Representing the Real World
|
|
|
- Janis Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Representing the Real World The theory of representing the real world in a GIS using digital data The nature of digital data and binary notation The discrete object view of the world Entities, data objects, and data models Topology and spatial relationships The field view of the world
2 Representing the Real World To map is to transform information from one form to another --- Mathematics Earth surface Paper map --- Geography
3 Representing the Real World Maps are a means by which to convey a lot of spatial information in a succinct package, because they allow us to gain knowledge of places we may never have seen ourselves Because we get to observe a very small part of the world with our own eyes, we rely on a variety of methods of representation to convey information: Photographs, spoken descriptions and written text (along with maps) are all familiar kinds of representation we use in everyday life to help us assemble more knowledge about the Earth
4 Representing the Real World In a GIS, the representation of real world phenomena makes use of digital data formats Earth surface Digital data representation
5 Digital Representations You probably have a fairly broad experience of digital representations through the use of computers and the Internet for other (non-geographic) purposes It is easy to be completely unaware of how digital representations function because technology has advanced sufficiently that their functioning is quite transparent to the consumer of information e.g. when you browse a web page, you see the formatted hypertext, not the html source code, nor the fundamental binary storage of the data
6 Digital Representations The term digital derives from digits (which in turn is a reference to our fingers) and our system of counting based on the 10 digits of our hands While our usual counting system makes use of the 10 symbols in the decimal counting system (0 9), digital computers use of system of counting that only uses 2 symbols that we represent with 0 and 1. Computers represent phenomena as binary digits. Every item of useful information about the Earth s surface is ultimately reduced by a GIS to some combination of 0s and 1s (p. 61 of text)
7 Binary Notation Everything is represented as 0s and 1s in a computer. These two-state forms correspond to yes/no, on/off, open/closed Binary Decimal 1 digit 0, 1 1 bit 0,1,2, 9 2 digits 00, 01 2 bits 00, 01, 10, 11 97, 99 3 digits 000, bits 000, 001, 010, , 003, 100, , , 999 One to one correspondence Decimal Binary ?
8 Binary Notation Decimal: 72,479 = 70,000 = ,000 = = = = Binary: Note: In binary = = 20
9 Electronic Representation of Bits Binary information can be represented by electrical pulses passing along wires with two different voltage levels as shown in the following sequence of pulses
10 Bits and Bytes 8 bits = 1 byte 1 bit = 1 binary digit 1 byte = 8 bits bytes = 1 Kb 1024 Kb = 1 Mb 1024 Mb = 1 Gb 1024 Gb = 1 Tb 1024 Tb = 1 Pb
11 ASCII Encoding If computers store everything using 0s and 1s, then how are characters represented? The ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) code assigns the numbers 0 through 127 to 128 characters, including upper and lower case alphabets plus various special characters, such as white space etc. e.g. decimal 85 is assigned to represent upper case U. In binary, = 85. Thus the computer represents U using Files which contain information encoded in ASCII are easily transferred and processed by different computers and programs. These are called ASCII or text files.
12 Representing the Real World Earth surface Digital data representation You now have some familiarity with how a digital representation works fundamentally. But now we encounter some key issues: What do we represent? What model should we use?
13 Representing the Real World We can think of geographic data as consisting of individual facts about the geographic world that link a place, a time, and some descriptive property, which we usually refer to as an attribute. A full and complete representation of the Earth would consists of an infinite number of geographic facts because The world is infinitely complex, but computer systems are finite. Representation is all about the choices that are made in capturing knowledge about the world (p. 65 of the text)
14 Two Fundamental Sorts of Representations Regardless of what phenomena of interest we chose to include in our geographic representation, we first must choose between a model that either represents geography as discrete objects OR represents geography as fields Most GIS approaches focus on the discrete object view, and we ll look at it in greater detail, although we will look at field representations as well
15 The Discrete Object View This view represents the world as objects with welldefined boundaries in empty space We can refer to these objects as entities -- real world phenomena that can be represented in a database
16 Entities Data Objects In the discrete object view, we associate each and every entity we wish to represent with its own data object a digital building block used in a data structure to represent an entity (x,y) (x,y) (x,y) (x,y) (x,y) (x,y) (x,y) (x,y) point line polygon (area) (x,y) (x,y)
17 Collection of Data Objects Data Model Taken all together, a set of data objects comprise a data model a collection of data objects represented in a particular format Road Network Elevation Buildings Land Cover
18 The Discrete Object View A data model is composed of data objects, each of which represents an entity Displayed schematically: Data Object Entity Data Model Data Object Data Object Entity Entity
19 Data Objects and their Attributes Each data object has associated attribute data, comprised of one or more variables, that describes the entity (and we have selected which attributes because they are descriptive of our phenomena of interest) Data Object Entity
20 Data Models We can consider two layers of data models: Conceptual data models these include sets of components and their relationships to each other, and are independent of a specific system These exist in your mind Logical data models these include the logical organization of the components of a data model in which the relationships among components are explicitly defined These exist in the GIS
21 Topology A key component of defining the rules of a spatial logical data model is defining the topological relations between objects Topology describes the relationship between objects, or entities, in space Do not confused topology with topography, which describes the third dimension of relief on the Earth s surface (elevation)
22 Conceptualizing Topology Topology defines certain spatial relationships between objects: Adjacency Connectivity Containment With topology defined, it becomes a simple matter to assess other spatial relationships such as: Direction Proximity
23 Topology - Adjacency Supposing we had a data model that included towns as represented by polygons If two town polygons were next to each other, we could describe them as topologically adjacent Springfield Shelbyville Capital City
24 Topology - Connectivity We might define the connectivity of the polygons in our model as well (perhaps based on some attributes, or the nature of the shared boundary ) Springfield South Springfield
25 Topology - Containment Our data model might also include point data that denotes the locations of businesses within the town polygons Using these we might assess whether a certain business was within a certain town using the containment relation Moe s Power Plant Kwik-E-Mart
