Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Chapter 3
|
|
|
- Marianna Hudson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VERSION 1H ANNEX 10, VOLUME 3, PART 1, CHAPTER 3 Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Chapter 3 Part 1 Version 0.1 >NOTE - SUPERSEDED WP5-10b (version 0.3) 07-June-1996 \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 1, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
2 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 2 1. DEFINITIONS A-FU A/G AAC AARE AARQ ABRT AC ACA ACAS Accounting Management ACSE ACSE ACSE. ACT Active User Authentication Functional Unit Air-ground Aeronautical Administrative Communications ACSE Associate Response APDU ACSE Associate Request APDU ACSE Abort APDU Accept Address compression algorithm Airborne Collision Avoidance System Accounting management enables charges to be established for the use of resources, and for costs to be identified for the use of those resources. Accounting management includes functions to inform users of costs incurred or resources consumed, enable accounting limits to be set and tariff schedules to be associated with the use of resources, and enable cos to be combined where multiple resources are invoked to achieve a given communications objective. Association control service element Association Control Service Element The Association Control Service Element is the common mechanism in t ALS for establishing and releasing ASO-associations Activity Management A user that is currently in an applications dialogue, such as for CM or CPDLC. Actual TSAP AD The actual TSAP is composed of the IDP and the long TSAP. Administrative domain \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 2, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
3 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 3 AD Address Domain Addressing (logical) Addressing (physical) Addressing Authority ADJBISMO ADJRIBMO ADM ADMD ADMF Administrative Domain ADS ADS ADS-AE Abstract Service Interface ADS-CF ADS abstract service interface Addendum (of an ISO/IEC standard) An Address Domain is a set of address formats and values administered b a single address authority. Under the ISO plan, any address authority ma define subdomains within its own domain, and delegate authority within those subdomains. Logical addressing means that the address defined in the addressing plan and used to locate the addressed object is a virtual address which is a substitute of the actual (physical) address of an object. Address mapping functions have to fulfil this substitution, carefully maintaining unambigu of identification of objects. Physical addressing means that the address defined in the addressing pla and used to locate the addressed object is the physical, i.e. hardwired, har coded, or configured address of the object. An example of a physical address is the ICAO 24-bit Aircraft Address used for the SSR Mode S Transponder. An Addressing Authority defines formats and/or values of NSAP address within its jurisdiction. Adjacent BIS MO Adjacent RIB MO Administrative identifier Administration management domain ADM Flag A collection of end systems, intermediate systems, and subnetworks operated by a single organisation or administrative authority. An administrative domain may be internally divided into one or more routin domains. Automatic Dependent Surveillance Automatic Dependent Surveillance The abstract interface between the ADS-users and the ADS-serviceprovider. That abstract part of the AE that performs the mapping between the ADS-ASE service primitives and other elements within the ADS application The abstract interface between the ADS-air-ASE and the ADS-air-user o between the ADS-ground-ASE and the ADS-ground-user \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 3, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
4 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 4 ADS emergency report ADS report ADS service primitive ADS service provider ADS-air-ASE ADS-air-user ADS-ASE Abstract Service Interface ADS-ATC ADS-ground-ASE ADS-ground-user AE AE AE Qualifier An ADS report provided as part of an emergency contract A report provided by the ADS-air-user and sent to the ADS-ground-user concerning conditions on the aircraft, notably its location and FOM See Service Primitive. See Service Provider. That abstract part of the aircraft system that performs the communication related functions of ADS That abstract part of the aircraft system that performs the non communications related functions of ADS The abstract interface through which the ADS-ASE services are accessed Note 1. In version 1 of the ADS application, this interface coincides w the ADS-AE abstract service interface. ADS-based Air Traffic Control system That abstract part of the ground system that performs the communication related functions of ADS That abstract part of the ground system that performs the non communications related functions of ADS Application Entity Application Entity That part of the AE title that unambiguously identifies the particular application entity. AE Title Aeronautical Administrative Communications (AAC) Aeronautical Administrative Messages An unambiguous name for an application entityth Communications used by aeronautical operating agencies related to the business aspects of operating their flights and transport services. These communications are used for a variety of purposes, such as flight and ground transportation bookings, deployment of crew and aircraft,, or any other logistic purposes that maintains or enhances the efficiency of overa flight operation. Messages regarding the operation or maintenance of facilities provided fo the safety or regularity of aircraft operation, messages concerning the functioning of the aeronautical telecommunication services, and message exchanged between government civil aviation authorities relating to aeronautical services. Aeronautical Industry Service AINSC comprises aeronautical industry communications between airline aeronautical industry service providers, general aviation operators, and a \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 4, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
5 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 5 Communication (AINSC) other industry stakeholders. This term is used for purposes of address administration. Aeronautical Information Service Messages. Aeronautical Mobile Satellite Service (AMSS) Aeronautical Operational Control (AOC) Aeronautical Passenger Communications (APC) Aeronautical stakeholder Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) AES AF-Address AFI AFS AFTN AINSC AINSC Administrative Domain AINSC RDC AINSC Routing Areas AINSC Routing Domains Messages concerning NOTAMS and messages concerning SNOWTAMS AMSS provides packet-mode data and circuit-mode data and voice servic to aircraft and ground users provided by a satellite subnetwork which comprises satellites, Aircraft Earth Stations (AESs), Ground Earth Statio (GESs), and associated ground facilities such as a network coordination center. Communications required for the exercise of authority over the initiation continuation, diversion, or termination of a flight in the interest of the safety of the aircraft and the regularity and efficiency of flight. Communications relating to the non-safety voice and data services to passengers and crew members for personal communications. Definition tbd The Aeronautical Telecommunication Network is an internetwork architecture which allows ground, air-to-ground, and avionics data subnetworks to interoperate by adopting common interface services and protocols based on the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model. Aircraft earth station AFTN-form address Authority and format identifier Aeronautical fixed service Aeronautical fixed telecommunication network Aeronautical Industry Service Communication An AINSC Administrative Domain is an ATN Administrative Domain owned and/or administered by an aeronautical industry service organisation. The ATN AINSC RDC consists of all AINSC RDs in the ATN. An AINSC Routing Area is a routing subdomain comprising one or more ISs, and optionally, one or more ESs owned and/or administered by an aeronautical industry service organisation. For example, an AINSC Routing Area may correspond to a physical location such as an airline s systems located at an airport. An AINSC Routing Domain comprises ESs and ISs that are part of an \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 5, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
6 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 6 AINSC Administrative Domain. Air Traffic Control(ATC) Air Traffic Management (ATM) Air Traffic Services (ATS) Air Traffic Services Communications (ATSC) ALS APDU AK ALS AMHS AMSS ANC AOC AOC AOM AP APC APDU API App Application ATC is a service operated by an appropriate authority to promote the safe orderly, and expeditious flow of air traffic. ATM consists of a ground and air part, both needed to ensure the safe an efficient movement of aircraft during all phases of operation. Services provided by governmental civil aviation authorities. Communications related to air traffic services including air traffic contro aeronautical and meteorological information, position reporting, and services related to safety and regularity of flight. This communication must involve one or more air traffic service administrations. This term is used for purposes of address administration. Data acknowledgement The Application Layer Structure (ALS) refers to the internal architecture the OSI Application Layer as described in ISO/IEC 9545, Edition 2. Application Layer Structure ATS message handling system Aeronautical mobile satellite service Air Navigation Commission Aeronautical Operational Communications Aeronautical Operational Control Systems Management Upper Layer profile Application process Aeronautical Passenger Communications An Application Protocol Data Unit (APDU) is an (N)-PDU where N refer to the Application Layer. An APDU is the basic unit of information exchanged between the airborne application and the ground application. Application Protocol Data Unit Application Program Interface Application Software providing services to its users, in the guise of a consistent set of functionality; example given, the ATC related functions implemented in the server(s) and/or controller work position host computers.(from \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 6, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
7 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 7 EATCHIP Glossary of Terms / COPS/CWP Report) Application Control Service Element (ACSE) Application Entity (AE) Application identifier Application Layer Application process (AP) Application service Application Service Element (ASE) Application Service Element (ASE) Application Service Object (ASO) Application-user APRL ARS ARSD ASE The association control service element (ACSE) establishes, maintains an releases associations between application entities. Part of an application process that is concerned with communications within the OSI environment. The aspects of an application process that need to be taken into account for the purposes of OSI are represented by one or more AEs.. An abstract identifier which distinguishes one application from another. The layer of the OSI reference model that controls application user acces to the communication system. A set of resources, including processing resources, within a real open system which may be used to perform a particular information processing activity. The abstract interface between the (N)-service and the (N)-service user, where N refers to the Application layer; thus it is the boundary between t ATN-App-AE and the Application-user. A set of functions which provide OSI communications capabilities for the interworking of AEs for a specific purpose. An AE may be composed of one ASE or several ASEs of different types. A set of application functions which provide a capability for the interworking of application-entity-invocations for a specific purpose; ASE are a component of application service objects. An ASE can be considere to be a protocol module that is combined with others to form a complete protocol. An active element within (or equivalent to the whole of) the applicationentity embodying a set of capabilities defined for the Application Layer th corresponds to a specific ASO-type (without any extra capabilities being used). An ASO is a combination of ASEs and ASOs that perform a specific function. An ASO that provides the functions of the establishme and data transfer phases is considered a complete protocol. That abstract part of the aircraft or ground system that performs the noncommunications related functions of the Application ATN profile requirements list Administrative Region Selector ARS Default [Flag] Application Service Element \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 7, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
