Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems
|
|
|
- Oswin Roberts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems Part 4. IFD Design Considerations and Reference Design Information Bull CP8, a Bull Company Gemplus SA Hewlett-Packard Company IBM Corporation Microsoft Corporation Schlumberger SA Siemens Nixdorf Informationssysteme AG Sun MicroSystems Inc. Toshiba Corporation VeriFone Inc. Version 1.0 December 1997
2 Copyright 1996, Bull CP8, Gemplus, Hewlett-Packard, IBM, Microsoft, Schlumberger, Siemens Nixdorf, Sun MicroSystems, Toshiba and VeriFone All rights reserved. INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY DISCLAIMER THIS SPECIFICATION IS PROVIDED AS IS WITH NO WARRANTIES WHATSOEVER INCLUDING ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR ANY WARRANTY OTHERWISE ARISING OUT OF ANY PROPOSAL, SPECIFICATION, OR SAMPLE. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED OR INTENDED HEREBY. BULL CP8, GEMPLUS, HEWLETT-PACKARD, IBM, MICROSOFT, SCHLUMBERGER, SIEMENS NIXDORF, SUN MICROSYSTEMS, TOSHIBA AND VERIFONE DISCLAIM ALL LIABILITY, INCLUDING LIABILITY FOR INFRINGEMENT OF PROPRIETARY RIGHTS, RELATING TO IMPLEMENTATION OF INFORMATION IN THIS SPECIFICATION. BULL CP8, GEMPLUS, HEWLETT-PACKARD, IBM, MICROSOFT, SCHLUMBERGER, SIEMENS NIXDORF, SUN MICROSYSTEMS, TOSHIBA AND VERIFONE DO NOT WARRANT OR REPRESENT THAT SUCH IMPLEMENTATION(S) WILL NOT INFRINGE SUCH RIGHTS. Windows and Windows NT are trademarks and Microsoft and Win32 are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. PS/2 is a registered trademark of IBM Corporation. JAVA is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. All other product names are trademarks, registered trademarks, or servicemarks of their respective owners.
3 Contents 1. SCOPE General Purpose of this Document Scope of Information Found in this Document 3 2. PS/2 KEYBOARD INTEGRATED IFD Rationale Design Assumptions PS/2 Keyboard Communication Interface Keyboard Electronics Incremental IFD Requirements Card Socket ICC Interface Power Keyboard/IFD-to-PC Interface IFD Command Set Summary PC to Keyboard Extended Commands Keyboard-to-PC Extended Commands IFD Status Register IFD Error Register Security Assurance Feature Register Requirements for Multiplexed Operation Security Assurance Features USB ICC IFDS Rationale Device Configuration USB IFD Functionality 24 MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page i
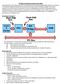
4 1. Scope 1.1 General Purpose of this Document This document discusses design information for IFD devices compliant with the Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems. An ICC Reader Device (IFD), as depicted in Figure 1.1, is a hardware device that : Provides an interface with the ICC, as described in Part 2 of this specification. Communicates with the PC-Hosted IFD Handler software (described in Part 3 of this specification), through a given I/O channel. The purpose of this document is to present design information on several types of IFDs, and especially design information related to the I/O channel used by those IFDs to communicate with the PC. Smartcard Aware Application Smartcard Service Provider Service Provider Manager Reader Handler Interface : Scope of Part 3 Reader Handler Reader Handler Reader Handler I/O Device Driver I/O Device Driver I/O Device Driver I/O Channel Reader Device PS/2 RS 232 USB Reader Device Reader Device Scope of this Part 4 Interface between Reader and ICC : Scope of Part 2 ICC ICC ICC Figure 0-1. IFD Subsytem components and interfaces with other components MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 2
5 Four types of IFDs will be mentionned in this document : Integrated PS/2 keyboard IFDs, which the authors of these specifications strongly believe will be widely adopted as PC-connected IFDs USB IFDs RS-232-connected IFDs, which are today the most common type of IFDs connected to desktop PC s PC Card based IFDs, targeted to the laptop and notebooks environment 1.2 Scope of Information Found in this Document As depicted in Figure 1.2, a device (and its counterpart on the PC side) can be layered into three levels. Examples : - Operating system or application level SW Client Software Device Commands & Responses Set Device Function Function Layer Examples : - KBD device driver - USB Host System SW - Com Port driver I/O Device Driver Data Packets I/O Channel Control Control Layer Examples : controller - USB Host controller - RS 232 I/O Channel Controller Bits I/O Channel Controller Physical Layer Figure 0-2. Device layers Among the different IFDs available on the market (that are either serial or PC Card IFD s) as of today, there does not exist a standard set of commands for IFDs, that is, there is no standardization at the Function layer. No reference design will be presented neither for serial nor PC Card readers; vendors providing those types of readers should provide interoperability at the IFD handler level (this topic is discussed in Part 3 of these specifications). The situation is different for the PS/2 keyboard: information related to the three levels is presented, especially a complete command set that can provide a standard at the Function layer, for PS/2 keyboard based IFDs. Finally, for USB IFDs, the rationale for building USB IFDs and the basic design assumptions are exposed. All requirements at the Control and Physical layers can be found in the USB specifications. MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 3
6 2. PS/2 Keyboard Integrated IFD This section provides design information for vendors wishing to build a compliant IFD integrated with an industry-standard PS/2 PC keyboard. It is believed this design will become the preferred approach to deploying IFDs for desktop PCs. The PS/2-compatible keyboard is the most widely deployed keyboard on PC/workstation-class machines and is supported by multiple Operating Systems. In addition, a PS/2-based design limits the amount of desktop space required to deploy such IFDs and places them in a position that is readily visible and accessible for the user. This information is included herein to encourage multiple vendors to produce compliant products that will work with common device drivers. The design information provided addresses only the components and I/O interfaces required to build a PS/2 keyboard integrated IFD. That is, it covers design from the keyboard connector on a PC to the ICC socket on the keyboard, inclusive. 2.1 Rationale An obvious place to put an IFD is in the PC keyboard. It is a convenient location, being situated for easy access by the PC user, and acting as a primary interface to the PC. In particular, it tends to be directly in front of the user, making ICC insertion/removal simple and keeping the ICC in view of the user. In addition, it is a large enough device to allow incorporation of an IFD without major redesign. Furthermore, by using the keyboard microprocessor to control the IFD, the incremental cost can be very low. Three different keyboard interface specifications exist for PCs compatible with IBM hardware specifications. The older PC/XT keyboard is obsolete, unidirectional, and will not be discussed here. The PS/2 keyboard is the current standard, and is bidirectional. It is likely however that Universal Serial Bus (USB) based keyboards will be dominant, in the future. 2.2 Design Assumptions The design presented herein is appropriate for IFDs that take maximum advantage of existing PS/2 keyboard components to minimize device cost. In particular, it is assumed that the design will take advantage of the existing keyboard microprocessor, clock circuits, power, and so on. As such, it is appropriate to limit the sophistication and flexibility of the IFD. The following table summarizes expected functionality and how this is implemented between the IFD and IFD Handler. The Keyboard device driver is assumed to act as a part of the transmission path, but to provide no intelligence related to the IFD. MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 4
7 Table 2-1. Functionality Assignment for PS/2-Integrated IFD ICC insertion detection ICC contact management ICC initialization Protocol support I/O line management Security Assurance and Authentication Devices Detect ICC insertion/removal and generate an event. Automatically activate ICC contacts on card insertion; de-activate upon removal. May optionally support ability to deactivate ICC contacts under PC control. Must perform cold reset following ICC contact activation, read ATR sequence if present, and send ATR to the PC. If ATR response time is exceeded, shall mark card type as unknown. Implements physical layer, including T=0 mandatory handling of bit-parity error processing. IFD is expected to implement only default CLK frequency and timing parameters. Following reset and ATR sequence, assumes transmission control is determined by the IFD Handler. Will transmit to the ICC when a block of data is received from the IFD Handler. It then returns bytes from the ICC to the Handler as received until the next Handler data block is received. Implementation optional. Function IFD IFD Handler IFD activation Upon initialization request from IFD Handler. Must request device activation/determine device presence, following poweron sequence. Field event and pass to active Service Provider, if any. No direct requirements, unless IFD implements deactivation of ICC contacts while card inserted. May request warm reset of ICC. Should process ATR, validate and determine whether T=0 or T=1 protocol is to be used. Implements T=0 and T=1 data link layer processing and associated error handling. Must send ICC data to the device only when it has the right to transmit. At other times, it should wait for ICC response. Implementation optional. MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 5
8 2.3 PS/2 Keyboard Communication Interface The PS/2 keyboard communicates with a PC over a 5 wire I/O port. The interface supports: Clock Data Spare Gnd +5V The channel is bidirectional, half duplex. Arbitration is handled by holding the clock and data lines in various states. There are 11 clocks per character : start bit (low), eight data bits, parity bit, stop bit (high) with a nominal data rate of 10,000 cps. MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 6
