Internet. Discovering Computers 2012
 Objectives Overview Discuss the evolution of the Identify and briefly describe various broadband connections and state differences between broadband connections and dialup connections Describe the types
Objectives Overview Discuss the evolution of the Identify and briefly describe various broadband connections and state differences between broadband connections and dialup connections Describe the types
Multimedia Technology (IT-204-F) Section A Introduction to multimedia. Lecture 4. Multimedia Networks
 Multimedia Technology (IT-204-F) Section A Introduction to multimedia Lecture 4 Multimedia Networks 1 Multimedia Networks: Five basic types that provide multimedia communication services: -- Telephone
Multimedia Technology (IT-204-F) Section A Introduction to multimedia Lecture 4 Multimedia Networks 1 Multimedia Networks: Five basic types that provide multimedia communication services: -- Telephone
Networking. Prof. Abdul Hameed
 Networking Prof. Abdul Hameed http://informationtechnology.pk http://informationtechnology.pk 0 Chapter Topics Networking Fundamentals Network Architectures and Components Connecting to the Internet Installing
Networking Prof. Abdul Hameed http://informationtechnology.pk http://informationtechnology.pk 0 Chapter Topics Networking Fundamentals Network Architectures and Components Connecting to the Internet Installing
The Internet and the World Wide Web
 Technology Briefing The Internet and the World Wide Web TB5-1 Learning Objectives TB5-2 Learning Objectives TB5-3 How Did the Internet Get Started? Internet derived from internetworking 1960s U.S. Defense
Technology Briefing The Internet and the World Wide Web TB5-1 Learning Objectives TB5-2 Learning Objectives TB5-3 How Did the Internet Get Started? Internet derived from internetworking 1960s U.S. Defense
A+ Guide to Managing & Maintaining Your PC, 8th Edition. Chapter 16 Networking Types, Devices, and Cabling
 A+ Guide to Managing & Maintaining Your PC, Chapter 16 Networking Types, Devices, and Cabling Objectives Learn about network types and topologies Learn about the hardware used to build local networks Learn
A+ Guide to Managing & Maintaining Your PC, Chapter 16 Networking Types, Devices, and Cabling Objectives Learn about network types and topologies Learn about the hardware used to build local networks Learn
Unit 3 Networks. Computer Concepts Unit Contents. 3 Communication Systems. 3 Section A: Network Basics
 Unit 3 Networks Computer Concepts 2016 ENHANCED EDITION 3 Unit Contents Section A: Network Basics Section B: The Internet Section C: Internet Access Section D: Local Area Networks Section E: File Sharing
Unit 3 Networks Computer Concepts 2016 ENHANCED EDITION 3 Unit Contents Section A: Network Basics Section B: The Internet Section C: Internet Access Section D: Local Area Networks Section E: File Sharing
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
Chapter 1 Introduction A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you can add, modify, and delete
16/06/56. Communications and Networks. Communications and Networks. Communications and Networks
 Discuss connectivity, the wireless revolution, and communication systems. Describe physical and wireless communications channels. Discuss connection devices and services, including dial-up, DSL, cable,
Discuss connectivity, the wireless revolution, and communication systems. Describe physical and wireless communications channels. Discuss connection devices and services, including dial-up, DSL, cable,
8 9 Before: Computers are categorized into three main categories from least to most powerful: microcomputers minicomputers mainframe computers Today:
 1 Computer, Internet, and Network Basics 2 Computer Basics A computer system includes a computer, peripheral devices, and software Computer refers to a device that accepts data as input, processes data,
1 Computer, Internet, and Network Basics 2 Computer Basics A computer system includes a computer, peripheral devices, and software Computer refers to a device that accepts data as input, processes data,
Wireless (Select Models Only) User Guide
 Wireless (Select Models Only) User Guide Copyright 2008 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Windows is a U.S. registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Bluetooth is a trademark owned by its
Wireless (Select Models Only) User Guide Copyright 2008 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Windows is a U.S. registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Bluetooth is a trademark owned by its
WHAT IS THE INTERNET?