8 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 8 ASI ASN.1 ASO ATC ATFM ATIS ATM ATM/ATS Applications ATN ATN App ATN Applications ATN Environment ATN host computer ATN Internet (ATNI) ATN Island Backbone RDC ATN Island Bridge Abstract Service Interface Abstract Syntax Notation One Application Service Object Air Traffic Control Air traffic flow management Automatic Terminal Information Service Air Traffic Management These are applications supporting ATM or other ATS functions and do n necessarily correspond to ATN applications. The term is usually used to distinguish between ATM functions and other non-atm functions using the same communication service. Aeronautical Telecommunication Network A generic name for an ATN application. Refers to applications that support ATM or aeronautical industry function and that are designed to operate across an OSI communications system. ATN applications are always distributed applications, i.e. peer processes are hosted by different end systems which are interconnected. The term ATN environment relates to functional and operational aspects around the ATN as a complete end-to-end communication system. An ATN host computer is a civil aeronautical computer system which contains one or more end user applications and that communicates using the ATN internet. In OSI terms, it denotes an End System. An ATN Ho Computer may also implement the upper layers necessary to support the Systems Management Agent and Systems Management Manager and upp layer protocols as specified for the supported end-user applications. An implementation of the ISO OSI network layer services and protocols support of interprocess data communication between aeronautical host computers. It is defined to be the collection of the connected internetwor routers and subnetworks that conform to ATN internetwork requirements An ATN backbone is an RDC comprising a subset of Transit Routing Domains within an ATN Island which provide general connectivity. A bridge between two ATN Islands is a communications link between backbones over a suitable subnetwork. ATN Island RDC An ATN Island is an RDC comprising CAA-operated ATN RDs within a geographical region, and may include associated ATN service providers, an RDC comprising Aeronautical Industry members which are users of \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 8, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
9 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 9 communications services of a single Aeronautical Industry Service Provider, or more than one such provider providing services in combination with each other. ATN Network Operating Concept ATN Presentation Address ATN Profile Requirement List (APRL) ATN Router ATN Routing Domain Confederation ATN Services ATN System Applications ATN Systems Management ATN-App ASE ATNI An ATN Network Operating Concept will address the administrative, operational, institutional, and policy issues and additional (non-sarps relevant) technical aspects to enable the efficient and correct operation of the ATN. In the ATN, presentation addresses must, as a minimum, include an NSA Address and a TSAP Selector and may include a PSAP Selector and SSA Selector based on the addressing structure adopted within the ES and whether the application requires the OSI session or presentation protocol APRLs contained in the Draft ATN SARPs identify, in a tabular form, requirements together with the options and parameters for protocols used in the ATN. The supplier of an ATN protocol implementation claiming conform to the ATN SARPs must indicate conformance to those requirements by preparing a Protocol Implementation Conformance Statement (PICS) based on the set of APRLs presented in the SARPs. The communication element that manages the relaying and routing of da while in transit from an originating ATN host computer to a destination ATN host computer. In ISO terms, an ATN router comprises an OSI intermediate system and an end system supporting a systems managemen agent. The ATN RDC is the set of interconnected RDs that together form the ATN. The ATN services are provided to ATN users that require ground-ground or air-ground data communication. The ATN internet service is provided at the transport layer (service access point). The ATN accommodates different grades of services which can be expressed by Quality of Service parameters. System Applications support the operation of the ATN communication services and are either not directly or not at all used by ATN users but rather by the service providers or operators. Typical examples of ATN system applications are the ATN directory service, ATN context management or ATN systems management. The ATN Systems Management provides mechanisms for monitoring, control and co-ordination of resources necessary to provide ATN services ATN Systems Management is based on OSI System Management principles and may be distributed, centralised, or local. That abstract part of the ATN end system that performs the communications related functions of the ATN application. Examples of the ATN-App ASE include: the ADS-Air ASE and the CM-Air ASE. ATN internet \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 9, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
10 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 10 ATNPA ATNSM ATS ATS Message ATS Message Handling Service ATSC ATSC Administrative Domain ATSC RDC ATSC Routing Areas ATSC Routing Domain ATSU AU Authentication information Automatic Dependent Surveillance (ADS) BCD BER BIS BISPDU ATN protocol architecture ATN systems management Air Traffic Services A unit of user-data, coded in binary form, which is conveyed from an originator of the data to one or more recipients of the data. It is possible associate a unique message identifier and a priority with each ATS message. Procedures used to exchange ATS Messages over the ATN such that the conveyance of an ATS Message is in general not correlated with the conveyance of another ATS Message by the service provider. Two ATS Message Handling Services are defined in Sub-Volume III. They are the ATS Message Service and the ATN Pass-Through Service. Air Traffic Services Communications An ATSC Administrative Domain is an ATN Administrative Domain owned and/or administered by an air traffic services organisation. The ATN ATSC RDC consists of all ATSC RDs in the ATN. An AINSC Routing Area is a routing subdomain comprising one or more ISs, and optionally, one or more ESs owned and/or administered by an ATS organisation. For example, an ATSC Routing Area may correspon to a physical location such as an airport. An ATSC Routing Domain comprises ESs and ISs that are part of an ATSC Administrative Domain. Air Traffic Services Unit Access unit Information used to authenticate the identity of an application or user. A technique in which aircraft automatically provide, via a data link, data derived from on-board navigation and position-fixing systems, including aircraft identification, four-dimensional position, and additional data as appropriate. ADS is a data link application. Binary Coded Decimal Basic Encoding Rules (of ASN.1) Boundary intermediate system BIS PDU \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 10, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
11 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 11 Boundary Intermediate System (BIS) BPS Broadcast Subnetwork C CAA CAN CC CCITT CDSE CDT CE CF CF CIDIN CL CLNP CLNPMMO CLNS CLTP CLTPMMO CM CM-CF An intermediate system that is able to relay data between two separate routing or administrative domains. Bits per second Broadcast subnetworks (e.g. LANs) are often used to connect ISs and ES within a small geographical area with media offering relatively high data throughput with relatively low delays. Counter Civil aviation administration Cancellation Connection confirm International Telegraph and Telephone Consultative Committee Confirmed Data Service Element Credit Congestion experienced flag That abstract part of the AE that performs the mapping between the ATN App ASE service primitives, the ACSE service primitives, and other elements within the Application Entity. Control Function Common ICAO data interchange network Connectionless mode CL network protocol CL network protocol machine MO CL network service CL transport protocol CL transport protocol machine MO Context Management That abstract part of the application entity that performs the mapping between the CM-ASE service primitives and other elements within the C application. \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 11, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
12 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 12 CM AE abstract service interface CM service primitive CM service provider CM-air-ASE CM-air-user CM-ASE abstract service interface CM-ground-ASE CM-ground-user CMIP CMIS CMISE CN CNS CNS/ATM CO COMSEC Configuration Management Congestion Congestion Avoidance The abstract interface between the CM-users and the CM-service provide See Service Primitive. See Service Provider. An abstract part of the aircraft system that performs the communication related functions of CM. The abstract part of the aircraft system that performs the non communication related functions of CM. The abstract interface through which the CM-ASE service are accessed.. An abstract part of the ground system that performs the communication related functions of CM. The abstract part of the ground system that performs the non communication related functions of CM. Common management information protocol Common management information service CMIS element Connect Communications, Navigation, and Surveillance Communications Navigation Surveillance / Air Traffic Managemen Connection mode Communications security Configuration management identifies, exercises control over, collects dat from and provides data to open systems for the purpose of preparing for, initialising, starting, providing for the continuous operation of, and terminating interconnection services. In the ATN Internet sense, congestion describes the state where the network is overloaded. Typical effects of congestion are extended transit delays, drastically reduced throughput, and the loss of data packets. Techniques which continuously control the data flow into the network in order to prevent the network from getting overloaded. These encompass both open-loop techniques which ensure that a traffic contract specified b the source is respected, and closed-loop techniques which monitor signal generated by the network and adapt the traffic generated by the sources accordingly. \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 12, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
13 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 13 Congestion Management Congestion Recovery / Congestion Control Connection mode Service (CO) Connectionless mode Service (CL) Context Management contract COTP COTP COTPMMO COTS CP CPA CPC CPDLC CPDLC AE abstract service interface CPDLC ASE abstract service interface A set of rules and techniques that prevent congestion, e.g. by monitoring actual network load. Co-operative interaction of all end systems is requir in order to prevent individual end-systems taking up the throughput save by well-behaving systems. A mechanism that reacts to congestion after it has occurred in order to remove the overload condition. Congestion Recovery can be initiated on after congestion has been experienced, and is not able to safely prevent congestion in the network. The communication service technique that transfers data between peer layers using a prior connection to logically associate the sequence of protocol data units (PDUs). The communication service technique transfers data between peer layers without prior coordination. All protocol data units (PDUs) are transferre with no explicit association between them. Refers to an ATN application. This application implements an ATN log service allowing initial aircraft introduction into the ATN. The logon service also allows indication of all other data link applications on the aircraft. CM also includes functionality to forward addresses between AT centres. Thus, CM is a logon and simple directory service. Note: Conte Management is a recognised OSI presentation layer term. The OSI use and the ATN use have nothing in common. An agreement between the ADS-ground-user and the ADS-air-user that t latter will provide reports to the former under the conditions specified in the contract. CO transport protocol Connection-oriented transport protocol COTP protocol machine MO CO transport service Connect PPDU Connect Accept PPDU Controller-Pilot Communications Controller-Pilot Data Link Communications The abstract interface between the CPDLC-users and the CPDLC-service provider. The abstract interface through which the CM-ASE service are accessed.. \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 13, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
