It is desired to analyze the shaft and ring shown in the following figure: All lengths in mm E = N/mm2 = 0.29
|
|
|
- Damian Payne
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Problem description It is desired to analyze the shaft and ring shown in the following figure: Outer surface fixed 2 N/mm All lengths in mm E = N/mm2 = 0.29 The shaft is glued into the ring. This problem could be modeled using one geometry body. However, in this problem, we use two geometry bodies, one for the shaft and the other for the ring. We use the gluemesh feature to glue the shaft to the ring. In this problem solution, we will demonstrate the following topics that have not been presented in previous problems: Running an unstable model in static analysis. Applying a traction load that acts in a specified direction. Using the gluemesh feature. Using incompatible modes Before you begin Please refer to the Icon Locator Tables chapter of the Primer for the locations of all of the AUI icons. Please refer to the Hints chapter of the Primer for useful hints. Note that you must have an ADINA-M/PS license to do this problem. This problem cannot be solved with the 900 nodes version of the ADINA System because there are too many nodes in the model. Much of the input for this problem is stored in file prob40_1.in. ou need to copy files prob40_1.in from the folder samples\primer into a working directory or folder before beginning this analysis. ADINA R & D, Inc. 40-1
2 Invoking the AUI and choosing the finite element program Invoke the AUI and set the Program Module drop-down list to ADINA Structures. Defining the model We have prepared a batch file (prob40_1.in) which contains the entire model definition, with the exception of the load and gluemesh definitions. Choose File Open Batch, navigate to the working directory or folder, select the file prob40_1.in and click Open. The graphics window should look something like this: Selection of incompatible modes Choose Control Analysis Assumptions Kinematics, set Use Incompatible Modes in Element Formulation to es, then click OK. Traction load definition Click the Apply Load icon, set the Load Type to Pressure and click the Define... button to the right of the Load Number field. In the Define Pressure dialog box, add pressure 1, set the Magnitude to 2 and click OK. In the Apply Load dialog box, set Apply to to Face, and, in the first row of the table, set the Face to 2, the Body to 1 and the Load Direction to -Direction. Click OK to close the Apply Load dialog box ADINA Primer
3 When you click the Load Plot icon, the graphics window should look something like this: PRESCRIBED PRESSURE Generating the data file, running ADINA Structures We now demonstrate the effect of not gluing the parts together. Click the Save icon and save the database to file prob40. Click the Data File/Solution icon, set the file name to prob40, make sure that the Run Solution button is checked and click Save. Since the two parts are not connected, the shaft has rigid body modes, so the model is unstable in static analysis. Depending upon round-off, ADINA Structures either stops with the message *** Stiffness matrix not positive definite *** (which indicates that the model is unstable), or ADINA Structures runs to completion. In the latter case, you will find that the shaft undergoes very large displacements. ADINA R & D, Inc. 40-3
4 Using the gluemesh feature We need to glue the parts together. The following figure shows how the faces of the model line up. Face 6 of body 2 Face 1 of body 1 Face 4 of body 1 Face 1 of body 2 Section through model, parts separated for clarity We also note that the faces on body 1 should be masters, because each node on a slave should find an element face on the master. Choose Meshing Glue Mesh, add Glue Mesh Set 1, make sure that the Apply To field is set to Surface/Face, make sure that Show is set to Slave, then enter the following information into the table (do not click OK yet). Surf/Face Body # Now set Show to Master, enter the following information into the table and click OK. Surf/Face Body # When you click the Redraw icon, the graphics window should look something like the figure on the next page. Notice that the gluemesh boundary is drawn in thick lines ADINA Primer
5 PRESCRIBED PRESSURE Generating the data file, running ADINA Structures, loading the porthole file Click the Save icon to save the database file. Click the Data File/Solution icon, set the file name to prob40, make sure that the Run Solution button is checked and click Save. When ADINA Structures is finished, close all open dialog boxes, set the Program Module drop-down list to Post-Processing (you can discard all changes), click the Open icon open porthole file prob40. and Plotting the deformed mesh Click the Color Element Groups icon, the Scale Displacements icon and the Load Plot icon. The graphics window should look something like the figure on the next page. ADINA R & D, Inc. 40-5
6 DISP MAG PRESCRIBED PRESSURE The shaft appears to be glued to the ring. Total reaction force Choose List Value List one, set Variable 1 to (Reaction: -REACTION_SUM), Variable 2 to (Reaction: -REACTION_SUM) and Variable 3 to (Reaction: - REACTION_SUM), then click Apply. The and reaction sums should be very close to zero, and the reaction sum should be close to (N). Notice that the total applied force is a traction of 2 N/mm 2 applied over a circular area of radius 1 mm, resulting in a total applied force of N. The difference between the computed value of and the theoretical value of is due to the discretization of the shaft; the circular area is approximated by straight-sided quadrilateral element faces. Exiting the AUI: Choose File Exit (you can discard all changes) ADINA Primer
Problem description. Bolt. Upper bracket. Lower bracket. Nut. A bracket assemblage is shown below in an exploded view:
 Problem description A bracket assemblage is shown below in an exploded view: Bolt Upper bracket Lower bracket Nut The two parts of the bracket are bolted together. After the parts are bolted together,
Problem description A bracket assemblage is shown below in an exploded view: Bolt Upper bracket Lower bracket Nut The two parts of the bracket are bolted together. After the parts are bolted together,
It is desired to analyze the screwdriver shown in the following figure: The geometry of the screwdriver is given in a Parasolid file.
