CS377P Programming for Performance Single Thread Performance Caches I
|
|
|
- Helena May
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS377P Programming for Performance Single Thread Performance Caches I Sreepathi Pai UTCS September 21, 2015
2 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Caches 3 Performance of Caches
3 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Caches 3 Performance of Caches
4 Matrix Multiply IJK Multiplying two matrices: A (m n) B (n k) C (m k) [result] Here: m = n = k for(ii = 0; ii < m; ii++) for(jj = 0; jj < n; jj++) for(kk = 0; kk < k; kk++) C[ii * k + kk] += A[ii * n + jj] * B[jj * k + kk];
5 Matrix Multiply IKJ for(ii = 0; ii < m; ii++) for(kk = 0; kk < k; kk++) for(jj = 0; jj < n; jj++) C[ii * k + kk] += A[ii * n + jj] * B[jj * k + kk];
6 Performance of the two versions? on 1024x1024 matrices of ints which is faster? by how much?
7 Performance of the two versions on 1024x1024 matrices Time for IJK: 0554 s ± 0003s (95% CI) Time for IKJ: 6618 s ± 0032s (95% CI)
8 What caused the nearly 12X slowdown? Matrix Multiply has a large number of arithmetic operations But the number of operations did not change Matrix Multiply also refers to a large number of array elements Order in which they access elements changed But why should this matter?
9 Die shot of a processor (IBM Power 8)
10 Die shot of a processor (IBM Power 8) extremetech
11 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Caches 3 Performance of Caches
12 The question What are caches?
13 Answer? Caches are a kind of fast(er) memory
14 Obligatory question Why don t we build entire memory systems out of cache memory? see also: joke about black boxes in aeroplanes
15 Physical Issues Not all memory types are equal Consider: SRAM, DRAM and magnetic storage Speed to access Depends on size and type of memory SRAM > DRAM > Magnetic storage Density of storing Bits per square millimeter SRAM < DRAM < Magnetic storage
16 The Memory Hierarchy Registers managed by compiler logic L1 cache small (10s KB), usually 1-cycle access SRAM (also logic ) L2 cache largish (100s KB), 10s of cycles SRAM L3 cache usually on multicores much larger (MB), 100s of cycles SRAM or (recently) embedded DRAM RAM off-chip, large (GB) DRAM HDD Magnetic/Rotating Storage (TBs) Flash memory (GBs)
17 Performance of the hierarchy? Why structure memory in a hierarchy? Each level of hierarchy adds a delay Time to access memory increases! Or does it?
18 Performance of the hierarchy Structures in memory hierarchy duplicate stored further away original meaning of the word cache If is found at closer to processor (ie hit), read it from there Otherwise (ie miss), pass request one level up the hierarchy
19 Why the hierarchy works in practice Data Reuse (or locality ) Temporal (same will be referred again) Spatial ( close to each other in space will be referred close to each other in time) Speed differences Time to access L1: 1ns Branch mispredict: 3ns Time to access L2: 4ns Main memory access time: 100ns SSD access time: 16µs Rotating media access time: < 5 ms From Latency Numbers Every Programmer Should Know
20 The cache equation (informal) Assume a one-level cache (ie cache + RAM): latency = latency hit or latency = latency miss
21 The cache equation for one level of caches latency avg = (fraction hit ) latency hit + (1 fraction hit ) latency miss
22 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Caches 3 Performance of Caches
23 Cache Organization RAM is directly addressable Caches duplicate RAM contents accept same addresses translate that address internally Translation is a many-to-one function obviously, since caches are much smaller than RAM Therefore caches store: (original address or part of original address) is used to verify address
24 Cache Lookup Building blocks of translation functions: Direct Mapped Associative Lookup
25 A Direct Mapped Cache Converts address to cache location index = fn(address) n
26 A Fully Associative Cache Searches for address in cache also known as content-addressable memory address match
27 Set Associative Caches 4-way set-associative cache Lookup a set based on address (direct-mapped) Lookup address only within the set (associative) index = fn(address) n
28 The 3C model of cache misses Compulsory (or Cold) misses first reference to always occur (?) Capacity misses in cache is evicted once cache is full miss to being evicted from cache these are absent in an infinite cache Conflict misses miss due to many-to-one conflict two different addresses map to the same cache address these do not occur in a fully associative cache Due to Mark Hill
29 Next class Reducing misses using programming techniques
30 Summary Memory accesses are key to program performance nearly always the bottleneck in most programs The memory hierarchy lowers memory access latency Exploits locality of references Size/speed tradeoffs Caches are organized differently than RAM smaller implications for performance transparent to programmer not transparent to performance!
