Effect of memory latency
|
|
|
- James Gibbs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CACHE AWARENESS
2 Effect of memory latency Consider a processor operating at 1 GHz (1 ns clock) connected to a DRAM with a latency of 100 ns. Assume that the processor has two ALU units and it is capable of executing two instructions in each cycle of 1 ns. The peak processor rating is therefore 2 GFLOPS. Since the memory latency is equal to 100 cycles every time a memory request is made, the processor must wait 100 cycles before it can process the data. Consider the problem of computing the dot-product of two vectors. A dot-product computation performs one multiply-add on a single pair of vector elements, i.e., each floating point operation requires one data fetch. It is easy to see that the peak speed of this computation is limited to one multiply-add operation every 100 ns, or a speed of 10 MFLOPS.
3 Cache Memory processor cache memory word block/line Smaller and faster memory between the processor and the DRAM The data needed by the processor is first fetched into the cache. All subsequent accesses to data items residing in the cache are serviced by the cache. Performance improves in presence of High Locality Def Cache Hit Ratio: fraction of memory references being resolved by the cache memory
4 With Cache Consider a processor operating at 1 GHz (1 ns clock) connected to a DRAM with a latency of 100 ns. Assume that the processor has two ALU units and is capable of executing two instructions in each cycle of 1 ns. The peak processor rating is therefore 2 GFLOPS. Suppose we have a cache of 32KB, with a latency of 1 ns per word. We must multiply two matrices A and B of size 32*32. N.B.: A, B and A*B fit in cache The time needed to load A and B into cache is 32*32*2 * 100ns = 205 µs Multiplying two matrices of size n*n takes 2n 3 multiply-adds, in our case 2*32 3 = 66K multiply-adds, which implies 66 µs Total time is = 271 µs Throughput is 66K*2/271µs = 488 MFLOPS (> 10 MFLOPS) (<2 GFLOPS) Locality: n^3 operations on n^2 memory locations!!
5 Effect of memory bandwidth Consider the previous example If the cache block has a width of one single word, then it takes 32*32*2 * 100ns = 205 µs to load the two matrices in cache If the cache line has a width of four words, then it takes 32*32*2/4 * 100ns = 51 µs to load the two matrices in cache Total time is = 117 µs Throughput is 66K*2/117µs = 1282 MFLOPS (>488 MFLOPS) (> 10 MFLOPS) (<2 GFLOPS) Warning! We are assuming data is laid out linearly in memory.
6 Other approaches for hiding memory latency Multi-threading Split the problem in multiple sub-problems Run an independent thread for each sub-problem When a thread is idle on a miss, another thread can execute computational tasks Pre-fetching Anticipate load operations, so that data is already available when needed Drawbacks: They both impact on bandwidth and cache pollution
7 Cache-to-Memory coherence processor cache memory write After updating/writing data in cache, when to write to memory? Other devices might read the same data from memory Write-Through Policy Data is immediately written to memory Write delay (~100 cycles) When to write? Write-Back Policy Memory is updated upon eviction Less operations (especially in case of re-use/locality) In case of write to data not being in cache: n Write-allocate: first load into cache, then update cache (only) n Write no allocate: write (stream) to memory (no loads into cache)
8 Cache-to-Cache Coherence in Symmetric Multi-Processors P 1 P 2 P 3 P n $ u = 5 $ $ $ u = 5 7 BUS u = 5 Memory The processors see different values of u after event 3 Snooping Protocols I/O devices (Most) assume Write-through policy and a shared communication channel among processors/caches The Cache Controller snoops all the bus transactions a transaction is relevant for a cache if the referred data line (univocally identified by the (block) address) is present in cache the possible actions to guarantee the cache coherence are: n Invalidate: cache line is invalidated, and it must be re-loaded from memory first (write-through guarantees correctness) n Update: cache line is updated with the new value Note: There are strategies for non write-through policies Modern processors use point-to-point links among (multi-core) CPUs rather than a shared bus
9 Cache Invalidate vs. Cache Update Update cons: can waste unnecessarily the bandwidth of the bus n when a cache block is updated remotely, but is no longer read by the associated processor n subsequent writes by the same processor cause multiple updates pros: multiple R/W copies are kept coherent after each write. n This avoids misses for each subsequent read access (thus saving bus bandwidth) Invalidate pros: multiple writes by the same processors does not cause any additional bus traffic cons: an access that follows an invalidation causes a miss Pros and Cons of the two approaches depend on the application and its read/write patterns
10 False Sharing Coherence protocols work in terms of cache blocks/lines, rather than single words/bytes The block size plays an important role in the coherence protocol with small blocks, the protocols are more efficient (less data to transmit when update or flush) large blocks are better for spatial locality What if multiple processors access the same cache block?