 Problem description It is desired to analyze the screwdriver shown in the following figure: The geometry of the screwdriver is given in a Parasolid file. The purpose of the analysis is to show how to modify
Problem description It is desired to analyze the screwdriver shown in the following figure: The geometry of the screwdriver is given in a Parasolid file. The purpose of the analysis is to show how to modify
A block is pushed onto a rigid cylinder as shown:
 Problem description Problem 43: Contact between a block and a rigid cylinder, TLA-S method A block is pushed onto a rigid cylinder as shown: Prescribed force = 10 5 N 0.1 All lengths in meters 0.01 0.1
Problem description Problem 43: Contact between a block and a rigid cylinder, TLA-S method A block is pushed onto a rigid cylinder as shown: Prescribed force = 10 5 N 0.1 All lengths in meters 0.01 0.1
Dam removed at start of analysis. Air g = 9.8. Water SI units used. Water: Air: = 10, = Slip walls are used to model the basin.
 Problem description It is desired to analyze the motion of water within a basin. Initially, the basin contains a dam, and the water is confined by the dam as shown. At the start of the analysis, the dam
Problem description It is desired to analyze the motion of water within a basin. Initially, the basin contains a dam, and the water is confined by the dam as shown. At the start of the analysis, the dam
A plate with a hole is subjected to tension as shown: z p = 25.0 N/mm 2
 Problem description A plate with a hole is subjected to tension as shown: z p = 25.0 N/mm 2 56 y All lengths in mm. Thickness =1mm E = 7.0 10 4 N/mm = 0.25 10 20 This is the same problem as problem 2.
Problem description A plate with a hole is subjected to tension as shown: z p = 25.0 N/mm 2 56 y All lengths in mm. Thickness =1mm E = 7.0 10 4 N/mm = 0.25 10 20 This is the same problem as problem 2.
In this problem, we will demonstrate the following topics:
 Z Periodic boundary condition 1 1 0.001 Periodic boundary condition 2 Y v V cos t, V 1 0 0 The second Stokes problem is 2D fluid flow above a plate that moves horizontally in a harmonic manner, schematically
Z Periodic boundary condition 1 1 0.001 Periodic boundary condition 2 Y v V cos t, V 1 0 0 The second Stokes problem is 2D fluid flow above a plate that moves horizontally in a harmonic manner, schematically
Problem description. The figure shows a disc braking system.
 Problem description Problem 34: Thermo-mechanical coupling analysis of a disc braking system The figure shows a disc braking system. Applied pressure Piston Brake pad Brake disc Fixed plate Initially,
Problem description Problem 34: Thermo-mechanical coupling analysis of a disc braking system The figure shows a disc braking system. Applied pressure Piston Brake pad Brake disc Fixed plate Initially,
Plane strain conditions, 20 mm thick. b a. Material properties: E aa= N/mm2 Interface properties: G IC=0.28 N/mm E =E 00 N/mm2.
 Problem description The figure shows a double cantilever beam (DCB) of a composite material, subjected to displacement loads at its ends. u All lengths in mm. Not drawn to scale. Plane strain conditions,
Problem description The figure shows a double cantilever beam (DCB) of a composite material, subjected to displacement loads at its ends. u All lengths in mm. Not drawn to scale. Plane strain conditions,
Problem description. Prescribed. force. Unit thickness, plane stress. Transverse direction. Prescribed. displacement. Longitudinal direction
 Problem description Two desirable features in a material model are: 1) the ability to reproduce experimental data in an analysis that corresponds to the experiment and 2) that the material model be stable
Problem description Two desirable features in a material model are: 1) the ability to reproduce experimental data in an analysis that corresponds to the experiment and 2) that the material model be stable
Problem description. It is desired to analyze the cracked body shown using a 3D finite element mesh: Top view. 50 radius. Material properties:
 Problem description It is desired to analyze the cracked body shown using a 3D finite element mesh: Top view 30 50 radius 30 Material properties: 5 2 E = 2.07 10 N/mm = 0.29 All dimensions in mm Crack
Problem description It is desired to analyze the cracked body shown using a 3D finite element mesh: Top view 30 50 radius 30 Material properties: 5 2 E = 2.07 10 N/mm = 0.29 All dimensions in mm Crack
300 N All lengths in meters. Step load applied at time 0.0. The beam is initially undeformed and at rest.
 Problem description In this problem, we subject the beam structure of problem 1 to an impact load as shown. 300 N 0.02 0.02 1 All lengths in meters. Step load applied at time 0.0. E = 2.07 10 11 N/m 2
Problem description In this problem, we subject the beam structure of problem 1 to an impact load as shown. 300 N 0.02 0.02 1 All lengths in meters. Step load applied at time 0.0. E = 2.07 10 11 N/m 2
Problem description C L. Tank walls. Water in tank
 Problem description A cylindrical water tank is subjected to gravity loading and ground accelerations, as shown in the figures below: Tank walls Water in tank Wall thickness 0.05 C L 5 g=9.81 m/s 2 Water:
Problem description A cylindrical water tank is subjected to gravity loading and ground accelerations, as shown in the figures below: Tank walls Water in tank Wall thickness 0.05 C L 5 g=9.81 m/s 2 Water:
Problem description. Initial velocity mm/sec. Beveled end with varying thickness Thickness=0.5 Thickness=1. Tube cross-section.
 Problem 52: rushing of a crash tube Problem description onsider the crushing of a crash tube by a rigid weight: Initial velocity 12000 mm/sec eveled end with varying thickness Thickness=0.5 Thickness=1
Problem 52: rushing of a crash tube Problem description onsider the crushing of a crash tube by a rigid weight: Initial velocity 12000 mm/sec eveled end with varying thickness Thickness=0.5 Thickness=1
Problem description. The FCBI-C element is used in the fluid part of the model.
 Problem description This tutorial illustrates the use of ADINA for analyzing the fluid-structure interaction (FSI) behavior of a flexible splitter behind a 2D cylinder and the surrounding fluid in a channel.
Problem description This tutorial illustrates the use of ADINA for analyzing the fluid-structure interaction (FSI) behavior of a flexible splitter behind a 2D cylinder and the surrounding fluid in a channel.