9 The following commands are presently defined for PC communication with the PS/2 keyboard. Table 2-2. PC-to-Keyboard Command Set Command name Command code Description RESET FF Keyboard reboots itself. RESEND FE Keyboard resends last byte. SCAN SET 3 F7-FD Reserved for SCAN SET 3. SET DEFAULT F6 Keyboard resets to power-on state. DEFAULT DISABLE F5 Keyboard resets to power-on state, no key scanning. ENABLE F4 Keyboard resumes key scanning. SET TYPEMATIC RATE F3 Keyboard sends ACK ACK, and sets rate. ID BYTE REQUEST F2 Keyboard sends ACK, plus ID (xx,yy) INVALID F1 Keyboard responds with RESEND (fe). SET SCAN SET F0 Keyboard responds with ACK. INVALID EF Keyboard responds with RESEND (fe). ECHO EE Keyboard sends ECHO back (ee). INDICATOR CONTROL ED Keyboard sends ACK ACK, sets LEDs. The following commands may be sent by a PS/2 keyboard to the PC. Table 2-3. Keyboard-to-PC Command Set Command name Command code Description RESEND FE PC resends last byte. ACK FA Acks all except ECHO and RESEND. OVERRUN FF for ScanSet 1 Marks fifo as full. 00 for ScanSet 2 and 3 DIAGNOSTIC FC Error during bat, or other failure. FAILURE BREAK CODE PREFIX F0 Prefix for key release code. DIAG. COMPLETION AA Diags completed successfully. ECHO RESPONSE EE Sent in response to ECHO command. Note that the PS/2 data exchange protocol is an asymmetrical one. It requires that every byte sent by the PC to the keyboard be acknowledged by the keyboard, by sending an ACK, whereas data sent from the keyboard to the PC is not explicitly acknowledged. 2.4 Keyboard Electronics A typical keyboard has very simple electronics, a single voltage power line, buffers for the signal and clock lines to the PC, drivers for the LED s, and a microprocessor. The MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 7
10 microprocessor handles the communication protocol, scans the key switches, and controls the LEDs. 2.5 Incremental IFD Requirements The addition of an ICC IFD compliant with this specification will require the following components for a minimal implementation: ICC socket Interface lines between the ICC socket and the keyboard microprocessor/supporting circuitry: RST CLK I/O Card detection ICC power VCC GND Optional I/O line(s) for ICC status LED (s), alphanumeric displays, and so on Buffers for signals ROM code to implement the required IFD logic Card Socket ICC sockets are available in a wide range of form factors from simple manual insertion devices to sophisticated motor driven devices (socket pulls it in, software control ejects it). Given that compliant ICC IFDs are likely to be end-user devices operated in an office environment, it is believed that the simplicity and low cost associated with a manual socket will be preferred. This is, however, a vendor decision. In any event, it is strongly recommended that the vendor implement a Landing Card or Landing Contact socket, as opposed to a wiping contact socket, for long life and to minimize ICC damage. A microswitch is recommended over a blade switch for card present detection ICC Interface The keyboard microprocessor will require the following I/O lines, in addition to the ones already required for normal keyboard operations (Host I/O, key scanning, LED s, and others): ICC Reset (RST). ICC Clock (CLK). ICC I/O. ICC insertion switch. MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 8
11 Card Status LEDs (optional). These would logically be used to indicate status such as proper card insertion; contact activation status, and requests for user authentication input (if such devices are supported). PS/2 keyboard IFDs are expected to use the existing keyboard controller clock to generate the CLK signal to the ICC. As such, it is expected they will support only a default CLK frequency (in the range 1 5 MHz). It is also expected they will support only the default clock conversion factor (F) of 372 and default bit rate conversion factor (D) of 1, though a vendor may support alternate protocol parameters. Note that if an IFD does implement protocol and/or parameter selection, it must also implement the PTS protocol Power Most existing ICCs are +5.0-volt devices that draw less than 50 ma current (10 ma typical). This is well within the source capabilities of the +5V keyboard power supply provided by existing PCs. An external power supply should not be required. It is expected that lower-power ICC devices ( 3.3 V at < 10 ma) will be common. At present, there is no standard for determining the proper voltage for operation of ISO/IEC 7816 ICCs. ISO/IEC is currently being revised to address this issue. It has been proposed that two classes of cards be defined: (5 V - Class A and 3 V - Class B) IFDs will be designated as Class A, Class B, or Class AB. When the standard for voltage determination is established, support for < 5V ICC operation will be a required addition to this specification. 2.6 Keyboard/IFD-to-PC Interface When a PS/2 Keyboard with integrated IFD first powers up, it should appear to the PC as a normal PS/2 Keyboard. It is the responsibility of PC device drivers to initialize the IFD section of the device. Until this initialization occurs, insertion of an ICC into the IFD will not result in any signals/data being sent to the PC. The requirement on the IFD for managing the interface to the ICC in this situation. is that the vendor must leave the ICC contacts in the inactive state. Once the device driver has initialized the IFD, it must follow the activation sequence of the ICC in accordance with the operational requirements defined in this specification IFD Command Set Summary To support communication between the PC and the IFD, an extended command set is defined. These commands are exchanged between the PC and PS/2 keyboard controller using the existing command interface. The commands, as defined below, have some built-in redundancy to provide interface flexibility. MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 9
12 2.6.2 PC to Keyboard Extended Commands Table 2-4. Extended (IFD) PC to Keyboard Command Set Command name Command code Description PC_to_RDR_GetRdrTy 0x60 Gets IFD type. pe PC_to_RDR_SetMode 0x61 Sets mode. PC_to_RDR_CardPowe 0x62 Turns on power to the card socket. ron PC_to_RDR_CardPowe 0x63 Turns off power to the card socket. roff PC_to_RDR_Reset 0x64 Sends reset pulse to the smart card. PC_to_RDR_GetRdrSta 0x65 Gets IFD status. tus PC_to_RDR_SendRdrB 0x66 Sends one byte to IFD. yte PC_to_RDR_SendRdrBl 0x67 Sends data block to IFD. ock PC_to_RDR_ResendBlo 0x68 Resends last data block. ck PC_to_RDR_GetRdrCa 0x69 Gets IFD capabilities. ps PC_to_RDR_DeActivat 0x6A Deactivates IFD. erdr PC_to_RDR_Escape 0x6B Activates IFD-dependent feature(s). PC_to_RDR_RFU 0x6C - 0x6F Reserved for future use. MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 10
13 Table 2-5. Implementation Notes for Extended PC-to-Keyboard Commands Command name PC_to_RDR_GetRdrTy pe PC_to_RDR_SetMode PC_to_RDR_CardPowe ron Byte sequence Expected response (* = see Note 2.6.1) Notes 0x60 RDR_to_PC_Type The keyboard will activate the IFD following powerup only upon receipt of this command. This should be the first IFD command sent to the keyboard. 0x * Followed by five bytes rr, B61, rr, ss, tt, uu, vv. Before this ss, tt, uu, command is sent to the vv IFD, any command can be (cf. Table sent to the IFD except: 2-6 and PC_to_RDR_SendRdrB 2- yte 7)7) PC_to_RDR_SendRdrB 0x62 * followed by a RDR_to_PC_ DataBlock containing the ATR PC_to_RDR_CardPowe roff PC_to_RDR_Reset 0x64 * followed by a RDR_to_PC_ DataBlock containing the ATR PC_to_RDR_GetRdrSta tus PC_to_RDR_SendRdrB yte (See Note 2.6.2) PC_to_RDR_SendRdrB lock lock, Power saving mode, and others. 0x63 * Power saving mode, and others. Forces an immediate warm reset of the ICC if inserted. If no ICC is present, this is a no-op. 0x65 RDR_to_PC_Status IFD will send back 4-byte status. 0x66, rr * rr = data byte. The IFD shall immediately transmit the data byte to the ICC, if present. 0x B67, rr, ss, DataBloc k * followed by a RDR_to_PC_ DataBlock containing the answer from the ICC rr, ss = 16-bit block size. The block size may be optimized by the IFD vendor to minimize potential for blocking for keyboard input, but should never exceed the maximum T=1 block size of 260 MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 11
14 PC_to_RDR_ResendBlo ck PC_to_RDR_GetRdrCa ps PC_to_RDR_DeActivat erdr 0x68 RDR_to_PC_ DataBlock RDR_to_PC_Caps bytes. This is followed immediately by the specified number of data bytes, which should be immediately transmitted to the ICC, if present. IFD will resend last data block. Get IFD Capabilities as a 0x B69 TLV. 0x6A, * Resets the IFD section of a keyboard back to its power-up state. MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 12
15 PC_to_RDR_Escape 0x B6B, rr, ss, DataBloc k (vendordefined parameter s in DataBloc k) * followed by a RDR_to_PC_Escape rr, ss = 16-bit block size. The escape function allows the IFD manufacturer to define and access extended features. Information sent via this command is processed by the IFD control logic. This may be used, for example, to request that biometric input data be returned from IFDs so equipped. Table 2-6. PC_to_RDR_SetMode Parameters Paramet er ATR parameter( s) encoded Possible values rr T, C, CKS 00, 02, 10, 11, 12, rr T, C, CKS 00, 02, 10, 11, 12, 13 Description Protocol Type (b4=0 for T=0, b4=1 for T=1) Convention used (b1=0 for direct, b1=1 for inverse) Checksum type (b0=0 for LRC, b0=1 for CRC) Special case (See note 2.6.3) Waiting Time extension request (the value of the requested extension is specified by vv) Protocol Type (b4=0 for T=0, b4=1 for T=1) Convention used (b1=0 for direct, b1=1 for inverse) Checksum type (b0=0 for LRC, b0=1 for CRC) ss N 00 to FE Extra Guardtime (0 to 254 etu between two characters) tt WI 00 to FF Work Waiting Time (character time-out for T=0) uu BWI, CWI 00 to FF Block and Char. Waiting Time (block and character time-out for T=1) vv WTX 00 to FF Block Waiting Time Extension. 00 = no WTX is requested by the ICC. vv is the multiplier of the BWT value MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 13
16 In the event all the parameters are not transmitted in the ATR, the IFD Handler software should use the following default values. Table 2-7. Default values for the PC_to_RDR_SetMode Parameters Mode rr ss tt uu vv T= A T= D 00 MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 14
17 rr BYTE Bits Checksum type for T=1 Convention for T=1 BWT extension for T=1 RFU Protocol type RFU Figure 2-1. rr Byte encoding Table 2-8. rr Byte encoding Protocol Type T 0 if T=0 1 if T=1 Block Working Time 1 if WTX is requested Extension WTX Convention C 0 for direct convention 1 for inverse convention Checksum CK 0 for LRC 1 for CRC Note 2.6.1: The PS/2 protocol and, more precisely, its implementation by the various micro-controllers found on IBM PC compatibles types of PC s, require each byte sent by the PC be acknowledged by the keyboard. This holds true also for data sent to the ICC. In other words, every single byte of a given command must be acknowledged by the keyboard with a RDR_to_PC_Ack. This is clearly a trade-off that favors broad compatibility with the installed base versus data throughput. However, this should still be sufficient to accommodate the needs of today s smart cards. Note 2.6.2: A compliant IFD may not implement the PC_to_RDR_SendRdrByte command. If the keyboard consistently Nacks this command, the IFD Handler software layer should use the PC_to_Rdr_SendBlock commands instead. Note : The Waiting Time Extension, when requested, applies only to the outstanding transaction. It is automatically reset to 0 once the ICC has sent its response. MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 15
