LECTURE 2 SPATIAL DATA MODELS
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Willis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LECTURE 2 SPATIAL DATA MODELS
2 Computers and GIS cannot directly be applied to the real world: a data gathering step comes first. Digital computers operate in numbers and characters held internally as binary digits. The real-world phenomenon of interest must be represented in symbolic form. The abstraction process of representing any property of the earth s surface in a computeraccessible form involves the use of symbolic models.
3 Models are simplification of reality. A map is a symbolic model, because it is a simplified representation of part of the real world. The components of the model are spatial objects, approximating spatial entities of the real world; they are represented on the map by graphical symbols. The process of defining and organizing data about the real world into a consistent digital dataset that is useful and reveals information is called data modeling. The logical organization of data according to a scheme is known as data model.
4 Data can be defined as verifiable facts. Information is data organized to reveal patterns, and to facilitate search. Spatial information is difficult to extract from spatial data, unless the data are organized primarily by spatial attributes. Spatial objects are characterized by attributes that are both spatial and nonspatial, and the digital description of objects and their attributes comprise spatial datasets.
5 Spatial data can be organized in different ways, depending on the way they are collected, how they are stored, and the purpose they are put. A database is a collection of inter-related data and everything that is needed to maintain and use it. A Database Management System is a collection of software for storing, editing and retrieving data in a database.
6 SPATIAL OBJECTS DIMENSIONALITY GROUPING ZERO DIMENSIONS POINTS ONE DIMENSION LINES TWO DIMENSIONS AREAS THREE DIMENSIONS VOLUMES NATURAL SPATIAL OBJECTS, IMPOSED SPATIAL OBJECTS
7 RASTER MODEL Spatial data of different types can be overlaid without the need for the complex geometric calculations. Each layer of grid cells in a raster model records a separate attribute. The cells (pixels, picture elements) are constant in size and are generally square. It is unnecessary to store the coordinates of each cell as the cells are arranged in a regular pattern It is enough to determine the cell size and the parameters to transform the X and Y coordinates and the cell locations in the raster map (rows/lines and columns). This process is called georeferencing.
8 RASTER MODEL Through georeferencing we calculate the parameters used in the equation to transform between a coordinate system and cell (pixel) location in the image A point is described by the position of a single pixel. The position of each cell is defined by a row and column number. Lines are represented by strings of connected pixels The spatial resolution of a raster is the size of one pixel on the ground At 100m resolution, a square area of 100km on a side requires a raster of 1000 rows by 1000 columns or one million pixels.
9 RASTER MODEL Large storage space specially for high resolution images Levels of details that require high resolution are lost when using coarse resolution Raster data processing is efficient in neighbourhood query, filtering, overlay operations for combining two or more images
10 RASTER MODEL
11 VECTOR MODEL In a vector model the position of each spatial feature is defined by (a series of) x and y coordinates. Besides the location, the meaning of the feature is given by a code (label). Points : the location of a point is described by a single xy coordinate pair. Points are stored in point maps by registering their location in x and y coordinates and by coding them (e.g. A rainfall station, elevation, etc.).
12 VECTOR MODEL Segments: a line is stored as a series of x and y coordinates (points) that best reflect its characteristics. The points are connected by straight lines. Line features are called segments. A segment is described by the coordinates of its starting and ending points (its nodes) and the intermediate points. The code of a segment defines what the segment represents (e.g. Road, state boundary, contour value, etc.). Polygons: areas are represented by their borders or boundary lines, which are in fact lines stored in the same way as segments. A polygon is a closed area of one or more Boundary segments and a code. Boundary segments define both the boundary of the Polygon to their left as to their right (topological structure). An area defined by its Boundary line and by its code is called a polygon. The code of a polygon defines the Contents of the polygon (e.g. Forest, city, sandstone, etc.).
13 VECTOR MODEL Vector maps are point, segment, or polygon maps. Most of the maps are obtained by digitizing or by importing them. Vector maps require less disk storage space and are suitable for creating high quality outputs. They are less suitable for a number of GIS operations, especially those dealing with map overlaying. You can rasterize the vector maps into raster maps
14 VECTOR MODEL
15 ILWIS
Main concepts of ILWIS 3.0
 CHAPTER 2 Main concepts of ILWIS 3.0 In chapter one, Introduction to ILWIS, you started with ILWIS, and learned the basics of the user interface. This chapter presents some key concepts of ILWIS. In section
CHAPTER 2 Main concepts of ILWIS 3.0 In chapter one, Introduction to ILWIS, you started with ILWIS, and learned the basics of the user interface. This chapter presents some key concepts of ILWIS. In section
GIS Data Models. 4/9/ GIS Data Models
 GIS Data Models 1 Conceptual models of the real world The real world can be described using two conceptually different models: 1. As discrete objects, possible to represent as points, lines or polygons.
GIS Data Models 1 Conceptual models of the real world The real world can be described using two conceptually different models: 1. As discrete objects, possible to represent as points, lines or polygons.