300 N All lengths in meters. Step load applied at time 0.0.
 Problem description In this problem, we subject the beam structure of problem 1 to an impact load as shown. 300 N 0.02 0.02 1 All lengths in meters. Step load applied at time 0.0. E = 2.07 10 11 N/m 2
Problem description In this problem, we subject the beam structure of problem 1 to an impact load as shown. 300 N 0.02 0.02 1 All lengths in meters. Step load applied at time 0.0. E = 2.07 10 11 N/m 2
Wall thickness= Inlet: Prescribed mass flux. All lengths in meters kg/m, E Pa, 0.3,
 Problem description Problem 30: Analysis of fluid-structure interaction within a pipe constriction It is desired to analyze the flow and structural response within the following pipe constriction: 1 1
Problem description Problem 30: Analysis of fluid-structure interaction within a pipe constriction It is desired to analyze the flow and structural response within the following pipe constriction: 1 1
Air flows around a pipe containing hot steam, as shown: Air 293 K
 Problem description Air flows around a pipe containing hot steam, as shown: x y z Air 293 K Fan: P 1.0 10 10 Q 2 4 2 Steel Steam (ASME) 101 KPa 430 K The air inlet boundary condition is given as a function
Problem description Air flows around a pipe containing hot steam, as shown: x y z Air 293 K Fan: P 1.0 10 10 Q 2 4 2 Steel Steam (ASME) 101 KPa 430 K The air inlet boundary condition is given as a function
A rubber O-ring is pressed between two frictionless plates as shown: 12 mm mm
 Problem description A rubber O-ring is pressed between two frictionless plates as shown: Prescribed displacement C L 12 mm 48.65 mm A two-dimensional axisymmetric analysis is appropriate here. Data points
Problem description A rubber O-ring is pressed between two frictionless plates as shown: Prescribed displacement C L 12 mm 48.65 mm A two-dimensional axisymmetric analysis is appropriate here. Data points
It is desired to analyze the shell-shell intersection shown: 0.01 radius This end fixed Shell-shell intersection dimensions and loading
 Problem description It is desired to analyze the shell-shell intersection shown: 0.01 radius Material properties: 0.08 E = 2.07 1011 N/m2 = 0.29 All dimensions in meters Line load of 1000 N/m 0.0075 radius
Problem description It is desired to analyze the shell-shell intersection shown: 0.01 radius Material properties: 0.08 E = 2.07 1011 N/m2 = 0.29 All dimensions in meters Line load of 1000 N/m 0.0075 radius
Consider the following fluid flow problem: Slip wall. Steady-state laminar flow conditions are assumed.
 Problem description Consider the following fluid flow problem: Normal-traction prescribed on inlet Slip wall No-slip on cylinder walls Outlet Slip wall Steady-state laminar flow conditions are assumed.
Problem description Consider the following fluid flow problem: Normal-traction prescribed on inlet Slip wall No-slip on cylinder walls Outlet Slip wall Steady-state laminar flow conditions are assumed.
Defining shell thicknesses Plotting 5 and 6 DOF nodes Plotting shell thicknesses Plotting results on the top, midsurface and bottom of the shell
 Problem description A shell corner is analyzed first for its static response due to a concentrated load, then for its natural frequencies and mode shapes. In the static analysis, we will demonstrate the
Problem description A shell corner is analyzed first for its static response due to a concentrated load, then for its natural frequencies and mode shapes. In the static analysis, we will demonstrate the
Problem description. Internal heat generation. (kj/hr-m**3) Time (hr) Problem 25: Heat transfer from solidifying concrete blocks.
 Problem description During a twelve day period, concrete is added to a hole previously drilled into rock. At the beginning of each 4 day interval, a meter depth of concrete is poured. As the concrete solidifies,
Problem description During a twelve day period, concrete is added to a hole previously drilled into rock. At the beginning of each 4 day interval, a meter depth of concrete is poured. As the concrete solidifies,
A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel.
 Problem description A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y 15 12 P 9 Displacement gauge Cross-section: 0.432 18 x 6.625 All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel. E =
Problem description A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y 15 12 P 9 Displacement gauge Cross-section: 0.432 18 x 6.625 All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel. E =
In part 2, we demonstrate the following additional topics:
 Problem description In this problem, we analyze a simple beam structure. Each part of this lesson shows the solution of one of the analyses. In part 1, we demonstrate the following topics: Starting up/shutting
Problem description In this problem, we analyze a simple beam structure. Each part of this lesson shows the solution of one of the analyses. In part 1, we demonstrate the following topics: Starting up/shutting
A plate with a hole is subjected to tension as shown: p = 25.0 N/mm 2. Region to mesh
 Problem description A plate with a hole is subjected to tension as shown: y p = 25. N/mm 2 Region to mesh 56 x All lengths in mm. Thickness=1mm 4 E = 7. 1 N/mm =.25 1 2 This is the same model and loading
Problem description A plate with a hole is subjected to tension as shown: y p = 25. N/mm 2 Region to mesh 56 x All lengths in mm. Thickness=1mm 4 E = 7. 1 N/mm =.25 1 2 This is the same model and loading
It is desired to analyze the flow in the strongly curved channel shown. Inlet Prescribed velocity V. z x
 Problem description It is desired to analyze the flow in the strongly curved channel shown. z x y Inlet Prescribed velocity V 120 o R H R 2H Outlet Numerical data for this model is H 0.127, R 3H, V 3.
Problem description It is desired to analyze the flow in the strongly curved channel shown. z x y Inlet Prescribed velocity V 120 o R H R 2H Outlet Numerical data for this model is H 0.127, R 3H, V 3.
An axisymmetric analysis is appropriate here.