26 Topology - Direction We can also the relative position of data objects in terms of direction: Moe s is North-East of the Kwik-E-Mart The nuclear plant is South-East of the Kwik-E-Mart Moe s Power Plant Kwik-E-Mart
27 Topology - Proximity We can also calculate the distances between objects to determine their proximity: Homer lives near Ned Homer lives far from Grandpa (where near and far can be defined )
28 Why We Need Topology Without topology, all you have is a pretty picture You can t use a data model without topology to understand the relationships between the spatial objects
29 The Field View In contrast to the discrete object view, which models the world in terms of entities, the field view approaches the world as consisting of continuous phenomena: The field view represents the real world as a finite number of variables, each one defined at every possible position (p.69 of the text) This view is inherently problematic for digital representation, which necessarily has to discretize the world into some set of minimum units
30 Topography Lends Itself to the Field View Topography is measurable at any point on the Earth s surface and changes in value across the surface
31 Other Field-like Phenomena Anything that does not have a well-defined boundary is more easily represented as a field: E.g. When mapping soil, we do not find a crisp break between one soil type and another typically they simply continuously vary Similarly, when we try to define the boundary of a lake, we might run into trouble where the lake drains into a river where does the lake end and the river begin we might prefer to define any given point s lakeness
GIS Data Models. 4/9/ GIS Data Models
 GIS Data Models 1 Conceptual models of the real world The real world can be described using two conceptually different models: 1. As discrete objects, possible to represent as points, lines or polygons.
GIS Data Models 1 Conceptual models of the real world The real world can be described using two conceptually different models: 1. As discrete objects, possible to represent as points, lines or polygons.
Understanding Geospatial Data Models
 Understanding Geospatial Data Models 1 A geospatial data model is a formal means of representing spatially referenced information. It is a simplified view of physical entities and a conceptualization of
Understanding Geospatial Data Models 1 A geospatial data model is a formal means of representing spatially referenced information. It is a simplified view of physical entities and a conceptualization of
Representing Geography
 Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Chapter 3: Maps as Numbers
 Chapter 3: Maps as Numbers 3. Representing Maps as Numbers 3.2 Structuring Attributes 3.3 Structuring Maps 3.4 Why Topology Matters 3.5 Formats for GIS Data 3.6 Exchanging Data David Tenenbaum EEOS 265
Chapter 3: Maps as Numbers 3. Representing Maps as Numbers 3.2 Structuring Attributes 3.3 Structuring Maps 3.4 Why Topology Matters 3.5 Formats for GIS Data 3.6 Exchanging Data David Tenenbaum EEOS 265
Longley Chapter 3. Representations
 Longley Chapter 3 Digital Geographic Data Representation Geographic Data Type Data Models Representing Spatial and Temporal Data Attributes The Nature of Geographic Data Representations Are needed to convey
Longley Chapter 3 Digital Geographic Data Representation Geographic Data Type Data Models Representing Spatial and Temporal Data Attributes The Nature of Geographic Data Representations Are needed to convey
Spatial Data Models. Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities
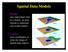 Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
[301] Bits and Memory. Tyler Caraza-Harter
![[301] Bits and Memory. Tyler Caraza-Harter [301] Bits and Memory. Tyler Caraza-Harter](/thumbs/88/116370212.jpg) [301] Bits and Memory Tyler Caraza-Harter Ones and Zeros 01111111110101011000110010011011000010010001100110101101 01000101110110000000110011101011101111000110101010010011 00011000100110001010111010110001010011101000100110100000
[301] Bits and Memory Tyler Caraza-Harter Ones and Zeros 01111111110101011000110010011011000010010001100110101101 01000101110110000000110011101011101111000110101010010011 00011000100110001010111010110001010011101000100110100000
SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015
 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 GIS Data Organization The basics Data can be organized in a variety of ways Spatial location, content (attributes), frequency of use Come up with a system
SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 GIS Data Organization The basics Data can be organized in a variety of ways Spatial location, content (attributes), frequency of use Come up with a system
M. Andrea Rodríguez-Tastets. I Semester 2008
 M. -Tastets Universidad de Concepción,Chile andrea@udec.cl I Semester 2008 Outline refers to data with a location on the Earth s surface. Examples Census data Administrative boundaries of a country, state
M. -Tastets Universidad de Concepción,Chile andrea@udec.cl I Semester 2008 Outline refers to data with a location on the Earth s surface. Examples Census data Administrative boundaries of a country, state
Data Models and Data processing in GIS
 PDHonline Course L155G (5 PDH) Data Models and Data processing in GIS Instructor: Steve Ramroop, Ph.D. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088
PDHonline Course L155G (5 PDH) Data Models and Data processing in GIS Instructor: Steve Ramroop, Ph.D. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088
Suitability Modeling with GIS
 Developed and Presented by Juniper GIS 1/33 Course Objectives What is Suitability Modeling? The Suitability Modeling Process Cartographic Modeling GIS Tools for Suitability Modeling Demonstrations of Models
Developed and Presented by Juniper GIS 1/33 Course Objectives What is Suitability Modeling? The Suitability Modeling Process Cartographic Modeling GIS Tools for Suitability Modeling Demonstrations of Models
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
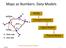 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
LECTURE 2 SPATIAL DATA MODELS
 LECTURE 2 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Computers and GIS cannot directly be applied to the real world: a data gathering step comes first. Digital computers operate in numbers and characters held internally as binary
LECTURE 2 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Computers and GIS cannot directly be applied to the real world: a data gathering step comes first. Digital computers operate in numbers and characters held internally as binary
Module 1: Information Representation I -- Number Systems
 Unit 1: Computer Systems, pages 1 of 7 - Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences CS 1305 Intro to Computer Technology 1 Module 1: Information Representation I -- Number Systems Objectives: Learn
Unit 1: Computer Systems, pages 1 of 7 - Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences CS 1305 Intro to Computer Technology 1 Module 1: Information Representation I -- Number Systems Objectives: Learn
CMPS 10 Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes
 CMPS Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes Binary Numbers Until now we have considered the Computing Agent that executes algorithms to be an abstract entity. Now we will be concerned with techniques
CMPS Introduction to Computer Science Lecture Notes Binary Numbers Until now we have considered the Computing Agent that executes algorithms to be an abstract entity. Now we will be concerned with techniques
Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models
 Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
a- As a special case, if there is only one symbol, no bits are required to specify it.