 The Internet WHAT IS THE INTERNET? A world-wide network of computers allows people to share information electronically It is a BIG book with many web-pages on different topics. It Can be accessed anywhere
The Internet WHAT IS THE INTERNET? A world-wide network of computers allows people to share information electronically It is a BIG book with many web-pages on different topics. It Can be accessed anywhere
Data Communication. Introduction of Communication. Data Communication. Elements of Data Communication (Communication Model)
 Data Communication Introduction of Communication The need to communicate is part of man s inherent being. Since the beginning of time the human race has communicated using different techniques and methods.
Data Communication Introduction of Communication The need to communicate is part of man s inherent being. Since the beginning of time the human race has communicated using different techniques and methods.
LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology
 LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology Erick Setiawan tukangbajaksawah@gmail.com 1 Become a necessity today, where the wireless broadband technology needed to meet increasing expectations in terms
LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology Erick Setiawan tukangbajaksawah@gmail.com 1 Become a necessity today, where the wireless broadband technology needed to meet increasing expectations in terms
end systems, access networks, links circuit switching, packet switching, network structure
 Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge end systems, access networks, links 1.3 Network core circuit switching, packet switching, network structure 1.4 Delay, loss and throughput
Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge end systems, access networks, links 1.3 Network core circuit switching, packet switching, network structure 1.4 Delay, loss and throughput
Chapter 7. Video cases:
 Chapter 7 Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology Video cases: Case 1: Telepresence Moves Out of the Boardrooom and Into the Field Case 2: Unified Communications Systems: Virtual Collaboration
Chapter 7 Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology Video cases: Case 1: Telepresence Moves Out of the Boardrooom and Into the Field Case 2: Unified Communications Systems: Virtual Collaboration
Lecture #25: Networks and Communications. Communication and Networks. What will we learn?
 Lecture #25: Networks and Communications Communication and Networks What will we learn? How a communications system works What a network is What networks used for What network operating systems do What
Lecture #25: Networks and Communications Communication and Networks What will we learn? How a communications system works What a network is What networks used for What network operating systems do What
ECS 15; Lectures 17 and 18. The Internet. What is the internet, and how does it work? TA feedback
 ECS 15; Lectures 17 and 18 The Internet What is the internet, and how does it work? TA feedback Python -- Run your code!! Term paper: Start a paragraph with the point of the paragraph, not in modern times
ECS 15; Lectures 17 and 18 The Internet What is the internet, and how does it work? TA feedback Python -- Run your code!! Term paper: Start a paragraph with the point of the paragraph, not in modern times
Computer Networks. Computer Networks. Telecommunication Links. CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing - Spring Chapter 12: Computer Networks 1
 Computer Networks Chapter 12 Topics: Communication links LAN / WAN Internet / WWW CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing (c) Yngvi Bjornsson 1 Computer Networks A computer network is a set of independent computer
Computer Networks Chapter 12 Topics: Communication links LAN / WAN Internet / WWW CMPUT101 Introduction to Computing (c) Yngvi Bjornsson 1 Computer Networks A computer network is a set of independent computer
Chapter 3. E-commerce The Evolution of the Internet 1961 Present. The Internet: Technology Background. The Internet: Key Technology Concepts
 E-commerce 2015 business. technology. society. eleventh edition Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver Chapter 3 E-commerce Infrastructure: The Internet, Web, and Mobile Platform Copyright 2015 Pearson
E-commerce 2015 business. technology. society. eleventh edition Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver Chapter 3 E-commerce Infrastructure: The Internet, Web, and Mobile Platform Copyright 2015 Pearson
