CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture
|
|
|
- Bathsheba Poole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 9// CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Lecture 4 Cache Performance (Cache III) Instructors: ike Franklin Dan Garcia hfp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa In the News ajor Expansion of World s Centers The next great expansion of the world s digital infrastructure is under way in developing markets like those of China, Brazil and ArgenTna Growth expected to match levels from economy s boom years despite global slowdown hfp://wwwnytmescom//9//technology/worlds- data- centers- expected- to- grow- survey- sayshtml 9// Agenda Review Direct apped Caches easuring Performance ult- Level Caches AssociaTve Caches Cache Wrap Up Review: ultword Block Direct apped Cache Four words/block, cache size = K words (56 blocks) (4KB Total data) Byte offset Valid Block offset 3 9// 3 9// 4 easuring Performance Computers use a clock to determine when events takes place within hardware Clock cycles discrete Tme intervals aka clocks, cycles, clock periods, clock Tcks Clock rate or clock frequency clock cycles per second (inverse of clock cycle Tme) 3 GigaHertz clock rate => clock cycle Tme = /3x 9 seconds clock cycle Tme = 333 picoseconds (ps) CPU Performance Factors But a program executes instructons Time = Seconds Program InstrucTons Clock cycles Seconds = Program InstrucTon Clock Cycle st term called Instruc;on Count 3 rd term is Clock Cycle Time ( / Clock rate) nd term abbreviated CPI for average Clock cycles Per Instruc;on Why CPI =? Why CP >? Can CPI be <? 9// 5 9// 6
2 9// Average emory Access Time (AAT) Average emory Access Time (AAT) is the average to access memory considering both hits and misses AAT = Time for a hit + iss rate x iss penalty What is the AAT for a processor with a psec clock, a miss penalty of 5 clock cycles, a miss rate of misses per instructon and a cache access Tme of clock cycle? + x 5 = clock cycles Or x = 4 psecs PotenTal impact of much larger cache on AAT? ) Lower iss rate ) Longer Access Tme ( Tme): smaller is faster Increase in hit Tme will likely add another stage to the pipeline At some point, increase in hit Tme for a larger cache may overcome the improvement in hit rate, yielding a decrease in performance 9// 7 easuring Cache Performance Effect on CPI Assuming cache hit costs are included as part of the normal CPU executon cycle, then CPU Tme = IC CPI CC = IC (CPI ideal + Average emory- stall cycles) CC CPI stall A simple model for emory- stall cycles emory- stall cycles = accesses/instructon miss rate miss penalty This ignores extra costs of write misses which were described previously 9// Impacts of Cache Performance RelaTve $ penalty increases as processor performance improves (faster clock rate and/or lower CPI) emory speed unlikely to improve as fast as processor cycle Tme When calculatng CPI stall, cache miss penalty is measured in processor clock cycles needed to handle a miss Lower the CPI ideal, more pronounced impact of stalls Processor with a CPI ideal of, a cycle miss penalty, 36% load/store instr s, and % I$ and 4% D$ miss rates emory- stall cycles = % + 36% 4% = 344 So CPI stalls = = 544 ore than twice the CPI ideal! What if the CPI ideal is reduced to? What if the D$ miss rate went up by %? CPU em Access ultple Cache Levels Path of Back to CPU 9// 9 9// L$ iss L$ iss ain emory ultple Cache Levels With advancing technology, have more room on die for bigger L caches and for second level cache normally a unified L cache (ie, it holds both instructons and data,) and in some cases even a unified L3 cache New AAT CalculaTon: AAT = L Time + L iss Rate * L iss Penalty L iss Penalty = L Time + L iss Rate * L iss Penalty and so forth (final miss penalty is ain emory access Tme) New AAT Example cycle L Time, % L iss Rate, 5 cycle L Time, 5% L iss Rate cycle ain emory access Tme No L Cache: AAT = + * = 3 With L Cache: AAT = + *(5 + 5*) =! 9// 9//
3 9// Core Area Breakdown Nehalem Die Photo 36 mm (54 inch) emory Controller i s c I O Core P I Core e m o r y u e u e Core Core 3 Fall - - Lecture #4 9 mm (75 inch) 9// Fall - - Lecture #4 4 Load Store ueue Reducing Cache isses First access to block impossible to avoid; small effect for long running programs SoluTon: increase block size (increases miss penalty; very large blocks could increase miss rate) Capacity: Cache cannot contain all blocks accessed by the program SoluTon: increase cache size (may increase access Tme) Conflict (collision): ultple memory locatons mapped to the same cache locaton SoluTon : increase cache size Solu3on : increase associa3vity (may increase access 3me) L Cache & Interrupt Servicing L Inst cache & Inst Fetch Compulsory (cold start or process migraton, st reference): Fall - - Lecture #4 L cache L3 Cache Sources of Cache isses: The 3Cs ExecuTon Units 3KB I$ per core 3KB D$ per core 5KB L$ per core Share one - B L3$ P I Shared L3 Cache 9// i s c I O emory Controller Allow more flexible block placement in cache Direct mapped $: memory block maps to exactly one cache block Fully associa;ve $: allow a memory block to be mapped to any cache block Compromise: divide $ into sets, each of which consists of n ways (n- way set associa;ve) to place memory block emory block maps to unique set determined by index field and is placed in any of the n- ways of that set CalculaTon: (block address) modulo (# sets in the cache) 5 Fall - - Lecture #4 6 Example: 4- Word Direct- apped $ Worst- Case Reference String AlternaTve Block Placement Schemes Consider the sequence of memory accesses Start with an empty cache - all b locks initally marked as not valid miss 4 miss 4 em() em() miss em(4) D placement: mem block in block cache: only one cache block where mem block can be found ( modulo ) = 4 SA placement: four sets x - ways ( cache blocks), memory block in set ( mod 4) = ; either element of the set FA placement: mem block can appear in any cache blocks Fall - - Lecture #4 7 miss em(4) 4 miss 4 miss em() em(4) 4 miss 4 em() 4 miss 4 em() requests, misses Ping pong effect due to conflict misses - two memory locatons that map into the same cache block Fall - - Lecture #4 3
