M. Andrea Rodríguez-Tastets. I Semester 2008
|
|
|
- Vivien Golden
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 M. -Tastets Universidad de Concepción,Chile I Semester 2008
2 Outline
3 refers to data with a location on the Earth s surface. Examples Census data Administrative boundaries of a country, state and county Relief data (e.g. from contours) on transport networks A text about a specific place (e.g., textual description of touristics places) A photograph or painting of a building A satellite image
4 information can be used to answer where is a specific entity (physical object) or what is at a particular location on the Earth s surface.
5 Andrea Rodrı guez
6 Andrea Rodrı guez What is it?
7 Andrea Rodrı guez lake
8 Andrea Rodrı guez Where is it? lake
9 information differs in nature depending on the type of application and the way it is obtained. Data From Primary data collection in the field. Data is collected from field surveys or remotely collected using remote sensing techniques. An important issue when collecting data is to include delimiting geographic objects and associating thematic attributes. Existing maps. It may imply to integrate maps, which could come with different scale and reference system.
10 GIS as a Type of Software A computer system that allows us to handle information about the location of features or phenomena on the Earth s surface. A system that has all the functionality of a conventional DBMS plus much of the functionality of a computer mapping system. GIS as a Tool-Kit Spatial manipulation (determination of spatial relations, changes in scales and projections,... ) Spatial analysis (quantitative and qualitative spatial analysis) Visualization of spatial data (maps, tables, 3D surfaces)
11 In GIS, themes gather geographical information about a particular topic (e.g., rivers, cities, and countries). They are displayed as maps (e.g., topographic maps, weather maps, soil-type maps). Until now, GIS has been concentrated on the geometric aspects of spatial representation and manipulation, and how these aspects change over time.
12 GIS and DBMS GIS Interface to spatial applicaction Core Spatial Functionality Taxonomy Data Representation Operations Query Languages Algorithms Access Methods Interface to DBMS DBMS
13 Data of a specific domain, with its own semantics and where particular rules apply. Support multiple spatial data models Support spatial operations Support query languages and query processing over spatial data (indexing and search) Should: Contain a good framework to combine geometric with thematic information Be as general as possible and not designed for one particular area of applications Have a formally defined semantics that is closed under set theoretic, geometric and topological operations, and that is defined in terms of finite representations Be independent of a particular DBMS but cooperate with any Use efficient implementation techniques Have a gateway to multimedia and visual interface
14 Characteristics of There is no clear separation between what is handled by the SDBMS and an application. For example, is the query find the shortest path part of the query language? Modeling of a single conceptual object: city, river and road. Modeling a collection of objects Coverage-partitions: administrative boundaries Network: transportation networks Aggregation: counties - states -country Terrain digital models
15 Geo- Requirements information deals with spatial and non-spatial (aspatial) data Data are highly structured by the notion of object aggregation The existence of user-defined operations that require an extensible underlying model The existence of functions that exist at different levels of abstraction (geometric types and maps)
16 Types of Users Manipulate spatial data Transportation system monitoring Cadastral systems Spatial data analysis Analysis of flood risk areas Comparing resonance images Final users (high-level users) Navigation systems
17 Database of spatial data in secondary memory Spatial semantics embedded in the query language Spatial Access methods GIS Motivate SDBMS Clients of SDBMS A large number Quantitative ofdata spa SDBMS allows GIS to
18 Two views of the space are: objects (where) and fields (what). They lead us to different abstractions and representations of space.
19 Discrete Items: Objects Individuals with an identity. Individuals whose spatial extend is described by their boundaries. They usually have some property values throughout the entire individual. Examples: this town the trajectory from home to work the parking lot
20 Objects and Aggregate Objects Objects are grouped into themes or maps. theme = {geographic object} geographic object = (thematic description, spatial description)//atomic (thematic description, {geographic object})//complex
21 Objects: Spatial Geometry (location and shape) b z B A a x y Topology x a A B b y
22 Spatial Relations: Topological Relations Disjoint (d) Meet (m) Overlap (o) Covered_by (cb) Covers (cv) Inside (i) Equal (e) Contains (ct) Topological relations are invariant under rotation, translation and scaling.
