Memory Hierarchy. Memory Flavors Principle of Locality Program Traces Memory Hierarchies Associativity. (Study Chapter 5)
|
|
|
- Lily Booth
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Memory Hierarchy It makes me look faster, don t you think? Are you dressed like the Easter Bunny? Memory Flavors Principle of Locality Program Traces Memory Hierarchies Associativity (Study Chapter 5) L19 Memory Hierarchy 1
2 What Do We Want in a Memory? minimips PC INST MADDR MDATA Wr ADDR DOUT ADDR DATA R/W MEMORY Capacity Latency Cost Register 1000 s of bits 10 ps $$$$ SRAM 100 s Kbytes 0.2 ns $$$ DRAM 100 s Mbytes 5 ns $ Hard disk* 100 s Gbytes 10 ms Want? * non-volatile 4 Gbyte 0.2 ns cheap L19 Memory Hierarchy 2
3 Tricks for Increasing Throughput Multiplexed Address Col. 1 Col. 2 Col. 3 bit lines word lines The first thing that should pop into you mind when asked to speed up a digital design N Row Address Decoder Col. 2 M Row 1 Row 2 Row 2 N PIPELINING Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM) ($10 per Gbyte) N Column Multiplexer/Shifter memory cell (one bit) Double Data Rate Synchronous DRAM (DDR) Clock t 1 t 2 t 3 t 4 D Data out L19 Memory Hierarchy 3
4 Hard Disk Drives Typical high-end drive: Average latency = 4 ms (7200 rpm) Average seek time = 8.5 ms Transfer rate = 300 Mbytes/s (SATA) Capacity = 1000 G byte Cost = $100 (10 Gbyte) figures from L19 Memory Hierarchy 4
5 Quantity vs Quality Memory systems can be either: BIG and SLOW... or SMALL and FAST. $/GB We ve explored a range of device-design trade-offs SRAM (1000$/GB, 0.2 ns) DRAM (25$/GB, 5 ns) DISK (0.10$/GB, 10 ms) DVD Burner (0.02$/GB, 120ms) Is there an ARCHITECTURAL solution to this DELIMA? Access Time L19 Memory Hierarchy 5
6 Managing Memory via Programming In reality, systems are built with a mixture of all these various memory types SRAM CPU MAIN MEM How do we make the most effective use of each memory? We could push all of these issues off to programmers Keep most frequently used variables and stack in SRAM Keep large data structures (arrays, lists, etc) in DRAM Keep bigger data structures on disk (databases) on DISK It is harder than you think data usage evolves over a program s execution L19 Memory Hierarchy 6
7 Best of Both Worlds What we REALLY want: A BIG, FAST memory! (Keep everything within instant access) We d like to have a memory system that PERFORMS like 2 GBytes of SRAM; but COSTS like 512 MBytes of slow memory. SURPRISE: We can (nearly) get our wish! KEY: Use a hierarchy of memory technologies: SRAM CPU MAIN MEM L19 Memory Hierarchy 7
8 Key IDEA Keep the most often-used data in a small, fast SRAM (often on to CPU chip) Refer to Main Memory only rarely, for remaining data. The reason this strategy works: LOCALITY Locality of Reference: Reference to location X at time t implies that reference to location X+ΔX at time t+δt becomes more probable as ΔX and Δt approach zero. L19 Memory Hierarchy 8
9 Typical Memory Reference Patterns address stack data program MEMORY TRACE A temporal sequence of memory references (addresses) from a real program. TEMPORAL LOCALITY If an item is referenced, it will tend to be referenced again soon SPATIAL LOCALITY If an item is referenced, nearby items will tend to be referenced soon. time L19 Memory Hierarchy 9
10 Working Set address S stack Δ t data program S is the set of locations accessed during Δt. Working set: a set S which changes slowly w.r.t. access time. Working set size, S Δt time L19 Memory Hierarchy 10
11 Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy Approach 1 (Cray, others): Expose Hierarchy Registers, Main Memory, Disk each available as storage alternatives; Tell programmers: Use them cleverly Approach 2: Hide Hierarchy SRAM CPU MAIN MEM Programming model: SINGLE kind of memory, single address space. Machine AUTOMATICALLY assigns locations to fast or slow memory, depending on usage patterns. CPU Small Static Dynamic RAM HARD DISK MAIN MEMORY L19 Memory Hierarchy 11
12 Why We Care CPU performance is dominated by memory performance. More significant than: ISA, circuit optimization, pipelining, super-scalar, etc CPU Small Static Dynamic RAM HARD DISK CACHE MAIN MEMORY VIRTUAL MEMORY SWAP SPACE TRICK #1: How to make slow MAIN MEMORY appear faster than it is. Technique: CACHEING Next 2 Lectures TRICK #2: How to make a small MAIN MEMORY appear bigger than it is. Technique: VIRTUAL MEMORY Lecture after that L19 Memory Hierarchy 12
13 The Cache Idea: Program-Transparent Memory Hierarchy CPU 1.0 (1.0-α) DYNAMIC RAM "CACHE" "MAIN MEMORY" Cache contains TEMPORARY COPIES of selected main memory locations... eg. Mem[100] = 37 GOALS: 1) Improve the average access time α (1-α) HIT RATIO: Fraction of refs found in CACHE. MISS RATIO: Remaining references. Challenge: To make the hit ratio as high as possible. t ave = αt c + (1 α)(t c + t m ) = t c + (1 α)t m 2) Transparency (compatibility, programming ease) Why, on a miss, do I incur the access penalty for both main memory and cache? L19 Memory Hierarchy 13