Caches. Han Wang CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University. See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes)
 Caches Han Wang CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes) This week: Announcements PA2 Work-in-progress submission Next six weeks: Two labs and two projects
Caches Han Wang CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes) This week: Announcements PA2 Work-in-progress submission Next six weeks: Two labs and two projects
Outline. Issues with the Memory System Loop Transformations Data Transformations Prefetching Alias Analysis
 Memory Optimization Outline Issues with the Memory System Loop Transformations Data Transformations Prefetching Alias Analysis Memory Hierarchy 1-2 ns Registers 32 512 B 3-10 ns 8-30 ns 60-250 ns 5-20
Memory Optimization Outline Issues with the Memory System Loop Transformations Data Transformations Prefetching Alias Analysis Memory Hierarchy 1-2 ns Registers 32 512 B 3-10 ns 8-30 ns 60-250 ns 5-20
211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016
 211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016 Liu Liu Topic: Assembly Programming Storage - Assembly Programming: Recap - Call-chain - Factorial - Storage: - RAM - Caching - Direct - Mapping Rutgers University
211: Computer Architecture Summer 2016 Liu Liu Topic: Assembly Programming Storage - Assembly Programming: Recap - Call-chain - Factorial - Storage: - RAM - Caching - Direct - Mapping Rutgers University
CSCI-UA.0201 Computer Systems Organization Memory Hierarchy
 CSCI-UA.0201 Computer Systems Organization Memory Hierarchy Mohamed Zahran (aka Z) mzahran@cs.nyu.edu http://www.mzahran.com Programmer s Wish List Memory Private Infinitely large Infinitely fast Non-volatile
CSCI-UA.0201 Computer Systems Organization Memory Hierarchy Mohamed Zahran (aka Z) mzahran@cs.nyu.edu http://www.mzahran.com Programmer s Wish List Memory Private Infinitely large Infinitely fast Non-volatile
Memory Hierarchy. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Memory Hierarchy Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Time (ns) The CPU-Memory Gap The gap widens between DRAM, disk, and CPU speeds
Memory Hierarchy Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Time (ns) The CPU-Memory Gap The gap widens between DRAM, disk, and CPU speeds
Inside out of your computer memories (III) Hung-Wei Tseng
 Inside out of your computer memories (III) Hung-Wei Tseng Why memory hierarchy? CPU main memory lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3, $t2, $a1 addi $a0, $a0, 4 subi $a1, $a1, 1 bne $a1, LOOP lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3,
Inside out of your computer memories (III) Hung-Wei Tseng Why memory hierarchy? CPU main memory lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3, $t2, $a1 addi $a0, $a0, 4 subi $a1, $a1, 1 bne $a1, LOOP lw $t2, 0($a0) add $t3,
Algorithm Performance Factors. Memory Performance of Algorithms. Processor-Memory Performance Gap. Moore s Law. Program Model of Memory II
 Memory Performance of Algorithms CSE 32 Data Structures Lecture Algorithm Performance Factors Algorithm choices (asymptotic running time) O(n 2 ) or O(n log n) Data structure choices List or Arrays Language
Memory Performance of Algorithms CSE 32 Data Structures Lecture Algorithm Performance Factors Algorithm choices (asymptotic running time) O(n 2 ) or O(n log n) Data structure choices List or Arrays Language
Algorithm Performance Factors. Memory Performance of Algorithms. Processor-Memory Performance Gap. Moore s Law. Program Model of Memory I
 Memory Performance of Algorithms CSE 32 Data Structures Lecture Algorithm Performance Factors Algorithm choices (asymptotic running time) O(n 2 ) or O(n log n) Data structure choices List or Arrays Language
Memory Performance of Algorithms CSE 32 Data Structures Lecture Algorithm Performance Factors Algorithm choices (asymptotic running time) O(n 2 ) or O(n log n) Data structure choices List or Arrays Language
CISC 360. Cache Memories Nov 25, 2008
 CISC 36 Topics Cache Memories Nov 25, 28 Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of caches on performance Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based
CISC 36 Topics Cache Memories Nov 25, 28 Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of caches on performance Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM-based
Systems Programming and Computer Architecture ( ) Timothy Roscoe
 Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Systems Programming and Computer Architecture (252-0061-00) Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 2016 AS 2016 Caches 1 16: Caches Computer Architecture
Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Systems Programming and Computer Architecture (252-0061-00) Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 2016 AS 2016 Caches 1 16: Caches Computer Architecture
Lecture 12. Memory Design & Caches, part 2. Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University
 Lecture 12 Memory Design & Caches, part 2 Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements HW3 is due today PA2 is available on-line today Part 1 is due on 2/27
Lecture 12 Memory Design & Caches, part 2 Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements HW3 is due today PA2 is available on-line today Part 1 is due on 2/27
Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science. TDT4255 Memory hierarchies
 TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
Cache Memories. EL2010 Organisasi dan Arsitektur Sistem Komputer Sekolah Teknik Elektro dan Informatika ITB 2010
 Cache Memories EL21 Organisasi dan Arsitektur Sistem Komputer Sekolah Teknik Elektro dan Informatika ITB 21 Topics Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of
