Robotics and Autonomous Systems
|
|
|
- Douglas Porter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 13: Navigation in LeJOS Richard Williams Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 1 / 40
2 Today From navigation to motion control. 2 / 40
3 Navigation and path execution We started this course with three questions:? Where am I? Where am I going? How do I get there? Digging into the detail of how you do the last two. 3 / 40
4 Navigation and path execution Last time convered how to go from: Map Start point End point to a sequence of waypoints that the robot has to traverse to get from the start to the goal. Turns out LeJOS has quite a lot of support for this. LeJOS can also help with the business of following the waypoints. 4 / 40
5 Path following The planning methods we covered last time returned a sequence of waypoints. Sequence of robot poses: px s, y s, θ s q px 1, y 1, θ 1 q. px g, y g, θ g q Robot then needs to know how to move between the points. 5 / 40
6 Path following Plan doesn t restrict movement between waypoints. 6 / 40
7 Path following γ β α Simplest route is to turn to face the next point, then drive straight. 7 / 40
8 Path following In this case we need to: Rotate α Drive Rotate β Drive Rotate γ Not trivial to figure out the rotations required. Distances are pretty easy using the Euclidian distance formula from the previous lecture. 8 / 40
9 Navigator LeJOS supports this through the Navigator class. 9 / 40
10 LeJOS Navigator Provides all the functionality you need to have the robot follow a sequence of waypoints. Controls the robot using our old friend: DifferentialPilot with all the good and bad things that entails. Tracks where the robot is currently using: PoseProvider Default is OdometryPoseProvider But you can use MCLPoseProvider also 10 / 40
11 LeJOS Navigator The pilot allows it to control the robot... by sending it rotations and translations. The pose provider allows it to keep track of where it is.... so it can compute what movements are necessary. 11 / 40
12 LeJOS Navigator Navigator can be fed a sequence of waypoints. Or it can be fed a path. 12 / 40
13 Waypoint LeJOS has an object to represent waypoints. A waypoint can be a point: Point object x and y coordinate. or it can be a pose: Pose object x and y coordinate, plus a heading. A waypoint that is a point has heading / 40
14 Waypoint API for waypoint includes the method: boolean checkvalidity(pose p) which checks if the pose is close enough to the waypoint to count as having reached it. So, you can extend the class and override the function to create your own waypoint that is reached approximately. 14 / 40
15 Path Path is an ordered sequence of Waypoints. Implemented as a Java ArrayList of Waypoints But you don t need to manipulate it. 15 / 40
16 Navigator example Key functions are the following: Navigator(MoveController p) Constructor, takes a pilot object as an argument. The navigator then uses this to drive the robot. void addwaypoint(float x, float y) void addwaypoint(float x, float y, float heading) Adds a waypoint to the path. void followpath() Drive to each waypoint in the path, in turn. 16 / 40
17 Navigator example That s all you need to use the Navigator 17 / 40
18 Navigator example My code (below) uses a couple of additional functions, mainly for show. boolean pathcompleted() Reports if the robot has completed the current path. Waypoint getwaypoint() Returns the current waypoint, the one the robot is heading to. 18 / 40
19 Navigator example public class PathFollower{ private DifferentialPilot pilot = new DifferentialPilot(3.25, 19.8, Motor.C, Motor.B); private Navigator navigator = new Navigator(pilot); private Waypoint next; public void newwaypoint(int x, int y){ navigator.addwaypoint(x, y); } public void navigate(){ while(!navigator.pathcompleted()){ navigator.followpath(); next = navigator.getwaypoint(); LCD.drawString("Moving to...", 0, 0); LCD.drawString("(" + (int)next.getx() + "," + (int)next.gety() + ")", 0, 1); } } } 19 / 40
20 Navigator example Note the use of private members for the PathFollower class. These, naturally, need public access functions. IMHO, this is good Java (and OO) style. 20 / 40
21 Navigator example The navigator runs its own thread, so the while loop is really just for driving the LCD display. Should work perfectly well as: public void navigate(){ navigator.followpath(); while(!navigator.pathcompleted()){ next = navigator.getwaypoint(); LCD.drawString("Moving to...", 0, 0); LCD.drawString("(" + (int)next.getx() + "," + (int)next.gety() + ")", 0, 1); } (though I haven t tested this version). 21 / 40
22 Navigator example The main() is in another class, which creates a Pathfinder object, and sets up the waypoints. public class RunNavigator{ public static void main(string[] args) throws Exception{ PathFollower pfollow = new PathFollower(); pfollow.newwaypoint(40, 0); pfollow.newwaypoint(40, 40); pfollow.newwaypoint(0, 40); pfollow.newwaypoint(0, 0); } } pfollow.navigate(); 22 / 40
23 Navigator example This is another version of the drive in a square program. 23 / 40
24 Navigator example Both these classes are available from the module website. 24 / 40
25 Path finding What we have so far is a program that will work when it already knows what the waypoints are. Not much use if you don t don t them. But LeJOS can help with this too. 25 / 40
26 LineMap To do any pathfinding, we need a map, and LeJOS gives us the LineMap class. We set up a LineMap like this: Line[] lines = new Line[3]; lines[0] = new Line(50, 100, 100, 100); lines[1] = new Line(100, 100, 100, 50); lines[2] = new Line(50, 100, 100, 50); Rectangle bounds = new Rectangle(-50, -50, 200, 200); LineMap map = new LineMap(lines, bounds); 26 / 40
27 LineMap A LineMap is an array of lines and a bounding box. A bounding box is just a rectangle, specified by the: bottom left (smallest x and y coordinates) top right (largest x and y coordinates) Each line is defined by two pairs of coordinates that mark the end points of the line. 27 / 40
28 LineMap (50, 200) (200, 200) (200, 100) (200, 50) ( 50, 50) (100, 50) 28 / 40
29 PathFinder Then all we have to do is: Pose start = new Pose(0, 0, 270); Waypoint goal = new Waypoint(125, 150); ShortestPathFinder finder = new ShortestPathFinder(map); finder.lengthenlines(5); PathFollower pfollow = new PathFollower(); pfollow.newpose(start); Path path = finder.findroute(start, goal); pfollow.newpath(path); pfollow.navigate(); 29 / 40
30 PathFinder Set up start and end points. For some reason they are different types of object. Create a path finder object and give it the map. ShortestPathFinder DijkstraPathFinder Not clear what the difference is between these. Create clearance for the robot Basic path finder only works for infinitely small robots/points. Create an instance of our PathFollower class. Call the PathFinder on the start and goal points, and get a path back. Pass the path to the PathFollower and let it use its navigator to follow it. 30 / 40
31 PathFinder (50, 200) (200, 200) G (200, 100) (200, 50) S ( 50, 50) (100, 50) 31 / 40
32 Other forms of navigation Having seen how LeJOS can implement path finding in a map, let s look at a couple of other forms of navigation that we might implement on the NXT. Simpler in some ways. Not necessarily as good at getting to the goal. 32 / 40
33 Potential field Robot is treated as a point under the influence of an artificial potential field. The goal attracts it and obstacles repel it. 33 / 40