14 How High of a Hit Ratio? Suppose we can easily build an on-chip static memory with a 800 ps access time, but the fastest dynamic memories that we can buy for main memory have an average access time of 10 ns. How high of a hit rate do we need to sustain an average access time of 1 ns? Solve forα t ave = t c + (1 α)t m α = 1 t t ave c = 1 = 98% t m 10 WOW, a cache really needs to be good? L19 Memory Hierarchy 14
15 The Cache Principle Find Hart, Lee 5-Minute Access Time: 5-Second Access Time: ALGORTHIM: Look on your desk for the requested information first, if its not there check secondary storage L19 Memory Hierarchy 15
16 Basic Cache Algorithm Tag A B CPU Data Mem[A] Mem[B] (1-α) MAIN MEMORY ON REFERENCE TO Mem[X]: Look for X among cache tags... HIT: X = TAG(i), for some cache line i READ: return DATA(i) WRITE: change DATA(i); Start Write to Mem(X) MISS: X not found in TAG of any cache line REPLACEMENT SELECTION: Select some LINE k to hold Mem[X] (Allocation) READ: Read Mem[X] Set TAG(k)=X, DATA(K)=Mem[X] X here is a memory address. WRITE: Start Write to Mem(X) Set TAG(k)=X, DATA(K)= new Mem[X] L19 Memory Hierarchy 16
17 Cache Sits between CPU and main memory Very fast memory that stores TAGs and DATA TAG is the memory address (or part of it) DATA is a copy of memory at the address given by TAG Line 0 Line 1 Line 2 Line Tag Cache Data Memory L19 Memory Hierarchy 17
18 Cache Access On load we compare TAG entries to the ADDRESS we re loading If Found a HIT return the DATA If Not Found a MISS go to memory get the data decide where it goes in the cache, put it and its address (TAG) in the cache Line 0 Line 1 Line 2 Line Tag Cache Data Memory L19 Memory Hierarchy 18
19 How Many Words per Tag? Caches usually get more data than requested (Why?) Each LINE typically stores more than 1 word, bytes (4-16 Words) per line is common A bigger LINE means: 1) fewer misses because of spatial locality 2) fewer TAG bits per DATA bits but bigger LINE means longer time on miss Cache Memory Line 0 Line 1 Line 2 Line Tag Data L19 Memory Hierarchy 19
20 How do we Search the Cache TAGs? Find Hart, Lee Nope, Smith Nope, Jones Associativity: The degree of parallelism used in the lookup of Tags HERE IT IS! Nope, LeVile L19 Memory Hierarchy 20
21 Fully-Associative Cache Incoming Address TAG =? Data The extreme in associatively: All TAGS are searched in parallel TAG =? Data HIT Data items from *any* address can be located in *any* cache line TAG =? Data Data Out L19 Memory Hierarchy 21
22 Find Hart, Lee Direct-Mapped Cache (non-associative) NO Parallelism: Look in JUST ONE place, determined by parameters of incoming request (address bits)... can use ordinary RAM as table Z Y H B A L19 Memory Hierarchy 22
23 Direct-Map Example With 8 byte lines, 3 low-order bits determine the byte within the line With 4 cache lines, the next 2 bits determine which line to use Line 0 Line 1 Line 2 Line d = line = 00 2 = d = line = 01 2 = d = line = 10 2 = 2 10 Cache Tag Data Memory L19 Memory Hierarchy 23
24 Direct Mapping Miss What happens when we now ask for address 1008? = line = 10 2 = 2 10 but earlier we put 1040 there = line = 10 2 = Memory Line 0 Line 1 Line 2 Line 3 Cache Tag Data L19 Memory Hierarchy 24
25 Direct Mapped Cache LOW-COST Leader: Requires only a single comparator and use ordinary (fast) static RAM for cache tags & data: Incoming Address T K K-bit Cache Index K x (T + D)-bit static RAM Tag Data DISADVANTAGE: COLLISIONS T Upper-address bits QUESTION: Why not use HIGH-order bits as the Cache Index? =? HIT Data Out D-bit data word L19 Memory Hierarchy 25
26 A Problem with Collisions Find Heel, Art Find Here, Al T. Find Hart, Lee Nope, I ve got Heel under H PROBLEM: Contention among H s... - CAN T cache both Hart & Heel... Suppose H s tend to come at once? ==> BETTER IDEA: File by LAST letter! Z Y H B L19 Memory Hierarchy 26
27 Cache Questions = Cash Questions What lies between Fully Associate and Direct-Mapped? When I put something new into the cache, what data gets thrown out? How many processor words should there be per tag? When I write to cache, should I also write to memory? What do I do when a write misses cache, should space in cache be allocated for the written address. What if I have INPUT/OUTPUT devices located at certain memory addresses, do we cache them? L19 Memory Hierarchy 27
Memory Hierarchy. Memory Flavors Principle of Locality Program Traces Memory Hierarchies Associativity. (Study Chapter 5)
 Memory Hierarchy Why are you dressed like that? Halloween was weeks ago! It makes me look faster, don t you think? Memory Flavors Principle of Locality Program Traces Memory Hierarchies Associativity (Study
Memory Hierarchy Why are you dressed like that? Halloween was weeks ago! It makes me look faster, don t you think? Memory Flavors Principle of Locality Program Traces Memory Hierarchies Associativity (Study
