Introduction Attributed Graphs Rule Specification Implementation Conclusion. AGG and PROGRES. Bernhard Scholz. 27th January 2006.
|
|
|
- Marilyn Cannon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AGG and PROGRES 27th January 2006 AGG and PROGRES 1
2 Motivation AGG Attributed Graph Grammar System TU Berlin PROGRES PROgrammed Graph REwriting Systems RTWH Aachen How do these systems work? Graph model Data structures Rule specification Algorithms AGG and PROGRES 2
3 Motivation AGG Attributed Graph Grammar System TU Berlin PROGRES PROgrammed Graph REwriting Systems RTWH Aachen How do these systems work? Graph model Data structures Rule specification Algorithms AGG and PROGRES 2
4 Motivation Introduction Motivation Attributed Graphs Graphs Attributed Graphs Rule Specification General Definition AGG Specific PROGRES Specific Implementation Pattern Matching General Features Screenshots Conclusion Questions AGG and PROGRES 3
5 Graphs Graph A directed, node and edge labelled graph is a system G = (G V, G E, L, s, t, l) of nodes G V, edges G E (G V G E = ), labels (or types) L, mappings s, t : G E G V and l : G V G E L. Definition allows multiple edges between the same nodes. AGG and PROGRES 4
6 Graphs Example Labels L = {Shipping Company, Truck, Container, owns, on} AGG and PROGRES 5
7 Attributed Graphs Approaches to represent additional information Here: The contents of the container e.g. peanuts. By additional nodes and edges Pure graph approaches are not useful. AGG and PROGRES 6
8 Attributed Graphs Approaches to represent additional information Here: The contents of the container e.g. peanuts. By additional nodes and edges Pure graph approaches are not useful. AGG and PROGRES 6
9 Attributed Graphs Approaches to represent additional information Here: The contents of the container e.g. peanuts. By additional nodes and edges Pure graph approaches are not useful. AGG and PROGRES 6
10 Attributed Graphs Attributed Graphs Attributes Each graph object (nodes and edges) can have a list of attributes. Attribute: name, type, value Example: String content = "Peanuts" For all graph objects: same label same attribute declarations (name and type). AGG and PROGRES 7
11 Attributed Graphs Example AGG and PROGRES 8
12 General Definition Graph Rewrite Rule Rule Single pushout approach A (partial) morphism r : L R for graphs L, R. Structure and label (type) preserving. e dom(r E ) : r V (s L (e)) = s R (r E (e)), r V (t L (e)) = t R (r E (e)), o dom(r) : l L (o) = l R (r(o)) Partiality is needed to differ: objects to be deleted / objects to be preserved. AGG and PROGRES 9
13 General Definition Numbers (1:, 2:, 3:, 5:) specify the partial morphism. AGG and PROGRES 10
14 General Definition Attributed Graph Rewrite Rule AGG and PROGRES 11
15 General Definition Rule Application AGG and PROGRES 12
16 AGG Specific AGG Conditions for Rule Application Match conditions A total morphism m : L G that preserves structure e L E : m V (s L (e)) = s G (m E (e)), m V (t L (e)) = t G (m E (e)) and types o L V L E : l L (o) = l G (m(o)) Attribute value conditions (e.g. weight < 10.0) Negative application conditions (NACs) Ability to express which graph objects are not desired in the environment of a match. AGG and PROGRES 13
17 AGG Specific NAC Negative Application Condition AGG and PROGRES 14
18 AGG Specific NAC Negative Application Condition Formal specification NAC: A (partial) morphism l : L N for graphs L, N. An NAC is satisfied by a match m : L G iff we cannot find a total morphism n : N G such that n l = m dom(l) Intuitionally... NAC fails if the graph N can be matched onto G such that the images of L and N are at the same place. AGG and PROGRES 15
19 AGG Specific NAC Negative Application Condition Formal specification NAC: A (partial) morphism l : L N for graphs L, N. An NAC is satisfied by a match m : L G iff we cannot find a total morphism n : N G such that n l = m dom(l) Intuitionally... NAC fails if the graph N can be matched onto G such that the images of L and N are at the same place. AGG and PROGRES 15
20 PROGRES Specific PROGRES Extended Rule Elements PROGRES rules allow the use of nondeterministic and/or partial variables. Cardinality for nodes single node non-empty set of nodes optional node optional set of nodes AGG and PROGRES 16
21 PROGRES Specific Example AGG and PROGRES 17
22 PROGRES Specific PROGRES Production vs. Transaction Production left- and right-hand side graph pattern, in/out parameters. Transaction imperative structure, calls tests and productions. allows (guarded) alternatives, loops,..., for example: AGG and PROGRES 18
23 Pattern Matching PROGRES Pattern Matching with Search Plan Search plan pattern graph, operation graph calculated as soon as the rule has been specified, i.e. at compile time does not account for the current working graph AGG and PROGRES 19
24 Pattern Matching AGG Pattern Matching as CSP Constraint Satisfaction Problem well known from artifical intelligence a lot of implementations (backtracking, backjumping,... ) Variable order / search plan is calculated during application. first-fail principle partial match = partial assignment of CSP variables. frequency of object types? AGG and PROGRES 20
25 General Features AGG Implementation written in Java. 1:1 image of the theoretical formalism. extended by some redundancies. Advantages easy writing, understanding and expanding of the code. easy proof of correctness. easy access by Java API. Disadvantages bad time performance. huge Java overhead. AGG and PROGRES 21
26 General Features AGG Implementation written in Java. 1:1 image of the theoretical formalism. extended by some redundancies. Advantages easy writing, understanding and expanding of the code. easy proof of correctness. easy access by Java API. Disadvantages bad time performance. huge Java overhead. AGG and PROGRES 21
27 General Features PROGRES Implementation written in Modula optimized for performance Advantages performs lots of rule applications in huge graphs very fast. provides sophisticated language constructs. best horror GUI ever :-). Disadvantages has a usability of ± zero. AGG and PROGRES 22
28 General Features PROGRES Implementation written in Modula optimized for performance Advantages performs lots of rule applications in huge graphs very fast. provides sophisticated language constructs. best horror GUI ever :-). Disadvantages has a usability of ± zero. AGG and PROGRES 22
29 General Features PROGRES Implementation written in Modula optimized for performance Advantages performs lots of rule applications in huge graphs very fast. provides sophisticated language constructs. best horror GUI ever :-). Disadvantages has a usability of ± zero. AGG and PROGRES 22
30 Screenshots AGG and PROGRES 23
31 Screenshots AGG and PROGRES 24
32 Questions Thanks for your attention! Any questions? AGG and PROGRES 25
A Matching Algorithm and AGG Overview
