CHAPTER 11. Learn to use GEOPAK Automated Superelevation dialog box and Autoshape Builder to apply superelevation to a roadway.
|
|
|
- Jonathan Francis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 11 Superelevation 11.1 Introduction Objectives Project Manager Learn to use GEOPAK Automated Superelevation dialog box and Autoshape Builder to apply superelevation to a roadway. Calculate Superelevation Tools Menu Bar Application GEOPAK Road > Cross Sections >Superelevation Shape Manager Tools GEOPAK supports a myriad of options for the definition of pavement on proposed cross sections. They range from a single slope specification emanating from a baseline / profile on each section, to a complicated multiple roadway, each with its own superelevation transitions. The most basic is the project where no superelevation transitions are required, i.e., the roadway slope for all pavement (if any) can be specified as a single value. In this case, the slope can be defined with the proposed cross section processing and any additional superelevation work is not required. Another option is the definition of superelevation when roadways are constant widths without tapers, i.e., turn lanes, acceleration and deceleration lanes, etc. In these areas, the automated superelevation can be utilized, based on a user-defined design speed and considering the geometry of the specified roadway. After careful review of the data (in ASCII format) and overriding the computed values, GEOPAK draws pavement representations as complex shapes into a MicroStation 2D design file. A third option is the definition of superelevation when roadways are not constant widths, i.e., gore areas, turn lanes, acceleration and deceleration lanes, etc. In these areas, graphic elements within a MicroStation 2D design file are utilized to create complex shapes which define the superelevation transitions. A combination of these tools can be combined with a project, or even within a single roadway. The shapeless mode is excellent for rural applications, low volume city streets, frontage roads, etc., while the automated method quickly generates automated shapes for more complex roadways. Any area, which cannot be defined via the automated method, can be augmented by the graphical method. For some users, only simple narrow shapes will be required when designing new roadways or performing slope correction for reconstruction projects. The proposed cross section criteria will stretch the pavement out to the true proposed edge of pavement based on finding plan view elements that represent the EOP. GEOPAK 2001MR Superelevation 11-1
2 GEOPAK 11.2 Automated Superelevation (AutoShape Input File Maker) Project Manager Calculate superelevation Tools The GEOPAK Superelevation package enables the user to create, edit, and run an autoshape input file quickly, basing it on an existing COGO alignment. A rich set of preferences is available which gives the user complete control over every aspect of the standardization of the superelevation design process. AASHTO Method V is available as a default, along with the ability to employ user-defined lookup tables both for e (superelevation rate) and for runoff length. User-defined equations may also be entered to compute these values. A thorough set of options is available for resolving the superelevation conflicts of Reverse Curves, Compound Curves, Broken Back Curves, and Short Curves. GEOPAK calculates superelevation transition locations for any alignment stored into the coordinate geometry database. The main superelevation dialog box is simple and straightforward, allowing the user to select which preference file is to be used for the current session, as well as enabling the entry of the typical section lane configuration in the simple engineering terms of Number of Lanes, Lane Widths, Median Width (if any), and Cross Slope. More complex lane configurations may be represented as needed. Upon computation of the superelevation parameters (cross slopes and stationing), the information is stored in an ASCII file, where the user may review and modify the transitions, if desired. After reviewing the information, the ASCII file is executed from the Autoshape Builder to generate superelevation shapes. Job Chain Coordinate geometry database wherein the desired chains and profiles are stored. GEOPAK baseline chain dictating the horizontal geometry for which superelevation transitions are calculated. This chain is also called the Shape Cluster Baseline in the Auto Shape input file VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
3 GEOPAK Begin Station End Station Design Speed Preference File e selection L selection Facility Left / Right tabs When the chain is defined, GEOPAK populates the Begin Station with the default beginning of the chain. To compute superelevation for part of a chain, adjust the station. When the chain is defined, GEOPAK populates the End Station with the default beginning of the chain. To compute superelevation for part of a chain, adjust the station. Design speed that determines what Design Speed is to be used either in the tables or equations for e and length computations. The Preferences File combo box selects which Preference File is to be used for this computation. The various Preferences Files which are available in the combo box are determined by what files have the.sep file extension in the Preference Files Path on the User Directories dialog box. When it is set, the available e and length Selection combo boxes are filled in according to the csv file names as specified in the Preferences File. Those combo boxes determine which table within the.csv file will be used for computation. Facility determines whether the roadway cross section is to be divided or undivided. This option determines two things. For the dialog box box, it determines whether or not the values Profile, Tie (Offset or PGL), and or the Tie or PGL values may be different. If they are different then two shape clusters are to be generated, which usually is required for a median. The state of the Facility option button also determines which Preference is used as found on the Distribution tab of the Preferences dialog box. The area enclosed in the Left / Right tabs are for the determination of values specific to shape clusters. NOTE: The right and left tabs contain data pertaining to each lane within each roadway. If the Facility is undivided, then the left tab is for the left lane(s) while the right tab is for the right lane(s). If the Facility is divided, then the right tab is for the entire right roadway, while the left tab is for the left roadway. Create Input File Generate Superelevation Transitions Profile Tie ASCII file wherein GEOPAK creates the autoshape input file. DO NOT include the extension, as GEOPAK adds.inp to the field. Commence automatic superelevation calculations GEOPAK profile defined as the Shape Cluster Profile in the Auto Shape input file. Offset - Horizontal distance from the Profile (PGL) to the Chain. PGL Chain - Chain stored in the gpk file that the shapes will be computed from. This chain does not require a profile be stored with it as the defined profile will be applied to this chain. Offsets Offsets define the dimension of the shape (usually a lane) by two offset distances from the baseline. Note that tapers are not supported. Offset distances are negative if measured to the left.. Each lane must have the same offset on the left as the left adjacent lane and must have the same offset on the right as the right adjacent lane (no gaps in offsets). Computation may not proceed if this condition is not met. GEOPAK 2001MR Superelevation 11-3
4 GEOPAK % Slope Cross slope of each shape in normal crown in percent format. A negative sign denotes the roadway going downward, while emanating away from the PGL. A Normal Crown section of 2.0% would, therefore, be entered as 2.0. Lane offset values are entered in terms of master units, i.e., feet or meters. Dependent / Independent One dependent shape, which is based on the profile, is required for each cluster. Other shapes, drawn not based on the profile, but on adjoining lanes, are independent. For example, turn lanes are drawn abutting next to the mainline roadway, so they are independent. However, a lane based on the profile for its initial elevation, such as one of the through lanes, is profile dependent. Edit buttons: Add Delete Edit Quick Entry To add a line to the list box, type in the values in the edit fields, then click the Add icon. To delete a line, highlight the desired line, then click the Delete icon. To modify a line, highlight the desired line, (which is then displayed in the edit fields), change the desired values, then click the Edit icon, which updates the list box. Enables the user to populate the shape cluster list boxes quickly while entering the data using engineering terminology. When clicked, the dialog box depicted below opens. Selection of the Generate Superelevation Transitions button performs the actual superelevation computations. Three things happen at this point. First, the superelevation transitions as computed by GEOPAK are written to the Autoshape Input File specified by the user (in the Create Input File field). Second, the log file is written. Finally, the Autoshape Input File is loaded into the text editor running within MicroStation. This Autoshape Input File Editor has an icon at the top that allows the Autoshape Input File to be run. Autoshape Input files can also be run from the Autoshape Builder VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
5 GEOPAK Example - Auto Shape ASCII Input File /* Superelevation Settings and Parameters: Project Name: C:\data\geo\vdot\road1\17682.prj User: C:\data\geo\vdot\road1\projdbs\VDOT Run Name: MAINLINE Unit System is english. Created input file "mainline_shapes.inp". Created activity log file "mainline_shapes.log". Created on Wed, Nov 06, 2002 at 13:11. Using Preference File "english standard" Using e Selection of "rural". Using Length Selection of "rural" Using Design Speed of */ auto shape job number = 101 auto shape set shape cluster baseline = MAINLINE shape cluster profile = MAINLINE shape cluster tie = dependent shape chain / offset MAINLINE MAINLINE filler line station / slope /* Curve ML-1 */ /* Curve ML-1 */ /* Curve ML-2 */ /* Curve ML-2 */ auto shape set shape cluster baseline = MAINLINE shape cluster profile = MAINLINE shape cluster tie = independent shape chain / offset MAINLINE MAINLINE filler line station / slope /* Curve ML-1 */ /* Curve ML-1 */ /* Curve ML-2 */ /* Curve ML-2 */ GEOPAK 2001MR Superelevation 11-5