Cache Memories EL21 Organisasi dan Arsitektur Sistem Komputer Sekolah Teknik Elektro dan Informatika ITB 21 Topics Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of
Caches! Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2011 Computer Science Cornell University. See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes)
 Caches! Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2011 Computer Science Cornell University See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes) Announcements! HW3 available due next Tuesday Work with alone partner Be responsible
Caches! Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2011 Computer Science Cornell University See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes) Announcements! HW3 available due next Tuesday Work with alone partner Be responsible
Giving credit where credit is due
 CSCE 23J Computer Organization Cache Memories Dr. Steve Goddard goddard@cse.unl.edu http://cse.unl.edu/~goddard/courses/csce23j Giving credit where credit is due Most of slides for this lecture are based
CSCE 23J Computer Organization Cache Memories Dr. Steve Goddard goddard@cse.unl.edu http://cse.unl.edu/~goddard/courses/csce23j Giving credit where credit is due Most of slides for this lecture are based
Lecture 15: Caches and Optimization Computer Architecture and Systems Programming ( )
 Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Lecture 15: Caches and Optimization Computer Architecture and Systems Programming (252-0061-00) Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 2012 Last time Program
Systems Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Lecture 15: Caches and Optimization Computer Architecture and Systems Programming (252-0061-00) Timothy Roscoe Herbstsemester 2012 Last time Program
Cache Memories October 8, 2007
 15-213 Topics Cache Memories October 8, 27 Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of caches on performance The memory mountain class12.ppt Cache Memories Cache
15-213 Topics Cache Memories October 8, 27 Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of caches on performance The memory mountain class12.ppt Cache Memories Cache
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review. UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016
 Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016 1 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only 10-20% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016 1 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only 10-20% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss
14:332:331. Week 13 Basics of Cache
 14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Fall 2003 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Lec20.1 Fall 2003 Head
14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Fall 2003 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Lec20.1 Fall 2003 Head
EEC 170 Computer Architecture Fall Cache Introduction Review. Review: The Memory Hierarchy. The Memory Hierarchy: Why Does it Work?
 EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
Cache Memories. Cache Memories Oct. 10, Inserting an L1 Cache Between the CPU and Main Memory. General Org of a Cache Memory
 5-23 The course that gies CMU its Zip! Topics Cache Memories Oct., 22! Generic cache memory organization! Direct mapped caches! Set associatie caches! Impact of caches on performance Cache Memories Cache
5-23 The course that gies CMU its Zip! Topics Cache Memories Oct., 22! Generic cache memory organization! Direct mapped caches! Set associatie caches! Impact of caches on performance Cache Memories Cache
ν Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory 2 CISC 360, Fa09 Cache is an array of sets. Each set contains one or more lines.
 Topics CISC 36 Cache Memories Dec, 29 ν Generic cache memory organization ν Direct mapped caches ν Set associatie caches ν Impact of caches on performance Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast
Topics CISC 36 Cache Memories Dec, 29 ν Generic cache memory organization ν Direct mapped caches ν Set associatie caches ν Impact of caches on performance Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast
Cache memories The course that gives CMU its Zip! Cache Memories Oct 11, General organization of a cache memory
 5-23 The course that gies CMU its Zip! Cache Memories Oct, 2 Topics Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associatie caches Impact of caches on performance Cache memories Cache memories
5-23 The course that gies CMU its Zip! Cache Memories Oct, 2 Topics Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associatie caches Impact of caches on performance Cache memories Cache memories
10/16/2017. Miss Rate: ABC. Classifying Misses: 3C Model (Hill) Reducing Conflict Misses: Victim Buffer. Overlapping Misses: Lockup Free Cache
 Classifying Misses: 3C Model (Hill) Divide cache misses into three categories Compulsory (cold): never seen this address before Would miss even in infinite cache Capacity: miss caused because cache is
Classifying Misses: 3C Model (Hill) Divide cache misses into three categories Compulsory (cold): never seen this address before Would miss even in infinite cache Capacity: miss caused because cache is
Memory Hierarchy. Maurizio Palesi. Maurizio Palesi 1
 Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II John Wawrzynek Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~johnw
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II John Wawrzynek Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~johnw
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review. UCSB CS240A, Fall 2017
 Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS24A, Fall 27 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only - 2% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss is in the