Typical Network Uses
 Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Chapter 9 Introduction to Networks
 Chapter 9 Introduction to Networks 9.1 Uses of a network Networks are used in many situations. We can see networks in places like offices, airports and factories. In fact we use networks in many situations
Chapter 9 Introduction to Networks 9.1 Uses of a network Networks are used in many situations. We can see networks in places like offices, airports and factories. In fact we use networks in many situations
VoIP Dictionary, Glossary and Terminology
 VoIP Dictionary, Glossary and Terminology The following provides a glossary of terms and definitions that are commonly used in VoIP Solutions. We hope this will provide a good reference for you during
VoIP Dictionary, Glossary and Terminology The following provides a glossary of terms and definitions that are commonly used in VoIP Solutions. We hope this will provide a good reference for you during
Acknowledgment and Disclaimer:
 What is the Internet Acknowledgment and Disclaimer: This presentation is supported in part by the National Science Foundation under Grant 1240841. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations
What is the Internet Acknowledgment and Disclaimer: This presentation is supported in part by the National Science Foundation under Grant 1240841. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations
Network Communications Standards. Applied Information Technology
 Network Communications Standards Applied Information Technology Network Standards Why do we need network standards? Defined guidelines for how computers or networked devices communicate Think of it as
Network Communications Standards Applied Information Technology Network Standards Why do we need network standards? Defined guidelines for how computers or networked devices communicate Think of it as
Networking Jamie Tees
 Ethernet is the main networking technology, UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cabling is the main networking cable types, this cabling uses RJ-45 connectors either end. While UTP is the main type we have STP
Ethernet is the main networking technology, UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cabling is the main networking cable types, this cabling uses RJ-45 connectors either end. While UTP is the main type we have STP
has square plastic RJ-45 connector 12 Network Building Blocks Another option is coaxial cable resembles cable-tv cable round, silver BNC connector 13
 1 Internet and LAN Technology 2 Network Building Blocks A communications network is a collection of computers and other devices that communicate to share data, hardware and software In 1948, Claude Shannon
1 Internet and LAN Technology 2 Network Building Blocks A communications network is a collection of computers and other devices that communicate to share data, hardware and software In 1948, Claude Shannon
CNT 4007 Computer Networks - Chapter 1 : Overview
 CNT 4007 Computer Networks - Chapter 1 : Overview Jonathan Kavalan, Ph.D. Department of Computer, Information Science and Engineering (CISE), University of Florida 1 Chapter 1: Introduction Our goal: get
CNT 4007 Computer Networks - Chapter 1 : Overview Jonathan Kavalan, Ph.D. Department of Computer, Information Science and Engineering (CISE), University of Florida 1 Chapter 1: Introduction Our goal: get
Introduction to Computer Science 2017 Networking. Sören Schwertfeger
 Sören Schwertfeger Outline Internet History of the Internet Internet Structure Internet Protocols Network layer details 1. Physical Layer 2. Data Link Layer 3. Network Layer Internet: Huge network of networks
Sören Schwertfeger Outline Internet History of the Internet Internet Structure Internet Protocols Network layer details 1. Physical Layer 2. Data Link Layer 3. Network Layer Internet: Huge network of networks
INTERNET PROGRAMMING INTRODUCTION
 INTERNET PROGRAMMING INTRODUCTION Software Engineering Branch / 4 th Class Computer Engineering Department University of Technology ORGANIZATION Lecture Mondays, 08:30-10:30 (Hall 4). Project 1. The project
INTERNET PROGRAMMING INTRODUCTION Software Engineering Branch / 4 th Class Computer Engineering Department University of Technology ORGANIZATION Lecture Mondays, 08:30-10:30 (Hall 4). Project 1. The project
No required additional monthly fees just use the wireless minutes and data from your existing plan.