 Codes A single bit is useful if exactly two answers to a question are possible. Examples include the result of a coin toss (heads or tails), Most situations in life are more complicated. This chapter concerns
Codes A single bit is useful if exactly two answers to a question are possible. Examples include the result of a coin toss (heads or tails), Most situations in life are more complicated. This chapter concerns
Final Labs and Tutors
 ICT106 Fundamentals of Computer Systems - Topic 2 REPRESENTATION AND STORAGE OF INFORMATION Reading: Linux Assembly Programming Language, Ch 2.4-2.9 and 3.6-3.8 Final Labs and Tutors Venue and time South
ICT106 Fundamentals of Computer Systems - Topic 2 REPRESENTATION AND STORAGE OF INFORMATION Reading: Linux Assembly Programming Language, Ch 2.4-2.9 and 3.6-3.8 Final Labs and Tutors Venue and time South
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Dr. Arun K Saraf Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee
 Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Dr. Arun K Saraf Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Lecture 04 Raster data model and comparisons with vector Hello friends,
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Dr. Arun K Saraf Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Lecture 04 Raster data model and comparisons with vector Hello friends,
Basic data types. Building blocks of computation
 Basic data types Building blocks of computation Goals By the end of this lesson you will be able to: Understand the commonly used basic data types of C++ including Characters Integers Floating-point values
Basic data types Building blocks of computation Goals By the end of this lesson you will be able to: Understand the commonly used basic data types of C++ including Characters Integers Floating-point values
LSGI 521: Principles of GIS. Lecture 5: Spatial Data Management in GIS. Dr. Bo Wu
 Lecture 5: Spatial Data Management in GIS Dr. Bo Wu lsbowu@polyu.edu.hk Department of Land Surveying & Geo-Informatics The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Contents 1. Learning outcomes 2. From files to
Lecture 5: Spatial Data Management in GIS Dr. Bo Wu lsbowu@polyu.edu.hk Department of Land Surveying & Geo-Informatics The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Contents 1. Learning outcomes 2. From files to
Chapter 8: Elevation Data
 Chapter 8: Elevation Data SADA permits user s to bring in elevation data into their analysis. The same types of grid file formats for importing gridded data discussed in the previous chapter apply to elevation
Chapter 8: Elevation Data SADA permits user s to bring in elevation data into their analysis. The same types of grid file formats for importing gridded data discussed in the previous chapter apply to elevation
17/07/2013 RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES RASTER DATA MODEL& STRUCTURE TIN- TRIANGULAR IRREGULAR NETWORK
 RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES Space is subdivided into regular grids of square grid cells or other forms of polygonal meshes known as picture elements (pixels) the
RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES Space is subdivided into regular grids of square grid cells or other forms of polygonal meshes known as picture elements (pixels) the
Experimental Methods I
 Experimental Methods I Computing: Data types and binary representation M.P. Vaughan Learning objectives Understanding data types for digital computers binary representation of different data types: Integers
Experimental Methods I Computing: Data types and binary representation M.P. Vaughan Learning objectives Understanding data types for digital computers binary representation of different data types: Integers
MAPLOGIC CORPORATION. GIS Software Solutions. Getting Started. With MapLogic Layout Manager
 MAPLOGIC CORPORATION GIS Software Solutions Getting Started With MapLogic Layout Manager Getting Started with MapLogic Layout Manager 2011 MapLogic Corporation All Rights Reserved 330 West Canton Ave.,
MAPLOGIC CORPORATION GIS Software Solutions Getting Started With MapLogic Layout Manager Getting Started with MapLogic Layout Manager 2011 MapLogic Corporation All Rights Reserved 330 West Canton Ave.,
Weighted and Continuous Clustering
 John (ARC/ICAM) Virginia Tech... Math/CS 4414: http://people.sc.fsu.edu/ jburkardt/presentations/ clustering weighted.pdf... ARC: Advanced Research Computing ICAM: Interdisciplinary Center for Applied
John (ARC/ICAM) Virginia Tech... Math/CS 4414: http://people.sc.fsu.edu/ jburkardt/presentations/ clustering weighted.pdf... ARC: Advanced Research Computing ICAM: Interdisciplinary Center for Applied
Bits, bytes, binary numbers, and the representation of information
 Bits, bytes, binary numbers, and the representation of information computers represent, process, store, copy, and transmit everything as numbers hence "digital computer" the numbers can represent anything
Bits, bytes, binary numbers, and the representation of information computers represent, process, store, copy, and transmit everything as numbers hence "digital computer" the numbers can represent anything