11 False Sharing P1 P2 P1 P cache line cache update False sharing cache line cache line cache update cache line consider two unrelated variables (e.g., variables that are logically private to distinct threads), which are allocated in the same block write accesses to a block by different processors running the threads are considered conflicts by the coherence protocol n even if the two processors access disjoint words of the same block thus, it is needed to put on the same block related variables n e.g., all of which are logically private for a given thread n compiling techniques, programmer
12 Intel Core i7 (4770) Intel i (Haswell), 3.4 GHz (Turbo Boost off), 22 nm. RAM: 32GB L1 Data cache L1 Instruction cache = 32 KB, 64B/line L2 cache = 256 KB, 64B/line L3 cache L1 Data Cache Latency = 4-5 cycles L2 Cache Latency L3 Cache Latency = 36 cycles RAM Latency = 36 + ~200 cycles = 32 KB, 64B/line = 8 MB, 64B/line = 12 cycles
13 So Far Cache has a significant impact in the performance of modern applications How can we study the cache access patterns of an algorithm? How can we improve algorithm design? Two examples: Sort Matrix Multiplication
14 External Memory Model We use cache vs. disk to make it clear the relative costs Transfers occur in blocks of size B The cache has size M>=B With M/B entries Model Properties: Simple Asks to Minimize I/O cost Optimize for a specific M and B Explicitly issue read/write ops. Explicitly manage cache n Can you do this? n [J.S. Vitter, ACM Computing Surveys, 2001]
15 Example: Linear Scan Theorem: Scanning N elements stored in a contiguous segment of memory costs at most N/B + 1 memory transfers
16 Cache Oblivious Model Simple Idea: Design an algorithm optimal for any B and M Properties: CPU W work M/B Z L Cache lines Don t need to know M and B, which can be hard to know, and can harm the generality of an algorithm Only one cache level Do not explicitly manage the cache Cache Assumptions: n Tall cache assumption : M = Ω(B 2 ) n Ideal cache model = optimal cache replacement vs. FIFO, LRU n Full associativity vs. n-way associativity organized by optimal replacement strategy Cache Lines of length LB Q cache misses Main Memory n [Frigo et al., FOCS 99]
17 Cache Oblivious Model: Generalization to multiple cache levels Theorem: (from one level to many) If algorithm A is cache-oblivious optimal then it is optimal on any two adjacent memory levels in a complex hierarchy. Proof: If the inclusion property holds, i.e. M i M i+1 Consider M i+1 the external memory, A is optimal w.r.t. M i and B i M N, B N M 3, B 3 M 2, B 2 M 1, B 1 CPU Theorem: (levels of different cost) Let C i be the cost of accessing memory M i, if A is cache oblivious optimal up to a constant factor, then A is optimal for any possible set of constant factors C i.
18 Cache Oblivious Model : Generalization to multiple cache levels The following theorems make the model feasible: Theorem: (from optimal replacement strategy to LRU/FIFO) If A takes T transfers and cache size M/2, then A takes at most 2T transfers on a cache of size M with LRU or FIFO replacement policy. Theorem: (from fully associative to 1-way associative) An LRU/FIFO cache with of size M, and block size B, can be simulated in O(M) space, such that an access to a block takes O(1) expected time. Conclusion: A cache oblivious algorithm can be translated in a FIFO/LRU cache with 1-associativity paying only constant factors.
19 Matrix Multiplication Compute C = A * B With B and A being NxN matrices Preliminaries: how to store matrices? Row-major order vs. Column-major order
20 Cache cost/complexity For each element C ij Scan the i-th row of A Scan the j-th column of B (Compute multiply-add) Each element of C involves O(1+N/B) transfers Since there are N 2 elements in C, the complexity is: O(N 2 +N 3 /B) Simple approaches to reduce this cost: If M>N then row i of A can be stored in cache memory and used to compute all the C ix values In order to keep matrix A in cache, M should be >N 2
21 Improved Algorithm This can be improved to optimal complexity of O(N 2 /B + N 3 /(B* M)) with block matrices: A11 A12 B11 B12 A11*B11 + A11*B12 + A21 A22 * B21 B22 = A12*B21 A21*B11 + A12*B22 A21*B12 + A22*B21 A22*B22
22 Improved Algorithm What is the best strategy given M and B? What is the best Cache-Conscious algorithm? What is the best algorithm according to the external memory model? Simple: use blocks of size s*s, such that 3 * s 2 = M. Use blocked memory layout
23 Cache Oblivious Algorithm Divide-and-Conquer Approach A11 A21 A12 A22 * B11 B21 B12 B22 = A11 A21 A12 A22 * B11 B21 B12 B22 = A11 A21 A12 A22 * B11 B21 B12 B22 = At some point the recursion will fit in the cache, whatever its size
24 Data layout We don t know when it will fit!!!!!! We need a recursive data layout, such that however we recursively split the matrix, at some point all the data will be in (almost) consecutive memory locations that can be easily loaded in cache. Space filling curves: Z-Order
25 How to implement Z-Order For any subscript of 2 dimensional array such as array [ 2, 3 ] Binary value of row 2 -> 1 0 Binary value of col 3 -> 1 1 value is stored at location location, i.e. 13th position.