6 GEOPAK auto shape set shape cluster baseline = MAINLINE shape cluster profile = MAINLINE shape cluster tie = dependent shape chain / offset MAINLINE MAINLINE filler line station / slope /* Curve ML-1 */ /* Curve ML-1 */ /* Curve ML-2 */ /* Curve ML-2 */ auto shape set shape cluster baseline = MAINLINE shape cluster profile = MAINLINE shape cluster tie = independent shape chain / offset MAINLINE MAINLINE filler line station / slope /* Curve ML-1 */ /* Curve ML-1 */ /* Curve ML-2 */ /* Curve ML-2 */ Plot Parameters Dependent Shape lv = 63 co = 6 lc = 0 wt = 2 Dependent Text lv = 63 co = 6 Independent Shape lv = 63 co = 1 lc = 0 wt = 2 Independent Text lv = 63 co = 1 Write shapes into dgn = C:\data\geo\vdot\road1\d17682work.dgn 11-6 VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
7 GEOPAK 11.3 Draw Shapes into Plan View File Project Manager None Tools Menu Bar Application GEOPAK Road > Cross Sections >Superelevation Shape Manager Tools Once the shape input file (fname.inp) has been created and reviewed, the designer can run the input file to place the superelevation shapes into the specified graphics file. To use the interactive method to define roadway superelevation (in a.dgn file) the designer pushes the Autoshape Builder icon from the Superelevation Shape Manager Tools tool bar (or alternately from this same icon within the Text Editor as described above). Input File Display Only Name of.inp file (fname.inp) created by the Automated superelevation generation containing the transitions. Create the shapes in "Display Only" mode. That is, they are not written to the design file and a view Update operation eliminates them, as does zoom in, etc. The shapes are placed in a 2D graphics file on level 63 by default. The plot parameters can be modified in the input file with a text editor prior to building the shapes into the graphics file or with the User > Symbologies pull down on the Automated Superelevation dialog box. GEOPAK 2001MR Superelevation 11-7
8 GEOPAK 11.4 Shape Analysis Tools Tools Menu Bar Application GEOPAK Road > Cross Sections >Superelevation Shape Manager Tools The tools in the Superelevation Shape Manager Tools toolbox are detailed below. Auto. Superelevation Autoshape Builder Shape Maker Shape Analyst Shape Profiler Shape Editor Shape Selector Performs the actual calculations and stores the results in an ASCII file, known as the autoshape input file. Processes the autoshape input file and draws corresponding complex shapes in the specified 2D design file. Graphical method of drawing irregular superelevation shapes. This method is utilized for gore areas, turn lanes, etc. The Shape Analyst tool provides information on any point within a GEOPAK superelevation shape. The Shape Profiler tool provides profile information based on user-define increments intersecting a GEOPAK superelevation shape. The Shape Editor tool enables the user to dynamically change parameters on a previously created shape. This includes filler line stationing, dynamic moving of shapes, etc. The Shape Selector tool highlights or selects shapes based on a wide range of user queries or filters. Shape Properties The Shape Properties tool provides information on any GEOPAK superelevation shape. In addition, this shape information can be modified on individual shapes of selections of shapes VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
9 GEOPAK Shape Analyst The Shape Analyst tool is extremely useful, as it provides information on any point within a GEOPAK superelevation shape. Before using this tool, the Job Number must be selected. Upon selecting a Job Number, a Chain must be selected that the shapes are defined relative to. If Display Only is enabled, information like elevation and a flow arrow are drawn to the view, but they are not written as elements to the active MicroStation file. When the Cross Section toggle is not activated and a data point is issued within a shape, the elevation of the data point and a flow arrow are displayed. When the toggle is activated, a dashed line is placed through the data point, radial to the shaped cluster baseline. In addition to the elevation and flow arrow placed at the data point, elevations are displayed where the cross section line intersects any superelevation shape and cross slopes are labeled for each shape. The By Sta/Offset button causes the current Station / Offset value to be projected back onto the shape cluster baseline and the elevation of the projected point is displayed. This option can be manual entry only and requires no data point on the screen. The DP button works within a superelevation shape whose X, Y coordinates are utilized to compute station / offset from the specified shape cluster baseline, which is subsequently utilized in conjunction with the shape to compute the various slopes and elevations. After the DP button is clicked, numerous data points can be placed. It is not necessary to click the DP button again. Each corresponding station / offset is displayed along with the associated output information. The Dynamic button activates the dynamic mode. As the cursor moves across the screen, any momentary pause places the elevation and flow arrow in the MicroStation file and computes and displays the analysis information. The Extrapolate Fixed Slope toggle is another option supported in the Shape Analyst tool. The option is utilized when the data point, dynamic point or station / offset is outside of the shape. When the option is not activated, the data point is projected back to the shape's chain. The elevations at the edges of the shape are displayed and the slope of the outside shape is projected to the data point. When the toggle is enabled, the user defined slope is projected from the outer most shape to the data point to determine an elevation. GEOPAK 2001MR Superelevation 11-9
10 GEOPAK Shape Profiler The Shape Profiler tool computes elevations along any GEOPAK Shape or MicroStation element at a user specified interval. The element can be inside or outside of the shapes. The Job field can be populated by key in or using the Select button. After selecting a GPK file, click Identify Shape and data point on any shape along the desired Chain. Set the From Station and To Station fields by keying in values or using the DP buttons. Even should be selected when it is desired to have the elevations compute at the even station values. Increment will allow the elevations to be computed starting at the From Station, then adding the increment value to that station. Intersect is used with an element to compute elevations at all locations that the element intersects the shape(s). The Elevation Along toggle can be set to Shape or Element. When set to Shape, elevations will be computed based on the Even/Increment value along both longitudinal edges of the shape. When set to Element the elevations are computed along the element based on the Even/Increment/Intersect toggle. Continuous Extrapolation allows the user to identify multiple longitudinal elements outside of the shape area and compute elevations by a user defined Slope and one of three methods: Radial to Baseline, Radial From Element, or Radial to Element VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
11 GEOPAK LAB 11: Superelevation As a reminder, our project contains distinct sections: Section 1 4 lane divided highway with depressed median from Sta to Sta Left side of the roadway will be resurfacing while the right side is new construction. Section 2 4 lane divided highway with raised median from Sta to Sta Left side of the roadway will be resurfacing while the right side is new construction. Section 3 4 lane undivided highway from Sta to Sta Section 4 2 Lane highway with Entrances and Exit Ramps from Sta to Sta Section 5 Exit Ramp (RampA) Based on this information, we will need to process the Superelevation separately for each of the above sections. Each process will create a shape input file that can be run individually Automated Superelevation Section 1 Step 1. Step 2. Step 3. Step 4. Step 5. Execute C:\data\geo\VDOT\road1\LAB11.EXE. Open the MicroStation file c:\data\geo\vdot\road1\d17682work.dgn Open Project Manager. Click Calculate Superelevation button from the Road Project: prj workflow dialog box. Create a new run called ML1 and click OK. Once the Automated Superelevation dialog box has been invoked, the dialog box on the right will be displayed. Fill out the upper portion of the dialog box as shown. Step 6. Step 7. The profile should be set to MAINLINE for both the Left and Right tabs. The Tie option should be set to offset and the offset value should be set to 0.0 to force the PGL (Profile Grade Line) to run along the centerline of construction (MAINLINE). GEOPAK 2001MR LAB 11: Superelevation 11-11
12 GEOPAK Step 8. Press the Quick Entry icon as shown in the image below. Step 9. Fill out the Quick Entry dialog box as shown to the right and press OK. NOTE: Quick Entry can be used only if the lane configuration to the left and right sides of the baseline are the same VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
13 GEOPAK The dialog box should appear as shown: NOTE: Quick Entry may reset your OFFSET. Please ensure that the offset for both the left and right roadways is set to 0. Step 10. Step 11. Provide an Input Filename (ml1_shapes.inp) to store the computed transitions for this station range. Click the Generate Superelevation Transitions button to initiate the calculation of the transitions for the Left and Right roadway. Step 12. Review the computations within the Text Editor dialog box. GEOPAK 2001MR LAB 11: Superelevation 11-13
14 GEOPAK Step 13. Step 14. Step 15. To build these shapes into the graphics file, click the Autoshape Builder icon within the Text Editor dialog box. This will automatically draw the shapes into your design file on level 63. Close the Text Editor dialog box as well as the automated superelevation dialog box. When prompted to Save Superelevation settings, click Yes. Review the Superelevation shapes created in the design file VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
15 GEOPAK 11.2 Automated Superelevation Section 2 Step 1. Step 2. Click the Calculate Superelevation button from the Road Project: prj workflow dialog box. Create a new run called ML2 and click OK. Once the Automated Superelevation dialog box has been invoked, the dialog box on the right will be displayed. Fill out the upper portion of the dialog box as shown. Step 3. Step 4. The profile from which the shapes should be computed should be set to MAINLINE for both the Left and Right roadway tabs. The Tie option should be set to offset and the offset value should be set to 0.0 to force the PGL (Profile Grade Line) to run along the centerline of construction (MAINLINE). Step 5. Press the Quick Entry icon as shown in the image below. GEOPAK 2001MR LAB 11: Superelevation 11-15