23 A Model of Topological Relations The 9-intersection model defines topological relations between regions in terms of the set-intersection of objects boundaries, interiors, and exteriors. For example, in the following we have the 9-intersection definition of disjoint. A B A δa A B δb B
24 Spatial Relations: Direction Relations NW N NE W SW S E SE
25 Spatial Relations: Distance Relations far
26 Distributions: Fields Properties values change across space. Continuos space and property values. Values are determined by sampling. Require interpolation to derive values at locations without observations. Examples: elevation over the Andes Mountains temperature on the coast the speed of my trip from home to work
27 Field Properties Position (space S and time T ) Value of type A α associated with a position Spatio-temporal function as a model of a field (interpolation function): F : S T A α
28 While quantitative spatial descriptions deal with data we can draw clear boundaries as on maps, qualitative spatial descriptions deal with data whose boundaries are unclear or unknown, but still with data we can apply some kind of spatial analysis.
29 Quantitative Size limited in terms of absolute units. Number of classes depending on granularity. Limited vocabulary. Infinite amount of valid sentences. Spatial configurations captured very precisely. s are typically complete. Bottom up.
30 Distinctions in terms of relations instead of absolute values. Limited vocabulary, but large vocabulary. Only necessary distinctions. Variable resolution. Finite amount of valid sentences. Vagueness. s are typically incomplete. Top down.
31 Spatial Reasoning Inference of missing information IF Chile is west of Argentina and Eastern island is part of Chile THEN Eastern island is west of Argentina Evaluation of consistency IF A is west B and Eastern island is part of Chile THEN Eastern island must west of Argentina
32 Changes over geometry (location/shape). So, we have geometries that are valid at a particular time instant or time interval. Changes may occur discretely. Changes may occur continuously. In addition to spatial relations, we have now temporal and spatio-temporal relations. We may be interesting in historical data or in predicting future data.
33 Represent geographical information in the n-dimensional real space R n (an infinite or non-enumerate set of points). They use (linear) approximations to represent objects boundaries or discrete approximations for objects and fields. They have an important influence on the operations (embedded in the model or user-defined operations). We would expect that they were closed under operations.
34 Three Broad Types of Tessellation or partitions of space Vector Linear constraints In theory, each of these types of data models can represent objects and fields.
35 Objects: Tessellation A regular (irregular) tessellation divides the space into regular (irregular) cells (pixels). An object is represented by the set of cells that contain it.
36 Objects: Spaghetti Model (Vector) point : [x : real, y : real] polyline : < point > polygon : < point > regions : {polygon} A [2,5] [3,3] B [6,3] [7,5] A :< [1, 1], [3, 3], [2, 5], [1, 1] > B :< [3, 3], [6, 3], [7, 5], [2, 5], [3, 3] > [1,1]
37 Objects: Network Model (Vector) a [1,1] n 2 [2,5] c A b point : [x : real, y : real] node : [point, < arc >] arc : [node, node, < point >] polygon : < point > regions : {polygon} f B n 1 [3,3] d [6,3] [7,5] e A :< a, b, c > B :< c, d, e, f > c : [n 1, n 2, < [3, 3], [2, 5] >] n 1 : [[3, 3], < b, d, c >] n 2 : [[2, 5], < a, c, f >]
38 Objects: Topological Model (Vector) a [1,1] n 2 [2,5] c A b point : [x : real, y : real] node : [point, < arc >] arc : [node, node, < point >] polygon : < arc > regions : {polygon} f B n 1 [3,3] d [6,3] [7,5] e A :< a, b, c > B :< c, d, e, f > c : [n 1, n 2, A, B, < [3, 3], [2, 5] >] n 1 : [[3, 3], < b, d, c >] n 2 : [[2, 5], < a, c, f >]
39 Objects: Linear Constraint Model Boundaries are represented by linear constraints of the form p i=1 a ix i Θa 0, with Θ a predicate =,, or, x i a variable, and a i a constant. [1,1] A [2,5] [3,3] B [6,3] [7,5] A : y x y 4x y + 2x 9 0 B : y 3 y 7 y 2x x + y 9 0
40 Fields: Tessellation A regular or irregular tessellation divides the space into cells (pixels). The field-based data is still represented as a function from space to a range; however, the function domain in not an infinite set of points but a finite set of pixels or cells.