18 2.6.3 Keyboard-to-PC Extended Commands Table 2-9 Extended (IFD) Keyboard-to-PC Command Set Command name Command code Description RDR_to_PC_Type 0x60 Sends type info to PC. RDR_to_PC_Status 0x61 Sends status to PC. RDR_to_PC_Ack 0x62 ACKS last IFD command from PC. RDR_to_PC_DataByte 0x63 One byte from IFD to PC. RDR_to_PC_DataBlock 0x64 Sends a Data Block to PC. RDR_to_PC_CardIn 0x65 Card inserted. RDR_to_PC_CardOut 0x66 Card removed. RDR_to_PC_Nack 0x67 Nacks last command (see Note 2.6.4). RDR_to_PC_Caps 0x68 Sends TLV structure of capabilities. RDR_to_PC_Escape 0x69 IFD-dependent feature. RDR_to_PC_RFU 0x6A - 0x6F Reserved for future use. Table 2-10 Implementation Notes for Extended Keyboard to-pc Commands Command name Byte sequence Notes RDR_to_PC_Type 0x60, Type Sequence This returns a 16-byte vendordefined IFD ID. It is recommended this be generated in a manner that ensures statistical uniqueness. It may be of the type PNPxxxx, as used by plug and play keyboards, or may be a vendor-specific ID. RDR_to_PC_Status 0x61,s1, s2, s3, s4 s1 = IFD status register as defined below. s2 = Error. s3 = Security Assurance feature register as defined below. s4 = RFU. RDR_to_PC_Ack 0x62 n/a RDR_to_PC_DataByte 0x63, rr RDR_to_PC_DataBlo ck One byte of data from the ICC. 0x64, rr, ss, DataBlock Block of data. Rr, ss = 16-bit block size. The block size may be optimized by the IFD vendor to minimize potential for blocking for keyboard input, but should never exceed the maximum T=0 command size of 260 bytes (5 bytes command; 255 bytes data). This is followed immediately by the specified number of data bytes that should be MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 16
19 immediately transmitted to the PC. RDR_to_PC_CardIn 0x65 Indicates an ICC insertion event has occurred. RDR_to_PC_CardOut 0x66 Indicates an ICC removal event has occurred. RDR_to_PC_Nack 0x67 Nacks last command (see Note 2.6.4). RDR_to_PC_Caps 0x68, rr, ss, DataBlock rrss = 16 bit block size. The DataBlock is a TLV structure that returns part of the information described in section of Part 3 of this specification. RDR_to_PC_Escape 0x69, rr, ss, DataBlock (vendor-defined parameters in DataBlock) rr, ss = 16-bit block size. The escape function allows the IFD manufacturer to define and access extended features. Information sent via this command is processed by the PC. This may be used for any feature that a vendor wishes to define. Note : After a command has been Nacked, the driver should query the Error status register and/or the IFD Status Register to find out the exact nature of the error (Card deactivated, Card Out, Wrong Command, Wrong Parameter Length, and so on) IFD Status Register BYTE Bits ICC type ICC present Active RFU Figure 2-2. IFD Status Register In the status register, the status bits are encoded as follows. Table IFD Status Register Encoding ICC type Three bits encoded as a value in the range 0 7 MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 17
20 0 = unknown 1 = 7816 Asynchronous 2 = 7816 Synchronous 3 7 are RFU The ICC type should be determined based on the presence or absence of an ATR sequence. ICC present 1 if an ICC is inserted in the IFD socket Active 1 if the ICC contacts are active IFD Error Register BYTE Bits Figure 2-3. IFD Error Register Defined error bits tbd error bits In the error register, the error bits are encoded as follows. Table IFD Error Register Encoding Bit 0 Set to 0: Communication parameters not set Bit 1 Set to 1: IFD turned OFF Bit 2 Set to 1: Invalid command received Bit 3 Set to 1: Length of block parameter > MAX Bit 4 Set to 1: Character parity error The value indicating no error for this register will be 0x01 (b0 = 1 indicating that the communication parameters have been set, and all other bits being set to 0). MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 18
21 2.6.6 Security Assurance Feature Register BYTE Bits ICC Input Device Authentication Device Figure 2-4. Security Assurance Feature Register MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 19
22 Table Security Assurance Feature Register Encoding ICC Input Device Four bits encoded as a value in the range 0 15 indicating which device, if any, is currently active and exchanging data with the ICC: 0 = no device active 1 = RFU 2 = PIN (numeric) keypad 3 = Keyboard 4 = Fingerprint scanner 5 = Retinal scanner 6 = Image scanner 7 = Voice print scanner 8 = Display device 9 11 are RFU may be used for vendor defined devices Authentication Device Four bits encoded as a value in the range 0 15 indicating which device, if any, is currently active collecting user authentication data for transmission to the PC: 0 = No device active 1 = RFU 2 = Encrypting PIN (numeric) keypad 3 = Encrypting keyboard 4 = Fingerprint scanner 5 = Retinal scanner 6 = Image scanner 7 = Voice scanner 8 = Display device 9 11 are RFU may be used for vendor defined devices Requirements for Multiplexed Operation Using the command protocols defined in the preceding subsections, both the PC drivers and keyboard controller can maintain logical separation between keyboard I/O and ICC I/O operations. Hence it is a fairly simple matter to support multiplexing of ICC and command data over the keyboard I/O channel. A more important issue is the potential impact of IFD operation on the processing of keyboard events. The keyboard is a primary input device for the system, hence operation of the IFD should not interfere with user input for extended periods of time. To insure logical separation of the event streams, it is necessary to treat IFD commands and standard keyboard commands as atomic transfers. This introduces the potential for MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 20
23 blocking normal keyboard operation for lengthy periods of time. Based on ISO/IEC 7816 protocols, the maximum data size of a single data block will not exceed 260 bytes (T=0, 5 command bytes followed by 255 data bytes). Hence, given standard keyboard I/O data rates, the maximum latency induced could be as high as 600 ms (time required for the PC to send a 260-byte block to the keyboard). Designers should consider this factor to insure that they have adequate keystroke buffering to avoid loss of user input during ICC operation. 2.7 Security Assurance Features A vendor may choose to implement security assurance features, such as PIN entry or biometric capabilities. Sections and define the associated status registers and the use of the escape commands to access these functions. In the opinion of the authors, these features are deemed to have significant value to end users, in terms of protecting their interests, which will generally exceed their implementation cost given the existing keyboard functionality. It should be noted that although this document has place holders for using these capabilities, much work remains to be done before these capabilities can be implemented in anything other than a vendor specific way. 3. USB ICC IFDs This section provides design information for vendors wishing to build a compliant USB ICC IFD. Both dependent and independent IFDs will be discussed. An independent IFD is a stand-alone device. A dependent IFD shares a USB interface processor with another device, such as a keyboard. 3.1 Rationale Today, the addition of external peripherals is constrained by port availability. The Universal Serial Bus is the answer to connectivity for PC s. It is a bidirectional, isochronous, and low-cost bus that enables hot plugging and supports data rates up to 12 Mbps. This is the reason why USB peripherals should become common on PCs. Because PC hardware platforms are starting to support USB devices, a USB IFD could be the lowcost solution for future PC s. 3.2 Device Configuration As described in figure 3.1, a USB device is made of three layers: the USB Interface layer, the USB Logical Device layer and the Function layer. The Interface layer provides the physical link to the USB and communicated with the USB Host controller. The Logical Device layer communicates with the PC driver. The Function layer provides a specific application like keyboard, IFD, phone, speaker, mouse, and so on. MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 21
24 Function USB Logical Device USB Bus Interface USB Figure 0-1. USB Device Architecture MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 22
25 Such an architecture enables several configurations for an IFD (see figure 3-2): The IFD can be a separate peripheral device with a cable that plugs into a port on a hub or directly on the Host PC. Such an IFD has its own USB interface processor and is called an independent IFD (device 1 on Figure 3-2) An independent IFD can implement an embedded HUB with a single USB cable. Such a device, known as a compound device, allows connections of other peripherals like phone, speakers, mouse or microphone. See device 2 on Figure 3-2. The IFD can also be part of a physical package that implements multiple functions with a single USB cable. Such an IFD is a called a dependent IFD. The different functions would share one USB interface processor. These functions, being keyboard and IFD (or phone and IFD, etc.), are permanently attached to an internal HUB connected to the USB. In USB terms, it is a compound device. See device 3 in Figure 3-2. Host PC Root HUB Mouse HUB HUB HUB ICC reader ICC reader ICC reader Keyboard Mouse Phone Speakers Figure 0-2. Different USB IFD configurations The authors of this specification believe the last configuration will be the most appropriate one. Indeed, it presents most of the advantages related to the PS/2 keyboard configuration (ergonomics, cost) and, given the higher speed of USB, it should also allow concurrent transactions from the PC to the keyboard and the IFD. Finally, such a device can also be used as a HUB to easily connect other peripherals. 3.3 MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 23
26 USB IFD Functionality The following table summarizes expected functionality for a USB IFD, which has low cost as a primary goal. Table 3-1. Functionality Assignment for USB IFDs Function IFD activation ICC insertion detection ICC contact management ICC initialization Description Automatic activation while IFD is attached (hotplugging USB functionality). Detection of ICC insertion/removal and generation of an event to PC. Automatic activation of ICC contacts on card insertion; IFD deactivates upon removal. May optionally support ability to deactivate ICC contacts under PC control. IFD must perform cold reset following ICC contact activation, read ATR sequence if present, and send ATR to the PC. If ATR response time is exceeded, shall mark card type as unknown. Protocol support IFD implements physical layer, including T=0 mandatory handling of bit-parity error processing. It is expected that USB IFDs could handle the whole T=0 and T=1 data link layer, taking full advantage of the USB bandwidth available. I/O line management Following reset and ATR sequence, IFD assumes transmission control is determined by PC. Will transmit to the ICC when a block of data is received by the PC. It then returns bytes from the ICC to the PC as received until the PC data block is received. MicroSystems, Toshiba, Verifone All Rights Reserved. Page 24