14 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 14 CPDLC service primitive CPDLC service provider CPDLC-air-ASE CPDLC-air-user CPDLC-CF CPDLC-ground-ASE CPDLC-ground-user CPR CR CR Current Data Authority CVER Data Communications Equipment (DCE) Data Link Applications Data Link Layer Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) Datagram service DC DC See Service Provider. See Service Provider. An abstract part of the aircraft system that performs the communication related functions of CPDLC. The abstract part of the aircraft system that performs the noncommunication related functions of CPDLC. That abstract part of the application entity that performs the mapping between the CPDLC-ASE service primitives and other elements within th CPDLC application. An abstract part of the ground system that performs the communication related functions of CPDLC. The abstract part of the ground system that performs the noncommunication related functions of CPDLC. Connect Reject PPDU Connection request Context Restoration The ground system that is permitted to conduct a CPDLC dialogue with a aircraft. Compressed VER An interface between data terminal equipment and the transmission mechanism. Applications using either a specific data link (air/ground subnetwork) or air-ground communications in general. ( should be replaced by the term ATN Air/Ground Applications.) The layer of the OSI reference model that manages the operations of the physical layer and may utilise special error detection or retransmission techniques to achieve acceptable error rates. A digital data transmitter/receiver device that includes terminals and computers. A service providing the transmission and reception of packets of data as discrete messages. Demand Contract Disconnect confirm \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 14, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
15 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 15 DCC DCE DCPC Demand Contract DFDAU Dialogue Dialogue service Directory Directory Service Distinguishing Path Attribute (DPA) DL DN Domain Domain Specific Part (DSP) Downstream Data Authority Data country code Data circuit terminating equipment Direct Controller-Pilot Communications A contract between a requestor and a provider of information service, such as ADS or FIS, to provide a single report to the requestor (vs. Continual reports to one request). Digital flight data acquisition unit A co-operative relationship between elements which enables communication and joint operation. The lower service boundary of an ATN-App ASE; the service allows two ATN-App ASEs to communicate, such as a CM-ground-ASE to communicate with a CM-air-ASE. A facility that supports on request the retrieval of ATN address informati or the resolution of application names. Provides the ATN user with the addressing information that is associated with the application process title or application entity title used as input t the directory. The addressing information provided by the directory serv includes the network address as well as further technical addresses on the layers above, as required or applicable. Furthermore, the ATN Directory Service resolves generic application process titles or application entity titles, i.e. names which may be incomplete or contain don t care elements, into the corresponding (list of) non-generic application process titles or application entity titles. Used to discriminate among multiple routes to a destination, based on differences in the quality of service between the routes (for example, expense, transit delay or residual error probability.) Distribution List Disconnect A set of end systems and intermediate systems that operate according to t same routing procedures and that is wholly contained within a single Administrative domain. An Addressing Authority is responsible for its own Addressing Subdoma and NSAP Addresses within that addressing domain are distinguished, where necessary, by the value of the DSP. The ground system that is permitted to conduct a DSC dialogue with an aircraft. \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 15, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
16 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 16 DPA DR DS DSP DSP DST-REF DT DT DTE E/C E/R E/T EA ED EGP emergency contract emergency contract emergency mode End Routing Domain (ERD) End System (ES) end user Engineering Trials Entity Distinguishing path attribute Disconnect request Dialogue Service Data link service provider Domain specific part Destination reference Data Data Transfer SPDU Data terminal equipment Error probability over cost flag Error report requested Error probability over transit delay flag ED acknowledge Expedited data Exterior gateway protocol A contract to provide ADS reports at regular intervals during an emergency situation A contract to provide ADS reports at regular intervals during an emergency situation A mode of operation of the aircraft when a Active User: a user that is currently involved in a CM dialogue. A RD that only routes PDUs from/to its own RD. A system that contains the seven OSI layers and contains one or more en user application processes. The human who is using the user interface to the system Trials based on pre-operational, prototype, or experimental equipment. Aim is to demonstrate the technical feasibility and correctness of applied techniques, concepts, and specifications. An active element in any layer which can either be a software entity (suc \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 16, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
17 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 17 as a process) or a hardware entity (such as an intelligent I/O chip). EoS EOT ER ER ER ERD ERP ERQ ES ESCT ESH Ethernet event contract EX EXCEP EXP Expected Quality of Service (QoS) Expected Transit Delay Expense extended projected profile F/M Element of Service End of TSDU Error [TPDU] Error report [NPDU] Error report requested flag End routing domain Echo Response [NPDU] Echo Request [NPDU] End System ES configuration timer ES hello Based on the local area network standard, ISO Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) Access Method, a Physical Layer Specifications using broadcast technology which may connect as an ATN subnetwork. A contract to provide ADS reports when certain events occur. Expedited Data SPDU Exceptions LOCREF extension flag A combination of a priori knowledge and analysis of performance information received from the operation of routing protocols. The time elapsed between the invocation of CLNS by the source ATN NS user and the arrival of an NSDU at the destination ATN NS user, based o an NPDU size of 512 octets. Transit Delay values are typically expressed in increments of 500 milliseconds. The cost to perform some task. In the context of internetworking, expens is defined in terms of the incremental expense incurred for transfer of a single NSDU of 512 octets in size. A projected profile extended up to a number of way points. Fixed/Mobile \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 17, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
18 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 18 FANS Fast Byte Fault Management FD FD FDPS FG FIB FIBMO FIFO FIS FIS-AE Abstract Service Interface FIS Abstract Service Interface FIS service-primitive FIS service-provider FIS-air-ASE FIS-air-user FIS-ASE FIS-ASE Abstract Service Interface Future Air Navigation Systems definition tbd. Encompasses fault detection, isolation, and the correction of abnormal operation, and includes functions to maintain and examine error logs, accept and act upon error detection notifications, trace and identify faults carry out sequences of diagnostic tests, and correct faults. Functional Description Full Duplex Flight Data Processing System Functional Group Forwarding information base FIB MO First in first out Flight Information Services The abstract interface between the FIS-users and the FIS-service-provide The abstract interface between the FIS-air-AE and the FIS-air-user or between the FIS-ground-AE and the FIS-ground-user. In CNS/ATM-1 Package, this interface identifies both the FIS AE abstract service interfa and the FIS-ASE abstract service interface. A function of an FIS AE that is not broken down further into subfunction and is presented as part of the abstract service interface (i.e. request, indication, response, or confirmation). Composed of the ground and airborne FIS AEs, all underlying data communication protocol entities and the physical media. As a consequence, it encompasses everything between the FIS-AE service interfaces of the end-users of the FIS application. The abstract part of the aircraft system that performs the communication related functions of FIS. The abstract part of the aircraft system that performs the non communication related functions of FIS. The FIS-air-ASE and the FIS-ground-ASE. The abstract interface through which the FIS-ASE services are accessed. \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 18, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
19 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 19 FIS-CF FIS-ground-ASE FIS-ground-user FIS-user Fixed ATN RDC flight id Flight plan The abstract part of the AE that performs the mapping between the FIS-ASE service primitives and others elements within the FIS Application. The abstract part of the ground system that performs the communications related functions of FIS. The abstract part of the ground system that performs the non communication related functions of FIS. The FIS-air-user or the FIS-ground-user. The Fixed ATN RDC consists of all ground-based RDs that form the AT An identifier, to an ICAO approved format, for a particular flight. Specified information provided to air traffic services units, relative to an intended flight or portion of a flight of an aircraft. NOTE: Specifications for flight plans are contained in Annex 2. Flow control FMS FN FOM FOM forward contract Forwarding Information Base (FIB) Four-D profile FP FSM FTAM FU Function A function that controls the flow of data to perform buffer management within a layer or between adjacent layers. Flight management system Finish SPDU An indication of the level of accuracy of positional information given in ADS report. Figure Of Merit A contract to provide a ground ADS system with ADS reports. The information base that is maintained by each ATN router and contain the set of forwarding paths reflecting the various policy and QoS ranking available to reach each known destination. TBD Full/Prefix Finite state machine File transfer, access and management Functional Unit a coherent set of activities which fulfils, by itself or together with other functionality, a concept. Examples of functions: conflict free planning; \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 19, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
20 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 20 electronic representation of the flight. Functional Requirements G GA Gateway GDMO General Communications General Topology Subnetwork GES Global Network Addressing Global Network Addressing Domain GT HD HF HI Operational requirements that determine what function a system should perform. They can usually be expressed by a verb applying to a type of data, e.g. display aircraft position. Gauge General Aviation A system used to interconnect dissimilar networks. A gateway may conta all seven layers of the OSI reference model. Guideline for definition of MOs A category of communications which includes APC, public correspondence, and other non-operational and non-administrative communications. Used to connect geographically dispersed ISs and ESs. Ground earth station An internetwork addressing plan covering worldwide aeronautical operations which enables all participating subnetworks to function in a single integrated global network. An addressing domain consisting of all the NSAP addresses in the OSI environment. Give Tokens SPDU Half Duplex High Frequency High Interface IA5 International Alphabet Number 5 IATA ICAO ICC ICC ICD ICS International Air Transport Association International Civil Aviation Organization Inter-Centre Coordination Inter-Centre Communications International code designator Implementation conformance statement \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 20, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
21 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 21 ID ID IDI IDP IDRP IDRPCFGMO IIH Indicated QoS Initial Domain Part (IDP) Institutional Issues Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) Intermediate System (IS) Internetwork Internetwork Protocol Interoperable Intra-domain routing information exchange protocol IOC Identification Identifier Initial domain identifier Initial Domain Part Interdomain routing protocol IDRP configuration MO IS-IS hello Determined by the QoS parameters passed in protocol control informatio and may reflect varying accuracy with respect to actual characteristics. The Addressing Authority responsible for an Addressing Subdomain that assigned the NSAP Address, and that specified the abstract syntax and structure of the remainder of the NSAP Address. Issues related to ownership, control, and responsibility for correct implementation and operation of systems that involve more than one stat or organisation. A public telecommunications network that supports the transmission of digitised voice and data traffic on the same transmission links. A system comprising the lower three layers of the OSI reference model a performing relaying and routing functions. A set of interconnected, logically independent heterogeneous subnetwork The constituent subnetworks are usually administrated separately and ma employ different transmission media. A protocol that performs the basic end-to-end mechanism for the transfer of data packets between network entities. In the ATN Internet, the ISO 8473 internetwork protocol is used. Describes the ability of the ATN to provide, as a minimum, a transparent data transfer service between end systems even though the ATN comprise various ground, air-to-ground, and avionics subnetworks. The ability to interoperate between end systems can be extended to include commonalit of upper layer protocols. In the ATN, the ISO IS-IS intra-domain routing information exchange protocol may be used to exchange connectivity and topology information between ATN routers within a routing domain. Internet operations centre \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 21, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