34 Potential field If you know your location and the goal, can compute the force on the robot. Navigator will make direct the robot towards the goal point. Just make it the next waypoint. Obstacle avoidance provides the repulsion from obstacles. Steer a path that is a combination of repulsion from obstacle and heading to goal. This will require taking control back from the Navigator. Don t need a map. 34 / 40
35 Potential field 35 / 40
36 Bug algorithms The bug algorithms assume localization but no map. Here we see the first such algorithm, bug 1, working. 36 / 40
37 Bug algorithms When you meet an obstacle you follow around the edge. Leave the obstacle at the point closest to the goal. Circle the obstacle to be sure that you know where this point is. 37 / 40
38 Bug algorithms Here s the second bug algorithm in action. Improves on the performance of bug 1 38 / 40
39 Bug algorithms Follow the obstacle always on the left or right side. Leave the obstacle if you cross the direct (line of sight) connection between start and goal. 39 / 40
40 Summary Today we looked more at navigation. Primarily we looked at the support LeJOS provides for navigation: Path following Path finding which make it possible to carry out the kind of navigation discussed in Lecture 12. We also looked at a couple of additional navigation techniques. 40 / 40
Navigation and path execution NAVIGATION IN LEJOS ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS. Today. Digging into the detail of how you do the last two.
 ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 13 comp329-2013-parsons-lect13 2/43 Today From navigation to motion control. NAVIGATION IN LEJOS
ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 13 comp329-2013-parsons-lect13 2/43 Today From navigation to motion control. NAVIGATION IN LEJOS
ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS
 ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 6 PERCEPTION/ODOMETRY comp329-2013-parsons-lect06 2/43 Today We ll talk about perception and
ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 6 PERCEPTION/ODOMETRY comp329-2013-parsons-lect06 2/43 Today We ll talk about perception and
Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 6: Perception/Odometry Terry Payne Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 1 / 47 Today We ll talk about perception and motor control. 2 / 47 Perception
Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 6: Perception/Odometry Terry Payne Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 1 / 47 Today We ll talk about perception and motor control. 2 / 47 Perception
Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 6: Perception/Odometry Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 1 / 47 Today We ll talk about perception and motor control. 2 / 47 Perception
Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 6: Perception/Odometry Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 1 / 47 Today We ll talk about perception and motor control. 2 / 47 Perception
Today. Robotics and Autonomous Systems. Today. Communication on the NXT. Lecture 14: Communication and other useful things.
 Today Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 14: Communication and other useful things Richard Williams Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool We will cover things from all parts of robotics
Today Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 14: Communication and other useful things Richard Williams Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool We will cover things from all parts of robotics
Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 14: Communication and other useful things Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 1 / 43 Today We will cover things from all parts of
Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 14: Communication and other useful things Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 1 / 43 Today We will cover things from all parts of
COMMUNICATION AND OTHER USEFUL THINGS
 ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 14 comp329-2013-parsons-lect14 2/42 Today We will cover things from all parts of robotics COMMUNICATION
ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 14 comp329-2013-parsons-lect14 2/42 Today We will cover things from all parts of robotics COMMUNICATION
INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
 DATA15001 INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE THE FINAL EPISODE (11): ROBOTICS TODAY S MENU 1. "GRAND CHALLENGE" 2. LEGO MIND- STORMS 3. ROBO WORKSHOPS ROBOTICS AS A "GRAND CHALLENGE" OF AI actuators:
DATA15001 INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE THE FINAL EPISODE (11): ROBOTICS TODAY S MENU 1. "GRAND CHALLENGE" 2. LEGO MIND- STORMS 3. ROBO WORKSHOPS ROBOTICS AS A "GRAND CHALLENGE" OF AI actuators:
Today. Robotics and Autonomous Systems. The scenario (again) Basic control loop
 Today Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 3 Programming robots Richard Williams Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool Before the labs start on Monday, we will look a bit at programming
Today Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 3 Programming robots Richard Williams Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool Before the labs start on Monday, we will look a bit at programming
Agreement. Objectives. General Guidelines for Labs. Reading Assignment
 1 CMPSC 111 Introduction to Computer Science I Fall 2016 Janyl Jumadinova Lab 9 for Section 1 17 November 2016 Due: 1 December, by 2:30 pm This is a team-based assignment. You have to work in teams of
1 CMPSC 111 Introduction to Computer Science I Fall 2016 Janyl Jumadinova Lab 9 for Section 1 17 November 2016 Due: 1 December, by 2:30 pm This is a team-based assignment. You have to work in teams of
Today. Robotics and Autonomous Systems. Jason and LeJOS. Jason and LeJOS. Lecture 23: LeJOS and Jason. Richard Williams
 Today Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 23: LeJOS and Jason Richard Williams Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool Today we will just go through an example of how to interface Jason
Today Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 23: LeJOS and Jason Richard Williams Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool Today we will just go through an example of how to interface Jason
Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 1 / 38 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 10: Threads and Multitasking Robots Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 2 / 38 Today Some more programming techniques that
1 / 38 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 10: Threads and Multitasking Robots Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 2 / 38 Today Some more programming techniques that
THREADS AND MULTITASKING ROBOTS
 ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 10 comp329-2013-parsons-lect10 2/37 Today Some more programming techniques that will be helpful
ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 10 comp329-2013-parsons-lect10 2/37 Today Some more programming techniques that will be helpful
ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS
 ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 10 THREADS AND MULTITASKING ROBOTS comp329-2013-parsons-lect10 2/37 Today Some more programming
ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 10 THREADS AND MULTITASKING ROBOTS comp329-2013-parsons-lect10 2/37 Today Some more programming
Robotics. Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation. See course website for up to date information.