16 GEOPAK Step 6. Fill out the Quick Entry dialog box as shown below and press OK. NOTE: Quick Entry can be used only if the lane configuration to the left and right sides of the baseline are the same. The dialog box should appear as shown: NOTE: Quick Entry may reset your OFFSET. Please ensure that the offset for both the left and right roadways is set to 0. Step 7. Provide an Input Filename (ml2_shapes.inp) to store the computed transitions for this station range VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
17 GEOPAK Step 8. Step 9. Click the Generate Superelevation Transitions button to initiate the calculation of the transitions for the Left and Right roadway. Review the computations within the Text Editor dialog box. Step 10. Step 11. Step 12. To build these shapes into the graphics file, click the Autoshape Builder icon within the Text Editor dialog box. This will automatically draw the shapes into your design file on level 63. Close the Text Editor dialog box as well as the automated superelevation dialog box. When prompted to Save Superelevation settings, click Yes. Review the Superelevation shapes created in the design file. GEOPAK 2001MR LAB 11: Superelevation 11-17
18 GEOPAK 11.3 Automated Superelevation Section 3 Step 1. Step 2. Click the Calculate Superelevation button from the Road Project: prj workflow dialog box. Create a new run called ML3 and click OK. Once the Automated Superelevation dialog box has been invoked, the dialog box on the right will be displayed. Fill out the upper portion of the dialog box as shown. Step 3. The profile from which the shapes should be computed should be set to MAINLINE for both the Left and Right roadway tabs. Step 4. The Tie option should be set to offset and the offset value should be set to 0.0 to force the PGL (Profile Grade Line) to run along the centerline of construction (MAINLINE). Step 5. Press the Quick Entry icon as shown in the image below VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
19 GEOPAK Step 6. Fill out the Quick Entry dialog box as shown below and press OK. NOTE: Quick Entry can be used only if the lane configuration to the left and right sides of the baseline are the same. The dialog box should appear as shown: Step 7. Step 8. Provide an Input Filename (ml3_shapes.inp) to store the computed transitions for this station range. Click the Generate Superelevation Transitions button to initiate the calculation of the transitions for the Left and Right roadway. GEOPAK 2001MR LAB 11: Superelevation 11-19
20 GEOPAK Step 9. Review the computations within the Text Editor dialog box. Step 10. Step 11. Step 12. To build these shapes into the graphics file, click the Autoshape Builder icon within the Text Editor dialog box. This will automatically draw the shapes into your design file on level 63. Close the Text Editor dialog box as well as the automated superelevation dialog box. When prompted to Save Superelevation settings, click Yes. Review the Superelevation shapes created in the design file VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
21 GEOPAK 11.4 Automated Superelevation Section 4 Step 1. Step 2. Click the Calculate Superelevation button from the Road Project: prj workflow dialog box. Create a new run called ML4 and click OK. Once the Automated Superelevation dialog box has been invoked, the dialog box on the right will be displayed. Fill out the upper portion of the dialog box as shown. Step 3. Step 4. The profile from which the shapes should be computed should be set to MAINLINE for both the Left and Right roadway tabs. The Tie option should be set to offset and the offset value should be set to 0.0 to force the PGL (Profile Grade Line) to run along the centerline of construction (MAINLINE). Step 5. Press the Quick Entry icon as shown in the image below. GEOPAK 2001MR LAB 11: Superelevation 11-21
22 GEOPAK Step 6. Fill out the Quick Entry dialog box as shown below and press OK. NOTE: Quick Entry can be used only if the lane configuration to the left and right sides of the baseline are the same. The dialog box should appear as shown: Step 10. Step 11. Step 12. Provide an Input Filename (ml4_shapes.inp) to store the computed transitions for this station range. Click the Generate Superelevation Transitions button to initiate the calculation of the transitions for the Left and Right roadway. Review the computations within the Text Editor dialog box VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
23 GEOPAK Here s where the ability to review your calculations and make changes comes in handy. Notice that from Sta to Sta we used an Urban Standard, which gave us a slope of % at Sta But notice now we ve used a Rural standard from Sta to Sta , which gives us a slope of % at Sta Let s fix this by hand-editing the superelevation calculations and changing the slope at Sta from to to match the slope coming out of the urban area. Important: You must SAVE the file before processing it. Step 13. Step 14. To build these shapes into the graphics file, click the Autoshape Builder icon within the Text Editor dialog box. This will automatically draw the shapes into your design file on level 63. Close the Text Editor dialog box. When prompted to Save Changes, click Yes. Close the automated superelevation dialog box. When prompted to Save Superelevation settings, click Yes. Step 15. Review the Superelevation shapes created in the design file. GEOPAK 2001MR LAB 11: Superelevation 11-23
24 GEOPAK 11.5 Automated Superelevation Section 5 Step 1. Step 2. Click the Calculate Superelevation button from the Road Project: prj workflow dialog box. Create a new run called RampA and click OK. Once the Automated Superelevation dialog box has been invoked, the dialog box on the right will be displayed. Fill out the upper portion of the dialog box as shown. Step 3. Step 4. The profile from which the shapes should be computed should be set to RAMPA for both the Left and Right roadway tabs. The Tie option should be set to offset and the offset value should be set to 0.0 to force the PGL (Profile Grade Line) to run along chain RAMPA. NOTE: Quick Entry cannot be used this time since the lane configuration for RampA is not the same on both sides of the baseline VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
25 GEOPAK Step 5. Since Quick Entry cannot be used for the lane configuration, we ll fill out the lane offsets and slopes manually. Fill out the %Slope and Offset fields as shown and then add them to the list box by pressing the Add icon. The dialog box should appear as shown: Step 6. Step 7. Provide an Input Filename (rampa_shapes.inp) to store the computed transitions for this station range. Click the Generate Superelevation Transitions button to initiate the calculation of the transitions for the Left Roadway. GEOPAK 2001MR LAB 11: Superelevation 11-25
26 GEOPAK Step 8. Review the computations within the Text Editor dialog box. Step 9. Step 10. Step 11. To build these shapes into the graphics file, click the Autoshape Builder icon within the Text Editor dialog box. This will automatically draw the shapes into your design file on level 63. Close the Text Editor dialog box as well as the automated superelevation dialog box. When prompted to Save Superelevation settings, click Yes. Review the Superelevation shapes created in the design file VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
27 GEOPAK 11.6 Building Manual Shapes NOTE: There are times when the Autoshape Builder cannot be used. These normally occur in areas of lane transition where standard offsets are not sufficient enough to define the shape. Step 1. Step 2. From the MicroStation menu bar select Utilities > Saved Views, access the Saved View TRANS1. Click the Superelevation Shapes button from the Road Project: prj workflow dialog box. NOTE: When building manual shapes, it s desirable to only display the graphics that are absolutely required to define edges of the shapes. Also note that there may be times you will need to add graphical elements to the design file (such as lane lines) in order to be able to build a shape correctly. Step 3. Step 4. Turn off the Reference File Levels 4,7 and 31. Also, turn off the patterns (Level 50) in the active design file. Create the first slope filler line by filling out the dialog box as shown and pressing Create. Style = 0 and Weight = 2 GEOPAK 2001MR LAB 11: Superelevation 11-27
28 GEOPAK Step 5. Create the second slope filler line by filling out the dialog box as shown and pressing Create. Step 6. Now press the DRAW button and issue a DP inside the lane as shown in the image below. X Step 7. Repeat Steps 4-6, this time issuing a DP for the other inside lane as shown in the image below. X VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
29 GEOPAK Step 8. Change the Class, Color and Fill in the dialog box as shown below. Step 9. Repeat Steps 4-6 twice more to create the shapes for the two outside lanes. GEOPAK 2001MR LAB 11: Superelevation 11-29
30 GEOPAK 11.7 Draw Superelevation Diagram In the next steps we ll draw a Superelevation Diagram on the Profile Cell using a custom 3PC application. We will run this in two passes. One from Station R 1 to R 1 and one from Station R 1 to R 1. Step 1. Step 2. Step 3. Open the MicroStation file c:\data\geo\vdot\road1\d17682prof.dgn Open Design and Computation Manager. Double click item Road Design > Special Applications > Super Diagram. Populate the dialog box as show below. Click OK R1 to R 1 NOTE: Use the Identify Cell button to populate the upper left portion of the dialog box. Shapes Input File = ml3_shapes.inp Proposed Design File = d17682des.dgn Step 4. Click OK when the prompt below appears VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
31 GEOPAK Step 5. Step 6. Double click item Road Design > Special Applications > Super Diagram again. Populate the dialog box as show below. Click OK R1 to R 1 Step 7. NOTE: Use the Identify Cell button to populate the upper left portion of the dialog box. Shapes Input File = ml4_shapes.inp Proposed Design File = d17682des.dgn Click OK when the prompt below appears. GEOPAK 2001MR LAB 11: Superelevation 11-31
32 GEOPAK 11.8 Update the Project Manager We are completing the Plan View category of the Working Alignment Definition in Project Manager. Step 1. Step 2. From the Workflow dialog box of Project Manager, click the Define button. Highlight the Plan View > Shapes option and populate the Shapes Design file as shown below: Step 3. Step 4. Click the OK button to save the updates and close the dialog box. Exit MicroStation VDOT Road I Training GEOPAK 2001MR
The ODOT_XSLabeling.mvba application is used to draw basic labels on cross sections extracted from a Roadway Designer DTM file.