 A Matching Algorithm and AGG Overview Marc Provost McGill University marc.provost@mail.mcgill.ca March 29, 2004 Abstract This presentation go over the basic features of agg for graph rewriting. Typeset
A Matching Algorithm and AGG Overview Marc Provost McGill University marc.provost@mail.mcgill.ca March 29, 2004 Abstract This presentation go over the basic features of agg for graph rewriting. Typeset
AGG: A Graph Transformation Environment for Modeling and Validation of Software
 AGG: A Graph Transformation Environment for Modeling and Validation of Software Gabriele Taentzer Technische Universität Berlin, Germany gabi@cs.tu-berlin.de Abstract. AGG is a general development environment
AGG: A Graph Transformation Environment for Modeling and Validation of Software Gabriele Taentzer Technische Universität Berlin, Germany gabi@cs.tu-berlin.de Abstract. AGG is a general development environment
Graph Programming: Tools and Techniques
 Graph Programming: Tools and Techniques Literature Review Seminar Chris Bak The University of York January 19, 2012 Chris Bak (The University of York) Graph Programming:Tools and Techniques January 19,
Graph Programming: Tools and Techniques Literature Review Seminar Chris Bak The University of York January 19, 2012 Chris Bak (The University of York) Graph Programming:Tools and Techniques January 19,
On the Use of Graph Transformations for Model Refactoring
 On the Use of Graph Transformations for Model Refactoring Tom Mens Service de Génie Logiciel Université de Mons-Hainaut, Belgium tom.mens@umh.ac.be http://w3.umh.ac.be/genlog Abstract. Model-driven software
On the Use of Graph Transformations for Model Refactoring Tom Mens Service de Génie Logiciel Université de Mons-Hainaut, Belgium tom.mens@umh.ac.be http://w3.umh.ac.be/genlog Abstract. Model-driven software
Extending the Groove Control Language with Variables
 Master s Thesis Extending the Groove Control Language with Variables Author: Olaf Keijsers Graduation Committee: Dr. ir. A. Rensink Dr. ir. R. Langerak S. Ciraci, PhD June 2010 University of Twente Faculty
Master s Thesis Extending the Groove Control Language with Variables Author: Olaf Keijsers Graduation Committee: Dr. ir. A. Rensink Dr. ir. R. Langerak S. Ciraci, PhD June 2010 University of Twente Faculty
A Visual Editor for Reconfigurable Object Nets based on the ECLIPSE Graphical Editor Framework
 A Visual Editor for Reconfigurable Object Nets based on the ECLIPSE Graphical Editor Framework Enrico Biermann, Claudia Ermel, Frank Hermann and Tony Modica Technische Universität Berlin, Germany {enrico,lieske,frank,modica}@cs.tu-berlin.de
A Visual Editor for Reconfigurable Object Nets based on the ECLIPSE Graphical Editor Framework Enrico Biermann, Claudia Ermel, Frank Hermann and Tony Modica Technische Universität Berlin, Germany {enrico,lieske,frank,modica}@cs.tu-berlin.de
Editor Manual. Gruppe 3 Christoph Höger, Jonas Hurrelmann, Peggy Sylopp, Sebastian Szczepanski
 Editor Manual Gruppe 3 Christoph Höger, Jonas Hurrelmann, Peggy Sylopp, Sebastian Szczepanski September 5, 2007 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Motivation..................................... 2 1.2 Formal
Editor Manual Gruppe 3 Christoph Höger, Jonas Hurrelmann, Peggy Sylopp, Sebastian Szczepanski September 5, 2007 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Motivation..................................... 2 1.2 Formal
Compilers Project Proposals
 Compilers Project Proposals Dr. D.M. Akbar Hussain These proposals can serve just as a guide line text, it gives you a clear idea about what sort of work you will be doing in your projects. Still need
Compilers Project Proposals Dr. D.M. Akbar Hussain These proposals can serve just as a guide line text, it gives you a clear idea about what sort of work you will be doing in your projects. Still need
Efficient Clustering and Scheduling for Task-Graph based Parallelization
 Center for Information Services and High Performance Computing TU Dresden Efficient Clustering and Scheduling for Task-Graph based Parallelization Marc Hartung 02. February 2015 E-Mail: marc.hartung@tu-dresden.de
Center for Information Services and High Performance Computing TU Dresden Efficient Clustering and Scheduling for Task-Graph based Parallelization Marc Hartung 02. February 2015 E-Mail: marc.hartung@tu-dresden.de
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2018 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp18/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Section 2.2 Define push-down automata informally and formally Trace the computation
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2018 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp18/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Section 2.2 Define push-down automata informally and formally Trace the computation
Correctness and Completeness of Generalised Concurrent Model Synchronisation Based on Triple Graph Grammars
 Correctness and Completeness of Generalised Concurrent Model Synchronisation Based on Triple Graph Grammars Susann Gottmann 1, Frank Hermann 1, Nico Nachtigall 1, Benjamin Braatz 1, Claudia Ermel 2, Hartmut
Correctness and Completeness of Generalised Concurrent Model Synchronisation Based on Triple Graph Grammars Susann Gottmann 1, Frank Hermann 1, Nico Nachtigall 1, Benjamin Braatz 1, Claudia Ermel 2, Hartmut
Incremental Unidirectional Model Transformation via Graph Transformation with emoflon::ibex
 Faculty for Computer Science, Electrical Engineering and Mathematics Department of Computer Science Database and Information Systems Fürstenallee 11, 33102 Paderborn Incremental Unidirectional Model Transformation
Faculty for Computer Science, Electrical Engineering and Mathematics Department of Computer Science Database and Information Systems Fürstenallee 11, 33102 Paderborn Incremental Unidirectional Model Transformation
The Turing Machine. Unsolvable Problems. Undecidability. The Church-Turing Thesis (1936) Decision Problem. Decision Problems
 The Turing Machine Unsolvable Problems Motivating idea Build a theoretical a human computer Likened to a human with a paper and pencil that can solve problems in an algorithmic way The theoretical machine
The Turing Machine Unsolvable Problems Motivating idea Build a theoretical a human computer Likened to a human with a paper and pencil that can solve problems in an algorithmic way The theoretical machine
Programming for Engineers in Python
 Programming for Engineers in Python Lecture 13: Shit Happens Autumn 2011-12 1 Lecture 12: Highlights Dynamic programming Overlapping subproblems Optimal structure Memoization Fibonacci Evaluating trader
Programming for Engineers in Python Lecture 13: Shit Happens Autumn 2011-12 1 Lecture 12: Highlights Dynamic programming Overlapping subproblems Optimal structure Memoization Fibonacci Evaluating trader
Well, you need to capture the notions of atomicity, non-determinism, fairness etc. These concepts are not built into languages like JAVA, C++ etc!