Presentation of the Interoperability specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems, Revision 2.0
 PC/SC Workgroup White Paper Presentation of the Interoperability specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems, Revision 2.0 Abstract This document presents the upcoming revision 2.0 of the Interoperability
PC/SC Workgroup White Paper Presentation of the Interoperability specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems, Revision 2.0 Abstract This document presents the upcoming revision 2.0 of the Interoperability
More on IO: The Universal Serial Bus (USB)
 ecture 37 Computer Science 61C Spring 2017 April 21st, 2017 More on IO: The Universal Serial Bus (USB) 1 Administrivia Project 5 is: USB Programming (read from a mouse) Optional (helps you to catch up
ecture 37 Computer Science 61C Spring 2017 April 21st, 2017 More on IO: The Universal Serial Bus (USB) 1 Administrivia Project 5 is: USB Programming (read from a mouse) Optional (helps you to catch up
Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems
 Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems Part 10 IFDs with Secure PIN Entry Capabilities Supplement - IFDs with Feature Capabilities Gemalto HID Global Identive Oracle America
Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems Part 10 IFDs with Secure PIN Entry Capabilities Supplement - IFDs with Feature Capabilities Gemalto HID Global Identive Oracle America
Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems
 Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems Bull CP8, a Bull Company Gemplus SA Hewlett-Packard Company IBM Corporation Microsoft Corporation Schlumberger SA Siemens Nixdorf Informationssysteme
Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems Bull CP8, a Bull Company Gemplus SA Hewlett-Packard Company IBM Corporation Microsoft Corporation Schlumberger SA Siemens Nixdorf Informationssysteme
PCI-X Addendum to the PCI Compliance Checklist. Revision 1.0a
 PCI-X Addendum to the PCI Compliance Checklist Revision 1.0a August 29, 2000 PCI-X Addendum to the PCI Compliance Checklist REVISION REVISION HISTORY DATE 1.0 Initial Release 3/1/00 1.0a Updates for PCI-X
PCI-X Addendum to the PCI Compliance Checklist Revision 1.0a August 29, 2000 PCI-X Addendum to the PCI Compliance Checklist REVISION REVISION HISTORY DATE 1.0 Initial Release 3/1/00 1.0a Updates for PCI-X
Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems
 Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems Part 3. Requirements for PC-Connected Interface Devices Gemalto HID Global NXP Semiconductors N.V. Oracle America SCM Microsystems
Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems Part 3. Requirements for PC-Connected Interface Devices Gemalto HID Global NXP Semiconductors N.V. Oracle America SCM Microsystems
GCR410 / GCR410-P. Application Note. Version 1.0
 GCR410 / GCR410-P Application Note Version 1.0 October 1999 SPECIFIC WARNING NOTICE All information herein is either public information or is the property of and owned solely by GEMPLUS who shall have
GCR410 / GCR410-P Application Note Version 1.0 October 1999 SPECIFIC WARNING NOTICE All information herein is either public information or is the property of and owned solely by GEMPLUS who shall have
Architecture Specification
 PCI-to-PCI Bridge Architecture Specification, Revision 1.2 June 9, 2003 PCI-to-PCI Bridge Architecture Specification Revision 1.1 December 18, 1998 Revision History REVISION ISSUE DATE COMMENTS 1.0 04/05/94
PCI-to-PCI Bridge Architecture Specification, Revision 1.2 June 9, 2003 PCI-to-PCI Bridge Architecture Specification Revision 1.1 December 18, 1998 Revision History REVISION ISSUE DATE COMMENTS 1.0 04/05/94
ED1021 I/O Expander with UART interface & analog inputs
 Preliminary Highlights 2.7V 5V power supply range. 12 GPIOs. Up to 40mA maximum current in each output except GPIO8 (up to a total device current of 175mA). Most GPIOs can be an input to a 10bit ADC. Simple
Preliminary Highlights 2.7V 5V power supply range. 12 GPIOs. Up to 40mA maximum current in each output except GPIO8 (up to a total device current of 175mA). Most GPIOs can be an input to a 10bit ADC. Simple
Smart cards and smart objects communication protocols: Looking to the future. ABSTRACT KEYWORDS
 Smart cards and smart objects communication protocols: Looking to the future. Denis PRACA Hardware research manager, Gemplus research Lab, France Anne-Marie PRADEN Silicon design program manager, Gemplus
Smart cards and smart objects communication protocols: Looking to the future. Denis PRACA Hardware research manager, Gemplus research Lab, France Anne-Marie PRADEN Silicon design program manager, Gemplus
PCI-X Protocol Addendum to the PCI Local Bus Specification Revision 2.0a
 PCI-X Protocol Addendum to the PCI Local Bus Specification Revision 2.0a July 22, 2003 REVISION REVISION HISTORY DATE 1.0 Initial release. 9/22/99 1.0a Clarifications and typographical corrections. 7/24/00
PCI-X Protocol Addendum to the PCI Local Bus Specification Revision 2.0a July 22, 2003 REVISION REVISION HISTORY DATE 1.0 Initial release. 9/22/99 1.0a Clarifications and typographical corrections. 7/24/00
Bus Example: Pentium II
 Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Conventional PCI, often shortened to PCI, is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer. PCI stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Conventional PCI, often shortened to PCI, is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer. PCI stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect
Microprocessors LCD Parallel Port USB Port
 Microprocessors LCD Parallel Port USB Port H. Abdoli Bu-Ali Sina University 1 New LCDs Interfacing Lower prices Display numbers, characters, graphics Integrated refreshing controller Ease of programming
Microprocessors LCD Parallel Port USB Port H. Abdoli Bu-Ali Sina University 1 New LCDs Interfacing Lower prices Display numbers, characters, graphics Integrated refreshing controller Ease of programming
ED1021 I/O Expander with UART interface & analog inputs
 Preliminary Highlights 4.5V 5.5V power supply range. 12 GPIOs. Up to 40mA maximum current in each output except GPIO8 (up to a total device current of 175mA). Most GPIOs can be an input to a 10bit ADC.
Preliminary Highlights 4.5V 5.5V power supply range. 12 GPIOs. Up to 40mA maximum current in each output except GPIO8 (up to a total device current of 175mA). Most GPIOs can be an input to a 10bit ADC.
SBAT90USB162 Atmel. SBAT90USB162 Development Board User s Manual
 SBAT90USB162 Atmel AT90USB162 Development Board User s manual 1 1. INTRODUCTION Thank you for choosing the SBAT90USB162 Atmel AT90USB162 development board. This board is designed to give a quick and cost-effective
SBAT90USB162 Atmel AT90USB162 Development Board User s manual 1 1. INTRODUCTION Thank you for choosing the SBAT90USB162 Atmel AT90USB162 development board. This board is designed to give a quick and cost-effective
Low-Power-Radio Transceiver IC
 Addressed Mode With Acknowledge Broadcast Mode Automatic Retry Serial Interface Stand Alone Operation Achieves Maximum Range From RF Modules Flow Control Option Two Telemetry I/O Lines (addressed mode
Addressed Mode With Acknowledge Broadcast Mode Automatic Retry Serial Interface Stand Alone Operation Achieves Maximum Range From RF Modules Flow Control Option Two Telemetry I/O Lines (addressed mode
AN1527 APPLICATION NOTE
 AN1527 APPLICATION NOTE DEVELOPING A USB SMARTCARD READER WITH ST7SCR by Microcontroller Division Applications INTRODUCTION This document describes a firmware implementation developed by STMicroelectronics
AN1527 APPLICATION NOTE DEVELOPING A USB SMARTCARD READER WITH ST7SCR by Microcontroller Division Applications INTRODUCTION This document describes a firmware implementation developed by STMicroelectronics
LBAT90USB162 Atmel. LBAT90USB162 Development Board User s Manual
 LBAT90USB162 Atmel AT90USB162 Development Board User s manual 1 1. INTRODUCTION Thank you for choosing the LBAT90USB162 Atmel AT90USB162 development board. This board is designed to give quick and cost-effective
LBAT90USB162 Atmel AT90USB162 Development Board User s manual 1 1. INTRODUCTION Thank you for choosing the LBAT90USB162 Atmel AT90USB162 development board. This board is designed to give quick and cost-effective
PCI-X Addendum to the PCI Compliance Checklist. Revision 1.0b
 PCI-X Addendum to the PCI Compliance Checklist Revision 1.0b April 16, 2003 PCI-X 1.0b Addendum to the PCI Compliance Checklist REVISION REVISION HISTORY DATE 1.0 Initial Release 3/1/00 1.0a Updates for
PCI-X Addendum to the PCI Compliance Checklist Revision 1.0b April 16, 2003 PCI-X 1.0b Addendum to the PCI Compliance Checklist REVISION REVISION HISTORY DATE 1.0 Initial Release 3/1/00 1.0a Updates for
APPLICATION NOTE DEMONSTRATION BOARD CAKE 8020_06-D FOR DUAL SMART CARD INTERFACE TDA8020HL AN00058
 APPLICATION NOTE DEMONSTRATION BOARD CAKE 8020_06-D FOR DUAL SMART CARD INTERFACE TDA8020HL Abstract This report describes the demonstration board CAKE 8020_06-D that has been developed in order to demonstrate
APPLICATION NOTE DEMONSTRATION BOARD CAKE 8020_06-D FOR DUAL SMART CARD INTERFACE TDA8020HL Abstract This report describes the demonstration board CAKE 8020_06-D that has been developed in order to demonstrate
ACR38 CCID Smart Card Reader
 ACR38 CCID Smart Card Reader Reference Manual Subject to change without prior notice Table of Contents 1.0. Introduction... 3 2.0. Features... 4 3.0. Supported Card Types... 5 3.1. Microcontroller-based
ACR38 CCID Smart Card Reader Reference Manual Subject to change without prior notice Table of Contents 1.0. Introduction... 3 2.0. Features... 4 3.0. Supported Card Types... 5 3.1. Microcontroller-based
PCI-X Protocol Addendum to the PCI Local Bus Specification Revision 2.0a
 PCI-X Protocol Addendum to the PCI Local Bus Specification Revision 2.0a July 29, 2002July 22, 2003 REVISION REVISION HISTORY DATE 1.0 Initial release. 9/22/99 1.0a Clarifications and typographical corrections.
PCI-X Protocol Addendum to the PCI Local Bus Specification Revision 2.0a July 29, 2002July 22, 2003 REVISION REVISION HISTORY DATE 1.0 Initial release. 9/22/99 1.0a Clarifications and typographical corrections.
