Defining shell thicknesses Plotting 5 and 6 DOF nodes Plotting shell thicknesses Plotting results on the top, midsurface and bottom of the shell
|
|
|
- Bernice Small
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
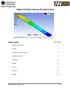
1 Problem description A shell corner is analyzed first for its static response due to a concentrated load, then for its natural frequencies and mode shapes. In the static analysis, we will demonstrate the following topics that have not been presented in previous problems: Defining shell thicknesses Plotting 5 and 6 DOF nodes Plotting shell thicknesses Plotting results on the top, midsurface and bottom of the shell In the frequency analysis, we will demonstrate the following topics that have not been presented in previous problems: Setting up a frequency analysis Plotting mode shapes We assume that you have worked through problems 1 to 7, or have equivalent experience with the ADINA System. efore you begin Please refer to the Icon Locator Tables chapter of the Primer for the locations of all of the AUI icons. Please refer to the Hints chapter of the Primer for useful hints. This problem can be solved with the 9 nodes version of the ADINA System. Static analysis 5 N 2 E = N/mm 2 =.3 = N-s 2 /mm 4 ADINA R & D, Inc. 8-1
2 Invoking the AUI and choosing the finite element program Invoke the AUI and set the Program Module drop-down list to ADINA Structures. Defining model control data Problem heading: Choose Control Heading, enter the heading Problem 8: Analysis of a shell corner, static analysis and click OK. Defining model geometry Here is a diagram showing the key geometry used in defining this model: z P3 P4 S1 P1 P2 S2 P6 y P5 L6 x Geometry points: Click the Define Points icon table and click OK., enter the following information into the Point # ADINA Primer
3 Geometry surfaces: Click the Define Surfaces icon click OK., define the following surfaces and Surface Number Type Point 1 Point 2 Point 3 Point 4 1 Vertex Vertex Defining and applying loads Click the Apply Load icon, make sure that the Load Type is set to Force and click the Define... button to the right of the Load Number field. In the Define Concentrated Force dialog box, add force 1, set the Magnitude to 5, the direction to -1 and click OK. In the first row of the table in the Apply Load dialog box, set the Point # to 2, then click OK. Applying the boundary conditions We will fix the bottom of the structure, which corresponds to line 6 in the model (use the Query icon and the mouse to confirm the line number). Click the Apply Fixity icon, set the Apply to field to Edge/Line, set the Edge/Line to 6 in the first row of the table and click OK. Click the oundary Plot icon and the Load Plot icon. Then use the mouse to rotate the mesh plot until the graphics window looks something like the figure on the next page. Defining the material Click the Manage Materials icon and click the Elastic Isotropic button. In the Define Isotropic Linear Elastic Material dialog box, add material 1, set the oung's modulus to 2.7E5, the Poisson's ratio to.29 and click OK. Click Close to close the Manage Material Definitions dialog box. Defining the shell thicknesses Choose Geometry Surfaces Thickness, enter 2. in the Thickness column for both surfaces and click OK. ADINA R & D, Inc. 8-3
4 PRESCRIED FORCE 5. U 1 U 2 U Defining the elements Element group: Click the Element Groups icon, add element group number 1, set the Type to Shell, click the Advanced tab, set the Stress Reference System to Local and click OK. Subdivision data: We will use a uniform mesh for the solution. Choose Meshing Mesh Density Complete Model, set the Subdivision Mode to Use Length, set the Element Edge Length to 25 and click OK. Element generation: Click the Mesh Surfaces icon, set the Nodes per Element to 9, enter 1 and 2 in the first two rows of the table and click OK. The graphics window should look something like the figure on the next page. 8-4 ADINA Primer
5 PRESCRIED FORCE 5. U 1 U 2 U Generating the ADINA Structures data file, running ADINA Structures, loading the porthole file First click the Save icon and save the database to file prob8. To generate the ADINA Structures data file and run ADINA Structures, click the Data File/Solution icon, set the file name to prob8, make sure that the Run Solution button is checked and click Save. When ADINA Structures is finished, close all open dialog boxes. Then set the Program Module drop-down list to Post-Processing (you can discard all changes), click the Open icon open porthole file prob8. Examining the solution Visualizing the number of rotational degrees of freedom for the nodes: We would like to see which nodes are assigned 5 degrees of freedom and which nodes are assigned 6 degrees of freedom. Choose Display Geometry/Mesh Plot Define Style, set the Node Depiction field to ROTATIONAL_DOF using the drop-down list and click OK. Then click the Clear icon and and the Mesh Plot icon on the next page.. The graphics window should look something like the figure ADINA R & D, Inc. 8-5
6 The nodes that are assigned 5 degrees of freedom are drawn in red and the nodes that are assigned 6 degrees of freedom are drawn in green. Notice that the 6 degree of freedom nodes are on the shell-shell intersection and on the built-in edge. Visualizing the shell thickness: Click the Create and Plot icon, set the and Plot Variable to (Thickness: THICKNESS) and click OK. The graphics window should look something like the top figure on the next page. Click the Clear and Plot icon to delete the band plot. ou can also plot the shell elements as if they were solid elements (that is, with the actual shell thicknesses). Click the Modify Mesh Plot icon, click the Element Depiction button, set the Appearance of Shell Element to Top/ottom and click OK twice to close both dialog boxes. The graphics window should look something like the bottom figure on the next page. For the remaining plots, we do not want to plot the nodes. Click the Reset Mesh Plot Style icon. Then click the Clear icon and the Mesh Plot icon. 8-6 ADINA Primer
7 THICKNESS MAIMUM 2. EG 1, EL 1, LN 1 MINIMUM 2. EG 1, EL 1, LN 1 ADINA R & D, Inc. 8-7