 Robotics Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation See course website http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ajd/robotics/ for up to date information. Andrew Davison Department of Computing Imperial College London Review:
Robotics Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation See course website http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ajd/robotics/ for up to date information. Andrew Davison Department of Computing Imperial College London Review:
CS Project 2 - Experience with More lejos Classes
 CS 444 - Project 2 p. 1 CS 444 - Project 2 - Experience with More lejos Classes Experiment: Can you get a better feel for some of these lejos classes and methods entering pre-written classes as a team,
CS 444 - Project 2 p. 1 CS 444 - Project 2 - Experience with More lejos Classes Experiment: Can you get a better feel for some of these lejos classes and methods entering pre-written classes as a team,
Inf1-OP. Inf1-OP Exam Review. Timothy Hospedales, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein. March 20, School of Informatics
 Inf1-OP Inf1-OP Exam Review Timothy Hospedales, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein School of Informatics March 20, 2017 Overview Overview of examinable material: Lectures Week 1
Inf1-OP Inf1-OP Exam Review Timothy Hospedales, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein School of Informatics March 20, 2017 Overview Overview of examinable material: Lectures Week 1
Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 1 / 59 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 23: LeJOS and Jason Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 2 / 59 Today Today we will just go through an example of how to interface
1 / 59 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 23: LeJOS and Jason Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 2 / 59 Today Today we will just go through an example of how to interface
Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 23: LeJOS and Jason Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 1 / 59 Today Today we will just go through an example of how to interface
Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 23: LeJOS and Jason Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 1 / 59 Today Today we will just go through an example of how to interface
PROGRAMMING ROBOTS AN ABSTRACT VIEW
 ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 3 comp329-2013-parsons-lect03 2/50 Today Before the labs start on Monday, we will look a bit
ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 3 comp329-2013-parsons-lect03 2/50 Today Before the labs start on Monday, we will look a bit
Abstract. 1. What is an ABSTRACT METHOD? 2. Why you would want to declare a method as abstract? 3. A non-abstract CLASS is called a concrete class
 ABSTRACT 2 1. What is an ABSTRACT METHOD? 2 2. Why you would want to declare a method as abstract? 2 3. A non-abstract CLASS is called a concrete class 2 4. Abstract Example 2 5. If you are extending ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT 2 1. What is an ABSTRACT METHOD? 2 2. Why you would want to declare a method as abstract? 2 3. A non-abstract CLASS is called a concrete class 2 4. Abstract Example 2 5. If you are extending ABSTRACT
Inf1-OOP. OOP Exam Review. Perdita Stevens, adapting earlier version by Ewan Klein. March 16, School of Informatics
 Inf1-OOP OOP Exam Review Perdita Stevens, adapting earlier version by Ewan Klein School of Informatics March 16, 2015 Overview Overview of examinable material: Lectures Topics S&W sections Week 1 Compilation,
Inf1-OOP OOP Exam Review Perdita Stevens, adapting earlier version by Ewan Klein School of Informatics March 16, 2015 Overview Overview of examinable material: Lectures Topics S&W sections Week 1 Compilation,
a correct statement? You need to know what the statement is supposed to do.
 Using assertions for correctness How can we know that software is correct? It is only correct if it does what it is supposed to do. But how do we know what it is supposed to do? We need a specification.
Using assertions for correctness How can we know that software is correct? It is only correct if it does what it is supposed to do. But how do we know what it is supposed to do? We need a specification.
LEJOS AND JASON ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS. Today. Today we will just go through an example of how to interface. Department of Computer Science
 ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 24 comp329-2013-parsons-lect24 2/58 Today Today we will just go through an example of how to
ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 24 comp329-2013-parsons-lect24 2/58 Today Today we will just go through an example of how to
n HW5 out, due Tuesday October 30 th n Part 1: Questions on material we ll cover today n Part 2: BFS using your graph from HW4
 Subtype, Subtyping vs. Subclassing, Liskov Substitution Principle Announcements n HW5 out, due Tuesday October 30 th n Part 1: Questions on material we ll cover today n Part 2: BFS using your graph from
Subtype, Subtyping vs. Subclassing, Liskov Substitution Principle Announcements n HW5 out, due Tuesday October 30 th n Part 1: Questions on material we ll cover today n Part 2: BFS using your graph from
Outline. Subtype Polymorphism, Subtyping vs. Subclassing, Liskov Substitution Principle. Benefits of Subtype Polymorphism. Subtype Polymorphism
 Subtype, Subtyping vs. Subclassing, Liskov Substitution Principle Outline Subtype polymorphism Subtyping vs. subclassing Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP) Function subtyping Java subtyping Composition:
Subtype, Subtyping vs. Subclassing, Liskov Substitution Principle Outline Subtype polymorphism Subtyping vs. subclassing Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP) Function subtyping Java subtyping Composition:
Intro to Programming the Lego Robots
 Intro to Programming the Lego Robots Hello Byng Roboticists! I'm writing this introductory guide will teach you the basic commands to control your Lego NXT Robots. Keep in mind there are many more commands
Intro to Programming the Lego Robots Hello Byng Roboticists! I'm writing this introductory guide will teach you the basic commands to control your Lego NXT Robots. Keep in mind there are many more commands
CSC207 Week 3. Larry Zhang
 CSC207 Week 3 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Readings will be posted before the lecture Lab 1 marks available in your repo 1 point for creating the correct project. 1 point for creating the correct classes.
CSC207 Week 3 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Readings will be posted before the lecture Lab 1 marks available in your repo 1 point for creating the correct project. 1 point for creating the correct classes.
the gamedesigninitiative at cornell university Lecture 20 Pathfinding
 Lecture 20 Take way for Today What are primary goals for pathfinding? Identify advantages/disadvantages of * In what situations does * fail (or look bad)? What can we do to fix se problems? Why combine
Lecture 20 Take way for Today What are primary goals for pathfinding? Identify advantages/disadvantages of * In what situations does * fail (or look bad)? What can we do to fix se problems? Why combine
List ADT. Announcements. The List interface. Implementing the List ADT
 Announcements Tutoring schedule revised Today s topic: ArrayList implementation Reading: Section 7.2 Break around 11:45am List ADT A list is defined as a finite ordered sequence of data items known as
Announcements Tutoring schedule revised Today s topic: ArrayList implementation Reading: Section 7.2 Break around 11:45am List ADT A list is defined as a finite ordered sequence of data items known as
Nested Loops. A loop can be nested inside another loop.
