Exploiting Parallelism to Support Scalable Hierarchical Clustering
|
|
|
- Sharleen Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exploiting Parallelism to Support Scalable Hierarchical Clustering Rebecca Cathey, Eric Jensen, Steven Beitzel, Ophir Frieder, David Grossman Information Retrieval Laboratory
2 Background Information Retrieval (IR) Goal: return documents relevant to a user s query Terminology Document sequence of terms expressing ideas about some topic in a natural language Query request for documents pertaining to some topic Relevancy is measured by how close documents are to the user s query
3 IR Example Find documents close to the user D1: The Dogs walked home <1, 1, 1,0> D: Home on the range <0, 0, 1, 1> Q: Dogs at home <1, 0, 1, 0> Dogs D1,1 Walked D1,1 Home D1,1 D,1 Range D,1 D Q D1
4 Document Clustering Automatically group related documents into clusters. Uses If a collection is well clustered, we can search only the cluster that will contain relevant documents. Searching a smaller collection should improve effectiveness and efficiency Types Hierarchical Agglomerative clustering Partitioning (Iterative) clustering
5 Document Clustering Partitioning vs. Hierarchical Hierarchical Computationally Expensive Non order dependent Always gives the same division of clusters Partitioning Potential to cluster larger document collections Order dependent Less accurate Combine Partitioning with Hierarchical Buckshot Algorithm Fast with reasonable accuracy
6 Hierarchical Clustering Produces a hierarchy of clusters Create n x n similarity matrix "n O( ) ABCDE BCE AD BE C A D B E
7 Sequential Hierarchical Algorithm 7 Phase 1 Assign each document to a cluster Build a similarity matrix for n documents Find the nearest neighbor and corresponding max similarity for each cluster Phase Search nearest neighbor array for the closest clusters Merge two clusters Update similarity matrix with the similarity to new cluster Update α elements in the nearest neighbor array Total Cost: n + (n)(αn) = O(αn )
8 Phase 1: Build a Similarity Matrix n= 1 nn array max array
9 Phase : Create the Clusters 1
10 Phase : Create Clusters Find Closest clusters 1 nn array max array
11 Phase : Create Clusters 1,
12 Phase : Create Clusters Update Similarity Scores 1, nn array max array ,
13 Phase : Create the Clusters, 1, 1 1
14 Phase : Create the Clusters 1,, nn array max array 1,. 8.,, 7. 1,
15 Phase : Create the Clusters, 1,, 1 1
16 Phase : Create the Clusters 1,,, nn array max array 1,.,,. 1,,.. 1,. 1
17 Phase : Create the Clusters 1,,,,, 1, 1 17
18 Phase : Create the Clusters 1,,,,, 1,,,,, 1, 1 18
19 Partitioning (Iterative) Clustering Divides the documents into several clusters according to some criteria Start with a random set of cluster centroids Iteratively adjust until some termination condition is set Linear time 1
20 Sequential Buckshot Algorithm Phase 1 Cluster randomly selected documents using the hierarchical agglomerative algorithm Phase kn Calculate centroids of clusters from phase 1 Assign every other document to the cluster it is closest too Total Cost: ( "kn ) + kn = O(αkn) 0
21 Example Buckshot Clustering n documents, want k clusters Randomly select kn documents O(kn) 1 1 kn kn 7 8 k clusters
22 Parallel Approach Split the tasks equally among p machines Reduces time and memory complexity by a factor of p Parallel Hierarchical Agglomerative Algorithm Allows clustering of larger document collections while still supporting accuracy Can be used with parallel buckshot algorithm to cluster larger collections
23 Parallel Hierarchical Algorithm Phase 1 Partition similarity matrix among p nodes. Each node finds the similarities for n/p rows Each node finds the maximum similarity and nearest neighbor for partition Phase Each node searches the nearest neighbor array for the closest clusters New node is selected to manage new cluster Every node calculates and sends the similarity between their clusters and the new cluster Every node updates α/p elements in the nearest neighbor aray Total Cost: n /p+ ((n)(αn))/p = O(αn /p)
24 Phase 1: Build Similarity Matrix Partition Documents 1 nn array max array N N N 8 7
25 Phase : Create the Clusters N1 chosen to manage new cluster 1 nn array max array N N N 8 7
26 Phase : Create the Clusters Update Similarity scores 1, N , N 7 7. N 8 nn array 1 max array
27 Parallel Buckshot Algorithm Phase 1 Cluster kn randomly selected documents using the parallel hierarchical agglomerative algorithm Phase Calculate centroids of clusters from phase 1 n! kn Partition remaining p documents into p partitions Each node assigns documents from a partition to the closest cluster Total Cost: ( "kn ) /p + kn/p = O(αkn/p) 7
28 Experiments Parallel computer consisting of 1 nodes Collections GB SGML Collection from TREC 8,0 documents Subset of GB collection 0,000 documents 8
29 Parallel Hierarchical Scalability according to the number of nodes
30 Parallel Hierarchical Scalability according to the collection size 0
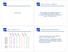
31 Hierarchical Cluster Evaluation Clusters Kmeans Hierarchical significance.87 e.1 e X. e.17 e X e. e X. e.88 e X 1.1 e 8. e X 1
32 Parallel Buckshot Scalability according to the number of nodes
33 Parallel Buckshot Scalability according to the number of clusters
34 Parallel Buckshot Scalability according to the collection size
35 Buckshot Cluster Evaluation Clusters Kmeans Buckshot significance.8 e. e X.0 e.0 e X 18.7 e. e X.8 e 7.0 e X 1.0 e 8.8 e X
36 Clustering Summary Clustering can be used to organize data Parallel Hierarchical Agglomerative Clustering can be used to accurately cluster somewhat large collections of documents Parallel Buckshot can be combined with the Parallel Hierarchical Agglomerative clustering algorithm to effectively cluster large quantities of data
Clustering (COSC 416) Nazli Goharian. Document Clustering.