26 Complexity Sketch: The base case of the recursion is when three blocks fit in cache, since successive recursion steps do not cause additional misses Assume the base case is with blocks of size k M * k M, for some constant k Such blocks fill the cache with M/B misses The computational complexity of the block-based multiplication is ( N/(k M) ) 3 Resulting in a number of misses ( N/(k M) ) 3 * M/B = O( N 3 /(B M) ) The sum across the various block generates misses O( N 2 /B ) The total cost is thus O(N 2 /B + N 3 /(B* M))
27 End of first part Parallel Programming for Multicore and Cluster Systems Sec. 2.7 Cache and Memory Hierarchy Cache-Oblivious Algorithms and Data Structures. Erik D. Demaine. Sec. 1, 2, 3.1.1, 3.2.3
CS 426 Parallel Computing. Parallel Computing Platforms
 CS 426 Parallel Computing Parallel Computing Platforms Ozcan Ozturk http://www.cs.bilkent.edu.tr/~ozturk/cs426/ Slides are adapted from ``Introduction to Parallel Computing'' Topic Overview Implicit Parallelism:
CS 426 Parallel Computing Parallel Computing Platforms Ozcan Ozturk http://www.cs.bilkent.edu.tr/~ozturk/cs426/ Slides are adapted from ``Introduction to Parallel Computing'' Topic Overview Implicit Parallelism:
Multilevel Memories. Joel Emer Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 1 Multilevel Memories Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Based on the material prepared by Krste Asanovic and Arvind CPU-Memory Bottleneck 6.823
1 Multilevel Memories Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Based on the material prepared by Krste Asanovic and Arvind CPU-Memory Bottleneck 6.823
External Memory. Philip Bille
 External Memory Philip Bille Outline Computationals models Modern computers (word) RAM I/O Cache-oblivious Shortest path in implicit grid graphs RAM algorithm I/O algorithms Cache-oblivious algorithm Computational
External Memory Philip Bille Outline Computationals models Modern computers (word) RAM I/O Cache-oblivious Shortest path in implicit grid graphs RAM algorithm I/O algorithms Cache-oblivious algorithm Computational
The Memory Hierarchy. Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2)
 The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
Cache-Oblivious Algorithms A Unified Approach to Hierarchical Memory Algorithms
 Cache-Oblivious Algorithms A Unified Approach to Hierarchical Memory Algorithms Aarhus University Cache-Oblivious Current Trends Algorithms in Algorithms, - A Unified Complexity Approach to Theory, Hierarchical
Cache-Oblivious Algorithms A Unified Approach to Hierarchical Memory Algorithms Aarhus University Cache-Oblivious Current Trends Algorithms in Algorithms, - A Unified Complexity Approach to Theory, Hierarchical
Systems Programming and Computer Architecture ( ) Timothy Roscoe
 Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Systems Programming and Computer Architecture (252-0061-00) Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 2016 AS 2016 Caches 1 16: Caches Computer Architecture
Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Systems Programming and Computer Architecture (252-0061-00) Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 2016 AS 2016 Caches 1 16: Caches Computer Architecture
Advanced Computer Architecture
 ECE 563 Advanced Computer Architecture Fall 2009 Lecture 3: Memory Hierarchy Review: Caches 563 L03.1 Fall 2010 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced DRAM... Four-issue 2GHz superscalar accessing 100ns DRAM could
ECE 563 Advanced Computer Architecture Fall 2009 Lecture 3: Memory Hierarchy Review: Caches 563 L03.1 Fall 2010 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced DRAM... Four-issue 2GHz superscalar accessing 100ns DRAM could
Algorithm Performance Factors. Memory Performance of Algorithms. Processor-Memory Performance Gap. Moore s Law. Program Model of Memory II
 Memory Performance of Algorithms CSE 32 Data Structures Lecture Algorithm Performance Factors Algorithm choices (asymptotic running time) O(n 2 ) or O(n log n) Data structure choices List or Arrays Language
Memory Performance of Algorithms CSE 32 Data Structures Lecture Algorithm Performance Factors Algorithm choices (asymptotic running time) O(n 2 ) or O(n log n) Data structure choices List or Arrays Language
Why memory hierarchy? Memory hierarchy. Memory hierarchy goals. CS2410: Computer Architecture. L1 cache design. Sangyeun Cho
 Why memory hierarchy? L1 cache design Sangyeun Cho Computer Science Department Memory hierarchy Memory hierarchy goals Smaller Faster More expensive per byte CPU Regs L1 cache L2 cache SRAM SRAM To provide
Why memory hierarchy? L1 cache design Sangyeun Cho Computer Science Department Memory hierarchy Memory hierarchy goals Smaller Faster More expensive per byte CPU Regs L1 cache L2 cache SRAM SRAM To provide
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS. Spring 2017 Lecture 15
 CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2017 Lecture 15 LAST TIME: CACHE ORGANIZATION Caches have several important parameters B = 2 b bytes to store the block in each cache line S = 2 s cache sets
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2017 Lecture 15 LAST TIME: CACHE ORGANIZATION Caches have several important parameters B = 2 b bytes to store the block in each cache line S = 2 s cache sets
Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science. TDT4255 Memory hierarchies
 TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
Chapter 2. Parallel Hardware and Parallel Software. An Introduction to Parallel Programming. The Von Neuman Architecture
 An Introduction to Parallel Programming Peter Pacheco Chapter 2 Parallel Hardware and Parallel Software 1 The Von Neuman Architecture Control unit: responsible for deciding which instruction in a program
An Introduction to Parallel Programming Peter Pacheco Chapter 2 Parallel Hardware and Parallel Software 1 The Von Neuman Architecture Control unit: responsible for deciding which instruction in a program
Memory Hierarchy Computing Systems & Performance MSc Informatics Eng. Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed)
 Computing Systems & Performance Memory Hierarchy MSc Informatics Eng. 2012/13 A.J.Proença Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed) AJProença, Computer Systems & Performance, MEI, UMinho, 2012/13 1 2
Computing Systems & Performance Memory Hierarchy MSc Informatics Eng. 2012/13 A.J.Proença Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed) AJProença, Computer Systems & Performance, MEI, UMinho, 2012/13 1 2
Memory Technology. Caches 1. Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Magnetic disk. Ideal memory. 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB
 Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Massive Data Algorithmics. Lecture 12: Cache-Oblivious Model
 Typical Computer Hierarchical Memory Basics Data moved between adjacent memory level in blocks A Trivial Program A Trivial Program: d = 1 A Trivial Program: d = 1 A Trivial Program: n = 2 24 A Trivial
Typical Computer Hierarchical Memory Basics Data moved between adjacent memory level in blocks A Trivial Program A Trivial Program: d = 1 A Trivial Program: d = 1 A Trivial Program: n = 2 24 A Trivial
Structure of Computer Systems
 222 Structure of Computer Systems Figure 4.64 shows how a page directory can be used to map linear addresses to 4-MB pages. The entries in the page directory point to page tables, and the entries in a
222 Structure of Computer Systems Figure 4.64 shows how a page directory can be used to map linear addresses to 4-MB pages. The entries in the page directory point to page tables, and the entries in a
Multi-core Computing Lecture 2
 Multi-core Computing Lecture 2 MADALGO Summer School 2012 Algorithms for Modern Parallel and Distributed Models Phillip B. Gibbons Intel Labs Pittsburgh August 21, 2012 Multi-core Computing Lectures: Progress-to-date
Multi-core Computing Lecture 2 MADALGO Summer School 2012 Algorithms for Modern Parallel and Distributed Models Phillip B. Gibbons Intel Labs Pittsburgh August 21, 2012 Multi-core Computing Lectures: Progress-to-date
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface. 5 th. Edition. Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address
LECTURE 10: Improving Memory Access: Direct and Spatial caches
 EECS 318 CAD Computer Aided Design LECTURE 10: Improving Memory Access: Direct and Spatial caches Instructor: Francis G. Wolff wolff@eecs.cwru.edu Case Western Reserve University This presentation uses
EECS 318 CAD Computer Aided Design LECTURE 10: Improving Memory Access: Direct and Spatial caches Instructor: Francis G. Wolff wolff@eecs.cwru.edu Case Western Reserve University This presentation uses
Memory Hierarchy Computing Systems & Performance MSc Informatics Eng. Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed)
 Computing Systems & Performance Memory Hierarchy MSc Informatics Eng. 2011/12 A.J.Proença Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed) AJProença, Computer Systems & Performance, MEI, UMinho, 2011/12 1 2
Computing Systems & Performance Memory Hierarchy MSc Informatics Eng. 2011/12 A.J.Proença Memory Hierarchy (most slides are borrowed) AJProença, Computer Systems & Performance, MEI, UMinho, 2011/12 1 2
10/16/2017. Miss Rate: ABC. Classifying Misses: 3C Model (Hill) Reducing Conflict Misses: Victim Buffer. Overlapping Misses: Lockup Free Cache
 Classifying Misses: 3C Model (Hill) Divide cache misses into three categories Compulsory (cold): never seen this address before Would miss even in infinite cache Capacity: miss caused because cache is
Classifying Misses: 3C Model (Hill) Divide cache misses into three categories Compulsory (cold): never seen this address before Would miss even in infinite cache Capacity: miss caused because cache is
Algorithm Performance Factors. Memory Performance of Algorithms. Processor-Memory Performance Gap. Moore s Law. Program Model of Memory I
 Memory Performance of Algorithms CSE 32 Data Structures Lecture Algorithm Performance Factors Algorithm choices (asymptotic running time) O(n 2 ) or O(n log n) Data structure choices List or Arrays Language
Memory Performance of Algorithms CSE 32 Data Structures Lecture Algorithm Performance Factors Algorithm choices (asymptotic running time) O(n 2 ) or O(n log n) Data structure choices List or Arrays Language
Chapter 5A. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5A Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) Fast, expensive Dynamic RAM (DRAM) In between Magnetic disk Slow, inexpensive Ideal memory Access time of SRAM
Chapter 5A Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) Fast, expensive Dynamic RAM (DRAM) In between Magnetic disk Slow, inexpensive Ideal memory Access time of SRAM
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review. UCSB CS240A, Fall 2017
 Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS24A, Fall 27 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only - 2% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss is in the
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS24A, Fall 27 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only - 2% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss is in the
Computer Architecture Memory hierarchies and caches
 Computer Architecture Memory hierarchies and caches S Coudert and R Pacalet January 23, 2019 Outline Introduction Localities principles Direct-mapped caches Increasing block size Set-associative caches
Computer Architecture Memory hierarchies and caches S Coudert and R Pacalet January 23, 2019 Outline Introduction Localities principles Direct-mapped caches Increasing block size Set-associative caches
Lecture 2. Memory locality optimizations Address space organization
 Lecture 2 Memory locality optimizations Address space organization Announcements Office hours in EBU3B Room 3244 Mondays 3.00 to 4.00pm; Thurs 2:00pm-3:30pm Partners XSED Portal accounts Log in to Lilliput
Lecture 2 Memory locality optimizations Address space organization Announcements Office hours in EBU3B Room 3244 Mondays 3.00 to 4.00pm; Thurs 2:00pm-3:30pm Partners XSED Portal accounts Log in to Lilliput
Page 1. Memory Hierarchies (Part 2)
 Memory Hierarchies (Part ) Outline of Lectures on Memory Systems Memory Hierarchies Cache Memory 3 Virtual Memory 4 The future Increasing distance from the processor in access time Review: The Memory Hierarchy
Memory Hierarchies (Part ) Outline of Lectures on Memory Systems Memory Hierarchies Cache Memory 3 Virtual Memory 4 The future Increasing distance from the processor in access time Review: The Memory Hierarchy
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review. UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016
 Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016 1 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only 10-20% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016 1 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only 10-20% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
Assignment 1 due Mon (Feb 4pm
 Announcements Assignment 1 due Mon (Feb 19) @ 4pm Next week: no classes Inf3 Computer Architecture - 2017-2018 1 The Memory Gap 1.2x-1.5x 1.07x H&P 5/e, Fig. 2.2 Memory subsystem design increasingly important!
Announcements Assignment 1 due Mon (Feb 19) @ 4pm Next week: no classes Inf3 Computer Architecture - 2017-2018 1 The Memory Gap 1.2x-1.5x 1.07x H&P 5/e, Fig. 2.2 Memory subsystem design increasingly important!