 Nested Loops A loop can be nested inside another loop. Nested loops consist of an outer loop and one or more inner loops. Each time the outer loop is repeated, the inner loops are reentered, and started
Nested Loops A loop can be nested inside another loop. Nested loops consist of an outer loop and one or more inner loops. Each time the outer loop is repeated, the inner loops are reentered, and started
Relationship of class to object
 Relationship of class to object Writing and programming Writing a program is similar to many other kinds of writing. The purpose of any kind of writing is to take your thoughts and let other people see
Relationship of class to object Writing and programming Writing a program is similar to many other kinds of writing. The purpose of any kind of writing is to take your thoughts and let other people see
LECTURE 6. Announcements
 LECTURE 6 Announcements Minecraft 3 Feedback Infinite worlds! Terrain looks good Gameplay not super varied Happy Birthday Hassan! The Voxel Engine You re done with your first collision engine! Environment
LECTURE 6 Announcements Minecraft 3 Feedback Infinite worlds! Terrain looks good Gameplay not super varied Happy Birthday Hassan! The Voxel Engine You re done with your first collision engine! Environment
Lecture 3. Lecture
 True Object-Oriented programming: Dynamic Objects Static Object-Oriented Programming Reference Variables Eckel: 30-31, 41-46, 107-111, 114-115 Riley: 5.1, 5.2 D0010E Object-Oriented Programming and Design
True Object-Oriented programming: Dynamic Objects Static Object-Oriented Programming Reference Variables Eckel: 30-31, 41-46, 107-111, 114-115 Riley: 5.1, 5.2 D0010E Object-Oriented Programming and Design
Lecture 10: building large projects, beginning C++, C++ and structs
 CIS 330: / / / / (_) / / / / _/_/ / / / / / \/ / /_/ / `/ \/ / / / _/_// / / / / /_ / /_/ / / / / /> < / /_/ / / / / /_/ / / / /_/ / / / / / \ /_/ /_/_/_/ _ \,_/_/ /_/\,_/ \ /_/ \ //_/ /_/ Lecture 10:
CIS 330: / / / / (_) / / / / _/_/ / / / / / \/ / /_/ / `/ \/ / / / _/_// / / / / /_ / /_/ / / / / /> < / /_/ / / / / /_/ / / / /_/ / / / / / \ /_/ /_/_/_/ _ \,_/_/ /_/\,_/ \ /_/ \ //_/ /_/ Lecture 10:
CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming
 CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 5 The Loop-the-Loop ( 2.3-2.4) 9/21/2011 CIS 110 (11fa) - University of Pennsylvania 1 Outline 1. For-loops! 2. Algorithm Design and Pseudocode 9/21/2011
CIS 110: Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 5 The Loop-the-Loop ( 2.3-2.4) 9/21/2011 CIS 110 (11fa) - University of Pennsylvania 1 Outline 1. For-loops! 2. Algorithm Design and Pseudocode 9/21/2011
Inf1-OP. Inf1-OP Exam Review. Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein. March 16, School of Informatics
 Inf1-OP Inf1-OP Exam Review Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein School of Informatics March 16, 2018 Examinable Material Overview Overview of examinable material:
Inf1-OP Inf1-OP Exam Review Volker Seeker, adapting earlier version by Perdita Stevens and Ewan Klein School of Informatics March 16, 2018 Examinable Material Overview Overview of examinable material:
1001ICT Introduction To Programming Lecture Notes
 1001ICT Introduction To Programming Lecture Notes School of Information and Communication Technology Griffith University Semester 2, 2015 1 2 Elements of Java Java is a popular, modern, third generation
1001ICT Introduction To Programming Lecture Notes School of Information and Communication Technology Griffith University Semester 2, 2015 1 2 Elements of Java Java is a popular, modern, third generation
Array Based Lists. Collections
 Array Based Lists Reading: RS Chapter 15 1 Collections Data structures stores elements in a manner that makes it easy for a client to work with the elements Specific collections are specialized for particular
Array Based Lists Reading: RS Chapter 15 1 Collections Data structures stores elements in a manner that makes it easy for a client to work with the elements Specific collections are specialized for particular
Software Paradigms (Lesson 3) Object-Oriented Paradigm (2)
 Software Paradigms (Lesson 3) Object-Oriented Paradigm (2) Table of Contents 1 Reusing Classes... 2 1.1 Composition... 2 1.2 Inheritance... 4 1.2.1 Extending Classes... 5 1.2.2 Method Overriding... 7 1.2.3
Software Paradigms (Lesson 3) Object-Oriented Paradigm (2) Table of Contents 1 Reusing Classes... 2 1.1 Composition... 2 1.2 Inheritance... 4 1.2.1 Extending Classes... 5 1.2.2 Method Overriding... 7 1.2.3
LECTURE 7. Announcements
 LECTURE 7 Announcements Minecraft 4 Feedback Looks good! A game that minimally involves platforms Not based on any game in particular Super Mario 64? Team Fortress 2? Completely up to you to make unique
LECTURE 7 Announcements Minecraft 4 Feedback Looks good! A game that minimally involves platforms Not based on any game in particular Super Mario 64? Team Fortress 2? Completely up to you to make unique
Jump Statements. The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls.
 Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
CSE 143. More ArrayIntList; pre/post; exceptions; debugging. Computer Programming II. CSE 143: Computer Programming II
 Adam Blank Lecture 3 Autumn 201 CSE 143 CSE 143: Computer Programming II More ArrayIntList; pre/post; exceptions; debugging Computer Programming II Drawings 1 Drawings 2 Drawings 3 Drawings 4 Drawings
Adam Blank Lecture 3 Autumn 201 CSE 143 CSE 143: Computer Programming II More ArrayIntList; pre/post; exceptions; debugging Computer Programming II Drawings 1 Drawings 2 Drawings 3 Drawings 4 Drawings
Adam Blank Lecture 3 Autumn 2016 CSE 143. Computer Programming II
 Adam Blank Lecture 3 Autumn 2016 CSE 143 Computer Programming II CSE 143: Computer Programming II More ArrayIntList; pre/post; exceptions; debugging Drawings 1 Drawings 2 Drawings 3 Drawings 4 Drawings
Adam Blank Lecture 3 Autumn 2016 CSE 143 Computer Programming II CSE 143: Computer Programming II More ArrayIntList; pre/post; exceptions; debugging Drawings 1 Drawings 2 Drawings 3 Drawings 4 Drawings
Type-indexed functions in Generic Haskell
 Type-indexed functions in Generic Haskell Johan Jeuring September 15, 2004 Introduction Today I will talk about: a Types of polymorphism. b Type-indexed functions. c Dependencies. Read about b, and c in
Type-indexed functions in Generic Haskell Johan Jeuring September 15, 2004 Introduction Today I will talk about: a Types of polymorphism. b Type-indexed functions. c Dependencies. Read about b, and c in
About this exam review
 Final Exam Review About this exam review I ve prepared an outline of the material covered in class May not be totally complete! Exam may ask about things that were covered in class but not in this review
Final Exam Review About this exam review I ve prepared an outline of the material covered in class May not be totally complete! Exam may ask about things that were covered in class but not in this review
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures. Lecture 6: The StringLog ADT David Mix Barrington 17 September 2012
 CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture 6: The StringLog ADT David Mix Barrington 17 September 2012 The StringLog ADT Data Abstraction Three Views of Data Java Interfaces Defining the StringLog
CMPSCI 187: Programming With Data Structures Lecture 6: The StringLog ADT David Mix Barrington 17 September 2012 The StringLog ADT Data Abstraction Three Views of Data Java Interfaces Defining the StringLog
Jump Statements. The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls.
 Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Jump Statements The keyword break and continue are often used in repetition structures to provide additional controls. break: the loop is terminated right after a break statement is executed. continue:
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
 Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Arrays, Part 1 of 2 Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 1 / 14 Modeling Aggregates As you ve seen, you
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Arrays, Part 1 of 2 Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Arrays, Part 1 of 2 1 / 14 Modeling Aggregates As you ve seen, you
Information System Design (IT60105)
 Information System Design (IT60105) Lecture 26 Object-Oriented System Testing Lecture #23 Procedural vs OO paradigms Why not Traditional Testing? Issues Methodology 2 Procedural Vs OO p Procedural Vs OO
Information System Design (IT60105) Lecture 26 Object-Oriented System Testing Lecture #23 Procedural vs OO paradigms Why not Traditional Testing? Issues Methodology 2 Procedural Vs OO p Procedural Vs OO
PRINCIPLES OF SOFTWARE BIM209DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT 10. PUTTING IT ALL TOGETHER. Are we there yet?
 PRINCIPLES OF SOFTWARE BIM209DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT 10. PUTTING IT ALL TOGETHER Are we there yet? Developing software, OOA&D style You ve got a lot of new tools, techniques, and ideas about how to develop
PRINCIPLES OF SOFTWARE BIM209DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT 10. PUTTING IT ALL TOGETHER Are we there yet? Developing software, OOA&D style You ve got a lot of new tools, techniques, and ideas about how to develop
CS61BL. Lecture 1: Welcome to CS61BL! Intro to Java and OOP Testing Error-handling
 CS61BL Lecture 1: Welcome to CS61BL! Intro to Java and OOP Testing Error-handling About me Name: Edwin Liao Email: edliao@berkeley.edu Office hours: Thursday 3pm - 5pm Friday 11am - 1pm 611 Soda Or by
CS61BL Lecture 1: Welcome to CS61BL! Intro to Java and OOP Testing Error-handling About me Name: Edwin Liao Email: edliao@berkeley.edu Office hours: Thursday 3pm - 5pm Friday 11am - 1pm 611 Soda Or by
CS 61B Discussion 5: Inheritance II Fall 2014
 CS 61B Discussion 5: Inheritance II Fall 2014 1 WeirdList Below is a partial solution to the WeirdList problem from homework 3 showing only the most important lines. Part A. Complete the implementation
CS 61B Discussion 5: Inheritance II Fall 2014 1 WeirdList Below is a partial solution to the WeirdList problem from homework 3 showing only the most important lines. Part A. Complete the implementation
The Maze Runner. Alexander Kirillov
 The Maze Runner URL: http://sigmacamp.org/mazerunner E-mail address: shurik179@gmail.com Alexander Kirillov This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License.
The Maze Runner URL: http://sigmacamp.org/mazerunner E-mail address: shurik179@gmail.com Alexander Kirillov This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License.
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 13 CSU 370 Fall 2008 (Pucella) Friday, Oct 31, 2008
 Object-Oriented Design Lecture 13 CSU 370 Fall 2008 (Pucella) Friday, Oct 31, 2008 Laziness For this lecture, I want to return to something that came up during the last homework, the third homework where
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 13 CSU 370 Fall 2008 (Pucella) Friday, Oct 31, 2008 Laziness For this lecture, I want to return to something that came up during the last homework, the third homework where
1B1b Inheritance. Inheritance. Agenda. Subclass and Superclass. Superclass. Generalisation & Specialisation. Shapes and Squares. 1B1b Lecture Slides
 1B1b Inheritance Agenda Introduction to inheritance. How Java supports inheritance. Inheritance is a key feature of object-oriented oriented programming. 1 2 Inheritance Models the kind-of or specialisation-of
1B1b Inheritance Agenda Introduction to inheritance. How Java supports inheritance. Inheritance is a key feature of object-oriented oriented programming. 1 2 Inheritance Models the kind-of or specialisation-of
Functional Programming in Java. CSE 219 Department of Computer Science, Stony Brook University
 Functional Programming in Java CSE 219, Stony Brook University What is functional programming? There is no single precise definition of functional programming (FP) We should think of it as a programming
Functional Programming in Java CSE 219, Stony Brook University What is functional programming? There is no single precise definition of functional programming (FP) We should think of it as a programming
Object Oriented Programming: In this course we began an introduction to programming from an object-oriented approach.