 Application Name: Current version: Required MicroStation Version: Required GEOPAK Version: ODOT_XSLabeling.mvba v11.07.15 XM or V8i XM or V8i The ODOT_XSLabeling.mvba application is used to draw basic
Application Name: Current version: Required MicroStation Version: Required GEOPAK Version: ODOT_XSLabeling.mvba v11.07.15 XM or V8i XM or V8i The ODOT_XSLabeling.mvba application is used to draw basic
Validation of Exported Field Data in GEOPAK Drainage (Survey to Drainage)
 Validation of Exported Field Data in GEOPAK Drainage (Survey to Drainage) 1.1 Overview The Export to GEOPAK Drainage tool can be utilized to leverage data collected by field surveys (i.e., pipes and structures)
Validation of Exported Field Data in GEOPAK Drainage (Survey to Drainage) 1.1 Overview The Export to GEOPAK Drainage tool can be utilized to leverage data collected by field surveys (i.e., pipes and structures)
NCDOT Civil Geometry for GEOPAK Users
 2018 NCDOT Civil Geometry for GEOPAK Users Oak Thammavong NCDOT Roadway Design Unit 7/31/2018 This page left intentionally blank Copyright 2018 NCDOT DO NOT DISTRIBUTE Printing for student use is permitted
2018 NCDOT Civil Geometry for GEOPAK Users Oak Thammavong NCDOT Roadway Design Unit 7/31/2018 This page left intentionally blank Copyright 2018 NCDOT DO NOT DISTRIBUTE Printing for student use is permitted
AUTODESK AUTOCAD CIVIL 2009 AND AUTOCAD CIVIL 3D Rule-Based Road Design using AutoCAD Civil and AutoCAD Civil 3D
 AUTODESK AUTOCAD CIVIL 2009 AND AUTOCAD CIVIL 3D 2009 Rule-Based Road Design using AutoCAD Civil and AutoCAD Civil 3D Contents Introduction... 3 Design Criteria Files... 3 Alignment Geometry... 4 Applying
AUTODESK AUTOCAD CIVIL 2009 AND AUTOCAD CIVIL 3D 2009 Rule-Based Road Design using AutoCAD Civil and AutoCAD Civil 3D Contents Introduction... 3 Design Criteria Files... 3 Alignment Geometry... 4 Applying
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event
 Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event F-2P - QuickStart for Roadway Modeling in OpenRoads Technology Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event F-2P - QuickStart for Roadway Modeling in OpenRoads Technology Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com
Roadway Alignments and Profiles
 NOTES Module 15 Roadway Alignments and Profiles In this module, you learn how to create horizontal alignments, surface profiles, layout (design) profiles, and profile views in AutoCAD Civil 3D. This module
NOTES Module 15 Roadway Alignments and Profiles In this module, you learn how to create horizontal alignments, surface profiles, layout (design) profiles, and profile views in AutoCAD Civil 3D. This module
Bentley Civil Guide. SELECT series 3. Setting Up Superelevation SEP Files. Written By: Lou Barrett, BSW-Development, Civil Design
 Bentley Civil Guide SELECT series 3 Setting Up Superelevation SEP Files Written By: Lou Barrett, BSW-Development, Civil Design Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com
Bentley Civil Guide SELECT series 3 Setting Up Superelevation SEP Files Written By: Lou Barrett, BSW-Development, Civil Design Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com
Appendix H Drainage Ditch Design - Lab TABLE OF CONTENTS APPENDIX H... 2
 Appendix H Drainage Ditch Design - Lab TABLE OF CONTENTS APPENDIX H... 2 H.1 Ditch Design... 2 H.1.1 Introduction... 2 H.1.2 Link/Ditch Configuration... 2 H.2 Lab 19: Ditch Design... 3 H.2.1 Introduction...
Appendix H Drainage Ditch Design - Lab TABLE OF CONTENTS APPENDIX H... 2 H.1 Ditch Design... 2 H.1.1 Introduction... 2 H.1.2 Link/Ditch Configuration... 2 H.2 Lab 19: Ditch Design... 3 H.2.1 Introduction...
Validation of Exported Field Data in GEOPAK Drainage (Survey to Drainage)
 Validation of Exported Field Data in GEOPAK Drainage (Survey to Drainage) 1.1 Overview The Export to GEOPAK Drainage tool can be utilized to leverage data collected by field surveys (i.e., pipes and structures)
Validation of Exported Field Data in GEOPAK Drainage (Survey to Drainage) 1.1 Overview The Export to GEOPAK Drainage tool can be utilized to leverage data collected by field surveys (i.e., pipes and structures)
Drainage Tools Overview Create Refined Watershed TIN CHAPTER 15
 CHAPTER 15 Drainage Tools 15.1 Overview GEOPAK supports a myriad of tools to analyze and evaluate drainage patterns of a GEOPAK Digital Terrain Model. Tools for delineating watersheds, flow paths, flow
CHAPTER 15 Drainage Tools 15.1 Overview GEOPAK supports a myriad of tools to analyze and evaluate drainage patterns of a GEOPAK Digital Terrain Model. Tools for delineating watersheds, flow paths, flow
VDOT Creating Plats with GEOPAK 2004 Edition (Version 8.8)
 VDOT Creating Plats with GEOPAK 2004 Edition (Version 8.8) TRN013000-1/0001 Copyright Information Trademarks Patents Copyrights AccuDraw, Bentley, the B Bentley logo, MDL, MicroStation and SmartLine are
VDOT Creating Plats with GEOPAK 2004 Edition (Version 8.8) TRN013000-1/0001 Copyright Information Trademarks Patents Copyrights AccuDraw, Bentley, the B Bentley logo, MDL, MicroStation and SmartLine are
Geometric Layout for Roadway Design with CAiCE Visual Roads
 December 2-5, 2003 MGM Grand Hotel Las Vegas Geometric Layout for Roadway Design with CAiCE Visual Roads Mathews Mathai CV32-3 This course describes and demonstrates various tools for defining horizontal
December 2-5, 2003 MGM Grand Hotel Las Vegas Geometric Layout for Roadway Design with CAiCE Visual Roads Mathews Mathai CV32-3 This course describes and demonstrates various tools for defining horizontal
Section 7 - Introducing Roadway Modeling
 Introducing Roadway Modeling Section 7 - Introducing Roadway Modeling Section Goals: Understand the Principles of InRoads Roadway Modeling Understand how to load Typical Section Libraries Understand how
Introducing Roadway Modeling Section 7 - Introducing Roadway Modeling Section Goals: Understand the Principles of InRoads Roadway Modeling Understand how to load Typical Section Libraries Understand how
THE REFERENCE FILE. Cadd Support Office May Included in this issue:
 THE REFERENCE FILE May 2018 Included in this issue: Page 2 Page 2 Page 2-3 Page 4-7 Page 8-10 Page 11 New Title Sheet Cells New Signal Cells Cross Section Sheets Guardrail Mash Standards RDM (AASHTO 2011)
THE REFERENCE FILE May 2018 Included in this issue: Page 2 Page 2 Page 2-3 Page 4-7 Page 8-10 Page 11 New Title Sheet Cells New Signal Cells Cross Section Sheets Guardrail Mash Standards RDM (AASHTO 2011)
Chapter 1: Introducing Roadway Modeling
 Introducing Roadway Modeling Chapter 1: Introducing Roadway Modeling Chapter Overview The chapter addresses the following topics: How Roadway Modeling Works in InRoads Opening and Exploring Typical Section
Introducing Roadway Modeling Chapter 1: Introducing Roadway Modeling Chapter Overview The chapter addresses the following topics: How Roadway Modeling Works in InRoads Opening and Exploring Typical Section
Bentley Civil Workshop
 Bentley Civil Workshop 2013 Bentley LEARNing Conference BCR3WK1 OpenRoads Technology Workshop: Horizontal Geometry Team Leader: Lou Barrett, Product Manager (BSW Civil Design) Team Members: Mike Wilson,
Bentley Civil Workshop 2013 Bentley LEARNing Conference BCR3WK1 OpenRoads Technology Workshop: Horizontal Geometry Team Leader: Lou Barrett, Product Manager (BSW Civil Design) Team Members: Mike Wilson,
CASE 1 TWO LANE TO FOUR LANE DIVIDED TRANSITION GEO-610-C NOT TO SCALE GEOMETRIC DESIGN GUIDE FOR MATCH LINE LINE MATCH. 2 (0.6m) shoulder transition
 CASE 1 2 (0.6m) Joint Line See sheet #5 for description of variables 4 (1.2m) Transition taper is tangent to Edge of Pavement curve at this point. 1:25 Paved shoulder transition 16 (4.m) Median width 16
CASE 1 2 (0.6m) Joint Line See sheet #5 for description of variables 4 (1.2m) Transition taper is tangent to Edge of Pavement curve at this point. 1:25 Paved shoulder transition 16 (4.m) Median width 16
Alignments CHAPTER INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES
 CHAPTER 5 Alignments INTRODUCTION This and the next four chapters focus on roadway design and its documentation. This chapter concentrates on roadway plan design. The next three chapters focus on the roadway
CHAPTER 5 Alignments INTRODUCTION This and the next four chapters focus on roadway design and its documentation. This chapter concentrates on roadway plan design. The next three chapters focus on the roadway
Bentley Civil Workshop
 Bentley Civil Workshop 2013 MACC Conference Day 2 OpenRoads Technology Workshop: Horizontal and Vertical Geometry Team Leader: Bob Rolle Team Members: Ray Filipiak, Dave Hoerner Bentley Systems, Incorporated
Bentley Civil Workshop 2013 MACC Conference Day 2 OpenRoads Technology Workshop: Horizontal and Vertical Geometry Team Leader: Bob Rolle Team Members: Ray Filipiak, Dave Hoerner Bentley Systems, Incorporated
Producing Project Deliverables: Creating a Plan Set
 Practice Workbook This workbook is designed for use in Live instructor-led training and for OnDemand selfstudy. The explanations and demonstrations are provided by the instructor in the classroom, or in
Practice Workbook This workbook is designed for use in Live instructor-led training and for OnDemand selfstudy. The explanations and demonstrations are provided by the instructor in the classroom, or in
Bentleyuser.dk Årsmøde 2012 Nordic Civil 2012
 Bentleyuser.dk Årsmøde 2012 Nordic Civil 2012 5.-7. November 2012, Munkebjerg Hotel, Vejle Workshop X13 Advanced Geometrical Layout for Compound and Reversed Curves Team Leader: Richard Bradshaw Bentley
Bentleyuser.dk Årsmøde 2012 Nordic Civil 2012 5.-7. November 2012, Munkebjerg Hotel, Vejle Workshop X13 Advanced Geometrical Layout for Compound and Reversed Curves Team Leader: Richard Bradshaw Bentley