 Clustering (COSC 416) Nazli Goharian nazli@cs.georgetown.edu 1 Document Clustering. Cluster Hypothesis : By clustering, documents relevant to the same topics tend to be grouped together. C. J. van Rijsbergen,
Clustering (COSC 416) Nazli Goharian nazli@cs.georgetown.edu 1 Document Clustering. Cluster Hypothesis : By clustering, documents relevant to the same topics tend to be grouped together. C. J. van Rijsbergen,
Machine Learning: Symbol-based
 10d Machine Learning: Symbol-based More clustering examples 10.5 Knowledge and Learning 10.6 Unsupervised Learning 10.7 Reinforcement Learning 10.8 Epilogue and References 10.9 Exercises Additional references
10d Machine Learning: Symbol-based More clustering examples 10.5 Knowledge and Learning 10.6 Unsupervised Learning 10.7 Reinforcement Learning 10.8 Epilogue and References 10.9 Exercises Additional references
5/15/16. Computational Methods for Data Analysis. Massimo Poesio UNSUPERVISED LEARNING. Clustering. Unsupervised learning introduction
 Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio UNSUPERVISED LEARNING Clustering Unsupervised learning introduction 1 Supervised learning Training set: Unsupervised learning Training set: 2 Clustering
Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio UNSUPERVISED LEARNING Clustering Unsupervised learning introduction 1 Supervised learning Training set: Unsupervised learning Training set: 2 Clustering
Clustering Results. Result List Example. Clustering Results. Information Retrieval
 Information Retrieval INFO 4300 / CS 4300! Presenting Results Clustering Clustering Results! Result lists often contain documents related to different aspects of the query topic! Clustering is used to
Information Retrieval INFO 4300 / CS 4300! Presenting Results Clustering Clustering Results! Result lists often contain documents related to different aspects of the query topic! Clustering is used to
Clustering (COSC 488) Nazli Goharian. Document Clustering.
 Clustering (COSC 488) Nazli Goharian nazli@ir.cs.georgetown.edu 1 Document Clustering. Cluster Hypothesis : By clustering, documents relevant to the same topics tend to be grouped together. C. J. van Rijsbergen,
Clustering (COSC 488) Nazli Goharian nazli@ir.cs.georgetown.edu 1 Document Clustering. Cluster Hypothesis : By clustering, documents relevant to the same topics tend to be grouped together. C. J. van Rijsbergen,
Unsupervised Learning
 Outline Unsupervised Learning Basic concepts K-means algorithm Representation of clusters Hierarchical clustering Distance functions Which clustering algorithm to use? NN Supervised learning vs. unsupervised
Outline Unsupervised Learning Basic concepts K-means algorithm Representation of clusters Hierarchical clustering Distance functions Which clustering algorithm to use? NN Supervised learning vs. unsupervised
Olmo S. Zavala Romero. Clustering Hierarchical Distance Group Dist. K-means. Center of Atmospheric Sciences, UNAM.
 Center of Atmospheric Sciences, UNAM November 16, 2016 Cluster Analisis Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster)
Center of Atmospheric Sciences, UNAM November 16, 2016 Cluster Analisis Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster)
CSE 494 Project C. Garrett Wolf
 CSE 494 Project C Garrett Wolf Introduction The main purpose of this project task was for us to implement the simple k-means and buckshot clustering algorithms. Once implemented, we were asked to vary
CSE 494 Project C Garrett Wolf Introduction The main purpose of this project task was for us to implement the simple k-means and buckshot clustering algorithms. Once implemented, we were asked to vary
Data Mining. Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed. University of Human Development, College of Science and Technology Department of Computer Science
 Data Mining Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed University of Human Development, College of Science and Technology Department of Computer Science 06 07 Department of CS - DM - UHD Road map Cluster Analysis: Basic
Data Mining Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed University of Human Development, College of Science and Technology Department of Computer Science 06 07 Department of CS - DM - UHD Road map Cluster Analysis: Basic
Information Retrieval and Web Search Engines
 Information Retrieval and Web Search Engines Lecture 7: Document Clustering December 4th, 2014 Wolf-Tilo Balke and José Pinto Institut für Informationssysteme Technische Universität Braunschweig The Cluster
Information Retrieval and Web Search Engines Lecture 7: Document Clustering December 4th, 2014 Wolf-Tilo Balke and José Pinto Institut für Informationssysteme Technische Universität Braunschweig The Cluster
Information Retrieval and Web Search Engines
 Information Retrieval and Web Search Engines Lecture 7: Document Clustering May 25, 2011 Wolf-Tilo Balke and Joachim Selke Institut für Informationssysteme Technische Universität Braunschweig Homework
Information Retrieval and Web Search Engines Lecture 7: Document Clustering May 25, 2011 Wolf-Tilo Balke and Joachim Selke Institut für Informationssysteme Technische Universität Braunschweig Homework
CSE494 Information Retrieval Project C Report
 CSE494 Information Retrieval Project C Report By: Jianchun Fan Introduction In project C we implement several different clustering methods on the query results given by pagerank algorithms. The clustering
CSE494 Information Retrieval Project C Report By: Jianchun Fan Introduction In project C we implement several different clustering methods on the query results given by pagerank algorithms. The clustering
BBS654 Data Mining. Pinar Duygulu. Slides are adapted from Nazli Ikizler
 BBS654 Data Mining Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Nazli Ikizler 1 Classification Classification systems: Supervised learning Make a rational prediction given evidence There are several methods for
BBS654 Data Mining Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Nazli Ikizler 1 Classification Classification systems: Supervised learning Make a rational prediction given evidence There are several methods for
Hierarchical and Ensemble Clustering
 Hierarchical and Ensemble Clustering Ke Chen Reading: [7.8-7., EA], [25.5, KPM], [Fred & Jain, 25] COMP24 Machine Learning Outline Introduction Cluster Distance Measures Agglomerative Algorithm Example
Hierarchical and Ensemble Clustering Ke Chen Reading: [7.8-7., EA], [25.5, KPM], [Fred & Jain, 25] COMP24 Machine Learning Outline Introduction Cluster Distance Measures Agglomerative Algorithm Example
Cluster Analysis: Agglomerate Hierarchical Clustering
 Cluster Analysis: Agglomerate Hierarchical Clustering Yonghee Lee Department of Statistics, The University of Seoul Oct 29, 2015 Contents 1 Cluster Analysis Introduction Distance matrix Agglomerative Hierarchical
Cluster Analysis: Agglomerate Hierarchical Clustering Yonghee Lee Department of Statistics, The University of Seoul Oct 29, 2015 Contents 1 Cluster Analysis Introduction Distance matrix Agglomerative Hierarchical
Based on Raymond J. Mooney s slides
 Instance Based Learning Based on Raymond J. Mooney s slides University of Texas at Austin 1 Example 2 Instance-Based Learning Unlike other learning algorithms, does not involve construction of an explicit
Instance Based Learning Based on Raymond J. Mooney s slides University of Texas at Austin 1 Example 2 Instance-Based Learning Unlike other learning algorithms, does not involve construction of an explicit
