Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) What is EIGRP? Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
|
|
|
- Spencer Pitts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) What is EIGRP? Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol Successor to Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) Cisco proprietary hybrid protocol Both istance Vector and Link State Behavior Really Advanced istance Vector Classless protocol Supports VLSM and summarization
2 Why Use EIGRP? Guarantees loop-free topology iffusing Update Algorithm (UAL) Fast convergence Fastest of all IGP in certain designs Reliable & Efficient Updating Forms active neighbor adjacencies Guarantees packet delivery with Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP) Supports partial updates Not all neighbors need all routes Why Use EIGRP? (cont.) Multiple routed protocol support IPv4, IPX, & Appletalk Legacy now, but originally important in nonconverged networks Granular Metric Hybrid metric derived from multiple factors Unequal Cost Load Balancing Only IGP that supports true load distribution Control Plane Security Supports M5 based authentication
3 How EIGRP Works Step 1 - iscover EIGRP Neighbors Step 2 - Exchange Topology Information Step 3 - Choose Best Path via UAL Step 4 - Neighbor and Topology Table Maintenance Step 1 - iscovering EIGRP Neighbors EIGRP uses multicast HELLO packets to discover neighbors on EIGRP enabled attached links Transport via IP protocol 88 (EIGRP) estination address Hello packets contain Autonomous System Number Hold Time Authentication Metric Weightings (K values) Neighbors found are inserted into EIGRP neighbor table show ip eigrp neighbors Neighbors that agree on attributes and exchange updates form active adjacency
4 Step 2 - Exchanging Topology Information Once neighbors are found, EIGRP UPATE messages used to exchange routes Sent as multicast to or as unicast RTP uses sequence numbers and acknowledgements (ACKs) to ensure delivery Update messages describe attributes of a route Prefix + Length Next-Hop Bandwidth elay Load Reliability MTU Hop Count External Attributes All routes learned from all neighbors make up the EIGRP topology table show ip eigrp topology Step 3 - Choosing The Best Path Once topology is learned, UAL runs to choose loop-free best path to each destination Unlike other protocols, EIGRP uses complex composite metric to choose best path Composite metric calculated from Administrative Weighting Bandwidth elay Load Reliability Path with lowest composite metric is considered best and installed in IP routing table One or more backup routes can also be pre-calculated per destination Only best route is advertised to other EIGRP neighbors
5 Step 4 - Neighbor and Topology Table Maintenance Unlike RIP or IGRP, active EIGRP neighbor adjacency reduces convergence time in event of network failure Adjacent neighbors hello packets contain hold time If no hello is received within hold time, neighbor declared unreachable When neighbor is lost Paths via that neighbor are removed from topology and routing table If backup routes exist, they become new best paths and are inserted in routing table In this case EIGRP can have sub-second convergence If no backup routes exist, UAL must run again UAL Reconvergence When best path is lost and no backup routes exist, route goes into active state and active timer starts Stable routes not in active state are considered passive EIGRP QUERY message is reliably sent to remaining neighbors asking if there is an alternate route QUERY is propagated to all neighbors within EIGRP query domain or flooding domain More on this later Neighbors respond with EIGRP REPLY packet indicating if alternate route is available If alternate route exists, UAL recalculates new best path If no alternate route, prefix removed from topology table If active timer expires and no REPLY received, route is declared Stuck-In-Active (SIA) and removed from topology table
6 EIGRP Loop Prevention EIGRP guarantees loop-free topology through usage of Split Horizon on t advertise routes out the link they came in on UAL Feasibility Condition If your metric is lower than mine, you are loop-free UAL Terms in etail Successor Best path to a destination Feasible istance (F) Composite metric of best path Feasible Successor (FS) Backup path to a destination Advertised istance (A) Composite metric learned from neighbor Local istance (L) Composite metric to reach local neighbor Feasibility Condition (FC) Criteria for valid backup paths
7 UAL Path Selection in etail Once adjacency occurs and update messages are exchanged, path selection begins Each update includes the metric the upstream router uses to reach destination (A) Local router knows the metric to reach each upstream router (L) Best path (successor) is chosen based on lowest A + L UAL Example Local istance Advertised istance Feasible istance R1 R1 R2 R5 X = 21 R1 R3 R5 X = 36 R1 R4 R5 X = 36 R2 R5 X = 11 R2 R3 R5 X = R3 R5 X = 16 R4 R5 X = R3 R2 R5 X = R3 R4 R5 X = R4 R3 R5 X = 26 R2 16 R3 16 R R5 VLAN X 1 R5 X = 1
8 Feasibility Condition in etail Once best path is chosen, additional paths are examined for backup routes Feasibility Condition (FC) finds loop-free backup routes via logic If A < F, path is loop-free and viable backup e.g. if your metric is lower than mine, you are closer to the destination and loop-free Paths that meet the FC are Feasible Successors (FS) Only Feasible Successors can be used for unequal cost load balancing Feasibility Condition Example Local istance Advertised istance Feasible istance R1 R2 R5 X = 21 R1 R3 R5 X = 36 R1 R4 R5 X = 36 F = 21 Find routes with A < 21 R2 R5 X = 11 R2 R3 R5 X = 26 R1 X via R4 = 21 X via R3 = 16 R4 IS NOT Feasible Successor 10R3 is Feasible Successor R3 R5 X = 16 R4 R5 X = 21 R3 R2 R5 X = 21 R4 R3 R5 X = R3 R4 R5 X = R2 R3 R VLAN X R5 1 R5 X = 1
9 Composite Metric Calculation in etail Unlike other IGPs hop count or BW-based cost, EIGRP metric is a hybrid value comprised of Inverse lowest bandwidth along path in Kbps scaled by 10 7 * 256 Cumulative delay along path in tens of microseconds (µs) scaled by 256 Worst load along path Worst reliability along path Composite metric is computed as metric = [k1 * bandwidth + (k2 * bandwidth)/(256 - load) + k3 * delay] If k5!= 0, metric = metric * [k5/(reliability + k4)] K values allow for manual administrative weighting Must match for adjacency to occur efault K values are K1 = 1, K2 = 0, K3 = 1, K4 = 0, K5 = 0 Implies default composite is bandwidth + delay Reliability and load typically not used since they are constantly changing Composite Metric Calculation Example All Links FastEthernet BW = 100,000Kbps LY = 100µs R1 R2 R5 X = (10 7 * 256 / BW ) + (30 LY * 256) = R1 R3 R5 X = (10 7 * 256 / BW ) + (30 LY * 256) = R1 R4 R5 X = (10 7 * 256 / BW ) + (30 LY * 256) = Advertised istance Feasible istance R3 R5 X = (10 7 * 256 / BW ) + (20 LY * 256) = R3 R2 R5 X = (10 7 * 256 / BW ) + (30 LY * ) = R3 R4 R5 X = (10 7 * 256 / BW ) + (30 LY * 256) = R2 R5 X = (10 7 * 256 / BW ) + (20 LY * 256) = R2 R3 R5 X = (10 7 * 256 / BW ) + (30 LY * 256) = R4 R5 X = (10 7 * 256 / BW ) + (20 LY * 256) = R4 R3 R5 X = (10 7 * 256 / BW ) + (30 LY * 256) = R5 X = (10 7 * 256 / BW ) + (10 LY * 256) R5 X = 28160
10 Implementing Basic EIGRP Initialize EIGRP process router eigrp [asn] Enable EIGRP on links network [address] [wildcard] Network statement does not control what is advertised, controls what interfaces run the protocol Verifying Basic EIGRP Verify EIGRP interfaces show ip eigrp interfaces Verify EIGRP neighbors show ip eigrp neighbors Verify EIGRP topology show ip eigrp topology Verify EIGRP routes in routing table show ip route [eigrp]
11 Implementing Basic EIGRP Example /24 VLAN 1 Fa0/0.1 Fa0/0.12 R /24 VLAN /24 VLAN 2 Fa0/ /24 VLAN 4 Fa0/0.2 R2 Fa0/ /24 VLAN /24 VLAN 34 Fa0/0.23 Fa0/0.23 R3 Fa0/ /24 VLAN 35 Fa0/0.34 Fa0/0.34 R4 Fa0/0.45 Fa0/ /24 VLAN 25 Fa0/ /24 VLAN 45 Fa0/0.25 Fa0/0.45 R5 Fa0/ /24 VLAN 5 Basic EIGRP Configuration R1#show run section router eigrp 1 router eigrp 1 network no auto-summary R2#show run section router eigrp 1 router eigrp 1 network no auto-summary R3#show run section router eigrp 1 router eigrp 1 network network network no auto-summary R4#show run section router eigrp 1 router eigrp 1 network network network no auto-summary R5#show run section router eigrp 1 router eigrp 1 network no auto-summary