4 9// Example: - Way Set AssociaTve $ Cache Set Way V (4 words = sets x ways per set) : Is it there? Compare all the cache tags in the set to the high order 3 memory address bits to tell if the memory block is in the cache xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx xx ain emory One word blocks Two low order bits define the byte in the word (3b words) : How do we find it? Use next low order memory address bit to determine which cache set (ie, modulo the number of sets in the cache) Example: 4- Word - Way SA $ Same Reference String Consider the sequence of memory accesses Start with an empty cache - all blocks initally marked as not valid miss 4 miss hit 4 hit em() em() em() em() em(4) em(4) em(4) requests, misses Solves the ping pong effect in a direct mapped cache due to conflict misses since now two memory locatons that map into the same cache set can co- exist! 9 Example: Eight- Block Cache with Different OrganizaTons Four- Way Set- AssociaTve Cache = 56 sets each with four ways (each with one block) Byte offset V V V V Way Way Way Way Total size of $ in blocks is equal to number of sets x associa;vity For fixed $ size, increasing associatvity decreases number of sets while increasing number of elements per set With eight blocks, an - way set- associatve $ is same as a fully associatve $ 4x select 3 Range of Set- AssociaTve Caches For a fixed- size cache, each increase by a factor of two in associatvity doubles the number of blocks per set (ie, the number or ways) and halves the number of sets decreases the size of the index by bit and increases the size of the tag by bit Used for tag compare Decreasing associatvity Direct mapped (only one way) Smaller tags, only a single comparator Selects the set Increasing associatvity Selects the word in the block Block offset Byte offset Fully associatve (only one set) is all the bits except block and byte offset Costs of Set- AssociaTve Caches N- way set- associatve cache costs N comparators for tag comparisons ust choose appropriate set (multplexer) before data is available When miss occurs, which way s block selected for replacement? Random Replacement: Hardware randomly selects a cache item and throw it out Least Recently Used (LRU): one that has been unused the longest 3 4 4
5 9// LRU Cache Block Replacement Least Recently Used Hardware keeps track of access history Replace the entry that has not been used for the longest Tme For - way set- associatve cache, need one bit for LRU replacement On access set access bit for used block, clear other one Example of a Simple Pseudo LRU ImplementaTon Assume 64 Fully AssociaTve entries in a set Hardware replacement pointer points to one cache entry Whenever access is made to the entry the pointer points to: ove the pointer to the next entry Otherwise: do not move the pointer Replacement Pointer Entry Entry : Entry 63 Benefits of Set- AssociaTve Caches Largest gains are in going from direct mapped to - way (%+ reducton in miss rate) 5 6 The Cache Design Space Several interactng dimensions Cache size Block size Write- through vs write- back Write allocaton AssociaTvity Replacement policy OpTmal choice is a compromise Depends on access characteristcs Workload Use (I- cache, D- cache) Depends on technology / cost Simplicity o en wins Cache Size (Associa3vity) Block Size Bad Good Factor A Factor B Less ore 9// 7 9// Summary AAT to measure cache performance Cache can have major impact on CPI ult- level caches - Reduce Cache iss Penalty OpTmize first level to be fast! OpTmize nd and 3 rd levels to minimize the memory access penalty Set- associatvity - Reduce Cache iss Rate emory block maps into more than cache block N- way: n possible places in cache to hold a memory block Lots and lots of cache parameters! Write- back vs write through, write allocaton, block size, cache size, associatvity, etc 9 5
Agenda. Recap: Components of a Computer. Agenda. Recap: Cache Performance and Average Memory Access Time (AMAT) Recap: Typical Memory Hierarchy
 // CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Set- Associa+ve Caches Instructors: Randy H Katz David A PaFerson hfp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa Cache Recap Recap: Components of
// CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Set- Associa+ve Caches Instructors: Randy H Katz David A PaFerson hfp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa Cache Recap Recap: Components of
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Cache Performance, Set Associative Caches
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Cache Performance, Set Associative Caches Instructor: Justin Hsia 7/09/2012 Summer 2012 Lecture #12 1 Great Idea #3: Principle of Locality/ Memory Hierarchy
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Cache Performance, Set Associative Caches Instructor: Justin Hsia 7/09/2012 Summer 2012 Lecture #12 1 Great Idea #3: Principle of Locality/ Memory Hierarchy
Agenda. Cache-Memory Consistency? (1/2) 7/14/2011. New-School Machine Structures (It s a bit more complicated!)