 Problem description A spherical monopole vibrates sinusoidally, producing spherical waves that propagate into the surrounding air, as shown:. u = 0.138230 sin t (m/sec) =2 f,f=10khz Air u R = 0.055 m Monopole
Problem description A spherical monopole vibrates sinusoidally, producing spherical waves that propagate into the surrounding air, as shown:. u = 0.138230 sin t (m/sec) =2 f,f=10khz Air u R = 0.055 m Monopole
Problem description. Problem 65: Free convection in a lightbulb. Filament (Tungsten): Globe (Glass): = FSI boundary. Gas (Argon):
 Problem description This tutorial demonstrates the use of ADINA for analyzing the fluid flow and heat transfer in a lightbulb using the Thermal Fluid-Structure Interaction (TFSI) features of ADINA. The
Problem description This tutorial demonstrates the use of ADINA for analyzing the fluid flow and heat transfer in a lightbulb using the Thermal Fluid-Structure Interaction (TFSI) features of ADINA. The
A cylinder is subjected to heat flux loadings as shown: 0.1 m. q = 500 W/m 2
 Problem description A cylinder is subjected to heat flux loadings as shown: 0.1 m L 0.1 m Thermal properties: k = 0.5 W/m- o h=5w/m2o - = 0.2 = 5.669 10-8 W/m 2 - o K 4 Environmental temperature = 20 o
Problem description A cylinder is subjected to heat flux loadings as shown: 0.1 m L 0.1 m Thermal properties: k = 0.5 W/m- o h=5w/m2o - = 0.2 = 5.669 10-8 W/m 2 - o K 4 Environmental temperature = 20 o
A block is pushed onto a rigid cylinder as shown:
 Problem description A block is pushed onto a rigid cylinder as shown: 0.1 Prescribed displacement All lengths in meters 0.1 Block: E=110 6 N/m 2 = 0.3 Plane strain conditions 0.05 Rigid cylinder, frictionless
Problem description A block is pushed onto a rigid cylinder as shown: 0.1 Prescribed displacement All lengths in meters 0.1 Block: E=110 6 N/m 2 = 0.3 Plane strain conditions 0.05 Rigid cylinder, frictionless
A solid cylinder is subjected to a tip load as shown:
 Problem description A solid cylinder is subjected to a tip load as shown: 1000 N 0.1 1 All lengths in meters E = 2.07 10 11 N/m 2 = 0.29 In this problem solution, we will demonstrate the following topics
Problem description A solid cylinder is subjected to a tip load as shown: 1000 N 0.1 1 All lengths in meters E = 2.07 10 11 N/m 2 = 0.29 In this problem solution, we will demonstrate the following topics
Part 1: Resonance in a 2D cavity
 Problem 54: Microwave heating by harmonic M fields in a cavity Problem description In this problem, we analyze microwave heating in a cavity. In part 1, we analyze the harmonic electromagnetic field resonance
Problem 54: Microwave heating by harmonic M fields in a cavity Problem description In this problem, we analyze microwave heating in a cavity. In part 1, we analyze the harmonic electromagnetic field resonance
Abaqus CAE Tutorial 6: Contact Problem
 ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 6: Contact Problem Problem Description In this problem, a segment of an electrical contact switch (steel) is modeled by displacing the upper
ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 6: Contact Problem Problem Description In this problem, a segment of an electrical contact switch (steel) is modeled by displacing the upper
1.992, 2.993, 3.04, 10.94, , Introduction to Modeling and Simulation Prof. F.-J. Ulm Spring FE Modeling Example Using ADINA
 1.992, 2.993, 3.04, 10.94, 18.996, 22.091 Introduction to Modeling and Simulation Prof. F.-J. Ulm Spring 2002 FE Modeling Example Using ADINA H Hgρ w ργ H = B = 10 m g = 9.81 m/s 2 ρ = 2400 kg/m 3 ρ w
1.992, 2.993, 3.04, 10.94, 18.996, 22.091 Introduction to Modeling and Simulation Prof. F.-J. Ulm Spring 2002 FE Modeling Example Using ADINA H Hgρ w ργ H = B = 10 m g = 9.81 m/s 2 ρ = 2400 kg/m 3 ρ w
All lengths in meters No-slip. Air: = N-s/m2 = 1.2 kg/m 3. o env = 293 K. c = 1006 J/kg-o. g = -9.8 m/s 2 = o C-1.
 Problem description Problem 21: onjugate heat transfer and natural convection within an enclosure We determine the fluid flow and temperature distribution within the enclosure shown in the figure. All
Problem description Problem 21: onjugate heat transfer and natural convection within an enclosure We determine the fluid flow and temperature distribution within the enclosure shown in the figure. All
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND
 1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec21_300k-mp4
 MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec21_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources
MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec21_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources
 Set No. 1 IV B.Tech. I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2010 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
Set No. 1 IV B.Tech. I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2010 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames
 Tutorial 10. Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames Introduction Many engineering problems involve rotating flow domains. One example is the centrifugal blower unit that is typically used in automotive
Tutorial 10. Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames Introduction Many engineering problems involve rotating flow domains. One example is the centrifugal blower unit that is typically used in automotive
INSTED /CFD Post-Processor. Post-Processor. Chapter 5 INSTED /CFD (2D) Post-Processor
 INSTED /CFD Chapter 5 INSTED /CFD (2D) The part of INSTED/CFD (2D) plots lines or filled contours of variables such as velocities, temperature, pressure, scalars, and stream function. The program also
INSTED /CFD Chapter 5 INSTED /CFD (2D) The part of INSTED/CFD (2D) plots lines or filled contours of variables such as velocities, temperature, pressure, scalars, and stream function. The program also
Lesson 6: Assembly Structural Analysis
 Lesson 6: Assembly Structural Analysis In this lesson you will learn different approaches to analyze the assembly using assembly analysis connection properties between assembly components. In addition
Lesson 6: Assembly Structural Analysis In this lesson you will learn different approaches to analyze the assembly using assembly analysis connection properties between assembly components. In addition
UTOMATIC YNAMIC NCREMENTAL ONLINEAR NALYSIS. Release Notes. ADINA October ADINA R & D, Inc.