8 Effective stresses: Click the Quick and Plot icon. Use the Pick icon and the mouse until the graphics window looks something like this: EFFECTIVE STRESS RST CALC SHELL T = MAIMUM EG 1, EL 2, IPT 112 (53.3) MINIMUM EG 1, EL 1, IPT 332 (3.243) The bands appear to have breaks between elements. (This is an indication that the mesh may not be fine enough.) To smooth the band plot, click the Smooth Plots icon window should look something like the top figure on the next page.. The graphics These are the results as presented onto the top of the shells. To find out which direction corresponds to the top of the shells, click the Modify Mesh Plot icon and click the Element Depiction button. Check the Display Local System Triad button and click OK twice to close both dialog boxes. The graphics window should look something like the bottom figure on the next page. A triad is plotted within each element showing the direction of the element local coordinate system. The triad is interpreted as follows: t r s in which r, s and t are the element local coordinates. 8-8 ADINA Primer
9 SMOOTHED EFFECTIVE STRESS RST CALC SHELL T = 1. MAIMUM 91.8 NODE 86 (91.49) MINIMUM NODE SMOOTHED EFFECTIVE STRESS RST CALC SHELL T = 1. MAIMUM 91.8 NODE 86 (91.49) MINIMUM NODE ADINA R & D, Inc. 8-9
10 To plot the results corresponding to the bottom of the shells, click the Modify and Plot icon, click the Result Control... button, set the t coordinate field within the Calculation of Shell Element Results on Midsurface box to -1 and click OK twice to close both dialog boxes. The graphics window should look something like this: SMOOTHED EFFECTIVE STRESS RST CALC SHELL T = -1. MAIMUM NODE 86 MINIMUM NODE To plot the results corresponding to the shell midsurface, click the Modify and Plot icon and click the Result Control... button. Choose From Shell Midsurface within the Calculation of Shell Element Results on Midsurface box and click OK twice to close both dialog boxes. The graphics window should look something like the top figure on the next page. ou can also plot the stresses on the top-bottom depiction of the shell elements that we presented earlier. Click the Modify Mesh Plot icon, click the Element Depiction button, set the Appearance of Shell Element to Top/ottom and click OK twice to close both dialog boxes. The AUI doesn t display anything, because the AUI cannot plot the smoothed stresses on a top-bottom depiction. Click the Clear and Plot icon the Quick and Plot icon figure on the next page., then click. The graphics window should look something like the bottom 8-1 ADINA Primer
11 SMOOTHED EFFECTIVE STRESS RST CALC SHELL MIDSURF MAIMUM NODE 5 MINIMUM.5894 NODE 3 (.513) EFFECTIVE STRESS RST CALC MAIMUM 11. EG 1, EL 2, IPT 111 (54.16) MINIMUM.1227 EG 1, EL 3, IPT 311 (41.2) ADINA R & D, Inc. 8-11
12 Frequency analysis Now we will determine the first few natural frequencies and mode shapes for the shell structure. Invoking the pre-processor: Set the Program Module drop-down list to ADINA Structures (you can discard all changes). Choose prob8.idb from the recent file list near the bottom of the File menu. Change the heading to Problem 8: Analysis of a shell corner, frequency analysis. Removing the concentrated load: In the Model Tree, click on the + next to the Loading text, then right-click on the 1. Force 1 on Point 2 text, choose Delete and click es to answer the prompt. Click the Load Plot icon to plot the mesh without the load. Defining a frequency analysis: Set the Analysis Type drop-down list to Frequencies/Modes. Then click the Analysis Options icon, set the Number of Frequencies/Mode Shapes to 6 and click OK. Modifying the material: In the Model Tree, click on the + next to the Material text, then rightclick on the 1. Elastic text and choose Modify. In the Define Isotropic Linear Elastic Material dialog box, set the Density to 7.8E-9 and click OK. Generating the ADINA Structures data file, running ADINA Structures, loading the porthole file First choose File Save As and save the database to file prob8a. To generate the ADINA Structures data file and run ADINA Structures, click the Data File/Solution icon, set the file name to prob8a, make sure that the Run Solution button is checked and click Save. When ADINA Structures is finished, close all open dialog boxes. Then set the Program Module drop-down list to Post-Processing (you can discard all changes), click the Open icon and open porthole file prob8a. Examining the solution Determining which solutions were calculated by ADINA Structures: Choose List Info Response. ADINA Structures calculated the following modal data for reference time.: natural frequencies, physical error norms and mode shapes, all for modes 1 to 6. Click Close to close the dialog box. Listing the natural frequencies: Choose List Value List one, set Variable 1 to (Frequency/Mode: FREQUENC) and click Apply. The frequencies are: E+1 (Hz), 8-12 ADINA Primer
13 1.9713E+2, E+2, E+2, 7.63E+2, E+3. Click Close to close the dialog box. Plotting the first mode shape: The AUI displays the first mode shape. We would also like to display the original (undeformed) mesh in the same plot. Click the Show Original Mesh icon. The graphics window should look something like this: To create a movie showing the model moving in its first mode shape, click the Movie Mode Shape icon. To animate the movie, click the Animate icon. To loop the movie 1 times, choose Display Animate, set the Number of Cycles to 1 and click OK. Click the Refresh icon Next Solution icon next page. to clear the animation. Now, to show mode shape 2, click the. The graphics window should look something like the figure on the ou can use the Previous Solution icon, Next Solution icon, First Solution icon and Last Solution icon to view all of the other modes. Exiting the AUI: Choose File Exit to exit the AUI. ou can discard all changes. ADINA R & D, Inc. 8-13
14 Additional note ecause the model in this primer problem is linear, the natural frequencies do not depend on the applied loads (in this case, the concentrated load). However, if the model is nonlinear, the natural frequencies depend on the applied loads. To obtain the natural frequencies of a nonlinear model in the presence of applied loads, it is necessary to first obtain the static solution corresponding to the applied loads, then perform a frequency analysis using the static solution as initial conditions. This frequency analysis is performed as a restart run. Primer problem 26 demonstrates the procedure ADINA Primer
A plate with a hole is subjected to tension as shown: z p = 25.0 N/mm 2
 Problem description A plate with a hole is subjected to tension as shown: z p = 25.0 N/mm 2 56 y All lengths in mm. Thickness =1mm E = 7.0 10 4 N/mm = 0.25 10 20 This is the same problem as problem 2.
Problem description A plate with a hole is subjected to tension as shown: z p = 25.0 N/mm 2 56 y All lengths in mm. Thickness =1mm E = 7.0 10 4 N/mm = 0.25 10 20 This is the same problem as problem 2.