12 EIGRP Interface Verification R1#show ip eigrp interfaces IP-EIGRP interfaces for process 1 Xmit Queue Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending Interface Peers Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes Fa0/ /0 0 0/1 0 0 Fa0/ /0 8 0/ Fa0/ /0 0 0/1 0 0 Fa0/ /0 0 0/1 0 0 R2#show ip eigrp interfaces IP-EIGRP interfaces for process 1 Xmit Queue Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending Interface Peers Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes Fa0/ /0 0 0/1 0 0 Fa0/ /0 4 0/ Fa0/ /0 6 0/ Fa0/ /0 9 0/ R3#show ip eigrp interfaces IP-EIGRP interfaces for process 1 Xmit Queue Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending Interface Peers Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes Fa0/ /0 6 0/ Fa0/ /0 1 0/ Fa0/ /0 8 0/ R4#show ip eigrp interfaces IP-EIGRP interfaces for process 1 Xmit Queue Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending Interface Peers Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes Fa0/ /0 1 0/ Fa0/ /0 0 0/1 0 0 Fa0/ /0 4 0/ R5#show ip eigrp interfaces IP-EIGRP interfaces for process 1 Xmit Queue Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending Interface Peers Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes Fa0/ /0 0 0/1 0 0 Fa0/ /0 13 0/ Fa0/ /0 15 0/ Fa0/ /0 7 0/ EIGRP Packet Level ebug R1#debug ip packet detail IP packet debugging is on (detailed) R1#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)#router eigrp 1 R1(config-router)#no auto-summary R1(config-router)#network R1(config-router)#end R1# IP: s= (local), d= (FastEthernet0/0.1), len 60, sending broad/multicast, proto=88 IP: s= (local), d= (FastEthernet0/0.12), len 60, sending broad/multicast, proto=88 IP: s= (FastEthernet0/0.12), d= , len 60, rcvd 2, proto=88 %UAL-5-NBRCHANGE: IP-EIGRP(0) 1: Neighbor (FastEthernet0/0.12) is up: new adjacency IP: tableid=0, s= (FastEthernet0/0.12), d= (FastEthernet0/0.12), routed via RIB IP: s= (FastEthernet0/0.12), d= (FastEthernet0/0.12), len 40, rcvd 3, proto=88 IP: s= (local), d= (FastEthernet0/0.12), len 60, sending broad/multicast, proto=88 IP: s= (local), d= (FastEthernet0/0.12), len 40, sending, proto=88 IP: s= (FastEthernet0/0.12), d= , len 77, rcvd 2, proto=88 IP: s= (FastEthernet0/0.12), d= , len 320, rcvd 2, proto=88 IP: s= (local), d= (FastEthernet0/0.12), len 77, sending R1(config-routbroad/multicast, proto=88 IP: s= (local), d= (FastEthernet0/0.12), len 68, sending broad/multicast, proto=88 IP: tableid=0, s= (FastEthernet0/0.12), d= (FastEthernet0/0.12), routed via RIB IP: s= (FastEthernet0/0.12), d= (FastEthernet0/0.12), len 320, rcvd 3, proto=88 <output omitted>
13 EIGRP Neighbor Adjacency Verification R1#show ip eigrp neighbors IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1 H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num Fa0/ :03: R2#show ip eigrp neighbors IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1 H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num Fa0/ :03: Fa0/ :27: Fa0/ :27: R3#show ip eigrp neighbors IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1 H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num Fa0/ :27: Fa0/ :27: Fa0/ :27: R4#show ip eigrp neighbors IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1 H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num Fa0/ :27: Fa0/ :27: R5#show ip eigrp neighbors IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1 H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num Fa0/ :27: Fa0/ :27: Fa0/ :27: EIGRP Topology Verification R2#show ip eigrp topology IP-EIGRP Topology Table for AS(1)/I( ) Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply, r - reply Status, s - sia Status P /24, 2 successors, F is via (33280/30720), FastEthernet0/0.23 via (33280/30720), FastEthernet0/0.25 P /24, 1 successors, F is via (30720/28160), FastEthernet0/0.23 P /24, 1 successors, F is via Connected, FastEthernet0/0.12 P /24, 1 successors, F is via Connected, FastEthernet0/0.2 P /24, 1 successors, F is via (30720/28160), FastEthernet0/0.12 P /24, 1 successors, F is via (30720/28160), FastEthernet0/0.25 P /24, 2 successors, F is via (33280/30720), FastEthernet0/0.23 via (33280/30720), FastEthernet0/0.25 P /24, 1 successors, F is via Connected, FastEthernet0/0.25 P /24, 1 successors, F is via Connected, FastEthernet0/0.23 P /24, 1 successors, F is via (30720/28160), FastEthernet0/0.25 P /24, 2 successors, F is via (30720/28160), FastEthernet0/0.23 via (30720/28160), FastEthernet0/0.25 P /24, 1 successors, F is via (30720/28160), FastEthernet0/0.23
14 EIGRP Topology Verification etail R2#show ip eigrp topology IP-EIGRP (AS 1): Topology entry for /24 State is Passive, Query origin flag is 1, 1 Successor(s), F is Routing escriptor Blocks: (FastEthernet0/0.25), from , Send flag is 0x0 Composite metric is (30720/28160), Route is Internal Vector metric: Minimum bandwidth is Kbit Total delay is 200 microseconds Reliability is 255/255 Load is 1/255 Minimum MTU is 1500 Hop count is (FastEthernet0/0.23), from , Send flag is 0x0 Composite metric is (33280/30720), Route is Internal Vector metric: Minimum bandwidth is Kbit Total delay is 300 microseconds Reliability is 255/255 Load is 1/255 Minimum MTU is 1500 Hop count is 2 EIGRP Routing Table Verification R2#show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - OR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set C C C C /24 is subnetted, 12 subnets [90/33280] via , 00:19:40, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/33280] via , 00:19:40, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:19:42, FastEthernet0/ is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:07:41, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 01:30:23, FastEthernet0/ [90/33280] via , 00:19:41, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/33280] via , 00:19:41, FastEthernet0/ is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 01:31:20, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 01:31:20, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/30720] via , 01:31:20, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 01:31:20, FastEthernet0/0.23
15 EIGRP Routing Table Verification etail R2#show ip route Routing entry for /24 Known via "eigrp 1", distance 90, metric 30720, type internal Redistributing via eigrp 1 Last update from on FastEthernet0/0.25, 01:30:53 ago Routing escriptor Blocks: * , from , 01:30:53 ago, via FastEthernet0/0.25 Route metric is 30720, traffic share count is 1 Total delay is 200 microseconds, minimum bandwidth is Kbit Reliability 255/255, minimum MTU 1500 bytes Loading 1/255, Hops 1 EIGRP efault Routing EIGRP supports default routing two ways Candidate default network ip default-network [network] Native advertisement of /0 prefix default-information command in EIGRP does not behave the same as other protocols
16 IP efault-network Candidate default network is backwards compatible with IGRP IGRP didn t support native /0 advertisement efault network must be ynamically learned through EIGRP Not directly connected Classful network Limited application due to these restrictions IP efault-network Example R1# interface Loopback0 ip address ! router eigrp 1 network R2# ip default-network R2#show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - OR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is to network * /8 [90/156160] via , 00:01:43, FastEthernet0/ /24 is subnetted, 10 subnets C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0.12 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:20:11, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:31:28, FastEthernet0/ [90/33280] via , 00:31:28, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/33280] via , 00:31:28, FastEthernet0/0.23 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0.25 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:31:29, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:31:29, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/30720] via , 00:31:29, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:31:29, FastEthernet0/0.23