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS24A, Fall 27 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only - 2% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss is in the
Announcements. ECE4750/CS4420 Computer Architecture L6: Advanced Memory Hierarchy. Edward Suh Computer Systems Laboratory
 ECE4750/CS4420 Computer Architecture L6: Advanced Memory Hierarchy Edward Suh Computer Systems Laboratory suh@csl.cornell.edu Announcements Lab 1 due today Reading: Chapter 5.1 5.3 2 1 Overview How to
ECE4750/CS4420 Computer Architecture L6: Advanced Memory Hierarchy Edward Suh Computer Systems Laboratory suh@csl.cornell.edu Announcements Lab 1 due today Reading: Chapter 5.1 5.3 2 1 Overview How to
Memory Hierarchy. Maurizio Palesi. Maurizio Palesi 1
 Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
The course that gives CMU its Zip! Memory System Performance. March 22, 2001
 15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Memory System Performance March 22, 2001 Topics Impact of cache parameters Impact of memory reference patterns memory mountain range matrix multiply Basic Cache
15-213 The course that gives CMU its Zip! Memory System Performance March 22, 2001 Topics Impact of cache parameters Impact of memory reference patterns memory mountain range matrix multiply Basic Cache
CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/73/69213006.jpg) CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
Introduction to OpenMP. Lecture 10: Caches
 Introduction to OpenMP Lecture 10: Caches Overview Why caches are needed How caches work Cache design and performance. The memory speed gap Moore s Law: processors speed doubles every 18 months. True for
Introduction to OpenMP Lecture 10: Caches Overview Why caches are needed How caches work Cache design and performance. The memory speed gap Moore s Law: processors speed doubles every 18 months. True for
Chapter 6 Caches. Computer System. Alpha Chip Photo. Topics. Memory Hierarchy Locality of Reference SRAM Caches Direct Mapped Associative
 Chapter 6 s Topics Memory Hierarchy Locality of Reference SRAM s Direct Mapped Associative Computer System Processor interrupt On-chip cache s s Memory-I/O bus bus Net cache Row cache Disk cache Memory
Chapter 6 s Topics Memory Hierarchy Locality of Reference SRAM s Direct Mapped Associative Computer System Processor interrupt On-chip cache s s Memory-I/O bus bus Net cache Row cache Disk cache Memory
Cache Performance (H&P 5.3; 5.5; 5.6)
 Cache Performance (H&P 5.3; 5.5; 5.6) Memory system and processor performance: CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st
Cache Performance (H&P 5.3; 5.5; 5.6) Memory system and processor performance: CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st
MANAGING MULTI-TIERED NON-VOLATILE MEMORY SYSTEMS FOR COST AND PERFORMANCE 8/9/16
 MANAGING MULTI-TIERED NON-VOLATILE MEMORY SYSTEMS FOR COST AND PERFORMANCE 8/9/16 THE DATA CHALLENGE Performance Improvement (RelaLve) 4.4 ZB Total data created, replicated, and consumed in a single year
MANAGING MULTI-TIERED NON-VOLATILE MEMORY SYSTEMS FOR COST AND PERFORMANCE 8/9/16 THE DATA CHALLENGE Performance Improvement (RelaLve) 4.4 ZB Total data created, replicated, and consumed in a single year
Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory
 Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory Readings: 5.1-5.4, 5.8 Big memories are slow Computer Fast memories are small Processor Memory Devices Control Input Datapath Output Need to get fast, big memories
Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory Readings: 5.1-5.4, 5.8 Big memories are slow Computer Fast memories are small Processor Memory Devices Control Input Datapath Output Need to get fast, big memories
Denison University. Cache Memories. CS-281: Introduction to Computer Systems. Instructor: Thomas C. Bressoud
 Cache Memories CS-281: Introduction to Computer Systems Instructor: Thomas C. Bressoud 1 Random-Access Memory (RAM) Key features RAM is traditionally packaged as a chip. Basic storage unit is normally
Cache Memories CS-281: Introduction to Computer Systems Instructor: Thomas C. Bressoud 1 Random-Access Memory (RAM) Key features RAM is traditionally packaged as a chip. Basic storage unit is normally
Chapter 5. Memory Technology
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Locality. CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture. Locality Example 2. Locality Example
 Locality CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Principle of Locality: Programs tend to reuse data and instructions near
Locality CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Principle of Locality: Programs tend to reuse data and instructions near
Cache Performance! ! Memory system and processor performance:! ! Improving memory hierarchy performance:! CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time
 Cache Performance!! Memory system and processor performance:! CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st = Pipeline time +
Cache Performance!! Memory system and processor performance:! CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st = Pipeline time +
ECE 552 / CPS 550 Advanced Computer Architecture I. Lecture 13 Memory Part 2
 ECE 552 / CPS 550 Advanced Computer Architecture I Lecture 13 Memory Part 2 Benjamin Lee Electrical and Computer Engineering Duke University www.duke.edu/~bcl15 www.duke.edu/~bcl15/class/class_ece252fall12.html
ECE 552 / CPS 550 Advanced Computer Architecture I Lecture 13 Memory Part 2 Benjamin Lee Electrical and Computer Engineering Duke University www.duke.edu/~bcl15 www.duke.edu/~bcl15/class/class_ece252fall12.html
Systems I. Optimizing for the Memory Hierarchy. Topics Impact of caches on performance Memory hierarchy considerations