CPU Pipelining Issues
 CPU Pipelining Issues What have you been beating your head against? This pipe stuff makes my head hurt! L17 Pipeline Issues & Memory 1 Pipelining Improve performance by increasing instruction throughput
CPU Pipelining Issues What have you been beating your head against? This pipe stuff makes my head hurt! L17 Pipeline Issues & Memory 1 Pipelining Improve performance by increasing instruction throughput
6.004 Computation Structures Spring 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.4 Computation Structures Spring 9 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. The Memory Hierarchy What we
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.4 Computation Structures Spring 9 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. The Memory Hierarchy What we
The Memory Hierarchy. Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. April 3, 2018 L13-1
 The Memory Hierarchy Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. April 3, 2018 L13-1 Memory Technologies Technologies have vastly different tradeoffs between capacity, latency,
The Memory Hierarchy Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. April 3, 2018 L13-1 Memory Technologies Technologies have vastly different tradeoffs between capacity, latency,
The Memory Hierarchy. Silvina Hanono Wachman Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T.
 The Memory Hierarchy Silvina Hanono Wachman Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L13-1 Memory Technologies Technologies have vastly different tradeoffs between capacity, latency, bandwidth,
The Memory Hierarchy Silvina Hanono Wachman Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L13-1 Memory Technologies Technologies have vastly different tradeoffs between capacity, latency, bandwidth,
EEC 170 Computer Architecture Fall Cache Introduction Review. Review: The Memory Hierarchy. The Memory Hierarchy: Why Does it Work?
 EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/73/69213006.jpg) CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
LECTURE 11. Memory Hierarchy
 LECTURE 11 Memory Hierarchy MEMORY HIERARCHY When it comes to memory, there are two universally desirable properties: Large Size: ideally, we want to never have to worry about running out of memory. Speed
LECTURE 11 Memory Hierarchy MEMORY HIERARCHY When it comes to memory, there are two universally desirable properties: Large Size: ideally, we want to never have to worry about running out of memory. Speed
Caches. Han Wang CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University. See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes)
 Caches Han Wang CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes) This week: Announcements PA2 Work-in-progress submission Next six weeks: Two labs and two projects
Caches Han Wang CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes) This week: Announcements PA2 Work-in-progress submission Next six weeks: Two labs and two projects
Memory. Lecture 22 CS301
 Memory Lecture 22 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (11/13) at 8am HW #8 due today at 5pm Program #2 due Friday, 11/16 at 11:59pm Test #2 Wednesday Pipelined Machine Fetch
Memory Lecture 22 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (11/13) at 8am HW #8 due today at 5pm Program #2 due Friday, 11/16 at 11:59pm Test #2 Wednesday Pipelined Machine Fetch
Page 1. Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash )
 Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Review: Performance Latency vs. Throughput. Time (seconds/program) is performance measure Instructions Clock cycles Seconds.
 Performance 980 98 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 99 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 2000 7/4/20 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Instructor: Michael Greenbaum
Performance 980 98 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 99 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 2000 7/4/20 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Instructor: Michael Greenbaum
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal locality Items accessed recently are likely to
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal locality Items accessed recently are likely to
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Direct Mapped Caches
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct Mapped Caches Instructor: Justin Hsia 7/05/2012 Summer 2012 Lecture #11 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single and double precision) approximates
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Direct Mapped Caches Instructor: Justin Hsia 7/05/2012 Summer 2012 Lecture #11 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single and double precision) approximates
CPS101 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 13: The Memory System. Outline of Today s Lecture. The Big Picture: Where are We Now?