It is desired to analyze the shell-shell intersection shown: 0.01 radius This end fixed Shell-shell intersection dimensions and loading
 Problem description It is desired to analyze the shell-shell intersection shown: 0.01 radius Material properties: 0.08 E = 2.07 1011 N/m2 = 0.29 All dimensions in meters Line load of 1000 N/m 0.0075 radius
Problem description It is desired to analyze the shell-shell intersection shown: 0.01 radius Material properties: 0.08 E = 2.07 1011 N/m2 = 0.29 All dimensions in meters Line load of 1000 N/m 0.0075 radius
A cylinder is subjected to heat flux loadings as shown: 0.1 m. q = 500 W/m 2
 Problem description A cylinder is subjected to heat flux loadings as shown: 0.1 m L 0.1 m Thermal properties: k = 0.5 W/m- o h=5w/m2o - = 0.2 = 5.669 10-8 W/m 2 - o K 4 Environmental temperature = 20 o
Problem description A cylinder is subjected to heat flux loadings as shown: 0.1 m L 0.1 m Thermal properties: k = 0.5 W/m- o h=5w/m2o - = 0.2 = 5.669 10-8 W/m 2 - o K 4 Environmental temperature = 20 o
A plate with a hole is subjected to tension as shown: p = 25.0 N/mm 2. Region to mesh
 Problem description A plate with a hole is subjected to tension as shown: y p = 25. N/mm 2 Region to mesh 56 x All lengths in mm. Thickness=1mm 4 E = 7. 1 N/mm =.25 1 2 This is the same model and loading
Problem description A plate with a hole is subjected to tension as shown: y p = 25. N/mm 2 Region to mesh 56 x All lengths in mm. Thickness=1mm 4 E = 7. 1 N/mm =.25 1 2 This is the same model and loading
300 N All lengths in meters. Step load applied at time 0.0.
 Problem description In this problem, we subject the beam structure of problem 1 to an impact load as shown. 300 N 0.02 0.02 1 All lengths in meters. Step load applied at time 0.0. E = 2.07 10 11 N/m 2
Problem description In this problem, we subject the beam structure of problem 1 to an impact load as shown. 300 N 0.02 0.02 1 All lengths in meters. Step load applied at time 0.0. E = 2.07 10 11 N/m 2
A solid cylinder is subjected to a tip load as shown:
 Problem description A solid cylinder is subjected to a tip load as shown: 1000 N 0.1 1 All lengths in meters E = 2.07 10 11 N/m 2 = 0.29 In this problem solution, we will demonstrate the following topics
Problem description A solid cylinder is subjected to a tip load as shown: 1000 N 0.1 1 All lengths in meters E = 2.07 10 11 N/m 2 = 0.29 In this problem solution, we will demonstrate the following topics
300 N All lengths in meters. Step load applied at time 0.0. The beam is initially undeformed and at rest.
 Problem description In this problem, we subject the beam structure of problem 1 to an impact load as shown. 300 N 0.02 0.02 1 All lengths in meters. Step load applied at time 0.0. E = 2.07 10 11 N/m 2
Problem description In this problem, we subject the beam structure of problem 1 to an impact load as shown. 300 N 0.02 0.02 1 All lengths in meters. Step load applied at time 0.0. E = 2.07 10 11 N/m 2
A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel.
 Problem description A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y 15 12 P 9 Displacement gauge Cross-section: 0.432 18 x 6.625 All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel. E =
Problem description A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y 15 12 P 9 Displacement gauge Cross-section: 0.432 18 x 6.625 All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel. E =
Wall thickness= Inlet: Prescribed mass flux. All lengths in meters kg/m, E Pa, 0.3,
 Problem description Problem 30: Analysis of fluid-structure interaction within a pipe constriction It is desired to analyze the flow and structural response within the following pipe constriction: 1 1
Problem description Problem 30: Analysis of fluid-structure interaction within a pipe constriction It is desired to analyze the flow and structural response within the following pipe constriction: 1 1
It is desired to analyze the screwdriver shown in the following figure: The geometry of the screwdriver is given in a Parasolid file.
 Problem description It is desired to analyze the screwdriver shown in the following figure: The geometry of the screwdriver is given in a Parasolid file. The purpose of the analysis is to show how to modify
Problem description It is desired to analyze the screwdriver shown in the following figure: The geometry of the screwdriver is given in a Parasolid file. The purpose of the analysis is to show how to modify
A rubber O-ring is pressed between two frictionless plates as shown: 12 mm mm
 Problem description A rubber O-ring is pressed between two frictionless plates as shown: Prescribed displacement C L 12 mm 48.65 mm A two-dimensional axisymmetric analysis is appropriate here. Data points
Problem description A rubber O-ring is pressed between two frictionless plates as shown: Prescribed displacement C L 12 mm 48.65 mm A two-dimensional axisymmetric analysis is appropriate here. Data points
Problem description. The figure shows a disc braking system.
 Problem description Problem 34: Thermo-mechanical coupling analysis of a disc braking system The figure shows a disc braking system. Applied pressure Piston Brake pad Brake disc Fixed plate Initially,
Problem description Problem 34: Thermo-mechanical coupling analysis of a disc braking system The figure shows a disc braking system. Applied pressure Piston Brake pad Brake disc Fixed plate Initially,
In part 2, we demonstrate the following additional topics:
 Problem description In this problem, we analyze a simple beam structure. Each part of this lesson shows the solution of one of the analyses. In part 1, we demonstrate the following topics: Starting up/shutting
Problem description In this problem, we analyze a simple beam structure. Each part of this lesson shows the solution of one of the analyses. In part 1, we demonstrate the following topics: Starting up/shutting
Dam removed at start of analysis. Air g = 9.8. Water SI units used. Water: Air: = 10, = Slip walls are used to model the basin.
 Problem description It is desired to analyze the motion of water within a basin. Initially, the basin contains a dam, and the water is confined by the dam as shown. At the start of the analysis, the dam
Problem description It is desired to analyze the motion of water within a basin. Initially, the basin contains a dam, and the water is confined by the dam as shown. At the start of the analysis, the dam
Problem description C L. Tank walls. Water in tank
 Problem description A cylindrical water tank is subjected to gravity loading and ground accelerations, as shown in the figures below: Tank walls Water in tank Wall thickness 0.05 C L 5 g=9.81 m/s 2 Water:
Problem description A cylindrical water tank is subjected to gravity loading and ground accelerations, as shown in the figures below: Tank walls Water in tank Wall thickness 0.05 C L 5 g=9.81 m/s 2 Water:
Problem description. Bolt. Upper bracket. Lower bracket. Nut. A bracket assemblage is shown below in an exploded view:
 Problem description A bracket assemblage is shown below in an exploded view: Bolt Upper bracket Lower bracket Nut The two parts of the bracket are bolted together. After the parts are bolted together,
Problem description A bracket assemblage is shown below in an exploded view: Bolt Upper bracket Lower bracket Nut The two parts of the bracket are bolted together. After the parts are bolted together,
Problem description. Initial velocity mm/sec. Beveled end with varying thickness Thickness=0.5 Thickness=1. Tube cross-section.
