beestanbul RoboCup 3D Simulation League Team Description Paper 2011
|
|
|
- Dylan Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 beestanbul RoboCup 3D Simulation League Team Description Paper 2011 Shahriar Asta, Tuna Sonmez, Onuralp Ulusoy, Alper Alimoglu, Mustafa Ersen, Ozdemir Sozmen, and Sanem Sariel-Talay Artificial Intelligence and Robotics Laboratory Istanbul Technical University Computer Engineering Department Istanbul, TURKEY Abstract. The main objective of the beestanbul project is to develop an efficient software system to correctly model the behaviors of simulated Nao robots in a competitive environment. Several AI algorithms are being used and developed for contributing to robotics research while also advancing the quality of competitions in 3D Simulation League. This team description paper presents important aspects of the overall system design and outlines the methods used in different modules. 1 Introduction The beestanbul project from the Artificial Intelligence and Robotics laboratory (AIR lab) at Istanbul Technical University (ITU) is the first initiative from ITU to participate in RoboCup competitions. Earlier projects in the AIR lab were mainly on cooperative multirobot systems. This challenging project was initiated in 2009 to apply the experience, gained from earlier research on multirobot systems [1 3], to competitive environments as well. The beestanbul team consists of undergraduate and graduate students from the Computer Engineering Department of ITU. The main goal of the team is to contribute for the main objective of the RoboCup project by an efficient design of a software system which will be successful during the main competition. The designed software system serves as a basis to apply several high-level intelligence, reasoning and learning methods. beestanbul team participated in the RoboCup 2010 competitions for the first time and had a change to score several goals during the competitions. The software architecture of the system has been revised and several promising motion types have already been developed since With the completion of the high-level modules, the team is expected to achieve the project s main goal. The organization of the rest of the paper is as follows. Section 2 presents the software system architecture for simulated Nao robots in the SimSpark simulation environment. Motions and behaviors available for an agent are presented in
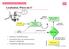
2 Sections 3 and 4 respectively. The developed team-strategy and planning methods are discussed in Section 5, followed by the conclusion in Section 6. 2 System Architecture The overall software system consists of several modules that interact with each other (Fig. 1). The Server Layer perfoms a two-way communication with the SimSpark server, decodes incoming messages and encodes outgoing messages. In order to carry out these operations, the SimSpark utilities and rcssnet library, provided by SimSpark, are used. Fig. 1. Overall Software Architecture The Agent Layer is responsible for performing the main functionalities of a robot. Each agent maintains its own world model for the environment and the agent model for its own state. The Localization module is responsible for determining the correct pose of the robot given an observation history. Localization
3 is performed by using Monte Carlo Localization Algorithm [4]. A short term memory (in accordance with the observation history) of the robot is maintained by ten consecutive frames in the world model. The Vision module is responsible for determining the positions of the observed objects in the environment. Based on the observation history, a semantic analysis of the objects (including the opponents) and predictions are made. The robot decides on a behavior based on its agent and world models, the selected team strategy and the assigned role for itself. The motion command for the corresponding behavior is sent to the Server Layer to generate the desired effect. Simultaneously, either informative or query messages might be sent to teammates based on the selected team role. The planner for the goalie is different than that of the field players. 3 Motions Robots use seven main body motion types for scoring or keeping a goal. These include straight walks (e.g., forward and side walk), diagonal walk, inward and outward turn, rotate, stand-up and kick. The first five motion types basically use the same approach with an oscillatory behavior while the last two have different phases during their executions. There are three head motions which can be executed simultaneously with the body motions. These include track object, search and reset. 3.1 Motions in Coronal Plane The Partial Fourier Series (PFS) model is used for motions in coronal plane. The PFS model is previously developed by [5] for the forward walk motion of a simulated Nao robot. The PFS model decomposes a bipedal walk periodic function into a set of oscillators. Each oscillator has four components namely, offset, amplitude, period and phase delay. The period is common for all the oscillators to maintain synchronization among all the joints of the robot. The general formulation is given as follows: JointValue = C +A sin((2 π t)/t +φ) (1) where C is the offset, A is the amplitude, T is the period and φ is the phase delay. Joint angular velocities are then set to: Joint = (targetangle currentangle) speed (2) In order to achieve the desired gait quality, speed and stability for each motion type, one needs to find the optimal parameter values for each component of the oscillator. In our work, this has been achieved [6] through applying natureinspired algorithms, mainly, Genetic Algorithm and Simulated Annealing. Simulated Annealing with restarts (SAR), in particular has a better performance in comparison to the original Simulated Annealing or Genetic Algorithm. Therefore, the best parameters are obtained by using SAR. These best parameters produce the desired motion trajectories for each walk motion (Figure 2).
4 Fig. 2. Two optimized motions in coronal plane: (left) sidewalk, (right) diagonal walk The objective of the optimization process is to produce the desired motion, with minimum deviation from the expected trajectory, maximum speed and stability. Our experiments show that the PFS model can be applied to produce motion types in coronal plane for a simulated NAO humanoid robot. All the motion types are then integrated, through a motion transition procedure which performs the necessary calculations to smoothly switch between two arbitrary motion types. Also, the motion model provides odometry data which is then used as a measurement step in localization. Forward kinematics model has been used to find the location of the foot end-effector with respect to torso. Mathematical simplicity of the PFS model helps finding the step length and height. Together with localization methods like Monte Carlo Localization, odometry provides a reliable source of location information even when there are no observed landmarks. 3.2 Kick The kick motion involves four phases, namely, expansion, preparation, execution and wrap-around. In all these phases, the support leg is shifted outwards in order to provide space and stability for the action. Some oscillations are then assigned to each joint of the kicking foot at each phase. In the expansion phase, the kicking leg moves along the y axis and is raised from the ground. In the preparation phase, the kicking leg is moved backwards along robot s x axis. The purpose is to gather adequate kicking force. In the execution phase, a value is assignedto each joint angle and the angularvelocityis set to its maximum value. This way, the leg is moved with maximum force and speed towards the ball. Finally, in the wrap-around phase, after the ball is kicked, the robot puts both support and kicking legs to their initial positions. Particle Swarm Optimization [7] method has been employed to optimize the parameters of kick motion and necessary joint values at each phase. The future work includes a new learning method for kick motion with a generic alignment approach.
5 4 Behaviors There is a layered motion selection architecture for motions, behaviors, plans and cases in the team strategy. Modularity and ease of maintenance could be achieved by using such a hierarchy. While motions operate on the lowest level, behaviors are constucted as sequences of low-level motions. Some behavior examples include move-to-target, turn-to-target and dribble-to-target. On top of these behaviors, static plans are constructed in the form of behavior sequences. The team strategy component uses these plans in a modular way. A sample instantiation of a plan is given in Figure 3. attacker attacker plans dribble-to-goal behaviors move-to-target dribble-to-target kick-to-goal turn in diagonal walk motions turn out turn a- ball side walk forward walk backward walk dribble stop Fig. 3. A sample instantiation of the dribble-to-goal plan. 5 Team Strategy and Planning Since one of the players is directly assigned to the goalie role, it has its own strategy as a FSM. The roles of the remaining robots are determined based on the Case Base Reasoning (CBR) method [8]. In each case, a play-based [9] high-level behavior selection is performed. A case represents a world situation, the corresponding role assignment and the behavior sequences for these roles. Since the environment is distributed in nature and the available information for a robot is limited with its own view, a distributed implementation of CBR is developed. Behavior sequences represent the behaviors of the agents who are represented in the case. Due to noise and uncertainty in the environment, rather than considering single points of positions, an abstraction is made for the locations. A limited number of cases are hand-coded and new cases are derived during a game. Case-based strategy algorithm runs on the robot which has the attacker role. A standing robot that is closest to ball becomes the attacker.