41 Fields: Vector An example of a vector model for fields is a TIN (Triangulated Irregular Network). A TIN is based on a triangular partition of 2D space. No assumption is made about the distribution of the points. The elevation (property) value is recorded at each vertex and inferred at any other point P by linear interpolation of the three vertices of the triangle that contains P.
42 Fields: Linear constraints We can use linear constraints for representing the equivalent of a TIN with a constraint of the form: c i (x, y) h = f (x, y) where c i (x, y) denotes a conjunction of inequalities on (x, y) representing the triangle o region associated with the property value defined by the equality constraint h = f (x, y) among variables h, x and y, with f being a linear function of x and y. h y h=f(x,y) c i (x,y) x
43 Beyond Classical Fields: A framework for Spatio-Temporal A model based on a theory that enables prediction is verifiable through new observations can be improved with higher resolution measurements
44 A continuous spatial field 1 + sinxy+ 1 2 cos2x+ 1 3 sin3y+ 1 4 cos4(x+y) 1+ sin5y+ 1 2 cos6x+ 1 3 sin7y+ 1 4 cos8x (sin10xy+ 1 2 cos10x+ 1 3 sin12y+ 1 4 cos13(x+y)) 1+ sin14y+ 1 2 cos15x+ 1 3 sin16y+ 1 4 cos17x A continuous change over time sinxy+ 1 2 costx+ 1 3 sinty+ 1 4 cos4(x+y) 1+ sin5y+ 1 2 cos6x+ 1 3 sin7y+ 1 4 cos8x 1 + (sin10xy+ 1 2 cos10x+ 1 3 sin12y+ 1 4 cos13(x+y)) t+ sin14y+ 1 2 cos15x+ 1 3 sin16y+ 1 cos17x 4
45 Geometric Geometric integrity constraints are defined according to the spatial data model to ensure spatial data consistency. They may also be a requirement for geometric algorithms. Typical geometric integrity constraints are: Tessellation: for every point p, p is in only one cell, and every cell has a corresponding property value. Polyline: with the exception of the extreme point, each line segment ends when it starts the next line segment. Polygon: is a closed polyline. Simple polyline: two polylines only intersect at the extreme point of a line segment.
46 Topological Without concerning the semantics of physical objects, I also distinguish constraints that are not related to the spatial data model, but to the manipulation of data. I refer to these constraints as topological constraints, which are particularly useful among multiple representations of the same physical objects or when there are continuous changes of objects geometry.
47 Data : Unary Operations Unary operations with Boolean result: op : spatial Boolean: convex test connected test Unary operations with scalar results op : spatial int: length area perimeter Unary operations with spatial result: op : spatial spatial: topological transformations (e.g., rotation, translation and scaling) transformation to another object of different dimension (e.g., boundary) object extraction (e.g., minimal bounding rectangle, centroide, buffering)
48 Data : N- ary Operations N-ary operations with spatial result: op : spatial spatial: Voronoi Convex hull
49 Data : Binary Operations Binary operations with spatial result: op : spatial spatial spatial: union U intersection difference / U = = =
50 Data : Binary Operations Binary operations with Boolean result: op : spatial spatial Boolean: topological predicates direction predicates metric predicates Binary operations with scalar result: op : spatial spatial int: distance
Class #2. Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures
 Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
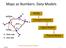 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Representing Geography
 Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Multidimensional Data and Modelling - Operations
 Multidimensional Data and Modelling - Operations 1 Problems of multidimensional data structures l multidimensional (md-data or spatial) data and their implementation of operations between objects (spatial
Multidimensional Data and Modelling - Operations 1 Problems of multidimensional data structures l multidimensional (md-data or spatial) data and their implementation of operations between objects (spatial
Understanding Geospatial Data Models
 Understanding Geospatial Data Models 1 A geospatial data model is a formal means of representing spatially referenced information. It is a simplified view of physical entities and a conceptualization of
Understanding Geospatial Data Models 1 A geospatial data model is a formal means of representing spatially referenced information. It is a simplified view of physical entities and a conceptualization of
Multidimensional Data and Modelling - DBMS