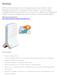 Detials AT&T 3G MicroCell acts like a mini cellular tower in your home or small business environment. It connects to AT&T's network via your existing broadband Internet service (such as U-verse, DSL or
Detials AT&T 3G MicroCell acts like a mini cellular tower in your home or small business environment. It connects to AT&T's network via your existing broadband Internet service (such as U-verse, DSL or
Chapter 1: introduction
 Chapter 1: introduction our goal: v get feel and terminology v more depth, detail later in course v approach: use Internet as example overview: v what s the Internet? v what s a protocol? v edge; hosts,
Chapter 1: introduction our goal: v get feel and terminology v more depth, detail later in course v approach: use Internet as example overview: v what s the Internet? v what s a protocol? v edge; hosts,
GLOSSARY OF CELLUAR TERMS
 GLOSSARY OF CELLUAR TERMS Air Interface: It is the operating system of a wireless network.. Airtime: The amount of time a person spends talking on their cellular device. AMPS: Advanced mobile phone service
GLOSSARY OF CELLUAR TERMS Air Interface: It is the operating system of a wireless network.. Airtime: The amount of time a person spends talking on their cellular device. AMPS: Advanced mobile phone service
Chapter 9. Introduction. Communications
 Chapter 9 Communications and Networks McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction Page 247 Cell phones and other wireless technologies are allowing
Chapter 9 Communications and Networks McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Introduction Page 247 Cell phones and other wireless technologies are allowing
WIMAX. WIMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access ): Field of application:
 WIMAX WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) is a technology that focuses on providing data over long distances in a wireless mode, very similar to the cellular mobile concept. WiMAX is
WIMAX WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) is a technology that focuses on providing data over long distances in a wireless mode, very similar to the cellular mobile concept. WiMAX is
WEBINAR. Web Browsing 101 1/12/2012 WEBINAR TIPS:
 Browsing 101 WEBINAR TIPS: 1. Power off cell phones. 2. If accessing webinar through telephone, turn down volume of computer speakers (or mute them.) 3. Conference attendees will be muted during webinar
Browsing 101 WEBINAR TIPS: 1. Power off cell phones. 2. If accessing webinar through telephone, turn down volume of computer speakers (or mute them.) 3. Conference attendees will be muted during webinar
Wireless (Select Models Only) User Guide
 Wireless (Select Models Only) User Guide Copyright 2008 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Windows is a U.S. registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Bluetooth is a trademark owned by its
Wireless (Select Models Only) User Guide Copyright 2008 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Windows is a U.S. registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Bluetooth is a trademark owned by its
INTRODUCTION TO ICT.
 INTRODUCTION TO ICT. (Introducing Basic Network Concepts) Lecture # 24-25 By: M.Nadeem Akhtar. Department of CS & IT. URL: https://sites.google.com/site/nadeemcsuoliict/home/lectures 1 INTRODUCTION TO
INTRODUCTION TO ICT. (Introducing Basic Network Concepts) Lecture # 24-25 By: M.Nadeem Akhtar. Department of CS & IT. URL: https://sites.google.com/site/nadeemcsuoliict/home/lectures 1 INTRODUCTION TO
CSEN 503 Introduction to Communication Networks
 CSEN 503 Introduction to Communication Networks 1-1 Mervat AbuElkheir Hana Medhat Ayman Dayf ** Slides are attributed to J. F. Kurose People and Resources 1-2 Course Name Introduction to Communication
CSEN 503 Introduction to Communication Networks 1-1 Mervat AbuElkheir Hana Medhat Ayman Dayf ** Slides are attributed to J. F. Kurose People and Resources 1-2 Course Name Introduction to Communication
Internet. In this section: Links: Video: Did You Know - The power of the internet. Concepts > Internet
 Internet is the world s largest public computer network, a network of networks that provides a vast array of services to individuals, businesses, and organizations around the world. In this section: Internet
Internet is the world s largest public computer network, a network of networks that provides a vast array of services to individuals, businesses, and organizations around the world. In this section: Internet
Network Programming I Computer Network Design
 Network Programming I Computer Network Design Flavio Esposito http://cs.slu.edu/~esposito/teaching/3650/ Lecture 2 Lecture Goals Get feel and terminology of some components of real nets More depth & details