 Hwajung Lee Why do we need these? Don t we already know a lot about programming? Well, you need to capture the notions of atomicity, non-determinism, fairness etc. These concepts are not built into languages
Hwajung Lee Why do we need these? Don t we already know a lot about programming? Well, you need to capture the notions of atomicity, non-determinism, fairness etc. These concepts are not built into languages
Autotuning. John Cavazos. University of Delaware UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE COMPUTER & INFORMATION SCIENCES DEPARTMENT
 Autotuning John Cavazos University of Delaware What is Autotuning? Searching for the best code parameters, code transformations, system configuration settings, etc. Search can be Quasi-intelligent: genetic
Autotuning John Cavazos University of Delaware What is Autotuning? Searching for the best code parameters, code transformations, system configuration settings, etc. Search can be Quasi-intelligent: genetic
Model Transformation by Graph Transformation: A Comparative Study
 Model Transformation by Graph Transformation: A Comparative Study Karsten Ehrig 1, Esther Guerra 2, Juan de Lara 3, Laszlo Lengyel 4, Tihamer Levendovszky 4, Ulrike Prange 1, Gabriele Taentzer 1, Daniel
Model Transformation by Graph Transformation: A Comparative Study Karsten Ehrig 1, Esther Guerra 2, Juan de Lara 3, Laszlo Lengyel 4, Tihamer Levendovszky 4, Ulrike Prange 1, Gabriele Taentzer 1, Daniel
Recursive Search with Backtracking
 CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Friday, October 2, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005 2009 Glenn G.
CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Friday, October 2, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005 2009 Glenn G.
Minion: Fast, Scalable Constraint Solving. Ian Gent, Chris Jefferson, Ian Miguel
 Minion: Fast, Scalable Constraint Solving Ian Gent, Chris Jefferson, Ian Miguel 1 60 Second Introduction to CSPs Standard Definition A CSP is a tuple V: list of variables D: a domain for each
Minion: Fast, Scalable Constraint Solving Ian Gent, Chris Jefferson, Ian Miguel 1 60 Second Introduction to CSPs Standard Definition A CSP is a tuple V: list of variables D: a domain for each
G Programming Languages - Fall 2012
 G22.2110-003 Programming Languages - Fall 2012 Lecture 4 Thomas Wies New York University Review Last week Control Structures Selection Loops Adding Invariants Outline Subprograms Calling Sequences Parameter
G22.2110-003 Programming Languages - Fall 2012 Lecture 4 Thomas Wies New York University Review Last week Control Structures Selection Loops Adding Invariants Outline Subprograms Calling Sequences Parameter
IBM Labs in Haifa. Overview of Core Technology. Eitan Marcus
 IBM Labs in Haifa Overview of Core Technology Eitan Marcus marcus@il.ibm.com Core Technology: Why, What, Who Develop and enhance SBVT s common infrastructure to support the development of hardware verification
IBM Labs in Haifa Overview of Core Technology Eitan Marcus marcus@il.ibm.com Core Technology: Why, What, Who Develop and enhance SBVT s common infrastructure to support the development of hardware verification
Chapter 11, Testing. Using UML, Patterns, and Java. Object-Oriented Software Engineering
 Chapter 11, Testing Using UML, Patterns, and Java Object-Oriented Software Engineering Outline Terminology Types of errors Dealing with errors Quality assurance vs Testing Component Testing! Unit testing!
Chapter 11, Testing Using UML, Patterns, and Java Object-Oriented Software Engineering Outline Terminology Types of errors Dealing with errors Quality assurance vs Testing Component Testing! Unit testing!
APCS Semester #1 Final Exam Practice Problems
 Name: Date: Per: AP Computer Science, Mr. Ferraro APCS Semester #1 Final Exam Practice Problems The problems here are to get you thinking about topics we ve visited thus far in preparation for the semester
Name: Date: Per: AP Computer Science, Mr. Ferraro APCS Semester #1 Final Exam Practice Problems The problems here are to get you thinking about topics we ve visited thus far in preparation for the semester
Parsing II Top-down parsing. Comp 412
 COMP 412 FALL 2018 Parsing II Top-down parsing Comp 412 source code IR Front End Optimizer Back End IR target code Copyright 2018, Keith D. Cooper & Linda Torczon, all rights reserved. Students enrolled
COMP 412 FALL 2018 Parsing II Top-down parsing Comp 412 source code IR Front End Optimizer Back End IR target code Copyright 2018, Keith D. Cooper & Linda Torczon, all rights reserved. Students enrolled
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp17/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2, 3.1 State and use the Church-Turing thesis. Describe several variants of Turing
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp17/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2, 3.1 State and use the Church-Turing thesis. Describe several variants of Turing
CS61C Machine Structures. Lecture 3 Introduction to the C Programming Language. 1/23/2006 John Wawrzynek. www-inst.eecs.berkeley.
 CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to the C Programming Language 1/23/2006 John Wawrzynek (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~johnw) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ CS 61C L03 Introduction to C (1) Administrivia
CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to the C Programming Language 1/23/2006 John Wawrzynek (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~johnw) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ CS 61C L03 Introduction to C (1) Administrivia
Torben./Egidius Mogensen. Introduction. to Compiler Design. ^ Springer
 Torben./Egidius Mogensen Introduction to Compiler Design ^ Springer Contents 1 Lexical Analysis 1 1.1 Regular Expressions 2 1.1.1 Shorthands 4 1.1.2 Examples 5 1.2 Nondeterministic Finite Automata 6 1.3
Torben./Egidius Mogensen Introduction to Compiler Design ^ Springer Contents 1 Lexical Analysis 1 1.1 Regular Expressions 2 1.1.1 Shorthands 4 1.1.2 Examples 5 1.2 Nondeterministic Finite Automata 6 1.3
Simply-Typed Lambda Calculus
 #1 Simply-Typed Lambda Calculus #2 Back to School What is operational semantics? When would you use contextual (small-step) semantics? What is denotational semantics? What is axiomatic semantics? What
#1 Simply-Typed Lambda Calculus #2 Back to School What is operational semantics? When would you use contextual (small-step) semantics? What is denotational semantics? What is axiomatic semantics? What
Formal Languages and Grammars. Chapter 2: Sections 2.1 and 2.2
 Formal Languages and Grammars Chapter 2: Sections 2.1 and 2.2 Formal Languages Basis for the design and implementation of programming languages Alphabet: finite set Σ of symbols String: finite sequence
Formal Languages and Grammars Chapter 2: Sections 2.1 and 2.2 Formal Languages Basis for the design and implementation of programming languages Alphabet: finite set Σ of symbols String: finite sequence
CS 390 Chapter 2 Homework Solutions
 CS 390 Chapter 2 Homework Solutions 2.1 What is the purpose of... System calls are used by user-level programs to request a service from the operating system. 2.5 What is the purpose of... The purpose
CS 390 Chapter 2 Homework Solutions 2.1 What is the purpose of... System calls are used by user-level programs to request a service from the operating system. 2.5 What is the purpose of... The purpose
CPSC 3740 Programming Languages University of Lethbridge. Control Structures
 Control Structures A control structure is a control statement and the collection of statements whose execution it controls. Common controls: selection iteration branching Control Structures 1 15 Howard
Control Structures A control structure is a control statement and the collection of statements whose execution it controls. Common controls: selection iteration branching Control Structures 1 15 Howard
Patterns for polymorphic operations
 Patterns for polymorphic operations Three small object structural patterns for dealing with polymorphism Alexander A. Horoshilov hor@epsylontech.com Abstract Polymorphism is one of the main elements of
Patterns for polymorphic operations Three small object structural patterns for dealing with polymorphism Alexander A. Horoshilov hor@epsylontech.com Abstract Polymorphism is one of the main elements of
Static Program Analysis
 Static Program Analysis Thomas Noll Software Modeling and Verification Group RWTH Aachen University https://moves.rwth-aachen.de/teaching/ws-1617/spa/ Recap: Taking Conditional Branches into Account Extending
Static Program Analysis Thomas Noll Software Modeling and Verification Group RWTH Aachen University https://moves.rwth-aachen.de/teaching/ws-1617/spa/ Recap: Taking Conditional Branches into Account Extending
Why are there so many programming languages? Why do we have programming languages? What is a language for? What makes a language successful?
 Chapter 1 :: Introduction Introduction Programming Language Pragmatics Michael L. Scott Why are there so many programming languages? evolution -- we've learned better ways of doing things over time socio-economic
Chapter 1 :: Introduction Introduction Programming Language Pragmatics Michael L. Scott Why are there so many programming languages? evolution -- we've learned better ways of doing things over time socio-economic
Dynamic Constraint Models for Planning and Scheduling Problems
 Dynamic Constraint Models for Planning and Scheduling Problems Roman Barták * Charles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Department of Theoretical Computer Science, Malostranske namesti 2/25,
Dynamic Constraint Models for Planning and Scheduling Problems Roman Barták * Charles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Department of Theoretical Computer Science, Malostranske namesti 2/25,
Project Compiler. CS031 TA Help Session November 28, 2011
 Project Compiler CS031 TA Help Session November 28, 2011 Motivation Generally, it s easier to program in higher-level languages than in assembly. Our goal is to automate the conversion from a higher-level
Project Compiler CS031 TA Help Session November 28, 2011 Motivation Generally, it s easier to program in higher-level languages than in assembly. Our goal is to automate the conversion from a higher-level
versat: A Verified Modern SAT Solver
 Computer Science, The University of Iowa, USA Satisfiability Problem (SAT) Is there a model for the given propositional formula? Model: assignments to the variables that makes the formula true. SAT if
Computer Science, The University of Iowa, USA Satisfiability Problem (SAT) Is there a model for the given propositional formula? Model: assignments to the variables that makes the formula true. SAT if
Department of Computer Science
 Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks Application Development for Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing LunchBox Final Presentation Group 12 Dana Henkens
Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks Application Development for Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing LunchBox Final Presentation Group 12 Dana Henkens
Computer Organization & Assembly Language Programming
 Computer Organization & Assembly Language Programming CSE 2312 Lecture 11 Introduction of Assembly Language 1 Assembly Language Translation The Assembly Language layer is implemented by translation rather
Computer Organization & Assembly Language Programming CSE 2312 Lecture 11 Introduction of Assembly Language 1 Assembly Language Translation The Assembly Language layer is implemented by translation rather
On the Recognizability of Arrow and Graph Languages
 On the Recognizability of Arrow and Graph Languages Christoph Blume Sander Bruggink Barbara König Universität Duisburg-Essen, Germany Background Applications of finite automata and regular (word) languages
On the Recognizability of Arrow and Graph Languages Christoph Blume Sander Bruggink Barbara König Universität Duisburg-Essen, Germany Background Applications of finite automata and regular (word) languages
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computation. Lecture #1: Things, Sets and Strings David Mix Barrington 22 January 2014
 CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computation Lecture #1: Things, Sets and Strings David Mix Barrington 22 January 2014 Things, Sets, and Strings The Mathematical Method Administrative Stuff The Objects of Mathematics
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computation Lecture #1: Things, Sets and Strings David Mix Barrington 22 January 2014 Things, Sets, and Strings The Mathematical Method Administrative Stuff The Objects of Mathematics
2nd Belgian-Dutch workshop on Software Evolution
 2nd Belgian-Dutch workshop on Software Evolution BENEVOL 2004 8-9 July 2004 University of Antwerp Belgium Problem statement More and better tool support needed for software evolution traceability management
2nd Belgian-Dutch workshop on Software Evolution BENEVOL 2004 8-9 July 2004 University of Antwerp Belgium Problem statement More and better tool support needed for software evolution traceability management