 Problem 52: rushing of a crash tube Problem description onsider the crushing of a crash tube by a rigid weight: Initial velocity 12000 mm/sec eveled end with varying thickness Thickness=0.5 Thickness=1
Problem 52: rushing of a crash tube Problem description onsider the crushing of a crash tube by a rigid weight: Initial velocity 12000 mm/sec eveled end with varying thickness Thickness=0.5 Thickness=1
Problem description. It is desired to analyze the cracked body shown using a 3D finite element mesh: Top view. 50 radius. Material properties:
 Problem description It is desired to analyze the cracked body shown using a 3D finite element mesh: Top view 30 50 radius 30 Material properties: 5 2 E = 2.07 10 N/mm = 0.29 All dimensions in mm Crack
Problem description It is desired to analyze the cracked body shown using a 3D finite element mesh: Top view 30 50 radius 30 Material properties: 5 2 E = 2.07 10 N/mm = 0.29 All dimensions in mm Crack
An axisymmetric analysis is appropriate here.
 Problem description A spherical monopole vibrates sinusoidally, producing spherical waves that propagate into the surrounding air, as shown:. u = 0.138230 sin t (m/sec) =2 f,f=10khz Air u R = 0.055 m Monopole
Problem description A spherical monopole vibrates sinusoidally, producing spherical waves that propagate into the surrounding air, as shown:. u = 0.138230 sin t (m/sec) =2 f,f=10khz Air u R = 0.055 m Monopole
Problem description. The FCBI-C element is used in the fluid part of the model.
 Problem description This tutorial illustrates the use of ADINA for analyzing the fluid-structure interaction (FSI) behavior of a flexible splitter behind a 2D cylinder and the surrounding fluid in a channel.
Problem description This tutorial illustrates the use of ADINA for analyzing the fluid-structure interaction (FSI) behavior of a flexible splitter behind a 2D cylinder and the surrounding fluid in a channel.
Problem description. Internal heat generation. (kj/hr-m**3) Time (hr) Problem 25: Heat transfer from solidifying concrete blocks.
 Problem description During a twelve day period, concrete is added to a hole previously drilled into rock. At the beginning of each 4 day interval, a meter depth of concrete is poured. As the concrete solidifies,
Problem description During a twelve day period, concrete is added to a hole previously drilled into rock. At the beginning of each 4 day interval, a meter depth of concrete is poured. As the concrete solidifies,
A block is pushed onto a rigid cylinder as shown:
 Problem description Problem 43: Contact between a block and a rigid cylinder, TLA-S method A block is pushed onto a rigid cylinder as shown: Prescribed force = 10 5 N 0.1 All lengths in meters 0.01 0.1
Problem description Problem 43: Contact between a block and a rigid cylinder, TLA-S method A block is pushed onto a rigid cylinder as shown: Prescribed force = 10 5 N 0.1 All lengths in meters 0.01 0.1
It is desired to analyze the shaft and ring shown in the following figure: All lengths in mm E = N/mm2 = 0.29
 Problem description It is desired to analyze the shaft and ring shown in the following figure: Outer surface fixed 2 N/mm 2 1 2 4 2 4 All lengths in mm E = 2.07 105 N/mm2 = 0.29 The shaft is glued into
Problem description It is desired to analyze the shaft and ring shown in the following figure: Outer surface fixed 2 N/mm 2 1 2 4 2 4 All lengths in mm E = 2.07 105 N/mm2 = 0.29 The shaft is glued into
Plane strain conditions, 20 mm thick. b a. Material properties: E aa= N/mm2 Interface properties: G IC=0.28 N/mm E =E 00 N/mm2.
 Problem description The figure shows a double cantilever beam (DCB) of a composite material, subjected to displacement loads at its ends. u All lengths in mm. Not drawn to scale. Plane strain conditions,
Problem description The figure shows a double cantilever beam (DCB) of a composite material, subjected to displacement loads at its ends. u All lengths in mm. Not drawn to scale. Plane strain conditions,
1.992, 2.993, 3.04, 10.94, , Introduction to Modeling and Simulation Prof. F.-J. Ulm Spring FE Modeling Example Using ADINA
 1.992, 2.993, 3.04, 10.94, 18.996, 22.091 Introduction to Modeling and Simulation Prof. F.-J. Ulm Spring 2002 FE Modeling Example Using ADINA H Hgρ w ργ H = B = 10 m g = 9.81 m/s 2 ρ = 2400 kg/m 3 ρ w
1.992, 2.993, 3.04, 10.94, 18.996, 22.091 Introduction to Modeling and Simulation Prof. F.-J. Ulm Spring 2002 FE Modeling Example Using ADINA H Hgρ w ργ H = B = 10 m g = 9.81 m/s 2 ρ = 2400 kg/m 3 ρ w
A block is pushed onto a rigid cylinder as shown:
 Problem description A block is pushed onto a rigid cylinder as shown: 0.1 Prescribed displacement All lengths in meters 0.1 Block: E=110 6 N/m 2 = 0.3 Plane strain conditions 0.05 Rigid cylinder, frictionless
Problem description A block is pushed onto a rigid cylinder as shown: 0.1 Prescribed displacement All lengths in meters 0.1 Block: E=110 6 N/m 2 = 0.3 Plane strain conditions 0.05 Rigid cylinder, frictionless
Problem description. Problem 65: Free convection in a lightbulb. Filament (Tungsten): Globe (Glass): = FSI boundary. Gas (Argon):
 Problem description This tutorial demonstrates the use of ADINA for analyzing the fluid flow and heat transfer in a lightbulb using the Thermal Fluid-Structure Interaction (TFSI) features of ADINA. The
Problem description This tutorial demonstrates the use of ADINA for analyzing the fluid flow and heat transfer in a lightbulb using the Thermal Fluid-Structure Interaction (TFSI) features of ADINA. The
Air flows around a pipe containing hot steam, as shown: Air 293 K
 Problem description Air flows around a pipe containing hot steam, as shown: x y z Air 293 K Fan: P 1.0 10 10 Q 2 4 2 Steel Steam (ASME) 101 KPa 430 K The air inlet boundary condition is given as a function
Problem description Air flows around a pipe containing hot steam, as shown: x y z Air 293 K Fan: P 1.0 10 10 Q 2 4 2 Steel Steam (ASME) 101 KPa 430 K The air inlet boundary condition is given as a function
In this problem, we will demonstrate the following topics:
 Z Periodic boundary condition 1 1 0.001 Periodic boundary condition 2 Y v V cos t, V 1 0 0 The second Stokes problem is 2D fluid flow above a plate that moves horizontally in a harmonic manner, schematically
Z Periodic boundary condition 1 1 0.001 Periodic boundary condition 2 Y v V cos t, V 1 0 0 The second Stokes problem is 2D fluid flow above a plate that moves horizontally in a harmonic manner, schematically
All lengths in meters No-slip. Air: = N-s/m2 = 1.2 kg/m 3. o env = 293 K. c = 1006 J/kg-o. g = -9.8 m/s 2 = o C-1.