 Systems I Optimizing for the Memory Hierarchy Topics Impact of caches on performance Memory hierarchy considerations Cache Performance Metrics Miss Rate Fraction of memory references not found in cache
Systems I Optimizing for the Memory Hierarchy Topics Impact of caches on performance Memory hierarchy considerations Cache Performance Metrics Miss Rate Fraction of memory references not found in cache
L2 cache provides additional on-chip caching space. L2 cache captures misses from L1 cache. Summary
 HY425 Lecture 13: Improving Cache Performance Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos University of Crete and FORTH-ICS November 25, 2011 Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos HY425 Lecture 13: Improving Cache Performance 1 / 40
HY425 Lecture 13: Improving Cache Performance Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos University of Crete and FORTH-ICS November 25, 2011 Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos HY425 Lecture 13: Improving Cache Performance 1 / 40
LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY
 LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.5 Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal
LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.5 Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal
CS241 Computer Organization Spring Principle of Locality
 CS241 Computer Organization Spring 2015 Principle of Locality 4-21 2015 Outline! Optimization! Memory Hierarchy Locality temporal spatial Cache Readings: CSAPP2: Chapter 5, sections 5.1-5.6; 5.13 CSAPP2:
CS241 Computer Organization Spring 2015 Principle of Locality 4-21 2015 Outline! Optimization! Memory Hierarchy Locality temporal spatial Cache Readings: CSAPP2: Chapter 5, sections 5.1-5.6; 5.13 CSAPP2:
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/24/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #16 1 Software
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/24/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #16 1 Software
Cray XE6 Performance Workshop
 Cray XE6 Performance Workshop Mark Bull David Henty EPCC, University of Edinburgh Overview Why caches are needed How caches work Cache design and performance. 2 1 The memory speed gap Moore s Law: processors
Cray XE6 Performance Workshop Mark Bull David Henty EPCC, University of Edinburgh Overview Why caches are needed How caches work Cache design and performance. 2 1 The memory speed gap Moore s Law: processors
What is Cache Memory? EE 352 Unit 11. Motivation for Cache Memory. Memory Hierarchy. Cache Definitions Cache Address Mapping Cache Performance
 What is EE 352 Unit 11 Definitions Address Mapping Performance memory is a small, fast memory used to hold of data that the processor will likely need to access in the near future sits between the processor
What is EE 352 Unit 11 Definitions Address Mapping Performance memory is a small, fast memory used to hold of data that the processor will likely need to access in the near future sits between the processor
Sarah L. Harris and David Money Harris. Digital Design and Computer Architecture: ARM Edition Chapter 8 <1>
 Chapter 8 Digital Design and Computer Architecture: ARM Edition Sarah L. Harris and David Money Harris Digital Design and Computer Architecture: ARM Edition 215 Chapter 8 Chapter 8 :: Topics Introduction
Chapter 8 Digital Design and Computer Architecture: ARM Edition Sarah L. Harris and David Money Harris Digital Design and Computer Architecture: ARM Edition 215 Chapter 8 Chapter 8 :: Topics Introduction
Memory Hierarchy. ENG3380 Computer Organization and Architecture Cache Memory Part II. Topics. References. Memory Hierarchy
 ENG338 Computer Organization and Architecture Part II Winter 217 S. Areibi School of Engineering University of Guelph Hierarchy Topics Hierarchy Locality Motivation Principles Elements of Design: Addresses
ENG338 Computer Organization and Architecture Part II Winter 217 S. Areibi School of Engineering University of Guelph Hierarchy Topics Hierarchy Locality Motivation Principles Elements of Design: Addresses
Last class. Caches. Direct mapped
 Memory Hierarchy II Last class Caches Direct mapped E=1 (One cache line per set) Each main memory address can be placed in exactly one place in the cache Conflict misses if two addresses map to same place
Memory Hierarchy II Last class Caches Direct mapped E=1 (One cache line per set) Each main memory address can be placed in exactly one place in the cache Conflict misses if two addresses map to same place
+ Random-Access Memory (RAM)
 + Memory Subsystem + Random-Access Memory (RAM) Key features RAM is traditionally packaged as a chip. Basic storage unit is normally a cell (one bit per cell). Multiple RAM chips form a memory. RAM comes
+ Memory Subsystem + Random-Access Memory (RAM) Key features RAM is traditionally packaged as a chip. Basic storage unit is normally a cell (one bit per cell). Multiple RAM chips form a memory. RAM comes
Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches
 Cache Memories 1 Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging loops to improve spatial locality Using blocking to improve temporal locality
Cache Memories 1 Today Cache memory organization and operation Performance impact of caches The memory mountain Rearranging loops to improve spatial locality Using blocking to improve temporal locality
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2
 EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache performance optimization Bandwidth increase Reduce hit time Reduce miss penalty Reduce miss
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache performance optimization Bandwidth increase Reduce hit time Reduce miss penalty Reduce miss
Cache memories are small, fast SRAM based memories managed automatically in hardware.
 Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and
Cache Memories Cache memories are small, fast SRAM based memories managed automatically in hardware. Hold frequently accessed blocks of main memory CPU looks first for data in caches (e.g., L1, L2, and
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS. Spring 2014 Lecture 14
 CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2014 Lecture 14 LAST TIME! Examined several memory technologies: SRAM volatile memory cells built from transistors! Fast to use, larger memory cells (6+ transistors
CS24: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS Spring 2014 Lecture 14 LAST TIME! Examined several memory technologies: SRAM volatile memory cells built from transistors! Fast to use, larger memory cells (6+ transistors
write-through v. write-back write-through v. write-back write-through v. write-back option 1: write-through write 10 to 0xABCD CPU RAM Cache ABCD: FF
 write-through v. write-back option 1: write-through 1 write 10 to 0xABCD CPU Cache ABCD: FF RAM 11CD: 42 ABCD: FF 1 2 write-through v. write-back option 1: write-through write-through v. write-back option
write-through v. write-back option 1: write-through 1 write 10 to 0xABCD CPU Cache ABCD: FF RAM 11CD: 42 ABCD: FF 1 2 write-through v. write-back option 1: write-through write-through v. write-back option
Effect of memory latency
 CACHE AWARENESS Effect of memory latency Consider a processor operating at 1 GHz (1 ns clock) connected to a DRAM with a latency of 100 ns. Assume that the processor has two ALU units and it is capable
CACHE AWARENESS Effect of memory latency Consider a processor operating at 1 GHz (1 ns clock) connected to a DRAM with a latency of 100 ns. Assume that the processor has two ALU units and it is capable
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture. Memory Hierarchy
 ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Hierarchy ECE468 memory.1 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Control Input Datapath Output Today s Topic:
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Hierarchy ECE468 memory.1 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Control Input Datapath Output Today s Topic:
Administrivia. Expect new HW out today (functions in assembly!)
 Caching 1/25/19 Administrivia Expect new HW out today (functions in assembly!) Memory so far Big array indexed by the memory address accessed by load and store of various types Implicitly assumed: One
Caching 1/25/19 Administrivia Expect new HW out today (functions in assembly!) Memory so far Big array indexed by the memory address accessed by load and store of various types Implicitly assumed: One
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Cache Memories. Topics. Next time. Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of caches on performance
 Cache Memories Topics Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of caches on performance Next time Dynamic memory allocation and memory bugs Fabián E. Bustamante,
Cache Memories Topics Generic cache memory organization Direct mapped caches Set associative caches Impact of caches on performance Next time Dynamic memory allocation and memory bugs Fabián E. Bustamante,
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 8 - Memory Hierarchy-III
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 8 - Memory Hierarchy-III Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 8 - Memory Hierarchy-III Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste
ECE 252 / CPS 220 Advanced Computer Architecture I. Lecture 13 Memory Part 2
 ECE 252 / CPS 220 Advanced Computer Architecture I Lecture 13 Memory Part 2 Benjamin Lee Electrical and Computer Engineering Duke University www.duke.edu/~bcl15 www.duke.edu/~bcl15/class/class_ece252fall11.html
ECE 252 / CPS 220 Advanced Computer Architecture I Lecture 13 Memory Part 2 Benjamin Lee Electrical and Computer Engineering Duke University www.duke.edu/~bcl15 www.duke.edu/~bcl15/class/class_ece252fall11.html
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste!
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste!
CS 261 Fall Mike Lam, Professor. Memory
 CS 261 Fall 2016 Mike Lam, Professor Memory Topics Memory hierarchy overview Storage technologies SRAM DRAM PROM / flash Disk storage Tape and network storage I/O architecture Storage trends Latency comparisons
CS 261 Fall 2016 Mike Lam, Professor Memory Topics Memory hierarchy overview Storage technologies SRAM DRAM PROM / flash Disk storage Tape and network storage I/O architecture Storage trends Latency comparisons
L7: Performance. Frans Kaashoek Spring 2013
 L7: Performance Frans Kaashoek kaashoek@mit.edu 6.033 Spring 2013 Overview Technology fixes some performance problems Ride the technology curves if you can Some performance requirements require thinking
L7: Performance Frans Kaashoek kaashoek@mit.edu 6.033 Spring 2013 Overview Technology fixes some performance problems Ride the technology curves if you can Some performance requirements require thinking
Why memory hierarchy? Memory hierarchy. Memory hierarchy goals. CS2410: Computer Architecture. L1 cache design. Sangyeun Cho
 Why memory hierarchy? L1 cache design Sangyeun Cho Computer Science Department Memory hierarchy Memory hierarchy goals Smaller Faster More expensive per byte CPU Regs L1 cache L2 cache SRAM SRAM To provide
Why memory hierarchy? L1 cache design Sangyeun Cho Computer Science Department Memory hierarchy Memory hierarchy goals Smaller Faster More expensive per byte CPU Regs L1 cache L2 cache SRAM SRAM To provide
Memory Hierarchy. Announcement. Computer system model. Reference
 Announcement Memory Hierarchy Computer Organization and Assembly Languages Yung-Yu Chuang 26//5 Grade for hw#4 is online Please DO submit homework if you haen t Please sign up a demo time on /6 or /7 at
Announcement Memory Hierarchy Computer Organization and Assembly Languages Yung-Yu Chuang 26//5 Grade for hw#4 is online Please DO submit homework if you haen t Please sign up a demo time on /6 or /7 at