Introduction to cache memories
 Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Introduction to cache memories Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Summary Summary Main goal Spatial and temporal
Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Introduction to cache memories Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Summary Summary Main goal Spatial and temporal
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache
 Removing The Ideal Memory Assumption: The Memory Hierarchy & Cache The impact of real memory on CPU Performance. Main memory basic properties: Memory Types: DRAM vs. SRAM The Motivation for The Memory
Removing The Ideal Memory Assumption: The Memory Hierarchy & Cache The impact of real memory on CPU Performance. Main memory basic properties: Memory Types: DRAM vs. SRAM The Motivation for The Memory
Chapter 5 (Part II) Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy. Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs
 Chapter 5 (Part II) Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Virtual Machines Host computer emulates guest operating system and machine resources Improved isolation of multiple
Chapter 5 (Part II) Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Virtual Machines Host computer emulates guest operating system and machine resources Improved isolation of multiple
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal locality Items accessed recently are likely to
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal locality Items accessed recently are likely to
Roadmap. Java: Assembly language: OS: Machine code: Computer system:
 Roadmap C: car *c = malloc(sizeof(car)); c->miles = 100; c->gals = 17; float mpg = get_mpg(c); free(c); Assembly language: Machine code: get_mpg: pushq movq... popq ret %rbp %rsp, %rbp %rbp 0111010000011000
Roadmap C: car *c = malloc(sizeof(car)); c->miles = 100; c->gals = 17; float mpg = get_mpg(c); free(c); Assembly language: Machine code: get_mpg: pushq movq... popq ret %rbp %rsp, %rbp %rbp 0111010000011000
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste!
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste!
Agenda Cache memory organization and operation Chapter 6 Performance impact of caches Cache Memories
 Agenda Chapter 6 Cache Memories Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging loops to improve spatial locality Using blocking to improve temporal
Agenda Chapter 6 Cache Memories Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging loops to improve spatial locality Using blocking to improve temporal
Memory Hierarchy. Reading. Sections 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.8 (some elements), 5.9 (2) Lecture notes from MKP, H. H. Lee and S.
 Memory Hierarchy Lecture notes from MKP, H. H. Lee and S. Yalamanchili Sections 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.8 (some elements), 5.9 Reading (2) 1 SRAM: Value is stored on a pair of inerting gates Very fast but
Memory Hierarchy Lecture notes from MKP, H. H. Lee and S. Yalamanchili Sections 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.8 (some elements), 5.9 Reading (2) 1 SRAM: Value is stored on a pair of inerting gates Very fast but
Computer Systems Architecture
 Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 24 Mahadevan Gomathisankaran April 29, 2010 04/29/2010 Lecture 24 CSCE 4610/5610 1 Reminder ABET Feedback: http://www.cse.unt.edu/exitsurvey.cgi?csce+4610+001 Student
Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 24 Mahadevan Gomathisankaran April 29, 2010 04/29/2010 Lecture 24 CSCE 4610/5610 1 Reminder ABET Feedback: http://www.cse.unt.edu/exitsurvey.cgi?csce+4610+001 Student
Page 1. Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash )
 Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Spring 2016 :: CSE 502 Computer Architecture. Caches. Nima Honarmand
 Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
Report Seminar Algorithm Engineering
 Report Seminar Algorithm Engineering G. S. Brodal, R. Fagerberg, K. Vinther: Engineering a Cache-Oblivious Sorting Algorithm Iftikhar Ahmad Chair of Algorithm and Complexity Department of Computer Science
Report Seminar Algorithm Engineering G. S. Brodal, R. Fagerberg, K. Vinther: Engineering a Cache-Oblivious Sorting Algorithm Iftikhar Ahmad Chair of Algorithm and Complexity Department of Computer Science
EE/CSCI 451 Midterm 1
 EE/CSCI 451 Midterm 1 Spring 2018 Instructor: Xuehai Qian Friday: 02/26/2018 Problem # Topic Points Score 1 Definitions 20 2 Memory System Performance 10 3 Cache Performance 10 4 Shared Memory Programming
EE/CSCI 451 Midterm 1 Spring 2018 Instructor: Xuehai Qian Friday: 02/26/2018 Problem # Topic Points Score 1 Definitions 20 2 Memory System Performance 10 3 Cache Performance 10 4 Shared Memory Programming
CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/76/74076691.jpg) CSF Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
CSF Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
Cache-oblivious Programming
 Cache-oblivious Programming Story so far We have studied cache optimizations for array programs Main transformations: loop interchange, loop tiling Loop tiling converts matrix computations into block matrix
Cache-oblivious Programming Story so far We have studied cache optimizations for array programs Main transformations: loop interchange, loop tiling Loop tiling converts matrix computations into block matrix
Matrix Multiplication
 Matrix Multiplication CPS343 Parallel and High Performance Computing Spring 2013 CPS343 (Parallel and HPC) Matrix Multiplication Spring 2013 1 / 32 Outline 1 Matrix operations Importance Dense and sparse
Matrix Multiplication CPS343 Parallel and High Performance Computing Spring 2013 CPS343 (Parallel and HPC) Matrix Multiplication Spring 2013 1 / 32 Outline 1 Matrix operations Importance Dense and sparse
Computer Systems Architecture
 Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 23 Mahadevan Gomathisankaran April 27, 2010 04/27/2010 Lecture 23 CSCE 4610/5610 1 Reminder ABET Feedback: http://www.cse.unt.edu/exitsurvey.cgi?csce+4610+001 Student
Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 23 Mahadevan Gomathisankaran April 27, 2010 04/27/2010 Lecture 23 CSCE 4610/5610 1 Reminder ABET Feedback: http://www.cse.unt.edu/exitsurvey.cgi?csce+4610+001 Student
Performance metrics for caches
 Performance metrics for caches Basic performance metric: hit ratio h h = Number of memory references that hit in the cache / total number of memory references Typically h = 0.90 to 0.97 Equivalent metric:
Performance metrics for caches Basic performance metric: hit ratio h h = Number of memory references that hit in the cache / total number of memory references Typically h = 0.90 to 0.97 Equivalent metric:
Lecture 12: Instruction Execution and Pipelining. William Gropp
 Lecture 12: Instruction Execution and Pipelining William Gropp www.cs.illinois.edu/~wgropp Yet More To Consider in Understanding Performance We have implicitly assumed that an operation takes one clock
Lecture 12: Instruction Execution and Pipelining William Gropp www.cs.illinois.edu/~wgropp Yet More To Consider in Understanding Performance We have implicitly assumed that an operation takes one clock
Cache Memory COE 403. Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar. Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals
 Cache Memory COE 403 Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline The Need for Cache Memory The Basics
Cache Memory COE 403 Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline The Need for Cache Memory The Basics
Chap. 4 Multiprocessors and Thread-Level Parallelism
 Chap. 4 Multiprocessors and Thread-Level Parallelism Uniprocessor performance Performance (vs. VAX-11/780) 10000 1000 100 10 From Hennessy and Patterson, Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach,
Chap. 4 Multiprocessors and Thread-Level Parallelism Uniprocessor performance Performance (vs. VAX-11/780) 10000 1000 100 10 From Hennessy and Patterson, Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach,
Computer Architecture Computer Science & Engineering. Chapter 5. Memory Hierachy BK TP.HCM
 Computer Architecture Computer Science & Engineering Chapter 5 Memory Hierachy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic
Computer Architecture Computer Science & Engineering Chapter 5 Memory Hierachy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic
Virtual Memory: From Address Translation to Demand Paging
 Constructive Computer Architecture Virtual Memory: From Address Translation to Demand Paging Arvind Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab. Massachusetts Institute of Technology November 9, 2015
Constructive Computer Architecture Virtual Memory: From Address Translation to Demand Paging Arvind Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab. Massachusetts Institute of Technology November 9, 2015
What is Cache Memory? EE 352 Unit 11. Motivation for Cache Memory. Memory Hierarchy. Cache Definitions Cache Address Mapping Cache Performance
 What is EE 352 Unit 11 Definitions Address Mapping Performance memory is a small, fast memory used to hold of data that the processor will likely need to access in the near future sits between the processor
What is EE 352 Unit 11 Definitions Address Mapping Performance memory is a small, fast memory used to hold of data that the processor will likely need to access in the near future sits between the processor
Caches. Hiding Memory Access Times
 Caches Hiding Memory Access Times PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O N T R O L ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH INSTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMORY
Caches Hiding Memory Access Times PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O N T R O L ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH INSTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMORY
How to Write Fast Numerical Code
 How to Write Fast Numerical Code Lecture: Memory hierarchy, locality, caches Instructor: Markus Püschel TA: Alen Stojanov, Georg Ofenbeck, Gagandeep Singh Organization Temporal and spatial locality Memory
How to Write Fast Numerical Code Lecture: Memory hierarchy, locality, caches Instructor: Markus Püschel TA: Alen Stojanov, Georg Ofenbeck, Gagandeep Singh Organization Temporal and spatial locality Memory
Introduction to OpenMP. Lecture 10: Caches
 Introduction to OpenMP Lecture 10: Caches Overview Why caches are needed How caches work Cache design and performance. The memory speed gap Moore s Law: processors speed doubles every 18 months. True for
Introduction to OpenMP Lecture 10: Caches Overview Why caches are needed How caches work Cache design and performance. The memory speed gap Moore s Law: processors speed doubles every 18 months. True for
211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016
 211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016 Liu Liu Topic: Assembly Programming Storage - Assembly Programming: Recap - Call-chain - Factorial - Storage: - RAM - Caching - Direct - Mapping Rutgers University
211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016 Liu Liu Topic: Assembly Programming Storage - Assembly Programming: Recap - Call-chain - Factorial - Storage: - RAM - Caching - Direct - Mapping Rutgers University
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS. Spring 2015 Lecture 15
 CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2015 Lecture 15 LAST TIME! Discussed concepts of locality and stride Spatial locality: programs tend to access values near values they have already accessed
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2015 Lecture 15 LAST TIME! Discussed concepts of locality and stride Spatial locality: programs tend to access values near values they have already accessed
CS 31: Intro to Systems Caching. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 24, 2015
 CS 3: Intro to Systems Caching Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 24, 205 Reading Quiz Abstraction Goal Reality: There is no one type of memory to rule them all! Abstraction: hide the complex/undesirable
CS 3: Intro to Systems Caching Kevin Webb Swarthmore College March 24, 205 Reading Quiz Abstraction Goal Reality: There is no one type of memory to rule them all! Abstraction: hide the complex/undesirable
COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 08 Thread Level Parallelism and Coherence
 1 COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 08 Thread Level Parallelism and Coherence Cristinel Ababei Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Marquette University Credits: Slides adapted from presentations
1 COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 08 Thread Level Parallelism and Coherence Cristinel Ababei Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Marquette University Credits: Slides adapted from presentations
The levels of a memory hierarchy. Main. Memory. 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms
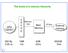 The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
 EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
High performance computing. Memory
 High performance computing Memory Performance of the computations For many programs, performance of the calculations can be considered as the retrievability from memory and processing by processor In fact