University of Florida CISE department Gator Engineering. Clustering Part 2
 Clustering Part 2 Dr. Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville Partitional Clustering Original Points A Partitional Clustering Hierarchical
Clustering Part 2 Dr. Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville Partitional Clustering Original Points A Partitional Clustering Hierarchical
Cluster Analysis. Ying Shen, SSE, Tongji University
 Cluster Analysis Ying Shen, SSE, Tongji University Cluster analysis Cluster analysis groups data objects based only on the attributes in the data. The main objective is that The objects within a group
Cluster Analysis Ying Shen, SSE, Tongji University Cluster analysis Cluster analysis groups data objects based only on the attributes in the data. The main objective is that The objects within a group
Clustering Part 3. Hierarchical Clustering
 Clustering Part Dr Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville Hierarchical Clustering Two main types: Agglomerative Start with the points
Clustering Part Dr Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville Hierarchical Clustering Two main types: Agglomerative Start with the points
CS7267 MACHINE LEARNING
 S7267 MAHINE LEARNING HIERARHIAL LUSTERING Ref: hengkai Li, Department of omputer Science and Engineering, University of Texas at Arlington (Slides courtesy of Vipin Kumar) Mingon Kang, Ph.D. omputer Science,
S7267 MAHINE LEARNING HIERARHIAL LUSTERING Ref: hengkai Li, Department of omputer Science and Engineering, University of Texas at Arlington (Slides courtesy of Vipin Kumar) Mingon Kang, Ph.D. omputer Science,
Indexing in Search Engines based on Pipelining Architecture using Single Link HAC
 Indexing in Search Engines based on Pipelining Architecture using Single Link HAC Anuradha Tyagi S. V. Subharti University Haridwar Bypass Road NH-58, Meerut, India ABSTRACT Search on the web is a daily
Indexing in Search Engines based on Pipelining Architecture using Single Link HAC Anuradha Tyagi S. V. Subharti University Haridwar Bypass Road NH-58, Meerut, India ABSTRACT Search on the web is a daily
Chapter 18 Clustering
 Chapter 18 Clustering CS4811 Artificial Intelligence Nilufer Onder Department of Computer Science Michigan Technological University 1 Outline Examples Centroid approaches Hierarchical approaches 2 Example:
Chapter 18 Clustering CS4811 Artificial Intelligence Nilufer Onder Department of Computer Science Michigan Technological University 1 Outline Examples Centroid approaches Hierarchical approaches 2 Example:
 http://www.xkcd.com/233/ Text Clustering David Kauchak cs160 Fall 2009 adapted from: http://www.stanford.edu/class/cs276/handouts/lecture17-clustering.ppt Administrative 2 nd status reports Paper review
http://www.xkcd.com/233/ Text Clustering David Kauchak cs160 Fall 2009 adapted from: http://www.stanford.edu/class/cs276/handouts/lecture17-clustering.ppt Administrative 2 nd status reports Paper review
INF4820, Algorithms for AI and NLP: Hierarchical Clustering
 INF4820, Algorithms for AI and NLP: Hierarchical Clustering Erik Velldal University of Oslo Sept. 25, 2012 Agenda Topics we covered last week Evaluating classifiers Accuracy, precision, recall and F-score
INF4820, Algorithms for AI and NLP: Hierarchical Clustering Erik Velldal University of Oslo Sept. 25, 2012 Agenda Topics we covered last week Evaluating classifiers Accuracy, precision, recall and F-score
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING
 CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10. Cluster
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10. Cluster
Unsupervised Learning and Clustering
 Unsupervised Learning and Clustering Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2009 CS 551, Spring 2009 c 2009, Selim Aksoy (Bilkent University)
Unsupervised Learning and Clustering Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2009 CS 551, Spring 2009 c 2009, Selim Aksoy (Bilkent University)
Clustering: Overview and K-means algorithm
 Clustering: Overview and K-means algorithm Informal goal Given set of objects and measure of similarity between them, group similar objects together K-Means illustrations thanks to 2006 student Martin
Clustering: Overview and K-means algorithm Informal goal Given set of objects and measure of similarity between them, group similar objects together K-Means illustrations thanks to 2006 student Martin
Working with Unlabeled Data Clustering Analysis. Hsiao-Lung Chan Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan
 Working with Unlabeled Data Clustering Analysis Hsiao-Lung Chan Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan chanhl@mail.cgu.edu.tw Unsupervised learning Finding centers of similarity using
Working with Unlabeled Data Clustering Analysis Hsiao-Lung Chan Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan chanhl@mail.cgu.edu.tw Unsupervised learning Finding centers of similarity using
Hierarchical Clustering
 Hierarchical Clustering Produces a set of nested clusters organized as a hierarchical tree Can be visualized as a dendrogram A tree like diagram that records the sequences of merges or splits 0 0 0 00
Hierarchical Clustering Produces a set of nested clusters organized as a hierarchical tree Can be visualized as a dendrogram A tree like diagram that records the sequences of merges or splits 0 0 0 00
Unsupervised Learning and Data Mining
 Unsupervised Learning and Data Mining Unsupervised Learning and Data Mining Clustering Supervised Learning ó Decision trees ó Artificial neural nets ó K-nearest neighbor ó Support vectors ó Linear regression
Unsupervised Learning and Data Mining Unsupervised Learning and Data Mining Clustering Supervised Learning ó Decision trees ó Artificial neural nets ó K-nearest neighbor ó Support vectors ó Linear regression
Clustering in Data Mining
 Clustering in Data Mining Classification Vs Clustering When the distribution is based on a single parameter and that parameter is known for each object, it is called classification. E.g. Children, young,
Clustering in Data Mining Classification Vs Clustering When the distribution is based on a single parameter and that parameter is known for each object, it is called classification. E.g. Children, young,
Administrative. Machine learning code. Supervised learning (e.g. classification) Machine learning: Unsupervised learning" BANANAS APPLES
 Administrative Machine learning: Unsupervised learning" Assignment 5 out soon David Kauchak cs311 Spring 2013 adapted from: http://www.stanford.edu/class/cs276/handouts/lecture17-clustering.ppt Machine
Administrative Machine learning: Unsupervised learning" Assignment 5 out soon David Kauchak cs311 Spring 2013 adapted from: http://www.stanford.edu/class/cs276/handouts/lecture17-clustering.ppt Machine
Hierarchical Clustering 4/5/17
 Hierarchical Clustering 4/5/17 Hypothesis Space Continuous inputs Output is a binary tree with data points as leaves. Useful for explaining the training data. Not useful for making new predictions. Direction
Hierarchical Clustering 4/5/17 Hypothesis Space Continuous inputs Output is a binary tree with data points as leaves. Useful for explaining the training data. Not useful for making new predictions. Direction
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING
 CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University 09/25/2017 Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10.