 7/4/ CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches II Instructor: Michael Greenbaum New-School Machine Structures (It s a bit more complicated!) Parallel Requests Assigned to
7/4/ CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches II Instructor: Michael Greenbaum New-School Machine Structures (It s a bit more complicated!) Parallel Requests Assigned to
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Direct Mapped Caches, Set Associative Caches, Cache Performance
 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct Mapped Caches, Set Associative Caches, Cache Performance Instructor: Justin Hsia 7//23 Summer 23 Lecture # Great Idea #3: Principle of Locality/ Memory
CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct Mapped Caches, Set Associative Caches, Cache Performance Instructor: Justin Hsia 7//23 Summer 23 Lecture # Great Idea #3: Principle of Locality/ Memory
CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/76/74076691.jpg) CSF Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
CSF Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. PaGerson hgp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa10. 10/4/10 Fall Lecture #16. Agenda
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. PaGerson hgp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa10 1 Agenda Cache Sizing/Hits and Misses Administrivia
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. PaGerson hgp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa10 1 Agenda Cache Sizing/Hits and Misses Administrivia
ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)]
![ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)]](/thumbs/72/68075397.jpg) ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] Measuring Cache Performance Assuming cache hit costs are included as part of the normal CPU execution cycle, then CPU
ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] Measuring Cache Performance Assuming cache hit costs are included as part of the normal CPU execution cycle, then CPU
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Caches Part 2 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/fa15 Software Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg,
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Caches Part 2 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/fa15 Software Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg,
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures)
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. PaGerson hgp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa10 1 2 Cache Field Sizes Number of bits in a cache includes
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. PaGerson hgp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa10 1 2 Cache Field Sizes Number of bits in a cache includes
Page 1. Memory Hierarchies (Part 2)
 Memory Hierarchies (Part ) Outline of Lectures on Memory Systems Memory Hierarchies Cache Memory 3 Virtual Memory 4 The future Increasing distance from the processor in access time Review: The Memory Hierarchy
Memory Hierarchies (Part ) Outline of Lectures on Memory Systems Memory Hierarchies Cache Memory 3 Virtual Memory 4 The future Increasing distance from the processor in access time Review: The Memory Hierarchy
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ Typical Memory Hierarchy Datapath On-Chip
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: John Wawrzynek & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ Typical Memory Hierarchy Datapath On-Chip
CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1
 CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall 2008 Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1 Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson
CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall 2008 Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1 Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures)
 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Instructors: Randy H Katz David A PaHerson hhp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa Direct Mapped (contnued) - Interface CharacterisTcs of the
CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Instructors: Randy H Katz David A PaHerson hhp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa Direct Mapped (contnued) - Interface CharacterisTcs of the
Caches Part 1. Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger. School of Information Science and Technology SIST
 CS 110 Computer Architecture Caches Part 1 Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on UC Berkley's
CS 110 Computer Architecture Caches Part 1 Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on UC Berkley's
CS3350B Computer Architecture
 CS335B Computer Architecture Winter 25 Lecture 32: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy: How? Marc Moreno Maza wwwcsduwoca/courses/cs335b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design, Patterson &
CS335B Computer Architecture Winter 25 Lecture 32: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy: How? Marc Moreno Maza wwwcsduwoca/courses/cs335b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design, Patterson &
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 3//5 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part Instructors: Krste Asanovic & Vladimir Stojanovic hfp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/ Parallel Requests Assigned to computer
3//5 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part Instructors: Krste Asanovic & Vladimir Stojanovic hfp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/ Parallel Requests Assigned to computer
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design. Lecture 08: Cache Review. Bei Yu
 CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Cache Review Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 A Typical Memory Hierarchy q Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Cache Review Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 A Typical Memory Hierarchy q Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design. Lecture 08: Memory - I. Bei Yu
 CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Memory - I Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 Outline q Why Memory Hierarchy q How Memory Hierarchy? SRAM (Cache) & DRAM (main memory) Memory System
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Memory - I Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 Outline q Why Memory Hierarchy q How Memory Hierarchy? SRAM (Cache) & DRAM (main memory) Memory System
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
 EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
10/19/17. You Are Here! Review: Direct-Mapped Cache. Typical Memory Hierarchy
 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/ Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg, Search
CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/ Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg, Search
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/16/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/16/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
10/16/17. Outline. Outline. Typical Memory Hierarchy. Adding Cache to Computer. Key Cache Concepts