22 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 22 IP IPI IPM IPMS IPN IPRL IS IS IS-SME ISDN ISH ISN ISO ISOPA ISORM ISP ISPICS Internetwork protocol Initial protocol identifier Interpersonal message Interpersonal Messaging System Interpersonal notification ISP Protocol RL International Standard Intermediate system IS SME Integrated Services Digital Network IS hello Initial sequence number International Organization for Standardization ISO protocol architecture ISO reference model International standardized profile ISP Implementation Conformance Statement ITA-2 International Telegraph Alphabet No. 2 ITU ITU-T IUT IVMO K L1R L2R LAN International Telecommunication Union ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector Implementation under test Initial value MO Kilo Level 1 Router Level 2 Router Local area network \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 22, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
23 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 23 Level 1 subdomain Level 2 subdomain LI LI LINKMO LOC Local Area Network (LAN) LOCD LOCREF LOCRIBMO Long TSAP Lower layers LSP M MA MAC MAD Managed Object Management Administrative Domain A routing subdomain of end systems and intermediate systems that maintains detailed routing information about its own internal compositio and routing information which allows it to reach other routing areas. A level 1 subdomain area is also denoted a routing area. The subset of all level 2 intermediate systems within a routing domain. Low Interface Length indicator Linkage MO Location Identifier A network connecting various data communication devices in a localised geographical area such as a single aircraft, office building, or a group of buildings. LOC Default [Flag] Local reference Local RIB MO Composed of the RDP and the short TSAP. The physical, data link, network and transport layers of the OSI reference model. Link state PDU More [bit] (X.25) Major Synchronisation Medium Access Control Management administrative domain Data processing and data communication resources that may be managed through the use of the OSI Management protocol. A management domain where the managed objects in the domain are all under the responsibility of one, and only one, administrative authority. Management Agent Performs management operations on managed objects within its local environment as a consequence of management operations communicated from a manager. An Agent may also forward notifications emitted by managed objects to a manager. \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 23, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
24 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 24 Management Domain Management Information Base (MIB) Management Information System (MIS)-User Manager MD MD4 Mean Transit Delay Message Message Element Message Element Identifier Message Header (air/ground) Message Header (ground/ground) Message Identification Number Message Reference Number MET Resources that for systems management purposes are represented by managed objects. A management domain possesses at least the following quantities: a name that uniquely identifies that management domain, identification of a collection of managed objects that are members of the domain, and identification of any inter-domain relationships between thi domain and other domains. A conceptual composite of management information within an open system. A management application. For the purposes of network management, a MIS-User is allowed to take on one of two possible roles either an age role or a manager role. The term given to a system that requests or otherwise receives informatio about managed objects. Management Domain Message Digest Algorithm The average time it takes to transfer a standard packet size from source to destination. Basic unit of user information exchanged between an airborne applicatio and its ground counterpart, or between two ground applications. Messag are passed in one or more data blocks from one end user to another throu different subnetworks. A component of a message used to define the context of the information exchanged. The ASN.1 tag of the ATCUplinkMsgElementID or the ATCDownlinkMsgElementId. The control information used to maintain synchronisation between the aircraft and the ground ATC system. Control information used to maintain synchronisation between the two ground ATC systems. A unique number assigned to each air/ground message. This number is used to differentiate messages and is conveyed in an air/ground message header. Used to uniquely associate a response with a previously received message The Message Identification Number of a previously received message becomes the Message reference number of the response message. The Message Reference number is conveyed in the message header. Meteorological \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 24, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
25 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 25 MF-Address MHS MHS MIB MIDS MIS MO MOA Mobile Routing Domains Mobile Subnetwork MOCS MOD Mode S Mode Select (Mode S) MORTS MOTIS MS MS MTA MTS MTSE MHS-form address Message Handling Services Message handling system Management information base Management information definition statement Management information service Managed object MO attribute Formed from ATSC and AINSC systems onboard an aircraft (or any othe mobile platform), within the aircraft operator s Administrative Domain. mobile RD is characterised as an End Routing Domain (ERD). A subnetwork connecting a mobile system with another system not reside in the same mobile platform. These subnetworks tend to use free-radiatin media (e.g. VHF/UHF radio, D-band satellite or D-band secondary surveillance radar) rather than contained media (e.g. wire or coaxial cable); thus they exhibit broadcast capabilities in the truest sense. MO conformance statement Modulus Mode Select An enhanced mode of secondary surveillance radar (SSR) which permits the selective interrogation of Mode S transponders, the two-way exchang of digital data between Mode S interrogators and transponders, and also interrogation of Mode A or Mode C transponders. MO requirement template specification Message-oriented text interchange system More segments flag Message store Message transfer agent Message Transfer System Message transfer service element \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 25, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
26 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 26 Multi-homed End Routing Domain N/A navigational intent NE NEMO NET Network Addressing Domain Network Entity Network Entity Title (NET) Network Layer Network Management Network Service Access Point (NSAP) Network Service Access Point (NSAP) Address An ERD that is in communication with more than one RD. Not applicable The intended path of the aircraft for a period of time in the future. Network entity NE MO NE title A subset of the global addressing domain consisting of all the NSAP addresses allocated by one or more addressing authorities. A functional portion of an internetwork router or host computer that is responsible for the operation of internetwork data transfer, routing information exchange, and network layer management protocols. The global address of a network entity. Provides a uniform service interface for the transfer of data among end systems and intermediate systems (ISs) utilising the ISO protocol architecture. The set of functions related to the management of various OSI resources and their status across the Network Layer of the OSI architecture. Point within the ISO protocol architecture at which global end users may be uniquely addressed on an end-to-end basis. A hierarchically organised global address, supporting international, geographical, and telephony-oriented formats by way of an address forma identifier located within the protocol header. Although the top level of th NSAP address hierarchy is internationally administered by ISO, subordinate address domains are administered by appropriate local organisations. Network Topology Map Provides an overall view of the global network connectivity, and is used path computations by the operative routing algorithm. Next Data Authority NL NLE NLM NLPI The ground system so designated by the Current Data Authority. Network layer NL entity NL management NL protocol information \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 26, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
27 ANNEX 10 VOL III CHAPTER 3 Version 0.1 PART 1, page 27 NLRI NLSP NM NOR NOTAM NPAI NPDU NR NRN NS NSAP NSAP address prefix NSAPMO NSDU NSMO O/R OA OCA OCN OCNB OHI OID OOC Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Protocol Architecture NL reachability information NL security protocol Network management No orderly release Notice to Airmen Network protocol address information Network protocol data unit Negotiated Release Non-Receipt Notification Network service Network Service Access Point Used to identify groups of systems that reside in a given routing domain confederation. An NSAP prefix may have a length that is either smaller than, or the same size as, the base NSAP address. NSAP MO NS data unit Network subsystem MO Originator/recipient Overflow Accept Object class attributes Object class notifications Object class name bindings Optional Heading Information Object Identifier Operations on object classes A set of protocols used to implement the OSI reference model. \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp315.Doc, page 27, last saved 21-Jun-96 WinWord 6.0c
Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs)
 Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) Sub-Volume 1 Introduction and System-Level Requirements Version 0.7 19-June-1996 \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp316.Doc,
Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) Sub-Volume 1 Introduction and System-Level Requirements Version 0.7 19-June-1996 \\Olympus\Eurocontrol\Library\ATNP\WG2\Wps\W2wp316.Doc,
AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL(ATNP) WORKING GROUP 3 - APPLICATIONS AND UPPER LAYERS. Proposed amendment to the ATN Lexicon Ver.
 ATNP/WG3 WP/ 15-39 17/03/00 AERONAUTICA TEECOMMUNICATIONS NETWOR PANE(ATNP) WORING GROUP 3 - APPICATIONS AND UPPER AYERS Honolulu, 19 anuary 99 22 anuary 99 (fifteenth meeting) Agenda Item 10 : Any Other
ATNP/WG3 WP/ 15-39 17/03/00 AERONAUTICA TEECOMMUNICATIONS NETWOR PANE(ATNP) WORING GROUP 3 - APPICATIONS AND UPPER AYERS Honolulu, 19 anuary 99 22 anuary 99 (fifteenth meeting) Agenda Item 10 : Any Other
ROUTING TRAFFIC WITH SUBNETWORK PRIORITY 14 ON THE AMSS
 ROUTING TRAFFIC WITH SUBNETWORK PRIORITY 14 ON THE AMSS 1. Introduction... 2 2. Routing Initiation over the AMSS... 3 3. Establishment of an IDRP Connection... 4 4. Route Updates... 5 5. Periodic Exchanges
ROUTING TRAFFIC WITH SUBNETWORK PRIORITY 14 ON THE AMSS 1. Introduction... 2 2. Routing Initiation over the AMSS... 3 3. Establishment of an IDRP Connection... 4 4. Route Updates... 5 5. Periodic Exchanges
International Civil Aviation Organization. ATN Seminar and Third ATN Transition Task Force Meeting Singapore, March 2001
 ATNS - 1/2 International Civil Aviation Organization ATN Seminar and Third ATN Transition Task Force Meeting Singapore, 26-30 March 2001 Agenda Item 1: Basic ATN Concept ATN INTERNET COMMUNICATION ARCHITECTURE
ATNS - 1/2 International Civil Aviation Organization ATN Seminar and Third ATN Transition Task Force Meeting Singapore, 26-30 March 2001 Agenda Item 1: Basic ATN Concept ATN INTERNET COMMUNICATION ARCHITECTURE
ASIA/PACIFIC REGIONAL AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK (ATN) AIR TRAFFIC SERVICE (ATS) MESSAGE HANDLING SYSTEM (AMHS) DESCRIPTION
 INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATIONA ASIA AND PACIFIC OFFICE ASIA/PACIFIC REGIONAL AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK () AIR TRAFFIC SERVICE (ATS) MESSAGE HANDLING SYSTEM (AMHS) DESCRIPTION First
INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATIONA ASIA AND PACIFIC OFFICE ASIA/PACIFIC REGIONAL AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK () AIR TRAFFIC SERVICE (ATS) MESSAGE HANDLING SYSTEM (AMHS) DESCRIPTION First
ATN Presentation. December 2001
 ATN Presentation December 2001 The ATN Overview ATN (Aeronautical Telecommunication Network) ATN is a global aviation standard telecommunications network, and is intended to provide seamless ground-toground
ATN Presentation December 2001 The ATN Overview ATN (Aeronautical Telecommunication Network) ATN is a global aviation standard telecommunications network, and is intended to provide seamless ground-toground
The ATN SARPs. Sub-Volume IV. Upper Layer Communications Service. Editors Draft
 The ATN SARPs Sub-Volume IV Upper Layer Communications Service Editors Draft Please note that this is the final editor s draft circulated within the ATNP. This text will be passed to ICAO for publication.
The ATN SARPs Sub-Volume IV Upper Layer Communications Service Editors Draft Please note that this is the final editor s draft circulated within the ATNP. This text will be passed to ICAO for publication.