 UTOMATIC YNAMIC NCREMENTAL ONLINEAR NALYSIS Release Notes ADINA 9.2.5 October 2016 ADINA R & D, Inc. ADINA System 9.2 Release Notes (for version 9.2.5) October 2016 ADINA R & D, Inc. 71 Elton Avenue Watertown,
UTOMATIC YNAMIC NCREMENTAL ONLINEAR NALYSIS Release Notes ADINA 9.2.5 October 2016 ADINA R & D, Inc. ADINA System 9.2 Release Notes (for version 9.2.5) October 2016 ADINA R & D, Inc. 71 Elton Avenue Watertown,
3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) Figure 3.1 Geometry of a circular footing on a sand layer
 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) 3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) In the previous chapter some general aspects and basic features of the PLAXIS program were presented.
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) 3 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND (LESSON 1) In the previous chapter some general aspects and basic features of the PLAXIS program were presented.
Chapter 7 Practical Considerations in Modeling. Chapter 7 Practical Considerations in Modeling
 CIVL 7/8117 1/43 Chapter 7 Learning Objectives To present concepts that should be considered when modeling for a situation by the finite element method, such as aspect ratio, symmetry, natural subdivisions,
CIVL 7/8117 1/43 Chapter 7 Learning Objectives To present concepts that should be considered when modeling for a situation by the finite element method, such as aspect ratio, symmetry, natural subdivisions,
Finite Element Method. Chapter 7. Practical considerations in FEM modeling
 Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
Geometry Definition in the ADINA User Interface (AUI) Daniel Jose Payen, Ph.D. March 7, 2016
 Geometry Definition in the ADINA User Interface (AUI) Daniel Jose Payen, Ph.D. March 7, 2016 ADINA R&D, Inc., 2016 1 Topics Presented ADINA에서쓰이는 Geometry 종류 Simple (AUI) geometry ADINA-M geometry ADINA-M
Geometry Definition in the ADINA User Interface (AUI) Daniel Jose Payen, Ph.D. March 7, 2016 ADINA R&D, Inc., 2016 1 Topics Presented ADINA에서쓰이는 Geometry 종류 Simple (AUI) geometry ADINA-M geometry ADINA-M
Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames
 Tutorial 9. Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames Introduction Many engineering problems involve rotating flow domains. One example is the centrifugal blower unit that is typically used in automotive
Tutorial 9. Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames Introduction Many engineering problems involve rotating flow domains. One example is the centrifugal blower unit that is typically used in automotive
Getting Started. These tasks should take about 20 minutes to complete. Getting Started
 Getting Started Getting Started This tutorial will guide you step-by-step through your first ELFINI and Generative Part Structural Analysis session, allowing you to get acquainted with the product. You
Getting Started Getting Started This tutorial will guide you step-by-step through your first ELFINI and Generative Part Structural Analysis session, allowing you to get acquainted with the product. You
TRINITAS. a Finite Element stand-alone tool for Conceptual design, Optimization and General finite element analysis. Introductional Manual
 TRINITAS a Finite Element stand-alone tool for Conceptual design, Optimization and General finite element analysis Introductional Manual Bo Torstenfelt Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Starting the Program
TRINITAS a Finite Element stand-alone tool for Conceptual design, Optimization and General finite element analysis Introductional Manual Bo Torstenfelt Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Starting the Program
Assignment 2 Simulation and modeling, Spring 2010
 Assignment 2 Simulation and modeling, Spring 2010 1 Background The consultant company B&W (Besser & Wisser) AB has decided to develop an in-house FEcode. With this code the company intends to offer their
Assignment 2 Simulation and modeling, Spring 2010 1 Background The consultant company B&W (Besser & Wisser) AB has decided to develop an in-house FEcode. With this code the company intends to offer their
2: Static analysis of a plate
 2: Static analysis of a plate Topics covered Project description Using SolidWorks Simulation interface Linear static analysis with solid elements Finding reaction forces Controlling discretization errors
2: Static analysis of a plate Topics covered Project description Using SolidWorks Simulation interface Linear static analysis with solid elements Finding reaction forces Controlling discretization errors
Engine Gasket Model Instructions
 SOL 600 Engine Gasket Model Instructions Demonstrated:! Set up the Model Database! 3D Model Import from a MSC.Nastran BDF! Creation of Groups from Element Properties! Complete the Material Models! Import
SOL 600 Engine Gasket Model Instructions Demonstrated:! Set up the Model Database! 3D Model Import from a MSC.Nastran BDF! Creation of Groups from Element Properties! Complete the Material Models! Import
ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis
 R50 ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis Example 1 Static Analysis of a Bracket 1. Problem Description: The objective of the problem is to demonstrate the basic ANSYS procedures
R50 ANSYS 5.6 Tutorials Lecture # 2 - Static Structural Analysis Example 1 Static Analysis of a Bracket 1. Problem Description: The objective of the problem is to demonstrate the basic ANSYS procedures
Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University
 Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to find various icons that you would need in a real engineering analysis.
Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to find various icons that you would need in a real engineering analysis.
CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007
 CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007 FE Project 1: 2D Plane Stress Analysis of acantilever Beam (Due date =TBD) Figure 1 shows a cantilever beam that is subjected to a concentrated
CE366/ME380 Finite Elements in Applied Mechanics I Fall 2007 FE Project 1: 2D Plane Stress Analysis of acantilever Beam (Due date =TBD) Figure 1 shows a cantilever beam that is subjected to a concentrated
Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements
 Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements In structural analysis using finite element method, the analysis model is created by dividing the entire structure into finite elements. This procedure is known
Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements In structural analysis using finite element method, the analysis model is created by dividing the entire structure into finite elements. This procedure is known
All lengths in meters. E = = 7800 kg/m 3
 Poblem desciption In this poblem, we apply the component mode synthesis (CMS) technique to a simple beam model. 2 0.02 0.02 All lengths in metes. E = 2.07 10 11 N/m 2 = 7800 kg/m 3 The beam is a fee-fee
Poblem desciption In this poblem, we apply the component mode synthesis (CMS) technique to a simple beam model. 2 0.02 0.02 All lengths in metes. E = 2.07 10 11 N/m 2 = 7800 kg/m 3 The beam is a fee-fee
Solid and shell elements
 Solid and shell elements Theodore Sussman, Ph.D. ADINA R&D, Inc, 2016 1 Overview 2D and 3D solid elements Types of elements Effects of element distortions Incompatible modes elements u/p elements for incompressible
Solid and shell elements Theodore Sussman, Ph.D. ADINA R&D, Inc, 2016 1 Overview 2D and 3D solid elements Types of elements Effects of element distortions Incompatible modes elements u/p elements for incompressible
Generative Part Structural Analysis Fundamentals
 CATIA V5 Training Foils Generative Part Structural Analysis Fundamentals Version 5 Release 19 September 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_GPF_FI_V5R19 About this course Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course
CATIA V5 Training Foils Generative Part Structural Analysis Fundamentals Version 5 Release 19 September 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_GPF_FI_V5R19 About this course Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course
Example Plate with a hole
 Course in ANSYS Example Plate with a hole A Objective: Determine the maximum stress in the x-direction for point A and display the deformation figure Tasks: Create a submodel to increase the accuracy of
Course in ANSYS Example Plate with a hole A Objective: Determine the maximum stress in the x-direction for point A and display the deformation figure Tasks: Create a submodel to increase the accuracy of
Sliding Split Tube Telescope
 LESSON 15 Sliding Split Tube Telescope Objectives: Shell-to-shell contact -accounting for shell thickness. Creating boundary conditions and loads by way of rigid surfaces. Simulate large displacements,
LESSON 15 Sliding Split Tube Telescope Objectives: Shell-to-shell contact -accounting for shell thickness. Creating boundary conditions and loads by way of rigid surfaces. Simulate large displacements,
Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering. Introduction
 Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Introduction A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to
Revision of the SolidWorks Variable Pressure Simulation Tutorial J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Introduction A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 36
 Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 In last class, we have derived element equations for two d elasticity problems
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 In last class, we have derived element equations for two d elasticity problems
v Basic FESWMS Analysis SMS 11.2 Tutorial Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements FESWMS Fst2dh Mesh Module
 v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This lesson teaches how to prepare a mesh for a FESWMS simulation. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements FESWMS Fst2dh Mesh Module Time 15-30 minutes Page 1
v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This lesson teaches how to prepare a mesh for a FESWMS simulation. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements FESWMS Fst2dh Mesh Module Time 15-30 minutes Page 1
Engineering Effects of Boundary Conditions (Fixtures and Temperatures) J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering
 Engineering Effects of Boundary Conditions (Fixtures and Temperatures) J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Here SolidWorks stress simulation tutorials will be re-visited to show how they
Engineering Effects of Boundary Conditions (Fixtures and Temperatures) J.E. Akin, Rice University, Mechanical Engineering Here SolidWorks stress simulation tutorials will be re-visited to show how they
Example 24 Spring-back
 Example 24 Spring-back Summary The spring-back simulation of sheet metal bent into a hat-shape is studied. The problem is one of the famous tests from the Numisheet 93. As spring-back is generally a quasi-static
Example 24 Spring-back Summary The spring-back simulation of sheet metal bent into a hat-shape is studied. The problem is one of the famous tests from the Numisheet 93. As spring-back is generally a quasi-static
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Contents: Problem Specification 3 Learning Goals 4 Pre-Analysis & Start Up 5 Calculation
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Contents: Problem Specification 3 Learning Goals 4 Pre-Analysis & Start Up 5 Calculation
Linear Buckling Analysis of a Plate
 Workshop 9 Linear Buckling Analysis of a Plate Objectives Create a geometric representation of a plate. Apply a compression load to two apposite sides of the plate. Run a linear buckling analysis. 9-1
Workshop 9 Linear Buckling Analysis of a Plate Objectives Create a geometric representation of a plate. Apply a compression load to two apposite sides of the plate. Run a linear buckling analysis. 9-1
v Basic FESWMS Analysis SMS Tutorials Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial instructs on how to prepare a mesh for a FESWMS simulation. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements FESWMS Fst2dh Mesh Module Time 15 30 minutes
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial instructs on how to prepare a mesh for a FESWMS simulation. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements FESWMS Fst2dh Mesh Module Time 15 30 minutes
ME Optimization of a Frame
 ME 475 - Optimization of a Frame Analysis Problem Statement: The following problem will be analyzed using Abaqus. 4 7 7 5,000 N 5,000 N 0,000 N 6 6 4 3 5 5 4 4 3 3 Figure. Full frame geometry and loading
ME 475 - Optimization of a Frame Analysis Problem Statement: The following problem will be analyzed using Abaqus. 4 7 7 5,000 N 5,000 N 0,000 N 6 6 4 3 5 5 4 4 3 3 Figure. Full frame geometry and loading
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Tutorial 1: Mill 2D. Mill
 Mill This tutorial details the simulation of a process with granular non-cohesive material, concretely a Mill. Advanced and specific aspects should be clarified during training seminars using the present
Mill This tutorial details the simulation of a process with granular non-cohesive material, concretely a Mill. Advanced and specific aspects should be clarified during training seminars using the present
BE PLATES. Manual. July Friedel Hartmann. statik.de statik.de
 INSTALLATION Manual July 2017 Friedel Hartmann www.be statik.de www.winfem.de hartmann@be statik.de 1.1 INSTALLATION 1. INSTALLATION... 4 1.1. STARTING THE PROGRAM... 4 1.2. THE MAIN MENU... 4 1.3. POSITIONS...
INSTALLATION Manual July 2017 Friedel Hartmann www.be statik.de www.winfem.de hartmann@be statik.de 1.1 INSTALLATION 1. INSTALLATION... 4 1.1. STARTING THE PROGRAM... 4 1.2. THE MAIN MENU... 4 1.3. POSITIONS...