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices nodes tart node nd node arcs Reality Conceptual Models The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can be queried and analyzed Translate: Real World Locations,
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices nodes tart node nd node arcs Reality Conceptual Models The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can be queried and analyzed Translate: Real World Locations,
14.1 Encoding for different models of computation
 Lecture 14 Decidable languages In the previous lecture we discussed some examples of encoding schemes, through which various objects can be represented by strings over a given alphabet. We will begin this
Lecture 14 Decidable languages In the previous lecture we discussed some examples of encoding schemes, through which various objects can be represented by strings over a given alphabet. We will begin this
Raster: The Other GIS Data
 Raster_The_Other_GIS_Data.Docx Page 1 of 11 Raster: The Other GIS Data Objectives Understand the raster format and how it is used to model continuous geographic phenomena. Understand how projections &
Raster_The_Other_GIS_Data.Docx Page 1 of 11 Raster: The Other GIS Data Objectives Understand the raster format and how it is used to model continuous geographic phenomena. Understand how projections &
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models Feature Types and Data Models How Does a GIS Work? - a GIS operates on the premise that all of the features in the real world can
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models Feature Types and Data Models How Does a GIS Work? - a GIS operates on the premise that all of the features in the real world can
Class #2. Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures
 Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Data Representation 1
 1 Data Representation Outline Binary Numbers Adding Binary Numbers Negative Integers Other Operations with Binary Numbers Floating Point Numbers Character Representation Image Representation Sound Representation
1 Data Representation Outline Binary Numbers Adding Binary Numbers Negative Integers Other Operations with Binary Numbers Floating Point Numbers Character Representation Image Representation Sound Representation
Computation of Slope
 Computation of Slope Prepared by David R. Maidment and David Tarboton GIS in Water Resources Class University of Texas at Austin September 2011, Revised December 2011 There are various ways in which slope
Computation of Slope Prepared by David R. Maidment and David Tarboton GIS in Water Resources Class University of Texas at Austin September 2011, Revised December 2011 There are various ways in which slope
Introduction to GIS. Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 9/24/2015. R. Khosla Fall Semester The real world. What in the world is GIS?
 Introduction to GIS Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 What in the world is GIS? GIS is simultaneously the telescope, the microscope, the computer and the Xerox machine of regional analysis and synthesis
Introduction to GIS Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 What in the world is GIS? GIS is simultaneously the telescope, the microscope, the computer and the Xerox machine of regional analysis and synthesis
Some basic set theory (and how it relates to Haskell)
 Some basic set theory (and how it relates to Haskell) John Longley School of Informatics University of Edinburgh jrl@inf.ed.ac.uk Inf1-FP guest lecture 25 September 2017 1 / 17 Sets Intuitively, a set
Some basic set theory (and how it relates to Haskell) John Longley School of Informatics University of Edinburgh jrl@inf.ed.ac.uk Inf1-FP guest lecture 25 September 2017 1 / 17 Sets Intuitively, a set
COMP 102: Computers and Computing
 COMP 102: Computers and Computing Lecture 2: Bits&bytes, Switches, and Boolean Logic Instructor: Kaleem Siddiqi (siddiqi@cim.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cim.mcgill.ca/~siddiqi/102.html The Lowly Bit
COMP 102: Computers and Computing Lecture 2: Bits&bytes, Switches, and Boolean Logic Instructor: Kaleem Siddiqi (siddiqi@cim.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cim.mcgill.ca/~siddiqi/102.html The Lowly Bit
An Example of Regional Web Resources: Massachusetts, USA Digital Data
 An Example of Regional Web Resources: Massachusetts, USA Digital Data Author Attribution Major contributors to this curriculum include (alphabetical): Maria Fernandez Michael Hamel Quentin Lewis Maili
An Example of Regional Web Resources: Massachusetts, USA Digital Data Author Attribution Major contributors to this curriculum include (alphabetical): Maria Fernandez Michael Hamel Quentin Lewis Maili
Introduction to Geographic Information Science. Some Updates. Last Lecture 4/6/2017. Geography 4103 / Raster Data and Tesselations.
 Geography 43 / 3 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Raster Data and Tesselations Schedule Some Updates Last Lecture We finished DBMS and learned about storage of data in complex databases Relational
Geography 43 / 3 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Raster Data and Tesselations Schedule Some Updates Last Lecture We finished DBMS and learned about storage of data in complex databases Relational
Introduction :- Storage of GIS Database :- What is tiling?