 // CS C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) s Part Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~csc/ Organization and Principles Write Back vs Write Through
// CS C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) s Part Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~csc/ Organization and Principles Write Back vs Write Through
EEC 170 Computer Architecture Fall Improving Cache Performance. Administrative. Review: The Memory Hierarchy. Review: Principle of Locality
 Administrative EEC 7 Computer Architecture Fall 5 Improving Cache Performance Problem #6 is posted Last set of homework You should be able to answer each of them in -5 min Quiz on Wednesday (/7) Chapter
Administrative EEC 7 Computer Architecture Fall 5 Improving Cache Performance Problem #6 is posted Last set of homework You should be able to answer each of them in -5 min Quiz on Wednesday (/7) Chapter
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ 10/18/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 2 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/ 10/18/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #15 1 Outline
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/19/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #16 1 Parallel
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/19/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #16 1 Parallel
Improving Cache Performance
 Improving Cache Performance Tuesday 27 October 15 Many slides adapted from: and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 5th Edition, 2014, MK and from Prof. Mary Jane Irwin, PSU Summary Previous Class Memory hierarchy
Improving Cache Performance Tuesday 27 October 15 Many slides adapted from: and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 5th Edition, 2014, MK and from Prof. Mary Jane Irwin, PSU Summary Previous Class Memory hierarchy
Improving Cache Performance
 Improving Cache Performance Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing Tuesday 28 October 14 Many slides adapted from: Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 4th Edition,
Improving Cache Performance Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing Tuesday 28 October 14 Many slides adapted from: Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 4th Edition,
CS3350B Computer Architecture
 CS3350B Computer Architecture Winter 2015 Lecture 3.1: Memory Hierarchy: What and Why? Marc Moreno Maza www.csd.uwo.ca/courses/cs3350b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design, Patterson
CS3350B Computer Architecture Winter 2015 Lecture 3.1: Memory Hierarchy: What and Why? Marc Moreno Maza www.csd.uwo.ca/courses/cs3350b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design, Patterson
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) More Cache: Set Associa0vity. Smart Phone. Today s Lecture. Core.
 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) More Cache: Set Associavity Instructors: Randy H Katz David A PaGerson Guest Lecture: Krste Asanovic hgp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa
CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) More Cache: Set Associavity Instructors: Randy H Katz David A PaGerson Guest Lecture: Krste Asanovic hgp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa
Show Me the $... Performance And Caches
 Show Me the $... Performance And Caches 1 CPU-Cache Interaction (5-stage pipeline) PCen 0x4 Add bubble PC addr inst hit? Primary Instruction Cache IR D To Memory Control Decode, Register Fetch E A B MD1
Show Me the $... Performance And Caches 1 CPU-Cache Interaction (5-stage pipeline) PCen 0x4 Add bubble PC addr inst hit? Primary Instruction Cache IR D To Memory Control Decode, Register Fetch E A B MD1
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Mul$- Level Caches
 Costs of Set AssociaRve s CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Mul$- Level s Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. PaGerson hgp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa10 1 When miss
Costs of Set AssociaRve s CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Mul$- Level s Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. PaGerson hgp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa10 1 When miss
COSC3330 Computer Architecture Lecture 19. Cache
 COSC3330 Computer Architecture Lecture 19 Cache Instructor: Weidong Shi (Larry), PhD Computer Science Department University of Houston Cache Topics 3 Cache Hardware Cost How many total bits are required
COSC3330 Computer Architecture Lecture 19 Cache Instructor: Weidong Shi (Larry), PhD Computer Science Department University of Houston Cache Topics 3 Cache Hardware Cost How many total bits are required
CMPT 300 Introduction to Operating Systems
 CMPT 300 Introduction to Operating Systems Cache 0 Acknowledgement: some slides are taken from CS61C course material at UC Berkeley Agenda Memory Hierarchy Direct Mapped Caches Cache Performance Set Associative
CMPT 300 Introduction to Operating Systems Cache 0 Acknowledgement: some slides are taken from CS61C course material at UC Berkeley Agenda Memory Hierarchy Direct Mapped Caches Cache Performance Set Associative
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Multilevel Caches, Cache Questions
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Multilevel Caches, Cache Questions Instructor: Alan Christopher 7/14/2014 Summer 2014 -- Lecture #12 1 Great Idea #3: Principle of Locality/ Memory Hierarchy
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Multilevel Caches, Cache Questions Instructor: Alan Christopher 7/14/2014 Summer 2014 -- Lecture #12 1 Great Idea #3: Principle of Locality/ Memory Hierarchy
Review: Performance Latency vs. Throughput. Time (seconds/program) is performance measure Instructions Clock cycles Seconds.
 Performance 980 98 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 99 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 2000 7/4/20 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Instructor: Michael Greenbaum
Performance 980 98 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 99 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 2000 7/4/20 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Instructor: Michael Greenbaum
Course Administration
 Spring 207 EE 363: Computer Organization Chapter 5: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy - Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 4570
Spring 207 EE 363: Computer Organization Chapter 5: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy - Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 4570
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Lecture 15: Caches, Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Lecture 15: Caches, Part 2 Instructor: Sagar Karandikar sagark@eecsberkeleyedu hbp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c 1 So/ware Parallel Requests Assigned to computer
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Lecture 15: Caches, Part 2 Instructor: Sagar Karandikar sagark@eecsberkeleyedu hbp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c 1 So/ware Parallel Requests Assigned to computer
Mo Money, No Problems: Caches #2...