Intersection Design with Autodesk Civil 3D
 12/1/2005-8:00 am - 11:30 am Room:Osprey 1 [Lab] (Swan) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida Intersection Design with Autodesk Civil 3D Daniel Philbrick - Autodesk and James Wedding
12/1/2005-8:00 am - 11:30 am Room:Osprey 1 [Lab] (Swan) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida Intersection Design with Autodesk Civil 3D Daniel Philbrick - Autodesk and James Wedding
Bentley Civil Workshop
 Bentley Civil Workshop 2015 IBUG Spring Conference Templates 101 Team Leader: Chuck Lawson, PE Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 This page left intentionally blank. Table
Bentley Civil Workshop 2015 IBUG Spring Conference Templates 101 Team Leader: Chuck Lawson, PE Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 This page left intentionally blank. Table
Interactive Highway Safety Design Model (IHSDM) Workshop Nevada DOT Las Vegas, NV February 13, 2014
 Interactive Highway Safety Design Model (IHSDM) Workshop Nevada DOT Las Vegas, NV February 13, 2014 Overview Hands-on Exercises: IHSDM Crash Prediction Module (CPM) The Crash Prediction Module estimates
Interactive Highway Safety Design Model (IHSDM) Workshop Nevada DOT Las Vegas, NV February 13, 2014 Overview Hands-on Exercises: IHSDM Crash Prediction Module (CPM) The Crash Prediction Module estimates
Trimble s RoadLink Utility Tutorials
 Trimble s RoadLink utility is an interface between third-party road definitions and Trimble survey devices. It lets you import or key in road definitions, view them graphically, edit them if required,
Trimble s RoadLink utility is an interface between third-party road definitions and Trimble survey devices. It lets you import or key in road definitions, view them graphically, edit them if required,
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Spring Training Event
 Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Spring Training Event 431 - Approach and Driveway Modeling in OpenRoads Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Spring Training Event 431 - Approach and Driveway Modeling in OpenRoads Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook
Pipe Networks CHAPTER INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES
 CHAPTER 11 Pipe Networks INTRODUCTION Pipe networks are integral to a site-design solution. The piping system s complexity can vary from simple culverts to several storm and sanitary networks that service
CHAPTER 11 Pipe Networks INTRODUCTION Pipe networks are integral to a site-design solution. The piping system s complexity can vary from simple culverts to several storm and sanitary networks that service
Grading and Volumes CHAPTER INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES
 CHAPTER 10 Grading and Volumes INTRODUCTION AutoCAD Civil 3D uses surface breaklines, cogo points, contours, feature lines, and grading objects to create a surface design. There are numerous ways to grade
CHAPTER 10 Grading and Volumes INTRODUCTION AutoCAD Civil 3D uses surface breaklines, cogo points, contours, feature lines, and grading objects to create a surface design. There are numerous ways to grade
That CAD Girl. J ennifer dib ona. Carlson 2008 Creating Roadway Templates. Website:
 That CAD Girl J ennifer dib ona Website: www.thatcadgirl.com Email: thatcadgirl@aol.com Phone: (919) 417-8351 Fax: (919) 573-0351 Carlson 2008 Creating Roadway Templates Defining roadway templates can
That CAD Girl J ennifer dib ona Website: www.thatcadgirl.com Email: thatcadgirl@aol.com Phone: (919) 417-8351 Fax: (919) 573-0351 Carlson 2008 Creating Roadway Templates Defining roadway templates can
VDOT GEOPAK Drainage Training Manual
 VDOT GEOPAK Drainage Training Manual Training Manual 2004 Edition TRN007630-1/0002 Trademarks AccuDraw, Bentley, the B Bentley logo, MDL, MicroStation and SmartLine are registered trademarks; PopSet and
VDOT GEOPAK Drainage Training Manual Training Manual 2004 Edition TRN007630-1/0002 Trademarks AccuDraw, Bentley, the B Bentley logo, MDL, MicroStation and SmartLine are registered trademarks; PopSet and
Civil 3-D PROFILE CREATION
 Civil 3-D PROFILE CREATION 1 Alignment Overview: As in previous CAD versions, an alignment is a line that describes where you intend the centerline of your planned work to be. That s all. But, in Civil
Civil 3-D PROFILE CREATION 1 Alignment Overview: As in previous CAD versions, an alignment is a line that describes where you intend the centerline of your planned work to be. That s all. But, in Civil
VDOT Survey Training GEOPAK 2004 Edition Training Manual
 VDOT Survey Training GEOPAK 2004 Edition Training Manual TRN008650-1/0001 Trademarks AccuDraw, Bentley, the B Bentley logo, MDL, MicroStation, Micro Station/J, MicroStation MasterPiece, MicroStation Modeler,
VDOT Survey Training GEOPAK 2004 Edition Training Manual TRN008650-1/0001 Trademarks AccuDraw, Bentley, the B Bentley logo, MDL, MicroStation, Micro Station/J, MicroStation MasterPiece, MicroStation Modeler,
Practice Workbook. Using the Model - Preparing for Plan Production in OpenRoads. SELECTseries 4 ( ) or newer
 Practice Workbook This workbook is designed for use in Live instructor-led training and for OnDemand self study. The explanations and demonstrations are provided by the instructor in the classroom, or
Practice Workbook This workbook is designed for use in Live instructor-led training and for OnDemand self study. The explanations and demonstrations are provided by the instructor in the classroom, or
Civil 3D Introduction
 Civil 3D Introduction Points Overview Points are data collected by surveyors which represent existing site conditions (elevations, boundaries, utilities, etc.). Each point is numbered (or named) and has
Civil 3D Introduction Points Overview Points are data collected by surveyors which represent existing site conditions (elevations, boundaries, utilities, etc.). Each point is numbered (or named) and has
VDOT Advanced GEOPAK Survey 2004 Edition (Version 8.8)
 VDOT Advanced GEOPAK Survey 2004 Edition (Version 8.8) TRN010900-1/0002 Copyright Information Trademarks Patents AccuDraw, Bentley, the B Bentley logo, MDL, MicroStation and SmartLine are registered trademarks;
VDOT Advanced GEOPAK Survey 2004 Edition (Version 8.8) TRN010900-1/0002 Copyright Information Trademarks Patents AccuDraw, Bentley, the B Bentley logo, MDL, MicroStation and SmartLine are registered trademarks;
InRoads File Types. Below is a list of the primary file types used for InRoads in the road design process.
 Section 6 InRoads Basic File Types Retrieving InRoads Base Files Internal Naming Convention Alignment Styles and Surface Styles Alignment Point Abbreviations Feature Naming Conventions Project Defaults
Section 6 InRoads Basic File Types Retrieving InRoads Base Files Internal Naming Convention Alignment Styles and Surface Styles Alignment Point Abbreviations Feature Naming Conventions Project Defaults
Overview September 7, 2017
 Overview September 7, 2017 Purpose The purpose of this presentation is to provide an overview of the changes to the required deliverables and workflow for developing plans and models for Illinois DOT projects
Overview September 7, 2017 Purpose The purpose of this presentation is to provide an overview of the changes to the required deliverables and workflow for developing plans and models for Illinois DOT projects
Lesson 14: Design Reports
 14 Lesson 14: Design Reports WELCOME! This lesson is about producing reports from the design data generated in the tutorial. Now that you have designed the commercial site, it is possible to extract information
14 Lesson 14: Design Reports WELCOME! This lesson is about producing reports from the design data generated in the tutorial. Now that you have designed the commercial site, it is possible to extract information
JCE 4600 Fundamentals of Traffic Engineering. Horizontal and Vertical Curves
 JCE 4600 Fundamentals of Traffic Engineering Horizontal and Vertical Curves Agenda Horizontal Curves Vertical Curves Passing Sight Distance 1 Roadway Design Motivations Vehicle performance Acceleration
JCE 4600 Fundamentals of Traffic Engineering Horizontal and Vertical Curves Agenda Horizontal Curves Vertical Curves Passing Sight Distance 1 Roadway Design Motivations Vehicle performance Acceleration
Tec Sheet NoiseMod Reverse.3pc
 What is NoiseModReverse.3pc? NoiseModReverse.3pc HELP DOCUMENTATION NoiseModReverse.3pc is a Geopak application that reads a FHWA Stamina noise model ASCII file and draws the roadways, barriers, and receivers
What is NoiseModReverse.3pc? NoiseModReverse.3pc HELP DOCUMENTATION NoiseModReverse.3pc is a Geopak application that reads a FHWA Stamina noise model ASCII file and draws the roadways, barriers, and receivers
Management Reports Centre. User Guide. Emmanuel Amekuedi
 Management Reports Centre User Guide Emmanuel Amekuedi Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Overview... 3 Key features... 4 Authentication methods... 4 System requirements... 5 Deployment options... 5 Getting
Management Reports Centre User Guide Emmanuel Amekuedi Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Overview... 3 Key features... 4 Authentication methods... 4 System requirements... 5 Deployment options... 5 Getting
AUTOCAD CIVIL 2009 AND AUTOCAD CIVIL 3D Road Rehabilitation and Reconstruction with AutoCAD Civil and AutoCAD. Civil 3D
 AUTOCAD CIVIL 2009 AND AUTOCAD CIVIL 3D 2009 Road Rehabilitation and Reconstruction with AutoCAD Civil and AutoCAD Civil 3D 1 Contents Introduction... 3 Introduction to Corridor Targets... 3 Surface Targets...