High performance computing Memory Performance of the computations For many programs, performance of the calculations can be considered as the retrievability from memory and processing by processor In fact
CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/73/69213006.jpg) CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
EE/CSCI 451: Parallel and Distributed Computation
 EE/CSCI 451: Parallel and Distributed Computation Lecture #11 2/21/2017 Xuehai Qian Xuehai.qian@usc.edu http://alchem.usc.edu/portal/xuehaiq.html University of Southern California 1 Outline Midterm 1:
EE/CSCI 451: Parallel and Distributed Computation Lecture #11 2/21/2017 Xuehai Qian Xuehai.qian@usc.edu http://alchem.usc.edu/portal/xuehaiq.html University of Southern California 1 Outline Midterm 1:
Multiprocessors & Thread Level Parallelism
 Multiprocessors & Thread Level Parallelism COE 403 Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline Introduction
Multiprocessors & Thread Level Parallelism COE 403 Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline Introduction
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Lecture 24 November 24, 2015
 CS 229r: Algorithms for Big Data Fall 2015 Prof. Jelani Nelson Lecture 24 November 24, 2015 Scribes: Zhengyu Wang 1 Cache-oblivious Model Last time we talked about disk access model (as known as DAM, or
CS 229r: Algorithms for Big Data Fall 2015 Prof. Jelani Nelson Lecture 24 November 24, 2015 Scribes: Zhengyu Wang 1 Cache-oblivious Model Last time we talked about disk access model (as known as DAM, or
Shared Memory Multiprocessors. Symmetric Shared Memory Architecture (SMP) Cache Coherence. Cache Coherence Mechanism. Interconnection Network
 Shared Memory Multis Processor Processor Processor i Processor n Symmetric Shared Memory Architecture (SMP) cache cache cache cache Interconnection Network Main Memory I/O System Cache Coherence Cache
Shared Memory Multis Processor Processor Processor i Processor n Symmetric Shared Memory Architecture (SMP) cache cache cache cache Interconnection Network Main Memory I/O System Cache Coherence Cache
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II)
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2018 Types of cache misses Compulsory Misses: first access to a block cannot be in the cache (cold start misses) Capacity
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2018 Types of cache misses Compulsory Misses: first access to a block cannot be in the cache (cold start misses) Capacity
Princeton University. Computer Science 217: Introduction to Programming Systems. The Memory/Storage Hierarchy and Virtual Memory
 Princeton University Computer Science 27: Introduction to Programming Systems The Memory/Storage Hierarchy and Virtual Memory Goals of this Lecture Help you learn about: Locality and caching The memory
Princeton University Computer Science 27: Introduction to Programming Systems The Memory/Storage Hierarchy and Virtual Memory Goals of this Lecture Help you learn about: Locality and caching The memory
LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY
 LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.5 Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal
LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.5 Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal
Memory Systems and Performance Engineering
 SPEED LIMIT PER ORDER OF 6.172 Memory Systems and Performance Engineering Fall 2010 Basic Caching Idea A. Smaller memory faster to access B. Use smaller memory to cache contents of larger memory C. Provide
SPEED LIMIT PER ORDER OF 6.172 Memory Systems and Performance Engineering Fall 2010 Basic Caching Idea A. Smaller memory faster to access B. Use smaller memory to cache contents of larger memory C. Provide
TDT Coarse-Grained Multithreading. Review on ILP. Multi-threaded execution. Contents. Fine-Grained Multithreading
 Review on ILP TDT 4260 Chap 5 TLP & Hierarchy What is ILP? Let the compiler find the ILP Advantages? Disadvantages? Let the HW find the ILP Advantages? Disadvantages? Contents Multi-threading Chap 3.5
Review on ILP TDT 4260 Chap 5 TLP & Hierarchy What is ILP? Let the compiler find the ILP Advantages? Disadvantages? Let the HW find the ILP Advantages? Disadvantages? Contents Multi-threading Chap 3.5
Cache memories are small, fast SRAM based memories managed automatically in hardware.
 Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and
Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and
Cache Memories. Topics. Next time. Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of caches on performance
 Cache Memories Topics Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of caches on performance Next time Dynamic memory allocation and memory bugs Fabián E. Bustamante,
Cache Memories Topics Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of caches on performance Next time Dynamic memory allocation and memory bugs Fabián E. Bustamante,
Chapter Seven. Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter Seven Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy 1 Memories: Review SRAM (Static Random Access Memory): value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM DRAM
Chapter Seven Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy 1 Memories: Review SRAM (Static Random Access Memory): value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM DRAM
Advanced Memory Organizations
 CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
Double-Precision Matrix Multiply on CUDA
 Double-Precision Matrix Multiply on CUDA Parallel Computation (CSE 60), Assignment Andrew Conegliano (A5055) Matthias Springer (A995007) GID G--665 February, 0 Assumptions All matrices are square matrices
Double-Precision Matrix Multiply on CUDA Parallel Computation (CSE 60), Assignment Andrew Conegliano (A5055) Matthias Springer (A995007) GID G--665 February, 0 Assumptions All matrices are square matrices
Caches. Cache Memory. memory hierarchy. CPU memory request presented to first-level cache first
 Cache Memory memory hierarchy CPU memory request presented to first-level cache first if data NOT in cache, request sent to next level in hierarchy and so on CS3021/3421 2017 jones@tcd.ie School of Computer
Cache Memory memory hierarchy CPU memory request presented to first-level cache first if data NOT in cache, request sent to next level in hierarchy and so on CS3021/3421 2017 jones@tcd.ie School of Computer
Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II John Wawrzynek Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~johnw
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II John Wawrzynek Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~johnw
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste
Advanced Parallel Programming I