 CMSC 131: Chapter 28 Final Review: What you learned this semester The Big Picture Object Oriented Programming: In this course we began an introduction to programming from an object-oriented approach. Java
CMSC 131: Chapter 28 Final Review: What you learned this semester The Big Picture Object Oriented Programming: In this course we began an introduction to programming from an object-oriented approach. Java
Design Patterns: State, Bridge, Visitor
 Design Patterns: State, Bridge, Visitor State We ve been talking about bad uses of case statements in programs. What is one example? Another way in which case statements are sometimes used is to implement
Design Patterns: State, Bridge, Visitor State We ve been talking about bad uses of case statements in programs. What is one example? Another way in which case statements are sometimes used is to implement
Motion Planning. Howie CHoset
 Motion Planning Howie CHoset Questions Where are we? Where do we go? Which is more important? Encoders Encoders Incremental Photodetector Encoder disk LED Photoemitter Encoders - Incremental Encoders -
Motion Planning Howie CHoset Questions Where are we? Where do we go? Which is more important? Encoders Encoders Incremental Photodetector Encoder disk LED Photoemitter Encoders - Incremental Encoders -
Chapter 31 Multi-GPU Programming
 Chapter 31 Multi-GPU Programming Part I. Preliminaries Part II. Tightly Coupled Multicore Part III. Loosely Coupled Cluster Part IV. GPU Acceleration Chapter 29. GPU Massively Parallel Chapter 30. GPU
Chapter 31 Multi-GPU Programming Part I. Preliminaries Part II. Tightly Coupled Multicore Part III. Loosely Coupled Cluster Part IV. GPU Acceleration Chapter 29. GPU Massively Parallel Chapter 30. GPU
Autonomous Mobile Robots, Chapter 6 Planning and Navigation Where am I going? How do I get there? Localization. Cognition. Real World Environment
 Planning and Navigation Where am I going? How do I get there?? Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Perception Real World Environment Path Motion Control Competencies
Planning and Navigation Where am I going? How do I get there?? Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Perception Real World Environment Path Motion Control Competencies
What is an Iterator? An iterator is an abstract data type that allows us to iterate through the elements of a collection one by one
 Iterators What is an Iterator? An iterator is an abstract data type that allows us to iterate through the elements of a collection one by one 9-2 2-2 What is an Iterator? An iterator is an abstract data
Iterators What is an Iterator? An iterator is an abstract data type that allows us to iterate through the elements of a collection one by one 9-2 2-2 What is an Iterator? An iterator is an abstract data
Synthesis by Example. Connecting Motion Planning and Example based Movement. Michael Gleicher
 Synthesis by Example Connecting Motion Planning and Example based Movement Michael Gleicher Dept of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison Case Study 1 Part I. Michael Gleicher 1 What is Motion
Synthesis by Example Connecting Motion Planning and Example based Movement Michael Gleicher Dept of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison Case Study 1 Part I. Michael Gleicher 1 What is Motion
CS/B.TECH/CSE(New)/SEM-5/CS-504D/ OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING. Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 GROUP A. (Multiple Choice Type Question)
 CS/B.TECH/CSE(New)/SEM-5/CS-504D/2013-14 2013 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
CS/B.TECH/CSE(New)/SEM-5/CS-504D/2013-14 2013 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
l e t print_name r = p r i n t _ e n d l i n e ( Name : ^ r. name)
 Chapter 8 Row polymorphism Consider the following code: type name_home = {name : s t r i n g ; home : s t r i n g } type name_mobile = {name : s t r i n g ; mobile : s t r i n g } l e t jane = {name =
Chapter 8 Row polymorphism Consider the following code: type name_home = {name : s t r i n g ; home : s t r i n g } type name_mobile = {name : s t r i n g ; mobile : s t r i n g } l e t jane = {name =
Honours Project Proposal. Luke Ross Supervisor: Dr. Karen Bradshaw Department of Computer Science, Rhodes University
 Honours Project Proposal Luke Ross Supervisor: Dr. Karen Bradshaw Department of Computer Science, Rhodes University 2 March 2012 1. Principal Investigator Investigator - Luke Allan Ross Supervisor - Dr.
Honours Project Proposal Luke Ross Supervisor: Dr. Karen Bradshaw Department of Computer Science, Rhodes University 2 March 2012 1. Principal Investigator Investigator - Luke Allan Ross Supervisor - Dr.
Comments are almost like C++
 UMBC CMSC 331 Java Comments are almost like C++ The javadoc program generates HTML API documentation from the javadoc style comments in your code. /* This kind of comment can span multiple lines */ //
UMBC CMSC 331 Java Comments are almost like C++ The javadoc program generates HTML API documentation from the javadoc style comments in your code. /* This kind of comment can span multiple lines */ //
Code Reuse: Inheritance
 Object-Oriented Design Lecture 14 CSU 370 Fall 2008 (Pucella) Tuesday, Nov 4, 2008 Code Reuse: Inheritance Recall the Point ADT we talked about in Lecture 8: The Point ADT: public static Point make (int,
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 14 CSU 370 Fall 2008 (Pucella) Tuesday, Nov 4, 2008 Code Reuse: Inheritance Recall the Point ADT we talked about in Lecture 8: The Point ADT: public static Point make (int,
Outline. Java Models for variables Types and type checking, type safety Interpretation vs. compilation. Reasoning about code. CSCI 2600 Spring
 Java Outline Java Models for variables Types and type checking, type safety Interpretation vs. compilation Reasoning about code CSCI 2600 Spring 2017 2 Java Java is a successor to a number of languages,
Java Outline Java Models for variables Types and type checking, type safety Interpretation vs. compilation Reasoning about code CSCI 2600 Spring 2017 2 Java Java is a successor to a number of languages,
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388)
 Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
CMSC 433 Section 0101 Fall 2012 Midterm Exam #1
 Name: CMSC 433 Section 0101 Fall 2012 Midterm Exam #1 Directions: Test is closed book, closed notes. Answer every question; write solutions in spaces provided. Use backs of pages for scratch work. Good
Name: CMSC 433 Section 0101 Fall 2012 Midterm Exam #1 Directions: Test is closed book, closed notes. Answer every question; write solutions in spaces provided. Use backs of pages for scratch work. Good
drawobject Circle draw
 25 THE VISITOR PATTERN The Visitor pattern turns the tables on our object-oriented model and creates an external class to act on data in other classes. This is useful if there are a fair number of instances
25 THE VISITOR PATTERN The Visitor pattern turns the tables on our object-oriented model and creates an external class to act on data in other classes. This is useful if there are a fair number of instances
CS210 Project 5 (Kd-Trees) Swami Iyer
 The purpose of this assignment is to create a symbol table data type whose keys are two-dimensional points. We ll use a 2d-tree to support efficient range search (find all the points contained in a query
The purpose of this assignment is to create a symbol table data type whose keys are two-dimensional points. We ll use a 2d-tree to support efficient range search (find all the points contained in a query
News and information! Review: Java Programs! Feedback after Lecture 2! Dead-lines for the first two lab assignment have been posted.!