AUTOCAD CIVIL 2009 AND AUTOCAD CIVIL 3D 2009 Road Rehabilitation and Reconstruction with AutoCAD Civil and AutoCAD Civil 3D 1 Contents Introduction... 3 Introduction to Corridor Targets... 3 Surface Targets...
Bentleyuser.dk Årsmøde 2012 Nordic Civil Bentley Civil Workshop
 Bentleyuser.dk Årsmøde 2012 Nordic Civil 2012 Bentley Civil Workshop X09 Power Railtrack Presented by: Richard Bradshaw, BSW Development, Civil Design This page left intentionally blank. Workshop: - X09
Bentleyuser.dk Årsmøde 2012 Nordic Civil 2012 Bentley Civil Workshop X09 Power Railtrack Presented by: Richard Bradshaw, BSW Development, Civil Design This page left intentionally blank. Workshop: - X09
TPC Desktop Series. Alignments Learning Guide 1/18
 TPC Desktop Series Alignments Learning Guide 1/18 NOTICE The information in this document is subject to change without notice. TRAVERSE PC. Inc. assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear
TPC Desktop Series Alignments Learning Guide 1/18 NOTICE The information in this document is subject to change without notice. TRAVERSE PC. Inc. assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear
AASHTOWare BrR - SIMPLE SPAN PRESTRESSED I BEAM EXAMPLE - BR 76015
 AASHTOWare BrR - SIMPLE SPAN PRESTRESSED I BEAM EXAMPLE - BR 76015 M N D O T B R I D G E S T A T E A I D Page 1 PS1 - Simple Span Prestressed I Beam Example (BrR 6.7.1) 1. From the Bridge Explorer create
AASHTOWare BrR - SIMPLE SPAN PRESTRESSED I BEAM EXAMPLE - BR 76015 M N D O T B R I D G E S T A T E A I D Page 1 PS1 - Simple Span Prestressed I Beam Example (BrR 6.7.1) 1. From the Bridge Explorer create
Select the options to assess for this credit. Only one option can be selected if the rating system is set to Healthcare.
 Surrounding Density and Diverse Uses LT Surrounding Density and Diverse Uses Select options to assess: Select the options to assess for this credit. Only one option can be selected if the rating system
Surrounding Density and Diverse Uses LT Surrounding Density and Diverse Uses Select options to assess: Select the options to assess for this credit. Only one option can be selected if the rating system
Bentley ConceptStation Workshop 2017 FLUG Spring Training Event
 Bentley ConceptStation Workshop 2017 FLUG Spring Training Event 430 - QuickStart using OpenRoads ConceptStation Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice
Bentley ConceptStation Workshop 2017 FLUG Spring Training Event 430 - QuickStart using OpenRoads ConceptStation Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice
Draping Overview Drape Vertices CHAPTER 13. Drape elements onto a triangulated model. Feature / Function Tools
 CHAPTER 13 Draping 13.1 Overview Feature / Function Tools Drape elements onto a triangulated model. DTM Menu Bar Drape > Vertices, Vectors GEOPAK provides tools to drape MicroStation elements onto a triangulated
CHAPTER 13 Draping 13.1 Overview Feature / Function Tools Drape elements onto a triangulated model. DTM Menu Bar Drape > Vertices, Vectors GEOPAK provides tools to drape MicroStation elements onto a triangulated
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Spring Training Event
 Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Spring Training Event 437 - QuickStart for Terrain & Geometry Using OpenRoads Technology Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Spring Training Event 437 - QuickStart for Terrain & Geometry Using OpenRoads Technology Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com
3D Model Submittal Preparation Power GEOPAK SS2
 3D Model Submittal Preparation Power GEOPAK SS2 General Information This document is intended to provide guidance in preparing the proposed 3D model data from Roadway Designer for submittal and is only
3D Model Submittal Preparation Power GEOPAK SS2 General Information This document is intended to provide guidance in preparing the proposed 3D model data from Roadway Designer for submittal and is only
Horizontal Alignment
 AMRC 2012 MODULE 8 Horizontal Alignment CONTENTS Overview... 8-1 Objectives... 8-1 Procedures... 8-1 8.1 Design Considerations and Circular Curves... 8-3 8.2 Superelevation and Transitional Spiral... 8-5
AMRC 2012 MODULE 8 Horizontal Alignment CONTENTS Overview... 8-1 Objectives... 8-1 Procedures... 8-1 8.1 Design Considerations and Circular Curves... 8-3 8.2 Superelevation and Transitional Spiral... 8-5
Piping Design. Site Map Preface Getting Started Basic Tasks Advanced Tasks Customizing Workbench Description Index
 Piping Design Site Map Preface Getting Started Basic Tasks Advanced Tasks Customizing Workbench Description Index Dassault Systèmes 1994-2001. All rights reserved. Site Map Piping Design member member
Piping Design Site Map Preface Getting Started Basic Tasks Advanced Tasks Customizing Workbench Description Index Dassault Systèmes 1994-2001. All rights reserved. Site Map Piping Design member member
SURVRD for Existing Feature Models file in FDOTSS4 OpenRoads
 SURVRD for Existing Feature Models file in FDOTSS4 OpenRoads Production Support Office - CADD Chris Thorp What is a SURVRD file? SURVRD Survey Development Model for 3D Design It is a critical file for
SURVRD for Existing Feature Models file in FDOTSS4 OpenRoads Production Support Office - CADD Chris Thorp What is a SURVRD file? SURVRD Survey Development Model for 3D Design It is a critical file for
Bentley Civil Workshop
 Bentley Civil Workshop 2015 Spring NCLUG Conference Workshop 32B Using Point Clouds in Civil Workflows Team Leader: Bob Rolle Team Members: Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341
Bentley Civil Workshop 2015 Spring NCLUG Conference Workshop 32B Using Point Clouds in Civil Workflows Team Leader: Bob Rolle Team Members: Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341
NYSAPLS 50 th Anniversary Surveyor's Conference and Exhibition
 Field to Finish - 3D Modeling and DTM (InRoads Survey and PowerSurvey Basics) Presenter: Gerald B. Danzy, Software/Product Consultant Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com
Field to Finish - 3D Modeling and DTM (InRoads Survey and PowerSurvey Basics) Presenter: Gerald B. Danzy, Software/Product Consultant Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com
Section 3 Laying Out Structures
 Mastering Storm&Sanitary Section 3 Laying Out Structures Section Goals: How to Set Drainage Options When to Set Structure Settings Using Preference Sets Laying Out Ditch Inlets Laying Out a connecting
Mastering Storm&Sanitary Section 3 Laying Out Structures Section Goals: How to Set Drainage Options When to Set Structure Settings Using Preference Sets Laying Out Ditch Inlets Laying Out a connecting
Explore some of the new functionality in ArcMap 10
 Explore some of the new functionality in ArcMap 10 Scenario In this exercise, imagine you are a GIS analyst working for Old Dominion University. Construction will begin shortly on renovation of the new
Explore some of the new functionality in ArcMap 10 Scenario In this exercise, imagine you are a GIS analyst working for Old Dominion University. Construction will begin shortly on renovation of the new
Terramodel Training Guide. Designing a Roadway
 Terramodel Training Guide Version 8 Revision A March 2002 Corporate Office Trimble Navigation Limited Engineering and Construction Division 5475 Kellenburger Road Dayton, Ohio 45424-1099 U.S.A. Copyright
Terramodel Training Guide Version 8 Revision A March 2002 Corporate Office Trimble Navigation Limited Engineering and Construction Division 5475 Kellenburger Road Dayton, Ohio 45424-1099 U.S.A. Copyright
Working with Plan Production ObjectsChapter1:
 Chapter 1 Working with Plan Production ObjectsChapter1: The lessons in this chapter guide you through the processes of creating and working with plan production objects. Plan production objects include
Chapter 1 Working with Plan Production ObjectsChapter1: The lessons in this chapter guide you through the processes of creating and working with plan production objects. Plan production objects include
Bentleyuser.dk Årsmøde 2012 Nordic Civil 2012
 Bentleyuser.dk Årsmøde 2012 Nordic Civil 2012 5.-7. November 2012, Munkebjerg Hotel, Vejle Workshop X7 Civil Design Review: 3D Modeling and Team Leader: Joe Waxmonsky, PE Bentley Systems, Incorporated
Bentleyuser.dk Årsmøde 2012 Nordic Civil 2012 5.-7. November 2012, Munkebjerg Hotel, Vejle Workshop X7 Civil Design Review: 3D Modeling and Team Leader: Joe Waxmonsky, PE Bentley Systems, Incorporated
Test Profiles for Digital Terrain Models
 Test Profiles for Digital Terrain Models 1.1 Overview Jointly developed by the Photogrammetics and GEOPAK Units within the Minnesota Department of Transportation, this procedure details the standard procedure
Test Profiles for Digital Terrain Models 1.1 Overview Jointly developed by the Photogrammetics and GEOPAK Units within the Minnesota Department of Transportation, this procedure details the standard procedure
Bentley Civil Workshop
 Bentley Civil Workshop 2015 IBUG Spring Conference Templates 202 Team Leader: Chuck Lawson, PE Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 This page left intentionally blank. Table
Bentley Civil Workshop 2015 IBUG Spring Conference Templates 202 Team Leader: Chuck Lawson, PE Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 This page left intentionally blank. Table
Mn/DOT MnCMAT Crash Analysis Application Help
 Mn/DOT MnCMAT Crash Analysis Application Contents Login... 5 User Login Dialog... 5 Login... 5 Request Access Dialog... 5 Forgotten Password Dialog... 6 Create/Open Project... 7 Create/Open Project Dialog...