17 Native efault Advertisement Native /0 network can be advertised via Static default route to an interface + network under EIGRP process Redistribution from static or another protocol Summarization /0 Advertisement Examples R1# router eigrp 1 network ! ip route Null0 R2#show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - OR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is to network /24 is subnetted, 10 subnets C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0.12 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:23:33, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:34:50, FastEthernet0/ [90/33280] via , 00:34:50, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/33280] via , 00:34:50, FastEthernet0/0.23 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0.25 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:34:51, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:34:51, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/30720] via , 00:34:51, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:34:51, FastEthernet0/0.23 * /0 [90/28160] via , 00:01:05, FastEthernet0/0.12
18 /0 Advertisement Examples (cont.) R1# router eigrp 1 redistribute static metric ! ip route Null0 R2#show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - OR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is to network /24 is subnetted, 10 subnets C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0.12 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:24:53, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:36:10, FastEthernet0/ [90/33280] via , 00:36:10, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/33280] via , 00:36:10, FastEthernet0/0.23 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0.25 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:36:11, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:36:11, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/30720] via , 00:36:11, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:36:11, FastEthernet0/0.23 *EX /0 [170/53760] via , 00:00:27, FastEthernet0/ /0 Advertisement Examples (cont.) R1# interface FastEthernet0/0.12 ip summary-address eigrp R2#show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - OR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is to network /24 is subnetted, 9 subnets C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0.12 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:38:16, FastEthernet0/ [90/33280] via , 00:38:16, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/33280] via , 00:38:16, FastEthernet0/0.23 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0.25 C is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:38:17, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:38:17, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/30720] via , 00:38:17, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:38:17, FastEthernet0/0.23 * /0 [90/30720] via , 00:00:26, FastEthernet0/0.12
19 EIGRP Summarization EIGRP summarization (aggregation) serves two purposes Minimize routing information needed in topology Limit EIGRP query domain More on this later Process level auto-summary automatically summarizes to classful boundary when passing major network boundaries On by default Interface level ip summary-address eigrp [network] [mask] [A] supports any bit boundary Automatically suppresses subnet advertisements Administrative istance defaults to 5 to allow for floating summaries EIGRP Auto-Summary Example R1# interface Loopback0 ip address ! interface Loopback1 ip address ! interface Loopback2 ip address ! interface Loopback3 ip address ! router eigrp 1 network auto-summary R2#show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - OR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set C C C C /8 [90/156160] via , 00:00:44, FastEthernet0/ /24 is subnetted, 10 subnets is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:02:25, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:49:15, FastEthernet0/ [90/33280] via , 00:49:15, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/33280] via , 00:49:15, FastEthernet0/ is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:49:16, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:49:16, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/30720] via , 00:49:16, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:49:16, FastEthernet0/0.23
20 EIGRP Manual Summarization Example R1# interface Loopback0 ip address ! interface Loopback1 ip address ! interface Loopback2 ip address ! interface Loopback3 ip address ! interface FastEthernet0/0.12 ip summary-address eigrp ! router eigrp 1 network no auto-summary R2#show ip route eigrp /14 is subnetted, 1 subnets [90/156160] via , 00:05:01, FastEthernet0/ /24 is subnetted, 10 subnets [90/30720] via , 00:09:57, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:56:46, FastEthernet0/ [90/33280] via , 00:56:46, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/33280] via , 00:56:46, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:56:46, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:56:46, FastEthernet0/0.25 [90/30720] via , 00:56:46, FastEthernet0/ [90/30720] via , 00:56:46, FastEthernet0/0.23 EIGRP Load Balancing EIGRP allows load distribution among unequal paths Not the same as other IGPs load balancing among equal cost paths Controlled by variance command If feasible distance * variance > feasible successor, load balancing occurs Only feasible successors are candidate for load balancing Automatically calculated traffic share count causes links to be used in ratio proportional to their composite metrics
21 EIGRP Unequal Cost Load Balancing BW = 100,000Kbps LY = 100µs BW = 100,000Kbps LY = 50µs BW = 100,000Kbps LY = 100µs EIGRP Unequal Cost Load Balancing R2# router eigrp 1 variance 2 R3# interface FastEthernet0/0.35 delay 5 R2#show ip eigrp topology IP-EIGRP (AS 1): Topology entry for /24 State is Passive, Query origin flag is 1, 1 Successor(s), F is Routing escriptor Blocks: (FastEthernet0/0.25), from , Send flag is 0x0 Composite metric is (30720/28160), Route is Internal Vector metric: Minimum bandwidth is Kbit Total delay is 200 microseconds Reliability is 255/255 Load is 1/255 Minimum MTU is 1500 Hop count is (FastEthernet0/0.23), from , Send flag is 0x0 Composite metric is (32000/29440), Route is Internal Vector metric: Minimum bandwidth is Kbit Total delay is 250 microseconds Reliability is 255/255 Load is 1/255 Minimum MTU is 1500 Hop count is 2
22 EIGRP Unequal Cost Load Balancing (cont.) R2#show ip route Routing entry for /24 Known via "eigrp 1", distance 90, metric 30720, type internal Redistributing via eigrp 1 Last update from on FastEthernet0/0.23, 00:03:39 ago Routing escriptor Blocks: * , from , 00:03:39 ago, via FastEthernet0/0.25 Route metric is 30720, traffic share count is 24 Total delay is 200 microseconds, minimum bandwidth is Kbit Reliability 255/255, minimum MTU 1500 bytes Loading 1/255, Hops , from , 00:03:39 ago, via FastEthernet0/0.23 Route metric is 32000, traffic share count is 23 Total delay is 250 microseconds, minimum bandwidth is Kbit Reliability 255/255, minimum MTU 1500 bytes Loading 1/255, Hops 2 EIGRP Link Utilization EIGRP control plane traffic is allowed to use up to 50% of each interface s configured bandwidth value Can be adjusted with interface level ip bandwidth-percent eigrp [asn] [percent] Can be an important design consideration when bandwidth is modified for routing policy, QoS, or where WAN link circuit speeds don t match underlying interface speeds (e.g. fractional T1)
23 EIGRP Authentication Routing control plane security is a must in today s networks to prevent os and other attacks EIGRP neighbor authentication prevents against malicious route injection attacks or errors in configuration Configured Key I and password are combined to generate M5 hash If M5 hash does not match in Hello packets, adjacency cannot occur Multiple keys can be configured for manual or automated key rotation key-chain accept & send lifetime EIGRP Authentication Example R1# key chain EIGRP-KEY-CHAIN key 1 key-string CISCO! interface FastEthernet0/0.12 ip authentication mode eigrp 1 md5 ip authentication key-chain eigrp 1 EIGRP-KEY-CHAIN R2# key chain EIGRP-KEY-CHAIN key 1 key-string CISCO! interface FastEthernet0/0.12 ip authentication mode eigrp 1 md5 ip authentication key-chain eigrp 1 EIGRP-KEY-CHAIN R1#show key chain Key-chain EIGRP-KEY-CHAIN: key 1 -- text "CISCO" accept lifetime (always valid) - (always valid) [valid now] send lifetime (always valid) - (always valid) [valid now] R1#debug eigrp packet hello EIGRP: Sending HELLO on FastEthernet0/0.12 AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 0/0 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 EIGRP: received packet with M5 authentication, key id = 1 EIGRP: Received HELLO on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 0/0 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0