 cps 14 memory.1 RW Fall 2 CPS11 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 13 The System Robert Wagner Outline of Today s Lecture System the BIG Picture? Technology Technology DRAM A Real Life Example
cps 14 memory.1 RW Fall 2 CPS11 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 13 The System Robert Wagner Outline of Today s Lecture System the BIG Picture? Technology Technology DRAM A Real Life Example
CSE 2021: Computer Organization
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-12a Caches-1 The basics of caches Shakil M. Khan Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-12a Caches-1 The basics of caches Shakil M. Khan Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB
Chapter 5. Memory Technology
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Memory. Objectives. Introduction. 6.2 Types of Memory
 Memory Objectives Master the concepts of hierarchical memory organization. Understand how each level of memory contributes to system performance, and how the performance is measured. Master the concepts
Memory Objectives Master the concepts of hierarchical memory organization. Understand how each level of memory contributes to system performance, and how the performance is measured. Master the concepts
Chapter Seven. Memories: Review. Exploiting Memory Hierarchy CACHE MEMORY AND VIRTUAL MEMORY
 Chapter Seven CACHE MEMORY AND VIRTUAL MEMORY 1 Memories: Review SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors) DRAM: value is stored
Chapter Seven CACHE MEMORY AND VIRTUAL MEMORY 1 Memories: Review SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors) DRAM: value is stored
Cache Structure. Replacement policies Overhead Implementation Handling writes Cache simulations. Comp 411. L18-Cache Structure 1
 Cache Structure Replacement policies Overhead Implementation Handling writes Cache simulations L18-Cache Structure 1 Tag A CPU Data Mem[A] Basic Caching Algorithm ON REFERENCE TO Mem[X]: Look for X among
Cache Structure Replacement policies Overhead Implementation Handling writes Cache simulations L18-Cache Structure 1 Tag A CPU Data Mem[A] Basic Caching Algorithm ON REFERENCE TO Mem[X]: Look for X among
The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory
 The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University The Simple View of Memory The simplest view
The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University The Simple View of Memory The simplest view
CSE 2021: Computer Organization
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-12 Caches-1 The basics of caches Shakil M. Khan Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-12 Caches-1 The basics of caches Shakil M. Khan Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB
EN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 06: Memory System
 EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
Key Point. What are Cache lines
 Caching 1 Key Point What are Cache lines Tags Index offset How do we find data in the cache? How do we tell if it s the right data? What decisions do we need to make in designing a cache? What are possible
Caching 1 Key Point What are Cache lines Tags Index offset How do we find data in the cache? How do we tell if it s the right data? What decisions do we need to make in designing a cache? What are possible
Multilevel Memories. Joel Emer Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 1 Multilevel Memories Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Based on the material prepared by Krste Asanovic and Arvind CPU-Memory Bottleneck 6.823
1 Multilevel Memories Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Based on the material prepared by Krste Asanovic and Arvind CPU-Memory Bottleneck 6.823
Announcement. Computer Architecture (CSC-3501) Lecture 20 (08 April 2008) Chapter 6 Objectives. 6.1 Introduction. 6.
 Announcement Computer Architecture (CSC-350) Lecture 0 (08 April 008) Seung-Jong Park (Jay) http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~sjpark Chapter 6 Objectives 6. Introduction Master the concepts of hierarchical memory
Announcement Computer Architecture (CSC-350) Lecture 0 (08 April 008) Seung-Jong Park (Jay) http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~sjpark Chapter 6 Objectives 6. Introduction Master the concepts of hierarchical memory
LECTURE 10: Improving Memory Access: Direct and Spatial caches
 EECS 318 CAD Computer Aided Design LECTURE 10: Improving Memory Access: Direct and Spatial caches Instructor: Francis G. Wolff wolff@eecs.cwru.edu Case Western Reserve University This presentation uses
EECS 318 CAD Computer Aided Design LECTURE 10: Improving Memory Access: Direct and Spatial caches Instructor: Francis G. Wolff wolff@eecs.cwru.edu Case Western Reserve University This presentation uses
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture. Memory Hierarchy
 ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Hierarchy ECE468 memory.1 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Control Input Datapath Output Today s Topic:
ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture Hierarchy ECE468 memory.1 The Big Picture: Where are We Now? The Five Classic Components of a Computer Processor Control Input Datapath Output Today s Topic:
Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science. TDT4255 Memory hierarchies
 TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
CpE 442. Memory System
 CpE 442 Memory System CPE 442 memory.1 Outline of Today s Lecture Recap and Introduction (5 minutes) Memory System: the BIG Picture? (15 minutes) Memory Technology: SRAM and Register File (25 minutes)
CpE 442 Memory System CPE 442 memory.1 Outline of Today s Lecture Recap and Introduction (5 minutes) Memory System: the BIG Picture? (15 minutes) Memory Technology: SRAM and Register File (25 minutes)
CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1
 CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall 2008 Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1 Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson
CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall 2008 Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1 Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson
EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits. Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver. Lecture 19: Caches EE141
 EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver Lecture 19: Caches Cache Introduction 40% of this ARM CPU is devoted to SRAM cache. But the role
EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver Lecture 19: Caches Cache Introduction 40% of this ARM CPU is devoted to SRAM cache. But the role
Chapter 5A. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5A Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) Fast, expensive Dynamic RAM (DRAM) In between Magnetic disk Slow, inexpensive Ideal memory Access time of SRAM
Chapter 5A Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) Fast, expensive Dynamic RAM (DRAM) In between Magnetic disk Slow, inexpensive Ideal memory Access time of SRAM
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Cache Structure. Replacement policies Overhead Implementation Handling writes Cache simulations. Comp 411. L15-Cache Structure 1
 Cache Structure Replacement policies Overhead Implementation Handling writes Cache simulations L15-Cache Structure 1 Tag A CPU Data Mem[A] Basic Caching Algorithm ON REFERENCE TO Mem[X]: Look for X among
Cache Structure Replacement policies Overhead Implementation Handling writes Cache simulations L15-Cache Structure 1 Tag A CPU Data Mem[A] Basic Caching Algorithm ON REFERENCE TO Mem[X]: Look for X among
Memory Hierarchy Y. K. Malaiya
 Memory Hierarchy Y. K. Malaiya Acknowledgements Computer Architecture, Quantitative Approach - Hennessy, Patterson Vishwani D. Agrawal Review: Major Components of a Computer Processor Control Datapath
Memory Hierarchy Y. K. Malaiya Acknowledgements Computer Architecture, Quantitative Approach - Hennessy, Patterson Vishwani D. Agrawal Review: Major Components of a Computer Processor Control Datapath
Memory hierarchy and cache
 Memory hierarchy and cache QUIZ EASY 1). What is used to design Cache? a). SRAM b). DRAM c). Blend of both d). None. 2). What is the Hierarchy of memory? a). Processor, Registers, Cache, Tape, Main memory,
Memory hierarchy and cache QUIZ EASY 1). What is used to design Cache? a). SRAM b). DRAM c). Blend of both d). None. 2). What is the Hierarchy of memory? a). Processor, Registers, Cache, Tape, Main memory,
EEC 483 Computer Organization
 EEC 483 Computer Organization Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Chansu Yu Table of Contents Ch.1 Introduction Ch. 2 Instruction: Machine Language Ch. 3-4 CPU Implementation Ch. 5 Cache
EEC 483 Computer Organization Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Chansu Yu Table of Contents Ch.1 Introduction Ch. 2 Instruction: Machine Language Ch. 3-4 CPU Implementation Ch. 5 Cache
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17: Cache System
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17 System March 17, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http//http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17 System March 17, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http//http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
Memory hierarchy Outline
 Memory hierarchy Outline Performance impact Principles of memory hierarchy Memory technology and basics 2 Page 1 Performance impact Memory references of a program typically determine the ultimate performance
Memory hierarchy Outline Performance impact Principles of memory hierarchy Memory technology and basics 2 Page 1 Performance impact Memory references of a program typically determine the ultimate performance
Cycle Time for Non-pipelined & Pipelined processors
 Cycle Time for Non-pipelined & Pipelined processors Fetch Decode Execute Memory Writeback 250ps 350ps 150ps 300ps 200ps For a non-pipelined processor, the clock cycle is the sum of the latencies of all
Cycle Time for Non-pipelined & Pipelined processors Fetch Decode Execute Memory Writeback 250ps 350ps 150ps 300ps 200ps For a non-pipelined processor, the clock cycle is the sum of the latencies of all
Contents. Memory System Overview Cache Memory. Internal Memory. Virtual Memory. Memory Hierarchy. Registers In CPU Internal or Main memory
 Memory Hierarchy Contents Memory System Overview Cache Memory Internal Memory External Memory Virtual Memory Memory Hierarchy Registers In CPU Internal or Main memory Cache RAM External memory Backing
Memory Hierarchy Contents Memory System Overview Cache Memory Internal Memory External Memory Virtual Memory Memory Hierarchy Registers In CPU Internal or Main memory Cache RAM External memory Backing
Chapter 5B. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5B Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy One Transistor Dynamic RAM 1-T DRAM Cell word access transistor V REF TiN top electrode (V REF ) Ta 2 O 5 dielectric bit Storage capacitor (FET gate,
Chapter 5B Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy One Transistor Dynamic RAM 1-T DRAM Cell word access transistor V REF TiN top electrode (V REF ) Ta 2 O 5 dielectric bit Storage capacitor (FET gate,
Chapter 6 Objectives
 Chapter 6 Memory Chapter 6 Objectives Master the concepts of hierarchical memory organization. Understand how each level of memory contributes to system performance, and how the performance is measured.
Chapter 6 Memory Chapter 6 Objectives Master the concepts of hierarchical memory organization. Understand how each level of memory contributes to system performance, and how the performance is measured.