EnGenius Mesh AP Reset Tool Quick Guide
 EnGenius Mesh AP Reset Tool Quick Guide Revision : 1.1 Table of Contents EnGenius MESH AP Reset Tool Quick Guide 1. Overview...3 2. Installation Procedure...3 3. Uninstallation Procedure...3 4. Tool Layout...4
EnGenius Mesh AP Reset Tool Quick Guide Revision : 1.1 Table of Contents EnGenius MESH AP Reset Tool Quick Guide 1. Overview...3 2. Installation Procedure...3 3. Uninstallation Procedure...3 4. Tool Layout...4
SDC. Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks. Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003
 Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003 Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SDC PUBLICATIONS Design Generator, Inc. Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003 Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SDC PUBLICATIONS Design Generator, Inc. Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
Direct Transient Response with Base Excitation
 WORKSHOP PROBLEM 7 Direct Transient Response with Base Excitation Z Y X Objectives Create a geometric representation of a flat rectangular plate. Use the geometry model to define an analysis model comprised
WORKSHOP PROBLEM 7 Direct Transient Response with Base Excitation Z Y X Objectives Create a geometric representation of a flat rectangular plate. Use the geometry model to define an analysis model comprised
ES 128: Computer Assignment #4. Due in class on Monday, 12 April 2010
 ES 128: Computer Assignment #4 Due in class on Monday, 12 April 2010 Task 1. Study an elastic-plastic indentation problem. This problem combines plasticity with contact mechanics and has many rich aspects.
ES 128: Computer Assignment #4 Due in class on Monday, 12 April 2010 Task 1. Study an elastic-plastic indentation problem. This problem combines plasticity with contact mechanics and has many rich aspects.
ME Week 12 Piston Mechanical Event Simulation
 Introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation The purpose of this introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation (MES) project is to explorer the dynamic simulation environment of Autodesk Simulation. This
Introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation The purpose of this introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation (MES) project is to explorer the dynamic simulation environment of Autodesk Simulation. This
Elfini Solver Verification
 Page 1 Elfini Solver Verification Preface Using this Guide Where to Find More Information Conventions What's new User Tasks Static Analysis Cylindrical Roof Under its Own Weight Morley's Problem Twisted
Page 1 Elfini Solver Verification Preface Using this Guide Where to Find More Information Conventions What's new User Tasks Static Analysis Cylindrical Roof Under its Own Weight Morley's Problem Twisted
Plasticity Bending Machine Tutorial (FFlex)
 Plasticity Bending Machine Tutorial (FFlex) Copyright 2018 FunctionBay, Inc. All rights reserved. User and training documentation from FunctionBay, Inc. is subjected to the copyright laws of the Republic
Plasticity Bending Machine Tutorial (FFlex) Copyright 2018 FunctionBay, Inc. All rights reserved. User and training documentation from FunctionBay, Inc. is subjected to the copyright laws of the Republic
Quarter Symmetry Tank Stress (Draft 4 Oct 24 06)
 Quarter Symmetry Tank Stress (Draft 4 Oct 24 06) Introduction You need to carry out the stress analysis of an outdoor water tank. Since it has quarter symmetry you start by building only one-fourth of
Quarter Symmetry Tank Stress (Draft 4 Oct 24 06) Introduction You need to carry out the stress analysis of an outdoor water tank. Since it has quarter symmetry you start by building only one-fourth of
Contact Analysis. Learn how to: define surface contact solve a contact analysis display contact results. I-DEAS Tutorials: Simulation Projects
 Contact Analysis I-DEAS Tutorials: Simulation Projects This tutorial shows how to analyze surface contact. The electrical flash contacts in a 35mm camera will be modeled to calculate the contact forces.
Contact Analysis I-DEAS Tutorials: Simulation Projects This tutorial shows how to analyze surface contact. The electrical flash contacts in a 35mm camera will be modeled to calculate the contact forces.
Tutorial 2: Rock Cuting Disc 3D. Rock Cutting Disc
 Rock Cutting Disc This tutorial details the simulation of a process with granular non-cohesive material, concretely a Mill. Advanced and specific aspects should be clarified during training seminars using
Rock Cutting Disc This tutorial details the simulation of a process with granular non-cohesive material, concretely a Mill. Advanced and specific aspects should be clarified during training seminars using
Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/Engineer
 Appendix A Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/Engineer A.1 INTRODUCTION Pro/ENGINEER is a three-dimensional product design tool that promotes practices in design while ensuring compliance with industry
Appendix A Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/Engineer A.1 INTRODUCTION Pro/ENGINEER is a three-dimensional product design tool that promotes practices in design while ensuring compliance with industry
Case Study 2: Piezoelectric Circular Plate
 Case Study 2: Piezoelectric Circular Plate PROBLEM - 3D Circular Plate, kp Mode, PZT4, D=50mm x h=1mm GOAL Evaluate the operation of a piezoelectric circular plate having electrodes in the top and bottom
Case Study 2: Piezoelectric Circular Plate PROBLEM - 3D Circular Plate, kp Mode, PZT4, D=50mm x h=1mm GOAL Evaluate the operation of a piezoelectric circular plate having electrodes in the top and bottom
ASSOCIATIVE SIZING OF AERONAUTICAL STRUCTURES FROM CATIA V5 TO SAMCEF : APPLICATIONS TO STATIC AND BIRD IMPACT ANALYSES
 ASSOCIATIVE SIZING OF AERONAUTICAL STRUCTURES FROM CATIA V5 TO SAMCEF : APPLICATIONS TO STATIC AND BIRD IMPACT ANALYSES A.P. Gonze & J. Verstuyft SONACA S.A. Abstract : This paper presents an associative
ASSOCIATIVE SIZING OF AERONAUTICAL STRUCTURES FROM CATIA V5 TO SAMCEF : APPLICATIONS TO STATIC AND BIRD IMPACT ANALYSES A.P. Gonze & J. Verstuyft SONACA S.A. Abstract : This paper presents an associative