6 Two different planning methods will also be developed and integreted into the CBR framework. One of them uses a Hierarchical Task Network (HTN) approach [10] and the other models the problem as a DEC-POMDP and solves it by using dynamic programming approach [11]. 6 Conclusion This team description report outlines different parts of the developed software system for beestanbul robots. The beestanbul is an ongoing project and the low-level modules of the architecture were designed and implemented. The future focus will be on the use of efficient planning and team strategies and the integration of learning capabilities for robots. References 1. Sariel, S.: An Integrated Planning, Scheduling and Execution Framework for Multi- Robot Cooperation and Coordination. Phd thesis, Istanbul Technical University, Turkey (2007) 2. Sariel, S., Balch, T., Erdogan, N.: Multiple traveling robot problem: A solution based on dynamic task selection and robust execution. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics 14(2) (2009) Sariel, S., Balch, T., Erdogan, N.: Naval mine countermeasure missions: A distributed, incremental multirobot task selection scheme. IEEE Robotics and Automation Magazine 15(1) (2008) Thrun, S., Fox, D., Burgard, W., Dallaert, F.: Robust monte carlo localization for mobile robots. Artif. Intell. 128 (May 2001) Picado, H., Gestal, M., Lau, N., Reis, L.P., Tomé, A.M.: Automatic generation of biped walk behavior using genetic algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Work-Conference on Artificial Neural Networks: Part I: Bio-Inspired Systems: Computational and Ambient Intelligence. IWANN 09, Berlin, Heidelberg, Springer-Verlag (2009) Asta, S., Sariel-Talay, S.: Nature-inspired optimization for biped robot locomotion and gait planning. In: Proceedings of the 6th European Event on Nature-inspired Techniques in Scheduling, Planning and Timetabling. evostim (2011) Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.: Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks IV. (1995) Ros, R., Arcos, J.L., Lopez de Mantaras, R., Veloso, M.: A case-based approach for coordinated action selection in robot soccer. Artif. Intell. 173 (June 2009) Mcmillen, C., Veloso, M.: Distributed, Play-Based Coordination for Robot Teams in Dynamic Environments. In: RoboCup 2006: Robot Soccer World Cup X. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg (2007) Hayashi, H., Tokura, S., Ozaki, F.: Towards real-world htn planning agents. In Jain, L., Nguyen, N., eds.: Knowledge Processing and Decision Making in Agent- Based Systems. Volume 170 of Studies in Computational Intelligence. Springer Berlin, Heidelberg (2009) Wu, F., Zilberstein, S., Chen, X.: Online planning for multi-agent systems with bounded communication. Artificial Intelligence 175(2) (2011)
SHARPKUNGFU TEAM DESCRIPTION 2006
 SHARPKUNGFU TEAM DESCRIPTION 2006 Qining Wang, Chunxia Rong, Yan Huang, Guangming Xie, Long Wang Intelligent Control Laboratory, College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China http://www.mech.pku.edu.cn/robot/fourleg/
SHARPKUNGFU TEAM DESCRIPTION 2006 Qining Wang, Chunxia Rong, Yan Huang, Guangming Xie, Long Wang Intelligent Control Laboratory, College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China http://www.mech.pku.edu.cn/robot/fourleg/
The University of Pennsylvania Robocup 2011 SPL Nao Soccer Team
 The University of Pennsylvania Robocup 2011 SPL Nao Soccer Team General Robotics Automation, Sensing and Perception (GRASP) Laboratory University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104 Abstract. This
The University of Pennsylvania Robocup 2011 SPL Nao Soccer Team General Robotics Automation, Sensing and Perception (GRASP) Laboratory University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104 Abstract. This
Humanoid Robotics. Monte Carlo Localization. Maren Bennewitz
 Humanoid Robotics Monte Carlo Localization Maren Bennewitz 1 Basis Probability Rules (1) If x and y are independent: Bayes rule: Often written as: The denominator is a normalizing constant that ensures
Humanoid Robotics Monte Carlo Localization Maren Bennewitz 1 Basis Probability Rules (1) If x and y are independent: Bayes rule: Often written as: The denominator is a normalizing constant that ensures
Mithras3D Team Description Paper 2014 Soccer Simulation 3D League
 Mithras3D Team Description Paper 2014 Soccer Simulation 3D League Armita Sabeti Ashraf, Atieh Alsadat Moosavian, Fatemeh Gerami Gohar, Fatima Tafazzoli Shadpour, Romina Moradi, Sama Moayeri Farzanegan
Mithras3D Team Description Paper 2014 Soccer Simulation 3D League Armita Sabeti Ashraf, Atieh Alsadat Moosavian, Fatemeh Gerami Gohar, Fatima Tafazzoli Shadpour, Romina Moradi, Sama Moayeri Farzanegan
UPennalizers. RoboCup Standard Platform League Team Report 2010
 UPennalizers RoboCup Standard Platform League Team Report 2010 Jordan Brindza, Levi Cai, Ashleigh Thomas, Ross Boczar, Alyin Caliskan, Alexandra Lee, Anirudha Majumdar, Roman Shor, Barry Scharfman, Dan
UPennalizers RoboCup Standard Platform League Team Report 2010 Jordan Brindza, Levi Cai, Ashleigh Thomas, Ross Boczar, Alyin Caliskan, Alexandra Lee, Anirudha Majumdar, Roman Shor, Barry Scharfman, Dan
Evolutionary approach for developing fast and stable offline humanoid walk
 Evolutionary approach for developing fast and stable offline humanoid walk Hafez Farazi #*1, Farzad Ahmadinejad *2, Farhad Maleki #3, M.E Shiri #4 # Mathematics and Computer Science Department, Amirkabir
Evolutionary approach for developing fast and stable offline humanoid walk Hafez Farazi #*1, Farzad Ahmadinejad *2, Farhad Maleki #3, M.E Shiri #4 # Mathematics and Computer Science Department, Amirkabir
Nao Devils Dortmund. Team Description Paper for RoboCup Matthias Hofmann, Ingmar Schwarz, and Oliver Urbann
 Nao Devils Dortmund Team Description Paper for RoboCup 2017 Matthias Hofmann, Ingmar Schwarz, and Oliver Urbann Robotics Research Institute Section Information Technology TU Dortmund University 44221 Dortmund,
Nao Devils Dortmund Team Description Paper for RoboCup 2017 Matthias Hofmann, Ingmar Schwarz, and Oliver Urbann Robotics Research Institute Section Information Technology TU Dortmund University 44221 Dortmund,
Brainstormers Team Description
 Brainstormers 2003 - Team Description M. Riedmiller, A. Merke, M. Nickschas, W. Nowak, and D. Withopf Lehrstuhl Informatik I, Universität Dortmund, 44221 Dortmund, Germany Abstract. The main interest behind
Brainstormers 2003 - Team Description M. Riedmiller, A. Merke, M. Nickschas, W. Nowak, and D. Withopf Lehrstuhl Informatik I, Universität Dortmund, 44221 Dortmund, Germany Abstract. The main interest behind
Particle-Filter-Based Self-Localization Using Landmarks and Directed Lines
 Particle-Filter-Based Self-Localization Using Landmarks and Directed Lines Thomas Röfer 1, Tim Laue 1, and Dirk Thomas 2 1 Center for Computing Technology (TZI), FB 3, Universität Bremen roefer@tzi.de,