Mn/DOT MnCMAT Crash Analysis Application Contents Login... 5 User Login Dialog... 5 Login... 5 Request Access Dialog... 5 Forgotten Password Dialog... 6 Create/Open Project... 7 Create/Open Project Dialog...
Let s see the use of each option available under create feature line window:
 FEATURE LINE: Feature line is a kind of a line or an object which we can use as a base line or foot print of grading object. In civil 3d if you want use grading tool you have some kind of base or foot
FEATURE LINE: Feature line is a kind of a line or an object which we can use as a base line or foot print of grading object. In civil 3d if you want use grading tool you have some kind of base or foot
RebarCAD Usage Hints and Tips
 RebarCAD Usage Hints and Tips Hints & Tips the Change Bar Style Command A drawing can have a combination of bar styles and bars can be changed from one style to another using the Change Bar Style command.
RebarCAD Usage Hints and Tips Hints & Tips the Change Bar Style Command A drawing can have a combination of bar styles and bars can be changed from one style to another using the Change Bar Style command.
WYOMING DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION
 PAGE 1 OF 5 WYOMING DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ROAD DESIGN MEMORANDUM #02 DATE OF ISSUE: December 01, 2004 Approved by: Paul P. Bercich, P.E. Highway Development Engineer Issued by: Engineering Services,
PAGE 1 OF 5 WYOMING DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ROAD DESIGN MEMORANDUM #02 DATE OF ISSUE: December 01, 2004 Approved by: Paul P. Bercich, P.E. Highway Development Engineer Issued by: Engineering Services,
OpenRoads Creating Subsurface Utility Models
 OpenRoads Creating Subsurface Utility Models Existing and Proposed Utilities Presenter: Robert Garrett, PE Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Before you Begin:...
OpenRoads Creating Subsurface Utility Models Existing and Proposed Utilities Presenter: Robert Garrett, PE Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Before you Begin:...
Quick Crash Scene Tutorial
 Quick Crash Scene Tutorial With Crash Zone or Crime Zone, even new users can create a quick crash scene diagram in less than 10 minutes! In this tutorial we ll show how to use Crash Zone s unique features
Quick Crash Scene Tutorial With Crash Zone or Crime Zone, even new users can create a quick crash scene diagram in less than 10 minutes! In this tutorial we ll show how to use Crash Zone s unique features
AEMLog Users Guide. Version 1.01
 AEMLog Users Guide Version 1.01 INTRODUCTION...2 DOCUMENTATION...2 INSTALLING AEMLOG...4 AEMLOG QUICK REFERENCE...5 THE MAIN GRAPH SCREEN...5 MENU COMMANDS...6 File Menu...6 Graph Menu...7 Analysis Menu...8
AEMLog Users Guide Version 1.01 INTRODUCTION...2 DOCUMENTATION...2 INSTALLING AEMLOG...4 AEMLOG QUICK REFERENCE...5 THE MAIN GRAPH SCREEN...5 MENU COMMANDS...6 File Menu...6 Graph Menu...7 Analysis Menu...8
Practice Workbook. Pad and Parking Lot Modeling
 Practice Workbook This workbook is designed for use in Live instructor-led training and for OnDemand selfstudy. The explanations and demonstrations are provided by the instructor in the classroom, or in
Practice Workbook This workbook is designed for use in Live instructor-led training and for OnDemand selfstudy. The explanations and demonstrations are provided by the instructor in the classroom, or in
DV20420 AutoCAD Civil 3D Visualization in 3ds Max, Infraworks or Navisworks
 DV20420 AutoCAD Civil 3D Visualization in 3ds Max, Infraworks or Navisworks Paul c.kirkendall MasterGraphics, Inc. Learning Objectives After this class, attendees will be able to import Civil 3D project
DV20420 AutoCAD Civil 3D Visualization in 3ds Max, Infraworks or Navisworks Paul c.kirkendall MasterGraphics, Inc. Learning Objectives After this class, attendees will be able to import Civil 3D project
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event
 Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event T-1E - Mastering the Corridor Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook This workbook is
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event T-1E - Mastering the Corridor Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook This workbook is
AED Design Requirements: Superelevation Road Design
 US Army Corps of Engineers Afghanistan Engineer District AED Design Requirements: Various Locations, Afghanistan MARCH 2009 TABLE OF CONTENTS AED DESIGN REQUIREMENTS FOR SUPERELEVATION ROAD DESIGN VARIOUS
US Army Corps of Engineers Afghanistan Engineer District AED Design Requirements: Various Locations, Afghanistan MARCH 2009 TABLE OF CONTENTS AED DESIGN REQUIREMENTS FOR SUPERELEVATION ROAD DESIGN VARIOUS
FDOT Traffic Plans Signing & Pavement Markings
 State of Florida Department of Transportation FDOT Traffic Plans Signing & Pavement Markings CE-11-0117 User Training Manual February 20, 2015 ENGINEERING / CADD SYSTEMS OFFICE TALLAHASSEE, FLORIDA http://www.dot.state.fl.us/ecso/
State of Florida Department of Transportation FDOT Traffic Plans Signing & Pavement Markings CE-11-0117 User Training Manual February 20, 2015 ENGINEERING / CADD SYSTEMS OFFICE TALLAHASSEE, FLORIDA http://www.dot.state.fl.us/ecso/
Practice Workbook. QuickStart using Subsurface Utility Engineering
 Practice Workbook This workbook is designed for use in Live instructor-led training and for OnDemand selfstudy. The explanations and demonstrations are provided by the instructor in the classroom, or in
Practice Workbook This workbook is designed for use in Live instructor-led training and for OnDemand selfstudy. The explanations and demonstrations are provided by the instructor in the classroom, or in
13 Vectorizing. Overview
 13 Vectorizing Vectorizing tools are used to create vector data from scanned drawings or images. Combined with the display speed of Image Manager, these tools provide an efficient environment for data
13 Vectorizing Vectorizing tools are used to create vector data from scanned drawings or images. Combined with the display speed of Image Manager, these tools provide an efficient environment for data
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event
 Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event F-1E - QuickStart using OpenRoads ConceptStation Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook
Bentley OpenRoads Workshop 2017 FLUG Fall Training Event F-1E - QuickStart using OpenRoads ConceptStation Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook
Bentley Civil Workshop
 Bentley Civil Workshop 2013 Bentley LEARNing Conference BCR4WK2 - IMPORTING AND EDITING SURVEY DATA Team Leader: Kevin Jackson Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com
Bentley Civil Workshop 2013 Bentley LEARNing Conference BCR4WK2 - IMPORTING AND EDITING SURVEY DATA Team Leader: Kevin Jackson Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com
Using EziField to Stake a Road (or other regular structure)
 Ezifield Road Stakeout Tutorial Page 1 Using EziField to Stake a Road (or other regular structure) Here we have a simple example of a section of road that is 240 metres long and contains a curve. We have
Ezifield Road Stakeout Tutorial Page 1 Using EziField to Stake a Road (or other regular structure) Here we have a simple example of a section of road that is 240 metres long and contains a curve. We have
AEMLog users guide V User Guide - Advanced Engine Management 2205 West 126 th st Hawthorne CA,
 AEMLog users guide V 1.00 User Guide - Advanced Engine Management 2205 West 126 th st Hawthorne CA, 90250 310-484-2322 INTRODUCTION...2 DOCUMENTATION...2 INSTALLING AEMLOG...4 TRANSFERRING DATA TO AND
AEMLog users guide V 1.00 User Guide - Advanced Engine Management 2205 West 126 th st Hawthorne CA, 90250 310-484-2322 INTRODUCTION...2 DOCUMENTATION...2 INSTALLING AEMLOG...4 TRANSFERRING DATA TO AND
TR17699 InfraWorks 360 in Motion: Getting Things Moving in Your Model Willy Campbell Autodesk
 TR17699 InfraWorks 360 in Motion: Getting Things Moving in Your Model Willy Campbell Autodesk Dave Lawrence Autodesk Learning Objectives Learn how to create paths using InfraWorks 360 road tools: Design
TR17699 InfraWorks 360 in Motion: Getting Things Moving in Your Model Willy Campbell Autodesk Dave Lawrence Autodesk Learning Objectives Learn how to create paths using InfraWorks 360 road tools: Design
Roundabout Design Using AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 Intersection Tools
 Roundabout Design Using AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 Intersection Tools Marie-Pierre Lebel Consortech Solutions CV214-1 Learn how to leverage the new intersection design tools from AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 for use
Roundabout Design Using AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 Intersection Tools Marie-Pierre Lebel Consortech Solutions CV214-1 Learn how to leverage the new intersection design tools from AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 for use
Quick Start Guide. ARIS Architect. Version 9.8 Service Release 2
 ARIS Architect Version 9.8 Service Release 2 October 2015 This document applies to ARIS Version 9.8 and to all subsequent releases. Specifications contained herein are subject to change and these changes
ARIS Architect Version 9.8 Service Release 2 October 2015 This document applies to ARIS Version 9.8 and to all subsequent releases. Specifications contained herein are subject to change and these changes
Components of Alignment. Horizontal Alignment. Vertical Alignment. Highway Design Project. Vertical Alignment. Vertical Alignment.