Network Programming I Computer Network Design Flavio Esposito http://cs.slu.edu/~esposito/teaching/3650/ Lecture 2 Lecture Goals Get feel and terminology of some components of real nets More depth & details
E-commerce Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver. business. technology. society. tenth edition
 E-commerce 2014 business. technology. society. tenth edition Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 3 E-commerce Infrastructure:
E-commerce 2014 business. technology. society. tenth edition Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 3 E-commerce Infrastructure:
AfriConnect Satellite Technology Overview
 AfriConnect Satellite Technology Overview Topics Why VSAT? Defining The Network Requirements Coverage Traffic & Connectivity Features Public & Private Networks Understanding The Technology VSAT Terminal
AfriConnect Satellite Technology Overview Topics Why VSAT? Defining The Network Requirements Coverage Traffic & Connectivity Features Public & Private Networks Understanding The Technology VSAT Terminal
E-commerce Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver. business. technology. society. tenth edition
 E-commerce 2014 business. technology. society. tenth edition Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall e Commerce Course : Chapter 3 E-commerce
E-commerce 2014 business. technology. society. tenth edition Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traver Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall e Commerce Course : Chapter 3 E-commerce
Chapter 4: Networking and the Internet. Network Classifications. Network topologies. Network topologies (continued) Connecting Networks.
 Chapter 4: Networking and the 4.1 Network Fundamentals 4.2 The 4.3 The World Wide Web 4.4 Protocols 4.5 Security Network Classifications Scope Local area network (LAN) Metropolitan area (MAN) Wide area
Chapter 4: Networking and the 4.1 Network Fundamentals 4.2 The 4.3 The World Wide Web 4.4 Protocols 4.5 Security Network Classifications Scope Local area network (LAN) Metropolitan area (MAN) Wide area
T e l e c o m m u n i c a t i o n s, t h e i n t e r n e t, a n d W i r e l e s s t e c h n o l o g y
 T e l e c o m m u n i c a t i o n s, t h e i n t e r n e t, a n d W i r e l e s s t e c h n o l o g y C h a p t e r 7 Jun Akizaki The Power of PowerPoint WELCOME group members: 1. Dewi Setyani 16808144017
T e l e c o m m u n i c a t i o n s, t h e i n t e r n e t, a n d W i r e l e s s t e c h n o l o g y C h a p t e r 7 Jun Akizaki The Power of PowerPoint WELCOME group members: 1. Dewi Setyani 16808144017
Wide Area Networks (WANs) Slide Set 6
 Wide Area Networks (WANs) Slide Set 6 Wide Area Networks (WANs) WAN Purposes Link sites (usually) within the same corporation Remote access for individuals who are off-site Internet access for individuals
Wide Area Networks (WANs) Slide Set 6 Wide Area Networks (WANs) WAN Purposes Link sites (usually) within the same corporation Remote access for individuals who are off-site Internet access for individuals
Twelfth Edition. Chapter 8: Wired and Wireless Communication. Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1
 Computers Are Your Future Twelfth Edition Chapter 8: Wired and Wireless Communication Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 Wired and Wireless Communication Copyright 2012
Computers Are Your Future Twelfth Edition Chapter 8: Wired and Wireless Communication Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 Wired and Wireless Communication Copyright 2012
Internet Load Balancing Guide. Peplink Balance Series. Peplink Balance. Internet Load Balancing Solution Guide
 Peplink Balance Internet Load Balancing Solution Guide http://www.peplink.com Copyright 2010 Peplink Internet Load Balancing Instant Improvement to Your Network Introduction Introduction Understanding
Peplink Balance Internet Load Balancing Solution Guide http://www.peplink.com Copyright 2010 Peplink Internet Load Balancing Instant Improvement to Your Network Introduction Introduction Understanding
networks List various types of networks and their
 Chapter 15 Networks Chapter Goals Describe the core issues related to computer networks List various types of networks and their characteristics Explain various topologies of local-area networks Explain
Chapter 15 Networks Chapter Goals Describe the core issues related to computer networks List various types of networks and their characteristics Explain various topologies of local-area networks Explain
Scale Yourself. Lesson 3: Introduction to Internet Technology. Computer Technology 3/13/2015
 Computer Technology Lesson 3: Introduction to Internet Technology Learning Goal: Students will be able to understand the elements of a network. Scale Yourself 4 I do understand the elements of a network.