Modern Computer Architecture
 Modern Computer Architecture Lecture3 Review of Memory Hierarchy Hongbin Sun 国家集成电路人才培养基地 Xi an Jiaotong University Performance 1000 Recap: Who Cares About the Memory Hierarchy? Processor-DRAM Memory Gap
Modern Computer Architecture Lecture3 Review of Memory Hierarchy Hongbin Sun 国家集成电路人才培养基地 Xi an Jiaotong University Performance 1000 Recap: Who Cares About the Memory Hierarchy? Processor-DRAM Memory Gap
Caches. Jin-Soo Kim Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Caches Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns
Caches Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface. 5 th. Edition. Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address
Textbook: Burdea and Coiffet, Virtual Reality Technology, 2 nd Edition, Wiley, Textbook web site:
 Textbook: Burdea and Coiffet, Virtual Reality Technology, 2 nd Edition, Wiley, 2003 Textbook web site: www.vrtechnology.org 1 Textbook web site: www.vrtechnology.org Laboratory Hardware 2 Topics 14:332:331
Textbook: Burdea and Coiffet, Virtual Reality Technology, 2 nd Edition, Wiley, 2003 Textbook web site: www.vrtechnology.org 1 Textbook web site: www.vrtechnology.org Laboratory Hardware 2 Topics 14:332:331
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache
 Removing The Ideal Memory Assumption: The Memory Hierarchy & Cache The impact of real memory on CPU Performance. Main memory basic properties: Memory Types: DRAM vs. SRAM The Motivation for The Memory
Removing The Ideal Memory Assumption: The Memory Hierarchy & Cache The impact of real memory on CPU Performance. Main memory basic properties: Memory Types: DRAM vs. SRAM The Motivation for The Memory
Memory Technology. Chapter 5. Principle of Locality. Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy 1
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy 5 th Edition Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy 5 th Edition Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic
Caching Basics. Memory Hierarchies
 Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ Components of a Computer Processor
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ Components of a Computer Processor
Module 1: Basics and Background Lecture 4: Memory and Disk Accesses. The Lecture Contains: Memory organisation. Memory hierarchy. Disks.
 The Lecture Contains: Memory organisation Example of memory hierarchy Memory hierarchy Disks Disk access Disk capacity Disk access time Typical disk parameters Access times file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture4/4_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Memory organisation Example of memory hierarchy Memory hierarchy Disks Disk access Disk capacity Disk access time Typical disk parameters Access times file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture4/4_1.htm[6/14/2012
Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches. Instructor: Nick Riasanovsky
 Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches Instructor: Nick Riasanovsky Review Hazards reduce effectiveness of pipelining Cause stalls/bubbles Structural Hazards Conflict in use of datapath component Data
Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches Instructor: Nick Riasanovsky Review Hazards reduce effectiveness of pipelining Cause stalls/bubbles Structural Hazards Conflict in use of datapath component Data
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design. Lecture 08: Cache Review. Bei Yu
 CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Cache Review Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 A Typical Memory Hierarchy q Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Cache Review Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 A Typical Memory Hierarchy q Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as
Memory Technology. Caches 1. Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Magnetic disk. Ideal memory. 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB
 Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
UCB CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 14 Caches III Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia Google Glass may be one vision of the future of post-pc interfaces augmented reality with video
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 14 Caches III Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia Google Glass may be one vision of the future of post-pc interfaces augmented reality with video
Memory Hierarchies. Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev. Fall Lecture 10, October 8, CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology
 Memory Hierarchies Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev Fall 2007 CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology Lecture 10, October 8, 2007 Memories SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast
Memory Hierarchies Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev Fall 2007 CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology Lecture 10, October 8, 2007 Memories SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast
Memory Hierarchy. ENG3380 Computer Organization and Architecture Cache Memory Part II. Topics. References. Memory Hierarchy
 ENG338 Computer Organization and Architecture Part II Winter 217 S. Areibi School of Engineering University of Guelph Hierarchy Topics Hierarchy Locality Motivation Principles Elements of Design: Addresses
ENG338 Computer Organization and Architecture Part II Winter 217 S. Areibi School of Engineering University of Guelph Hierarchy Topics Hierarchy Locality Motivation Principles Elements of Design: Addresses
registers data 1 registers MEMORY ADDRESS on-chip cache off-chip cache main memory: real address space part of virtual addr. sp.
 13 1 CMPE110 Computer Architecture, Winter 2009 Andrea Di Blas 110 Winter 2009 CMPE Cache Direct-mapped cache Reads and writes Cache associativity Cache and performance Textbook Edition: 7.1 to 7.3 Third
13 1 CMPE110 Computer Architecture, Winter 2009 Andrea Di Blas 110 Winter 2009 CMPE Cache Direct-mapped cache Reads and writes Cache associativity Cache and performance Textbook Edition: 7.1 to 7.3 Third
Lecture 12. Memory Design & Caches, part 2. Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University
 Lecture 12 Memory Design & Caches, part 2 Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements HW3 is due today PA2 is available on-line today Part 1 is due on 2/27
Lecture 12 Memory Design & Caches, part 2 Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements HW3 is due today PA2 is available on-line today Part 1 is due on 2/27
Lecture 16. Today: Start looking into memory hierarchy Cache$! Yay!