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis. GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University
 Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models
 Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS.
 GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015
 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 GIS Data Organization The basics Data can be organized in a variety of ways Spatial location, content (attributes), frequency of use Come up with a system
SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 GIS Data Organization The basics Data can be organized in a variety of ways Spatial location, content (attributes), frequency of use Come up with a system
Class #2. Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures
 Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Spatial Data Models. Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities
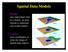 Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Data Models and Data processing in GIS
 PDHonline Course L155G (5 PDH) Data Models and Data processing in GIS Instructor: Steve Ramroop, Ph.D. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088
PDHonline Course L155G (5 PDH) Data Models and Data processing in GIS Instructor: Steve Ramroop, Ph.D. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088
17/07/2013 RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES RASTER DATA MODEL& STRUCTURE TIN- TRIANGULAR IRREGULAR NETWORK
 RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES Space is subdivided into regular grids of square grid cells or other forms of polygonal meshes known as picture elements (pixels) the
RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES Space is subdivided into regular grids of square grid cells or other forms of polygonal meshes known as picture elements (pixels) the
Introduction to Geographic Information Science. Some Updates. Last Lecture 4/6/2017. Geography 4103 / Raster Data and Tesselations.
 Geography 43 / 3 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Raster Data and Tesselations Schedule Some Updates Last Lecture We finished DBMS and learned about storage of data in complex databases Relational
Geography 43 / 3 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Raster Data and Tesselations Schedule Some Updates Last Lecture We finished DBMS and learned about storage of data in complex databases Relational
Exercise 1: Introduction to ILWIS with the Riskcity dataset
 Exercise 1: Introduction to ILWIS with the Riskcity dataset Expected time: 2.5 hour Data: data from subdirectory: CENN_DVD\ILWIS_ExerciseData\IntroRiskCity Objectives: After this exercise you will be able
Exercise 1: Introduction to ILWIS with the Riskcity dataset Expected time: 2.5 hour Data: data from subdirectory: CENN_DVD\ILWIS_ExerciseData\IntroRiskCity Objectives: After this exercise you will be able
Introduction to GIS. Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 9/24/2015. R. Khosla Fall Semester The real world. What in the world is GIS?
 Introduction to GIS Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 What in the world is GIS? GIS is simultaneously the telescope, the microscope, the computer and the Xerox machine of regional analysis and synthesis
Introduction to GIS Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 What in the world is GIS? GIS is simultaneously the telescope, the microscope, the computer and the Xerox machine of regional analysis and synthesis
Representing Geography
 Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Geographic Information Systems. using QGIS
 Geographic Information Systems using QGIS 1 - INTRODUCTION Generalities A GIS (Geographic Information System) consists of: -Computer hardware -Computer software - Digital Data Generalities GIS softwares
Geographic Information Systems using QGIS 1 - INTRODUCTION Generalities A GIS (Geographic Information System) consists of: -Computer hardware -Computer software - Digital Data Generalities GIS softwares
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models Feature Types and Data Models How Does a GIS Work? - a GIS operates on the premise that all of the features in the real world can
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models Feature Types and Data Models How Does a GIS Work? - a GIS operates on the premise that all of the features in the real world can
Graphic Display of Vector Object
 What is GIS? GIS stands for Geographic Information Systems, although the term Geographic Information Science is gaining popularity. A GIS is a software platform for storing, organizing, viewing, querying,
What is GIS? GIS stands for Geographic Information Systems, although the term Geographic Information Science is gaining popularity. A GIS is a software platform for storing, organizing, viewing, querying,
Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS
 Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS An ESRI White Paper August 2003 ESRI 380 New York St., Redlands, CA 92373-8100, USA TEL 909-793-2853 FAX 909-793-5953 E-MAIL info@esri.com WEB www.esri.com Copyright 2003
Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS An ESRI White Paper August 2003 ESRI 380 New York St., Redlands, CA 92373-8100, USA TEL 909-793-2853 FAX 909-793-5953 E-MAIL info@esri.com WEB www.esri.com Copyright 2003
Understanding Geospatial Data Models
 Understanding Geospatial Data Models 1 A geospatial data model is a formal means of representing spatially referenced information. It is a simplified view of physical entities and a conceptualization of
Understanding Geospatial Data Models 1 A geospatial data model is a formal means of representing spatially referenced information. It is a simplified view of physical entities and a conceptualization of