CS 415 Midterm Exam Spring 2002
 CS 415 Midterm Exam Spring 2002 Name KEY Email Address Student ID # Pledge: This exam is closed note, closed book. Good Luck! Score Fortran Algol 60 Compilation Names, Bindings, Scope Functional Programming
CS 415 Midterm Exam Spring 2002 Name KEY Email Address Student ID # Pledge: This exam is closed note, closed book. Good Luck! Score Fortran Algol 60 Compilation Names, Bindings, Scope Functional Programming
CS 242. Fundamentals. Reading: See last slide
 CS 242 Fundamentals Reading: See last slide Syntax and Semantics of Programs Syntax The symbols used to write a program Semantics The actions that occur when a program is executed Programming language
CS 242 Fundamentals Reading: See last slide Syntax and Semantics of Programs Syntax The symbols used to write a program Semantics The actions that occur when a program is executed Programming language
The SPIN Model Checker
 The SPIN Model Checker Metodi di Verifica del Software Andrea Corradini Lezione 1 2013 Slides liberamente adattate da Logic Model Checking, per gentile concessione di Gerard J. Holzmann http://spinroot.com/spin/doc/course/
The SPIN Model Checker Metodi di Verifica del Software Andrea Corradini Lezione 1 2013 Slides liberamente adattate da Logic Model Checking, per gentile concessione di Gerard J. Holzmann http://spinroot.com/spin/doc/course/
Towards Generating Domain-Specific Model Editors with Complex Editing Commands
 Towards Generating Domain-Specific Model Editors with Complex Editing Commands Gabriele Taentzer Technical University of Berlin Germany gabi@cs.tu-berlin.de May 10, 2006 Abstract Domain specific modeling
Towards Generating Domain-Specific Model Editors with Complex Editing Commands Gabriele Taentzer Technical University of Berlin Germany gabi@cs.tu-berlin.de May 10, 2006 Abstract Domain specific modeling
Parallel Rewriting of Graphs through the. Pullback Approach. Michel Bauderon 1. Laboratoire Bordelais de Recherche en Informatique
 URL: http://www.elsevier.nl/locate/entcs/volume.html 8 pages Parallel Rewriting of Graphs through the Pullback Approach Michel Bauderon Laboratoire Bordelais de Recherche en Informatique Universite Bordeaux
URL: http://www.elsevier.nl/locate/entcs/volume.html 8 pages Parallel Rewriting of Graphs through the Pullback Approach Michel Bauderon Laboratoire Bordelais de Recherche en Informatique Universite Bordeaux
Motivation: Model-driven. driven Engineering. Semantics of Model Transformation. Reiko Heckel University of Leicester, UK
 Semantics of Model Transformation Reiko Heckel University of Leicester, UK, University of Birmingham, 1 March 2007 Motivation: Model-driven driven Engineering Focus and primary artifacts are models instead
Semantics of Model Transformation Reiko Heckel University of Leicester, UK, University of Birmingham, 1 March 2007 Motivation: Model-driven driven Engineering Focus and primary artifacts are models instead
General Overview of Mozart/Oz
 General Overview of Mozart/Oz Peter Van Roy pvr@info.ucl.ac.be 2004 P. Van Roy, MOZ 2004 General Overview 1 At a Glance Oz language Dataflow concurrent, compositional, state-aware, object-oriented language
General Overview of Mozart/Oz Peter Van Roy pvr@info.ucl.ac.be 2004 P. Van Roy, MOZ 2004 General Overview 1 At a Glance Oz language Dataflow concurrent, compositional, state-aware, object-oriented language
Europe on a Disk Geodata Processing with Eclipse and OSGi. Harald Wellmann 10 Nov 2008
 Europe on a Disk Geodata Processing with Eclipse and OSGi Harald Wellmann 10 Nov 2008 Overview Past and Present of Navigation Data Processing Anaconda: The Future Our usage of OSGi and Eclipse 2008 Harman
Europe on a Disk Geodata Processing with Eclipse and OSGi Harald Wellmann 10 Nov 2008 Overview Past and Present of Navigation Data Processing Anaconda: The Future Our usage of OSGi and Eclipse 2008 Harman
Undergraduate Compilers in a Day
 Question of the Day Backpatching o.foo(); In Java, the address of foo() is often not known until runtime (due to dynamic class loading), so the method call requires a table lookup. After the first execution
Question of the Day Backpatching o.foo(); In Java, the address of foo() is often not known until runtime (due to dynamic class loading), so the method call requires a table lookup. After the first execution
Modelica3D. Platform Independent Simulation Visualization. Christoph Höger. Technische Universität Berlin Fraunhofer FIRST
 Modelica3D Platform Independent Simulation Visualization Christoph Höger Technische Universität Berlin Fraunhofer FIRST c Fraunhofer FIRST/TU Berlin 6. Februar 2012 Motivation - Goal Dymola MultiBody Visualization
Modelica3D Platform Independent Simulation Visualization Christoph Höger Technische Universität Berlin Fraunhofer FIRST c Fraunhofer FIRST/TU Berlin 6. Februar 2012 Motivation - Goal Dymola MultiBody Visualization
COMPUTING SCIENCE 3Z: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES 3
 Tuesday, 28 May 2009 2.00 pm 3.30 pm (Duration: 1 hour 30 minutes) DEGREES OF MSci, MEng, BEng, BSc, MA and MA (Social Sciences) COMPUTING SCIENCE 3Z: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES 3 Answer all 4 questions. This
Tuesday, 28 May 2009 2.00 pm 3.30 pm (Duration: 1 hour 30 minutes) DEGREES OF MSci, MEng, BEng, BSc, MA and MA (Social Sciences) COMPUTING SCIENCE 3Z: PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES 3 Answer all 4 questions. This
Legacy Metamorphosis. By Charles Finley, Transformix Computer Corporation
 Legacy Metamorphosis By Charles Finley, Transformix Computer Corporation Legacy Metamorphosis By Charles Finley, Transformix Computer Corporation Introduction A legacy application is any application based
Legacy Metamorphosis By Charles Finley, Transformix Computer Corporation Legacy Metamorphosis By Charles Finley, Transformix Computer Corporation Introduction A legacy application is any application based
Lecture 11 Usability of Graphical User Interfaces
 MAS dr. Inż. Mariusz Trzaska Lecture 11 Usability of Graphical User Interfaces Outline o An introduction o The usability o Usability formation o Usability tests o Usability and business o GUI checklist
MAS dr. Inż. Mariusz Trzaska Lecture 11 Usability of Graphical User Interfaces Outline o An introduction o The usability o Usability formation o Usability tests o Usability and business o GUI checklist
TYPE INFERENCE. François Pottier. The Programming Languages Mentoring ICFP August 30, 2015
 TYPE INFERENCE François Pottier The Programming Languages Mentoring Workshop @ ICFP August 30, 2015 What is type inference? What is the type of this OCaml function? let f verbose msg = if verbose then
TYPE INFERENCE François Pottier The Programming Languages Mentoring Workshop @ ICFP August 30, 2015 What is type inference? What is the type of this OCaml function? let f verbose msg = if verbose then
HCI in the software process
 chapter 6 HCI in the software process HCI in the software process Software engineering and the process for interactive systems Usability engineering Iterative and prototyping Design rationale the software
chapter 6 HCI in the software process HCI in the software process Software engineering and the process for interactive systems Usability engineering Iterative and prototyping Design rationale the software
HCI in the software. chapter 6. HCI in the software process. The waterfall model. the software lifecycle
 HCI in the software process chapter 6 HCI in the software process Software engineering and the process for interactive systems Usability engineering Iterative and prototyping Design rationale the software
HCI in the software process chapter 6 HCI in the software process Software engineering and the process for interactive systems Usability engineering Iterative and prototyping Design rationale the software
Formal specification in Event-B
 2IW80 Software specification and architecture Formal specification in Event-B Alexander Serebrenik, Ulyana Tikhonova Outline Introduction into formal specification Mathematical notation of Event-B Event-B