Particle-Filter-Based Self-Localization Using Landmarks and Directed Lines Thomas Röfer 1, Tim Laue 1, and Dirk Thomas 2 1 Center for Computing Technology (TZI), FB 3, Universität Bremen roefer@tzi.de,
Adaptive Motion Control: Dynamic Kick for a Humanoid Robot
 Adaptive Motion Control: Dynamic Kick for a Humanoid Robot Yuan Xu and Heinrich Mellmann Institut für Informatik, LFG Künstliche Intelligenz Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Germany {xu,mellmann}@informatik.hu-berlin.de
Adaptive Motion Control: Dynamic Kick for a Humanoid Robot Yuan Xu and Heinrich Mellmann Institut für Informatik, LFG Künstliche Intelligenz Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Germany {xu,mellmann}@informatik.hu-berlin.de
Eagle Knights 2007: Four-Legged League
 Eagle Knights 2007: Four-Legged League Alfredo Weitzenfeld 1, Alonso Martínez 1, Bernardo Muciño 1, Gabriela Serrano 1, Carlos Ramos 1, and Carlos Rivera 1 1 Robotics Laboratory Lab, ITAM, Rio Hondo 1,
Eagle Knights 2007: Four-Legged League Alfredo Weitzenfeld 1, Alonso Martínez 1, Bernardo Muciño 1, Gabriela Serrano 1, Carlos Ramos 1, and Carlos Rivera 1 1 Robotics Laboratory Lab, ITAM, Rio Hondo 1,
Ball tracking with velocity based on Monte-Carlo localization
 Book Title Book Editors IOS Press, 23 1 Ball tracking with velocity based on Monte-Carlo localization Jun Inoue a,1, Akira Ishino b and Ayumi Shinohara c a Department of Informatics, Kyushu University
Book Title Book Editors IOS Press, 23 1 Ball tracking with velocity based on Monte-Carlo localization Jun Inoue a,1, Akira Ishino b and Ayumi Shinohara c a Department of Informatics, Kyushu University
L3M-SIM Team Description
 L3M-SIM Team Description Nicolas Jouandeau 1, Vincent Hugel 2, and Thomas Da Costa 3 1 Université de Paris 8, Laboratoire d'informatique Avancée de Saint-Denis, France n@ai.univ-paris8.fr 2 Université
L3M-SIM Team Description Nicolas Jouandeau 1, Vincent Hugel 2, and Thomas Da Costa 3 1 Université de Paris 8, Laboratoire d'informatique Avancée de Saint-Denis, France n@ai.univ-paris8.fr 2 Université
The UPennalizers RoboCup 2015 Standard Platform League Team Description Paper
 The UPennalizers RoboCup 2015 Standard Platform League Team Description Paper Yongbo Qian, Yizheng He, Qiao (Rachel) Han, Sagar Poudel, Austin Small, Kyu Il Lee and Dr. Daniel Lee General Robotics Automation,
The UPennalizers RoboCup 2015 Standard Platform League Team Description Paper Yongbo Qian, Yizheng He, Qiao (Rachel) Han, Sagar Poudel, Austin Small, Kyu Il Lee and Dr. Daniel Lee General Robotics Automation,
Machine Learning on Physical Robots
 Machine Learning on Physical Robots Alfred P. Sloan Research Fellow Department or Computer Sciences The University of Texas at Austin Research Question To what degree can autonomous intelligent agents
Machine Learning on Physical Robots Alfred P. Sloan Research Fellow Department or Computer Sciences The University of Texas at Austin Research Question To what degree can autonomous intelligent agents
Motion Control in Dynamic Multi-Robot Environments
 Motion Control in Dynamic Multi-Robot Environments Michael Bowling mhb@cs.cmu.edu Manuela Veloso mmv@cs.cmu.edu Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213-3890 Abstract
Motion Control in Dynamic Multi-Robot Environments Michael Bowling mhb@cs.cmu.edu Manuela Veloso mmv@cs.cmu.edu Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213-3890 Abstract
Jolly Pochie 2005 in the Four Legged Robot League
 Jolly Pochie 2005 in the Four Legged Robot League Jun Inoue 1, Hayato Kobayashi 1, Akira Ishino 2, and Ayumi Shinohara 3 1 Department of Informatics, Kyushu University {j-inoue, h-koba}@i.kyushu-u.ac.jp
Jolly Pochie 2005 in the Four Legged Robot League Jun Inoue 1, Hayato Kobayashi 1, Akira Ishino 2, and Ayumi Shinohara 3 1 Department of Informatics, Kyushu University {j-inoue, h-koba}@i.kyushu-u.ac.jp
NuBot Team Description Paper 2013
 NuBot Team Description Paper 2013 Zhiwen Zeng, Dan Xiong, Qinghua Yu, Kaihong Huang, Shuai Cheng, Huimin Lu, Xiangke Wang, Hui Zhang, Xun Li, Zhiqiang Zheng College of Mechatronics and Automation, National
NuBot Team Description Paper 2013 Zhiwen Zeng, Dan Xiong, Qinghua Yu, Kaihong Huang, Shuai Cheng, Huimin Lu, Xiangke Wang, Hui Zhang, Xun Li, Zhiqiang Zheng College of Mechatronics and Automation, National
Improving Vision-Based Distance Measurements using Reference Objects
 Improving Vision-Based Distance Measurements using Reference Objects Matthias Jüngel, Heinrich Mellmann, and Michael Spranger Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Künstliche Intelligenz Unter den Linden 6,
Improving Vision-Based Distance Measurements using Reference Objects Matthias Jüngel, Heinrich Mellmann, and Michael Spranger Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Künstliche Intelligenz Unter den Linden 6,
Team Description Paper Team AutonOHM
 Team Description Paper Team AutonOHM Jon Martin, Daniel Ammon, Helmut Engelhardt, Tobias Fink, Tobias Scholz, and Marco Masannek University of Applied Science Nueremberg Georg-Simon-Ohm, Kesslerplatz 12,
Team Description Paper Team AutonOHM Jon Martin, Daniel Ammon, Helmut Engelhardt, Tobias Fink, Tobias Scholz, and Marco Masannek University of Applied Science Nueremberg Georg-Simon-Ohm, Kesslerplatz 12,
Plymouth Humanoids Team Description Paper for RoboCup 2013
 Plymouth Humanoids Team Description Paper for RoboCup 2013 Arron Griffiths 1, Clare Simpson, Paul Eastham, Alex Smith, Guido Bugmann, Chenguang Yang, Peter Gibbons, and Phil F. Culverhouse Centre for Robotics
Plymouth Humanoids Team Description Paper for RoboCup 2013 Arron Griffiths 1, Clare Simpson, Paul Eastham, Alex Smith, Guido Bugmann, Chenguang Yang, Peter Gibbons, and Phil F. Culverhouse Centre for Robotics
WrightEagle and UT Austin Villa: RoboCup 2011 Simulation League Champions
 WrightEagle and UT Austin Villa: RoboCup 2011 Simulation League Champions Aijun Bai, Xiaoping Chen, Patrick MacAlpine, Daniel Urieli, Samuel Barrett, and Peter Stone Department of Computer Science, University
WrightEagle and UT Austin Villa: RoboCup 2011 Simulation League Champions Aijun Bai, Xiaoping Chen, Patrick MacAlpine, Daniel Urieli, Samuel Barrett, and Peter Stone Department of Computer Science, University
NAO-Team Humboldt 2009
 NAO-Team Humboldt 2009 The RoboCup NAO Team of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin Alexander Borisov, Alireza Ferdowsizadeh, Christian Mohr, Heinrich Mellmann, Martin Martius, Thomas Krause, Tobias Hermann,
NAO-Team Humboldt 2009 The RoboCup NAO Team of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin Alexander Borisov, Alireza Ferdowsizadeh, Christian Mohr, Heinrich Mellmann, Martin Martius, Thomas Krause, Tobias Hermann,
Trot Gait Design details for Quadrupeds
 Trot Gait Design details for Quadrupeds Vincent Hugel, Pierre Blazevic, Olivier Stasse, and Patrick Bonnin Laboratoire de Robotique de Versailles (LRV), 10/12 avenue de l Europe, 78140 Vélizy, France hugel@robot.uvsq.fr