AMCP/4-WP/70. b) requirements and recommendations together with their rationale; and
 Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item 3 3A-1 APPENDIX A VHF DIGITAL LINK (VDL) DESIGN GUIDELINES 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 In the absence of a comprehensive and detailed set of operational requirements, the
Appendix A to the Report on Agenda Item 3 3A-1 APPENDIX A VHF DIGITAL LINK (VDL) DESIGN GUIDELINES 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 In the absence of a comprehensive and detailed set of operational requirements, the
ASIA/PACIFIC REGIONAL AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK (ATN) GROUND-GROUND ROUTER DESCRIPTION
 INTENATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION OGANIZATION ASIA AND PACIFIC OFFICE ASIA/PACIFIC EGIONAL AEONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWOK (ATN) GOUND-GOUND OUTE DESCIPTION Edition 1.2 May 2004 ISSUE 1.2- MAY 2004 Table
INTENATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION OGANIZATION ASIA AND PACIFIC OFFICE ASIA/PACIFIC EGIONAL AEONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWOK (ATN) GOUND-GOUND OUTE DESCIPTION Edition 1.2 May 2004 ISSUE 1.2- MAY 2004 Table
Proposed ATN Naming and Addressing Extensions
 ATNP/WG3/WP 13-11 12 June1998 EUROCONTROL AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK PANEL WORKING GROUP 3 (APPLICATIONS AND UPPER LAYERS) Utrecht, Netherlands, 29 June - 3 July 1998 Presented by: Tony Kerr
ATNP/WG3/WP 13-11 12 June1998 EUROCONTROL AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK PANEL WORKING GROUP 3 (APPLICATIONS AND UPPER LAYERS) Utrecht, Netherlands, 29 June - 3 July 1998 Presented by: Tony Kerr
Tel.: +1 (514) ext Ref.: AN 7/ /39 22 June 2007
 International Civil Aviation Organization Organisation de l aviation civile internationale Organización de Aviación Civil Internacional Ìåæäóíàðîäíàÿ îðãàíèçàöèÿ ãðàæäàíñêîé àâèàöèè Tel.: +1 (514) 954-8219
International Civil Aviation Organization Organisation de l aviation civile internationale Organización de Aviación Civil Internacional Ìåæäóíàðîäíàÿ îðãàíèçàöèÿ ãðàæäàíñêîé àâèàöèè Tel.: +1 (514) 954-8219
REPORT ON AGENDA ITEM 4
 15/2/00 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK PANEL (ATNP) THIRD MEETING Montreal, 7 to 18 February 2000 Agenda Item 4: Review of existing technical and procedural provisions relating to the aeronautical
15/2/00 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK PANEL (ATNP) THIRD MEETING Montreal, 7 to 18 February 2000 Agenda Item 4: Review of existing technical and procedural provisions relating to the aeronautical
MANUAL ON DETAILED TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK (ATN) using ISO/OSI standards and protocols
 Doc 9880-AN/466 PART III MANUAL ON DETAILED TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK (ATN) using ISO/OSI standards and protocols PART III INTERNET COMMUNICATION SERVICE,
Doc 9880-AN/466 PART III MANUAL ON DETAILED TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK (ATN) using ISO/OSI standards and protocols PART III INTERNET COMMUNICATION SERVICE,
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION )454 X.227 TELECOMMUNICATION (04/95) STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU $!4!.%47/2+3!.$ /0%. 3934%- #/--5.)#!4)/.3 /0%. 3934%-3 ).4%2#/..%#4)/. #/..%#4)/.-/$% 02/4/#/,
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION )454 X.227 TELECOMMUNICATION (04/95) STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU $!4!.%47/2+3!.$ /0%. 3934%- #/--5.)#!4)/.3 /0%. 3934%-3 ).4%2#/..%#4)/. #/..%#4)/.-/$% 02/4/#/,
MANUAL ON DETAILED TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK (ATN) using ISO/OSI standards and protocols
 Doc 9880-AN/466 PART IIA MANUAL ON DETAILED TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK (ATN) using ISO/OSI standards and protocols PART IIA GROUND-GROUND APPLICATIONS ATS INTERFACILITY
Doc 9880-AN/466 PART IIA MANUAL ON DETAILED TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK (ATN) using ISO/OSI standards and protocols PART IIA GROUND-GROUND APPLICATIONS ATS INTERFACILITY
Federal Aviation Administration (FAA)
 Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) CHANG MAI - ATN SEMINAR CPDLC OVERVIEW December 2001 Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) William J. Hughes Technical l Center (WJHTC) Vic Patel, FAA/ACT-550 ISSP
Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) CHANG MAI - ATN SEMINAR CPDLC OVERVIEW December 2001 Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) William J. Hughes Technical l Center (WJHTC) Vic Patel, FAA/ACT-550 ISSP
ATN ROUTING APPENDIX 6. A6.1 Introduction. A6.1.3 Applicability of Requirements. A6.1.1 Scope. A6.1.2 References
 APPENDIX 6 ATN ROUTING Exchange between Systems - OSI Routeing Framework A6.1 Introduction A6.1.1 Scope This appendix provides requirements and recommendations pertaining to the deployment of ATN components
APPENDIX 6 ATN ROUTING Exchange between Systems - OSI Routeing Framework A6.1 Introduction A6.1.1 Scope This appendix provides requirements and recommendations pertaining to the deployment of ATN components
The ATN Routing Concept
 ATNP/WP/ ATNP/WG2-WP/ 10 October 1994 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL Working Group Two San Diego 17.10.94-28.10.94 The ATN Routing Concept Presented By Eike Meyenberg and Henk Hof Prepared
ATNP/WP/ ATNP/WG2-WP/ 10 October 1994 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL Working Group Two San Diego 17.10.94-28.10.94 The ATN Routing Concept Presented By Eike Meyenberg and Henk Hof Prepared
Manual on Detailed Technical Specifications for the Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) using ISO/OSI Standards and Protocols
 Doc 9880 AN/466 Manual on Detailed Technical Specifications for the Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) using ISO/OSI Standards and Protocols Part II Ground-Ground Applications Air Traffic Services
Doc 9880 AN/466 Manual on Detailed Technical Specifications for the Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) using ISO/OSI Standards and Protocols Part II Ground-Ground Applications Air Traffic Services
Functional areas of the communications domain. List of example constituents and standards for the air-ground applications functional area
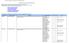 Air-ground communication applications Air-ground communication networks Air-ground datalink communication Air-ground voice communications Ground-ground communication applications Ground-ground communication
Air-ground communication applications Air-ground communication networks Air-ground datalink communication Air-ground voice communications Ground-ground communication applications Ground-ground communication
International Civil Aviation Organization. AIDC Review Task Force Meeting. Brisbane, Australia, March 2003
 AIDC/R TF/IP/3 International Civil Aviation Organization AIDC Review Task Force Meeting Brisbane, Australia, 27-28 March 2003 Agenda Item 2: Agenda Item 4: Review of experience gained and lessons learned
AIDC/R TF/IP/3 International Civil Aviation Organization AIDC Review Task Force Meeting Brisbane, Australia, 27-28 March 2003 Agenda Item 2: Agenda Item 4: Review of experience gained and lessons learned
DATA COMMUNICATION NETWORKS INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY OPEN SYSTEMS INTERCONNECTION SYSTEMS MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION CCITT X.701 THE INTERNATIONAL TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE CONSULTATIVE COMMITTEE DATA COMMUNICATION NETWORKS INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY OPEN SYSTEMS INTERCONNECTION SYSTEMS
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION CCITT X.701 THE INTERNATIONAL TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE CONSULTATIVE COMMITTEE DATA COMMUNICATION NETWORKS INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY OPEN SYSTEMS INTERCONNECTION SYSTEMS
International Civil Aviation Organization. Fifth Meeting of Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Transition Task Force of APANPIRG
 ATTF/5-IP/11 International Civil Aviation Organization Fifth Meeting of Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Transition Task Force of APANPIRG Phuket, Thailand, 9-13 June, 2003 Agenda Item 9: Review
ATTF/5-IP/11 International Civil Aviation Organization Fifth Meeting of Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) Transition Task Force of APANPIRG Phuket, Thailand, 9-13 June, 2003 Agenda Item 9: Review
ATN Upper Layers Guidance Material
 ATN Upper Layers Guidance Material ATNP/WG3/SG3, 15 October 1997 Version 5.1 ii ATN Upper Layers Guidance Material REVISION STATUS Version Date Comment 1.0 Feb 1996 First draft Guidance Material for Upper
ATN Upper Layers Guidance Material ATNP/WG3/SG3, 15 October 1997 Version 5.1 ii ATN Upper Layers Guidance Material REVISION STATUS Version Date Comment 1.0 Feb 1996 First draft Guidance Material for Upper
Proposed Modifications to CNS/ATM-1 Applications To Support Package-2 Security Services
 ATNP/WG3/WP 15-31 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL Working Group 3 (Applications and Upper Layers) Honolulu (U.S.A), 19 22 January 1999 Proposed Modifications to CNS/ATM-1 Applications To
ATNP/WG3/WP 15-31 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL Working Group 3 (Applications and Upper Layers) Honolulu (U.S.A), 19 22 January 1999 Proposed Modifications to CNS/ATM-1 Applications To
ISO/IEC 8348 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Information technology Open Systems Interconnection Network service definition
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 8348 Third edition 2002-11-01 Information technology Open Systems Interconnection Network service definition Technologies de l'information Interconnexion des systèmes ouverts
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 8348 Third edition 2002-11-01 Information technology Open Systems Interconnection Network service definition Technologies de l'information Interconnexion des systèmes ouverts
CNS/ATM-1 Package Internet SARPs Validation Objectives
 ATNP/WG2-WP/ 12-Apr-96 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL WORKING GROUP 2 Bruxelles, Belgium, 22-26 April 1996 CNS/ATM-1 Package Internet SARPs Validation Objectives Prepared by Jean-Pierre
ATNP/WG2-WP/ 12-Apr-96 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL WORKING GROUP 2 Bruxelles, Belgium, 22-26 April 1996 CNS/ATM-1 Package Internet SARPs Validation Objectives Prepared by Jean-Pierre
Aeronautical Communication Panel. Application Level Security Considerations
 ACP SGN4 WP0306 ACP WGN04 WP18 Aeronautical Communication Panel Working Group N Networking Subgroup N4 - November 2004 New Orleans, LA, USA Application Level Considerations Prepared By: Tom McParland,
ACP SGN4 WP0306 ACP WGN04 WP18 Aeronautical Communication Panel Working Group N Networking Subgroup N4 - November 2004 New Orleans, LA, USA Application Level Considerations Prepared By: Tom McParland,
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Routing Protocol
 CHAPTER 41 Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Protocol Background The International Organization for Standardization (O) developed a complete suite of routing protocols for use in the Open Systems Interconnection
CHAPTER 41 Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Protocol Background The International Organization for Standardization (O) developed a complete suite of routing protocols for use in the Open Systems Interconnection
Eurocontrol ATN Trials End System - Status Update
 ATNP/WG3/WP 15-18 17 January 1999 EUROCONTROL AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK PANEL WORKING GROUP 3 (APPLICATIONS AND UPPER LAYERS) Honolulu, USA, 19-22 January 1999 (Information paper) Eurocontrol
ATNP/WG3/WP 15-18 17 January 1999 EUROCONTROL AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK PANEL WORKING GROUP 3 (APPLICATIONS AND UPPER LAYERS) Honolulu, USA, 19-22 January 1999 (Information paper) Eurocontrol
Network Working Group Request for Comments: UMich February 1989
 Network Working Group Request for Comments: 1069 Obsoletes: RFC 986 R. Callon DEC H.W. Braun UMich February 1989 Guidelines for the use of Internet-IP addresses in the ISO Connectionless-Mode Network Protocol
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 1069 Obsoletes: RFC 986 R. Callon DEC H.W. Braun UMich February 1989 Guidelines for the use of Internet-IP addresses in the ISO Connectionless-Mode Network Protocol
AFI AMHS Manual, Appendix A
 AFI AMHS Manual AFI AMHS Manual Appendix A Abbreviations, Glossary and Definitions Document Reference: Author: AFI AMHS Manual, Appendix A AFI AMHS Taskforce Team Revision Number: Version 2.0 Date: 27/07/2013
AFI AMHS Manual AFI AMHS Manual Appendix A Abbreviations, Glossary and Definitions Document Reference: Author: AFI AMHS Manual, Appendix A AFI AMHS Taskforce Team Revision Number: Version 2.0 Date: 27/07/2013
REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON AMHS
 AMHS WORKSHOP International Civil Aviation Organization REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON AMHS AMHS Detailed specifications (Dakar, 28-29 May 2013) Outline High level requirements ATS Message Service Validation performed
AMHS WORKSHOP International Civil Aviation Organization REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON AMHS AMHS Detailed specifications (Dakar, 28-29 May 2013) Outline High level requirements ATS Message Service Validation performed
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 941 April Addendum to the Network Service Definition Covering Network Layer Addressing
 Network Working Group ISO Request for Comments: 941 April 1985 Addendum to the Network Service Definition Covering Status of this RFC: ISO/DP8348/DAD2 (also TC 97/SC 6/N 3444) This document is distributed
Network Working Group ISO Request for Comments: 941 April 1985 Addendum to the Network Service Definition Covering Status of this RFC: ISO/DP8348/DAD2 (also TC 97/SC 6/N 3444) This document is distributed
ATNP WG2 Utrecht, Netherlands 29 June 1 July IDRP Security. Prepared by Ron Jones. Summary
 ATNP WG2/WP 450 8 June 1998 ATNP WG2 Utrecht, Netherlands 29 June 1 July 1998 IDRP Security Prepared by Ron Jones Summary This working paper presents a review of ISO/IEC 10747 and Sub-Volume 5 as regards
ATNP WG2/WP 450 8 June 1998 ATNP WG2 Utrecht, Netherlands 29 June 1 July 1998 IDRP Security Prepared by Ron Jones Summary This working paper presents a review of ISO/IEC 10747 and Sub-Volume 5 as regards
Manual on Detailed Technical Specifications for the Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) using ISO/OSI Standards and Protocols
 Doc 9880 AN/466 Manual on Detailed Technical Specifications for the Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) using ISO/OSI Standards and Protocols Part IV Directory Services, Security and Systems ManagementIdentifier
Doc 9880 AN/466 Manual on Detailed Technical Specifications for the Aeronautical Telecommunication Network (ATN) using ISO/OSI Standards and Protocols Part IV Directory Services, Security and Systems ManagementIdentifier
AFTN/CIDIN system SUN/Solaris platform Linux platform
 In the context of the ATN (Aeronautical Telecommunication Network), Vitrociset provides some systems for the exchanging of ATS (Air Traffic Service) messages. The systems cover the exchanging of messages
In the context of the ATN (Aeronautical Telecommunication Network), Vitrociset provides some systems for the exchanging of ATS (Air Traffic Service) messages. The systems cover the exchanging of messages
CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer
 CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer LOCAL CISCO ACADEMY ELSYS TU INSTRUCTOR: STELA STEFANOVA 1 Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission; Objectives Describe how the
CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer LOCAL CISCO ACADEMY ELSYS TU INSTRUCTOR: STELA STEFANOVA 1 Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission; Objectives Describe how the
AFI AMHS Manual. AFI AMHS Manual. AFI AMHS Manual. AFI AMHS Taskforce Team. Revision Number: Version 1.0. Date: 21/07/2011. AFI AMHS Manual_V1.0.