Computer Technology Lesson 3: Introduction to Internet Technology Learning Goal: Students will be able to understand the elements of a network. Scale Yourself 4 I do understand the elements of a network.
Class X Subject : IT (Vocational) Chapter -1 Ouestion / Answer
 Class X Subject : IT (Vocational) Chapter -1 Ouestion / Answer Q1 What is a computer network? A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of computers and other hardware
Class X Subject : IT (Vocational) Chapter -1 Ouestion / Answer Q1 What is a computer network? A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of computers and other hardware
end systems, access networks, links 1.3 network core
 Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 what is the Inter? 1.2 work edge end systems, works, links 1.3 work core packet switching, circuit switching, work structure 1.4 delay, loss, throughput in works 1.5 protocol layers,
Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 what is the Inter? 1.2 work edge end systems, works, links 1.3 work core packet switching, circuit switching, work structure 1.4 delay, loss, throughput in works 1.5 protocol layers,
Network and Mobile Compu4ng in the 20 th Century and Beyond. COMP 1400 Memorial University Winter 2015
 Network and Mobile Compu4ng in the 20 th Century and Beyond COMP 1400 Memorial University Winter 2015 What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view PC server wireless laptop smartphone wireless links wired
Network and Mobile Compu4ng in the 20 th Century and Beyond COMP 1400 Memorial University Winter 2015 What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view PC server wireless laptop smartphone wireless links wired
What s a protocol? What s a protocol? A closer look at network structure: What s the Internet? Hardware view: What s the Internet?
 What s the Internet? Hardware view: What s the Internet? Hardware view: PC server wireless laptop cellular handheld access points wired s connected computing devices: hosts = end systems running apps communication
What s the Internet? Hardware view: What s the Internet? Hardware view: PC server wireless laptop cellular handheld access points wired s connected computing devices: hosts = end systems running apps communication
Introduction to computer networking
 edge core Introduction to computer networking Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 The edge core Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 edge core Billions of connected computing
edge core Introduction to computer networking Comp Sci 3600 Security Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 The edge core Outline edge core 1 2 edge 3 core 4 5 6 edge core Billions of connected computing
Introductory Visualizing Technology
 Introductory Visualizing Technology Seventh Edition Chapter 6 Digital Devices and Multimedia Learning Objectives 6.1 Explain the Features of Digital Cameras 6.2 Compare Methods for Transferring Images
Introductory Visualizing Technology Seventh Edition Chapter 6 Digital Devices and Multimedia Learning Objectives 6.1 Explain the Features of Digital Cameras 6.2 Compare Methods for Transferring Images
Chapter Topics. The History of the Internet. Chapter 7: Computer Networks, the Internet, and the World Wide Web
 Chapter Topics Chapter 7: Computer Networks, the Internet, and the World Wide Web CS10051: Intro. to Computer Science Kent State University History of the Internet History of the World Wide Web Internet
Chapter Topics Chapter 7: Computer Networks, the Internet, and the World Wide Web CS10051: Intro. to Computer Science Kent State University History of the Internet History of the World Wide Web Internet
The Internet Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) How the Internet Works Transport Control Protocol (TCP)
 The Internet, Intranets, and Extranets 1 The Internet The Internet is a collection of interconnected network of computers, all freely exchanging information. These computers use specialized software to
The Internet, Intranets, and Extranets 1 The Internet The Internet is a collection of interconnected network of computers, all freely exchanging information. These computers use specialized software to
Chapter 3. The Basics of Networking