Announcements. ! Previous lecture. Caches. Inf3 Computer Architecture
 Announcements! Previous lecture Caches Inf3 Computer Architecture - 2016-2017 1 Recap: Memory Hierarchy Issues! Block size: smallest unit that is managed at each level E.g., 64B for cache lines, 4KB for
Announcements! Previous lecture Caches Inf3 Computer Architecture - 2016-2017 1 Recap: Memory Hierarchy Issues! Block size: smallest unit that is managed at each level E.g., 64B for cache lines, 4KB for
Memory Hierarchy. Computer Systems Organization (Spring 2017) CSCI-UA 201, Section 3. Instructor: Joanna Klukowska
 Memory Hierarchy Computer Systems Organization (Spring 2017) CSCI-UA 201, Section 3 Instructor: Joanna Klukowska Slides adapted from Randal E. Bryant and David R. O Hallaron (CMU) Mohamed Zahran (NYU)
Memory Hierarchy Computer Systems Organization (Spring 2017) CSCI-UA 201, Section 3 Instructor: Joanna Klukowska Slides adapted from Randal E. Bryant and David R. O Hallaron (CMU) Mohamed Zahran (NYU)
Advanced Memory Organizations
 CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
Memory Hierarchy. Cache Memory Organization and Access. General Cache Concept. Example Memory Hierarchy Smaller, faster,
 Memory Hierarchy Computer Systems Organization (Spring 2017) CSCI-UA 201, Section 3 Cache Memory Organization and Access Instructor: Joanna Klukowska Slides adapted from Randal E. Bryant and David R. O
Memory Hierarchy Computer Systems Organization (Spring 2017) CSCI-UA 201, Section 3 Cache Memory Organization and Access Instructor: Joanna Klukowska Slides adapted from Randal E. Bryant and David R. O
Speicherarchitektur. Who Cares About the Memory Hierarchy? Technologie-Trends. Speicher-Hierarchie. Referenz-Lokalität. Caches
 11 Speicherarchitektur Speicher-Hierarchie Referenz-Lokalität Caches 1 Technologie-Trends Kapazitäts- Geschwindigkeitssteigerung Logik 2 fach in 3 Jahren 2 fach in 3 Jahren DRAM 4 fach in 3 Jahren 1.4
11 Speicherarchitektur Speicher-Hierarchie Referenz-Lokalität Caches 1 Technologie-Trends Kapazitäts- Geschwindigkeitssteigerung Logik 2 fach in 3 Jahren 2 fach in 3 Jahren DRAM 4 fach in 3 Jahren 1.4
Agenda. EE 260: Introduction to Digital Design Memory. Naive Register File. Agenda. Memory Arrays: SRAM. Memory Arrays: Register File
 EE 260: Introduction to Digital Design Technology Yao Zheng Department of Electrical Engineering University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa 2 Technology Naive Register File Write Read clk Decoder Read Write 3 4 Arrays:
EE 260: Introduction to Digital Design Technology Yao Zheng Department of Electrical Engineering University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa 2 Technology Naive Register File Write Read clk Decoder Read Write 3 4 Arrays:
Module Outline. CPU Memory interaction Organization of memory modules Cache memory Mapping and replacement policies.
 M6 Memory Hierarchy Module Outline CPU Memory interaction Organization of memory modules Cache memory Mapping and replacement policies. Events on a Cache Miss Events on a Cache Miss Stall the pipeline.
M6 Memory Hierarchy Module Outline CPU Memory interaction Organization of memory modules Cache memory Mapping and replacement policies. Events on a Cache Miss Events on a Cache Miss Stall the pipeline.
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17: Cache System
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17 System March 17, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http//http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17 System March 17, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http//http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
Caches. Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University. See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes)
 s akim Weatherspoon CS, Spring Computer Science Cornell University See P&.,. (except writes) Big Picture: : big & slow vs s: small & fast compute jump/branch targets memory PC + new pc Instruction Fetch
s akim Weatherspoon CS, Spring Computer Science Cornell University See P&.,. (except writes) Big Picture: : big & slow vs s: small & fast compute jump/branch targets memory PC + new pc Instruction Fetch
EE 660: Computer Architecture Advanced Caches
 EE 660: Computer Architecture Advanced Caches Yao Zheng Department of Electrical Engineering University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Based on the slides of Prof. David Wentzlaff Agenda Review Three C s Basic Cache
EE 660: Computer Architecture Advanced Caches Yao Zheng Department of Electrical Engineering University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Based on the slides of Prof. David Wentzlaff Agenda Review Three C s Basic Cache
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
CS 261 Fall Mike Lam, Professor. Memory
 CS 261 Fall 2017 Mike Lam, Professor Memory Topics Memory hierarchy overview Storage technologies I/O architecture Storage trends Latency comparisons Locality Memory Until now, we've referred to memory
CS 261 Fall 2017 Mike Lam, Professor Memory Topics Memory hierarchy overview Storage technologies I/O architecture Storage trends Latency comparisons Locality Memory Until now, we've referred to memory
Cache Performance! ! Memory system and processor performance:! ! Improving memory hierarchy performance:! CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time
 Cache Performance!! Memory system and processor performance:! CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st = Pipeline time +
Cache Performance!! Memory system and processor performance:! CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st = Pipeline time +
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 8 - Memory Hierarchy-III
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 8 - Memory Hierarchy-III Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste!