 Document Reference: Author:, Main Part AFI AMHS Taskforce Team Revision Number: Version 1.0 Date: Filename: _V1.0.doc [1] Version 1.0 Document Control Log Edition Date Comments section/pages affected 1.0
Document Reference: Author:, Main Part AFI AMHS Taskforce Team Revision Number: Version 1.0 Date: Filename: _V1.0.doc [1] Version 1.0 Document Control Log Edition Date Comments section/pages affected 1.0
Review of the ATN CAR/SAM Planning/Implementation Activities. (Presented by the Coordinator) SUMMARY
 WP/2 5/05/10 International Civil Aviation Organization CAR/SAM Regional Planning Implementation Group (GREPECAS) CNS/ATM Subgroup Coordination meeting of the ATN ground-ground and ground-air applications
WP/2 5/05/10 International Civil Aviation Organization CAR/SAM Regional Planning Implementation Group (GREPECAS) CNS/ATM Subgroup Coordination meeting of the ATN ground-ground and ground-air applications
Validating ATN with VDL
 ATNP WG-2 WP 346 bis AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL (ATNP) Validating ATN with VDL Prepared by Nicholas Xenocostas and David Leahy Presented by H. Thulin SUMMARY This Working paper presents
ATNP WG-2 WP 346 bis AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK PANEL (ATNP) Validating ATN with VDL Prepared by Nicholas Xenocostas and David Leahy Presented by H. Thulin SUMMARY This Working paper presents
Validation Tool Descriptions for ATN Applications
 ATNP/WG3/IP EUROCONTROL 12 April 1996 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK PANEL WORKING GROUP 3 (APPLICATIONS AND UPPER LAYERS) Brussels, 15-26 April, 1996 Validation Tool Descriptions for ATN Applications
ATNP/WG3/IP EUROCONTROL 12 April 1996 AERONAUTICAL TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORK PANEL WORKING GROUP 3 (APPLICATIONS AND UPPER LAYERS) Brussels, 15-26 April, 1996 Validation Tool Descriptions for ATN Applications
The Internet. The Internet is an interconnected collection of netw orks.
 The Internet The Internet is an interconnected collection of netw orks. Internetw orking-1 Internetworking! Communications Network: A facility that provides a data transfer service among stations attached
The Internet The Internet is an interconnected collection of netw orks. Internetw orking-1 Internetworking! Communications Network: A facility that provides a data transfer service among stations attached
Network Working Group ISO Request for Comments: 905 April 1984
 Network Working Group ISO Request for Comments: 905 April 1984 ISO Transport Protocol Specification ISO DP 8073 Status of this Memo: This document is distributed as an RFC for information only. does not
Network Working Group ISO Request for Comments: 905 April 1984 ISO Transport Protocol Specification ISO DP 8073 Status of this Memo: This document is distributed as an RFC for information only. does not
EUR AMHS Manual, Appendix G
 EUR AMHS Manual EUR Doc 020 EUR AMHS Manual Appendix G European Directory Service Document Reference: Author: EUR AMHS Manual, Appendix G EUROCONTROL, Revision Number: Version 12.0 Date: 28/04/17 Filename:
EUR AMHS Manual EUR Doc 020 EUR AMHS Manual Appendix G European Directory Service Document Reference: Author: EUR AMHS Manual, Appendix G EUROCONTROL, Revision Number: Version 12.0 Date: 28/04/17 Filename:
EUR AMHS Manual, Appendix A
 EUR AMHS Manual EUR Doc 020 EUR AMHS Manual Appendix A Abbreviations, Glossary and Definitions Document Reference: Author: EUR AMHS Manual, Appendix A Revision Number: Version 12.0 Date: 28/04/17 Filename:
EUR AMHS Manual EUR Doc 020 EUR AMHS Manual Appendix A Abbreviations, Glossary and Definitions Document Reference: Author: EUR AMHS Manual, Appendix A Revision Number: Version 12.0 Date: 28/04/17 Filename:
Sixth Meeting of CNS/MET Sub-Group of APANPIRG
 CNS/MET/SG/6-IP/32 International Civil Aviation Organization Sixth Meeting of CNS/MET Sub-Group of APANPIRG Bangkok, Thailand, 15-19 July 2002 Agenda Item 3: ATN transition planning TECHNICAL DOCUMENT
CNS/MET/SG/6-IP/32 International Civil Aviation Organization Sixth Meeting of CNS/MET Sub-Group of APANPIRG Bangkok, Thailand, 15-19 July 2002 Agenda Item 3: ATN transition planning TECHNICAL DOCUMENT
REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON AMHS
 International Civil Aviation Organization REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON AMHS System Level Provisions (Dakar, 28-29 May 2013) Outline ATSMHS users AMHS model Organization of the AMHS AMHS management domain Naming
International Civil Aviation Organization REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON AMHS System Level Provisions (Dakar, 28-29 May 2013) Outline ATSMHS users AMHS model Organization of the AMHS AMHS management domain Naming
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T Q.772 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (06/97) SERIES Q: SWITCHING AND SIGNALLING Specifications of Signalling System No. 7 Transaction capabilities
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T Q.772 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (06/97) SERIES Q: SWITCHING AND SIGNALLING Specifications of Signalling System No. 7 Transaction capabilities
ATSMHS SARPs Validation Report
 ATNP/WG3 WP/9-4a 05/03/97 ATSMHS SARPs Validation Report Presented by Jean-Yves Piram (SG1 Chairman) Prepared by Jean-Marc Vacher Version 2.0a Appendix G: ATSMHS SARPs Validation report Appendix G: ATSMHS
ATNP/WG3 WP/9-4a 05/03/97 ATSMHS SARPs Validation Report Presented by Jean-Yves Piram (SG1 Chairman) Prepared by Jean-Marc Vacher Version 2.0a Appendix G: ATSMHS SARPs Validation report Appendix G: ATSMHS
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE INTERFACE STANDARD STANDARDIZED PROFILE FOR ASYNCHRONOUS TRANSFER MODE (ATM)
 NOTICE OF CHANGE INCH-POUND DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE INTERFACE STANDARD STANDARDIZED PROFILE FOR ASYNCHRONOUS TRANSFER MODE (ATM) TO ALL HOLDERS OF : 1. THE FOLLOWING PAGES OF HAVE BEEN REVISED AND SUPERSEDE
NOTICE OF CHANGE INCH-POUND DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE INTERFACE STANDARD STANDARDIZED PROFILE FOR ASYNCHRONOUS TRANSFER MODE (ATM) TO ALL HOLDERS OF : 1. THE FOLLOWING PAGES OF HAVE BEEN REVISED AND SUPERSEDE
Frame Relay. Frame Relay Information 1 of 18
 Frame Relay Information 1 of 18 This document was retrieved from the Web and has been been edited by Thomas Jerry Scott for use in his TCP/IP network classes. Chapter Goals Describe the history of Frame
Frame Relay Information 1 of 18 This document was retrieved from the Web and has been been edited by Thomas Jerry Scott for use in his TCP/IP network classes. Chapter Goals Describe the history of Frame
International Civil Aviation Organization. ATN Seminar and Third ATN Transition Task Force Meeting Singapore, March 2001
 ATNS - 4/1 International Civil Aviation Organization ATN Seminar and Third ATN Transition Task Force Meeting Singapore, 26-30 March 2001 Agenda Item 4: ATN Air-Ground Application CONTROLLER PILOT DATA
ATNS - 4/1 International Civil Aviation Organization ATN Seminar and Third ATN Transition Task Force Meeting Singapore, 26-30 March 2001 Agenda Item 4: ATN Air-Ground Application CONTROLLER PILOT DATA
Network Working Group ANSI X3S Request for Comments: 994 ISO TC97/SC6/N 3998 March 1986
 Network Working Group ANSI X3S3.3 86-80 Request for Comments: 994 ISO TC97/SC6/N 3998 March 1986 I S O INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION ISO/TC
Network Working Group ANSI X3S3.3 86-80 Request for Comments: 994 ISO TC97/SC6/N 3998 March 1986 I S O INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION ISO/TC
INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION
 ICAO EUR DOC 005 INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION EUR CIDIN MANUAL Sixth Edition Published by the European and North Atlantic Office of ICAO April 2011 EUR CIDIN MANUAL Record of Amendments and
ICAO EUR DOC 005 INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION EUR CIDIN MANUAL Sixth Edition Published by the European and North Atlantic Office of ICAO April 2011 EUR CIDIN MANUAL Record of Amendments and
Switched Multimegabit Data Service (SMDS)
 CHAPTER 14 Switched Multimegabit Data Service (SMDS) Background Switched Multimegabit Data Service (SMDS) is a high-speed, packet-switched, datagram-based WAN networking technology used for communication
CHAPTER 14 Switched Multimegabit Data Service (SMDS) Background Switched Multimegabit Data Service (SMDS) is a high-speed, packet-switched, datagram-based WAN networking technology used for communication
Request for Comments: 1007 June 1987
 Network Working Group Wayne McCoy Request for Comments: 1007 June 1987 MILITARY SUPPLEMENT TO THE ISO TRANSPORT PROTOCOL Status of this Memo This RFC is being distributed to members of the Internet community
Network Working Group Wayne McCoy Request for Comments: 1007 June 1987 MILITARY SUPPLEMENT TO THE ISO TRANSPORT PROTOCOL Status of this Memo This RFC is being distributed to members of the Internet community
Standardizing Information and Communication Systems
 Standard ECMA-155 2nd Edition - June 1997 Standardizing Information and Communication Systems Private Integrated Services Networks - Addressing Phone: +41 22 849.60.00 - Fax: +41 22 849.60.01 - URL: http://www.ecma.ch
Standard ECMA-155 2nd Edition - June 1997 Standardizing Information and Communication Systems Private Integrated Services Networks - Addressing Phone: +41 22 849.60.00 - Fax: +41 22 849.60.01 - URL: http://www.ecma.ch
AC-B. Seminar Documentation ATS Message Handling System (AMHS) Part 1: AMHS Basics