 Introduction :- GIS storage and editing subsystems provides a variety of tools for storing and maintaining the digital representation of a study area. It also provide tools for examining each theme for
Introduction :- GIS storage and editing subsystems provides a variety of tools for storing and maintaining the digital representation of a study area. It also provide tools for examining each theme for
The type of all data used in a C (or C++) program must be specified
 The type of all data used in a C (or C++) program must be specified A data type is a description of the data being represented That is, a set of possible values and a set of operations on those values
The type of all data used in a C (or C++) program must be specified A data type is a description of the data being represented That is, a set of possible values and a set of operations on those values
REPRESENTING INFORMATION:
 REPRESENTING INFORMATION: BINARY, HEX, ASCII CORRESPONDING READING: WELL, NONE IN YOUR TEXT. SO LISTEN CAREFULLY IN LECTURE (BECAUSE IT WILL BE ON THE EXAM(S))! CMSC 150: Fall 2015 Controlling Information
REPRESENTING INFORMATION: BINARY, HEX, ASCII CORRESPONDING READING: WELL, NONE IN YOUR TEXT. SO LISTEN CAREFULLY IN LECTURE (BECAUSE IT WILL BE ON THE EXAM(S))! CMSC 150: Fall 2015 Controlling Information
9/3/2015. Data Representation II. 2.4 Signed Integer Representation. 2.4 Signed Integer Representation
 Data Representation II CMSC 313 Sections 01, 02 The conversions we have so far presented have involved only unsigned numbers. To represent signed integers, computer systems allocate the high-order bit
Data Representation II CMSC 313 Sections 01, 02 The conversions we have so far presented have involved only unsigned numbers. To represent signed integers, computer systems allocate the high-order bit
Chapter 2. Data Representation in Computer Systems
 Chapter 2 Data Representation in Computer Systems Chapter 2 Objectives Understand the fundamentals of numerical data representation and manipulation in digital computers. Master the skill of converting
Chapter 2 Data Representation in Computer Systems Chapter 2 Objectives Understand the fundamentals of numerical data representation and manipulation in digital computers. Master the skill of converting
Geodatabase over Taita Hills, Kenya
 Geodatabase over Taita Hills, Kenya Anna Broberg & Antero Keskinen Abstract This article introduces the basics of geographical information systems (GIS) and explains how the Taita Hills project can benefit
Geodatabase over Taita Hills, Kenya Anna Broberg & Antero Keskinen Abstract This article introduces the basics of geographical information systems (GIS) and explains how the Taita Hills project can benefit
Coding & Computation or What s all this about 1s and 0s? File: coding-computation-slides.tex.
 Coding & Computation or What s all this about 1s and 0s? File: coding-computation-slides.tex. 1 File: coding-computation-slides.tex. Created: January 28, 2001, sok. 1-1 Topics Aim: Communicate certain
Coding & Computation or What s all this about 1s and 0s? File: coding-computation-slides.tex. 1 File: coding-computation-slides.tex. Created: January 28, 2001, sok. 1-1 Topics Aim: Communicate certain
Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS.
 GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
Minnesota Department of Natural Resources ArcView Utilities Extension User s Guide
 Introduction This document describes the functionality and use of the ArcView Utilities extension for the ArcView desktop GIS software. These tools were developed out of the need for additional geoprocessing
Introduction This document describes the functionality and use of the ArcView Utilities extension for the ArcView desktop GIS software. These tools were developed out of the need for additional geoprocessing
EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 8 Page 1 of 6
 EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 8 Page 1 of 6 Algorithms (3.1-3.3) Algorithms are a huge topic. In CSE we have 2 theory classes purely dedicated to algorithms (EECS 477 and EECS 586) and a number of classes
EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 8 Page 1 of 6 Algorithms (3.1-3.3) Algorithms are a huge topic. In CSE we have 2 theory classes purely dedicated to algorithms (EECS 477 and EECS 586) and a number of classes
INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE
 111 Mulford Hall, College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley (510) 643-4539 INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE This exercise is a survey of some GIS and spatial analysis tools for ecological and natural
111 Mulford Hall, College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley (510) 643-4539 INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE This exercise is a survey of some GIS and spatial analysis tools for ecological and natural
1. Draw the state graphs for the finite automata which accept sets of strings composed of zeros and ones which:
 P R O B L E M S Finite Autom ata. Draw the state graphs for the finite automata which accept sets of strings composed of zeros and ones which: a) Are a multiple of three in length. b) End with the string
P R O B L E M S Finite Autom ata. Draw the state graphs for the finite automata which accept sets of strings composed of zeros and ones which: a) Are a multiple of three in length. b) End with the string
Discussion. Why do we use Base 10?
 MEASURING DATA Data (the plural of datum) are anything in a form suitable for use with a computer. Whatever a computer receives as an input is data. Data are raw facts without any clear meaning. Computers
MEASURING DATA Data (the plural of datum) are anything in a form suitable for use with a computer. Whatever a computer receives as an input is data. Data are raw facts without any clear meaning. Computers
Information and Creative Technology
 Information and Creative Technology Unit 2 Technology Systems Analogue and Digital data Introduction Analogue data occurs in the natural world and changes constantly with time. Examples include the human
Information and Creative Technology Unit 2 Technology Systems Analogue and Digital data Introduction Analogue data occurs in the natural world and changes constantly with time. Examples include the human
MapInfo ProViewer 11.0 USER GUIDE
 MapInfo ProViewer 11.0 USER GUIDE Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of the vendor or its representatives. No part of this
MapInfo ProViewer 11.0 USER GUIDE Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of the vendor or its representatives. No part of this
Analogue vs. Discrete data
 CL 1 Analogue vs. Discrete data analogue data Analogue vs. Discrete data Data is the raw information that is input into the computer. In other words, data is information that is not yet processed by the
CL 1 Analogue vs. Discrete data analogue data Analogue vs. Discrete data Data is the raw information that is input into the computer. In other words, data is information that is not yet processed by the
Chapter 101. Coding & Computation. Coding & Computation or What s all this about 1s and 0s? Topics
 Chapter 101 Coding & Computation 101.0.1 Coding & Computation 1 or What s all this about 1s and 0s? 101.0.2 Topics Aim: Communicate certain fundamental concepts about computers and computing. Relax. Digital
Chapter 101 Coding & Computation 101.0.1 Coding & Computation 1 or What s all this about 1s and 0s? 101.0.2 Topics Aim: Communicate certain fundamental concepts about computers and computing. Relax. Digital
(Refer Slide Time: 00:23)
 In this session, we will learn about one more fundamental data type in C. So, far we have seen ints and floats. Ints are supposed to represent integers and floats are supposed to represent real numbers.