v Importing Rasters SMS 11.2 Tutorial Requirements Raster Module Map Module Mesh Module Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial
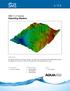 v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial teaches how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots,
v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial teaches how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots,
Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical
 Lecture 6 Modeling Connections 15.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical 1 2012 ANSYS, Inc. February 12, 2014 Chapter Overview In this chapter, we will extend the discussion of contact control begun
Lecture 6 Modeling Connections 15.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical 1 2012 ANSYS, Inc. February 12, 2014 Chapter Overview In this chapter, we will extend the discussion of contact control begun
CONTACT STATE AND STRESS ANALYSIS IN A KEY JOINT BY FEM
 PERJODICA POLYTECHNICA SER. ME CH. ENG. VOL. 36, NO. 1, PP. -15-60 (1992) CONTACT STATE AND STRESS ANALYSIS IN A KEY JOINT BY FEM K. VARADI and D. M. VERGHESE Institute of Machine Design Technical University,
PERJODICA POLYTECHNICA SER. ME CH. ENG. VOL. 36, NO. 1, PP. -15-60 (1992) CONTACT STATE AND STRESS ANALYSIS IN A KEY JOINT BY FEM K. VARADI and D. M. VERGHESE Institute of Machine Design Technical University,
Introduction to FEM Modeling
 Total Analysis Solution for Multi-disciplinary Optimum Design Apoorv Sharma midas NFX CAE Consultant 1 1. Introduction 2. Element Types 3. Sample Exercise: 1D Modeling 4. Meshing Tools 5. Loads and Boundary
Total Analysis Solution for Multi-disciplinary Optimum Design Apoorv Sharma midas NFX CAE Consultant 1 1. Introduction 2. Element Types 3. Sample Exercise: 1D Modeling 4. Meshing Tools 5. Loads and Boundary
Using Periodic Boundary Conditions
 1 of 6 2004 11 08 15:20 Use periodic boundary conditions, periodic edge conditions, and periodic point conditions to define a constraint that makes two quantities equal on two different (but usually equally
1 of 6 2004 11 08 15:20 Use periodic boundary conditions, periodic edge conditions, and periodic point conditions to define a constraint that makes two quantities equal on two different (but usually equally
DMU Engineering Analysis Review
 DMU Engineering Analysis Review Overview Conventions What's New? Getting Started Entering DMU Engineering Analysis Review Workbench Generating an Image Visualizing Extrema Generating a Basic Analysis Report
DMU Engineering Analysis Review Overview Conventions What's New? Getting Started Entering DMU Engineering Analysis Review Workbench Generating an Image Visualizing Extrema Generating a Basic Analysis Report
Learning Module 8 Shape Optimization
 Learning Module 8 Shape Optimization What is a Learning Module? Title Page Guide A Learning Module (LM) is a structured, concise, and self-sufficient learning resource. An LM provides the learner with
Learning Module 8 Shape Optimization What is a Learning Module? Title Page Guide A Learning Module (LM) is a structured, concise, and self-sufficient learning resource. An LM provides the learner with
An Introductory SIGMA/W Example
 1 Introduction An Introductory SIGMA/W Example This is a fairly simple introductory example. The primary purpose is to demonstrate to new SIGMA/W users how to get started, to introduce the usual type of
1 Introduction An Introductory SIGMA/W Example This is a fairly simple introductory example. The primary purpose is to demonstrate to new SIGMA/W users how to get started, to introduce the usual type of
Lecture 5 Modeling Connections
 Lecture 5 Modeling Connections 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical 1 2015 ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015 Chapter Overview In this chapter, we will extend the discussion of contact control begun
Lecture 5 Modeling Connections 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical 1 2015 ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015 Chapter Overview In this chapter, we will extend the discussion of contact control begun
FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY
 1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
RD-1070: Analysis of an Axi-symmetric Structure using RADIOSS
 RADIOSS, MotionSolve, and OptiStruct RD-1070: Analysis of an Axi-symmetric Structure using RADIOSS In this tutorial, you will learn the method of modeling an axi- symmetry problem in RADIOSS. The figure
RADIOSS, MotionSolve, and OptiStruct RD-1070: Analysis of an Axi-symmetric Structure using RADIOSS In this tutorial, you will learn the method of modeling an axi- symmetry problem in RADIOSS. The figure
Module 1: Introduction to Finite Element Analysis. Lecture 4: Steps in Finite Element Analysis
 25 Module 1: Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Lecture 4: Steps in Finite Element Analysis 1.4.1 Loading Conditions There are multiple loading conditions which may be applied to a system. The load
25 Module 1: Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Lecture 4: Steps in Finite Element Analysis 1.4.1 Loading Conditions There are multiple loading conditions which may be applied to a system. The load
Slicing. Slice multiple parts 13,0601,1489,1664(SP6P1)
 Slicing 13,0601,1489,1664(SP6P1) In this exercise, we will learn how to perform Slicing on multiple part. Slicing is the stage where the printing layers are set according to the printer definition or printing
Slicing 13,0601,1489,1664(SP6P1) In this exercise, we will learn how to perform Slicing on multiple part. Slicing is the stage where the printing layers are set according to the printer definition or printing
Finite Element Model for Axial Stiffness of Metal-Plate-Connected Tension Splice Wood Truss Joint
 Finite Element Model for Axial Stiffness of Metal-Plate-Connected Tension Splice Wood Truss Joint Jose M. Cabrero Assistant Professor University of Navarra, Department of Structural Analysis and Design,
Finite Element Model for Axial Stiffness of Metal-Plate-Connected Tension Splice Wood Truss Joint Jose M. Cabrero Assistant Professor University of Navarra, Department of Structural Analysis and Design,