24 EIGRP Authentication Troubleshooting R1#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)#key chain EIGRP-KEY-CHAIN R1(config-keychain)#key 1 R1(config-keychain-key)#key-string WRONG_PASSWOR %UAL-5-NBRCHANGE: IP-EIGRP(0) 1: Neighbor (FastEthernet0/0.12) is down: Auth failure R1(config-keychain-key)#do debug eigrp packet hello EIGRP Packets debugging is on (HELLO) R1(config-keychain-key)# EIGRP: pkt key id = 1, authentication mismatch <output omitted> R1(config-keychain-key)#do undebug all All possible debugging has been turned off R1(config-keychain-key)#no key 1 R1(config)#key chain EIGRP-KEY-CHAIN R1(config-keychain)#key 2 R1(config-keychain-key)#key-string WRONG_KEY_NUMBER R1(config-keychain-key)#do debug eigrp packet hello EIGRP Packets debugging is on (HELLO) R1(config-keychain-key)# EIGRP: Sending HELLO on FastEthernet0/0.12 AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 0/0 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 EIGRP: pkt authentication key id = 1, key not defined or not live EIGRP Scalability EIGRP Scalability is a combined function of evice CPU & memory Protocol timers Number of prefixes in topology Size of query domain Physical resources are fixed, but software optimization can reduce convergence time and increase availability through Modifying hello/hold timers Ensuring Feasible Successors are available Topology reduction through summarization Query domain reduction through summarization & stub routing
25 EIGRP Query omain and SIA When an EIGRP route is lost and there are no Feasible Successors, the route goes into active state and a QUERY message is sent to all neighbors EIGRP state machine must wait for REPLY messages from all neighbors indicating either a new route or no route for the active prefix If REPLY is not received before active timer expires, prefix is declared Stuck-in-Active (SIA), and EIGRP neighbors are reset and must be re-established The larger or more overloaded the network is, the more likely SIA events are to occur and to cause network downtime Occurrence of SIA events can be reduced by shrinking where QUERY message must be sent (i.e. query domain ) through EIGRP Summarization EIGRP Stub EIGRP Summarization and Query Reduction When a QUERY message is received from an EIGRP neighbor, a topology lookup occurs for an exact match of the prefix I.e. if QUERY is received for /24, topology is checked for /24 exactly If exact match is found but no Feasible Successors exist, local device re-generates QUERY to all other neighbors Process continues until REPLY is sent or SIA occurs If exact match is not found, REPLY is sent immediately and new QUERY is not generated Based on this logic, summarization terminates query domain for subnets of the summary I.e. if QUERY is received for /24, but I have only /16, send REPLY and do not generate QUERY
26 EIGRP Query/Reply Verification R1#debug eigrp packet query reply EIGRP Packets debugging is on (QUERY, REPLY) R2#debug eigrp packet query reply EIGRP Packets debugging is on (QUERY, REPLY) R1#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)#interface Loopback0 R1(config-if)#shutdown EIGRP: Enqueueing QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.12 iidbq un/rely 0/1 serno EIGRP: Enqueueing QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0 serno EIGRP: Sending QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.12 AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 58/0 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 serno EIGRP: Received REPLY on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 231/58 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0 R2# EIGRP: Received QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 58/0 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0 EIGRP: Enqueueing QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.25 iidbq un/rely 0/1 serno EIGRP: Enqueueing QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.23 iidbq un/rely 0/1 serno EIGRP: Enqueueing QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.12 iidbq un/rely 0/1 serno EIGRP: Enqueueing QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.25 nbr iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0 serno EIGRP: Sending QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.25 AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 228/0 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 serno EIGRP: Enqueueing QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.23 nbr iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0 serno EIGRP: Sending QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.23 AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 229/0 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 serno EIGRP: Enqueueing QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0 serno EIGRP: Received REPLY on FastEthernet0/0.25 nbr AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 201/228 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0 EIGRP: Received REPLY on FastEthernet0/0.23 nbr AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 248/229 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0 EIGRP: Enqueueing REPLY on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr iidbq un/rely 0/1 peerq un/rely 0/0 serno EIGRP: Sending REPLY on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 231/58 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/1 serno EIGRP Query Reduction and Summarization R1# interface FastEthernet0/0.12 ip summary-address eigrp R1#debug eigrp packet query reply EIGRP Packets debugging is on (QUERY, REPLY) R2#debug eigrp packet query reply EIGRP Packets debugging is on (QUERY, REPLY) R1#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)#interface loopback0 R1(config-if)#shutdown R1(config-if)# EIGRP: Enqueueing QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.12 iidbq un/rely 0/1 serno EIGRP: Enqueueing QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0 serno EIGRP: Sending QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.12 AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 53/0 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 serno EIGRP: Received REPLY on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 216/53 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0 %LINK-5-CHANGE: Interface Loopback0, changed state to administratively down %LINEPROTO-5-UPOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to down R2# EIGRP: Received QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 53/0 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0 EIGRP: Enqueueing REPLY on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr iidbq un/rely 0/1 peerq un/rely 0/0 serno EIGRP: Sending REPLY on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 216/53 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/1 serno
27 EIGRP Stub and Query Reduction In certain physical topologies, the query domain extends to portions of the network that can never be used as alternate paths QUERY/REPLY messages sent into these portions waste network resources and increase convergence time Hub-and-Spoke Example: EIGRP Stub and Query Reduction (cont.) EIGRP Stub is used to inform adjacent neighbors that QUERY messages should not be sent to them Useful whenever an EIGRP router is not used for transit for the rest of the network Routes received by a stub router are not advertised to other adjacent neighbors Process level eigrp stub [connected] [leak-map] [receive-only] [redistributed] [static] [summary] Arguments control what prefixes can be advertised outbound