 Advanced Parallel Programming I Alexander Leutgeb, RISC Software GmbH RISC Software GmbH Johannes Kepler University Linz 2016 22.09.2016 1 Levels of Parallelism RISC Software GmbH Johannes Kepler University
Advanced Parallel Programming I Alexander Leutgeb, RISC Software GmbH RISC Software GmbH Johannes Kepler University Linz 2016 22.09.2016 1 Levels of Parallelism RISC Software GmbH Johannes Kepler University
CHAPTER 6 Memory. CMPS375 Class Notes (Chap06) Page 1 / 20 Dr. Kuo-pao Yang
 CHAPTER 6 Memory 6.1 Memory 341 6.2 Types of Memory 341 6.3 The Memory Hierarchy 343 6.3.1 Locality of Reference 346 6.4 Cache Memory 347 6.4.1 Cache Mapping Schemes 349 6.4.2 Replacement Policies 365
CHAPTER 6 Memory 6.1 Memory 341 6.2 Types of Memory 341 6.3 The Memory Hierarchy 343 6.3.1 Locality of Reference 346 6.4 Cache Memory 347 6.4.1 Cache Mapping Schemes 349 6.4.2 Replacement Policies 365
Motivation for Caching and Optimization of Cache Utilization
 Motivation for Caching and Optimization of Cache Utilization Agenda Memory Technologies Bandwidth Limitations Cache Organization Prefetching/Replacement More Complexity by Coherence Performance Optimization
Motivation for Caching and Optimization of Cache Utilization Agenda Memory Technologies Bandwidth Limitations Cache Organization Prefetching/Replacement More Complexity by Coherence Performance Optimization
Last class. Caches. Direct mapped
 Memory Hierarchy II Last class Caches Direct mapped E=1 (One cache line per set) Each main memory address can be placed in exactly one place in the cache Conflict misses if two addresses map to same place
Memory Hierarchy II Last class Caches Direct mapped E=1 (One cache line per set) Each main memory address can be placed in exactly one place in the cache Conflict misses if two addresses map to same place
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Memory Hierarchy. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Memory Hierarchy Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Time (ns) The CPU-Memory Gap The gap widens between DRAM, disk, and CPU speeds
Memory Hierarchy Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Time (ns) The CPU-Memory Gap The gap widens between DRAM, disk, and CPU speeds
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1)
 Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1) 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Depar rtment of Electr rical Engineering,
Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1) 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Depar rtment of Electr rical Engineering,
I/O Model. Cache-Oblivious Algorithms : Algorithms in the Real World. Advantages of Cache-Oblivious Algorithms 4/9/13
 I/O Model 15-853: Algorithms in the Real World Locality II: Cache-oblivious algorithms Matrix multiplication Distribution sort Static searching Abstracts a single level of the memory hierarchy Fast memory
I/O Model 15-853: Algorithms in the Real World Locality II: Cache-oblivious algorithms Matrix multiplication Distribution sort Static searching Abstracts a single level of the memory hierarchy Fast memory
Cray XE6 Performance Workshop
 Cray XE6 Performance Workshop Mark Bull David Henty EPCC, University of Edinburgh Overview Why caches are needed How caches work Cache design and performance. 2 1 The memory speed gap Moore s Law: processors
Cray XE6 Performance Workshop Mark Bull David Henty EPCC, University of Edinburgh Overview Why caches are needed How caches work Cache design and performance. 2 1 The memory speed gap Moore s Law: processors
Lecture 15: Caches and Optimization Computer Architecture and Systems Programming ( )
 Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Lecture 15: Caches and Optimization Computer Architecture and Systems Programming (252-0061-00) Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 2012 Last time Program
Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Lecture 15: Caches and Optimization Computer Architecture and Systems Programming (252-0061-00) Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 2012 Last time Program
CS377P Programming for Performance Single Thread Performance Caches I
 CS377P Programming for Performance Single Thread Performance Caches I Sreepathi Pai UTCS September 21, 2015 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Caches 3 Performance of Caches Outline 1 Introduction 2 Caches 3 Performance
CS377P Programming for Performance Single Thread Performance Caches I Sreepathi Pai UTCS September 21, 2015 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Caches 3 Performance of Caches Outline 1 Introduction 2 Caches 3 Performance
Cache Coherence. CMU : Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming (Spring 2012)
 Cache Coherence CMU 15-418: Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming (Spring 2012) Shared memory multi-processor Processors read and write to shared variables - More precisely: processors issues
Cache Coherence CMU 15-418: Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming (Spring 2012) Shared memory multi-processor Processors read and write to shared variables - More precisely: processors issues
Today. Cache Memories. General Cache Concept. General Cache Organization (S, E, B) Cache Memories. Example Memory Hierarchy Smaller, faster,
 Today Cache Memories CSci 2021: Machine Architecture and Organization November 7th-9th, 2016 Your instructor: Stephen McCamant Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory
Today Cache Memories CSci 2021: Machine Architecture and Organization November 7th-9th, 2016 Your instructor: Stephen McCamant Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory
EEC 170 Computer Architecture Fall Cache Introduction Review. Review: The Memory Hierarchy. The Memory Hierarchy: Why Does it Work?
 EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
Caches III. CSE 351 Spring Instructor: Ruth Anderson
 Caches III CSE 351 Spring 2017 Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis Administrivia Office Hours Changes check
Caches III CSE 351 Spring 2017 Instructor: Ruth Anderson Teaching Assistants: Dylan Johnson Kevin Bi Linxing Preston Jiang Cody Ohlsen Yufang Sun Joshua Curtis Administrivia Office Hours Changes check
I, J A[I][J] / /4 8000/ I, J A(J, I) Chapter 5 Solutions S-3.
![I, J A[I][J] / /4 8000/ I, J A(J, I) Chapter 5 Solutions S-3. I, J A[I][J] / /4 8000/ I, J A(J, I) Chapter 5 Solutions S-3.](/thumbs/81/83055456.jpg) 5 Solutions Chapter 5 Solutions S-3 5.1 5.1.1 4 5.1.2 I, J 5.1.3 A[I][J] 5.1.4 3596 8 800/4 2 8 8/4 8000/4 5.1.5 I, J 5.1.6 A(J, I) 5.2 5.2.1 Word Address Binary Address Tag Index Hit/Miss 5.2.2 3 0000
5 Solutions Chapter 5 Solutions S-3 5.1 5.1.1 4 5.1.2 I, J 5.1.3 A[I][J] 5.1.4 3596 8 800/4 2 8 8/4 8000/4 5.1.5 I, J 5.1.6 A(J, I) 5.2 5.2.1 Word Address Binary Address Tag Index Hit/Miss 5.2.2 3 0000