 Lecture 16 Today: Start looking into memory hierarchy Cache$! Yay! Note: There are no slides labeled Lecture 15. Nothing omitted, just that the numbering got out of sequence somewhere along the way. 1
Lecture 16 Today: Start looking into memory hierarchy Cache$! Yay! Note: There are no slides labeled Lecture 15. Nothing omitted, just that the numbering got out of sequence somewhere along the way. 1
CENG3420 Lecture 08: Memory Organization
 CENG3420 Lecture 08: Memory Organization Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk (Latest update: February 22, 2018) Spring 2018 1 / 48 Overview Introduction Random Access Memory (RAM) Interleaving Secondary Memory
CENG3420 Lecture 08: Memory Organization Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk (Latest update: February 22, 2018) Spring 2018 1 / 48 Overview Introduction Random Access Memory (RAM) Interleaving Secondary Memory
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Review: Major Components of a Computer Processor Devices Control Memory Input Datapath Output Secondary Memory (Disk) Main Memory Cache Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Review: Major Components of a Computer Processor Devices Control Memory Input Datapath Output Secondary Memory (Disk) Main Memory Cache Performance
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. The Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture The Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches Instructor: Alan Christopher 7/09/2014 Summer 2014 -- Lecture #10 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture The Memory Hierarchy, Fully Associative Caches Instructor: Alan Christopher 7/09/2014 Summer 2014 -- Lecture #10 1 Review of Last Lecture Floating point (single
Memory Hierarchy. Maurizio Palesi. Maurizio Palesi 1
 Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching
 CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2016 Reminder: Memory Hierarchy L0: Registers CPU registers hold words retrieved from L1 cache Smaller, faster,
CMPSC 311- Introduction to Systems Programming Module: Caching Professor Patrick McDaniel Fall 2016 Reminder: Memory Hierarchy L0: Registers CPU registers hold words retrieved from L1 cache Smaller, faster,
Memory Hierarchy. Maurizio Palesi. Maurizio Palesi 1
 Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review. UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016
 Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016 1 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only 10-20% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS240A, Winter 2016 1 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only 10-20% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss
ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 7: Memory Organization Part II
 ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 7: Organization Part II Ujjwal Guin, Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn,
ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 7: Organization Part II Ujjwal Guin, Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn,
Course Administration
 Spring 207 EE 363: Computer Organization Chapter 5: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy - Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 4570
Spring 207 EE 363: Computer Organization Chapter 5: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy - Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 4570
Computer Organization and Structure. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
EN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 06: Memory System
 EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY
 LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.5 Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal
LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.5 Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal
CENG4480 Lecture 09: Memory 1
 CENG4480 Lecture 09: Memory 1 Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk (Latest update: November 8, 2017) Fall 2017 1 / 37 Overview Introduction Memory Principle Random Access Memory (RAM) Non-Volatile Memory Conclusion
CENG4480 Lecture 09: Memory 1 Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk (Latest update: November 8, 2017) Fall 2017 1 / 37 Overview Introduction Memory Principle Random Access Memory (RAM) Non-Volatile Memory Conclusion
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 16: Memory System
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 16: System March 15, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http://http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 16: System March 15, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http://http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
V. Primary & Secondary Memory!
 V. Primary & Secondary Memory! Computer Architecture and Operating Systems & Operating Systems: 725G84 Ahmed Rezine 1 Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
V. Primary & Secondary Memory! Computer Architecture and Operating Systems & Operating Systems: 725G84 Ahmed Rezine 1 Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
MEMORY. Objectives. L10 Memory
 MEMORY Reading: Chapter 6, except cache implementation details (6.4.1-6.4.6) and segmentation (6.5.5) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/probability 2 Objectives Understand the concepts and terminology of hierarchical
MEMORY Reading: Chapter 6, except cache implementation details (6.4.1-6.4.6) and segmentation (6.5.5) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/probability 2 Objectives Understand the concepts and terminology of hierarchical
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design
 ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 21: Memory Hierarchy Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Ideally, computer memory would be large and fast
ECE232: Hardware Organization and Design Lecture 21: Memory Hierarchy Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, UCB Overview Ideally, computer memory would be large and fast
1" 0" d" c" b" a" ...! ! Benefits of Larger Block Size. " Very applicable with Stored-Program Concept " Works well for sequential array accesses
 Asst. Proflecturer SOE Miki Garcia inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 14 Caches III WHEN FIBER OPTICS IS TOO SLOW 07/16/2014: Wall Street Buys NATO Microwave Towers in
Asst. Proflecturer SOE Miki Garcia inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 14 Caches III WHEN FIBER OPTICS IS TOO SLOW 07/16/2014: Wall Street Buys NATO Microwave Towers in
14:332:331. Week 13 Basics of Cache
 14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Fall 2003 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Lec20.1 Fall 2003 Head
14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Fall 2003 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Lec20.1 Fall 2003 Head
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Lecture 7: Memory Hierarchy and Caches Dr. Ahmed Sallam Suez Canal University Spring 2015 Based on original slides by Prof. Onur Mutlu Memory (Programmer s View) 2 Abstraction: Virtual
Computer Architecture Lecture 7: Memory Hierarchy and Caches Dr. Ahmed Sallam Suez Canal University Spring 2015 Based on original slides by Prof. Onur Mutlu Memory (Programmer s View) 2 Abstraction: Virtual
CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems. Cache $$$$$
 CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems Cache $$$$$ Memory Systems! How can we supply the CPU with enough data to keep it busy?! We will focus on memory issues,! which are frequently bottlenecks
CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems Cache $$$$$ Memory Systems! How can we supply the CPU with enough data to keep it busy?! We will focus on memory issues,! which are frequently bottlenecks
Memory Hierarchies &
 Memory Hierarchies & Cache Memory CSE 410, Spring 2009 Computer Systems http://www.cs.washington.edu/410 4/26/2009 cse410-13-cache 2006-09 Perkins, DW Johnson and University of Washington 1 Reading and
Memory Hierarchies & Cache Memory CSE 410, Spring 2009 Computer Systems http://www.cs.washington.edu/410 4/26/2009 cse410-13-cache 2006-09 Perkins, DW Johnson and University of Washington 1 Reading and
10/11/17. New-School Machine Structures. Review: Single Cycle Instruction Timing. Review: Single-Cycle RISC-V RV32I Datapath. Components of a Computer
 // CS C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) s Part Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~csc/ // Fall - Lecture # Parallel Requests Assigned to computer
// CS C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) s Part Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H Katz http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~csc/ // Fall - Lecture # Parallel Requests Assigned to computer
Caches. Hiding Memory Access Times
 Caches Hiding Memory Access Times PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O N T R O L ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH INSTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMORY
Caches Hiding Memory Access Times PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O N T R O L ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH INSTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMORY
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350):
 The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350): Motivation for The Memory Hierarchy: { CPU/Memory Performance Gap The Principle Of Locality Cache $$$$$ Cache Basics:
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350): Motivation for The Memory Hierarchy: { CPU/Memory Performance Gap The Principle Of Locality Cache $$$$$ Cache Basics:
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review. UCSB CS240A, Fall 2017
 Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS24A, Fall 27 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only - 2% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss is in the
Caches and Memory Hierarchy: Review UCSB CS24A, Fall 27 Motivation Most applications in a single processor runs at only - 2% of the processor peak Most of the single processor performance loss is in the
Lecture-14 (Memory Hierarchy) CS422-Spring
 Lecture-14 (Memory Hierarchy) CS422-Spring 2018 Biswa@CSE-IITK The Ideal World Instruction Supply Pipeline (Instruction execution) Data Supply - Zero-cycle latency - Infinite capacity - Zero cost - Perfect
Lecture-14 (Memory Hierarchy) CS422-Spring 2018 Biswa@CSE-IITK The Ideal World Instruction Supply Pipeline (Instruction execution) Data Supply - Zero-cycle latency - Infinite capacity - Zero cost - Perfect
UCB CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 14 Caches III Asst. Proflecturer SOE Miki Garcia WHEN FIBER OPTICS IS TOO SLOW 07/16/2014: Wall Street Buys NATO Microwave Towers in
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c UCB CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 14 Caches III Asst. Proflecturer SOE Miki Garcia WHEN FIBER OPTICS IS TOO SLOW 07/16/2014: Wall Street Buys NATO Microwave Towers in
Memory Hierarchy. Mehran Rezaei
 Memory Hierarchy Mehran Rezaei What types of memory do we have? Registers Cache (Static RAM) Main Memory (Dynamic RAM) Disk (Magnetic Disk) Option : Build It Out of Fast SRAM About 5- ns access Decoders
Memory Hierarchy Mehran Rezaei What types of memory do we have? Registers Cache (Static RAM) Main Memory (Dynamic RAM) Disk (Magnetic Disk) Option : Build It Out of Fast SRAM About 5- ns access Decoders
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
 EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
Registers. Instruction Memory A L U. Data Memory C O N T R O L M U X A D D A D D. Sh L 2 M U X. Sign Ext M U X ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH
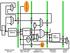 PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O T R O L ALU CTL ISTRUCTIO FETCH ISTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMOR ACCESS WRITE BACK A D D A D D A L U
PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O T R O L ALU CTL ISTRUCTIO FETCH ISTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMOR ACCESS WRITE BACK A D D A D D A L U
www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/
 CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 34 - Caches II 11/16/2007 John Wawrzynek (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~johnw) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 1 What to do on a write hit? Two Options: Write-through update
CS61C Machine Structures Lecture 34 - Caches II 11/16/2007 John Wawrzynek (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~johnw) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 1 What to do on a write hit? Two Options: Write-through update
Caches Part 1. Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger. School of Information Science and Technology SIST
 CS 110 Computer Architecture Caches Part 1 Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on UC Berkley's
CS 110 Computer Architecture Caches Part 1 Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on UC Berkley's
Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory
 Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory Readings: 5.1-5.4, 5.8 Big memories are slow Computer Fast memories are small Processor Memory Devices Control Input Datapath Output Need to get fast, big memories
Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory Readings: 5.1-5.4, 5.8 Big memories are slow Computer Fast memories are small Processor Memory Devices Control Input Datapath Output Need to get fast, big memories
COMP 3221: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems
 COMP 3: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems Lectures 7: Cache Memory - III http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs3 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session, 5 Outline Fully Associative Cache N-Way Associative Cache Block Replacement
COMP 3: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems Lectures 7: Cache Memory - III http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs3 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session, 5 Outline Fully Associative Cache N-Way Associative Cache Block Replacement
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/11/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #14 1 Parallel
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Caches Part 1 Instructors: Krste Asanović & Randy H. Katz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/ 10/11/17 Fall 2017 - Lecture #14 1 Parallel