28 EIGRP Stub Example EIGRP Stub Router EIGRP Stub Verification R1# router eigrp 1 eigrp stub connected summary R2#show ip eigrp neighbors detail Fa0/0.12 IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1 H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num Fa0/ :00: Version 12.4/1.2, Retrans: 0, Retries: 0, Prefixes: 4 Stub Peer Advertising ( CONNECTE SUMMARY ) Routes Suppressing queries R1#debug eigrp packet terse EIGRP Packets debugging is on (UPATE, REQUEST, QUERY, REPLY, IPXSAP, PROBE, ACK, STUB, SIAQUERY, SIAREPLY) R2#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R2(config)#interface Fa0/0.2 R2(config-subif)#shutdown R1# EIGRP: Received UPATE on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 333/0 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0 EIGRP: Enqueueing ACK on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr Ack seq 333 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 1/0 EIGRP: Sending ACK on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 0/333 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 1/0 EIGRP: Enqueueing QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.12 iidbq un/rely 0/1 serno EIGRP: Enqueueing QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0 serno EIGRP: Sending QUERY on FastEthernet0/0.12 AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 80/0 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 serno EIGRP: Received ACK on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 0/80 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/1 EIGRP: FastEthernet0/0.12 multicast flow blocking cleared EIGRP: Received REPLY on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 336/80 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 0/0 EIGRP: Enqueueing ACK on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr Ack seq 336 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 1/0 EIGRP: Sending ACK on FastEthernet0/0.12 nbr AS 1, Flags 0x0, Seq 0/336 idbq 0/0 iidbq un/rely 0/0 peerq un/rely 1/0
29 EIGRP Q&A
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies Topology Objectives Background Configure EIGRP on multiple routers. Configure the bandwidth command to modify the EIGRP metric. Verify
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies Topology Objectives Background Configure EIGRP on multiple routers. Configure the bandwidth command to modify the EIGRP metric. Verify
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
Chapter 2: Configuring the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
 : Configuring the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe the basic operation of EIGRP. Plan and implement EIGRP routing. Configure
: Configuring the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe the basic operation of EIGRP. Plan and implement EIGRP routing. Configure
Lab 2-5 EIGRP Authentication and Timers
 Lab 2-5 EIGRP Authentication and Timers Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters Configure EIGRP hello interval and hold time Verify
Lab 2-5 EIGRP Authentication and Timers Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters Configure EIGRP hello interval and hold time Verify
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
CCNP ROUTE Workbook - EIGRP
 CCNP ROUTE Workbook - EIGRP EIGRP Initial Configuration Load the task1-1 initial configurations before starting. Task Configure EIGRP on Routers-1, 2, and 4 using the following guidelines: Classic-mode
CCNP ROUTE Workbook - EIGRP EIGRP Initial Configuration Load the task1-1 initial configurations before starting. Task Configure EIGRP on Routers-1, 2, and 4 using the following guidelines: Classic-mode
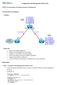
Introduction. Lab Diagram
 Introduction The onfiguring EIGRP module provides you with the instructions and isco hardware to develop your hands on skills in EIGRP, including authentication and receiving routes over a wide area network.
Introduction The onfiguring EIGRP module provides you with the instructions and isco hardware to develop your hands on skills in EIGRP, including authentication and receiving routes over a wide area network.
Configuration and Management of Networks
 EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
IP Enhanced IGRP Commands
 IP Enhanced IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor IP Enhanced IGRP. For configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IP Enhanced IGRP chapter of the
IP Enhanced IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor IP Enhanced IGRP. For configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IP Enhanced IGRP chapter of the
Section 6. Implementing EIGRP ICND2
 ICND2 Section 6 Implementing EIGRP Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 9.21 as an enhancement to the limitations of IGRP. IGRP was developed by Cisco
ICND2 Section 6 Implementing EIGRP Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 9.21 as an enhancement to the limitations of IGRP. IGRP was developed by Cisco
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
Chapter 2 Lab 2-5, EIGRP Authentication and Timers
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-5, EIGRP Authentication and Timers Topology Objectives Background Review a basic configuration of EIGRP. Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters. Configure EIGRP hello interval
Chapter 2 Lab 2-5, EIGRP Authentication and Timers Topology Objectives Background Review a basic configuration of EIGRP. Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters. Configure EIGRP hello interval
Topology & EIGRP Invocation. Router# show ipv6 protocols. Router# show ipv6 eigrp neighbors [ detail fa0/0 ]
![Topology & EIGRP Invocation. Router# show ipv6 protocols. Router# show ipv6 eigrp neighbors [ detail fa0/0 ] Topology & EIGRP Invocation. Router# show ipv6 protocols. Router# show ipv6 eigrp neighbors [ detail fa0/0 ]](/thumbs/78/78661316.jpg) Topology & EIGRP Invocation Router-ID is in the EIGRP block Interfaces included at each interface Passive interfaces designated in the EIGRP block The EIGRP block may require a no shutdown R5 ipv6 unicast-routing
Topology & EIGRP Invocation Router-ID is in the EIGRP block Interfaces included at each interface Passive interfaces designated in the EIGRP block The EIGRP block may require a no shutdown R5 ipv6 unicast-routing
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Instructor Lab Manual
 CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Instructor Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Instructor Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
Lab 2-3 Summarization and Default Network Advertisement
 Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions. Net412- Network troubleshooting
 Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions Net412- Network troubleshooting Troubleshooting Routing Network Layer Connectivity EIGRP OSPF 2 Network Connectivity Just like we did when we looked
Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions Net412- Network troubleshooting Troubleshooting Routing Network Layer Connectivity EIGRP OSPF 2 Network Connectivity Just like we did when we looked
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
LAB2: Named EIGRP IPv4
 Page1 AB2: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB2: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing
 Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 9 EIGRP João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts Introduction to EIGRP EIGRP:
Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 9 EIGRP João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts Introduction to EIGRP EIGRP:
LAB1: EIGRP IPv4. EIGRP: Initial Config. Disclaimer
 Page1 AB1: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB1: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration
 Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration Topology Objectives Configure IPv6 addressing. Configure and verify RIPng on R1 and R2. Configure IPv6 static routes between R2 and R3.
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration Topology Objectives Configure IPv6 addressing. Configure and verify RIPng on R1 and R2. Configure IPv6 static routes between R2 and R3.