In this session, we will learn about one more fundamental data type in C. So, far we have seen ints and floats. Ints are supposed to represent integers and floats are supposed to represent real numbers.
DIGITAL SYSTEM DESIGN
 DIGITAL SYSTEM DESIGN UNIT I: Introduction to Number Systems and Boolean Algebra Digital and Analog Basic Concepts, Some history of Digital Systems-Introduction to number systems, Binary numbers, Number
DIGITAL SYSTEM DESIGN UNIT I: Introduction to Number Systems and Boolean Algebra Digital and Analog Basic Concepts, Some history of Digital Systems-Introduction to number systems, Binary numbers, Number
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models
 Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
FROM A RELATIONAL TO A MULTI-DIMENSIONAL DATA BASE
 FROM A RELATIONAL TO A MULTI-DIMENSIONAL DATA BASE David C. Hay Essential Strategies, Inc In the buzzword sweepstakes of 1997, the clear winner has to be Data Warehouse. A host of technologies and techniques
FROM A RELATIONAL TO A MULTI-DIMENSIONAL DATA BASE David C. Hay Essential Strategies, Inc In the buzzword sweepstakes of 1997, the clear winner has to be Data Warehouse. A host of technologies and techniques
Data Representation From 0s and 1s to images CPSC 101
 Data Representation From 0s and 1s to images CPSC 101 Learning Goals After the Data Representation: Images unit, you will be able to: Recognize and translate between binary and decimal numbers Define bit,
Data Representation From 0s and 1s to images CPSC 101 Learning Goals After the Data Representation: Images unit, you will be able to: Recognize and translate between binary and decimal numbers Define bit,
Creating raster DEMs and DSMs from large lidar point collections. Summary. Coming up with a plan. Using the Point To Raster geoprocessing tool
 Page 1 of 5 Creating raster DEMs and DSMs from large lidar point collections ArcGIS 10 Summary Raster, or gridded, elevation models are one of the most common GIS data types. They can be used in many ways
Page 1 of 5 Creating raster DEMs and DSMs from large lidar point collections ArcGIS 10 Summary Raster, or gridded, elevation models are one of the most common GIS data types. They can be used in many ways
layers in a raster model
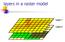 layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
The GIS Spatial Data Model
 The GIS Spatial Data Model Introduction: Spatial data are what drive a GIS. Every piece of functionality that makes a GIS separate from another analytical environment is rooted in the spatially explicit
The GIS Spatial Data Model Introduction: Spatial data are what drive a GIS. Every piece of functionality that makes a GIS separate from another analytical environment is rooted in the spatially explicit
Slides for Faculty Oxford University Press All rights reserved.
 Oxford University Press 2013 Slides for Faculty Assistance Preliminaries Author: Vivek Kulkarni vivek_kulkarni@yahoo.com Outline Following topics are covered in the slides: Basic concepts, namely, symbols,
Oxford University Press 2013 Slides for Faculty Assistance Preliminaries Author: Vivek Kulkarni vivek_kulkarni@yahoo.com Outline Following topics are covered in the slides: Basic concepts, namely, symbols,
Main concepts of ILWIS 3.0
 CHAPTER 2 Main concepts of ILWIS 3.0 In chapter one, Introduction to ILWIS, you started with ILWIS, and learned the basics of the user interface. This chapter presents some key concepts of ILWIS. In section
CHAPTER 2 Main concepts of ILWIS 3.0 In chapter one, Introduction to ILWIS, you started with ILWIS, and learned the basics of the user interface. This chapter presents some key concepts of ILWIS. In section
IT 1204 Section 2.0. Data Representation and Arithmetic. 2009, University of Colombo School of Computing 1
 IT 1204 Section 2.0 Data Representation and Arithmetic 2009, University of Colombo School of Computing 1 What is Analog and Digital The interpretation of an analog signal would correspond to a signal whose
IT 1204 Section 2.0 Data Representation and Arithmetic 2009, University of Colombo School of Computing 1 What is Analog and Digital The interpretation of an analog signal would correspond to a signal whose
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WATS 4930/6920 WHERE WE RE GOING WATS 6915 welcome to tag along for any, all or none WEEK FIVE Lecture VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton HOUSEKEEPING
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WATS 4930/6920 WHERE WE RE GOING WATS 6915 welcome to tag along for any, all or none WEEK FIVE Lecture VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton HOUSEKEEPING
Introduction to Scientific Computing Lecture 1
 Introduction to Scientific Computing Lecture 1 Professor Hanno Rein Last updated: September 10, 2017 1 Number Representations In this lecture, we will cover two concept that are important to understand
Introduction to Scientific Computing Lecture 1 Professor Hanno Rein Last updated: September 10, 2017 1 Number Representations In this lecture, we will cover two concept that are important to understand
Building Vector Layers
 Building Vector Layers in QGIS Introduction: Spatially referenced data can be separated into two categories, raster and vector data. This week, we focus on the building of vector features. Vector shapefiles
Building Vector Layers in QGIS Introduction: Spatially referenced data can be separated into two categories, raster and vector data. This week, we focus on the building of vector features. Vector shapefiles
Introduction to Google Earth Tutorial Haiti. 3/15/2011. Tufts GIS Center. Data Exploration
 Introduction to Google Earth Tutorial Haiti. 3/15/2011. Tufts GIS Center. Data Exploration 1. Open Google Earth 2. On the left you will see a navigation pane with 3 sections: Search, Places and Layers.
Introduction to Google Earth Tutorial Haiti. 3/15/2011. Tufts GIS Center. Data Exploration 1. Open Google Earth 2. On the left you will see a navigation pane with 3 sections: Search, Places and Layers.