DATA MODELS IN GIS. Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi
 DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
Terms and definitions * keep definitions of processes and terms that may be useful for tests, assignments
 Lecture 1 Core of GIS Thematic layers Terms and definitions * keep definitions of processes and terms that may be useful for tests, assignments Lecture 2 What is GIS? Info: value added data Data to solve
Lecture 1 Core of GIS Thematic layers Terms and definitions * keep definitions of processes and terms that may be useful for tests, assignments Lecture 2 What is GIS? Info: value added data Data to solve
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
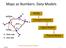 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment
 Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World Rotation Differential Scaling Distortion Skew Translation 1 The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World Rotation Differential Scaling Distortion Skew Translation 1 The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations,
 Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Cell based GIS. Introduction to rasters
 Week 9 Cell based GIS Introduction to rasters topics of the week Spatial Problems Modeling Raster basics Application functions Analysis environment, the mask Application functions Spatial Analyst in ArcGIS
Week 9 Cell based GIS Introduction to rasters topics of the week Spatial Problems Modeling Raster basics Application functions Analysis environment, the mask Application functions Spatial Analyst in ArcGIS
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment 2/13/2018
 Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment The Problem Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment The Problem Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in
The Problem. Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment. Nature Of The Problem: For Example: Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment 9/20/2016
 Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in
EAT 233/3 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM (GIS)
 EAT 233/3 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM (GIS) CO3: Ability to produce detail mapping using geographic information systems (GIS) BY : AYU WAZIRA AZHARI SPATIAL DATA & THE MODELLING Spatial Data in GIS Spatial
EAT 233/3 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM (GIS) CO3: Ability to produce detail mapping using geographic information systems (GIS) BY : AYU WAZIRA AZHARI SPATIAL DATA & THE MODELLING Spatial Data in GIS Spatial
Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models
 Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary Learning Objectives Learning
Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary Learning Objectives Learning
Bharath Setturu Research scholar, EWRG, Center for Ecological Sciences, IISc, Bangalore & EWRG-CES IIIT-HYDERABAD
 Bharath Setturu Research scholar, EWRG, Center for Ecological Sciences, IISc, Bangalore settur@ces.iisc.ernet.in & IIIT-HYDERABAD Introduction to QGIS oquantum GIS (QGIS) is a GIS tool for managing geographical
Bharath Setturu Research scholar, EWRG, Center for Ecological Sciences, IISc, Bangalore settur@ces.iisc.ernet.in & IIIT-HYDERABAD Introduction to QGIS oquantum GIS (QGIS) is a GIS tool for managing geographical
LSGI 521: Principles of GIS. Lecture 5: Spatial Data Management in GIS. Dr. Bo Wu
 Lecture 5: Spatial Data Management in GIS Dr. Bo Wu lsbowu@polyu.edu.hk Department of Land Surveying & Geo-Informatics The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Contents 1. Learning outcomes 2. From files to
Lecture 5: Spatial Data Management in GIS Dr. Bo Wu lsbowu@polyu.edu.hk Department of Land Surveying & Geo-Informatics The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Contents 1. Learning outcomes 2. From files to
Lecture 06. Raster and Vector Data Models. Part (1) Common Data Models. Raster. Vector. Points. Points. ( x,y ) Area. Area Line.
 Lecture 06 Raster and Vector Data Models Part (1) 1 Common Data Models Vector Raster Y Points Points ( x,y ) Line Area Line Area 2 X 1 3 Raster uses a grid cell structure Vector is more like a drawn map
Lecture 06 Raster and Vector Data Models Part (1) 1 Common Data Models Vector Raster Y Points Points ( x,y ) Line Area Line Area 2 X 1 3 Raster uses a grid cell structure Vector is more like a drawn map
Bharath Setturu Research scholar, EWRG, Center for Ecological Sciences, IISc, Bangalore & IIIT-HYDERABAD
 Bharath Setturu Research scholar, EWRG, Center for Ecological Sciences, IISc, Bangalore settur@ces.iisc.ernet.in & IIIT-HYDERABAD Introduction to QGIS oquantum GIS (QGIS) is a GIS tool for managing geographical
Bharath Setturu Research scholar, EWRG, Center for Ecological Sciences, IISc, Bangalore settur@ces.iisc.ernet.in & IIIT-HYDERABAD Introduction to QGIS oquantum GIS (QGIS) is a GIS tool for managing geographical
Spatial data and QGIS
 Spatial data and QGIS Xue Jingbo IT Center 2017.08.07 A GIS consists of: Spatial Data. Computer Hardware. Computer Software. Longitude Latitude Disease Date 26.870436-31.909519 Mumps 13/12/2008 26.868682-31.909259
Spatial data and QGIS Xue Jingbo IT Center 2017.08.07 A GIS consists of: Spatial Data. Computer Hardware. Computer Software. Longitude Latitude Disease Date 26.870436-31.909519 Mumps 13/12/2008 26.868682-31.909259
Geodatabase over Taita Hills, Kenya
 Geodatabase over Taita Hills, Kenya Anna Broberg & Antero Keskinen Abstract This article introduces the basics of geographical information systems (GIS) and explains how the Taita Hills project can benefit