EIGRP 04/01/2008. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 Modified by Tony Chen
 EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 Modified by Tony Chen 04/01/2008 1 Introduction 2 EIGRP Roots of EIGRP: IGRP -Developed in 1985 to overcome RIPv1 s limited hop count -Distance vector routing
EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 Modified by Tony Chen 04/01/2008 1 Introduction 2 EIGRP Roots of EIGRP: IGRP -Developed in 1985 to overcome RIPv1 s limited hop count -Distance vector routing
Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ]
![Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ]](/thumbs/78/78661506.jpg) s@lm@n Cisco Exam 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Topic 1, Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements Cisco
s@lm@n Cisco Exam 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Topic 1, Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements Cisco
Implementing an EIGRP Solution
 Chapter 3 Implementing an EIGRP Solution This chapter contains the following sections: Dynamic Routing Review EIGRP Features and Function Troubleshooting EIGRP Implementing EIGRP for IPv6 Chapter Summary
Chapter 3 Implementing an EIGRP Solution This chapter contains the following sections: Dynamic Routing Review EIGRP Features and Function Troubleshooting EIGRP Implementing EIGRP for IPv6 Chapter Summary
IPv4 IGP Troubleshooting. IPv4 Routing Workflow. IPv4 routing can be subdivided into three discrete steps
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp IPv4 IGP Troubleshooting http:// IPv4 Routing Workflow IPv4 routing can be subdivided into three discrete steps Routing lookup Switching method Layer 2 encapsulation
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp IPv4 IGP Troubleshooting http:// IPv4 Routing Workflow IPv4 routing can be subdivided into three discrete steps Routing lookup Switching method Layer 2 encapsulation
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7
 EIGRP Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7 Copyleft 2014 Hacklab Cosenza (http://hlcs.it) Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright
EIGRP Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7 Copyleft 2014 Hacklab Cosenza (http://hlcs.it) Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright
EIGRP. About EIGRP. CLI Book 1: Cisco ASA Series General Operations CLI Configuration Guide, 9.7 1
 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (). About, page 1
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (). About, page 1
EIGRP. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9. Video Frank Schneemann, MS EdTech
 Video Frank Schneemann, MS EdTech EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 9.0.1 Introduction Enhanced Interior
Video Frank Schneemann, MS EdTech EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 9.0.1 Introduction Enhanced Interior
Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab Topology Diagram Address Table 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase
Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab Topology Diagram Address Table 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase
Configuring EIGRP. 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc.
 Configuring EIGRP 4-1 EIGRP Overview 4-2 What Is EIGRP? IPX Routing Protocols IP Routing Protocols AppleTalk Routing Protocol Enhanced IGRP IP Routing Protocols AppleTalk Routing Protocol IPX Routing Protocols
Configuring EIGRP 4-1 EIGRP Overview 4-2 What Is EIGRP? IPX Routing Protocols IP Routing Protocols AppleTalk Routing Protocol Enhanced IGRP IP Routing Protocols AppleTalk Routing Protocol IPX Routing Protocols
Configuring EIGRP. Overview CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 24 This chapter describes how to configure the adaptive security appliance to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information, using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
CHAPTER 24 This chapter describes how to configure the adaptive security appliance to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information, using the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2
 ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Volume 2 Version 1.0 Student Guide Editorial, Production, and Web Services (EPWS): 07.25.07 DISCLAIMER WARRANTY: THIS CONTENT IS BEING PROVIDED AS
ICND2 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Volume 2 Version 1.0 Student Guide Editorial, Production, and Web Services (EPWS): 07.25.07 DISCLAIMER WARRANTY: THIS CONTENT IS BEING PROVIDED AS
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Exam Code : Version: Free Demo. IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way!
 Vendor : Cisco Exam Code : 642-832 Version: Free Demo IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way Cheat-Test.us - The Worldwide Renowned IT Certification Material Provider The safer, easier way to help you
Vendor : Cisco Exam Code : 642-832 Version: Free Demo IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way Cheat-Test.us - The Worldwide Renowned IT Certification Material Provider The safer, easier way to help you
Networkers 2001, Australia
 Networkers 2001, Australia March 28-30, Brisbane 1 Troubleshooting EIGRP Neale Rowe Presentation_ID 2 Agenda Troubleshooting Common EIGRP Problems Neighbor Stability Stuck-in-Active Routes Troubleshooting
Networkers 2001, Australia March 28-30, Brisbane 1 Troubleshooting EIGRP Neale Rowe Presentation_ID 2 Agenda Troubleshooting Common EIGRP Problems Neighbor Stability Stuck-in-Active Routes Troubleshooting
Routing with a distance vector protocol - EIGRP
 Routing with a distance vector protocol - EIGRP Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 5.2 Copyleft 2012 Vincenzo Bruno (www.vincenzobruno.it) Released under Crative Commons License
Routing with a distance vector protocol - EIGRP Introducing Routing and Switching in the Enterprise Chapter 5.2 Copyleft 2012 Vincenzo Bruno (www.vincenzobruno.it) Released under Crative Commons License
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0
 Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4
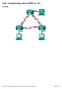 Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Lab10- Configuring EIGRP
 Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Topology Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Page 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup
Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Topology Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Page 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup
Lab 4: Routing using OSPF
 Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Part II. Chapter 3. Determining IP Routes
 Part II Chapter 3 Routers perform two main functions: switching and routing. The switching function is the process of moving packets from an inbound interface to an outbound interface. The switching function
Part II Chapter 3 Routers perform two main functions: switching and routing. The switching function is the process of moving packets from an inbound interface to an outbound interface. The switching function
EXAM Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE)
 CISCO EXAM - 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) TYPE: DEMO http://www.examskey.com/642-902.html Examskey CISCO 642-902 exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product. This
CISCO EXAM - 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) TYPE: DEMO http://www.examskey.com/642-902.html Examskey CISCO 642-902 exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product. This
ASA 9.x EIGRP Configuration Example
 ASA 9.x EIGRP Configuration Example Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Guidelines and Limitations EIGRP and Failover Configure Network Diagram ASDM
ASA 9.x EIGRP Configuration Example Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Guidelines and Limitations EIGRP and Failover Configure Network Diagram ASDM
Introduction. Lab Diagram
 Introduction The Troubleshooting routing protocols module provides you with the instructions and isco hardware to develop your hands on skills in troubleshooting routing protocols, specifically EIGRP.
Introduction The Troubleshooting routing protocols module provides you with the instructions and isco hardware to develop your hands on skills in troubleshooting routing protocols, specifically EIGRP.
9.1. Routing Protocols
 9.1. Routing Protocols Each organization that has been assigned a network address from an ISP is considered an autonomous system (AS). That organization is free to create one large network, or divide the
9.1. Routing Protocols Each organization that has been assigned a network address from an ISP is considered an autonomous system (AS). That organization is free to create one large network, or divide the
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-7-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-7-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers
Chapter 5 RIP version 1
 Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 5 RIP version 1 João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts RIPv1: A Distance Vector,
Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 5 RIP version 1 João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts RIPv1: A Distance Vector,
ITE PC v4.0. Chapter Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
 EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 1 Objectives Describe the background and history of Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP). Examine the basic EIGRP configuration commands and
EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 1 Objectives Describe the background and history of Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP). Examine the basic EIGRP configuration commands and
Configuring EIGRP. Finding Feature Information
 The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is an enhanced version of the Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) developed by Cisco. The convergence properties and the operating efficiency
The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is an enhanced version of the Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) developed by Cisco. The convergence properties and the operating efficiency
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF. Topology. Objectives. CCNPv7 ROUTE
 hapter 4 Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Summarize in OSPF at an ABR. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize in OSPF at an ASBR.
hapter 4 Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Summarize in OSPF at an ABR. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize in OSPF at an ASBR.