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University 09/25/2017 Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10.
K-Means Clustering 3/3/17
 K-Means Clustering 3/3/17 Unsupervised Learning We have a collection of unlabeled data points. We want to find underlying structure in the data. Examples: Identify groups of similar data points. Clustering
K-Means Clustering 3/3/17 Unsupervised Learning We have a collection of unlabeled data points. We want to find underlying structure in the data. Examples: Identify groups of similar data points. Clustering
4. Ad-hoc I: Hierarchical clustering
 4. Ad-hoc I: Hierarchical clustering Hierarchical versus Flat Flat methods generate a single partition into k clusters. The number k of clusters has to be determined by the user ahead of time. Hierarchical
4. Ad-hoc I: Hierarchical clustering Hierarchical versus Flat Flat methods generate a single partition into k clusters. The number k of clusters has to be determined by the user ahead of time. Hierarchical
Unsupervised Learning Partitioning Methods
 Unsupervised Learning Partitioning Methods Road Map 1. Basic Concepts 2. K-Means 3. K-Medoids 4. CLARA & CLARANS Cluster Analysis Unsupervised learning (i.e., Class label is unknown) Group data to form
Unsupervised Learning Partitioning Methods Road Map 1. Basic Concepts 2. K-Means 3. K-Medoids 4. CLARA & CLARANS Cluster Analysis Unsupervised learning (i.e., Class label is unknown) Group data to form
CHAPTER 4: CLUSTER ANALYSIS
 CHAPTER 4: CLUSTER ANALYSIS WHAT IS CLUSTER ANALYSIS? A cluster is a collection of data-objects similar to one another within the same group & dissimilar to the objects in other groups. Cluster analysis
CHAPTER 4: CLUSTER ANALYSIS WHAT IS CLUSTER ANALYSIS? A cluster is a collection of data-objects similar to one another within the same group & dissimilar to the objects in other groups. Cluster analysis
Clustering & Classification (chapter 15)
 Clustering & Classification (chapter 5) Kai Goebel Bill Cheetham RPI/GE Global Research goebel@cs.rpi.edu cheetham@cs.rpi.edu Outline k-means Fuzzy c-means Mountain Clustering knn Fuzzy knn Hierarchical
Clustering & Classification (chapter 5) Kai Goebel Bill Cheetham RPI/GE Global Research goebel@cs.rpi.edu cheetham@cs.rpi.edu Outline k-means Fuzzy c-means Mountain Clustering knn Fuzzy knn Hierarchical
Hierarchical Clustering
 Hierarchical Clustering Hierarchical Clustering Produces a set of nested clusters organized as a hierarchical tree Can be visualized as a dendrogram A tree-like diagram that records the sequences of merges
Hierarchical Clustering Hierarchical Clustering Produces a set of nested clusters organized as a hierarchical tree Can be visualized as a dendrogram A tree-like diagram that records the sequences of merges
Clustering. Partition unlabeled examples into disjoint subsets of clusters, such that:
 Text Clustering 1 Clustering Partition unlabeled examples into disjoint subsets of clusters, such that: Examples within a cluster are very similar Examples in different clusters are very different Discover
Text Clustering 1 Clustering Partition unlabeled examples into disjoint subsets of clusters, such that: Examples within a cluster are very similar Examples in different clusters are very different Discover
A Comparison of Document Clustering Techniques
 A Comparison of Document Clustering Techniques M. Steinbach, G. Karypis, V. Kumar Present by Leo Chen Feb-01 Leo Chen 1 Road Map Background & Motivation (2) Basic (6) Vector Space Model Cluster Quality
A Comparison of Document Clustering Techniques M. Steinbach, G. Karypis, V. Kumar Present by Leo Chen Feb-01 Leo Chen 1 Road Map Background & Motivation (2) Basic (6) Vector Space Model Cluster Quality
Unsupervised Learning and Clustering
 Unsupervised Learning and Clustering Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2008 CS 551, Spring 2008 c 2008, Selim Aksoy (Bilkent University)
Unsupervised Learning and Clustering Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2008 CS 551, Spring 2008 c 2008, Selim Aksoy (Bilkent University)
Clustering Lecture 3: Hierarchical Methods
 Clustering Lecture 3: Hierarchical Methods Jing Gao SUNY Buffalo 1 Outline Basics Motivation, definition, evaluation Methods Partitional Hierarchical Density-based Mixture model Spectral methods Advanced
Clustering Lecture 3: Hierarchical Methods Jing Gao SUNY Buffalo 1 Outline Basics Motivation, definition, evaluation Methods Partitional Hierarchical Density-based Mixture model Spectral methods Advanced
Clustering. RNA-seq: What is it good for? Finding Similarly Expressed Genes. Data... And Lots of It!