Geodatabase over Taita Hills, Kenya Anna Broberg & Antero Keskinen Abstract This article introduces the basics of geographical information systems (GIS) and explains how the Taita Hills project can benefit
Lecture 20 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part1)
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 20 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part) 4 lectures on rasters - but won t cover everything (Raster GIS course: Geol 588: GIS II (Spring 20) Today: Raster data,
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 20 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part) 4 lectures on rasters - but won t cover everything (Raster GIS course: Geol 588: GIS II (Spring 20) Today: Raster data,
Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models
 Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
GIS in agriculture scale farm level - used in agricultural applications - managing crop yields, monitoring crop rotation techniques, and estimate
 Types of Input GIS in agriculture scale farm level - used in agricultural applications - managing crop yields, monitoring crop rotation techniques, and estimate soil loss from individual farms or agricultural
Types of Input GIS in agriculture scale farm level - used in agricultural applications - managing crop yields, monitoring crop rotation techniques, and estimate soil loss from individual farms or agricultural
Blacksburg, VA July 24 th 30 th, 2010 Georeferencing images and scanned maps Page 1. Georeference
 George McLeod Prepared by: With support from: NSF DUE-0903270 in partnership with: Geospatial Technician Education Through Virginia s Community Colleges (GTEVCC) Georeference The process of defining how
George McLeod Prepared by: With support from: NSF DUE-0903270 in partnership with: Geospatial Technician Education Through Virginia s Community Colleges (GTEVCC) Georeference The process of defining how
Multidimensional Data and Modelling
 Multidimensional Data and Modelling 1 Problems of multidimensional data structures l multidimensional (md-data or spatial) data and their implementation of operations between objects (spatial data practically
Multidimensional Data and Modelling 1 Problems of multidimensional data structures l multidimensional (md-data or spatial) data and their implementation of operations between objects (spatial data practically
Lecture 8. Vector Data Analyses. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 Lecture 8 Vector Data Analyses Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Vector Data Analysis Vector data analysis involves one or a combination of: Measuring
Lecture 8 Vector Data Analyses Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Vector Data Analysis Vector data analysis involves one or a combination of: Measuring
The Problem. Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment. Nature of the problem: For Example: Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment 2/4/2014
 Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to a GIS The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in geographical
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to a GIS The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in geographical
Raster Data. James Frew ESM 263 Winter
 Raster Data 1 Vector Data Review discrete objects geometry = points by themselves connected lines closed polygons attributes linked to feature ID explicit location every point has coordinates 2 Fields
Raster Data 1 Vector Data Review discrete objects geometry = points by themselves connected lines closed polygons attributes linked to feature ID explicit location every point has coordinates 2 Fields
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Dr. Arun K Saraf Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee
 Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Dr. Arun K Saraf Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Lecture 04 Raster data model and comparisons with vector Hello friends,
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Dr. Arun K Saraf Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Lecture 04 Raster data model and comparisons with vector Hello friends,
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices nodes tart node nd node arcs Reality Conceptual Models The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can be queried and analyzed Translate: Real World Locations,
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices nodes tart node nd node arcs Reality Conceptual Models The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can be queried and analyzed Translate: Real World Locations,
Multidimensional Data and Modelling - DBMS
 Multidimensional Data and Modelling - DBMS 1 DBMS-centric approach Summary: l Spatial data is considered as another type of data beside conventional data in a DBMS. l Enabling advantages of DBMS (data
Multidimensional Data and Modelling - DBMS 1 DBMS-centric approach Summary: l Spatial data is considered as another type of data beside conventional data in a DBMS. l Enabling advantages of DBMS (data
Steps for Modeling a Proposed New Reservoir in GIS
 Steps for Modeling a Proposed New Reservoir in GIS Requirements: ArcGIS ArcMap, ArcScene, Spatial Analyst, and 3D Analyst There s a new reservoir proposed for Right Hand Fork in Logan Canyon. I wanted
Steps for Modeling a Proposed New Reservoir in GIS Requirements: ArcGIS ArcMap, ArcScene, Spatial Analyst, and 3D Analyst There s a new reservoir proposed for Right Hand Fork in Logan Canyon. I wanted
Attribute Accuracy. Quantitative accuracy refers to the level of bias in estimating the values assigned such as estimated values of ph in a soil map.
 Attribute Accuracy Objectives (Entry) This basic concept of attribute accuracy has been introduced in the unit of quality and coverage. This unit will teach a basic technique to quantify the attribute
Attribute Accuracy Objectives (Entry) This basic concept of attribute accuracy has been introduced in the unit of quality and coverage. This unit will teach a basic technique to quantify the attribute
Longley Chapter 3. Representations
 Longley Chapter 3 Digital Geographic Data Representation Geographic Data Type Data Models Representing Spatial and Temporal Data Attributes The Nature of Geographic Data Representations Are needed to convey
Longley Chapter 3 Digital Geographic Data Representation Geographic Data Type Data Models Representing Spatial and Temporal Data Attributes The Nature of Geographic Data Representations Are needed to convey
RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O
 RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O TOPICS COVERED Spatial Analyst basics Raster / Vector conversion Raster data
RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O TOPICS COVERED Spatial Analyst basics Raster / Vector conversion Raster data
Raster GIS applications Columns
 Raster GIS applications Columns Rows Image: cell value = amount of reflection from surface Thematic layer: cell value = category or measured value - In both cases, there is only one value per cell (in
Raster GIS applications Columns Rows Image: cell value = amount of reflection from surface Thematic layer: cell value = category or measured value - In both cases, there is only one value per cell (in
Algorithms for GIS. Spatial data: Models and representation (part I) Laura Toma. Bowdoin College
 Algorithms for GIS Spatial data: Models and representation (part I) Laura Toma Bowdoin College Outline Spatial data in GIS applications Point data Networks Terrains Planar maps and meshes Data structures
Algorithms for GIS Spatial data: Models and representation (part I) Laura Toma Bowdoin College Outline Spatial data in GIS applications Point data Networks Terrains Planar maps and meshes Data structures
An Introduction to Lidar & Forestry May 2013
 An Introduction to Lidar & Forestry May 2013 Introduction to Lidar & Forestry Lidar technology Derivatives from point clouds Applied to forestry Publish & Share Futures Lidar Light Detection And Ranging
An Introduction to Lidar & Forestry May 2013 Introduction to Lidar & Forestry Lidar technology Derivatives from point clouds Applied to forestry Publish & Share Futures Lidar Light Detection And Ranging
Building Vector Layers
 Building Vector Layers in QGIS Introduction: Spatially referenced data can be separated into two categories, raster and vector data. This week, we focus on the building of vector features. Vector shapefiles
Building Vector Layers in QGIS Introduction: Spatially referenced data can be separated into two categories, raster and vector data. This week, we focus on the building of vector features. Vector shapefiles
Remote Sensing and GIS. GIS Spatial Overlay Analysis
 Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Geology Remote Sensing and GIS GIS Spatial Overlay Analysis RS & GIS XXXI Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator
Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Geology Remote Sensing and GIS GIS Spatial Overlay Analysis RS & GIS XXXI Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator
IMPORTANCE OF TOPOLOGY IN A GIS PROJECT OF MONITORING THE SOILS IN AGRICULTURAL LAND
 IMPORTANCE OF TOPOLOGY IN A GIS PROJECT OF MONITORING THE SOILS IN AGRICULTURAL LAND Abstract Gabriela BIALI, Paula COJOCARU Gheorghe Asachi Technical University of Iasi, 65 Mangeron Blvd, Iasi, Romania
IMPORTANCE OF TOPOLOGY IN A GIS PROJECT OF MONITORING THE SOILS IN AGRICULTURAL LAND Abstract Gabriela BIALI, Paula COJOCARU Gheorghe Asachi Technical University of Iasi, 65 Mangeron Blvd, Iasi, Romania
Raster GIS applications
 Raster GIS applications Columns Rows Image: cell value = amount of reflection from surface DEM: cell value = elevation (also slope/aspect/hillshade/curvature) Thematic layer: cell value = category or measured
Raster GIS applications Columns Rows Image: cell value = amount of reflection from surface DEM: cell value = elevation (also slope/aspect/hillshade/curvature) Thematic layer: cell value = category or measured
Algorithms for GIS csci3225
 Algorithms for GIS csci3225 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Spatial data types and models Spatial data in GIS satellite imagery planar maps surfaces networks point cloud (LiDAR) Spatial data in GIS satellite
Algorithms for GIS csci3225 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Spatial data types and models Spatial data in GIS satellite imagery planar maps surfaces networks point cloud (LiDAR) Spatial data in GIS satellite
Chapter 3: Maps as Numbers
 Chapter 3: Maps as Numbers 3. Representing Maps as Numbers 3.2 Structuring Attributes 3.3 Structuring Maps 3.4 Why Topology Matters 3.5 Formats for GIS Data 3.6 Exchanging Data David Tenenbaum EEOS 265
Chapter 3: Maps as Numbers 3. Representing Maps as Numbers 3.2 Structuring Attributes 3.3 Structuring Maps 3.4 Why Topology Matters 3.5 Formats for GIS Data 3.6 Exchanging Data David Tenenbaum EEOS 265
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 ADVANCED GIS
 Slides by Wheaton et al. (2009-2014) are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 ADVANCED GIS VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton
Slides by Wheaton et al. (2009-2014) are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 ADVANCED GIS VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton
v TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics SMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
MODULE 1 BASIC LIDAR TECHNIQUES
 MODULE SCENARIO One of the first tasks a geographic information systems (GIS) department using lidar data should perform is to check the quality of the data delivered by the data provider. The department