 Problem description Problem 21: onjugate heat transfer and natural convection within an enclosure We determine the fluid flow and temperature distribution within the enclosure shown in the figure. All
Problem description Problem 21: onjugate heat transfer and natural convection within an enclosure We determine the fluid flow and temperature distribution within the enclosure shown in the figure. All
Consider the following fluid flow problem: Slip wall. Steady-state laminar flow conditions are assumed.
 Problem description Consider the following fluid flow problem: Normal-traction prescribed on inlet Slip wall No-slip on cylinder walls Outlet Slip wall Steady-state laminar flow conditions are assumed.
Problem description Consider the following fluid flow problem: Normal-traction prescribed on inlet Slip wall No-slip on cylinder walls Outlet Slip wall Steady-state laminar flow conditions are assumed.
It is desired to analyze the flow in the strongly curved channel shown. Inlet Prescribed velocity V. z x
 Problem description It is desired to analyze the flow in the strongly curved channel shown. z x y Inlet Prescribed velocity V 120 o R H R 2H Outlet Numerical data for this model is H 0.127, R 3H, V 3.
Problem description It is desired to analyze the flow in the strongly curved channel shown. z x y Inlet Prescribed velocity V 120 o R H R 2H Outlet Numerical data for this model is H 0.127, R 3H, V 3.
Problem description. Prescribed. force. Unit thickness, plane stress. Transverse direction. Prescribed. displacement. Longitudinal direction
 Problem description Two desirable features in a material model are: 1) the ability to reproduce experimental data in an analysis that corresponds to the experiment and 2) that the material model be stable
Problem description Two desirable features in a material model are: 1) the ability to reproduce experimental data in an analysis that corresponds to the experiment and 2) that the material model be stable
Part 1: Resonance in a 2D cavity
 Problem 54: Microwave heating by harmonic M fields in a cavity Problem description In this problem, we analyze microwave heating in a cavity. In part 1, we analyze the harmonic electromagnetic field resonance
Problem 54: Microwave heating by harmonic M fields in a cavity Problem description In this problem, we analyze microwave heating in a cavity. In part 1, we analyze the harmonic electromagnetic field resonance
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Exercise 1. 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method
 Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method Contents Learn how to... 1 Given... 2 Questions... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 2 A. Preprocessor (Setting up the Model)... 3 A.1
Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method Contents Learn how to... 1 Given... 2 Questions... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 2 A. Preprocessor (Setting up the Model)... 3 A.1
Normal Modes - Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2 and CONM2
 APPENDIX A Normal Modes - Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2 and CONM2 T 1 Z R Y Z X Objectives: Create a geometric representation of a tube. Use the geometry model to define an analysis model comprised
APPENDIX A Normal Modes - Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2 and CONM2 T 1 Z R Y Z X Objectives: Create a geometric representation of a tube. Use the geometry model to define an analysis model comprised
Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007
 CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007 FE Project 1: 2D Plane Stress Analysis of acantilever Beam (Due date =TBD) Figure 1 shows a cantilever beam that is subjected to a concentrated
CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007 FE Project 1: 2D Plane Stress Analysis of acantilever Beam (Due date =TBD) Figure 1 shows a cantilever beam that is subjected to a concentrated
Normal Modes - Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2 and CONM2
 APPENDIX A Normal Modes - Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2 and CONM2 T 1 Z R Y Z X Objectives: Create a geometric representation of a tube. Use the geometry model to define an analysis model comprised
APPENDIX A Normal Modes - Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2 and CONM2 T 1 Z R Y Z X Objectives: Create a geometric representation of a tube. Use the geometry model to define an analysis model comprised
Analysis Steps 1. Start Abaqus and choose to create a new model database
 Source: Online tutorials for ABAQUS Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections (b=0.25, h=0.25, I=0.125, t f =t w =0.05), is simply supported at its lower
Source: Online tutorials for ABAQUS Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections (b=0.25, h=0.25, I=0.125, t f =t w =0.05), is simply supported at its lower
Abaqus CAE Tutorial 6: Contact Problem
 ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 6: Contact Problem Problem Description In this problem, a segment of an electrical contact switch (steel) is modeled by displacing the upper
ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 6: Contact Problem Problem Description In this problem, a segment of an electrical contact switch (steel) is modeled by displacing the upper
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.10) Stringer Tutorial
 Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.10) Stringer Tutorial Problem Description A table made of steel tubing with a solid steel top and shelf is loaded with an oblique impulse load. Determine the transient response of the
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.10) Stringer Tutorial Problem Description A table made of steel tubing with a solid steel top and shelf is loaded with an oblique impulse load. Determine the transient response of the
Course in ANSYS. Example0303. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0303 Example Gear axle 3D Objective: Compute the maximum stress von Mise Tasks: How should this be modeled? Topics: Element type, Real constants, modeling, Plot results, output graphics,
Course in Example0303 Example Gear axle 3D Objective: Compute the maximum stress von Mise Tasks: How should this be modeled? Topics: Element type, Real constants, modeling, Plot results, output graphics,
ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis
 R50 ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis Example 1 Static Analysis of a Bracket 1. Problem Description: The objective of the problem is to demonstrate the basic ANSYS procedures
R50 ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis Example 1 Static Analysis of a Bracket 1. Problem Description: The objective of the problem is to demonstrate the basic ANSYS procedures
Figure E3-1 A plane struss structure under applied loading. Start MARC Designer. From the main menu, select STATIC STRESS ANALYSIS.