Technical Reference for Micro Controller: N01B-4824-B406 for Ergo Trac Pointing Device: FID /N01B-4828-B100
 Technical Reference for Micro Controller: N01B-4824-B406 for Ergo Trac Pointing Device: FID-828-100/N01B-4828-B100 1. APPLICATION: This technical reference is prepared and applied for the usage of the
Technical Reference for Micro Controller: N01B-4824-B406 for Ergo Trac Pointing Device: FID-828-100/N01B-4828-B100 1. APPLICATION: This technical reference is prepared and applied for the usage of the
USB Feature Specification: Shared Endpoints
 USB Feature Specification: Shared Endpoints SYSTEMSOFT CORPORATION INTEL CORPORATION Revision 1.0 October 27, 1999 USB Feature Specification: Shared Endpoints Revision 1.0 Revision History Revision Issue
USB Feature Specification: Shared Endpoints SYSTEMSOFT CORPORATION INTEL CORPORATION Revision 1.0 October 27, 1999 USB Feature Specification: Shared Endpoints Revision 1.0 Revision History Revision Issue
Essential Components for Today s Industrial Connections
 Essential Components for Today s Industrial Connections 724-746-5500 blackbox.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Understanding How USB Became Dominant... 3 Technical Capacities and Specifications
Essential Components for Today s Industrial Connections 724-746-5500 blackbox.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Understanding How USB Became Dominant... 3 Technical Capacities and Specifications
Smart Card Bridge to Full-Speed USB, SPI, and UART Interfaces
 SEC00/SEC200 Bridge to Full-Speed USB, SPI, and UART Interfaces PRODUCT FEATURES Data Brief General Description The SEC00 and SEC200 provide a single-chip solution for a bridge to USB, SPI, and UART interfaces.
SEC00/SEC200 Bridge to Full-Speed USB, SPI, and UART Interfaces PRODUCT FEATURES Data Brief General Description The SEC00 and SEC200 provide a single-chip solution for a bridge to USB, SPI, and UART interfaces.
AES, DES, and RSA Support (Intended for Domestic Use) SASEBO-W Smart Card OS Specification
 AES, DES, and RSA Support (Intended for Domestic Use) SASEBO-W Smart Card OS Specification Version 0.4-5 April 1, 2011 National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) Table of Contents
AES, DES, and RSA Support (Intended for Domestic Use) SASEBO-W Smart Card OS Specification Version 0.4-5 April 1, 2011 National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) Table of Contents
Bluetooth PC Card Transport Layer
 Bluetooth WHITE PAPER DATE 25 August 99 N.B. DOCUMENT NO. 1.C.123/1.0 RESPONSIBLE Riku Mettala E-MAIL ADDRESS Riku.Mettala@nmp.nokia.com STATUS Bluetooth PC Card Transport Layer Version 1.0 The Bluetooth
Bluetooth WHITE PAPER DATE 25 August 99 N.B. DOCUMENT NO. 1.C.123/1.0 RESPONSIBLE Riku Mettala E-MAIL ADDRESS Riku.Mettala@nmp.nokia.com STATUS Bluetooth PC Card Transport Layer Version 1.0 The Bluetooth
Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems
 Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems Apple Computer, Inc. Axalto Gemplus SA Infineon Technologies AG Ingenico SA Microsoft Corporation Philips Semiconductors Toshiba Corporation
Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems Apple Computer, Inc. Axalto Gemplus SA Infineon Technologies AG Ingenico SA Microsoft Corporation Philips Semiconductors Toshiba Corporation
ELAN DIGITAL SYSTEMS LTD. CF428 COMPACT FLASH CF+ CARD USER S GUIDE
 ELAN DIGITAL SYSTEMS LTD. LITTLE PARK FARM ROAD, SEGENSWORTH WEST, FAREHAM, HANTS. PO15 5SJ. TEL: (44) (0)1489 579799 FAX: (44) (0)1489 577516 e-mail: support@pccard.co.uk website: http://www.pccard.co.uk
ELAN DIGITAL SYSTEMS LTD. LITTLE PARK FARM ROAD, SEGENSWORTH WEST, FAREHAM, HANTS. PO15 5SJ. TEL: (44) (0)1489 579799 FAX: (44) (0)1489 577516 e-mail: support@pccard.co.uk website: http://www.pccard.co.uk
OPB Universal Serial Bus 2.0 Device (v1.00a)
 OPB Universal Serial Bus 2. Device (v1.a) DS591 May 1, 27 Introduction The Xilinx Universal Serial Bus 2. High Speed Device with On-chip Peripheral Bus (OPB) enables USB connectivity to the user s design
OPB Universal Serial Bus 2. Device (v1.a) DS591 May 1, 27 Introduction The Xilinx Universal Serial Bus 2. High Speed Device with On-chip Peripheral Bus (OPB) enables USB connectivity to the user s design
Enterprise and Datacenter. SSD Form Factor. Connector Specification
 Enterprise and Datacenter SSD Form Factor Connector Specification Revision 0.9 Draft August 2, 2017 Enterprise and Datacenter SSD Form Factor Working Group 1 INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY DISCLAIMER THIS DRAFT
Enterprise and Datacenter SSD Form Factor Connector Specification Revision 0.9 Draft August 2, 2017 Enterprise and Datacenter SSD Form Factor Working Group 1 INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY DISCLAIMER THIS DRAFT
CE-ATA Embedded Cable and Connector Specification
 CE-ATA Embedded Cable and Connector Specification Révision 1.0 23-August-2005 Apple Computer Corporation Hitachi Global Storage Technologies Corporation Intel Corporation Marvell Semiconductor Corporation
CE-ATA Embedded Cable and Connector Specification Révision 1.0 23-August-2005 Apple Computer Corporation Hitachi Global Storage Technologies Corporation Intel Corporation Marvell Semiconductor Corporation
Table of Contents. 一 RS232 bus Data level Signal level... 2 二 Command for ISO-7816 Card... 3
 Design Specification For B60 Table of Contents 一 RS232 bus... 1 1.1. Data level... 1 1.2. Signal level... 2 二 Command for ISO-7816 Card... 3 2.1 MSG_PC_to_RDR_IccPowerOn... 4 2.2 2.3 MSG_PC_to_RDR_IccPowerOff...
Design Specification For B60 Table of Contents 一 RS232 bus... 1 1.1. Data level... 1 1.2. Signal level... 2 二 Command for ISO-7816 Card... 3 2.1 MSG_PC_to_RDR_IccPowerOn... 4 2.2 2.3 MSG_PC_to_RDR_IccPowerOff...
HP 48 I/O Technical Interfacing Guide
 HP 48 I/O Technical Interfacing Guide HP 48 I/0 Technical Interfacing Guide CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 3 WIRED SERIAL I/O HARDWARE... 3 CABLE WIRING... 3 SERIAL FORMAT... 5 Example: an 'H' (48 hex)... 5
HP 48 I/O Technical Interfacing Guide HP 48 I/0 Technical Interfacing Guide CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 3 WIRED SERIAL I/O HARDWARE... 3 CABLE WIRING... 3 SERIAL FORMAT... 5 Example: an 'H' (48 hex)... 5
Chapter 11: Input/Output Organisation. Lesson 17: Standard I/O buses USB (Universal Serial Bus) and IEEE1394 FireWire Buses
 Chapter 11: Input/Output Organisation Lesson 17: Standard I/O buses USB (Universal Serial Bus) and IEEE1394 FireWire Buses Objective Familiarize with a standard I/O interface synchronous serial buses USB
Chapter 11: Input/Output Organisation Lesson 17: Standard I/O buses USB (Universal Serial Bus) and IEEE1394 FireWire Buses Objective Familiarize with a standard I/O interface synchronous serial buses USB
A.G.P. Pro Specification
 A.G.P. Pro Specification Revision 1.0 Intel Corporation August 1998 A.G.P. Pro Specification Copyright Intel Corporation 1998 All rights reserved. This specification is provided AS IS with no warranties
A.G.P. Pro Specification Revision 1.0 Intel Corporation August 1998 A.G.P. Pro Specification Copyright Intel Corporation 1998 All rights reserved. This specification is provided AS IS with no warranties
ESP8266 Application Note Firmware Download Protocol
 ESP8266 Application Note Firmware Download Protocol Version 1.0 Copyright 2016 About This Guide This document introduces ESP8266 firmware download protocol with a structure as follows. Chapter Title Subject
ESP8266 Application Note Firmware Download Protocol Version 1.0 Copyright 2016 About This Guide This document introduces ESP8266 firmware download protocol with a structure as follows. Chapter Title Subject
BOOST YOUR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE USING THE ZILOG ESCC CONTROLLER
 BOOST YOUR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE USING THE ZILOG ESCC CONTROLLER AN030001-0509 For greater testability, larger interface flexibility, and increased CPU/ DMA offloading, replace the SCC with the ESCC Controller...
BOOST YOUR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE USING THE ZILOG ESCC CONTROLLER AN030001-0509 For greater testability, larger interface flexibility, and increased CPU/ DMA offloading, replace the SCC with the ESCC Controller...
AN EZ-USB FX3 I 2 C Boot Option. Application Note Abstract. Introduction. FX3 Boot Options
 EZ-USB FX3 I 2 C Boot Option Application Note Abstract AN68914 Author: Shruti Maheshwari Associated Project: No Associated Part Family: EZ-USB FX3 Software Version: None Associated Application Notes: None
EZ-USB FX3 I 2 C Boot Option Application Note Abstract AN68914 Author: Shruti Maheshwari Associated Project: No Associated Part Family: EZ-USB FX3 Software Version: None Associated Application Notes: None
IEEE 1284 Interface Design Solutions
 AN-5010 Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note July 1999 Revised November 2000 IEEE 1284 Interface Design Solutions Applications note supporting the 74ACT1284, 74VHC161284 and 74LVX161284 devices Introduction
AN-5010 Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note July 1999 Revised November 2000 IEEE 1284 Interface Design Solutions Applications note supporting the 74ACT1284, 74VHC161284 and 74LVX161284 devices Introduction
Security Policy for Schlumberger Cyberflex Access 32K Smart Card with ActivCard Applets
 Security Policy for Schlumberger Cyberflex Access 32K Smart Card with ActivCard Applets TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 SCOPE OF DOCUMENT... 1 2 INTRODUCTION... 1 3 SECURITY LEVELS... 1 3.1 CRYPTOGRAPHIC MODULE SPECIFICATION...