 Mo Money, No Problems: Caches #2... 1 Reminder: Cache Terms... Cache: A small and fast memory used to increase the performance of accessing a big and slow memory Uses temporal locality: The tendency to
Mo Money, No Problems: Caches #2... 1 Reminder: Cache Terms... Cache: A small and fast memory used to increase the performance of accessing a big and slow memory Uses temporal locality: The tendency to
Review. You Are Here! Agenda. Recap: Typical Memory Hierarchy. Recap: Components of a Computer 11/6/12
 /6/ Review CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture More Cache: Set Associavity Instructors: Krste Asanovic, Randy H Katz hbp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa Big Ideas of InstrucPon- Level Parallelism
/6/ Review CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture More Cache: Set Associavity Instructors: Krste Asanovic, Randy H Katz hbp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa Big Ideas of InstrucPon- Level Parallelism
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Lecture 15: Caches, Part 2
 7/6/5 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Lecture 5: Caches, Part Instructor: Sagar Karandikar sagark@eecsberkeleyedu hdp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg,
7/6/5 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Lecture 5: Caches, Part Instructor: Sagar Karandikar sagark@eecsberkeleyedu hdp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg,
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 24: Cache Performance Analysis Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Last time: Associative caches How do we
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 24: Cache Performance Analysis Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Last time: Associative caches How do we
Direct-Mapped and Set Associative Caches. Instructor: Steven Ho
 Direct-Mapped and Set Associative Caches Instructor: Steven Ho Great Idea #3: Principle of Locality/ Memory Hierarchy 7/6/28 CS6C Su8 - Lecture 5 2 Extended Review of Last Lecture Why have caches? Intermediate
Direct-Mapped and Set Associative Caches Instructor: Steven Ho Great Idea #3: Principle of Locality/ Memory Hierarchy 7/6/28 CS6C Su8 - Lecture 5 2 Extended Review of Last Lecture Why have caches? Intermediate
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
EEC 170 Computer Architecture Fall Cache Introduction Review. Review: The Memory Hierarchy. The Memory Hierarchy: Why Does it Work?
 EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
Chapter Seven. SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors)
 Chapter Seven emories: Review SRA: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRA (4 to transistors) DRA: value is stored as a charge on capacitor (must be refreshed)
Chapter Seven emories: Review SRA: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRA (4 to transistors) DRA: value is stored as a charge on capacitor (must be refreshed)
CPE 631 Lecture 04: CPU Caches
 Lecture 04 CPU Caches Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville Outline Memory Hierarchy Four Questions for Memory Hierarchy Cache Performance 26/01/2004 UAH- 2 1 Processor-DR
Lecture 04 CPU Caches Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville Outline Memory Hierarchy Four Questions for Memory Hierarchy Cache Performance 26/01/2004 UAH- 2 1 Processor-DR
CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/73/69213006.jpg) CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
Memory Hierarchy Design (Appendix B and Chapter 2)
 CS359: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy Design (Appendix B and Chapter 2) Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering 1 Four Memory Hierarchy Questions Q1 (block placement): where
CS359: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy Design (Appendix B and Chapter 2) Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering 1 Four Memory Hierarchy Questions Q1 (block placement): where
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/24/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #16 1 Software
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Bernhard Boser & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/24/16 Fall 2016 - Lecture #16 1 Software
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 23: Associative Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Last time: Write-Back Alternative: On data-write hit, just
ECE331: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 23: Associative Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Last time: Write-Back Alternative: On data-write hit, just
ECE ECE4680
 ECE468. -4-7 The otivation for s System ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture DRA Hierarchy System otivation Large memories (DRA) are slow Small memories (SRA) are fast ake the average access time
ECE468. -4-7 The otivation for s System ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture DRA Hierarchy System otivation Large memories (DRA) are slow Small memories (SRA) are fast ake the average access time
3Introduction. Memory Hierarchy. Chapter 2. Memory Hierarchy Design. Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
14:332:331. Week 13 Basics of Cache
 14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Spring 2006 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Week131 Spring 2006
14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Spring 2006 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Week131 Spring 2006
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ Components of a Computer Processor
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ Components of a Computer Processor
Caches. Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University. See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes)
 Caches akim Weatherspoon CS 341, Spring 212 Computer Science Cornell University See P& 5.1, 5.2 (except writes) ctrl ctrl ctrl inst imm B A B D D Big Picture: emory emory: big & slow vs Caches: small &
Caches akim Weatherspoon CS 341, Spring 212 Computer Science Cornell University See P& 5.1, 5.2 (except writes) ctrl ctrl ctrl inst imm B A B D D Big Picture: emory emory: big & slow vs Caches: small &
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanovic & Vladimir Stojanovic hfp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ Parallel Requests Assigned to computer
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanovic & Vladimir Stojanovic hfp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ Parallel Requests Assigned to computer
EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits. Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver. Lecture 19: Caches EE141
 EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver Lecture 19: Caches Cache Introduction 40% of this ARM CPU is devoted to SRAM cache. But the role
EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver Lecture 19: Caches Cache Introduction 40% of this ARM CPU is devoted to SRAM cache. But the role
Caching Basics. Memory Hierarchies
 Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
ECEC 355: Cache Design
 ECEC 355: Cache Design November 28, 2007 Terminology Let us first define some general terms applicable to caches. Cache block or line. The minimum unit of information (in bytes) that can be either present
ECEC 355: Cache Design November 28, 2007 Terminology Let us first define some general terms applicable to caches. Cache block or line. The minimum unit of information (in bytes) that can be either present
14:332:331. Week 13 Basics of Cache
 14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Fall 2003 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Lec20.1 Fall 2003 Head
14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Fall 2003 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Lec20.1 Fall 2003 Head
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Direct Mapped Caches
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct Mapped Caches Instructor: Justin Hsia 7/05/2012 Summer 2012 Lecture #11 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single and double precision) approximates
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct Mapped Caches Instructor: Justin Hsia 7/05/2012 Summer 2012 Lecture #11 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single and double precision) approximates
The Memory Hierarchy. Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2)
 The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
Cache Optimization. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Cache Optimization Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Cache Misses On cache hit CPU proceeds normally On cache miss Stall the CPU pipeline
Cache Optimization Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Cache Misses On cache hit CPU proceeds normally On cache miss Stall the CPU pipeline
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanovic & Vladimir Stojanovic hcp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ So$ware Parallel Requests Assigned
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 3 Instructors: Krste Asanovic & Vladimir Stojanovic hcp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ So$ware Parallel Requests Assigned
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #24 Cache II 27-8-6 Scott Beamer, Instructor New Flow Based Routers CS61C L24 Cache II (1) www.anagran.com Caching Terminology When we try
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #24 Cache II 27-8-6 Scott Beamer, Instructor New Flow Based Routers CS61C L24 Cache II (1) www.anagran.com Caching Terminology When we try
UCB CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 14 Caches III Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia Google Glass may be one vision of the future of post-pc interfaces augmented reality with video
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 14 Caches III Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia Google Glass may be one vision of the future of post-pc interfaces augmented reality with video
CS 465 Final Review. Fall 2017 Prof. Daniel Menasce
 CS 465 Final Review Fall 2017 Prof. Daniel Menasce Ques@ons What are the types of hazards in a datapath and how each of them can be mi@gated? State and explain some of the methods used to deal with branch
CS 465 Final Review Fall 2017 Prof. Daniel Menasce Ques@ons What are the types of hazards in a datapath and how each of them can be mi@gated? State and explain some of the methods used to deal with branch
Modern Computer Architecture
 Modern Computer Architecture Lecture3 Review of Memory Hierarchy Hongbin Sun 国家集成电路人才培养基地 Xi an Jiaotong University Performance 1000 Recap: Who Cares About the Memory Hierarchy? Processor-DRAM Memory Gap
Modern Computer Architecture Lecture3 Review of Memory Hierarchy Hongbin Sun 国家集成电路人才培养基地 Xi an Jiaotong University Performance 1000 Recap: Who Cares About the Memory Hierarchy? Processor-DRAM Memory Gap
COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 3 Review of Caches and Virtual Memory
 1 COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 3 Review of Caches and Virtual Memory Cristinel Ababei Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Marquette University Credits: Slides adapted from presentations
1 COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 3 Review of Caches and Virtual Memory Cristinel Ababei Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Marquette University Credits: Slides adapted from presentations
Memory Hierarchy. ENG3380 Computer Organization and Architecture Cache Memory Part II. Topics. References. Memory Hierarchy
 ENG338 Computer Organization and Architecture Part II Winter 217 S. Areibi School of Engineering University of Guelph Hierarchy Topics Hierarchy Locality Motivation Principles Elements of Design: Addresses
ENG338 Computer Organization and Architecture Part II Winter 217 S. Areibi School of Engineering University of Guelph Hierarchy Topics Hierarchy Locality Motivation Principles Elements of Design: Addresses
Caches and Memory. Anne Bracy CS 3410 Computer Science Cornell University. See P&H Chapter: , 5.8, 5.10, 5.13, 5.15, 5.17
 Caches and emory Anne Bracy CS 34 Computer Science Cornell University Slides by Anne Bracy with 34 slides by Professors Weatherspoon, Bala, ckee, and Sirer. See P&H Chapter: 5.-5.4, 5.8, 5., 5.3, 5.5,
Caches and emory Anne Bracy CS 34 Computer Science Cornell University Slides by Anne Bracy with 34 slides by Professors Weatherspoon, Bala, ckee, and Sirer. See P&H Chapter: 5.-5.4, 5.8, 5., 5.3, 5.5,
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture. - Memory Hierarchies (I)
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Hierarchies (I) Fall 2007 Slides are based on a lecture by David Culler, University of California, Berkley http//www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler/courses/cs252-s05 Recap
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Hierarchies (I) Fall 2007 Slides are based on a lecture by David Culler, University of California, Berkley http//www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler/courses/cs252-s05 Recap
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct- Mapped Caches. Increasing distance from processor, decreasing speed.