 Chapter 3 The Basics of Networking Learning Objectives Tell whether a communication technology (Internet, radio, LAN, etc.) is synchronous or asynchronous; broadcast or point-to-point Explain the roles
Chapter 3 The Basics of Networking Learning Objectives Tell whether a communication technology (Internet, radio, LAN, etc.) is synchronous or asynchronous; broadcast or point-to-point Explain the roles
St name:mariam darbi St number :1699
 St name:mariam darbi St number :1699 what is the internet &how it work? The internet : is a network of networks and is a global comput er network, it is offspring of the ARPANET project. This idea of connecting
St name:mariam darbi St number :1699 what is the internet &how it work? The internet : is a network of networks and is a global comput er network, it is offspring of the ARPANET project. This idea of connecting
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Computer Engineering g Dept
 King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Computer Engineering g Dept COE 540 Computer Networks Term 121 Dr. Ashraf S. Hasan Mahmoud Rm 22-420 Ext. 1724 Email: ashraf@kfupm.edu.sa 9/1/2012 Dr. Ashraf
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Computer Engineering g Dept COE 540 Computer Networks Term 121 Dr. Ashraf S. Hasan Mahmoud Rm 22-420 Ext. 1724 Email: ashraf@kfupm.edu.sa 9/1/2012 Dr. Ashraf
Chapter 7 TELECOMMUNICATIONS, THE INTERNET, AND WIRELESS TECHNOLOGY. Management Information Systems MANAGING THE DIGITAL FIRM, 12 TH EDITION
 MANAGING THE DIGITAL FIRM, 12 TH EDITION Chapter 7 TELECOMMUNICATIONS, THE INTERNET, VIDEO CASES Case 1: Traveling the Internet and Wireless Technology Case 2: Unified Communications Systems With Virtual
MANAGING THE DIGITAL FIRM, 12 TH EDITION Chapter 7 TELECOMMUNICATIONS, THE INTERNET, VIDEO CASES Case 1: Traveling the Internet and Wireless Technology Case 2: Unified Communications Systems With Virtual
Chapter 9. Internet. Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc 10-1
 Chapter 9 Internet Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc 10-1 Outline 9.2 How Internet Works - Basic Architecture - Connecting to an ISP - Internet Today 9.3 - Internet Access Technologies DSL Cable modems
Chapter 9 Internet Copyright 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc 10-1 Outline 9.2 How Internet Works - Basic Architecture - Connecting to an ISP - Internet Today 9.3 - Internet Access Technologies DSL Cable modems
Defining the Internet
 Defining the Internet Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Communications and Networking Brigham Young University What is the Internet? 2/23 Internet Map, courtesy Barrett Lyon, 2003 What is the Internet? 3/23
Defining the Internet Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Communications and Networking Brigham Young University What is the Internet? 2/23 Internet Map, courtesy Barrett Lyon, 2003 What is the Internet? 3/23
Internet Architecture
 Internet Architecture Lecture 8: How Wireless Connections and WiFi Work Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Introduction The wired world created a revolution of allowing people to connect to the
Internet Architecture Lecture 8: How Wireless Connections and WiFi Work Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Introduction The wired world created a revolution of allowing people to connect to the
BLM6196 COMPUTER NETWORKS AND COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS
 BLM6196 COMPUTER NETWORKS AND COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (1 st Week) Outline Course Information and Policies Course Syllabus 1. Data Communications, Data Networks, and the Internet
BLM6196 COMPUTER NETWORKS AND COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (1 st Week) Outline Course Information and Policies Course Syllabus 1. Data Communications, Data Networks, and the Internet
Module 11. OSI Model, Network Devices, and Network Standards
 Module 11 OSI Model, Network Devices, and Network Standards Objectives 1. Networking A.Differentiate between layers of the OSI model B.2.9 Compare network devices C.Compare network standards D.2.7 Compare
Module 11 OSI Model, Network Devices, and Network Standards Objectives 1. Networking A.Differentiate between layers of the OSI model B.2.9 Compare network devices C.Compare network standards D.2.7 Compare
CS 204: Advanced Computer Networks