Security Policy for Schlumberger Cyberflex Access 32K Smart Card with ActivCard Applets TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 SCOPE OF DOCUMENT... 1 2 INTRODUCTION... 1 3 SECURITY LEVELS... 1 3.1 CRYPTOGRAPHIC MODULE SPECIFICATION...
Hints and tips when using RC1xx0 RF Modules
 AN001 : HI NTSANDTI PS WHENUSI NGRC1 XX0RFMODULES WeMakeEmbeddedWi r el ess Easyt ouse Hints and tips when using RC1xx0 RF Modules By H.Moholdt Keywords Interfacing to RS232/RS485/RS422 level shifters
AN001 : HI NTSANDTI PS WHENUSI NGRC1 XX0RFMODULES WeMakeEmbeddedWi r el ess Easyt ouse Hints and tips when using RC1xx0 RF Modules By H.Moholdt Keywords Interfacing to RS232/RS485/RS422 level shifters
MIDI-Scope. Artistic Licence Engineering Ltd. Software Version V1.3 Manual Revision V1.91
 MIDI-Scope Artistic Licence Engineering Ltd Software Version V1.3 Manual Revision V1.91 Product Registration Form Product: MIDI-Scope Version No. Serial No. Date Purchased: Supplier: Name: Company Name:
MIDI-Scope Artistic Licence Engineering Ltd Software Version V1.3 Manual Revision V1.91 Product Registration Form Product: MIDI-Scope Version No. Serial No. Date Purchased: Supplier: Name: Company Name:
PAK-VIa PS/2 Coprocessor Data Sheet by AWC
 PAK-VIa PS/2 Coprocessor Data Sheet 1999-2003 by AWC AWC 310 Ivy Glen League City, TX 77573 (281) 334-4341 http://www.al-williams.com/awce.htm V1.5 30 Aug 2003 Table of Contents Overview...1 If You Need
PAK-VIa PS/2 Coprocessor Data Sheet 1999-2003 by AWC AWC 310 Ivy Glen League City, TX 77573 (281) 334-4341 http://www.al-williams.com/awce.htm V1.5 30 Aug 2003 Table of Contents Overview...1 If You Need
LAN9513/LAN9513i. USB 2.0 Hub and 10/100 Ethernet Controller PRODUCT FEATURES PRODUCT PREVIEW. Highlights. Target Applications.
 LAN9513/LAN9513i 2.0 Hub and 10/100 Ethernet Controller PRODUCT FEATURES Data Brief Highlights Three downstream ports, one upstream port Three integrated downstream 2.0 PHYs One integrated upstream 2.0
LAN9513/LAN9513i 2.0 Hub and 10/100 Ethernet Controller PRODUCT FEATURES Data Brief Highlights Three downstream ports, one upstream port Three integrated downstream 2.0 PHYs One integrated upstream 2.0
ACR100F SIMFlash (CCID)
 ACR00F SIMFlash (CCID) Reference Manual Subject to change without prior prior notice notice Table of Contents.0. Introduction... 3 2.0. Features... 3.0. System Block Diagram... 5.0. Power Supply... 6..
ACR00F SIMFlash (CCID) Reference Manual Subject to change without prior prior notice notice Table of Contents.0. Introduction... 3 2.0. Features... 3.0. System Block Diagram... 5.0. Power Supply... 6..
EDBG. Description. Programmers and Debuggers USER GUIDE
 Programmers and Debuggers EDBG USER GUIDE Description The Atmel Embedded Debugger (EDBG) is an onboard debugger for integration into development kits with Atmel MCUs. In addition to programming and debugging
Programmers and Debuggers EDBG USER GUIDE Description The Atmel Embedded Debugger (EDBG) is an onboard debugger for integration into development kits with Atmel MCUs. In addition to programming and debugging
DELPHI CORPORATION. LIN to RS-232 Gateway Systems Analysis INterface Tool (SAINT) Users Guide
 DELPHI CORPORATION LIN to RS-232 Gateway Systems Analysis INterface Tool (SAINT) Users Guide Document Number TBD Version D, Draft 1 August 15, 2003 Copyright Delphi Corporation, 2003 Maintained by: Chris
DELPHI CORPORATION LIN to RS-232 Gateway Systems Analysis INterface Tool (SAINT) Users Guide Document Number TBD Version D, Draft 1 August 15, 2003 Copyright Delphi Corporation, 2003 Maintained by: Chris
USB2 Debug Device A Functional Device Specification
 USB2 Debug Device A Functional Device Specification Date: March 25, 2003 Revision: 0.9 The information is this document is under review and is subject to change. USB2 Revision 0.9 3/25/2003 Scope of this
USB2 Debug Device A Functional Device Specification Date: March 25, 2003 Revision: 0.9 The information is this document is under review and is subject to change. USB2 Revision 0.9 3/25/2003 Scope of this
Locus Engineering Inc
 Locus Engineering Inc PS/2 Keyboard to ASCII Converter PS/2 Keyboard PS/2 to ACII Converter Host Microcontroller FEATURES Decodes PS/2 Scanset 2 keystrokes to a single ASCII byte on make Offload process
Locus Engineering Inc PS/2 Keyboard to ASCII Converter PS/2 Keyboard PS/2 to ACII Converter Host Microcontroller FEATURES Decodes PS/2 Scanset 2 keystrokes to a single ASCII byte on make Offload process
V-Series V30x Module Electrical, Physical Layer, and Application Integration. Customer Information Brief Version 1.4
 V-Series V30x Module Electrical, Physical Layer, and Application Integration Customer Information Brief Version 1.4 THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED AS IS WITH NO WARRANTIES WHATSOEVER, INCLUDING ANY WARRANTY
V-Series V30x Module Electrical, Physical Layer, and Application Integration Customer Information Brief Version 1.4 THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED AS IS WITH NO WARRANTIES WHATSOEVER, INCLUDING ANY WARRANTY
S1R72U01 Technical Manual
 S1R72U01 Technical Manual Rev. 1.00 NOTICE No part of this material may be reproduced or duplicated in any form or by any means without the written permission of Seiko Epson. Seiko Epson reserves the right
S1R72U01 Technical Manual Rev. 1.00 NOTICE No part of this material may be reproduced or duplicated in any form or by any means without the written permission of Seiko Epson. Seiko Epson reserves the right
STANDARD I/O INTERFACES
 STANDARD I/O INTERFACES The processor bus is the bus defied by the signals on the processor chip itself. Devices that require a very high-speed connection to the processor, such as the main memory, may
STANDARD I/O INTERFACES The processor bus is the bus defied by the signals on the processor chip itself. Devices that require a very high-speed connection to the processor, such as the main memory, may
Installation Guide of Hi-Speed USB-to-Optically Isolated RS-422/485 Adapter
 Installation Guide of Hi-Speed USB-to-Optically Isolated RS-422/485 Adapter Introduction of ES-U-2101-M The USB-to-Optically Isolated RS-422/485 Adapter is designed to make industrial communication port
Installation Guide of Hi-Speed USB-to-Optically Isolated RS-422/485 Adapter Introduction of ES-U-2101-M The USB-to-Optically Isolated RS-422/485 Adapter is designed to make industrial communication port
MicroToys Guide: PS/2 Mouse N. Pinckney April 2005
 Introduction A computer mouse provides an excellent device to acquire 2D coordinate-based user input, since most users are already familiar with it. Most mice usually come with two or three buttons, though
Introduction A computer mouse provides an excellent device to acquire 2D coordinate-based user input, since most users are already familiar with it. Most mice usually come with two or three buttons, though
DATASHEET 4D SYSTEMS TURNING TECHNOLOGY INTO ART. USB to Serial UART Bridge Converter. Document Date: 5 th September 2012 Document Revision: 1.
 TURNING TECHNOLOGY INTO ART DATASHEET USB to Serial UART Bridge Converter µusb-mb5 Document Date: 5 th September 2012 Document Revision: 1.0 Uncontrolled Copy when printed or downloaded. Please refer to
TURNING TECHNOLOGY INTO ART DATASHEET USB to Serial UART Bridge Converter µusb-mb5 Document Date: 5 th September 2012 Document Revision: 1.0 Uncontrolled Copy when printed or downloaded. Please refer to
Preliminary. PACKAGE - 28-pin MLP (5mm X 5mm) Example Circuit Diagram CP V. 48MHz Oscillator. USB Function Controller 512B EEPROM
 Preliminary Single-Chip USB to UART Bridge SINGLE-CHIP USB to UART DATA TRANSFER - Integrated USB Transceiver; No External Resistors Required - Integrated Clock; No External Crystal Required - Integrated
Preliminary Single-Chip USB to UART Bridge SINGLE-CHIP USB to UART DATA TRANSFER - Integrated USB Transceiver; No External Resistors Required - Integrated Clock; No External Crystal Required - Integrated
SUMIT Industry Standard Module (SUMIT-ISM) SPECIFICATION
 SUMIT Industry Standard Module (SUMIT-ISM) SPECIFICATION Revision 1.0 August 25, 2009 IMPORTANT INFORMATION AND DISCLAIMERS The Small Form Factor Special Interest Group, Inc. (SFF-SIG) does not make any
SUMIT Industry Standard Module (SUMIT-ISM) SPECIFICATION Revision 1.0 August 25, 2009 IMPORTANT INFORMATION AND DISCLAIMERS The Small Form Factor Special Interest Group, Inc. (SFF-SIG) does not make any
Preliminary Product Overview
 Preliminary Product Overview Features 1.0 A per channel / 3.0 A Total Current Maximum Voltage (AC or DC): +150 V Low On-State Resistance < 1.0 Ω 10 GΩ Input to Output Isolation < 10us Switching Time High
Preliminary Product Overview Features 1.0 A per channel / 3.0 A Total Current Maximum Voltage (AC or DC): +150 V Low On-State Resistance < 1.0 Ω 10 GΩ Input to Output Isolation < 10us Switching Time High
Interlaken Look-Aside Protocol Definition
 Interlaken Look-Aside Protocol Definition Contents Terms and Conditions This document has been developed with input from a variety of companies, including members of the Interlaken Alliance, all of which
Interlaken Look-Aside Protocol Definition Contents Terms and Conditions This document has been developed with input from a variety of companies, including members of the Interlaken Alliance, all of which
UniFinger SFM5060-OH
 Ver. 1.0 Revision History Rev No. Issued date Description 1.0 Feb. 8, 2012 Initial Release Important Notice Information in this document is provided in connection with Suprema products. No license, express
Ver. 1.0 Revision History Rev No. Issued date Description 1.0 Feb. 8, 2012 Initial Release Important Notice Information in this document is provided in connection with Suprema products. No license, express
EVB-USB2514Q48 48-Pin QFN Evaluation Board Revision A1
 EVB-USB2514Q48 48-Pin QFN Evaluation Board Revision A1 Copyright 2007 SMSC or its subsidiaries. All rights reserved. The information contained herein is proprietary to SMSC and shall be used solely in
EVB-USB2514Q48 48-Pin QFN Evaluation Board Revision A1 Copyright 2007 SMSC or its subsidiaries. All rights reserved. The information contained herein is proprietary to SMSC and shall be used solely in
USER MANUAL CAMPUS-RS FRACTIONAL INTERFACE CARD
 USER MANUAL FRACTIONAL V.35 CAMPUS-RS FRACTIONAL INTERFACE CARD Copyright July, 2002 2002 ADC DSL Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright 2002 ADC Technologies, Inc. ADC, Campus-384, Campus-768, Campus-E1,
USER MANUAL FRACTIONAL V.35 CAMPUS-RS FRACTIONAL INTERFACE CARD Copyright July, 2002 2002 ADC DSL Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright 2002 ADC Technologies, Inc. ADC, Campus-384, Campus-768, Campus-E1,
Enhanced Serial Peripheral Interface (espi)
 Enhanced Serial Peripheral Interface (espi) Addendum for Server Platforms December 2013 Revision 0.7 329957 0BIntroduction Intel hereby grants you a fully-paid, non-exclusive, non-transferable, worldwide,
Enhanced Serial Peripheral Interface (espi) Addendum for Server Platforms December 2013 Revision 0.7 329957 0BIntroduction Intel hereby grants you a fully-paid, non-exclusive, non-transferable, worldwide,
LAN bit Non-PCI Small Form Factor 10/100 Ethernet Controller with Variable Voltage I/O & HP Auto-MDIX Support PRODUCT FEATURES.