 Example 3 Static Stress Analysis on a Plane Truss Structure Problem Statement: In this exercise, you will use MARC Designer software to carry out a static stress analysis on a simple plane truss structure,
Example 3 Static Stress Analysis on a Plane Truss Structure Problem Statement: In this exercise, you will use MARC Designer software to carry out a static stress analysis on a simple plane truss structure,
Abaqus/CAE Axisymmetric Tutorial (Version 2016)
 Abaqus/CAE Axisymmetric Tutorial (Version 2016) Problem Description A round bar with tapered diameter has a total load of 1000 N applied to its top face. The bottom of the bar is completely fixed. Determine
Abaqus/CAE Axisymmetric Tutorial (Version 2016) Problem Description A round bar with tapered diameter has a total load of 1000 N applied to its top face. The bottom of the bar is completely fixed. Determine
Quick Start Guide to midas NFX
 Quick Start Guide to midas NFX This guide is made for non-experienced FEA users. It provides basic knowledge needed to run midas NFX successfully and begin your analysis. Experienced FEA analysts can also
Quick Start Guide to midas NFX This guide is made for non-experienced FEA users. It provides basic knowledge needed to run midas NFX successfully and begin your analysis. Experienced FEA analysts can also
Sliding Split Tube Telescope
 LESSON 15 Sliding Split Tube Telescope Objectives: Shell-to-shell contact -accounting for shell thickness. Creating boundary conditions and loads by way of rigid surfaces. Simulate large displacements,
LESSON 15 Sliding Split Tube Telescope Objectives: Shell-to-shell contact -accounting for shell thickness. Creating boundary conditions and loads by way of rigid surfaces. Simulate large displacements,
Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial
 Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket Problem Specification Problem Description Build Geometry Define Materials Generate Mesh Apply
Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket Problem Specification Problem Description Build Geometry Define Materials Generate Mesh Apply
file://c:\documents and Settings\sala\Configuración local\temp\~hha54f.htm
 Página 1 de 26 Tutorials Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial 2.1. Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket 2.1.1. Problem Specification Applicable ANSYS Products: Level of Difficulty: Interactive Time Required:
Página 1 de 26 Tutorials Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial 2.1. Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket 2.1.1. Problem Specification Applicable ANSYS Products: Level of Difficulty: Interactive Time Required:
Normal Modes - Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2 and CONM2
 LESSON 16 Normal Modes - Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2 and CONM2 Y Y Z Z X Objectives: Create a geometric representation of a tube. Use the geometry model to define an analysis model comprised of plate
LESSON 16 Normal Modes - Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2 and CONM2 Y Y Z Z X Objectives: Create a geometric representation of a tube. Use the geometry model to define an analysis model comprised of plate
Rigid Element Analysis with RBAR
 WORKSHOP 4 Rigid Element Analysis with RBAR Y Objectives: Idealize the tube with QUAD4 elements. Use RBAR elements to model a rigid end. Produce a Nastran input file that represents the cylinder. Submit
WORKSHOP 4 Rigid Element Analysis with RBAR Y Objectives: Idealize the tube with QUAD4 elements. Use RBAR elements to model a rigid end. Produce a Nastran input file that represents the cylinder. Submit
Coustyx Tutorial Indirect Model
 Coustyx Tutorial Indirect Model 1 Introduction This tutorial is created to outline the steps required to compute radiated noise from a gearbox housing using Coustyx software. Detailed steps are given on
Coustyx Tutorial Indirect Model 1 Introduction This tutorial is created to outline the steps required to compute radiated noise from a gearbox housing using Coustyx software. Detailed steps are given on
Modeling a Shell to a Solid Element Transition
 LESSON 9 Modeling a Shell to a Solid Element Transition Objectives: Use MPCs to replicate a Solid with a Surface. Compare stress results of the Solid and Surface 9-1 9-2 LESSON 9 Modeling a Shell to a
LESSON 9 Modeling a Shell to a Solid Element Transition Objectives: Use MPCs to replicate a Solid with a Surface. Compare stress results of the Solid and Surface 9-1 9-2 LESSON 9 Modeling a Shell to a
Example Cantilever beam
 Course in ANSYS Example0300 Example Cantilever beam Objective: Compute the maximum deflection and locate point of maximum deflection Tasks: How should this be modelled? Compare results with results obtained
Course in ANSYS Example0300 Example Cantilever beam Objective: Compute the maximum deflection and locate point of maximum deflection Tasks: How should this be modelled? Compare results with results obtained
Important Note - Please Read:
 Important Note - Please Read: This tutorial requires version 6.01 or later of SAFE to run successfully. You can determine what version of SAFE you have by starting the program and then clicking the Help
Important Note - Please Read: This tutorial requires version 6.01 or later of SAFE to run successfully. You can determine what version of SAFE you have by starting the program and then clicking the Help
Materials, Load Cases and LBC Assignment
 LESSON 4 Materials, Load Cases and LBC Assignment 5.013 5.000 4.714 30000 4.429 4.143 3.858 3.572 3.287 3.001 2.716 2.430 2.145 1.859 20000 1.574 1.288 default_fringe : 1.003 Max 2.277 @Elm 40079.1 Min
LESSON 4 Materials, Load Cases and LBC Assignment 5.013 5.000 4.714 30000 4.429 4.143 3.858 3.572 3.287 3.001 2.716 2.430 2.145 1.859 20000 1.574 1.288 default_fringe : 1.003 Max 2.277 @Elm 40079.1 Min
ABAQUS for CATIA V5 Tutorials
 ABAQUS for CATIA V5 Tutorials AFC V2.5 Nader G. Zamani University of Windsor Shuvra Das University of Detroit Mercy SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com ABAQUS for CATIA V5,
ABAQUS for CATIA V5 Tutorials AFC V2.5 Nader G. Zamani University of Windsor Shuvra Das University of Detroit Mercy SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com ABAQUS for CATIA V5,
Introduction to MSC.Patran
 Exercise 1 Introduction to MSC.Patran Objectives: Create geometry for a Beam. Add Loads and Boundary Conditions. Review analysis results. MSC.Patran 301 Exercise Workbook - Release 9.0 1-1 1-2 MSC.Patran
Exercise 1 Introduction to MSC.Patran Objectives: Create geometry for a Beam. Add Loads and Boundary Conditions. Review analysis results. MSC.Patran 301 Exercise Workbook - Release 9.0 1-1 1-2 MSC.Patran
Solid and shell elements
 Solid and shell elements Theodore Sussman, Ph.D. ADINA R&D, Inc, 2016 1 Overview 2D and 3D solid elements Types of elements Effects of element distortions Incompatible modes elements u/p elements for incompressible
Solid and shell elements Theodore Sussman, Ph.D. ADINA R&D, Inc, 2016 1 Overview 2D and 3D solid elements Types of elements Effects of element distortions Incompatible modes elements u/p elements for incompressible
Workshop 15. Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate
 Introduction Workshop 15 Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate Rolling is a basic manufacturing technique used to transform preformed shapes into a form suitable for further processing. The rolling process
Introduction Workshop 15 Single Pass Rolling of a Thick Plate Rolling is a basic manufacturing technique used to transform preformed shapes into a form suitable for further processing. The rolling process
Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu.