2IW80 Software specification and architecture Formal specification in Event-B Alexander Serebrenik, Ulyana Tikhonova Outline Introduction into formal specification Mathematical notation of Event-B Event-B
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011
 Announcements Project 1: Search is due next week Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Piazza: check it out if you haven t CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 4: Constraint Satisfaction 9/6/2011
Announcements Project 1: Search is due next week Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Piazza: check it out if you haven t CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 4: Constraint Satisfaction 9/6/2011
Tiger EMF Model Transformation Framework (EMT)
 Tiger EMF Model Transformation Framework (EMT) Version 1.2.0 User Manual TU Berlin EMT Project Team: Enrico Biermann, Karsten Ehrig, Claudia Ermel, Christian Köhler, Günter Kuhns, Gabi Taentzer Email:
Tiger EMF Model Transformation Framework (EMT) Version 1.2.0 User Manual TU Berlin EMT Project Team: Enrico Biermann, Karsten Ehrig, Claudia Ermel, Christian Köhler, Günter Kuhns, Gabi Taentzer Email:
Human Computer Interaction Lecture 14. HCI in Software Process. HCI in the software process
 Human Computer Interaction Lecture 14 HCI in Software Process HCI in the software process Software engineering and the design process for interactive systems Usability engineering Iterative design and
Human Computer Interaction Lecture 14 HCI in Software Process HCI in the software process Software engineering and the design process for interactive systems Usability engineering Iterative design and
The York Abstract Machine
 Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science 211 (2008) 231 240 www.elsevier.com/locate/entcs The York Abstract Machine Greg Manning 1 Detlef Plump 2 Department of Computer Science The University of
Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science 211 (2008) 231 240 www.elsevier.com/locate/entcs The York Abstract Machine Greg Manning 1 Detlef Plump 2 Department of Computer Science The University of
DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence. Peter Ljunglöf. 30 January, 2018
 DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Chapter 7: Constraint satisfaction problems CHAPTER 7: CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Peter Ljunglöf 30 January, 2018 1 TABLE
DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Chapter 7: Constraint satisfaction problems CHAPTER 7: CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION PROBLEMS DIT411/TIN175, Artificial Intelligence Peter Ljunglöf 30 January, 2018 1 TABLE
Constraint Programming
 Constraint In Pursuit of The Holly Grail Roman Barták Charles University in Prague Constraint programming represents one of the closest approaches computer science has yet made to the Holy Grail of programming:
Constraint In Pursuit of The Holly Grail Roman Barták Charles University in Prague Constraint programming represents one of the closest approaches computer science has yet made to the Holy Grail of programming:
SAT Solvers. Ranjit Jhala, UC San Diego. April 9, 2013
 SAT Solvers Ranjit Jhala, UC San Diego April 9, 2013 Decision Procedures We will look very closely at the following 1. Propositional Logic 2. Theory of Equality 3. Theory of Uninterpreted Functions 4.
SAT Solvers Ranjit Jhala, UC San Diego April 9, 2013 Decision Procedures We will look very closely at the following 1. Propositional Logic 2. Theory of Equality 3. Theory of Uninterpreted Functions 4.
A Formal Resolution Strategy for Operation-Based Conflicts in Model Versioning Using Graph Modifications
 A Formal Resolution Strategy for Operation-Based Conflicts in Model Versioning Using Graph Modifications Hartmut Ehrig 1, Claudia Ermel 1 and Gabriele Taentzer 2 1 Technische Universität Berlin, Germany
A Formal Resolution Strategy for Operation-Based Conflicts in Model Versioning Using Graph Modifications Hartmut Ehrig 1, Claudia Ermel 1 and Gabriele Taentzer 2 1 Technische Universität Berlin, Germany
Intro to semantics; Small-step semantics Lecture 1 Tuesday, January 29, 2013
 Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences CS 152: Programming Languages Lecture 1 Tuesday, January 29, 2013 1 Intro to semantics What is the meaning of a program? When we write a program, we use
Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences CS 152: Programming Languages Lecture 1 Tuesday, January 29, 2013 1 Intro to semantics What is the meaning of a program? When we write a program, we use
Artificial Intelligence
 Torralba and Wahlster Artificial Intelligence Chapter 8: Constraint Satisfaction Problems, Part I 1/48 Artificial Intelligence 8. CSP, Part I: Basics, and Naïve Search What to Do When Your Problem is to
Torralba and Wahlster Artificial Intelligence Chapter 8: Constraint Satisfaction Problems, Part I 1/48 Artificial Intelligence 8. CSP, Part I: Basics, and Naïve Search What to Do When Your Problem is to
G Programming Languages Spring 2010 Lecture 4. Robert Grimm, New York University
 G22.2110-001 Programming Languages Spring 2010 Lecture 4 Robert Grimm, New York University 1 Review Last week Control Structures Selection Loops 2 Outline Subprograms Calling Sequences Parameter Passing
G22.2110-001 Programming Languages Spring 2010 Lecture 4 Robert Grimm, New York University 1 Review Last week Control Structures Selection Loops 2 Outline Subprograms Calling Sequences Parameter Passing
GP 2: Efficient Implementation of a Graph Programming Language
 GP : Efficient Implementation of a Graph Programming Language Christopher Bak Doctor of Philosophy University of York Computer Science September 05 Abstract The graph programming language GP (Graph Programs)
GP : Efficient Implementation of a Graph Programming Language Christopher Bak Doctor of Philosophy University of York Computer Science September 05 Abstract The graph programming language GP (Graph Programs)
Human Computer Interaction Lecture 06 [ HCI in Software Process ] HCI in the software process
![Human Computer Interaction Lecture 06 [ HCI in Software Process ] HCI in the software process Human Computer Interaction Lecture 06 [ HCI in Software Process ] HCI in the software process](/thumbs/81/84565251.jpg) Human Computer Interaction Lecture 06 [ HCI in Software Process ] Imran Ihsan Assistant Professor www.imranihsan.com aucs.imranihsan.com HCI06 - HCI in Software Process 1 HCI in the software process Software
Human Computer Interaction Lecture 06 [ HCI in Software Process ] Imran Ihsan Assistant Professor www.imranihsan.com aucs.imranihsan.com HCI06 - HCI in Software Process 1 HCI in the software process Software
9/21/17. Outline. Expression Evaluation and Control Flow. Arithmetic Expressions. Operators. Operators. Notation & Placement
 Outline Expression Evaluation and Control Flow In Text: Chapter 6 Notation Operator evaluation order Operand evaluation order Overloaded operators Type conversions Short-circuit evaluation of conditions
Outline Expression Evaluation and Control Flow In Text: Chapter 6 Notation Operator evaluation order Operand evaluation order Overloaded operators Type conversions Short-circuit evaluation of conditions
COMP 410 Lecture 1. Kyle Dewey
 COMP 410 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey About Me I research automated testing techniques and their intersection with CS education My dissertation used logic programming extensively This is my second semester at
COMP 410 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey About Me I research automated testing techniques and their intersection with CS education My dissertation used logic programming extensively This is my second semester at
An Extension to the Foundation Fieldbus Model for Specifying Process Control Strategies
 An Extension to the Foundation Fieldbus Model for Specifying Process Control Strategies EE382C: Embedded Software Systems, Spring 1999 Prof. Brian L. Evans Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