 LAN9220 16-bit Non-PCI Small Form Factor 10/100 Ethernet Controller with Variable Voltage I/O & HP Auto-MDIX Support PRODUCT FEATURES Highlights Efficient architecture with low CPU overhead Easily interfaces
LAN9220 16-bit Non-PCI Small Form Factor 10/100 Ethernet Controller with Variable Voltage I/O & HP Auto-MDIX Support PRODUCT FEATURES Highlights Efficient architecture with low CPU overhead Easily interfaces
USER GUIDE EDBG. Description
 USER GUIDE EDBG Description The Atmel Embedded Debugger (EDBG) is an onboard debugger for integration into development kits with Atmel MCUs. In addition to programming and debugging support through Atmel
USER GUIDE EDBG Description The Atmel Embedded Debugger (EDBG) is an onboard debugger for integration into development kits with Atmel MCUs. In addition to programming and debugging support through Atmel
Application Programming Interface
 Application Programming Interface ACR122 NFC Reader Advanced Card Systems Ltd. Website: www.acs.com.hk Email: info@acs.com.hk Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction...3 1.1 Features...3 1.2 USB Interface...3
Application Programming Interface ACR122 NFC Reader Advanced Card Systems Ltd. Website: www.acs.com.hk Email: info@acs.com.hk Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction...3 1.1 Features...3 1.2 USB Interface...3
THIS SPEC IS OBSOLETE
 THIS SPEC IS OBSOLETE Spec Number: 001-65252 Spec Title: AN1071 Single Versus Multiple Transaction Translator Sunset Owner: RSKV Replaced By: None Single Versus Multiple Transaction Translator Application
THIS SPEC IS OBSOLETE Spec Number: 001-65252 Spec Title: AN1071 Single Versus Multiple Transaction Translator Sunset Owner: RSKV Replaced By: None Single Versus Multiple Transaction Translator Application
PCI Host Controller 14a Hardware Reference Release 1.2 (October 16, 2017)
 PCI Host Controller 14a Hardware Reference 1 PCI Host Controller 14a Hardware Reference Release 1.2 (October 16, 2017) Purpose: Host Controller to support the PCI bus according to the PCI/104 specification.
PCI Host Controller 14a Hardware Reference 1 PCI Host Controller 14a Hardware Reference Release 1.2 (October 16, 2017) Purpose: Host Controller to support the PCI bus according to the PCI/104 specification.
ATC-AD8100K. 8 Channel 100 khz Simultaneous Burst A/D in 16 bits IndustryPack Module REFERENCE MANUAL Version 1.
 ATC-AD8100K 8 Channel 100 khz Simultaneous Burst A/D in 16 bits IndustryPack Module REFERENCE MANUAL 791-16-000-4000 Version 1.6 May 2003 ALPHI TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION 6202 S. Maple Avenue #120 Tempe, AZ
ATC-AD8100K 8 Channel 100 khz Simultaneous Burst A/D in 16 bits IndustryPack Module REFERENCE MANUAL 791-16-000-4000 Version 1.6 May 2003 ALPHI TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION 6202 S. Maple Avenue #120 Tempe, AZ
GT24C02. 2-Wire. 2Kb Serial EEPROM (Smart Card application)
 ADVANCED GT24C02 2-Wire 2Kb Serial EEPROM (Smart Card application) www.giantec-semi.com a0 1/19 Table of Content 1 FEATURES...3 2 DESCRIPTION...4 3 PIN CONFIGURATION...5 4 PIN DESCRIPTIONS...6 5 BLOCK
ADVANCED GT24C02 2-Wire 2Kb Serial EEPROM (Smart Card application) www.giantec-semi.com a0 1/19 Table of Content 1 FEATURES...3 2 DESCRIPTION...4 3 PIN CONFIGURATION...5 4 PIN DESCRIPTIONS...6 5 BLOCK
Introduction & Specifications of Hi-Speed USB to Industrial Dual Ports RS-422/485 Adapter
 Introduction & Specifications of Hi-Speed USB to Industrial Dual Ports RS-422/485 Adapter USB to Dual RS-422/485 Adapter (USB-2COMi-M) USB to Dual Opto-isolated RS-422/485 Adapter (USB-2COMi-SI-M) - with
Introduction & Specifications of Hi-Speed USB to Industrial Dual Ports RS-422/485 Adapter USB to Dual RS-422/485 Adapter (USB-2COMi-M) USB to Dual Opto-isolated RS-422/485 Adapter (USB-2COMi-SI-M) - with
M3H Group(2) Application Note Asynchronous Serial Communication Circuit (UART-C)
 M3H Group(2) Asynchronous Serial Communication Circuit (UART-C) Outlines This application note is a erence material for developing products using the asynchronous serial communication circuit (UART) function
M3H Group(2) Asynchronous Serial Communication Circuit (UART-C) Outlines This application note is a erence material for developing products using the asynchronous serial communication circuit (UART) function
StrongARM** SA-110/21285 Evaluation Board
 StrongARM** SA-110/21285 Evaluation Board Brief Datasheet Product Features Intel offers a StrongARM** SA-110/21285 Evaluation Board (EBSA-285) that provides a flexible hardware environment to help manufacturers
StrongARM** SA-110/21285 Evaluation Board Brief Datasheet Product Features Intel offers a StrongARM** SA-110/21285 Evaluation Board (EBSA-285) that provides a flexible hardware environment to help manufacturers
Using the MPC5777M MCAN Module to Exchange CAN FD Messages
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN5045 Application Note Rev. 0, 11/2014 Using the MPC5777M MCAN Module to Exchange CAN FD Messages by: Graham Rice 1 Introduction A CAN network (Controller Area
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN5045 Application Note Rev. 0, 11/2014 Using the MPC5777M MCAN Module to Exchange CAN FD Messages by: Graham Rice 1 Introduction A CAN network (Controller Area
Extending USB Connections. SMART Board 800 series interactive whiteboards and systems
 Extending USB Connections SMART Board 800 series interactive whiteboards and systems FCC warning This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant
Extending USB Connections SMART Board 800 series interactive whiteboards and systems FCC warning This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant
Course 10: Interfaces Agenda
 Course 10: Interfaces 1 Agenda Introduction V.24 interface (RS232) USB 2 Introduction 3 Definition(s) (from the web) A boundary across which two independent systems meet and act on or communicate with
Course 10: Interfaces 1 Agenda Introduction V.24 interface (RS232) USB 2 Introduction 3 Definition(s) (from the web) A boundary across which two independent systems meet and act on or communicate with
Ethernet1 Xplained Pro
 Ethernet1 Xplained Pro Part Number: ATETHERNET1-XPRO The Atmel Ethernet1 Xplained Pro is an extension board to the Atmel Xplained Pro evaluation platform. The board enables the user to experiment with
Ethernet1 Xplained Pro Part Number: ATETHERNET1-XPRO The Atmel Ethernet1 Xplained Pro is an extension board to the Atmel Xplained Pro evaluation platform. The board enables the user to experiment with
This package contains: 1 UC-232A USB-to-Serial Converter 1 Installation Disk 1 User Manual If anything is damaged or missing, contact your dealer.
 User Manual UC-232A Read this guide thoroughly and follow the installation and operation procedures carefully in order to prevent any damage to the units and/or any devices that connect to them. This package
User Manual UC-232A Read this guide thoroughly and follow the installation and operation procedures carefully in order to prevent any damage to the units and/or any devices that connect to them. This package
MF1ICS General description. Functional specification. 1.1 Key applications. 1.2 Anticollision. Energy. MIFARE card contacts La, Lb.