 1. BEAM MODEL Start New Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu. Create a new model with the New Icon. In the dialogue
1. BEAM MODEL Start New Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu. Create a new model with the New Icon. In the dialogue
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10
 Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Sliding Block LESSON 26. Objectives: Demonstrate the use of Contact LBCs in a simple exercise.
 LESSON 26 Sliding Block 5 Objectives: Demonstrate the use of Contact LBCs in a simple exercise. Present method for monitoring a non-linear analysis progress. 26-1 26-2 LESSON 26 Sliding Block Model Description:
LESSON 26 Sliding Block 5 Objectives: Demonstrate the use of Contact LBCs in a simple exercise. Present method for monitoring a non-linear analysis progress. 26-1 26-2 LESSON 26 Sliding Block Model Description:
Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2 and CONM2
 WORKSHOP PROBLEM 5 Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2 and CONM2 Y Y Z Z X Objectives: Idealize a rigid end using RBE2 elements. Define a concentrated mass, to represent the weight of the rigid enclosure
WORKSHOP PROBLEM 5 Rigid Element Analysis with RBE2 and CONM2 Y Y Z Z X Objectives: Idealize a rigid end using RBE2 elements. Define a concentrated mass, to represent the weight of the rigid enclosure
Course in ANSYS. Example0601. ANSYS Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Example0601 Example Turbine Blade Example0601 2 Example Turbine Blade Objective: Solve for the temperature distribution within the 6mm thick turbine blade, with 2mm x 6mm rectangular cooling
Course in Example0601 Example Turbine Blade Example0601 2 Example Turbine Blade Objective: Solve for the temperature distribution within the 6mm thick turbine blade, with 2mm x 6mm rectangular cooling
Module 1.7: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.7: Point Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Material Properties 7 Meshing 8 Loads 9 Solution 15 General
Module 1.7: Point Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Material Properties 7 Meshing 8 Loads 9 Solution 15 General
Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial
 Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Solidification of a Casting Problem Specification Problem Description Prepare for a Thermal Analysis Input Geometry Define Materials Generate
Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 3. Thermal Tutorial Solidification of a Casting Problem Specification Problem Description Prepare for a Thermal Analysis Input Geometry Define Materials Generate
Stiffened Plate With Pressure Loading
 Supplementary Exercise - 3 Stiffened Plate With Pressure Loading Objective: geometry and 1/4 symmetry finite element model. beam elements using shell element edges. MSC.Patran 301 Exercise Workbook Supp3-1
Supplementary Exercise - 3 Stiffened Plate With Pressure Loading Objective: geometry and 1/4 symmetry finite element model. beam elements using shell element edges. MSC.Patran 301 Exercise Workbook Supp3-1
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.12) Vibrations Tutorial
 Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.12) Vibrations Tutorial Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections, is simply supported at its lower corners. Determine the first 10
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.12) Vibrations Tutorial Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections, is simply supported at its lower corners. Determine the first 10
Modal Analysis of Interpolation Constraint Elements and Concentrated Mass
 APPENDIX B Modal Analysis of Interpolation Constraint Elements and Concentrated Mass Y Y Z Z X Objectives: Utilize the analysis model created in a previous exercise. Run an MSC.Nastran modal analysis with
APPENDIX B Modal Analysis of Interpolation Constraint Elements and Concentrated Mass Y Y Z Z X Objectives: Utilize the analysis model created in a previous exercise. Run an MSC.Nastran modal analysis with
CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 If you have any questions about this tutorial, feel free to contact Wenjin Tao (w.tao@mst.edu). CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a practical application of the Finite
If you have any questions about this tutorial, feel free to contact Wenjin Tao (w.tao@mst.edu). CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a practical application of the Finite
Example Plate with a hole
 Course in ANSYS Example Plate with a hole A Objective: Determine the maximum stress in the x-direction for point A and display the deformation figure Tasks: Create a submodel to increase the accuracy of
Course in ANSYS Example Plate with a hole A Objective: Determine the maximum stress in the x-direction for point A and display the deformation figure Tasks: Create a submodel to increase the accuracy of
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.9) Vibrations Tutorial
 Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.9) Vibrations Tutorial Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections, is simply supported at its lower corners. Determine the first 10
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.9) Vibrations Tutorial Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections, is simply supported at its lower corners. Determine the first 10
Case Study 2: Piezoelectric Circular Plate
 Case Study 2: Piezoelectric Circular Plate PROBLEM - 3D Circular Plate, kp Mode, PZT4, D=50mm x h=1mm GOAL Evaluate the operation of a piezoelectric circular plate having electrodes in the top and bottom
Case Study 2: Piezoelectric Circular Plate PROBLEM - 3D Circular Plate, kp Mode, PZT4, D=50mm x h=1mm GOAL Evaluate the operation of a piezoelectric circular plate having electrodes in the top and bottom
Exercise 1. 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of. Ansys Workbench 14.0
 Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of Contents Ansys Workbench 14.0 Learn how to...1 Given...2 Questions...2 Taking advantage of symmetries...2 A. Getting started...3 A.1 Choose
Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of Contents Ansys Workbench 14.0 Learn how to...1 Given...2 Questions...2 Taking advantage of symmetries...2 A. Getting started...3 A.1 Choose
Institute of Mechatronics and Information Systems
 EXERCISE 4 Free vibrations of an electrical machine model Target Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of a simplified model of an electrical machine, with the use of
EXERCISE 4 Free vibrations of an electrical machine model Target Getting familiar with the fundamental issues of free vibrations analysis of a simplified model of an electrical machine, with the use of
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Michael Schraiber, Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop v12.0, OptiStruct, HyperView This tutorial
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Michael Schraiber, Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop v12.0, OptiStruct, HyperView This tutorial
Installation Guide. Beginners guide to structural analysis
 Installation Guide To install Abaqus, students at the School of Civil Engineering, Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, should log on to \\studserver, whereas the staff at the Department of Civil Engineering should