 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct- Mapped s 9/27/2 Instructors: Krste Asanovic, Randy H Katz hdp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa2 Fall 2 - - Lecture #4 New- School Machine Structures (It
CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct- Mapped s 9/27/2 Instructors: Krste Asanovic, Randy H Katz hdp://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs6c/fa2 Fall 2 - - Lecture #4 New- School Machine Structures (It
Lecture 12. Memory Design & Caches, part 2. Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University
 Lecture 12 Memory Design & Caches, part 2 Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements HW3 is due today PA2 is available on-line today Part 1 is due on 2/27
Lecture 12 Memory Design & Caches, part 2 Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements HW3 is due today PA2 is available on-line today Part 1 is due on 2/27
Computer Organization and Structure. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems. Cache $$$$$
 CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems Cache $$$$$ Memory Systems! How can we supply the CPU with enough data to keep it busy?! We will focus on memory issues,! which are frequently bottlenecks
CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems Cache $$$$$ Memory Systems! How can we supply the CPU with enough data to keep it busy?! We will focus on memory issues,! which are frequently bottlenecks
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization. More Caches
 ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 217 More Caches 1 Prelim 2 stats High: 9 (out of 9) Mean: 7.2, Median: 73 Announcements Prelab 5(C) due tomorrow 2 Example: Direct Mapped (DM) Cache
ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 217 More Caches 1 Prelim 2 stats High: 9 (out of 9) Mean: 7.2, Median: 73 Announcements Prelab 5(C) due tomorrow 2 Example: Direct Mapped (DM) Cache
Lecture 11 Cache. Peng Liu.
 Lecture 11 Cache Peng Liu liupeng@zju.edu.cn 1 Associative Cache Example 2 Associative Cache Example 3 Associativity Example Compare 4-block caches Direct mapped, 2-way set associative, fully associative
Lecture 11 Cache Peng Liu liupeng@zju.edu.cn 1 Associative Cache Example 2 Associative Cache Example 3 Associativity Example Compare 4-block caches Direct mapped, 2-way set associative, fully associative
Block Size Tradeoff (1/3) Benefits of Larger Block Size. Lecture #22 Caches II Block Size Tradeoff (3/3) Block Size Tradeoff (2/3)
 CS61C L22 Caches II (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C Machine Structures CPS today! Lecture #22 Caches II 25-11-16 There is one handout today at the front and back of the room! Lecturer PSOE, new
CS61C L22 Caches II (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C Machine Structures CPS today! Lecture #22 Caches II 25-11-16 There is one handout today at the front and back of the room! Lecturer PSOE, new
A Framework for Memory Hierarchies
 Associativity schemes Scheme Number of sets Blocks per set Direct mapped Number of blocks in cache 1 Set associative Blocks in cache / Associativity Associativity (2-8) Fully associative 1 Number Blocks
Associativity schemes Scheme Number of sets Blocks per set Direct mapped Number of blocks in cache 1 Set associative Blocks in cache / Associativity Associativity (2-8) Fully associative 1 Number Blocks
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/su05 CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #21: Caches 3 2005-07-27 CS61C L22 Caches III (1) Andy Carle Review: Why We Use Caches 1000 Performance 100 10 1 1980 1981 1982 1983
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/su05 CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #21: Caches 3 2005-07-27 CS61C L22 Caches III (1) Andy Carle Review: Why We Use Caches 1000 Performance 100 10 1 1980 1981 1982 1983
UCB CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 32 Caches III 2008-04-16 Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia Hi to Chin Han from U Penn! Prem Kumar of Northwestern has created a quantum inverter
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 32 Caches III 2008-04-16 Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia Hi to Chin Han from U Penn! Prem Kumar of Northwestern has created a quantum inverter
Lecture 16: Memory Hierarchy Misses, 3 Cs and 7 Ways to Reduce Misses. Professor Randy H. Katz Computer Science 252 Fall 1995
 Lecture 16: Memory Hierarchy Misses, 3 Cs and 7 Ways to Reduce Misses Professor Randy H. Katz Computer Science 252 Fall 1995 Review: Who Cares About the Memory Hierarchy? Processor Only Thus Far in Course:
Lecture 16: Memory Hierarchy Misses, 3 Cs and 7 Ways to Reduce Misses Professor Randy H. Katz Computer Science 252 Fall 1995 Review: Who Cares About the Memory Hierarchy? Processor Only Thus Far in Course:
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures CS61C L22 Caches II (1) CPS today! Lecture #22 Caches II 2005-11-16 There is one handout today at the front and back of the room! Lecturer PSOE,
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures CS61C L22 Caches II (1) CPS today! Lecture #22 Caches II 2005-11-16 There is one handout today at the front and back of the room! Lecturer PSOE,
UC Berkeley CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UC Berkeley CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 33 Caches III 2007-04-11 Future of movies is 3D? Dreamworks says they may exclusively release movies in this format. It s based
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UC Berkeley CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 33 Caches III 2007-04-11 Future of movies is 3D? Dreamworks says they may exclusively release movies in this format. It s based
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350):
 The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350): Motivation for The Memory Hierarchy: { CPU/Memory Performance Gap The Principle Of Locality Cache $$$$$ Cache Basics:
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350): Motivation for The Memory Hierarchy: { CPU/Memory Performance Gap The Principle Of Locality Cache $$$$$ Cache Basics:
Caches and Memory Deniz Altinbuken CS 3410, Spring 2015
 s and emory Deniz Altinbuken CS, Spring Computer Science Cornell University See P& Chapter:.-. (except writes) Big Picture: emory Code Stored in emory (also, data and stack) compute jump/branch targets
s and emory Deniz Altinbuken CS, Spring Computer Science Cornell University See P& Chapter:.-. (except writes) Big Picture: emory Code Stored in emory (also, data and stack) compute jump/branch targets
Lecture 33 Caches III What to do on a write hit? Block Size Tradeoff (1/3) Benefits of Larger Block Size
 CS61C L33 Caches III (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UC Berkeley CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 33 Caches III 27-4-11 Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia Future of movies is 3D? Dreamworks
CS61C L33 Caches III (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UC Berkeley CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 33 Caches III 27-4-11 Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia Future of movies is 3D? Dreamworks
Caches. See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes) Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2013 Computer Science Cornell University
 s See P&.,. (except writes) akim Weatherspoon CS, Spring Computer Science Cornell University What will you do over Spring Break? A) Relax B) ead home C) ead to a warm destination D) Stay in (frigid) Ithaca
s See P&.,. (except writes) akim Weatherspoon CS, Spring Computer Science Cornell University What will you do over Spring Break? A) Relax B) ead home C) ead to a warm destination D) Stay in (frigid) Ithaca
Memory Hierarchies. Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev. Fall Lecture 10, October 8, CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology
 Memory Hierarchies Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev Fall 2007 CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology Lecture 10, October 8, 2007 Memories SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast
Memory Hierarchies Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev Fall 2007 CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology Lecture 10, October 8, 2007 Memories SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast
Caches. See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes) Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2013 Computer Science Cornell University
 s See P&.,. (except writes) akim Weatherspoon CS, Spring Computer Science Cornell University What will you do over Spring Break? A) Relax B) ead home C) ead to a warm destination D) Stay in (frigid) Ithaca
s See P&.,. (except writes) akim Weatherspoon CS, Spring Computer Science Cornell University What will you do over Spring Break? A) Relax B) ead home C) ead to a warm destination D) Stay in (frigid) Ithaca
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 22: Introduction to Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Caches hold a subset of data from the main
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 22: Introduction to Caches Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Caches hold a subset of data from the main
Memory Hierarchy. 2/18/2016 CS 152 Sec6on 5 Colin Schmidt
 Memory Hierarchy 2/18/2016 CS 152 Sec6on 5 Colin Schmidt Agenda Review Memory Hierarchy Lab 2 Ques6ons Return Quiz 1 Latencies Comparison Numbers L1 Cache 0.5 ns L2 Cache 7 ns 14x L1 cache Main Memory
Memory Hierarchy 2/18/2016 CS 152 Sec6on 5 Colin Schmidt Agenda Review Memory Hierarchy Lab 2 Ques6ons Return Quiz 1 Latencies Comparison Numbers L1 Cache 0.5 ns L2 Cache 7 ns 14x L1 cache Main Memory
Q3: Block Replacement. Replacement Algorithms. ECE473 Computer Architecture and Organization. Memory Hierarchy: Set Associative Cache
 Fundamental Questions Computer Architecture and Organization Hierarchy: Set Associative Q: Where can a block be placed in the upper level? (Block placement) Q: How is a block found if it is in the upper
Fundamental Questions Computer Architecture and Organization Hierarchy: Set Associative Q: Where can a block be placed in the upper level? (Block placement) Q: How is a block found if it is in the upper
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. The Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture The Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches Instructor: Alan Christopher 7/09/2014 Summer 2014 -- Lecture #10 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture The Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches Instructor: Alan Christopher 7/09/2014 Summer 2014 -- Lecture #10 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization. More Caches Measuring Performance
 ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 28 More s Measuring Performance Announcements HW7 due tomorrow :59pm Prelab 5(c) due Saturday 3pm Lab 6 (last one) released HW8 (last one) to be released
ECE 23 Digital Logic & Computer Organization Spring 28 More s Measuring Performance Announcements HW7 due tomorrow :59pm Prelab 5(c) due Saturday 3pm Lab 6 (last one) released HW8 (last one) to be released
MEMORY HIERARCHY BASICS. B649 Parallel Architectures and Programming
 MEMORY HIERARCHY BASICS B649 Parallel Architectures and Programming BASICS Why Do We Need Caches? 3 Overview 4 Terminology cache virtual memory memory stall cycles direct mapped valid bit block address
MEMORY HIERARCHY BASICS B649 Parallel Architectures and Programming BASICS Why Do We Need Caches? 3 Overview 4 Terminology cache virtual memory memory stall cycles direct mapped valid bit block address
The levels of a memory hierarchy. Main. Memory. 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms
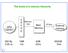 The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