 RNA-seq: What is it good for? Clustering High-throughput RNA sequencing experiments (RNA-seq) offer the ability to measure simultaneously the expression level of thousands of genes in a single experiment!
RNA-seq: What is it good for? Clustering High-throughput RNA sequencing experiments (RNA-seq) offer the ability to measure simultaneously the expression level of thousands of genes in a single experiment!
University of Florida CISE department Gator Engineering. Clustering Part 4
 Clustering Part 4 Dr. Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville DBSCAN DBSCAN is a density based clustering algorithm Density = number of
Clustering Part 4 Dr. Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville DBSCAN DBSCAN is a density based clustering algorithm Density = number of
INF 4300 Classification III Anne Solberg The agenda today:
 INF 4300 Classification III Anne Solberg 28.10.15 The agenda today: More on estimating classifier accuracy Curse of dimensionality and simple feature selection knn-classification K-means clustering 28.10.15
INF 4300 Classification III Anne Solberg 28.10.15 The agenda today: More on estimating classifier accuracy Curse of dimensionality and simple feature selection knn-classification K-means clustering 28.10.15
Lecture Notes for Chapter 7. Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition. by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar
 Data Mining Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms Lecture Notes for Chapter 7 Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar Hierarchical Clustering Produces a set
Data Mining Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms Lecture Notes for Chapter 7 Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar Hierarchical Clustering Produces a set
Clustering. So far in the course. Clustering. Clustering. Subhransu Maji. CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning. dist(x, y) = x y 2 2
 So far in the course Clustering Subhransu Maji : Machine Learning 2 April 2015 7 April 2015 Supervised learning: learning with a teacher You had training data which was (feature, label) pairs and the goal
So far in the course Clustering Subhransu Maji : Machine Learning 2 April 2015 7 April 2015 Supervised learning: learning with a teacher You had training data which was (feature, label) pairs and the goal
Clustering Part 4 DBSCAN
 Clustering Part 4 Dr. Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville DBSCAN DBSCAN is a density based clustering algorithm Density = number of
Clustering Part 4 Dr. Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville DBSCAN DBSCAN is a density based clustering algorithm Density = number of
CS 2750 Machine Learning. Lecture 19. Clustering. CS 2750 Machine Learning. Clustering. Groups together similar instances in the data sample
 Lecture 9 Clustering Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Clustering Groups together similar instances in the data sample Basic clustering problem: distribute data into k different groups
Lecture 9 Clustering Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Clustering Groups together similar instances in the data sample Basic clustering problem: distribute data into k different groups
Clustering CS 550: Machine Learning
 Clustering CS 550: Machine Learning This slide set mainly uses the slides given in the following links: http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~kumar/dmbook/ch8.pdf http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~kumar/dmbook/dmslides/chap8_basic_cluster_analysis.pdf
Clustering CS 550: Machine Learning This slide set mainly uses the slides given in the following links: http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~kumar/dmbook/ch8.pdf http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~kumar/dmbook/dmslides/chap8_basic_cluster_analysis.pdf
Cluster Analysis for Microarray Data
 Cluster Analysis for Microarray Data Seventh International Long Oligonucleotide Microarray Workshop Tucson, Arizona January 7-12, 2007 Dan Nettleton IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY 1 Clustering Group objects that
Cluster Analysis for Microarray Data Seventh International Long Oligonucleotide Microarray Workshop Tucson, Arizona January 7-12, 2007 Dan Nettleton IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY 1 Clustering Group objects that
Unsupervised Learning. Presenter: Anil Sharma, PhD Scholar, IIIT-Delhi
 Unsupervised Learning Presenter: Anil Sharma, PhD Scholar, IIIT-Delhi Content Motivation Introduction Applications Types of clustering Clustering criterion functions Distance functions Normalization Which
Unsupervised Learning Presenter: Anil Sharma, PhD Scholar, IIIT-Delhi Content Motivation Introduction Applications Types of clustering Clustering criterion functions Distance functions Normalization Which
CSE 255 Lecture 6. Data Mining and Predictive Analytics. Community Detection
 CSE 255 Lecture 6 Data Mining and Predictive Analytics Community Detection Dimensionality reduction Goal: take high-dimensional data, and describe it compactly using a small number of dimensions Assumption:
CSE 255 Lecture 6 Data Mining and Predictive Analytics Community Detection Dimensionality reduction Goal: take high-dimensional data, and describe it compactly using a small number of dimensions Assumption:
Search Engines. Information Retrieval in Practice
 Search Engines Information Retrieval in Practice All slides Addison Wesley, 2008 Classification and Clustering Classification and clustering are classical pattern recognition / machine learning problems
Search Engines Information Retrieval in Practice All slides Addison Wesley, 2008 Classification and Clustering Classification and clustering are classical pattern recognition / machine learning problems
CSE 158 Lecture 6. Web Mining and Recommender Systems. Community Detection
 CSE 158 Lecture 6 Web Mining and Recommender Systems Community Detection Dimensionality reduction Goal: take high-dimensional data, and describe it compactly using a small number of dimensions Assumption:
CSE 158 Lecture 6 Web Mining and Recommender Systems Community Detection Dimensionality reduction Goal: take high-dimensional data, and describe it compactly using a small number of dimensions Assumption:
Clustering. Subhransu Maji. CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning. 2 April April 2015
 Clustering Subhransu Maji CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning 2 April 2015 7 April 2015 So far in the course Supervised learning: learning with a teacher You had training data which was (feature, label) pairs
Clustering Subhransu Maji CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning 2 April 2015 7 April 2015 So far in the course Supervised learning: learning with a teacher You had training data which was (feature, label) pairs
Workload Characterization Techniques
 Workload Characterization Techniques Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu These slides are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse567-08/
Workload Characterization Techniques Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu These slides are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse567-08/