An Extension to the Foundation Fieldbus Model for Specifying Process Control Strategies EE382C: Embedded Software Systems, Spring 1999 Prof. Brian L. Evans Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Deterministic Parallel Programming
 Deterministic Parallel Programming Concepts and Practices 04/2011 1 How hard is parallel programming What s the result of this program? What is data race? Should data races be allowed? Initially x = 0
Deterministic Parallel Programming Concepts and Practices 04/2011 1 How hard is parallel programming What s the result of this program? What is data race? Should data races be allowed? Initially x = 0
challenges in domain-specific modeling raphaël mannadiar august 27, 2009
 challenges in domain-specific modeling raphaël mannadiar august 27, 2009 raphaël mannadiar challenges in domain-specific modeling 1/59 outline 1 introduction 2 approaches 3 debugging and simulation 4 differencing
challenges in domain-specific modeling raphaël mannadiar august 27, 2009 raphaël mannadiar challenges in domain-specific modeling 1/59 outline 1 introduction 2 approaches 3 debugging and simulation 4 differencing
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to the C Programming Language (pt 1)!!Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia!!!www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia CS61C L03 Introduction to C
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to the C Programming Language (pt 1)!!Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia!!!www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia CS61C L03 Introduction to C
The design of a programming language for provably correct programs: success and failure
 The design of a programming language for provably correct programs: success and failure Don Sannella Laboratory for Foundations of Computer Science School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/dts
The design of a programming language for provably correct programs: success and failure Don Sannella Laboratory for Foundations of Computer Science School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/dts
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010
 Announcements Project 1: Search is due Monday Looking for partners? After class or newsgroup Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Newsgroup: check it out CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010 Lecture
Announcements Project 1: Search is due Monday Looking for partners? After class or newsgroup Written 1: Search and CSPs out soon Newsgroup: check it out CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010 Lecture
Midwest Verification Day 2011
 Midwest Verification Day 2011 Analysis of CPS Control Systems Jason Biatek, University of Minnesota Rewriting approach to type assignment Peng Fu, University of Iowa In the paper "type preservation as
Midwest Verification Day 2011 Analysis of CPS Control Systems Jason Biatek, University of Minnesota Rewriting approach to type assignment Peng Fu, University of Iowa In the paper "type preservation as
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
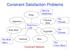 Constraint Satisfaction Problems Soup Must be Hot&Sour Appetizer Pork Dish Total Cost < $30 Chicken Dish Vegetable No Peanuts No Peanuts Not Both Spicy Seafood Rice Constraint Network Not Chow Mein 1 Formal
Constraint Satisfaction Problems Soup Must be Hot&Sour Appetizer Pork Dish Total Cost < $30 Chicken Dish Vegetable No Peanuts No Peanuts Not Both Spicy Seafood Rice Constraint Network Not Chow Mein 1 Formal
Everything is an object. Almost, but all objects are of type Object!
 Everything is an object Almost, but all objects are of type Object! In Java, every class is actually a subclass of Object...or has a superclass which has Object as superclass... There is a class called
Everything is an object Almost, but all objects are of type Object! In Java, every class is actually a subclass of Object...or has a superclass which has Object as superclass... There is a class called
Web-based system for learning of communication protocols
 38 Web-based system for learning of communication protocols Dan Komosny Brno University of Technology, Czech Republic Summary The paper introduces a new web-based system that provides on-line access to
38 Web-based system for learning of communication protocols Dan Komosny Brno University of Technology, Czech Republic Summary The paper introduces a new web-based system that provides on-line access to
CS 3304 Comparative Languages. Lecture 1: Introduction
 CS 3304 Comparative Languages Lecture 1: Introduction 17 January 2012 2012 Denis Gracanin Course Overview 2 Welcome What this course is about? What this course is not about? What will you learn? How will
CS 3304 Comparative Languages Lecture 1: Introduction 17 January 2012 2012 Denis Gracanin Course Overview 2 Welcome What this course is about? What this course is not about? What will you learn? How will
What are some common categories of system calls? What are common ways of structuring an OS? What are the principles behind OS design and
 What are the services provided by an OS? What are system calls? What are some common categories of system calls? What are the principles behind OS design and implementation? What are common ways of structuring
What are the services provided by an OS? What are system calls? What are some common categories of system calls? What are the principles behind OS design and implementation? What are common ways of structuring
Execution Architecture
 Execution Architecture Software Architecture VO (706.706) Roman Kern Institute for Interactive Systems and Data Science, TU Graz 2018-11-07 Roman Kern (ISDS, TU Graz) Execution Architecture 2018-11-07
Execution Architecture Software Architecture VO (706.706) Roman Kern Institute for Interactive Systems and Data Science, TU Graz 2018-11-07 Roman Kern (ISDS, TU Graz) Execution Architecture 2018-11-07
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. What is Search For? Constraint Satisfaction Problems. Constraint Satisfaction Problems
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems N variables domain D constraints x 1 x 2 Instructor: Marco Alvarez University of Rhode Island (These slides
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Constraint Satisfaction Problems Constraint Satisfaction Problems N variables domain D constraints x 1 x 2 Instructor: Marco Alvarez University of Rhode Island (These slides
Behavior Preservation in Model Refactoring using DPO Transformations with Borrowed Contexts
 Behavior Preservation in Model Refactoring using DPO Transformations with Borrowed Contexts Guilherme Rangel 1, Leen Lambers 1, Barbara König 2, Hartmut Ehrig 1, and Paolo Baldan 3 1 Institut für Softwaretechnik
Behavior Preservation in Model Refactoring using DPO Transformations with Borrowed Contexts Guilherme Rangel 1, Leen Lambers 1, Barbara König 2, Hartmut Ehrig 1, and Paolo Baldan 3 1 Institut für Softwaretechnik
3D Building Information Efficiently Acquired and Managed
 Technische Universität Berlin Department Chair of of Engineering Surveying and and Adjustment Techniques 3D Building Information Efficiently Acquired and Managed Lothar Gründig, Christian Clemen Chair
Technische Universität Berlin Department Chair of of Engineering Surveying and and Adjustment Techniques 3D Building Information Efficiently Acquired and Managed Lothar Gründig, Christian Clemen Chair
Decomposable Constraints
 Decomposable Constraints Ian Gent 1, Kostas Stergiou 2, and Toby Walsh 3 1 University of St Andrews, St Andrews, Scotland. ipg@dcs.st-and.ac.uk 2 University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, Scotland. ks@cs.strath.ac.uk
Decomposable Constraints Ian Gent 1, Kostas Stergiou 2, and Toby Walsh 3 1 University of St Andrews, St Andrews, Scotland. ipg@dcs.st-and.ac.uk 2 University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, Scotland. ks@cs.strath.ac.uk
Parsing. Note by Baris Aktemur: Our slides are adapted from Cooper and Torczon s slides that they prepared for COMP 412 at Rice.