 CS 204: Advanced Computer Networks Jiasi Chen Lectures: MWF 12:10-1pm Humanities and Social Sciences 1403 http://www.cs.ucr.edu/~jiasi/teaching/cs204_spring17/ 1 Why Networks? Supports the applications
CS 204: Advanced Computer Networks Jiasi Chen Lectures: MWF 12:10-1pm Humanities and Social Sciences 1403 http://www.cs.ucr.edu/~jiasi/teaching/cs204_spring17/ 1 Why Networks? Supports the applications
Introduction to Networks and the Internet
 Introduction to Networks and the Internet CMPE 80N Announcements First quiz on Friday, 01.16. Covers material up to and including 01.14. Closed books, notes, etc. Winter 2004 Lecture 5 1 2 Data Transmission
Introduction to Networks and the Internet CMPE 80N Announcements First quiz on Friday, 01.16. Covers material up to and including 01.14. Closed books, notes, etc. Winter 2004 Lecture 5 1 2 Data Transmission
Networks University of Stirling CSCU9B1 Essential Skills for the Information Age. Content
 Networks 2 Lecture Networks 2/Slide 1 Content How is Internet connected? Internet backbone Internet service providers (ISP) How to connect a home computer to the Internet? 1. Phone modem 2. Digital subscriber
Networks 2 Lecture Networks 2/Slide 1 Content How is Internet connected? Internet backbone Internet service providers (ISP) How to connect a home computer to the Internet? 1. Phone modem 2. Digital subscriber
MIS 14e Ch07. Chapter 7 25/04/2016. Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology
 MIS 14e Ch07 6.1 Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 7 Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology Video cases: Case 1: Telepresence Moves Out of the
MIS 14e Ch07 6.1 Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 7 Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology Video cases: Case 1: Telepresence Moves Out of the
Router Router Microprocessor controlled traffic direction home router DSL modem Computer Enterprise routers Core routers
 Router Router is a Microprocessor controlled device that forwards data packets across the computer network. It is used to connect two or more data lines from different net works. The function of the router
Router Router is a Microprocessor controlled device that forwards data packets across the computer network. It is used to connect two or more data lines from different net works. The function of the router
AT&T Collaborate TM. Network Assessment Tool
 AT&T Collaborate TM Network Assessment Tool 2016 AT&T Intellectual Property. All rights reserved. AT&T, Globe logo, Mobilizing Your World and DIRECTV are registered trademarks and service marks of AT&T
AT&T Collaborate TM Network Assessment Tool 2016 AT&T Intellectual Property. All rights reserved. AT&T, Globe logo, Mobilizing Your World and DIRECTV are registered trademarks and service marks of AT&T
Local area network (LAN) Wide area networks (WANs) Circuit. Circuit switching. Packets. Based on Chapter 2 of Gary Schneider.
 Local area network (LAN) Network of computers located close together Wide area networks (WANs) Networks of computers connected over greater distances Based on Chapter 2 of Gary Schneider. (2009). E-Business.
Local area network (LAN) Network of computers located close together Wide area networks (WANs) Networks of computers connected over greater distances Based on Chapter 2 of Gary Schneider. (2009). E-Business.
Broadband and Last Mile Networks
 Broadband and Last Mile Networks Last-Mile Network Design Concerns Infrastructure Cost Throughput: Upstream and Downstream Packet or Circuit Switching Congestion Control Latency History: Dial-up First
Broadband and Last Mile Networks Last-Mile Network Design Concerns Infrastructure Cost Throughput: Upstream and Downstream Packet or Circuit Switching Congestion Control Latency History: Dial-up First
A+ Guide to Software: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 9 Networking Practices
 : Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 9 Networking Practices Objectives Learn how to connect a computer or small network to the Internet using a broadband, satellite, or dialup connection
: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 9 Networking Practices Objectives Learn how to connect a computer or small network to the Internet using a broadband, satellite, or dialup connection