CS 347 Parallel and Distributed Data Processing
 CS 347 Parallel and Distributed Data Processing Spring 2016 Notes 12: Distributed Information Retrieval CS 347 Notes 12 2 CS 347 Notes 12 3 CS 347 Notes 12 4 CS 347 Notes 12 5 Web Search Engine Crawling
CS 347 Parallel and Distributed Data Processing Spring 2016 Notes 12: Distributed Information Retrieval CS 347 Notes 12 2 CS 347 Notes 12 3 CS 347 Notes 12 4 CS 347 Notes 12 5 Web Search Engine Crawling
CS 347 Parallel and Distributed Data Processing
 CS 347 Parallel and Distributed Data Processing Spring 2016 Notes 12: Distributed Information Retrieval CS 347 Notes 12 2 CS 347 Notes 12 3 CS 347 Notes 12 4 Web Search Engine Crawling Indexing Computing
CS 347 Parallel and Distributed Data Processing Spring 2016 Notes 12: Distributed Information Retrieval CS 347 Notes 12 2 CS 347 Notes 12 3 CS 347 Notes 12 4 Web Search Engine Crawling Indexing Computing
Lecture 24: Image Retrieval: Part II. Visual Computing Systems CMU , Fall 2013
 Lecture 24: Image Retrieval: Part II Visual Computing Systems Review: K-D tree Spatial partitioning hierarchy K = dimensionality of space (below: K = 2) 3 2 1 3 3 4 2 Counts of points in leaf nodes Nearest
Lecture 24: Image Retrieval: Part II Visual Computing Systems Review: K-D tree Spatial partitioning hierarchy K = dimensionality of space (below: K = 2) 3 2 1 3 3 4 2 Counts of points in leaf nodes Nearest
Data Mining Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms. Slides From Lecture Notes for Chapter 8. Introduction to Data Mining
 Data Mining Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms Slides From Lecture Notes for Chapter 8 Introduction to Data Mining by Tan, Steinbach, Kumar Tan,Steinbach, Kumar Introduction to Data Mining
Data Mining Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms Slides From Lecture Notes for Chapter 8 Introduction to Data Mining by Tan, Steinbach, Kumar Tan,Steinbach, Kumar Introduction to Data Mining
Midterm Examination CS 540-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Midterm Examination CS 54-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence March 9, 217 LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: Problem Score Max Score 1 15 2 17 3 12 4 6 5 12 6 14 7 15 8 9 Total 1 1 of 1 Question 1. [15] State
Midterm Examination CS 54-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence March 9, 217 LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: Problem Score Max Score 1 15 2 17 3 12 4 6 5 12 6 14 7 15 8 9 Total 1 1 of 1 Question 1. [15] State
INF4820. Clustering. Erik Velldal. Nov. 17, University of Oslo. Erik Velldal INF / 22
 INF4820 Clustering Erik Velldal University of Oslo Nov. 17, 2009 Erik Velldal INF4820 1 / 22 Topics for Today More on unsupervised machine learning for data-driven categorization: clustering. The task
INF4820 Clustering Erik Velldal University of Oslo Nov. 17, 2009 Erik Velldal INF4820 1 / 22 Topics for Today More on unsupervised machine learning for data-driven categorization: clustering. The task
INF4820, Algorithms for AI and NLP: Evaluating Classifiers Clustering
 INF4820, Algorithms for AI and NLP: Evaluating Classifiers Clustering Erik Velldal University of Oslo Sept. 18, 2012 Topics for today 2 Classification Recap Evaluating classifiers Accuracy, precision,
INF4820, Algorithms for AI and NLP: Evaluating Classifiers Clustering Erik Velldal University of Oslo Sept. 18, 2012 Topics for today 2 Classification Recap Evaluating classifiers Accuracy, precision,
Lecture-17: Clustering with K-Means (Contd: DT + Random Forest)
 Lecture-17: Clustering with K-Means (Contd: DT + Random Forest) Medha Vidyotma April 24, 2018 1 Contd. Random Forest For Example, if there are 50 scholars who take the measurement of the length of the
Lecture-17: Clustering with K-Means (Contd: DT + Random Forest) Medha Vidyotma April 24, 2018 1 Contd. Random Forest For Example, if there are 50 scholars who take the measurement of the length of the
Today s topic CS347. Results list clustering example. Why cluster documents. Clustering documents. Lecture 8 May 7, 2001 Prabhakar Raghavan
 Today s topic CS347 Clustering documents Lecture 8 May 7, 2001 Prabhakar Raghavan Why cluster documents Given a corpus, partition it into groups of related docs Recursively, can induce a tree of topics
Today s topic CS347 Clustering documents Lecture 8 May 7, 2001 Prabhakar Raghavan Why cluster documents Given a corpus, partition it into groups of related docs Recursively, can induce a tree of topics
Clustering & Bootstrapping
 Clustering & Bootstrapping Jelena Prokić University of Groningen The Netherlands March 25, 2009 Groningen Overview What is clustering? Various clustering algorithms Bootstrapping Application in dialectometry
Clustering & Bootstrapping Jelena Prokić University of Groningen The Netherlands March 25, 2009 Groningen Overview What is clustering? Various clustering algorithms Bootstrapping Application in dialectometry
Project C Report (Clustering Algorithms)
 Project C Report (Clustering Algorithms) This report contains details about clustering algorithms. It mainly compares two of the clustering algorithms, K-Means and Buckshot and some variation of these
Project C Report (Clustering Algorithms) This report contains details about clustering algorithms. It mainly compares two of the clustering algorithms, K-Means and Buckshot and some variation of these
Midterm Examination CS540-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Midterm Examination CS540-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence March 15, 2018 LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: Problem Score Max Score 1 12 2 13 3 9 4 11 5 8 6 13 7 9 8 16 9 9 Total 100 Question 1. [12] Search
Midterm Examination CS540-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence March 15, 2018 LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: Problem Score Max Score 1 12 2 13 3 9 4 11 5 8 6 13 7 9 8 16 9 9 Total 100 Question 1. [12] Search
Clustering k-mean clustering
 Clustering k-mean clustering Genome 373 Genomic Informatics Elhanan Borenstein The clustering problem: partition genes into distinct sets with high homogeneity and high separation Clustering (unsupervised)
Clustering k-mean clustering Genome 373 Genomic Informatics Elhanan Borenstein The clustering problem: partition genes into distinct sets with high homogeneity and high separation Clustering (unsupervised)
Data Mining Concepts & Techniques
 Data Mining Concepts & Techniques Lecture No 08 Cluster Analysis Naeem Ahmed Email: naeemmahoto@gmailcom Department of Software Engineering Mehran Univeristy of Engineering and Technology Jamshoro Outline
Data Mining Concepts & Techniques Lecture No 08 Cluster Analysis Naeem Ahmed Email: naeemmahoto@gmailcom Department of Software Engineering Mehran Univeristy of Engineering and Technology Jamshoro Outline
INF4820 Algorithms for AI and NLP. Evaluating Classifiers Clustering
 INF4820 Algorithms for AI and NLP Evaluating Classifiers Clustering Erik Velldal & Stephan Oepen Language Technology Group (LTG) September 23, 2015 Agenda Last week Supervised vs unsupervised learning.