 Rev. 1.1 29 January 2008 Product data sheet 132211 PUBLIC 1. General description NXP has developed the MIFARE to be used in a contactless smart card according to ISO/IEC 14443 Type A. The MIFARE IC is
Rev. 1.1 29 January 2008 Product data sheet 132211 PUBLIC 1. General description NXP has developed the MIFARE to be used in a contactless smart card according to ISO/IEC 14443 Type A. The MIFARE IC is
or between microcontrollers)
 : Communication Interfaces in Embedded Systems (e.g., to interface with sensors and actuators or between microcontrollers) Spring 2016 : Communication Interfaces in Embedded Systems Spring (e.g., 2016
: Communication Interfaces in Embedded Systems (e.g., to interface with sensors and actuators or between microcontrollers) Spring 2016 : Communication Interfaces in Embedded Systems Spring (e.g., 2016
Developing Plug-and-Play COM Ports using TI Plug-and-Play Controllers
 Developing Plug-and-Play COM Ports using TI Plug-and-Play Controllers Heinz-Peter Beckemeyer July 1997 SLLAE02 IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments (TI) reserves the right to make changes to its products
Developing Plug-and-Play COM Ports using TI Plug-and-Play Controllers Heinz-Peter Beckemeyer July 1997 SLLAE02 IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments (TI) reserves the right to make changes to its products
Operating instructions
 Operating instructions SPM Bi-Directional Communication Protocol Your Uptime Is Our Top Priority Congratulations on your purchase of the SPM Bi-Directional Communications Protocol. It will provide you
Operating instructions SPM Bi-Directional Communication Protocol Your Uptime Is Our Top Priority Congratulations on your purchase of the SPM Bi-Directional Communications Protocol. It will provide you
MOD-RFID125 User Manual. All boards produced by Olimex are ROHS compliant. Rev.A, February 2008 Copyright(c) 2008, OLIMEX Ltd, All rights reserved
 MOD-RFID125 User Manual All boards produced by Olimex are ROHS compliant Rev.A, February 2008 Copyright(c) 2008, OLIMEX Ltd, All rights reserved INTRODUCTION: FEATURES: MOD-RFID125 is an RFID station,
MOD-RFID125 User Manual All boards produced by Olimex are ROHS compliant Rev.A, February 2008 Copyright(c) 2008, OLIMEX Ltd, All rights reserved INTRODUCTION: FEATURES: MOD-RFID125 is an RFID station,
Terminal I/O Profile Client Implementation Guide
 [04.2016] Terminal I/O Profile Client Implementation Guide 30507ST10753A Rev. 6 2017-08-16 Mod. 0809 2016-08 Rev.7 SPECIFICATIONS ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE NOTICE While reasonable efforts have
[04.2016] Terminal I/O Profile Client Implementation Guide 30507ST10753A Rev. 6 2017-08-16 Mod. 0809 2016-08 Rev.7 SPECIFICATIONS ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE NOTICE While reasonable efforts have
MOD-RFID125-BOX User Manual
 MOD-RFID125-BOX User Manual All boards produced by Olimex are ROHS compliant Rev.B, May 2011 Copyright(c) 2011, OLIMEX Ltd, All rights reserved Page 1 INTRODUCTION: FEATURES: MOD-RFID125-BOX is an RFID
MOD-RFID125-BOX User Manual All boards produced by Olimex are ROHS compliant Rev.B, May 2011 Copyright(c) 2011, OLIMEX Ltd, All rights reserved Page 1 INTRODUCTION: FEATURES: MOD-RFID125-BOX is an RFID
Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems
 Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems Part 10 IFDs with Secure PIN Entry Capabilities Gemalto HID Global Identive NXP Semiconductors N.V. Oracle America Revision 2.02.08
Interoperability Specification for ICCs and Personal Computer Systems Part 10 IFDs with Secure PIN Entry Capabilities Gemalto HID Global Identive NXP Semiconductors N.V. Oracle America Revision 2.02.08
ACR122U SAM NFC Reader. Application Programming Interface
 Application Programming Interface ACR122U SAM NFC Reader Table of Contents ACR122T Application Programming 1.0 Introduction 3 1.1 Features 3 1.2 USB Interface 3 2.0 Communication between the Driver, Contactless
Application Programming Interface ACR122U SAM NFC Reader Table of Contents ACR122T Application Programming 1.0 Introduction 3 1.1 Features 3 1.2 USB Interface 3 2.0 Communication between the Driver, Contactless
DATASHEET 4D SYSTEMS. uusb-pa5 uusb-pa5-ii. microusb Programming Adaptor TURNING TECHNOLOGY INTO ART. USB to UART Serial Bridge
 DATASHEET TURNING TECHNOLOGY INTO ART microusb Programming Adaptor -II USB to UART Serial Bridge Document Date: 17 th July 2015 Document Revision: 2.0 Uncontrolled Copy when printed or downloaded. Please
DATASHEET TURNING TECHNOLOGY INTO ART microusb Programming Adaptor -II USB to UART Serial Bridge Document Date: 17 th July 2015 Document Revision: 2.0 Uncontrolled Copy when printed or downloaded. Please
Product Manual. 2 Port USB to RS-422 /485 Optical Isolated Adapter. Coolgear, Inc. Version 1.1 March 2018 Model Number: USB-2COMi-Si-M
 2 Port USB to RS-422 /485 Optical Isolated Adapter Product Manual Coolgear, Inc. Version 1.1 March 2018 Model Number: USB-2COMi-Si-M 2 USB-2COMi-Si-M Product Manual Revision History Revision Date Author
2 Port USB to RS-422 /485 Optical Isolated Adapter Product Manual Coolgear, Inc. Version 1.1 March 2018 Model Number: USB-2COMi-Si-M 2 USB-2COMi-Si-M Product Manual Revision History Revision Date Author
USB-ASC232. ASCII RS-232 Controlled USB Keyboard and Mouse Cable. User Manual
 USB-ASC232 ASCII RS-232 Controlled USB Keyboard and Mouse Cable User Manual Thank you for purchasing the model USB-ASC232 Cable HAGSTROM ELECTRONICS, INC. is pleased that you have selected this product
USB-ASC232 ASCII RS-232 Controlled USB Keyboard and Mouse Cable User Manual Thank you for purchasing the model USB-ASC232 Cable HAGSTROM ELECTRONICS, INC. is pleased that you have selected this product
Application Note 102 Pin and Bus Cycle Differences
 Application Note 102 Pin and Bus Cycle Differences Applicable to the Entire Line of 6x86 Cyrix Processors APPLICATION NOTE 102 Pin and Bus Cycle Differences 1. Introduction This application note describes
Application Note 102 Pin and Bus Cycle Differences Applicable to the Entire Line of 6x86 Cyrix Processors APPLICATION NOTE 102 Pin and Bus Cycle Differences 1. Introduction This application note describes
Installation Guide of Hi-Speed USB to Industrial I/O Adapter
 Installation Guide of Hi-Speed USB to Industrial I/O Adapter Introduction of USB-COMi-SI-M The USB Industrial I/O Adapter is designed to make industrial communication port expansion quick and simple. Connecting
Installation Guide of Hi-Speed USB to Industrial I/O Adapter Introduction of USB-COMi-SI-M The USB Industrial I/O Adapter is designed to make industrial communication port expansion quick and simple. Connecting
UNH-IOL MIPI Alliance Test Program
 DSI Receiver Protocol Conformance Test Report UNH-IOL 121 Technology Drive, Suite 2 Durham, NH 03824 +1-603-862-0090 mipilab@iol.unh.edu +1-603-862-0701 Engineer Name engineer@company.com Panel Company
DSI Receiver Protocol Conformance Test Report UNH-IOL 121 Technology Drive, Suite 2 Durham, NH 03824 +1-603-862-0090 mipilab@iol.unh.edu +1-603-862-0701 Engineer Name engineer@company.com Panel Company
QBridge. I2C, SPI, CAN Control Software User s Manual. Date: Rev 1.3
 QBridge I2C, SPI, CAN Control Software User s Manual Date: 9-10-2005 Rev 1.3 1. Introduction...1 1.1. What QBridge can do?... 1 1.2. Disclaimer... 1 1.3. Operational Format... 1 1.4. QBridge-V2... 1 2.
QBridge I2C, SPI, CAN Control Software User s Manual Date: 9-10-2005 Rev 1.3 1. Introduction...1 1.1. What QBridge can do?... 1 1.2. Disclaimer... 1 1.3. Operational Format... 1 1.4. QBridge-V2... 1 2.
UniFinger SFM3050-TC2
 UniFinger SFM3050-TC2 Ver. 1.01 UniFinger SFM3050-TC2 2 Revision History Rev No. Issued date Description 1.0 Dec 27, 2004 Initial Release 1.01 Aug. 13, 2010. Incorrect name of J2 connector is corrected,
UniFinger SFM3050-TC2 Ver. 1.01 UniFinger SFM3050-TC2 2 Revision History Rev No. Issued date Description 1.0 Dec 27, 2004 Initial Release 1.01 Aug. 13, 2010. Incorrect name of J2 connector is corrected,
DVN 16Pro. User Manual. 16-Port DVI-D KVM Switch with Audio and USB 2.0 Sharing
 DVN 16Pro User Manual 16-Port DVI-D KVM Switch with Audio and USB 2.0 Sharing Access and Control 16 Computers with One USB keyboard, USB Mouse and DVI-D Monitor Made in U.S.A. www.smartavi.com 1 1-800-AVI-2131
DVN 16Pro User Manual 16-Port DVI-D KVM Switch with Audio and USB 2.0 Sharing Access and Control 16 Computers with One USB keyboard, USB Mouse and DVI-D Monitor Made in U.S.A. www.smartavi.com 1 1-800-AVI-2131
8 Port USB to RS- 232/422/485 Octal Adapter. Product Manual. Coolgear, Inc. Version 1.1 April 2018 Model Number: USB-8COMi-RM.
 8 Port USB to RS- 232/422/485 Octal Adapter Product Manual Coolgear, Inc. Version 1.1 April 2018 Model Number: USB-8COMi-RM 2 USB-8COMi-RM Product Manual Revision History Revision Date Author Comments
8 Port USB to RS- 232/422/485 Octal Adapter Product Manual Coolgear, Inc. Version 1.1 April 2018 Model Number: USB-8COMi-RM 2 USB-8COMi-RM Product Manual Revision History Revision Date Author Comments
Optical Data Interface ODI-2 Transport Layer Preliminary Specification
 Optical Data Interface O-2 Transport Layer Preliminary Specification Revision 2, Date 180420 The O Specification is managed by the AXIe Consortium. For more information about O, go to http://axiestandard.org/odispecifications.html
Optical Data Interface O-2 Transport Layer Preliminary Specification Revision 2, Date 180420 The O Specification is managed by the AXIe Consortium. For more information about O, go to http://axiestandard.org/odispecifications.html