Trot Gait Design details for Quadrupeds Vincent Hugel, Pierre Blazevic, Olivier Stasse, and Patrick Bonnin Laboratoire de Robotique de Versailles (LRV), 10/12 avenue de l Europe, 78140 Vélizy, France hugel@robot.uvsq.fr
Simplified Walking: A New Way to Generate Flexible Biped Patterns
 1 Simplified Walking: A New Way to Generate Flexible Biped Patterns Jinsu Liu 1, Xiaoping Chen 1 and Manuela Veloso 2 1 Computer Science Department, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei,
1 Simplified Walking: A New Way to Generate Flexible Biped Patterns Jinsu Liu 1, Xiaoping Chen 1 and Manuela Veloso 2 1 Computer Science Department, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei,
Baset Teen-Size 2014 Team Description Paper
 Baset Teen-Size 2014 Team Description Paper Hafez Farazi 1, Mojtaba Hosseini 2, Vahid Mohammadi,Farhad Jafari, Donya Rahmati, Dr. Esfandiar Bamdad 1 Humanoid Robotic Laboratory, Robotic Center, Baset Pazhuh
Baset Teen-Size 2014 Team Description Paper Hafez Farazi 1, Mojtaba Hosseini 2, Vahid Mohammadi,Farhad Jafari, Donya Rahmati, Dr. Esfandiar Bamdad 1 Humanoid Robotic Laboratory, Robotic Center, Baset Pazhuh
WrightEagle and UT Austin Villa: RoboCup 2011 Simulation League Champions
 WrightEagle and UT Austin Villa: RoboCup 2011 Simulation League Champions Aijun Bai 1, Xiaoping Chen 1, Patrick MacAlpine 2,DanielUrieli 2, Samuel Barrett 2, and Peter Stone 2 1 Department of Computer
WrightEagle and UT Austin Villa: RoboCup 2011 Simulation League Champions Aijun Bai 1, Xiaoping Chen 1, Patrick MacAlpine 2,DanielUrieli 2, Samuel Barrett 2, and Peter Stone 2 1 Department of Computer
Fast and Robust Edge-Based Localization in the Sony Four-Legged Robot League
 Fast and Robust Edge-Based Localization in the Sony Four-Legged Robot League Thomas Röfer 1 and Matthias Jüngel 2 1 Bremer Institut für Sichere Systeme, Technologie-Zentrum Informatik, FB 3, Universität
Fast and Robust Edge-Based Localization in the Sony Four-Legged Robot League Thomas Röfer 1 and Matthias Jüngel 2 1 Bremer Institut für Sichere Systeme, Technologie-Zentrum Informatik, FB 3, Universität
BabyTigers-98: Osaka Legged Robot Team
 BabyTigers-98: saka Legged Robot Team Noriaki Mitsunaga and Minoru Asada and Chizuko Mishima Dept. of Adaptive Machine Systems, saka niversity, Suita, saka, 565-0871, Japan Abstract. The saka Legged Robot
BabyTigers-98: saka Legged Robot Team Noriaki Mitsunaga and Minoru Asada and Chizuko Mishima Dept. of Adaptive Machine Systems, saka niversity, Suita, saka, 565-0871, Japan Abstract. The saka Legged Robot
Using Layered Color Precision for a Self-Calibrating Vision System
 ROBOCUP2004 SYMPOSIUM, Instituto Superior Técnico, Lisboa, Portugal, July 4-5, 2004. Using Layered Color Precision for a Self-Calibrating Vision System Matthias Jüngel Institut für Informatik, LFG Künstliche
ROBOCUP2004 SYMPOSIUM, Instituto Superior Técnico, Lisboa, Portugal, July 4-5, 2004. Using Layered Color Precision for a Self-Calibrating Vision System Matthias Jüngel Institut für Informatik, LFG Künstliche
Localization of Multiple Robots with Simple Sensors
 Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics & Automation Niagara Falls, Canada July 2005 Localization of Multiple Robots with Simple Sensors Mike Peasgood and Christopher Clark Lab
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics & Automation Niagara Falls, Canada July 2005 Localization of Multiple Robots with Simple Sensors Mike Peasgood and Christopher Clark Lab
Thomas Bräunl EMBEDDED ROBOTICS. Mobile Robot Design and Applications with Embedded Systems. Second Edition. With 233 Figures and 24 Tables.
 Thomas Bräunl EMBEDDED ROBOTICS Mobile Robot Design and Applications with Embedded Systems Second Edition With 233 Figures and 24 Tables Springer CONTENTS PART I: EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 1 Robots and Controllers
Thomas Bräunl EMBEDDED ROBOTICS Mobile Robot Design and Applications with Embedded Systems Second Edition With 233 Figures and 24 Tables Springer CONTENTS PART I: EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 1 Robots and Controllers
Control of an 8-Legged, 24 DOF, Mechatronic Robot
 Control of an 8-Legged, 24 DOF, Mechatronic Robot Submitted by Brian Lim Youliang Kuvesvaran s/o Paramasivan National Junior College Assoc. Prof. Dr. Francis Malcolm John Nickols Abstract The objective
Control of an 8-Legged, 24 DOF, Mechatronic Robot Submitted by Brian Lim Youliang Kuvesvaran s/o Paramasivan National Junior College Assoc. Prof. Dr. Francis Malcolm John Nickols Abstract The objective
Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecturer: Patric Jensfelt KTH, March 16, 2010, 9-12 No aids are allowed on the exam, i.e. no notes, no books, no calculators, etc. You need a minimum of 20
Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecturer: Patric Jensfelt KTH, March 16, 2010, 9-12 No aids are allowed on the exam, i.e. no notes, no books, no calculators, etc. You need a minimum of 20
Robotics. Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation. See course website for up to date information.
 Robotics Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation See course website http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ajd/robotics/ for up to date information. Andrew Davison Department of Computing Imperial College London Review:
Robotics Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation See course website http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ajd/robotics/ for up to date information. Andrew Davison Department of Computing Imperial College London Review:
Instance-Based Action Models for Fast Action Planning
 In Visser, Ribeiro, Ohashi and Dellaert, editors, RoboCup-2007. Robot Soccer World Cup XI, pp. 1-16, Springer Verlag, 2008. Instance-Based Action Models for Fast Action Planning Mazda Ahmadi and Peter
In Visser, Ribeiro, Ohashi and Dellaert, editors, RoboCup-2007. Robot Soccer World Cup XI, pp. 1-16, Springer Verlag, 2008. Instance-Based Action Models for Fast Action Planning Mazda Ahmadi and Peter
Nao recognition and coordination
 Nao recognition and coordination Sander Nugteren August 24, 2012 1 Project In RoboCup soccer, it is important to have robots communicate and position themselves properly. This prevents them from getting
Nao recognition and coordination Sander Nugteren August 24, 2012 1 Project In RoboCup soccer, it is important to have robots communicate and position themselves properly. This prevents them from getting
Modeling Physically Simulated Characters with Motion Networks
 In Proceedings of Motion In Games (MIG), Rennes, France, 2012 Modeling Physically Simulated Characters with Motion Networks Robert Backman and Marcelo Kallmann University of California Merced Abstract.
In Proceedings of Motion In Games (MIG), Rennes, France, 2012 Modeling Physically Simulated Characters with Motion Networks Robert Backman and Marcelo Kallmann University of California Merced Abstract.