 Seminar Documentation ATS Message Handling System (AMHS) Part 1: AMHS Basics Manfred Okle c/o GmbH Robert-Bosch-Straße 20 88677 Markdorf Germany October 2005 ATS Message Handling System (AMHS) Part 1 AMHS
Seminar Documentation ATS Message Handling System (AMHS) Part 1: AMHS Basics Manfred Okle c/o GmbH Robert-Bosch-Straße 20 88677 Markdorf Germany October 2005 ATS Message Handling System (AMHS) Part 1 AMHS
Computer Networks with Internet Technology William Stallings. Chapter 2 Protocols and the TCP/IP Protocol Suite
 Computer Networks with Internet Technology William Stallings Chapter 2 Protocols and the TCP/IP Protocol Suite Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate comms. Path or inform
Computer Networks with Internet Technology William Stallings Chapter 2 Protocols and the TCP/IP Protocol Suite Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate comms. Path or inform
Mobitex Transport Protocol 1 (MTP/1)
 Mobitex Transport Protocol 1 (MTP/1) Contents 1 Introduction...5 2 Terminology...6 3 Transport Service Definition...11 3.1 General...11 3.1.1 Introduction...11 3.1.2 System Environment...12 3.1.3 Features
Mobitex Transport Protocol 1 (MTP/1) Contents 1 Introduction...5 2 Terminology...6 3 Transport Service Definition...11 3.1 General...11 3.1.1 Introduction...11 3.1.2 System Environment...12 3.1.3 Features
International Civil Aviation Organization. Fourth ATN Transition Task Force Meeting
 International Civil Aviation Organization ATTF/4 WP/21 Fourth ATN Transition Task Force Meeting Mumbai, India, 8-12 April 2002 Agenda Item 2: Develop ATN Interface Control Documents ASIA/PACIFIC REGIONAL
International Civil Aviation Organization ATTF/4 WP/21 Fourth ATN Transition Task Force Meeting Mumbai, India, 8-12 April 2002 Agenda Item 2: Develop ATN Interface Control Documents ASIA/PACIFIC REGIONAL
Configuring ISO CLNS. Understanding Addresses
 Configuring ISO CLNS The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Connectionless Network Service (CLNS) protocol is a standard for the network layer of the Open System Interconnection (OSI)
Configuring ISO CLNS The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Connectionless Network Service (CLNS) protocol is a standard for the network layer of the Open System Interconnection (OSI)
IS-IS basic configuration 37 DIS election configuration 41 Configuring IS-IS route redistribution 45 IS-IS GR configuration example 49 IS-IS FRR
 Contents Configuring IS-IS 1 IS-IS overview 1 Basic concepts 1 IS-IS area 3 IS-IS network type 5 IS-IS PDUs 6 Supported IS-IS features 13 Protocols and standards 15 IS-IS configuration task list 16 Configuring
Contents Configuring IS-IS 1 IS-IS overview 1 Basic concepts 1 IS-IS area 3 IS-IS network type 5 IS-IS PDUs 6 Supported IS-IS features 13 Protocols and standards 15 IS-IS configuration task list 16 Configuring
5/4/2016 ht.ttlms.com
 Order Template Screen 1 Free Form Lesson Overview 2 Free Form Performance Based CNS Requirements 3 Free Form Performance Based CNS Requirements 4 Single Answer Knowledge Check 5 Free Form Related ICAO
Order Template Screen 1 Free Form Lesson Overview 2 Free Form Performance Based CNS Requirements 3 Free Form Performance Based CNS Requirements 4 Single Answer Knowledge Check 5 Free Form Related ICAO
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION. SERIES Q: SWITCHING AND SIGNALLING Q3 interface. Lower layer protocol profiles for the Q and X interfaces
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T Q.811 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (02/2004) SERIES Q: SWITCHING AND SIGNALLING Q3 interface Lower layer protocol profiles for the Q and X
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T Q.811 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (02/2004) SERIES Q: SWITCHING AND SIGNALLING Q3 interface Lower layer protocol profiles for the Q and X
Introduction to Networking
 Introduction to Networking The fundamental purpose of data communications is to exchange information between user's computers, terminals and applications programs. Simplified Communications System Block
Introduction to Networking The fundamental purpose of data communications is to exchange information between user's computers, terminals and applications programs. Simplified Communications System Block
AERONAUTICAL FIXED SERVICES GROUP (AFSG) of the European Air Navigation Planning Group (EANPG)
 AFSG/16 WP/16 04/04/2012 AERONAUTICAL FIXED SERVICES GROUP (AFSG) of the European Air Navigation Planning Group (EANPG) SIXTEENTH MEETING (Paris, 23-27 April 2012) Agenda Item 4: AMHS Technical/Documentation
AFSG/16 WP/16 04/04/2012 AERONAUTICAL FIXED SERVICES GROUP (AFSG) of the European Air Navigation Planning Group (EANPG) SIXTEENTH MEETING (Paris, 23-27 April 2012) Agenda Item 4: AMHS Technical/Documentation
Computer Networks (Introduction to TCP/IP Protocols)
 Network Security(CP33925) Computer Networks (Introduction to TCP/IP Protocols) 부산대학교공과대학정보컴퓨터공학부 Network Type Elements of Protocol OSI Reference Model OSI Layers What we ll learn today 2 Definition of
Network Security(CP33925) Computer Networks (Introduction to TCP/IP Protocols) 부산대학교공과대학정보컴퓨터공학부 Network Type Elements of Protocol OSI Reference Model OSI Layers What we ll learn today 2 Definition of
AMHS Implementation Issues. Julio C. Siu Regional Officer/ Communication, Navigation and Surveillance
 AMHS Implementation Issues Julio C. Siu Regional Officer/ Communication, Navigation and Surveillance III Workshop/Meeting on the Follow up to the Implementation of the ATS Message Handling System (AMHS)
AMHS Implementation Issues Julio C. Siu Regional Officer/ Communication, Navigation and Surveillance III Workshop/Meeting on the Follow up to the Implementation of the ATS Message Handling System (AMHS)
Data & Computer Communication
 Basic Networking Concepts A network is a system of computers and other devices (such as printers and modems) that are connected in such a way that they can exchange data. A bridge is a device that connects
Basic Networking Concepts A network is a system of computers and other devices (such as printers and modems) that are connected in such a way that they can exchange data. A bridge is a device that connects
ISO 9542 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 9542 First edition 19880815 AENDENT 1 19990915 Information processing systems Telecommunications and information exchange between systems End system to Intermediate system routeing
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 9542 First edition 19880815 AENDENT 1 19990915 Information processing systems Telecommunications and information exchange between systems End system to Intermediate system routeing
Superseded by a more recent version INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T X.36 TELECOMMUNICATION (04/95) STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU DATA NETWORKS AND OPEN SYSTEM COMMUNICATIONS PUBLIC DATA NETWORKS INTERFACES INTERFACE BETWEEN DATA
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T X.36 TELECOMMUNICATION (04/95) STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU DATA NETWORKS AND OPEN SYSTEM COMMUNICATIONS PUBLIC DATA NETWORKS INTERFACES INTERFACE BETWEEN DATA
ET4254 Communications and Networking 1
 Topic 9 Internet Protocols Aims:- basic protocol functions internetworking principles connectionless internetworking IP IPv6 IPSec 1 Protocol Functions have a small set of functions that form basis of
Topic 9 Internet Protocols Aims:- basic protocol functions internetworking principles connectionless internetworking IP IPv6 IPSec 1 Protocol Functions have a small set of functions that form basis of
Need For Protocol Architecture
 Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
Data and Computer Communications. Chapter 2 Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet-Based Applications
 Data and Computer Communications Chapter 2 Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet-Based s 1 Need For Protocol Architecture data exchange can involve complex procedures better if task broken into subtasks
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 2 Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet-Based s 1 Need For Protocol Architecture data exchange can involve complex procedures better if task broken into subtasks
EUROPEAN ETS TELECOMMUNICATION June 1993 STANDARD
 EUROPEAN ETS 300 239 TELECOMMUNICATION June 1993 STANDARD Source: ETSI TC-ECMA Reference: DE/ECMA-0045 ICS: 33.080 Key words: PTN, QSIG-GF, ECMA-165 Private Telecommunication Network (PTN); Inter-exchange
EUROPEAN ETS 300 239 TELECOMMUNICATION June 1993 STANDARD Source: ETSI TC-ECMA Reference: DE/ECMA-0045 ICS: 33.080 Key words: PTN, QSIG-GF, ECMA-165 Private Telecommunication Network (PTN); Inter-exchange
DECnet. Background CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 28 DECnet Background DECnet is a group of data-communications products, including a protocol suite, developed and supported by Digital Equipment Corporation. The first version of DECnet, released
CHAPTER 28 DECnet Background DECnet is a group of data-communications products, including a protocol suite, developed and supported by Digital Equipment Corporation. The first version of DECnet, released
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T Q.774 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (06/97) SERIES Q: SWITCHING AND SIGNALLING Specifications of Signalling System. 7 Transaction capabilities
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T Q.774 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (06/97) SERIES Q: SWITCHING AND SIGNALLING Specifications of Signalling System. 7 Transaction capabilities