MODULE SCENARIO One of the first tasks a geographic information systems (GIS) department using lidar data should perform is to check the quality of the data delivered by the data provider. The department
The GIS Spatial Data Model
 The GIS Spatial Data Model Introduction: Spatial data are what drive a GIS. Every piece of functionality that makes a GIS separate from another analytical environment is rooted in the spatially explicit
The GIS Spatial Data Model Introduction: Spatial data are what drive a GIS. Every piece of functionality that makes a GIS separate from another analytical environment is rooted in the spatially explicit
v Importing Rasters SMS 11.2 Tutorial Requirements Raster Module Map Module Mesh Module Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial
 v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial teaches how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots,
v. 11.2 SMS 11.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial teaches how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots,
Introduction to ILWIS
 Introduction to ILWIS Source: Cees van Westen Associated Institute of the What is ILWIS? PC-based GIS & Remote Sensing package Developed by ITC A complete package: image processing spatial analysis digital
Introduction to ILWIS Source: Cees van Westen Associated Institute of the What is ILWIS? PC-based GIS & Remote Sensing package Developed by ITC A complete package: image processing spatial analysis digital
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images
 Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Raster Data Model & Analysis
 Topics: 1. Understanding Raster Data 2. Adding and displaying raster data in ArcMap 3. Converting between floating-point raster and integer raster 4. Converting Vector data to Raster 5. Querying Raster
Topics: 1. Understanding Raster Data 2. Adding and displaying raster data in ArcMap 3. Converting between floating-point raster and integer raster 4. Converting Vector data to Raster 5. Querying Raster
Lesson 5 overview. Concepts. Interpolators. Assessing accuracy Exercise 5
 Interpolation Tools Lesson 5 overview Concepts Sampling methods Creating continuous surfaces Interpolation Density surfaces in GIS Interpolators IDW, Spline,Trend, Kriging,Natural neighbors TopoToRaster
Interpolation Tools Lesson 5 overview Concepts Sampling methods Creating continuous surfaces Interpolation Density surfaces in GIS Interpolators IDW, Spline,Trend, Kriging,Natural neighbors TopoToRaster
The Reference Library Generating Low Confidence Polygons
 GeoCue Support Team In the new ASPRS Positional Accuracy Standards for Digital Geospatial Data, low confidence areas within LIDAR data are defined to be where the bare earth model might not meet the overall
GeoCue Support Team In the new ASPRS Positional Accuracy Standards for Digital Geospatial Data, low confidence areas within LIDAR data are defined to be where the bare earth model might not meet the overall
Multidimensional (spatial) Data and Modelling (2)
 Multidimensional (spatial) Data and Modelling (2) 1 Representative operations on maps l l l l l are operations on layers used in maps (all 2-d). Synonyms f. map: layer, spatial partition Def. properties:
Multidimensional (spatial) Data and Modelling (2) 1 Representative operations on maps l l l l l are operations on layers used in maps (all 2-d). Synonyms f. map: layer, spatial partition Def. properties:
VECTOR ANALYSIS: QUERIES, MEASUREMENTS & TRANSFORMATIONS
 VECTOR ANALYSIS: QUERIES, MEASUREMENTS & TRANSFORMATIONS GIS Analysis Winter 2016 Spatial Analysis Operations performed on spatial data that add value Can reveal things that might otherwise be invisible
VECTOR ANALYSIS: QUERIES, MEASUREMENTS & TRANSFORMATIONS GIS Analysis Winter 2016 Spatial Analysis Operations performed on spatial data that add value Can reveal things that might otherwise be invisible
Data handling 2: Transformations
 Intro Geo information Science (GRS 10306) Data handling 2: Transformations 2009/2010 CGI GIRS Transformation definition Query a data handling class of operators which doesn t change the thematic and geometric
Intro Geo information Science (GRS 10306) Data handling 2: Transformations 2009/2010 CGI GIRS Transformation definition Query a data handling class of operators which doesn t change the thematic and geometric
Lecture overview. Visualisatie BMT. Fundamental algorithms. Visualization pipeline. Structural classification - 1. Structural classification - 2
 Visualisatie BMT Fundamental algorithms Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl Lecture overview Classification of algorithms Scalar algorithms Vector algorithms Tensor algorithms Modeling algorithms 1 2 Visualization
Visualisatie BMT Fundamental algorithms Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl Lecture overview Classification of algorithms Scalar algorithms Vector algorithms Tensor algorithms Modeling algorithms 1 2 Visualization
Data handling 3: Alter Process
 Introduction Geo information Science (GRS 10306) Data handling 3: Alter Process 2009/2010 CGI GIRS 2 Alter / process / analysis / operations definition Query a data handling class of operators which doesn
Introduction Geo information Science (GRS 10306) Data handling 3: Alter Process 2009/2010 CGI GIRS 2 Alter / process / analysis / operations definition Query a data handling class of operators which doesn
Image representation. 1. Introduction
 Image representation Introduction Representation schemes Chain codes Polygonal approximations The skeleton of a region Boundary descriptors Some simple descriptors Shape numbers Fourier descriptors Moments
Image representation Introduction Representation schemes Chain codes Polygonal approximations The skeleton of a region Boundary descriptors Some simple descriptors Shape numbers Fourier descriptors Moments
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 17. PATH ANALYSIS AND NETWORK APPLICATIONS 17.1 Path Analysis 17.1.1 Source Raster 17.1.2 Cost Raster Box 17.1 Cost Raster for a Site Analysis of Pipelines 17.1.3 Cost Distance Measures 17.1.4