INF4820 Algorithms for AI and NLP Evaluating Classifiers Clustering Erik Velldal & Stephan Oepen Language Technology Group (LTG) September 23, 2015 Agenda Last week Supervised vs unsupervised learning.
Applications. Foreground / background segmentation Finding skin-colored regions. Finding the moving objects. Intelligent scissors
 Segmentation I Goal Separate image into coherent regions Berkeley segmentation database: http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/research/projects/cs/vision/grouping/segbench/ Slide by L. Lazebnik Applications Intelligent
Segmentation I Goal Separate image into coherent regions Berkeley segmentation database: http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/research/projects/cs/vision/grouping/segbench/ Slide by L. Lazebnik Applications Intelligent
Clustering. Bruno Martins. 1 st Semester 2012/2013
 Departamento de Engenharia Informática Instituto Superior Técnico 1 st Semester 2012/2013 Slides baseados nos slides oficiais do livro Mining the Web c Soumen Chakrabarti. Outline 1 Motivation Basic Concepts
Departamento de Engenharia Informática Instituto Superior Técnico 1 st Semester 2012/2013 Slides baseados nos slides oficiais do livro Mining the Web c Soumen Chakrabarti. Outline 1 Motivation Basic Concepts
Cluster Analysis. Prof. Thomas B. Fomby Department of Economics Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX April 2008 April 2010
 Cluster Analysis Prof. Thomas B. Fomby Department of Economics Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX 7575 April 008 April 010 Cluster Analysis, sometimes called data segmentation or customer segmentation,
Cluster Analysis Prof. Thomas B. Fomby Department of Economics Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX 7575 April 008 April 010 Cluster Analysis, sometimes called data segmentation or customer segmentation,
Computational Statistics The basics of maximum likelihood estimation, Bayesian estimation, object recognitions
 Computational Statistics The basics of maximum likelihood estimation, Bayesian estimation, object recognitions Thomas Giraud Simon Chabot October 12, 2013 Contents 1 Discriminant analysis 3 1.1 Main idea................................
Computational Statistics The basics of maximum likelihood estimation, Bayesian estimation, object recognitions Thomas Giraud Simon Chabot October 12, 2013 Contents 1 Discriminant analysis 3 1.1 Main idea................................
Unsupervised Learning. Clustering and the EM Algorithm. Unsupervised Learning is Model Learning
 Unsupervised Learning Clustering and the EM Algorithm Susanna Ricco Supervised Learning Given data in the form < x, y >, y is the target to learn. Good news: Easy to tell if our algorithm is giving the
Unsupervised Learning Clustering and the EM Algorithm Susanna Ricco Supervised Learning Given data in the form < x, y >, y is the target to learn. Good news: Easy to tell if our algorithm is giving the
Clustering Lecture 8. David Sontag New York University. Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, Carlos Guestrin, Andrew Moore, Dan Klein
 Clustering Lecture 8 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, Carlos Guestrin, Andrew Moore, Dan Klein Clustering: Unsupervised learning Clustering Requires
Clustering Lecture 8 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, Carlos Guestrin, Andrew Moore, Dan Klein Clustering: Unsupervised learning Clustering Requires
Objective of clustering
 Objective of clustering Discover structures and patterns in high-dimensional data. Group data with similar patterns together. This reduces the complexity and facilitates interpretation. Expression level
Objective of clustering Discover structures and patterns in high-dimensional data. Group data with similar patterns together. This reduces the complexity and facilitates interpretation. Expression level
Hierarchy. No or very little supervision Some heuristic quality guidances on the quality of the hierarchy. Jian Pei: CMPT 459/741 Clustering (2) 1
 Hierarchy An arrangement or classification of things according to inclusiveness A natural way of abstraction, summarization, compression, and simplification for understanding Typical setting: organize
Hierarchy An arrangement or classification of things according to inclusiveness A natural way of abstraction, summarization, compression, and simplification for understanding Typical setting: organize
Clustering. Robert M. Haralick. Computer Science, Graduate Center City University of New York
 Clustering Robert M. Haralick Computer Science, Graduate Center City University of New York Outline K-means 1 K-means 2 3 4 5 Clustering K-means The purpose of clustering is to determine the similarity
Clustering Robert M. Haralick Computer Science, Graduate Center City University of New York Outline K-means 1 K-means 2 3 4 5 Clustering K-means The purpose of clustering is to determine the similarity
Clustering. Chapter 10 in Introduction to statistical learning
 Clustering Chapter 10 in Introduction to statistical learning 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 1 Clustering ² Clustering is the art of finding groups in data (Kaufman and Rousseeuw, 1990). ² What
Clustering Chapter 10 in Introduction to statistical learning 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 1 Clustering ² Clustering is the art of finding groups in data (Kaufman and Rousseeuw, 1990). ² What
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence COMP307 Machine Learning 2: 3-K Techniques Yi Mei yi.mei@ecs.vuw.ac.nz 1 Outline K-Nearest Neighbour method Classification (Supervised learning) Basic NN (1-NN)
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence COMP307 Machine Learning 2: 3-K Techniques Yi Mei yi.mei@ecs.vuw.ac.nz 1 Outline K-Nearest Neighbour method Classification (Supervised learning) Basic NN (1-NN)
Scalable Nearest Neighbor Algorithms for High Dimensional Data Marius Muja (UBC), David G. Lowe (Google) IEEE 2014
 Scalable Nearest Neighbor Algorithms for High Dimensional Data Marius Muja (UBC), David G. Lowe (Google) IEEE 2014 Presenter: Derrick Blakely Department of Computer Science, University of Virginia https://qdata.github.io/deep2read/
Scalable Nearest Neighbor Algorithms for High Dimensional Data Marius Muja (UBC), David G. Lowe (Google) IEEE 2014 Presenter: Derrick Blakely Department of Computer Science, University of Virginia https://qdata.github.io/deep2read/
Clustering part II 1
 Clustering part II 1 Clustering What is Cluster Analysis? Types of Data in Cluster Analysis A Categorization of Major Clustering Methods Partitioning Methods Hierarchical Methods 2 Partitioning Algorithms:
Clustering part II 1 Clustering What is Cluster Analysis? Types of Data in Cluster Analysis A Categorization of Major Clustering Methods Partitioning Methods Hierarchical Methods 2 Partitioning Algorithms:
Clustering Algorithms for general similarity measures
 Types of general clustering methods Clustering Algorithms for general similarity measures general similarity measure: specified by object X object similarity matrix 1 constructive algorithms agglomerative
Types of general clustering methods Clustering Algorithms for general similarity measures general similarity measure: specified by object X object similarity matrix 1 constructive algorithms agglomerative
What is Clustering? Clustering. Characterizing Cluster Methods. Clusters. Cluster Validity. Basic Clustering Methodology
 Clustering Unsupervised learning Generating classes Distance/similarity measures Agglomerative methods Divisive methods Data Clustering 1 What is Clustering? Form o unsupervised learning - no inormation
Clustering Unsupervised learning Generating classes Distance/similarity measures Agglomerative methods Divisive methods Data Clustering 1 What is Clustering? Form o unsupervised learning - no inormation
Machine learning - HT Clustering
 Machine learning - HT 2016 10. Clustering Varun Kanade University of Oxford March 4, 2016 Announcements Practical Next Week - No submission Final Exam: Pick up on Monday Material covered next week is not
Machine learning - HT 2016 10. Clustering Varun Kanade University of Oxford March 4, 2016 Announcements Practical Next Week - No submission Final Exam: Pick up on Monday Material covered next week is not
Clustering. Informal goal. General types of clustering. Applications: Clustering in information search and analysis. Example applications in search
 Informal goal Clustering Given set of objects and measure of similarity between them, group similar objects together What mean by similar? What is good grouping? Computation time / quality tradeoff 1 2
Informal goal Clustering Given set of objects and measure of similarity between them, group similar objects together What mean by similar? What is good grouping? Computation time / quality tradeoff 1 2
Cluster Evaluation and Expectation Maximization! adapted from: Doug Downey and Bryan Pardo, Northwestern University
 Cluster Evaluation and Expectation Maximization! adapted from: Doug Downey and Bryan Pardo, Northwestern University Kinds of Clustering Sequential Fast Cost Optimization Fixed number of clusters Hierarchical
Cluster Evaluation and Expectation Maximization! adapted from: Doug Downey and Bryan Pardo, Northwestern University Kinds of Clustering Sequential Fast Cost Optimization Fixed number of clusters Hierarchical
2. Background. 2.1 Clustering
 2. Background 2.1 Clustering Clustering involves the unsupervised classification of data items into different groups or clusters. Unsupervised classificaiton is basically a learning task in which learning
2. Background 2.1 Clustering Clustering involves the unsupervised classification of data items into different groups or clusters. Unsupervised classificaiton is basically a learning task in which learning
Hard clustering. Each object is assigned to one and only one cluster. Hierarchical clustering is usually hard. Soft (fuzzy) clustering
 An unsupervised machine learning problem Grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (a cluster) are more similar (in some sense or another) to each other than to those in other
An unsupervised machine learning problem Grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (a cluster) are more similar (in some sense or another) to each other than to those in other
Multivariate Analysis (slides 9)
 Multivariate Analysis (slides 9) Today we consider k-means clustering. We will address the question of selecting the appropriate number of clusters. Properties and limitations of the algorithm will be
Multivariate Analysis (slides 9) Today we consider k-means clustering. We will address the question of selecting the appropriate number of clusters. Properties and limitations of the algorithm will be
Lesson 3. Prof. Enza Messina
 Lesson 3 Prof. Enza Messina Clustering techniques are generally classified into these classes: PARTITIONING ALGORITHMS Directly divides data points into some prespecified number of clusters without a hierarchical
Lesson 3 Prof. Enza Messina Clustering techniques are generally classified into these classes: PARTITIONING ALGORITHMS Directly divides data points into some prespecified number of clusters without a hierarchical
Data Mining Chapter 9: Descriptive Modeling Fall 2011 Ming Li Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University
 Data Mining Chapter 9: Descriptive Modeling Fall 2011 Ming Li Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University Descriptive model A descriptive model presents the main features of the data
Data Mining Chapter 9: Descriptive Modeling Fall 2011 Ming Li Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University Descriptive model A descriptive model presents the main features of the data
CS 1675 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 18. Clustering. Clustering. Groups together similar instances in the data sample
 CS 1675 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 18 Clustering Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Clustering Groups together similar instances in the data sample Basic clustering problem:
CS 1675 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 18 Clustering Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Clustering Groups together similar instances in the data sample Basic clustering problem:
Chapter 6: Cluster Analysis
 Chapter 6: Cluster Analysis The major goal of cluster analysis is to separate individual observations, or items, into groups, or clusters, on the basis of the values for the q variables measured on each
Chapter 6: Cluster Analysis The major goal of cluster analysis is to separate individual observations, or items, into groups, or clusters, on the basis of the values for the q variables measured on each
Principle Of Parallel Algorithm Design (cont.) Alexandre David B2-206
 Principle Of Parallel Algorithm Design (cont.) Alexandre David B2-206 1 Today Characteristics of Tasks and Interactions (3.3). Mapping Techniques for Load Balancing (3.4). Methods for Containing Interaction
Principle Of Parallel Algorithm Design (cont.) Alexandre David B2-206 1 Today Characteristics of Tasks and Interactions (3.3). Mapping Techniques for Load Balancing (3.4). Methods for Containing Interaction