 True object-oriented programming: Dynamic Objects Reference Variables D0010E Object-Oriented Programming and Design Lecture 3 Static Object-Oriented Programming UML" knows-about Eckel: 30-31, 41-46, 107-111,
True object-oriented programming: Dynamic Objects Reference Variables D0010E Object-Oriented Programming and Design Lecture 3 Static Object-Oriented Programming UML" knows-about Eckel: 30-31, 41-46, 107-111,
SSP ROBOT DESIGN A. DEAN 11/29/05 LAB: ROBOT OBJECTS IN LEJOS
 SSP 100.9 ROBOT DESIGN A. DEAN 11/29/05 LAB: ROBOT OBJECTS IN LEJOS As we saw in class last Tuesday (well, as at least a few of us saw the rest should check the web for the slides), everything in Java
SSP 100.9 ROBOT DESIGN A. DEAN 11/29/05 LAB: ROBOT OBJECTS IN LEJOS As we saw in class last Tuesday (well, as at least a few of us saw the rest should check the web for the slides), everything in Java
Object-oriented Programming and Software Engineering CITS1001. Multiple-choice Mid-semester Test
 Object-oriented Programming and Software Engineering CITS1001 Multiple-choice Mid-semester Test Semester 1, 2015 Mark your solutions on the provided answer page, by filling in the appropriate circles.
Object-oriented Programming and Software Engineering CITS1001 Multiple-choice Mid-semester Test Semester 1, 2015 Mark your solutions on the provided answer page, by filling in the appropriate circles.
Rules and syntax for inheritance. The boring stuff
 Rules and syntax for inheritance The boring stuff The compiler adds a call to super() Unless you explicitly call the constructor of the superclass, using super(), the compiler will add such a call for
Rules and syntax for inheritance The boring stuff The compiler adds a call to super() Unless you explicitly call the constructor of the superclass, using super(), the compiler will add such a call for
COMP 250 Winter 2011 Reading: Java background January 5, 2011
 Almost all of you have taken COMP 202 or equivalent, so I am assuming that you are familiar with the basic techniques and definitions of Java covered in that course. Those of you who have not taken a COMP
Almost all of you have taken COMP 202 or equivalent, so I am assuming that you are familiar with the basic techniques and definitions of Java covered in that course. Those of you who have not taken a COMP
Localization, Where am I?
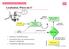 5.1 Localization, Where am I?? position Position Update (Estimation?) Encoder Prediction of Position (e.g. odometry) YES matched observations Map data base predicted position Matching Odometry, Dead Reckoning
5.1 Localization, Where am I?? position Position Update (Estimation?) Encoder Prediction of Position (e.g. odometry) YES matched observations Map data base predicted position Matching Odometry, Dead Reckoning
Game AI: The set of algorithms, representations, tools, and tricks that support the creation and management of real-time digital experiences
 Game AI: The set of algorithms, representations, tools, and tricks that support the creation and management of real-time digital experiences : A rule of thumb, simplification, or educated guess that reduces
Game AI: The set of algorithms, representations, tools, and tricks that support the creation and management of real-time digital experiences : A rule of thumb, simplification, or educated guess that reduces
CS Week 13. Jim Williams, PhD
 CS 200 - Week 13 Jim Williams, PhD This Week 1. Team Lab: Instantiable Class 2. BP2 Strategy 3. Lecture: Classes as templates BP2 Strategy 1. M1: 2 of 3 milestone tests didn't require reading a file. 2.
CS 200 - Week 13 Jim Williams, PhD This Week 1. Team Lab: Instantiable Class 2. BP2 Strategy 3. Lecture: Classes as templates BP2 Strategy 1. M1: 2 of 3 milestone tests didn't require reading a file. 2.
Final Exam Practice Fall Semester, 2012
 COS 495 - Autonomous Robot Navigation Final Exam Practice Fall Semester, 2012 Duration: Total Marks: 70 Closed Book 2 hours Start Time: End Time: By signing this exam, I agree to the honor code Name: Signature:
COS 495 - Autonomous Robot Navigation Final Exam Practice Fall Semester, 2012 Duration: Total Marks: 70 Closed Book 2 hours Start Time: End Time: By signing this exam, I agree to the honor code Name: Signature:
C++ for Java Programmers
 Basics all Finished! Everything we have covered so far: Lecture 5 Operators Variables Arrays Null Terminated Strings Structs Functions 1 2 45 mins of pure fun Introduction Today: Pointers Pointers Even
Basics all Finished! Everything we have covered so far: Lecture 5 Operators Variables Arrays Null Terminated Strings Structs Functions 1 2 45 mins of pure fun Introduction Today: Pointers Pointers Even
General Syntax. Operators. Variables. Arithmetic. Comparison. Assignment. Boolean. Types. Syntax int i; float j = 1.35; int k = (int) j;
 General Syntax Statements are the basic building block of any C program. They can assign a value to a variable, or make a comparison, or make a function call. They must be terminated by a semicolon. Every
General Syntax Statements are the basic building block of any C program. They can assign a value to a variable, or make a comparison, or make a function call. They must be terminated by a semicolon. Every
Controls Structure for Repetition
 Controls Structure for Repetition So far we have looked at the if statement, a control structure that allows us to execute different pieces of code based on certain conditions. However, the true power
Controls Structure for Repetition So far we have looked at the if statement, a control structure that allows us to execute different pieces of code based on certain conditions. However, the true power
Introduction to Intelligent System ( , Fall 2017) Instruction for Assignment 2 for Term Project. Rapidly-exploring Random Tree and Path Planning
 Instruction for Assignment 2 for Term Project Rapidly-exploring Random Tree and Path Planning Introduction The objective of this semester s term project is to implement a path planning algorithm for a
Instruction for Assignment 2 for Term Project Rapidly-exploring Random Tree and Path Planning Introduction The objective of this semester s term project is to implement a path planning algorithm for a
Chapter Two Bonus Lesson: JavaDoc
 We ve already talked about adding simple comments to your source code. The JDK actually supports more meaningful comments as well. If you add specially-formatted comments, you can then use a tool called
We ve already talked about adding simple comments to your source code. The JDK actually supports more meaningful comments as well. If you add specially-formatted comments, you can then use a tool called
Violations of the contract are exceptions, and are usually handled by special language constructs. Design by contract
 Specification and validation [L&G Ch. 9] Design patterns are a useful way to describe program structure. They provide a guide as to how a program fits together. Another dimension is the responsibilities
Specification and validation [L&G Ch. 9] Design patterns are a useful way to describe program structure. They provide a guide as to how a program fits together. Another dimension is the responsibilities
Notes - Recursion. A geeky definition of recursion is as follows: Recursion see Recursion.