CS 231. Control for articulate rigid-body dynamic simulation. Articulated rigid-body dynamics
 CS 231 Control for articulate rigid-body dynamic simulation Articulated rigid-body dynamics F = ma No control 1 No control Ragdoll effects, joint limits RT Speed: many sims at real-time rates on today
CS 231 Control for articulate rigid-body dynamic simulation Articulated rigid-body dynamics F = ma No control 1 No control Ragdoll effects, joint limits RT Speed: many sims at real-time rates on today
The 2012 UT Austin Villa Code Release
 To appear in Proceedings of the RoboCup International Symposium 2013 (RoboCup 2013), Eindhoven, Netherlands, July 2013. The 2012 UT Austin Villa Code Release Samuel Barrett, Katie Genter, Yuchen He, Todd
To appear in Proceedings of the RoboCup International Symposium 2013 (RoboCup 2013), Eindhoven, Netherlands, July 2013. The 2012 UT Austin Villa Code Release Samuel Barrett, Katie Genter, Yuchen He, Todd
An Efficient Need-Based Vision System in Variable Illumination Environment of Middle Size RoboCup
 An Efficient Need-Based Vision System in Variable Illumination Environment of Middle Size RoboCup Mansour Jamzad and Abolfazal Keighobadi Lamjiri Sharif University of Technology Department of Computer
An Efficient Need-Based Vision System in Variable Illumination Environment of Middle Size RoboCup Mansour Jamzad and Abolfazal Keighobadi Lamjiri Sharif University of Technology Department of Computer
FutBotIII: Towards a Robust Centralized Vision System for RoboCup Small League
 RoboCup-99 Team Descriptions Small Robots League, Team FutBotIII, pages 43 47 http: /www.ep.liu.se/ea/cis/1999/006/07/ 43 FutBotIII: Towards a Robust Centralized Vision System for RoboCup Small League
RoboCup-99 Team Descriptions Small Robots League, Team FutBotIII, pages 43 47 http: /www.ep.liu.se/ea/cis/1999/006/07/ 43 FutBotIII: Towards a Robust Centralized Vision System for RoboCup Small League
Mobile Robots: An Introduction.
 Mobile Robots: An Introduction Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & Information Technology Department http://ce.aut.ac.ir/~shiry/lecture/robotics-2004/robotics04.html Introduction
Mobile Robots: An Introduction Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & Information Technology Department http://ce.aut.ac.ir/~shiry/lecture/robotics-2004/robotics04.html Introduction
Practical Extensions to Vision-Based Monte Carlo Localization Methods for Robot Soccer Domain
 Practical Extensions to Vision-Based Monte Carlo Localization Methods for Robot Soccer Domain Kemal Kaplan 1, Buluç Çelik 1, Tekin Meriçli 2, Çetin Meriçli 1 and H. Levent Akın 1 1 Boğaziçi University
Practical Extensions to Vision-Based Monte Carlo Localization Methods for Robot Soccer Domain Kemal Kaplan 1, Buluç Çelik 1, Tekin Meriçli 2, Çetin Meriçli 1 and H. Levent Akın 1 1 Boğaziçi University
A Type-2 Fuzzy Planner with Semi Qualitative World Model for Robocup Domain
 Proceedings of the 3rd Annual IEEE Conference on Automation Science and Engineering Scottsdale, AZ, USA, Sept 22-25, 2007 MoRP-B06.6 A Type-2 Fuzzy Planner with Semi Qualitative World Model for Robocup
Proceedings of the 3rd Annual IEEE Conference on Automation Science and Engineering Scottsdale, AZ, USA, Sept 22-25, 2007 MoRP-B06.6 A Type-2 Fuzzy Planner with Semi Qualitative World Model for Robocup
The 2006 sharpkungfu Team Report
 The 2006 sharpkungfu Team Report Qining Wang, Chunxia Rong, Lianghuan Liu, Hua Li, and Guangming Xie Intelligent Control Laboratory, Center for Systems and Control, College of Engineering, Peking University,
The 2006 sharpkungfu Team Report Qining Wang, Chunxia Rong, Lianghuan Liu, Hua Li, and Guangming Xie Intelligent Control Laboratory, Center for Systems and Control, College of Engineering, Peking University,
PASS EVALUATING IN SIMULATED SOCCER DOMAIN USING ANT-MINER ALGORITHM
 PASS EVALUATING IN SIMULATED SOCCER DOMAIN USING ANT-MINER ALGORITHM Mohammad Ali Darvish Darab Qazvin Azad University Mechatronics Research Laboratory, Qazvin Azad University, Qazvin, Iran ali@armanteam.org
PASS EVALUATING IN SIMULATED SOCCER DOMAIN USING ANT-MINER ALGORITHM Mohammad Ali Darvish Darab Qazvin Azad University Mechatronics Research Laboratory, Qazvin Azad University, Qazvin, Iran ali@armanteam.org
Humanoid Robotics. Path Planning and Walking. Maren Bennewitz
 Humanoid Robotics Path Planning and Walking Maren Bennewitz 1 Introduction Given the robot s pose in a model of the environment Compute a path to a target location First: 2D path in a 2D grid map representation
Humanoid Robotics Path Planning and Walking Maren Bennewitz 1 Introduction Given the robot s pose in a model of the environment Compute a path to a target location First: 2D path in a 2D grid map representation
KgpKubs Team Description Paper
 KgpKubs Team Description Paper Robocup 3D Simulation League 2016 Akshay Gupta, Shrey Garg, Abhinav Agarwal, Nishant Nikhil, Vaibhav Agarwal, and Ishaan Sang Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur West
KgpKubs Team Description Paper Robocup 3D Simulation League 2016 Akshay Gupta, Shrey Garg, Abhinav Agarwal, Nishant Nikhil, Vaibhav Agarwal, and Ishaan Sang Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur West
Kouretes 2012 SPL Team Description Paper
 Kouretes 01 SPL Team Description Paper Maria Karamitrou, Nikolaos Kofinas, Nikolaos Pavlakis, Angeliki Topalidou-Kyniazopoulou, Astero-Dimitra Tzanetatou, Nikolaos I. Spanoudakis, Michail G. Lagoudakis
Kouretes 01 SPL Team Description Paper Maria Karamitrou, Nikolaos Kofinas, Nikolaos Pavlakis, Angeliki Topalidou-Kyniazopoulou, Astero-Dimitra Tzanetatou, Nikolaos I. Spanoudakis, Michail G. Lagoudakis
Tailored Real-Time Simulation for Teams of Humanoid Robots
 Tailored Real-Time Simulation for Teams of Humanoid Robots Martin Friedmann, Karen Petersen, and Oskar von Stryk Simulation and Systems Optimization Group Technische Universität Darmstadt Hochschulstr.
Tailored Real-Time Simulation for Teams of Humanoid Robots Martin Friedmann, Karen Petersen, and Oskar von Stryk Simulation and Systems Optimization Group Technische Universität Darmstadt Hochschulstr.