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS and Catalyst OS Software Images
 Configuring EIGRP This chapter describes how to configure Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP). For a complete description of the EIGRP commands listed in this chapter, refer to the EIGRP
Configuring EIGRP This chapter describes how to configure Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP). For a complete description of the EIGRP commands listed in this chapter, refer to the EIGRP
Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
EIGRP Lab / lo1. .1 lo / /30
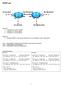 EIGRP Lab 172,16,1.0/24.1 lo1 192.168.20.0/30.2.1 Merida fa0 fa0 Vargas lo2.1 lo2.5.1 lo1 192.168.30.0/24 172.16.2.0/24 192.168.20.4.0/30 Scenario: Loopback0 is used for RouterID Loopback1 is a virtual
EIGRP Lab 172,16,1.0/24.1 lo1 192.168.20.0/30.2.1 Merida fa0 fa0 Vargas lo2.1 lo2.5.1 lo1 192.168.30.0/24 172.16.2.0/24 192.168.20.4.0/30 Scenario: Loopback0 is used for RouterID Loopback1 is a virtual
Final exam study Guide
 Final exam study Guide K-1A * In relationship to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through multiple hops of routers? - What happen to the
Final exam study Guide K-1A * In relationship to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through multiple hops of routers? - What happen to the
Configuring EIGRP. Finding Feature Information. Contents
 Configuring EIGRP First Published: 2005 Last Updated: September 10, 2010 Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is an enhanced version of the IGRP developed by Cisco. The convergence properties
Configuring EIGRP First Published: 2005 Last Updated: September 10, 2010 Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is an enhanced version of the IGRP developed by Cisco. The convergence properties
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
Implementing cisco ip routing
 Cisco 642-902 Implementing cisco ip routing Version Demo Topic 1: Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements QUESTION 1 Which three statements about the EIGRP routing
Cisco 642-902 Implementing cisco ip routing Version Demo Topic 1: Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements QUESTION 1 Which three statements about the EIGRP routing
Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features Topology
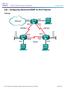 Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks
 Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks Lecturers Amnach Khawne Jirasak Sittigorn Chapter 1 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 8 : The Routing Table: A Closer Look Chapter 9 : EIGRP Chapter
Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks Lecturers Amnach Khawne Jirasak Sittigorn Chapter 1 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 8 : The Routing Table: A Closer Look Chapter 9 : EIGRP Chapter
OSPF Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols IP2R-61
 OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-6-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-6-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers
Deployment of IGRP/EIGRP
 1 eployment of IGRP/EIGRP Session 2 Presentation_I.scr 1 Understanding EIGRP Understanding and deploying EIGRP is like driving a car 3 genda Fundamentals of EIGRP UL Summarization and Load alancing EIGRP/IGRP
1 eployment of IGRP/EIGRP Session 2 Presentation_I.scr 1 Understanding EIGRP Understanding and deploying EIGRP is like driving a car 3 genda Fundamentals of EIGRP UL Summarization and Load alancing EIGRP/IGRP
Symbols. Numerics I N D E X
 I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
Introduction. Keith Barker, CCIE #6783. YouTube - Keith6783.
 Understanding, Implementing and troubleshooting BGP 01 Introduction http:// Instructor Introduction Keith Barker, CCIE #6783 CCIE Routing and Switching 2001 CCIE Security 2003 kbarker@ine.com YouTube -
Understanding, Implementing and troubleshooting BGP 01 Introduction http:// Instructor Introduction Keith Barker, CCIE #6783 CCIE Routing and Switching 2001 CCIE Security 2003 kbarker@ine.com YouTube -
CCNP IPSOFTWARE EIGRP ROUTE Lab Manual.
 Lab Manual CCNP ROUTE 300-101 EIGRP Lab - 1 : EIGRP-Basic Configuration Lab - 2 : EIGRP-Metric and Variance Load Sharing Lab - 3 : EIGRP-Summarization Lab - 4 : EIGRP-Query Control Lab - 5 : EIGRP-Authentication
Lab Manual CCNP ROUTE 300-101 EIGRP Lab - 1 : EIGRP-Basic Configuration Lab - 2 : EIGRP-Metric and Variance Load Sharing Lab - 3 : EIGRP-Summarization Lab - 4 : EIGRP-Query Control Lab - 5 : EIGRP-Authentication
Configuring Networking Protocols
 11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
Chapter 4: Manipulating Routing
 : Manipulating Routing Updates CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe network performance issues and ways to control routing updates and traffic (3). Describe the purpose of
: Manipulating Routing Updates CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe network performance issues and ways to control routing updates and traffic (3). Describe the purpose of
LAB15: EIGRP IPv4. LAB 15: Diagram. Disclaimer
 AB15: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as
AB15: EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as
CCNP ROUTE Exam (http://www.digitaltut.com)
 CCNP ROUTE Exam (http://www.digitaltut.com) Number: 642-902 Passing Score: 790 Time Limit: 90 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 642-902 ROUTE Exam Topics Exam Description The Implementing
CCNP ROUTE Exam (http://www.digitaltut.com) Number: 642-902 Passing Score: 790 Time Limit: 90 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 642-902 ROUTE Exam Topics Exam Description The Implementing
Chapter 9. Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Part I
 Chapter 9 Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Part I CCNA2-1 Chapter 9-2 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College
Chapter 9 Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Part I CCNA2-1 Chapter 9-2 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College
NAT Internetworking Standards and Technologies, Computer Engineering, KMITL 2
 EIGRP & NAT Jirasak Sittigorn Internetworking Standards & Technologies Department of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang EIGRP Characteristics
EIGRP & NAT Jirasak Sittigorn Internetworking Standards & Technologies Department of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang EIGRP Characteristics
cisco. Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min.