 Notes - Recursion So far we have only learned how to solve problems iteratively using loops. We will now learn how to solve problems recursively by having a method call itself. A geeky definition of recursion
Notes - Recursion So far we have only learned how to solve problems iteratively using loops. We will now learn how to solve problems recursively by having a method call itself. A geeky definition of recursion
public static boolean isoutside(int min, int max, int value)
 See the 2 APIs attached at the end of this worksheet. 1. Methods: Javadoc Complete the Javadoc comments for the following two methods from the API: (a) / @param @param @param @return @pre. / public static
See the 2 APIs attached at the end of this worksheet. 1. Methods: Javadoc Complete the Javadoc comments for the following two methods from the API: (a) / @param @param @param @return @pre. / public static
Readability [Skrien 4.0] Programs must be written for people to read, and only incidentally for machines to execute.
![Readability [Skrien 4.0] Programs must be written for people to read, and only incidentally for machines to execute. Readability [Skrien 4.0] Programs must be written for people to read, and only incidentally for machines to execute.](/thumbs/89/98819789.jpg) Readability [Skrien 4.0] Programs must be written for people to read, and only incidentally for machines to execute. Abelson & Sussman Use a good set of coding conventions, such as the ones given in the
Readability [Skrien 4.0] Programs must be written for people to read, and only incidentally for machines to execute. Abelson & Sussman Use a good set of coding conventions, such as the ones given in the
Need for synchronization: If threads comprise parts of our software systems, then they must communicate.
 Thread communication and synchronization There are two main aspects to Outline for Lecture 19 multithreaded programming in Java: I. Thread synchronization. thread lifecycle, and thread synchronization.
Thread communication and synchronization There are two main aspects to Outline for Lecture 19 multithreaded programming in Java: I. Thread synchronization. thread lifecycle, and thread synchronization.
Homework 2: Imperative Due: 5:00 PM, Feb 15, 2019
 CS18 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Fisler Homework 2: Imperative Due: 5:00 PM, Feb 15, 2019 Contents 1 Overview of Generic/Parameterized Types 2 2 Double the Fun with Doubly-Linked Lists
CS18 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Fisler Homework 2: Imperative Due: 5:00 PM, Feb 15, 2019 Contents 1 Overview of Generic/Parameterized Types 2 2 Double the Fun with Doubly-Linked Lists
Complex behavior emergent from simpler ones
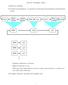 Reactive Paradigm: Basics Based on ethology Vertical decomposition, as opposed to horizontal decomposition of hierarchical model Primitive behaviors at bottom Higher behaviors at top Each layer has independent
Reactive Paradigm: Basics Based on ethology Vertical decomposition, as opposed to horizontal decomposition of hierarchical model Primitive behaviors at bottom Higher behaviors at top Each layer has independent
CISC-124. Passing Parameters. A Java method cannot change the value of any of the arguments passed to its parameters.
 CISC-124 20180215 These notes are intended to summarize and clarify some of the topics that have been covered recently in class. The posted code samples also have extensive explanations of the material.
CISC-124 20180215 These notes are intended to summarize and clarify some of the topics that have been covered recently in class. The posted code samples also have extensive explanations of the material.
Stable Trajectory Design for Highly Constrained Environments using Receding Horizon Control
 Stable Trajectory Design for Highly Constrained Environments using Receding Horizon Control Yoshiaki Kuwata and Jonathan P. How Space Systems Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology {kuwata,jhow}@mit.edu
Stable Trajectory Design for Highly Constrained Environments using Receding Horizon Control Yoshiaki Kuwata and Jonathan P. How Space Systems Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology {kuwata,jhow}@mit.edu
Object-Oriented Programming in Processing
 Object-Oriented Programming in Processing Object-Oriented Programming We ve (kinda) been doing this since Day 1: Python is a deeply object oriented language Most of the data types we were using (strings,
Object-Oriented Programming in Processing Object-Oriented Programming We ve (kinda) been doing this since Day 1: Python is a deeply object oriented language Most of the data types we were using (strings,
CS108, Stanford Handout #3. HW1 CodeCamp
 CS108, Stanford Handout #3 Fall, 2008-09 Osvaldo Jiménez HW1 CodeCamp Thanks to Nick Parlante for much of this handout For this first homework, you will run through a series of small coding problems to
CS108, Stanford Handout #3 Fall, 2008-09 Osvaldo Jiménez HW1 CodeCamp Thanks to Nick Parlante for much of this handout For this first homework, you will run through a series of small coding problems to
+ Today. Lecture 26: Concurrency 3/31/14. n Reading. n Objectives. n Announcements. n P&C Section 7. n Race conditions.
 + Lecture 26: Concurrency Slides adapted from Dan Grossman + Today n Reading n P&C Section 7 n Objectives n Race conditions n Announcements n Quiz on Friday 1 + This week s programming assignment n Answer
+ Lecture 26: Concurrency Slides adapted from Dan Grossman + Today n Reading n P&C Section 7 n Objectives n Race conditions n Announcements n Quiz on Friday 1 + This week s programming assignment n Answer