Processing Interaction Protocols in Parallel: a Logic Programming implementation for Robotic Soccer
 Processing Interaction Protocols in Parallel: a Logic Programming implementation for Robotic Soccer Mariano Tucat 1 Alejandro J. García 2 Artificial Intelligence Research and Development Laboratory Department
Processing Interaction Protocols in Parallel: a Logic Programming implementation for Robotic Soccer Mariano Tucat 1 Alejandro J. García 2 Artificial Intelligence Research and Development Laboratory Department
(a) (b) (c) Fig. 1. Omnidirectional camera: (a) principle; (b) physical construction; (c) captured. of a local vision system is more challenging than
 An Omnidirectional Vision System that finds and tracks color edges and blobs Felix v. Hundelshausen, Sven Behnke, and Raul Rojas Freie Universität Berlin, Institut für Informatik Takustr. 9, 14195 Berlin,
An Omnidirectional Vision System that finds and tracks color edges and blobs Felix v. Hundelshausen, Sven Behnke, and Raul Rojas Freie Universität Berlin, Institut für Informatik Takustr. 9, 14195 Berlin,
Automatic generation of humanoid s geometric model parameters
 Automatic generation of humanoid s geometric model parameters Vincent Hugel and Nicolas Jouandeau LISV, University of Versailles and LIASD, University of Paris 8 Abstract. This paper describes a procedure
Automatic generation of humanoid s geometric model parameters Vincent Hugel and Nicolas Jouandeau LISV, University of Versailles and LIASD, University of Paris 8 Abstract. This paper describes a procedure
A Hybrid Software Platform for Sony AIBO Robots
 A Hybrid Software Platform for Sony AIBO Robots Dragos Golubovic, Bo Li, Huosheng Hu Department of Computer Science, University of Essex, Wivenhoe Park, Colchester CO4 3SQ, United Kingdom Email: {dgolub,
A Hybrid Software Platform for Sony AIBO Robots Dragos Golubovic, Bo Li, Huosheng Hu Department of Computer Science, University of Essex, Wivenhoe Park, Colchester CO4 3SQ, United Kingdom Email: {dgolub,
Performance Analysis of Agent based IPSM for Windows based Operating Systems
 Performance Analysis of Agent based IPSM for based Operating Systems Deepshikha Bhargava, Madhavi Sinha Abstract All processes prevent casual exchange of data. However, occasionally two processes might
Performance Analysis of Agent based IPSM for based Operating Systems Deepshikha Bhargava, Madhavi Sinha Abstract All processes prevent casual exchange of data. However, occasionally two processes might
James Kuffner. The Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University. Digital Human Research Center (AIST) James Kuffner (CMU/Google)
 James Kuffner The Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University Digital Human Research Center (AIST) 1 Stanford University 1995-1999 University of Tokyo JSK Lab 1999-2001 Carnegie Mellon University The
James Kuffner The Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University Digital Human Research Center (AIST) 1 Stanford University 1995-1999 University of Tokyo JSK Lab 1999-2001 Carnegie Mellon University The
Practical Course WS12/13 Introduction to Monte Carlo Localization
 Practical Course WS12/13 Introduction to Monte Carlo Localization Cyrill Stachniss and Luciano Spinello 1 State Estimation Estimate the state of a system given observations and controls Goal: 2 Bayes Filter
Practical Course WS12/13 Introduction to Monte Carlo Localization Cyrill Stachniss and Luciano Spinello 1 State Estimation Estimate the state of a system given observations and controls Goal: 2 Bayes Filter
A Cost Oriented Humanoid Robot Motion Control System
 Preprints of the 19th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control A Cost Oriented Humanoid Robot Motion Control System J. Baltes*, P. Kopacek**,M. Schörghuber** *Department of Computer
Preprints of the 19th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control A Cost Oriented Humanoid Robot Motion Control System J. Baltes*, P. Kopacek**,M. Schörghuber** *Department of Computer
Probabilistic Robotics
 Probabilistic Robotics Sebastian Thrun Wolfram Burgard Dieter Fox The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England Preface xvii Acknowledgments xix I Basics 1 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Uncertainty in
Probabilistic Robotics Sebastian Thrun Wolfram Burgard Dieter Fox The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England Preface xvii Acknowledgments xix I Basics 1 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Uncertainty in
CAMBADA 2016: Team Description Paper
 CAMBADA 2016: Team Description Paper R. Dias, F. Amaral, J. L. Azevedo, B. Cunha, P. Dias, N. Lau, A. J. R. Neves, E. Pedrosa, A. Pereira, J. Silva and A. Trifan Intelligent Robotics and Intelligent Systems
CAMBADA 2016: Team Description Paper R. Dias, F. Amaral, J. L. Azevedo, B. Cunha, P. Dias, N. Lau, A. J. R. Neves, E. Pedrosa, A. Pereira, J. Silva and A. Trifan Intelligent Robotics and Intelligent Systems
Real time game field limits recognition for robot self-localization using collinearity in Middle-Size RoboCup Soccer
 Real time game field limits recognition for robot self-localization using collinearity in Middle-Size RoboCup Soccer Fernando Ribeiro (1) Gil Lopes (2) (1) Department of Industrial Electronics, Guimarães,
Real time game field limits recognition for robot self-localization using collinearity in Middle-Size RoboCup Soccer Fernando Ribeiro (1) Gil Lopes (2) (1) Department of Industrial Electronics, Guimarães,
Rule-Based Behavior Prediction of Opponent Agents using Robocup 3D Soccer Simulation League Logfiles
 Rule-Based Behavior Prediction of Opponent Agents using Robocup 3D Soccer Simulation League Logfiles Asma S.Larik and Sajjad Haider, Artificial Intelligence Lab, Faculty of Computer Science, Institute
Rule-Based Behavior Prediction of Opponent Agents using Robocup 3D Soccer Simulation League Logfiles Asma S.Larik and Sajjad Haider, Artificial Intelligence Lab, Faculty of Computer Science, Institute
Toward an Undergraduate League for RoboCup.
 Toward an Undergraduate League for RoboCup. John Anderson, Jacky Baltes, David Livingston, Elizabeth Sklar, and Jonah Tower Department of Computer Science Columbia University New York, NY, 10027, USA sklar,jpt2002@cs.columbia.edu
Toward an Undergraduate League for RoboCup. John Anderson, Jacky Baltes, David Livingston, Elizabeth Sklar, and Jonah Tower Department of Computer Science Columbia University New York, NY, 10027, USA sklar,jpt2002@cs.columbia.edu
Kouretes 2008 Team Description Paper Nao Standard Platform League
 Kouretes 2008 Team Description Paper Nao Standard Platform League Team Kouretes Technical University of Crete (TUC), Chania 73100, Crete, Greece Abstract. Kouretes is one of the 16 teams participating
Kouretes 2008 Team Description Paper Nao Standard Platform League Team Kouretes Technical University of Crete (TUC), Chania 73100, Crete, Greece Abstract. Kouretes is one of the 16 teams participating
Open Access The Kinematics Analysis and Configuration Optimize of Quadruped Robot. Jinrong Zhang *, Chenxi Wang and Jianhua Zhang
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 014, 6, 1685-1690 1685 Open Access The Kinematics Analysis and Configuration Optimize of Quadruped
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 014, 6, 1685-1690 1685 Open Access The Kinematics Analysis and Configuration Optimize of Quadruped
7-5 Parametric Equations
 3. Sketch the curve given by each pair of parametric equations over the given interval. Make a table of values for 6 t 6. t x y 6 19 28 5 16.5 17 4 14 8 3 11.5 1 2 9 4 1 6.5 7 0 4 8 1 1.5 7 2 1 4 3 3.5
3. Sketch the curve given by each pair of parametric equations over the given interval. Make a table of values for 6 t 6. t x y 6 19 28 5 16.5 17 4 14 8 3 11.5 1 2 9 4 1 6.5 7 0 4 8 1 1.5 7 2 1 4 3 3.5
Processing Interaction Protocols in Parallel: a Logic Programming implementation for Robotic Soccer
 Processing Interaction Protocols in Parallel: a Logic Programming implementation for Robotic Soccer Mariano Tucat Alejandro J. García mt@cs.uns.edu.ar ajg@cs.uns.edu.ar Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones
Processing Interaction Protocols in Parallel: a Logic Programming implementation for Robotic Soccer Mariano Tucat Alejandro J. García mt@cs.uns.edu.ar ajg@cs.uns.edu.ar Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones
NAVIGATION SYSTEM OF AN OUTDOOR SERVICE ROBOT WITH HYBRID LOCOMOTION SYSTEM
 NAVIGATION SYSTEM OF AN OUTDOOR SERVICE ROBOT WITH HYBRID LOCOMOTION SYSTEM Jorma Selkäinaho, Aarne Halme and Janne Paanajärvi Automation Technology Laboratory, Helsinki University of Technology, Espoo,
NAVIGATION SYSTEM OF AN OUTDOOR SERVICE ROBOT WITH HYBRID LOCOMOTION SYSTEM Jorma Selkäinaho, Aarne Halme and Janne Paanajärvi Automation Technology Laboratory, Helsinki University of Technology, Espoo,
Autonomous Navigation of Nao using Kinect CS365 : Project Report
 Autonomous Navigation of Nao using Kinect CS365 : Project Report Samyak Daga Harshad Sawhney 11633 11297 samyakd@iitk.ac.in harshads@iitk.ac.in Dept. of CSE Dept. of CSE Indian Institute of Technology,
Autonomous Navigation of Nao using Kinect CS365 : Project Report Samyak Daga Harshad Sawhney 11633 11297 samyakd@iitk.ac.in harshads@iitk.ac.in Dept. of CSE Dept. of CSE Indian Institute of Technology,
Multi Robot Object Tracking and Self Localization Using Visual Percept Relations
 Multi Robot Object Tracking and Self Localization Using Visual Percept Relations Daniel Göhring and Hans-Dieter Burkhard Department of Computer Science Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Humboldt-Universität
Multi Robot Object Tracking and Self Localization Using Visual Percept Relations Daniel Göhring and Hans-Dieter Burkhard Department of Computer Science Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Humboldt-Universität
Environments. Michael Bowling and Manuela Veloso. Carnegie Mellon University. Pittsburgh, PA
 Motion Control in Dynamic Multi-Robot Environments Michael Bowling and Manuela Veloso Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213-3890 Abstract. All mobile robots require
Motion Control in Dynamic Multi-Robot Environments Michael Bowling and Manuela Veloso Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213-3890 Abstract. All mobile robots require
Introduction to Robotics
 Introduction to Robotics Ph.D. Antonio Marin-Hernandez Artificial Intelligence Department Universidad Veracruzana Sebastian Camacho # 5 Xalapa, Veracruz Robotics Action and Perception LAAS-CNRS 7, av du
Introduction to Robotics Ph.D. Antonio Marin-Hernandez Artificial Intelligence Department Universidad Veracruzana Sebastian Camacho # 5 Xalapa, Veracruz Robotics Action and Perception LAAS-CNRS 7, av du
Localization, Where am I?