Installation Guide To install Abaqus, students at the School of Civil Engineering, Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, should log on to \\studserver, whereas the staff at the Department of Civil Engineering should
The Essence of Result Post- Processing
 APPENDIX E The Essence of Result Post- Processing Objectives: Manually create the geometry for the tension coupon using the given dimensions then apply finite elements. Manually define material and element
APPENDIX E The Essence of Result Post- Processing Objectives: Manually create the geometry for the tension coupon using the given dimensions then apply finite elements. Manually define material and element
ANSYS Workbench Guide
 ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.11) Nonlinear Buckling Tutorial
 Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.11) Nonlinear Buckling Tutorial Problem Description This is the NAFEMS 1 proposed benchmark (Lee s frame buckling) problem. The applied load is based on the normalized (EI/L 2 ) value
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.11) Nonlinear Buckling Tutorial Problem Description This is the NAFEMS 1 proposed benchmark (Lee s frame buckling) problem. The applied load is based on the normalized (EI/L 2 ) value
Module 3: Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam
 Module : Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Solution
Module : Buckling of 1D Simply Supported Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Solution
Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Loads
Module 1.5: Moment Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing 9 Loads
Linear Buckling Analysis of a Plate
 Workshop 9 Linear Buckling Analysis of a Plate Objectives Create a geometric representation of a plate. Apply a compression load to two apposite sides of the plate. Run a linear buckling analysis. 9-1
Workshop 9 Linear Buckling Analysis of a Plate Objectives Create a geometric representation of a plate. Apply a compression load to two apposite sides of the plate. Run a linear buckling analysis. 9-1
Mass Properties Calculations
 LESSON 15 Mass Properties Calculations Objectives Import a unigraphics express file and apply mass properties to the propeller. PAT302 Exercise Workbook MSC/PATRAN Version 8.0 15-1 15-2 PAT302 Exercise
LESSON 15 Mass Properties Calculations Objectives Import a unigraphics express file and apply mass properties to the propeller. PAT302 Exercise Workbook MSC/PATRAN Version 8.0 15-1 15-2 PAT302 Exercise
Exercise 1: Axle Structural Static Analysis
 Exercise 1: Axle Structural Static Analysis The purpose of this exercise is to cover the basic functionality of the Mechanical Toolbar (MTB) in the context of performing an actual analysis. Details of
Exercise 1: Axle Structural Static Analysis The purpose of this exercise is to cover the basic functionality of the Mechanical Toolbar (MTB) in the context of performing an actual analysis. Details of
Mesh Quality Tutorial
 Mesh Quality Tutorial Figure 1: The MeshQuality model. See Figure 2 for close-up of bottom-right area This tutorial will illustrate the importance of Mesh Quality in PHASE 2. This tutorial will also show
Mesh Quality Tutorial Figure 1: The MeshQuality model. See Figure 2 for close-up of bottom-right area This tutorial will illustrate the importance of Mesh Quality in PHASE 2. This tutorial will also show
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING. Part-1
 COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
2: Static analysis of a plate
 2: Static analysis of a plate Topics covered Project description Using SolidWorks Simulation interface Linear static analysis with solid elements Finding reaction forces Controlling discretization errors
2: Static analysis of a plate Topics covered Project description Using SolidWorks Simulation interface Linear static analysis with solid elements Finding reaction forces Controlling discretization errors
Post Processing of Displacement Results
 WORKSHOP 16 Post Processing of Displacement Results Objectives: Examine the deformation of the MSC.Nastran model to evaluate the validity of the assumptions made in the creation of the mesh density and
WORKSHOP 16 Post Processing of Displacement Results Objectives: Examine the deformation of the MSC.Nastran model to evaluate the validity of the assumptions made in the creation of the mesh density and
Linear Static Analysis of a Simply-Supported Stiffened Plate
 WORKSHOP 7 Linear Static Analysis of a Simply-Supported Stiffened Plate Objectives: Create a geometric representation of a stiffened plate. Use the geometry model to define an analysis model comprised
WORKSHOP 7 Linear Static Analysis of a Simply-Supported Stiffened Plate Objectives: Create a geometric representation of a stiffened plate. Use the geometry model to define an analysis model comprised
Two Dimensional Truss
 Two Dimensional Truss Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple 2D Truss problem. This is the first of four introductory ANSYS tutorials. Problem Description Determine the
Two Dimensional Truss Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple 2D Truss problem. This is the first of four introductory ANSYS tutorials. Problem Description Determine the
Ansys Lab Frame Analysis
 Ansys Lab Frame Analysis Analyze the highway overpass frame shown in Figure. The main horizontal beam is W24x162 (area = 47.7 in 2, moment of inertia = 5170 in 4, height = 25 in). The inclined members
Ansys Lab Frame Analysis Analyze the highway overpass frame shown in Figure. The main horizontal beam is W24x162 (area = 47.7 in 2, moment of inertia = 5170 in 4, height = 25 in). The inclined members
Plasticity Bending Machine Tutorial (FFlex)
 Plasticity Bending Machine Tutorial (FFlex) Copyright 2018 FunctionBay, Inc. All rights reserved. User and training documentation from FunctionBay, Inc. is subjected to the copyright laws of the Republic
Plasticity Bending Machine Tutorial (FFlex) Copyright 2018 FunctionBay, Inc. All rights reserved. User and training documentation from FunctionBay, Inc. is subjected to the copyright laws of the Republic
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
Post-Processing Modal Results of a Space Satellite
 LESSON 8 Post-Processing Modal Results of a Space Satellite 30000 7.61+00 5.39+00 30002 30001 mode 1 : Max 5.39+00 @Nd 977 Objectives: Post-process model results from an DB file. View and animate the eigenvector
LESSON 8 Post-Processing Modal Results of a Space Satellite 30000 7.61+00 5.39+00 30002 30001 mode 1 : Max 5.39+00 @Nd 977 Objectives: Post-process model results from an DB file. View and animate the eigenvector
Module 1.6: Distributed Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.6: Distributed Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing
Module 1.6: Distributed Loading of a 2D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Geometry 4 Preprocessor 7 Element Type 7 Real Constants and Material Properties 8 Meshing
MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec21_300k-mp4
 MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec21_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources
MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec21_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources