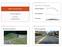 1/35 Components of Alignment Highway Design Project Horizontal Alignment Vertical Alignment Vertical Alignment Amir Samimi Civil Engineering Department Sharif University of Technology Cross-section /35
1/35 Components of Alignment Highway Design Project Horizontal Alignment Vertical Alignment Vertical Alignment Amir Samimi Civil Engineering Department Sharif University of Technology Cross-section /35
Quick Start Guide. ARIS Architect. Version 9.7
 ARIS Architect Version 9.7 October 2014 This document applies to ARIS Version 9.7 and to all subsequent releases. Specifications contained herein are subject to change and these changes will be reported
ARIS Architect Version 9.7 October 2014 This document applies to ARIS Version 9.7 and to all subsequent releases. Specifications contained herein are subject to change and these changes will be reported
ENGINEERING SURVEYING (221 BE)
 ENGINEERING SURVEYING (221 BE) Horizontal Circular Curves Sr Tan Liat Choon Email: tanliatchoon@gmail.com Mobile: 016-4975551 INTRODUCTION The centre line of road consists of series of straight lines interconnected
ENGINEERING SURVEYING (221 BE) Horizontal Circular Curves Sr Tan Liat Choon Email: tanliatchoon@gmail.com Mobile: 016-4975551 INTRODUCTION The centre line of road consists of series of straight lines interconnected
Mn/DOT CADD DATA Standards General Information
 Mn/DOT CADD DATA Standards General Information PREFACE The scope of this web-site is to document and standardize the Minnesota Department of Transportation s CADD (computer aided drafting and design file
Mn/DOT CADD DATA Standards General Information PREFACE The scope of this web-site is to document and standardize the Minnesota Department of Transportation s CADD (computer aided drafting and design file
INPUT DATA PROCEDURES
 79 SECTION 7 INPUT DATA PROCEDURES This section describes the forms and message boxes used to enter input data for an RSRAP optimization problem. These forms and message boxes implement Steps 1 through
79 SECTION 7 INPUT DATA PROCEDURES This section describes the forms and message boxes used to enter input data for an RSRAP optimization problem. These forms and message boxes implement Steps 1 through
Highway Performance Monitoring System
 Highway Performance Monitoring System Version 1.0 June 2011 Quick Start Guide for Version 8.0 Federal Highway Administration Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 Chapter 2 HPMS Workflow... 2 Chapter
Highway Performance Monitoring System Version 1.0 June 2011 Quick Start Guide for Version 8.0 Federal Highway Administration Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 Chapter 2 HPMS Workflow... 2 Chapter
Export Field Data to GEOPAK Drainage
 Export Field Data to GEOPAK Drainage 1.1 Overview The Export to GEOPAK Drainage tool can be utilized to leverage data collected by field surveys (i.e., pipes and structures) into a GEOPAK Drainage project.
Export Field Data to GEOPAK Drainage 1.1 Overview The Export to GEOPAK Drainage tool can be utilized to leverage data collected by field surveys (i.e., pipes and structures) into a GEOPAK Drainage project.
Land Development Suite for BricsCAD Manual: Survey and Cogo commands:
 Land Development Suite for BricsCAD Manual: Survey and Cogo commands: Before you begin go to Drafting -- Drawing Setup Drawing Setup - Select English or Metric units -changes the ltscale and labeling precision,
Land Development Suite for BricsCAD Manual: Survey and Cogo commands: Before you begin go to Drafting -- Drawing Setup Drawing Setup - Select English or Metric units -changes the ltscale and labeling precision,
DES 727 CORRIDOR MODELLING & PLAN PRODUCTION USING OPEN ROADS. April 2018 Design Division
 CORRIDOR MODELLING & PLAN PRODUCTION USING OPEN ROADS April 2018 Design Division Introduction The course has been developed to be completed with Power GeoPak SS4. Other versions of GeoPak SS4 may also
CORRIDOR MODELLING & PLAN PRODUCTION USING OPEN ROADS April 2018 Design Division Introduction The course has been developed to be completed with Power GeoPak SS4. Other versions of GeoPak SS4 may also
Bentley Civil Workshop
 Bentley Civil Workshop 2013 Bentley LEARNing Conference BCR2WK4 Creating End Conditions Team Leader: Dave Hoerner Team Members: Lisa Whitson & Derricke Gray Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive
Bentley Civil Workshop 2013 Bentley LEARNing Conference BCR2WK4 Creating End Conditions Team Leader: Dave Hoerner Team Members: Lisa Whitson & Derricke Gray Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive
ARIS Architect QUICK START GUIDE. Version Service Release 7
 ARIS Architect QUICK START GUIDE Version 9.8 - Service Release 7 December 2016 This document applies to ARIS Version 9.8 and to all subsequent releases. Specifications contained herein are subject to change
ARIS Architect QUICK START GUIDE Version 9.8 - Service Release 7 December 2016 This document applies to ARIS Version 9.8 and to all subsequent releases. Specifications contained herein are subject to change
ArcView QuickStart Guide. Contents. The ArcView Screen. Elements of an ArcView Project. Creating an ArcView Project. Adding Themes to Views
 ArcView QuickStart Guide Page 1 ArcView QuickStart Guide Contents The ArcView Screen Elements of an ArcView Project Creating an ArcView Project Adding Themes to Views Zoom and Pan Tools Querying Themes
ArcView QuickStart Guide Page 1 ArcView QuickStart Guide Contents The ArcView Screen Elements of an ArcView Project Creating an ArcView Project Adding Themes to Views Zoom and Pan Tools Querying Themes
Economic Crash Analysis Tool. Release Notes
 Release Notes August 2017 Release: 1. Project Information Worksheet: a. Update: Removed the design exception report option b. Enhancement: The first question has been expanded to provide better clarity
Release Notes August 2017 Release: 1. Project Information Worksheet: a. Update: Removed the design exception report option b. Enhancement: The first question has been expanded to provide better clarity
Understanding Acrobat Form Tools
 CHAPTER Understanding Acrobat Form Tools A Adobe Acrobat X PDF Bible PDF Forms Using Adobe Acrobat and LiveCycle Designer Bible Adobe Acrobat X PDF Bible PDF Forms Using Adobe Acrobat and LiveCycle Designer
CHAPTER Understanding Acrobat Form Tools A Adobe Acrobat X PDF Bible PDF Forms Using Adobe Acrobat and LiveCycle Designer Bible Adobe Acrobat X PDF Bible PDF Forms Using Adobe Acrobat and LiveCycle Designer
Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Analysis with CAD
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Analysis with CAD Data Setup an HY-12 storm drain model in the WMS interface using CAD data with inlet and pipe information Objectives Learn to define
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Storm Drain Modeling HY-12 Analysis with CAD Data Setup an HY-12 storm drain model in the WMS interface using CAD data with inlet and pipe information Objectives Learn to define
What's New or Changed in Bentley InRoads XM Edition
 08.09.02.13 Adds to 08.09.01.45 New General Enhancements File Added support for running Inroads Group within MicroStation on a 64 bit operating system. Running Inroads Group within AutoCAD on a 64 bit
08.09.02.13 Adds to 08.09.01.45 New General Enhancements File Added support for running Inroads Group within MicroStation on a 64 bit operating system. Running Inroads Group within AutoCAD on a 64 bit
Bentley OpenBridge Workshop 2017 FLUG Spring Training Event
 Bentley OpenBridge Workshop 2017 FLUG Spring Training Event 435 - Using Open Bridge Modeler and Lumenr RT Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook
Bentley OpenBridge Workshop 2017 FLUG Spring Training Event 435 - Using Open Bridge Modeler and Lumenr RT Bentley Systems, Incorporated 685 Stockton Drive Exton, PA 19341 www.bentley.com Practice Workbook