 5.1 Localization, Where am I?? position Position Update (Estimation?) Encoder Prediction of Position (e.g. odometry) YES matched observations Map data base predicted position Matching Odometry, Dead Reckoning
5.1 Localization, Where am I?? position Position Update (Estimation?) Encoder Prediction of Position (e.g. odometry) YES matched observations Map data base predicted position Matching Odometry, Dead Reckoning
Robot Motion Control Matteo Matteucci
 Robot Motion Control Open loop control A mobile robot is meant to move from one place to another Pre-compute a smooth trajectory based on motion segments (e.g., line and circle segments) from start to
Robot Motion Control Open loop control A mobile robot is meant to move from one place to another Pre-compute a smooth trajectory based on motion segments (e.g., line and circle segments) from start to
Dutch AIBO Team at RoboCup 2006
 Dutch AIBO Team at RoboCup 2006 Arnoud Visser 1, Paul van Rossum 2, Joost Westra 3, Jürgen Sturm 1, Dave van Soest 1, and Mark de Greef 1 1 Universiteit van Amsterdam 2 Technische Universiteit Delft 3
Dutch AIBO Team at RoboCup 2006 Arnoud Visser 1, Paul van Rossum 2, Joost Westra 3, Jürgen Sturm 1, Dave van Soest 1, and Mark de Greef 1 1 Universiteit van Amsterdam 2 Technische Universiteit Delft 3
Instance-Based Action Models for Fast Action Planning
 Instance-Based Action Models for Fast Action Planning Mazda Ahmadi and Peter Stone Department of Computer Sciences The University of Texas at Austin 1 University Station C0500, Austin, TX 78712-0233 Email:{mazda,pstone}@cs.utexas.edu
Instance-Based Action Models for Fast Action Planning Mazda Ahmadi and Peter Stone Department of Computer Sciences The University of Texas at Austin 1 University Station C0500, Austin, TX 78712-0233 Email:{mazda,pstone}@cs.utexas.edu
Automated Software Synthesis for Complex Robotic Systems
 Automated Software Synthesis for Complex Robotic Systems Indranil Saha Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Indranil Saha Automated Software Synthesis for
Automated Software Synthesis for Complex Robotic Systems Indranil Saha Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Indranil Saha Automated Software Synthesis for
AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS. PROBABILISTIC LOCALIZATION Monte Carlo Localization
 AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS PROBABILISTIC LOCALIZATION Monte Carlo Localization Maria Isabel Ribeiro Pedro Lima With revisions introduced by Rodrigo Ventura Instituto Superior Técnico/Instituto de Sistemas e Robótica
AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS PROBABILISTIC LOCALIZATION Monte Carlo Localization Maria Isabel Ribeiro Pedro Lima With revisions introduced by Rodrigo Ventura Instituto Superior Técnico/Instituto de Sistemas e Robótica
DETC THREE-DIMENSIONAL KINEMATIC ANALYSIS OF THE ACTUATED SPOKE WHEEL ROBOT. September 10-13, 2006, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA
 Proceedings Proceedings of IDETC/CIE of IDETC 06 2006 ASME 2006 ASME International International Design Design Engineering Engineering Technical Technical Conferences Conferences & September Computers
Proceedings Proceedings of IDETC/CIE of IDETC 06 2006 ASME 2006 ASME International International Design Design Engineering Engineering Technical Technical Conferences Conferences & September Computers
(ii) Calculate the maximum height reached by the ball. (iii) Calculate the times at which the ball is at half its maximum height.
 1 Inthis question take g =10. A golf ball is hit from ground level over horizontal ground. The initial velocity of the ball is 40 m s 1 at an angle α to the horizontal, where sin α = 0.6 and cos α = 0.8.
1 Inthis question take g =10. A golf ball is hit from ground level over horizontal ground. The initial velocity of the ball is 40 m s 1 at an angle α to the horizontal, where sin α = 0.6 and cos α = 0.8.