 Parsing Note by Baris Aktemur: Our slides are adapted from Cooper and Torczon s slides that they prepared for COMP 412 at Rice. Copyright 2010, Keith D. Cooper & Linda Torczon, all rights reserved. Students
Parsing Note by Baris Aktemur: Our slides are adapted from Cooper and Torczon s slides that they prepared for COMP 412 at Rice. Copyright 2010, Keith D. Cooper & Linda Torczon, all rights reserved. Students
Today s class. Operating System Machine Level. Informationsteknologi. Friday, November 16, 2007 Computer Architecture I - Class 12 1
 Today s class Operating System Machine Level Friday, November 16, 2007 Computer Architecture I - Class 12 1 Operating System Machine Friday, November 16, 2007 Computer Architecture I - Class 12 2 Paging
Today s class Operating System Machine Level Friday, November 16, 2007 Computer Architecture I - Class 12 1 Operating System Machine Friday, November 16, 2007 Computer Architecture I - Class 12 2 Paging
Java Swing Introduction
 Course Name: Advanced Java Lecture 18 Topics to be covered Java Swing Introduction What is Java Swing? Part of the Java Foundation Classes (JFC) Provides a rich set of GUI components Used to create a Java
Course Name: Advanced Java Lecture 18 Topics to be covered Java Swing Introduction What is Java Swing? Part of the Java Foundation Classes (JFC) Provides a rich set of GUI components Used to create a Java
Compiler Construction Lecture 1: Introduction Summer Semester 2017 Thomas Noll Software Modeling and Verification Group RWTH Aachen University
 Compiler Construction Thomas Noll Software Modeling and Verification Group RWTH Aachen University https://moves.rwth-aachen.de/teaching/ss-17/cc/ Preliminaries People Lectures: Thomas Noll (noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de)
Compiler Construction Thomas Noll Software Modeling and Verification Group RWTH Aachen University https://moves.rwth-aachen.de/teaching/ss-17/cc/ Preliminaries People Lectures: Thomas Noll (noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de)
A Case For. Binary Component Adaptation. Motivation. The Integration Problem. Talk Outline. Using Wrapper Classes. The Interface Evolution Problem
 Case For inary Modifying s On The Fly Urs Hölzle and Ralph Keller Department of Computer Science University of California, Santa arbara http://www.cs.ucsb.edu/oocsb/bca Motivation OOP vision: Pervasive
Case For inary Modifying s On The Fly Urs Hölzle and Ralph Keller Department of Computer Science University of California, Santa arbara http://www.cs.ucsb.edu/oocsb/bca Motivation OOP vision: Pervasive
A New Algorithm for Singleton Arc Consistency
 A New Algorithm for Singleton Arc Consistency Roman Barták, Radek Erben Charles University, Institute for Theoretical Computer Science Malostranské nám. 2/25, 118 Praha 1, Czech Republic bartak@kti.mff.cuni.cz,
A New Algorithm for Singleton Arc Consistency Roman Barták, Radek Erben Charles University, Institute for Theoretical Computer Science Malostranské nám. 2/25, 118 Praha 1, Czech Republic bartak@kti.mff.cuni.cz,
CMPT Data and Program Organization
 CMPT-201 - Data and Program Organization Professor: Bill Havens Office: APSC-10828 Lectures: MWF 2:30pm - 3:20pm Venue: C-9002 WWW: http://www.cs.sfu.ca/coursecentral/201 Office Hours: Monday @3:30pm January
CMPT-201 - Data and Program Organization Professor: Bill Havens Office: APSC-10828 Lectures: MWF 2:30pm - 3:20pm Venue: C-9002 WWW: http://www.cs.sfu.ca/coursecentral/201 Office Hours: Monday @3:30pm January
MERGESORT & QUICKSORT cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015
 MERGESORT & QUICKSORT cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 4 due tonight at midnight -assignment 5 is out -midterm next Tuesday 3 last time 4
MERGESORT & QUICKSORT cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 4 due tonight at midnight -assignment 5 is out -midterm next Tuesday 3 last time 4
Algebraic Properties of CSP Model Operators? Y.C. Law and J.H.M. Lee. The Chinese University of Hong Kong.
 Algebraic Properties of CSP Model Operators? Y.C. Law and J.H.M. Lee Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong Shatin, N.T., Hong Kong SAR, China fyclaw,jleeg@cse.cuhk.edu.hk
Algebraic Properties of CSP Model Operators? Y.C. Law and J.H.M. Lee Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong Shatin, N.T., Hong Kong SAR, China fyclaw,jleeg@cse.cuhk.edu.hk