CSE 220: System Fundamentals I Unit 14: MIPS Assembly: Multi-dimensional Arrays. Kevin McDonnell Stony Brook University CSE 220
 CSE 220: System Fundamentals I Unit 14: MIPS Assembly: Multi-dimensional Arrays 1 Memory Alignment Perhaps at some point in your MIPS assembly programming you tried to perform a lw and received an error
CSE 220: System Fundamentals I Unit 14: MIPS Assembly: Multi-dimensional Arrays 1 Memory Alignment Perhaps at some point in your MIPS assembly programming you tried to perform a lw and received an error
Functional Programming in Haskell Prof. Madhavan Mukund and S. P. Suresh Chennai Mathematical Institute
 Functional Programming in Haskell Prof. Madhavan Mukund and S. P. Suresh Chennai Mathematical Institute Module # 02 Lecture - 03 Characters and Strings So, let us turn our attention to a data type we have
Functional Programming in Haskell Prof. Madhavan Mukund and S. P. Suresh Chennai Mathematical Institute Module # 02 Lecture - 03 Characters and Strings So, let us turn our attention to a data type we have
EAT 233/3 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM (GIS)
 EAT 233/3 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM (GIS) CO3: Ability to produce detail mapping using geographic information systems (GIS) BY : AYU WAZIRA AZHARI SPATIAL DATA & THE MODELLING Spatial Data in GIS Spatial
EAT 233/3 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM (GIS) CO3: Ability to produce detail mapping using geographic information systems (GIS) BY : AYU WAZIRA AZHARI SPATIAL DATA & THE MODELLING Spatial Data in GIS Spatial
6th Bay Area Mathematical Olympiad
 6th Bay Area Mathematical Olympiad February 4, 004 Problems and Solutions 1 A tiling of the plane with polygons consists of placing the polygons in the plane so that interiors of polygons do not overlap,
6th Bay Area Mathematical Olympiad February 4, 004 Problems and Solutions 1 A tiling of the plane with polygons consists of placing the polygons in the plane so that interiors of polygons do not overlap,
Basics of Computational Geometry
 Basics of Computational Geometry Nadeem Mohsin October 12, 2013 1 Contents This handout covers the basic concepts of computational geometry. Rather than exhaustively covering all the algorithms, it deals
Basics of Computational Geometry Nadeem Mohsin October 12, 2013 1 Contents This handout covers the basic concepts of computational geometry. Rather than exhaustively covering all the algorithms, it deals
Flow on terrains. Laura Toma csci 3225 Algorithms for GIS Bowdoin College
 Flow on terrains Laura Toma csci 3225 Algorithms for GIS Bowdoin College Overview Flow on grids (discrete) flow direction flow accumulation algorithms for FD and FA dealing with flat areas watershed hierarchy
Flow on terrains Laura Toma csci 3225 Algorithms for GIS Bowdoin College Overview Flow on grids (discrete) flow direction flow accumulation algorithms for FD and FA dealing with flat areas watershed hierarchy
Theory of Computation Prof. Raghunath Tewari Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Theory of Computation Prof. Raghunath Tewari Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 01 Introduction to Finite Automata Welcome everybody. This is
Theory of Computation Prof. Raghunath Tewari Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 01 Introduction to Finite Automata Welcome everybody. This is
v TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics SMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
Variables and Data Representation
 You will recall that a computer program is a set of instructions that tell a computer how to transform a given set of input into a specific output. Any program, procedural, event driven or object oriented
You will recall that a computer program is a set of instructions that tell a computer how to transform a given set of input into a specific output. Any program, procedural, event driven or object oriented
Problem Solving through Programming In C Prof. Anupam Basu Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Problem Solving through Programming In C Prof. Anupam Basu Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 04 Introduction to Programming Language Concepts
Problem Solving through Programming In C Prof. Anupam Basu Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 04 Introduction to Programming Language Concepts
for (i=1; i<=100000; i++) { x = sqrt (y); // square root function cout << x+i << endl; }
 Ex: The difference between Compiler and Interpreter The interpreter actually carries out the computations specified in the source program. In other words, the output of a compiler is a program, whereas
Ex: The difference between Compiler and Interpreter The interpreter actually carries out the computations specified in the source program. In other words, the output of a compiler is a program, whereas
The Building Blocks: Binary Numbers, Boolean Logic, and Gates. Purpose of Chapter. External Representation of Information.