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 8 - Memory Hierarchy-III Krste Asanovic Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~krste!
Spring 2016 :: CSE 502 Computer Architecture. Caches. Nima Honarmand
 Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
MEMORY HIERARCHY DESIGN
 MEMORY HIERARCHY DESIGN Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 3 will be released on Oct. 31 st
MEMORY HIERARCHY DESIGN Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 3 will be released on Oct. 31 st
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal locality Items accessed recently are likely to
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal locality Items accessed recently are likely to
Memory Systems and Performance Engineering
 SPEED LIMIT PER ORDER OF 6.172 Memory Systems and Performance Engineering Fall 2010 Basic Caching Idea A. Smaller memory faster to access B. Use smaller memory to cache contents of larger memory C. Provide
SPEED LIMIT PER ORDER OF 6.172 Memory Systems and Performance Engineering Fall 2010 Basic Caching Idea A. Smaller memory faster to access B. Use smaller memory to cache contents of larger memory C. Provide
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Key Point. What are Cache lines
 Caching 1 Key Point What are Cache lines Tags Index offset How do we find data in the cache? How do we tell if it s the right data? What decisions do we need to make in designing a cache? What are possible
Caching 1 Key Point What are Cache lines Tags Index offset How do we find data in the cache? How do we tell if it s the right data? What decisions do we need to make in designing a cache? What are possible
Lecture 2: Caches. belongs to Milo Martin, Amir Roth, David Wood, James Smith, Mikko Lipasti
 Lecture 2: Caches http://wwwcssfuca/~ashriram/cs885/ belongs to Milo Martin, Amir Roth, David Wood, James Smith, Mikko Lipasti 1 Why focus on caches and memory? CPU can only compute as fast as memory Add
Lecture 2: Caches http://wwwcssfuca/~ashriram/cs885/ belongs to Milo Martin, Amir Roth, David Wood, James Smith, Mikko Lipasti 1 Why focus on caches and memory? CPU can only compute as fast as memory Add
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/19/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #16 1 Parallel
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/19/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #16 1 Parallel
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
 EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
Random-Access Memory (RAM) Systemprogrammering 2007 Föreläsning 4 Virtual Memory. Locality. The CPU-Memory Gap. Topics
 Systemprogrammering 27 Föreläsning 4 Topics The memory hierarchy Motivations for VM Address translation Accelerating translation with TLBs Random-Access (RAM) Key features RAM is packaged as a chip. Basic
Systemprogrammering 27 Föreläsning 4 Topics The memory hierarchy Motivations for VM Address translation Accelerating translation with TLBs Random-Access (RAM) Key features RAM is packaged as a chip. Basic
CPS101 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 13: The Memory System. Outline of Today s Lecture. The Big Picture: Where are We Now?
 cps 14 memory.1 RW Fall 2 CPS11 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 13 The System Robert Wagner Outline of Today s Lecture System the BIG Picture? Technology Technology DRAM A Real Life Example
cps 14 memory.1 RW Fall 2 CPS11 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 13 The System Robert Wagner Outline of Today s Lecture System the BIG Picture? Technology Technology DRAM A Real Life Example
Random-Access Memory (RAM) Systemprogrammering 2009 Föreläsning 4 Virtual Memory. Locality. The CPU-Memory Gap. Topics! The memory hierarchy
 Systemprogrammering 29 Föreläsning 4 Topics! The memory hierarchy! Motivations for VM! Address translation! Accelerating translation with TLBs Random-Access (RAM) Key features! RAM is packaged as a chip.!
Systemprogrammering 29 Föreläsning 4 Topics! The memory hierarchy! Motivations for VM! Address translation! Accelerating translation with TLBs Random-Access (RAM) Key features! RAM is packaged as a chip.!
Handout 4 Memory Hierarchy
 Handout 4 Memory Hierarchy Outline Memory hierarchy Locality Cache design Virtual address spaces Page table layout TLB design options (MMU Sub-system) Conclusion 2012/11/7 2 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced
Handout 4 Memory Hierarchy Outline Memory hierarchy Locality Cache design Virtual address spaces Page table layout TLB design options (MMU Sub-system) Conclusion 2012/11/7 2 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced
Portland State University ECE 587/687. Caches and Memory-Level Parallelism
 Portland State University ECE 587/687 Caches and Memory-Level Parallelism Revisiting Processor Performance Program Execution Time = (CPU clock cycles + Memory stall cycles) x clock cycle time For each
Portland State University ECE 587/687 Caches and Memory-Level Parallelism Revisiting Processor Performance Program Execution Time = (CPU clock cycles + Memory stall cycles) x clock cycle time For each
Course Administration
 Spring 207 EE 363: Computer Organization Chapter 5: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy - Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 4570
Spring 207 EE 363: Computer Organization Chapter 5: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy - Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 4570
The levels of a memory hierarchy. Main. Memory. 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms
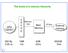 The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