 300-101.cisco Number: 300-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min Exam A QUESTION 1 Examine the following output of the show ip ospf interface command. What would be the effect of executing the auto-cost
300-101.cisco Number: 300-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min Exam A QUESTION 1 Examine the following output of the show ip ospf interface command. What would be the effect of executing the auto-cost
debug ip ospf database external default-metric subnet area 0 stub distribute-list in Serial0/1
 Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Lab 5-3 Redistribution Between EIGRP and IS-IS
 Lab 5-3 Redistribution Between EIGRP and IS-IS Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP and IS-IS Redistribute into EIGRP Redistribute into IS-IS Use a standard access list to select routes
Lab 5-3 Redistribution Between EIGRP and IS-IS Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP and IS-IS Redistribute into EIGRP Redistribute into IS-IS Use a standard access list to select routes
Routing Protocol. RIPv1
 Outline Routing Protocol RIPv1, RIPv2, EIGRP OSPF o RIPv1, RIPv2 o EIGRP o OSPF 2 3 RIPv1 RIP Characteristics A classful, Distance Vector (DV) routing protocol Metric = hop count Routes with a hop count
Outline Routing Protocol RIPv1, RIPv2, EIGRP OSPF o RIPv1, RIPv2 o EIGRP o OSPF 2 3 RIPv1 RIP Characteristics A classful, Distance Vector (DV) routing protocol Metric = hop count Routes with a hop count
scope scope {global vrf vrf-name} no scope {global vrf vrf-name} Syntax Description
 Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
This chapter covers the following subjects:
 This chapter covers the following subjects: Link-State Routing Protocol and OSPF Concepts Balanced Hybrid Routing Protocol and EIGRP Concepts OSPF Configuration EIGRP Configuration C H A P T E R 6 OSPF
This chapter covers the following subjects: Link-State Routing Protocol and OSPF Concepts Balanced Hybrid Routing Protocol and EIGRP Concepts OSPF Configuration EIGRP Configuration C H A P T E R 6 OSPF
Table of Contents. Cisco Introduction to EIGRP
 Table of Contents Introduction to EIGRP...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1 Components Used...1 What is IGRP?...2 What is EIGRP?...2 How Does EIGRP Work?...2 EIGRP
Table of Contents Introduction to EIGRP...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1 Components Used...1 What is IGRP?...2 What is EIGRP?...2 How Does EIGRP Work?...2 EIGRP
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs
 TDC 363 Introduction to LANs Routing Protocols and RIP Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 1 Dynamic Routing Routing Protocols Distance Vector vs. Link State Protocols RIPv1 & RIPv2 RIP Problems Slow
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs Routing Protocols and RIP Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 1 Dynamic Routing Routing Protocols Distance Vector vs. Link State Protocols RIPv1 & RIPv2 RIP Problems Slow
Explanation: In order to verify proper route redistribution, use the "show ip route" command on all routers
 QUESTION 401 The 192.168.0.0/16 network is not being propagated throughout the network via BGP as expected. Observe the BGP configuration commands from the advertising router shown below. Router bgp 65111
QUESTION 401 The 192.168.0.0/16 network is not being propagated throughout the network via BGP as expected. Observe the BGP configuration commands from the advertising router shown below. Router bgp 65111
Two types of routing protocols are used in internetworks: interior gateway protocols (IGPs) and exterior gateway protocols (EGPs).
 Introduction Dynamic routing is when protocols are used to find networks and update routing tables on routers. True, this is easier than using static or default routing, but it ll cost you in terms of
Introduction Dynamic routing is when protocols are used to find networks and update routing tables on routers. True, this is easier than using static or default routing, but it ll cost you in terms of
F. Configure a distribute-list on router RTA that allows it to advertise all routes to the spoke routers.
 Refer to the exhibit. Router RTA is the hub router for routers RTB and RTC. The Frame Relay network is configured with EIGRP, and the entire network is in autonomous system 1. However, router RTB and RTC
Refer to the exhibit. Router RTA is the hub router for routers RTB and RTC. The Frame Relay network is configured with EIGRP, and the entire network is in autonomous system 1. However, router RTB and RTC
Planning for Information Network
 Planning for Information Network Lecture 8: Network Routing Protocols Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Routing protocol features There are many ways to characterize routing protocols, including
Planning for Information Network Lecture 8: Network Routing Protocols Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Routing protocol features There are many ways to characterize routing protocols, including
LAB16: Named EIGRP IPv4
 AB16: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
AB16: Named EIGRP IPv4 isclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Requirements
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Inheritence with EIGRP Named mode Route Replication with EIGRP name mode Routing Context
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Inheritence with EIGRP Named mode Route Replication with EIGRP name mode Routing Context
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates. Topology. Objectives. CCNPv7 ROUTE
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates Topology Objectives Filter routes using a distribute list and ACL. Filter routes using a distribute list and prefix list. Filter redistributed routes using
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates Topology Objectives Filter routes using a distribute list and ACL. Filter routes using a distribute list and prefix list. Filter redistributed routes using
CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 11 Case Study
 bjectives: Consolidate SPF knowledge. Describe the operation of SPF multi-area. Introduce the concept of route summarization with SPF. Introduce the concept of SPF optimization. Intro: Trevni Inc. needed
bjectives: Consolidate SPF knowledge. Describe the operation of SPF multi-area. Introduce the concept of route summarization with SPF. Introduce the concept of SPF optimization. Intro: Trevni Inc. needed
Hands-On ROUTE Implementing Cisco IP Routing CCNP Course 1
 Hands-On CCNP Course 1 Course Description Revised CCNP Curriculum and Exams Cisco has redesigned the CCNP courses and exams to reflect the evolving job tasks of global network professionals. Course 1 ROUTE
Hands-On CCNP Course 1 Course Description Revised CCNP Curriculum and Exams Cisco has redesigned the CCNP courses and exams to reflect the evolving job tasks of global network professionals. Course 1 ROUTE
Route Redistribution 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1of 38
 1of 38 Basic Route Redistribution Presented by: Allan Johnson Cisco Academy Conference 2005 2of 38 Outline of Discussion Route Redistribution Overview Example 1: IGRP and EIGRP Automatic Redistribution
1of 38 Basic Route Redistribution Presented by: Allan Johnson Cisco Academy Conference 2005 2of 38 Outline of Discussion Route Redistribution Overview Example 1: IGRP and EIGRP Automatic Redistribution
IP Routing: EIGRP Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.1MT
 IP Routing: EIGRP Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.1MT Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS
IP Routing: EIGRP Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.1MT Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) What Is BGP?
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) http:// What Is BGP? Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 Standards based RFC 4271 A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Exterior Gateway Protocol
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) http:// What Is BGP? Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 Standards based RFC 4271 A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Exterior Gateway Protocol
EIGRP. Finding Feature Information
 The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol () is an enhanced version of the Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) developed by Cisco. The convergence properties and the operating efficiency of have
The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol () is an enhanced version of the Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) developed by Cisco. The convergence properties and the operating efficiency of have
Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks
 Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks Routers in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) Phase 3 network use Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Shortcut Switching to discover shorter paths
Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks Routers in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) Phase 3 network use Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Shortcut Switching to discover shorter paths
CCNP Route. Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.1. Cisco
 CCNP Route Number: 642-902 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.1 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Cisco 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 7.1 Cisco 642-902 Exam Sections
CCNP Route Number: 642-902 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.1 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Cisco 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 7.1 Cisco 642-902 Exam Sections
Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example
 Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example Document ID: 117974 Contributed by Fabrice Ducomble, Cisco TAC Engineer. Aug 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example Document ID: 117974 Contributed by Fabrice Ducomble, Cisco TAC Engineer. Aug 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-5-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-5-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1, Configure and Verify Path Control
 hapter 5 Lab 5-1, onfigure and Verify Path ontrol Topology Objectives Background onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations.
hapter 5 Lab 5-1, onfigure and Verify Path ontrol Topology Objectives Background onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations.
Routing Configuration Commands
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1.1 auto-summary...2 1.1.2 -information originate...3 1.1.3 -metric...3 1.1.4 ip rip authentication...4
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1.1 auto-summary...2 1.1.2 -information originate...3 1.1.3 -metric...3 1.1.4 ip rip authentication...4
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF
 hapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review configuration and verification of RIP and OSPF. onfigure passive interfaces in both RIP and OSPF. Filter routing updates
hapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review configuration and verification of RIP and OSPF. onfigure passive interfaces in both RIP and OSPF. Filter routing updates