 The Building Blocks: Binary Numbers, Boolean Logic, and Gates Chapter 4 Representing Information The Binary Numbering System Boolean Logic and Gates Building Computer Circuits Control Circuits CMPUT Introduction
The Building Blocks: Binary Numbers, Boolean Logic, and Gates Chapter 4 Representing Information The Binary Numbering System Boolean Logic and Gates Building Computer Circuits Control Circuits CMPUT Introduction
Bharath Setturu Research scholar, EWRG, Center for Ecological Sciences, IISc, Bangalore & EWRG-CES IIIT-HYDERABAD
 Bharath Setturu Research scholar, EWRG, Center for Ecological Sciences, IISc, Bangalore settur@ces.iisc.ernet.in & IIIT-HYDERABAD Introduction to QGIS oquantum GIS (QGIS) is a GIS tool for managing geographical
Bharath Setturu Research scholar, EWRG, Center for Ecological Sciences, IISc, Bangalore settur@ces.iisc.ernet.in & IIIT-HYDERABAD Introduction to QGIS oquantum GIS (QGIS) is a GIS tool for managing geographical
Information Science 1
 Information Science 1 -Basic Concepts of Computers: Opera4on, Architecture, Memory- Week 02 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Today s lecture outline l Recall the previous
Information Science 1 -Basic Concepts of Computers: Opera4on, Architecture, Memory- Week 02 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Today s lecture outline l Recall the previous
Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models
 Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary Learning Objectives Learning
Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary Learning Objectives Learning
Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, Graph Theory
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, 2017 Graph Theory Introduction Graph Theory is the
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, 2017 Graph Theory Introduction Graph Theory is the
Introduction to ILWIS 3.0
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to ILWIS 3.0 ILWIS is an acronym for the Integrated Land and Water Information System. It is a Geographic Information System (GIS) with Image Processing capabilities. ILWIS has been
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to ILWIS 3.0 ILWIS is an acronym for the Integrated Land and Water Information System. It is a Geographic Information System (GIS) with Image Processing capabilities. ILWIS has been
CS102 Unit 2. Sets and Mathematical Formalism Programming Languages and Simple Program Execution
 1 CS102 Unit 2 Sets and Mathematical Formalism Programming Languages and Simple Program Execution 2 Review Show how "Hi!\n" would be stored in the memory below Use decimal to represent each byte Remember
1 CS102 Unit 2 Sets and Mathematical Formalism Programming Languages and Simple Program Execution 2 Review Show how "Hi!\n" would be stored in the memory below Use decimal to represent each byte Remember
2 Sets. 2.1 Notation. last edited January 26, 2016
 2 Sets Sets show up in virtually every topic in mathematics, and so understanding their basics is a necessity for understanding advanced mathematics. As far as we re concerned, the word set means what
2 Sets Sets show up in virtually every topic in mathematics, and so understanding their basics is a necessity for understanding advanced mathematics. As far as we re concerned, the word set means what
Lecture 2: GIS Data Sources, Data Types and Representation. GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University
 Lecture 2: GIS Data Sources, Data Types and Representation GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University Geographic Data in GIS Can be obtained from various sources in different
Lecture 2: GIS Data Sources, Data Types and Representation GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University Geographic Data in GIS Can be obtained from various sources in different
How & Why We Subnet Lab Workbook
 i How & Why We Subnet Lab Workbook ii CertificationKits.com How & Why We Subnet Workbook Copyright 2013 CertificationKits LLC All rights reserved. No part of this book maybe be reproduced or transmitted
i How & Why We Subnet Lab Workbook ii CertificationKits.com How & Why We Subnet Workbook Copyright 2013 CertificationKits LLC All rights reserved. No part of this book maybe be reproduced or transmitted
Intermediate Programming & Design (C++) Notation
 Notation Byte = 8 bits (a sequence of 0 s and 1 s) To indicate larger amounts of storage, some prefixes taken from the metric system are used One kilobyte (KB) = 2 10 bytes = 1024 bytes 10 3 bytes One
Notation Byte = 8 bits (a sequence of 0 s and 1 s) To indicate larger amounts of storage, some prefixes taken from the metric system are used One kilobyte (KB) = 2 10 bytes = 1024 bytes 10 3 bytes One
Electronic Data and Instructions
 Lecture 2 - The information Layer Binary Values and Number Systems, Data Representation. Know the different types of numbers Describe positional notation Convert numbers in other bases to base 10 Convert
Lecture 2 - The information Layer Binary Values and Number Systems, Data Representation. Know the different types of numbers Describe positional notation Convert numbers in other bases to base 10 Convert
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS When we talk about computers, we really are talking about a Computer System. Computer System: It is a combination of Hardware and Software. This combination allows a computer
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS When we talk about computers, we really are talking about a Computer System. Computer System: It is a combination of Hardware and Software. This combination allows a computer
LECTURE NOTES ON SETS
 LECTURE NOTES ON SETS PETE L. CLARK Contents 1. Introducing Sets 1 2. Subsets 5 3. Power Sets 5 4. Operations on Sets 6 5. Families of Sets 8 6. Partitions 10 7. Cartesian Products 11 1. Introducing Sets
LECTURE NOTES ON SETS PETE L. CLARK Contents 1. Introducing Sets 1 2. Subsets 5 3. Power Sets 5 4. Operations on Sets 6 5. Families of Sets 8 6. Partitions 10 7. Cartesian Products 11 1. Introducing Sets
Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects. William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA
 Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA Overview 1. Some Ways to Structure Space 2. What to Put into a Grid 3. Objects and Fields 4. Hybrid Structures
Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA Overview 1. Some Ways to Structure Space 2. What to Put into a Grid 3. Objects and Fields 4. Hybrid Structures
Chapter 1. Math review. 1.1 Some sets
 Chapter 1 Math review This book assumes that you understood precalculus when you took it. So you used to know how to do things like factoring polynomials, solving high school geometry problems, using trigonometric
Chapter 1 Math review This book assumes that you understood precalculus when you took it. So you used to know how to do things like factoring polynomials, solving high school geometry problems, using trigonometric
presented by: Tim Haithcoat University of Missouri Columbia
 12 presented by: Tim Haithcoat University of Missouri Columbia Introduction Very early attempts to build GIS began from scratch, using limited tools like operating systems & compilers More recently, GIS
12 presented by: Tim Haithcoat University of Missouri Columbia Introduction Very early attempts to build GIS began from scratch, using limited tools like operating systems & compilers More recently, GIS
Lecture #3: Digital Music and Sound
 Lecture #3: Digital Music and Sound CS106E Spring 2018, Young In this lecture we take a look at how computers represent music and sound. One very important concept we ll come across when studying digital
Lecture #3: Digital Music and Sound CS106E Spring 2018, Young In this lecture we take a look at how computers represent music and sound. One very important concept we ll come across when studying digital