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 1768 Category: Experimental March 1995
 Network Working Group D. Marlow Request for Comments: 1768 NSWC-DD Category: Experimental March 1995 Status of this Memo Host Group Extensions for CLNP Multicasting This memo defines an Experimental Protocol
Network Working Group D. Marlow Request for Comments: 1768 NSWC-DD Category: Experimental March 1995 Status of this Memo Host Group Extensions for CLNP Multicasting This memo defines an Experimental Protocol
ISO/IEC : 1994(E) ITU-T Rec. X.200 (1994 E) Information Processing Systems OSI Reference Model The Basic Model
 ISO/IEC 7498-1 : 1994(E) ITU-T Rec. X.200 (1994 E) Information Processing Systems OSI Reference Model The Basic Model Table of content 1 SCOPE... 3 2 DEFINITIONS... 5 3 NOTATION... 6 4 INTRODUCTION TO
ISO/IEC 7498-1 : 1994(E) ITU-T Rec. X.200 (1994 E) Information Processing Systems OSI Reference Model The Basic Model Table of content 1 SCOPE... 3 2 DEFINITIONS... 5 3 NOTATION... 6 4 INTRODUCTION TO
Draft Upper Layer Guidance Material for CNS/ATM-1 Package
 CNS/ATM-1 IV GM WG3/WP6-5 ATNP WG3/SG3 (Upper Layer Architecture) Draft Upper Layer Guidance Material for CNS/ATM-1 Package (Presented by WG3/SG3) ATN Upper Layer Guidance Material REVISION STATUS Version
CNS/ATM-1 IV GM WG3/WP6-5 ATNP WG3/SG3 (Upper Layer Architecture) Draft Upper Layer Guidance Material for CNS/ATM-1 Package (Presented by WG3/SG3) ATN Upper Layer Guidance Material REVISION STATUS Version
AFI AMHS Manual, Appendix E
 AFI AMHS Manual AFI AMHS Manual Appendix E AMHS Interoperability s Document Reference: Author: AFI AMHS Manual, Appendix E AFI AMHS Taskforce Team Revision Number: Version 2.0 Date: 28/07/13 Filename:
AFI AMHS Manual AFI AMHS Manual Appendix E AMHS Interoperability s Document Reference: Author: AFI AMHS Manual, Appendix E AFI AMHS Taskforce Team Revision Number: Version 2.0 Date: 28/07/13 Filename:
EACI ATN INTERNET PROJECT (ATNIP)
 EACI ATN INTERNET PRJECT (ATNIP) Disposition of Deleted Requirements in Appendix 11 of the ATN Manual ATNIP Ref. Author : DED1/EAS3/STA_ATNP/DC/033 : Tony Whyman Rev. No. : Issue 1.0 Date : 12-Jun-95 DCUMENT
EACI ATN INTERNET PRJECT (ATNIP) Disposition of Deleted Requirements in Appendix 11 of the ATN Manual ATNIP Ref. Author : DED1/EAS3/STA_ATNP/DC/033 : Tony Whyman Rev. No. : Issue 1.0 Date : 12-Jun-95 DCUMENT
Superseded by a more recent version INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T X.162 TELECOMMUNICATION (04/95) STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU DATA NETWORKS AND OPEN SYSTEM COMMUNICATIONS PUBLIC DATA NETWORKS MAINTENANCE DEFINITION OF MANAGEMENT
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T X.162 TELECOMMUNICATION (04/95) STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU DATA NETWORKS AND OPEN SYSTEM COMMUNICATIONS PUBLIC DATA NETWORKS MAINTENANCE DEFINITION OF MANAGEMENT
DECnet. Chapter Goals. Introduction CHAPTER
 38 CHAPTER Chapter Goals Describe the development history of the protocol, used primarily in Digital Equipment Corporation minicomputers. Describe the architecture of networks. Discuss the addressing methods
38 CHAPTER Chapter Goals Describe the development history of the protocol, used primarily in Digital Equipment Corporation minicomputers. Describe the architecture of networks. Discuss the addressing methods
REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON AMHS
 International Civil Aviation Organization REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON AMHS AFTN/AMHS GATEWAY SPECIFICATIONS (Dakar, 28-29 May 2013) Outline General AFTN Gateway Components ATN Component Message Transfer and Control
International Civil Aviation Organization REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON AMHS AFTN/AMHS GATEWAY SPECIFICATIONS (Dakar, 28-29 May 2013) Outline General AFTN Gateway Components ATN Component Message Transfer and Control
Need For Protocol Architecture
 Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
Computer Networks and reference models. 1. List of Problems (so far)
 Computer s and reference models Chapter 2 1. List of Problems (so far) How to ensure connectivity between users? How to share a wire? How to pass a message through the network? How to build Scalable s?
Computer s and reference models Chapter 2 1. List of Problems (so far) How to ensure connectivity between users? How to share a wire? How to pass a message through the network? How to build Scalable s?
AERONAUTICAL COMMUNICATION PANEL WORKING GROUP N. PM-CPDLC Validation Report
 ACP WGN/5 WP19 AERONAUTICAL COMMUNICATION PANEL WORKING GROUP N PM-CPDLC Validation Report SUMMARY This paper gives the results of the PM-CPDLC ATN Application (version 1) validation effort. Version: 0.1
ACP WGN/5 WP19 AERONAUTICAL COMMUNICATION PANEL WORKING GROUP N PM-CPDLC Validation Report SUMMARY This paper gives the results of the PM-CPDLC ATN Application (version 1) validation effort. Version: 0.1
Switched Multimegabit Data Service
 CHAPTER 14 Chapter Goals Tell how SMDS works, and describe its components. Describe the operational elements of the SMDS environment, and outline its underlying protocol. Discuss related technologies.
CHAPTER 14 Chapter Goals Tell how SMDS works, and describe its components. Describe the operational elements of the SMDS environment, and outline its underlying protocol. Discuss related technologies.
EUROPEAN pr ETS TELECOMMUNICATION March 1996 STANDARD
 FINAL DRAFT EUROPEAN pr ETS 300 612-2 TELECOMMUNICATION March 1996 STANDARD Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: DE/SMG-061201P ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System
FINAL DRAFT EUROPEAN pr ETS 300 612-2 TELECOMMUNICATION March 1996 STANDARD Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: DE/SMG-061201P ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System
International Civil Aviation Organization. COM Co-ordination Meeting. 6 7 March 2013, Kunming, China
 CCM-WP/5 Agenda Item 5 06/03/13 International Civil Aviation Organization COM Co-ordination Meeting 6 7 March 2013, Kunming, China Agenda Item 5: Letter of agreement for technical and operational trial
CCM-WP/5 Agenda Item 5 06/03/13 International Civil Aviation Organization COM Co-ordination Meeting 6 7 March 2013, Kunming, China Agenda Item 5: Letter of agreement for technical and operational trial
Configuring ISO CLNS
 Configuring ISO CLNS First Published: March 01, 2004 Last Updated: February 26, 2010 The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Connectionless Network Service (CLNS) protocol is a standard
Configuring ISO CLNS First Published: March 01, 2004 Last Updated: February 26, 2010 The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Connectionless Network Service (CLNS) protocol is a standard
Introduction. Communication
 Introduction These slides are created by Dr. Yih Huang of George Mason University. Students registered in Dr. Huang's courses at GMU can make a single machine-readable copy and print a single copy of each
Introduction These slides are created by Dr. Yih Huang of George Mason University. Students registered in Dr. Huang's courses at GMU can make a single machine-readable copy and print a single copy of each
EUR AMHS Manual, Appendix H
 EUR AMHS Manual EUR Doc 020 EUR AMHS Manual Appendix H Application/Service oriented AMHS Profiles Document Reference: Author: EUR AMHS Manual, Appendix H Revision Number: Version 12.0 Date: 28/04/2017
EUR AMHS Manual EUR Doc 020 EUR AMHS Manual Appendix H Application/Service oriented AMHS Profiles Document Reference: Author: EUR AMHS Manual, Appendix H Revision Number: Version 12.0 Date: 28/04/2017
Chapter 15 Routing ISO CLNS
 Chapter 15 Routing ISO CLNS 15 This chapter describes Cisco Systems implementation of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Connectionless Network Services (CLNS) protocol, which is
Chapter 15 Routing ISO CLNS 15 This chapter describes Cisco Systems implementation of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Connectionless Network Services (CLNS) protocol, which is
Draft ICAO IPv6 Addressing Plan
 International Civil Aviation Organization ACP-WG I-07/WP-02 01/06/08 WORKING PAPER AERONAUTICAL COMMUNICATIONS PANEL (ACP) SEVENTH MEETING OF THE WORKING GROUP I (IPS) Montreal, Canada 2 6 June 2008 Agenda
International Civil Aviation Organization ACP-WG I-07/WP-02 01/06/08 WORKING PAPER AERONAUTICAL COMMUNICATIONS PANEL (ACP) SEVENTH MEETING OF THE WORKING GROUP I (IPS) Montreal, Canada 2 6 June 2008 Agenda
Internetworking Terms. Internet Structure. Internet Structure. Chapter 15&16 Internetworking. Internetwork Structure & Terms
 Chapter 15&16 Internetworking Internetwork Structure & Terms Internetworking Architecture Features Connection/Connectionless Architecture Fragmentation & Reassembly Internet Protocol & Services Addressing
Chapter 15&16 Internetworking Internetwork Structure & Terms Internetworking Architecture Features Connection/Connectionless Architecture Fragmentation & Reassembly Internet Protocol & Services Addressing
EUR AMHS Manual, Appendix E
 EUR AMHS Manual EUR Doc 020 EUR AMHS Manual Appendix E AMHS Interoperability s Document Reference: Author: EUR AMHS Manual, Appendix E Revision Number: Version 6.0c Date: 28/04/11 Filename: EUR_AMHS_Manual-Appx_E-v6_0c.doc
EUR AMHS Manual EUR Doc 020 EUR AMHS Manual Appendix E AMHS Interoperability s Document Reference: Author: EUR AMHS Manual, Appendix E Revision Number: Version 6.0c Date: 28/04/11 Filename: EUR_AMHS_Manual-Appx_E-v6_0c.doc