Robust and Accurate Detection of Object Orientation and ID without Color Segmentation
 0 Robust and Accurate Detection of Object Orientation and ID without Color Segmentation Hironobu Fujiyoshi, Tomoyuki Nagahashi and Shoichi Shimizu Chubu University Japan Open Access Database www.i-techonline.com
0 Robust and Accurate Detection of Object Orientation and ID without Color Segmentation Hironobu Fujiyoshi, Tomoyuki Nagahashi and Shoichi Shimizu Chubu University Japan Open Access Database www.i-techonline.com
Austin Villa 2010 Standard Platform Team Report
 Austin Villa 2010 Standard Platform Team Report Samuel Barrett, Katie Genter, Matthew Hausknecht, Todd Hester, Piyush Khandelwal, Juhyun Lee, Michael Quinlan, Aibo Tian and Peter Stone Department of Computer
Austin Villa 2010 Standard Platform Team Report Samuel Barrett, Katie Genter, Matthew Hausknecht, Todd Hester, Piyush Khandelwal, Juhyun Lee, Michael Quinlan, Aibo Tian and Peter Stone Department of Computer
Hough Transform Run Length Encoding for Real-Time Image Processing
 Hough Transform Run Length Encoding for Real-Time Image Processing C. H. Messom 1, G. Sen Gupta 2,3, S. Demidenko 4 1 IIMS, Massey University, Albany, New Zealand 2 IIS&T, Massey University, Palmerston
Hough Transform Run Length Encoding for Real-Time Image Processing C. H. Messom 1, G. Sen Gupta 2,3, S. Demidenko 4 1 IIMS, Massey University, Albany, New Zealand 2 IIS&T, Massey University, Palmerston
Noxious-Kouretes 2011 SPL Team Description Paper
 Noxious-Kouretes 2011 SPL Team Description Paper 1 E. Chatzilaris 3, I. Kyranou 3, J. Ma 2, E. Orfanoudakis 3, A. Panakos 1, A. Paraschos 1, G. Pierris 1, N. Spanoudakis 3, J. Threlfall 1, A. Topalidou
Noxious-Kouretes 2011 SPL Team Description Paper 1 E. Chatzilaris 3, I. Kyranou 3, J. Ma 2, E. Orfanoudakis 3, A. Panakos 1, A. Paraschos 1, G. Pierris 1, N. Spanoudakis 3, J. Threlfall 1, A. Topalidou
Robotics. Haslum COMP3620/6320
 Robotics P@trik Haslum COMP3620/6320 Introduction Robotics Industrial Automation * Repetitive manipulation tasks (assembly, etc). * Well-known, controlled environment. * High-power, high-precision, very
Robotics P@trik Haslum COMP3620/6320 Introduction Robotics Industrial Automation * Repetitive manipulation tasks (assembly, etc). * Well-known, controlled environment. * High-power, high-precision, very
ME5286 Robotics Spring 2014 Quiz 1 Solution. Total Points: 30
 Page 1 of 7 ME5286 Robotics Spring 2014 Quiz 1 Solution Total Points: 30 (Note images from original quiz are not included to save paper/ space. Please see the original quiz for additional information and
Page 1 of 7 ME5286 Robotics Spring 2014 Quiz 1 Solution Total Points: 30 (Note images from original quiz are not included to save paper/ space. Please see the original quiz for additional information and
EXPLOITING MOTION SYMMETRY IN CONTROL OF EXOSKELETON LIMBS
 EXPLOITING MOTION SYMMETRY IN CONTROL OF EXOSKELETON LIMBS Christian Reinicke Institut für Technische Informatik und Mikroelektronik, Technische Universität Berlin Berlin, Germany email: reinicke@cs.tu-berlin.de
EXPLOITING MOTION SYMMETRY IN CONTROL OF EXOSKELETON LIMBS Christian Reinicke Institut für Technische Informatik und Mikroelektronik, Technische Universität Berlin Berlin, Germany email: reinicke@cs.tu-berlin.de
Particle Attraction Localisation
 Particle Attraction Localisation Damien George (dpgeorge@students.cs.mu.oz.au) Nick Barnes (nmb@cs.mu.oz.au) Dept. Computer Science and Software Engineering The University of Melbourne, Vic, 31, AUSTRALIA
Particle Attraction Localisation Damien George (dpgeorge@students.cs.mu.oz.au) Nick Barnes (nmb@cs.mu.oz.au) Dept. Computer Science and Software Engineering The University of Melbourne, Vic, 31, AUSTRALIA
Dept. of Adaptive Machine Systems, Graduate School of Engineering Osaka University, Suita, Osaka , Japan
 An Application of Vision-Based Learning for a Real Robot in RoboCup - A Goal Keeping Behavior for a Robot with an Omnidirectional Vision and an Embedded Servoing - Sho ji Suzuki 1, Tatsunori Kato 1, Hiroshi
An Application of Vision-Based Learning for a Real Robot in RoboCup - A Goal Keeping Behavior for a Robot with an Omnidirectional Vision and an Embedded Servoing - Sho ji Suzuki 1, Tatsunori Kato 1, Hiroshi
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Bayes Filter Particle Filter and Monte Carlo Localization. Wolfram Burgard
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Bayes Filter Particle Filter and Monte Carlo Localization Wolfram Burgard 1 Motivation Recall: Discrete filter Discretize the continuous state space High memory complexity
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Bayes Filter Particle Filter and Monte Carlo Localization Wolfram Burgard 1 Motivation Recall: Discrete filter Discretize the continuous state space High memory complexity
Revising Stereo Vision Maps in Particle Filter Based SLAM using Localisation Confidence and Sample History
 Revising Stereo Vision Maps in Particle Filter Based SLAM using Localisation Confidence and Sample History Simon Thompson and Satoshi Kagami Digital Human Research Center National Institute of Advanced
Revising Stereo Vision Maps in Particle Filter Based SLAM using Localisation Confidence and Sample History Simon Thompson and Satoshi Kagami Digital Human Research Center National Institute of Advanced
Multi-Cue Localization for Soccer Playing Humanoid Robots
 Multi-Cue Localization for Soccer Playing Humanoid Robots Hauke Strasdat, Maren Bennewitz, and Sven Behnke University of Freiburg, Computer Science Institute, D-79110 Freiburg, Germany strasdat@gmx.de,{maren,behnke}@informatik.uni-freiburg.de,
Multi-Cue Localization for Soccer Playing Humanoid Robots Hauke Strasdat, Maren Bennewitz, and Sven Behnke University of Freiburg, Computer Science Institute, D-79110 Freiburg, Germany strasdat@gmx.de,{maren,behnke}@informatik.uni-freiburg.de,
Using the ikart mobile platform
 Using the mobile platform Marco Randazzo Sestri Levante, July 23th, 2012 General description A holonomic mobile base for icub: Omnidirectional movement (six omnidirectional wheels) Integrates an high-performance
Using the mobile platform Marco Randazzo Sestri Levante, July 23th, 2012 General description A holonomic mobile base for icub: Omnidirectional movement (six omnidirectional wheels) Integrates an high-performance
Visualization and Analysis of Inverse Kinematics Algorithms Using Performance Metric Maps
 Visualization and Analysis of Inverse Kinematics Algorithms Using Performance Metric Maps Oliver Cardwell, Ramakrishnan Mukundan Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Canterbury
Visualization and Analysis of Inverse Kinematics Algorithms Using Performance Metric Maps Oliver Cardwell, Ramakrishnan Mukundan Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Canterbury
Robust Control of Bipedal Humanoid (TPinokio)
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) 643 649 International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) Robust Control of Bipedal Humanoid (TPinokio)
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) 643 649 International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) Robust Control of Bipedal Humanoid (TPinokio)
Modeling the manipulator and flipper pose effects on tip over stability of a tracked mobile manipulator
 Modeling the manipulator and flipper pose effects on tip over stability of a tracked mobile manipulator Chioniso Dube Mobile Intelligent Autonomous Systems Council for Scientific and Industrial Research,
Modeling the manipulator and flipper pose effects on tip over stability of a tracked mobile manipulator Chioniso Dube Mobile Intelligent Autonomous Systems Council for Scientific and Industrial Research,
Towards a Calibration-Free Robot: The ACT Algorithm for Automatic Online Color Training
 Towards a Calibration-Free Robot: The ACT Algorithm for Automatic Online Color Training Patrick Heinemann, Frank Sehnke, Felix Streichert, and Andreas Zell Wilhelm-Schickard-Institute, Department of Computer
Towards a Calibration-Free Robot: The ACT Algorithm for Automatic Online Color Training Patrick Heinemann, Frank Sehnke, Felix Streichert, and Andreas Zell Wilhelm-Schickard-Institute, Department of Computer
HOG-Based Person Following and Autonomous Returning Using Generated Map by Mobile Robot Equipped with Camera and Laser Range Finder
 HOG-Based Person Following and Autonomous Returning Using Generated Map by Mobile Robot Equipped with Camera and Laser Range Finder Masashi Awai, Takahito Shimizu and Toru Kaneko Department of Mechanical
HOG-Based Person Following and Autonomous Returning Using Generated Map by Mobile Robot Equipped with Camera and Laser Range Finder Masashi Awai, Takahito Shimizu and Toru Kaneko Department of Mechanical
Matching Evaluation of 2D Laser Scan Points using Observed Probability in Unstable Measurement Environment
 Matching Evaluation of D Laser Scan Points using Observed Probability in Unstable Measurement Environment Taichi Yamada, and Akihisa Ohya Abstract In the real environment such as urban areas sidewalk,
Matching Evaluation of D Laser Scan Points using Observed Probability in Unstable Measurement Environment Taichi Yamada, and Akihisa Ohya Abstract In the real environment such as urban areas sidewalk,