Chapter 17. PATH ANALYSIS AND NETWORK APPLICATIONS 17.1 Path Analysis 17.1.1 Source Raster 17.1.2 Cost Raster Box 17.1 Cost Raster for a Site Analysis of Pipelines 17.1.3 Cost Distance Measures 17.1.4
Representing the Real World
 Representing the Real World The theory of representing the real world in a GIS using digital data The nature of digital data and binary notation The discrete object view of the world Entities, data objects,
Representing the Real World The theory of representing the real world in a GIS using digital data The nature of digital data and binary notation The discrete object view of the world Entities, data objects,
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WATS 4930/6920 WHERE WE RE GOING WATS 6915 welcome to tag along for any, all or none WEEK FIVE Lecture VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton HOUSEKEEPING
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WATS 4930/6920 WHERE WE RE GOING WATS 6915 welcome to tag along for any, all or none WEEK FIVE Lecture VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton HOUSEKEEPING
Using rasters for interpolation and visualization in GMS
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial Using rasters for interpolation and visualization in GMS Objectives This tutorial teaches how GMS uses rasters to support all kinds of digital elevation models and how rasters
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial Using rasters for interpolation and visualization in GMS Objectives This tutorial teaches how GMS uses rasters to support all kinds of digital elevation models and how rasters
DEVELOPING A THREE-DIMENSIONAL TOPOLOGICAL DATA MODEL
 DEVELOPING A THREE-DIMENSIONAL TOPOLOGICAL DATA MODEL Saadi MESGARI International Institute for Aerospace Survey and Earth Sciences (ITC) The Netherlands Mesgari@itc.nl Working Group IC/16 KEY WORDS: Data
DEVELOPING A THREE-DIMENSIONAL TOPOLOGICAL DATA MODEL Saadi MESGARI International Institute for Aerospace Survey and Earth Sciences (ITC) The Netherlands Mesgari@itc.nl Working Group IC/16 KEY WORDS: Data
Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Database Fundaments. Database. Review: Bits and Bytes
 Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Database Fundaments Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University Review: Bits and Bytes Data stored in a computer system is measured in bits
Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Database Fundaments Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University Review: Bits and Bytes Data stored in a computer system is measured in bits
Geographical Information Systems Institute. Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University. LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap
 Harvard University Introduction to ArcMap Geographical Information Systems Institute Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap Individual files (lab instructions,
Harvard University Introduction to ArcMap Geographical Information Systems Institute Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap Individual files (lab instructions,
v Working with Rasters SMS 12.1 Tutorial Requirements Raster Module Map Module Mesh Module Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial
 v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial teaches how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots,
v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial teaches how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots,
Lidar and GIS: Applications and Examples. Dan Hedges Clayton Crawford
 Lidar and GIS: Applications and Examples Dan Hedges Clayton Crawford Outline Data structures, tools, and workflows Assessing lidar point coverage and sample density Creating raster DEMs and DSMs Data area
Lidar and GIS: Applications and Examples Dan Hedges Clayton Crawford Outline Data structures, tools, and workflows Assessing lidar point coverage and sample density Creating raster DEMs and DSMs Data area
Statistical surfaces and interpolation. This is lecture ten
 Statistical surfaces and interpolation This is lecture ten Data models for representation of surfaces So far have considered field and object data models (represented by raster and vector data structures).
Statistical surfaces and interpolation This is lecture ten Data models for representation of surfaces So far have considered field and object data models (represented by raster and vector data structures).
An Introduction to Spatial Databases
 An Introduction to Spatial Databases R. H. Guting VLDB Journal v3, n4, October 1994 Speaker: Giovanni Conforti Outline: a rather old (but quite complete) survey on Spatial DBMS Introduction & definition
An Introduction to Spatial Databases R. H. Guting VLDB Journal v3, n4, October 1994 Speaker: Giovanni Conforti Outline: a rather old (but quite complete) survey on Spatial DBMS Introduction & definition
The Geographic Names Register of the National Land Survey of Finland
 7 June 2002 English only Eighth United Nations Conference on the Standardization of Geographical Names Berlin, 27 August-5 September 2002 Item 12 (d) of the provisional agenda * Toponymic data files: automated
7 June 2002 English only Eighth United Nations Conference on the Standardization of Geographical Names Berlin, 27 August-5 September 2002 Item 12 (d) of the provisional agenda * Toponymic data files: automated
Georeferencing. Georeferencing: = linking a layer or dataset with spatial coordinates. Registration: = lining up layers with each other
 Georeferencing How do we make sure all our data layers line up? Georeferencing: = linking a layer or dataset with spatial coordinates Registration: = lining up layers with each other Rectification: The
Georeferencing How do we make sure all our data layers line up? Georeferencing: = linking a layer or dataset with spatial coordinates Registration: = lining up layers with each other Rectification: The
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Quizzes Lab 8? WEEK EIGHT Lecture INTERPOLATION & SPATIAL ESTIMATION Joe Wheaton READING FOR TODAY WHAT CAN WE COLLECT AT POINTS?
HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Quizzes Lab 8? WEEK EIGHT Lecture INTERPOLATION & SPATIAL ESTIMATION Joe Wheaton READING FOR TODAY WHAT CAN WE COLLECT AT POINTS?
PART 1. Answers module 6: 'Transformations'
 Answers module 6: 'Transformations' PART 1 1 a A nominal measure scale refers to data that are in named categories. There is no order among these categories. That is, no category is better or more than
Answers module 6: 'Transformations' PART 1 1 a A nominal measure scale refers to data that are in named categories. There is no order among these categories. That is, no category is better or more than
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 4 Digital Image Fundamentals - II ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 4 Digital Image Fundamentals - II ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects. William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA
 Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA Overview 1. Some Ways to Structure Space 2. What to Put into a Grid 3. Objects and Fields 4. Hybrid Structures
Thoughts on Representing Spatial Objects William A. Huber Quantitative Decisions Rosemont, PA Overview 1. Some Ways to Structure Space 2. What to Put into a Grid 3. Objects and Fields 4. Hybrid Structures
Topic 3: GIS Models 10/2/2017. What is a Model? What is a GIS Model. Geography 38/42:477 Advanced Geomatics
 Geography 38/42:477 Advanced Geomatics Topic 3: GIS Models What is a Model? Simplified representation of real world Physical, Schematic, Mathematical Map GIS database Reduce complexity and help us understand
Geography 38/42:477 Advanced Geomatics Topic 3: GIS Models What is a Model? Simplified representation of real world Physical, Schematic, Mathematical Map GIS database Reduce complexity and help us understand
Accuracy, Support, and Interoperability. Michael F. Goodchild University of California Santa Barbara
 Accuracy, Support, and Interoperability Michael F. Goodchild University of California Santa Barbara The traditional view Every object has a true position and set of attributes with enough time and resources
Accuracy, Support, and Interoperability Michael F. Goodchild University of California Santa Barbara The traditional view Every object has a true position and set of attributes with enough time and resources
LIDAR in the Pines SD Macintosh Version Boyd Ostroff 12/23/2018
 LIDAR in the Pines SD Macintosh Version Boyd Ostroff 12/23/2018 LIDAR in the Pines SD is a lower resolution version of LIDAR in the Pines HD converted to Garmin s traditional.img file format. Although
LIDAR in the Pines SD Macintosh Version Boyd Ostroff 12/23/2018 LIDAR in the Pines SD is a lower resolution version of LIDAR in the Pines HD converted to Garmin s traditional.img file format. Although
M. Andrea Rodríguez-Tastets. I Semester 2008
 M. -Tastets Universidad de Concepción,Chile andrea@udec.cl I Semester 2008 Outline refers to data with a location on the Earth s surface. Examples Census data Administrative boundaries of a country, state
M. -Tastets Universidad de Concepción,Chile andrea@udec.cl I Semester 2008 Outline refers to data with a location on the Earth s surface. Examples Census data Administrative boundaries of a country, state
A DATA STRUCTURE FOR A RASTER MAP DATA BASE. Roger L.T. Cederberg National Defence Research Institute Box 1165, S Linkoping, Sweden.
 A DATA STRUCTURE FOR A RASTER MAP DATA BASE Introduction Roger L.T. Cederberg National Defence Research Institute Box 1165, S-581 11 Linkoping, Sweden. The increasing requirement for geographically referen
A DATA STRUCTURE FOR A RASTER MAP DATA BASE Introduction Roger L.T. Cederberg National Defence Research Institute Box 1165, S-581 11 Linkoping, Sweden. The increasing requirement for geographically referen
Spatial Analysis (Vector) II
 Spatial Analysis (Vector) II GEOG 300, Lecture 9 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 A Spatial Network is a set of geographic locations interconnected in a system by a number of routes is a system of linear features
Spatial Analysis (Vector) II GEOG 300, Lecture 9 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 A Spatial Network is a set of geographic locations interconnected in a system by a number of routes is a system of linear features
ArcScan. for ArcGIS. GIS by ESRI
 ArcScan for ArcGIS GIS by ESRI Copyright 2002 ESRI All rights reserved Printed in the United States of America The information contained in this document is the exclusive property of ESRI This work is
ArcScan for ArcGIS GIS by ESRI Copyright 2002 ESRI All rights reserved Printed in the United States of America The information contained in this document is the exclusive property of ESRI This work is