 Multidimensional Data and Modelling - DBMS 1 DBMS-centric approach Summary: l Spatial data is considered as another type of data beside conventional data in a DBMS. l Enabling advantages of DBMS (data
Multidimensional Data and Modelling - DBMS 1 DBMS-centric approach Summary: l Spatial data is considered as another type of data beside conventional data in a DBMS. l Enabling advantages of DBMS (data
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis. GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University
 Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
An Introduction to Spatial Databases
 An Introduction to Spatial Databases R. H. Guting VLDB Journal v3, n4, October 1994 Speaker: Giovanni Conforti Outline: a rather old (but quite complete) survey on Spatial DBMS Introduction & definition
An Introduction to Spatial Databases R. H. Guting VLDB Journal v3, n4, October 1994 Speaker: Giovanni Conforti Outline: a rather old (but quite complete) survey on Spatial DBMS Introduction & definition
Multidimensional (spatial) Data and Modelling (2)
 Multidimensional (spatial) Data and Modelling (2) 1 Representative operations on maps l l l l l are operations on layers used in maps (all 2-d). Synonyms f. map: layer, spatial partition Def. properties:
Multidimensional (spatial) Data and Modelling (2) 1 Representative operations on maps l l l l l are operations on layers used in maps (all 2-d). Synonyms f. map: layer, spatial partition Def. properties:
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices nodes tart node nd node arcs Reality Conceptual Models The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can be queried and analyzed Translate: Real World Locations,
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices nodes tart node nd node arcs Reality Conceptual Models The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can be queried and analyzed Translate: Real World Locations,
Multidimensional Data and Modelling
 Multidimensional Data and Modelling 1 Problems of multidimensional data structures l multidimensional (md-data or spatial) data and their implementation of operations between objects (spatial data practically
Multidimensional Data and Modelling 1 Problems of multidimensional data structures l multidimensional (md-data or spatial) data and their implementation of operations between objects (spatial data practically
layers in a raster model
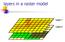 layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models
 Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary Learning Objectives Learning
Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary Learning Objectives Learning
Introduction to Spatial Database Systems. Outline
 Introduction to Spatial Database Systems by Cyrus Shahabi from Ralf Hart Hartmut Guting s VLDB Journal v3, n4, October 1994 1 Outline Introduction & definition Modeling Querying Data structures and algorithms
Introduction to Spatial Database Systems by Cyrus Shahabi from Ralf Hart Hartmut Guting s VLDB Journal v3, n4, October 1994 1 Outline Introduction & definition Modeling Querying Data structures and algorithms
SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015
 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 GIS Data Organization The basics Data can be organized in a variety of ways Spatial location, content (attributes), frequency of use Come up with a system
SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 GIS Data Organization The basics Data can be organized in a variety of ways Spatial location, content (attributes), frequency of use Come up with a system
Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models
 Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
Analytical and Computer Cartography Winter Lecture 9: Geometric Map Transformations
 Analytical and Computer Cartography Winter 2017 Lecture 9: Geometric Map Transformations Cartographic Transformations Attribute Data (e.g. classification) Locational properties (e.g. projection) Graphics
Analytical and Computer Cartography Winter 2017 Lecture 9: Geometric Map Transformations Cartographic Transformations Attribute Data (e.g. classification) Locational properties (e.g. projection) Graphics
Contents of Lecture. Surface (Terrain) Data Models. Terrain Surface Representation. Sampling in Surface Model DEM
 Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Chapter 1: Introduction to Spatial Databases
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Spatial Databases 1.1 Overview 1.2 Application domains 1.3 Compare a SDBMS with a GIS 1.4 Categories of Users 1.5 An example of an SDBMS application 1.6 A Stroll though a spatial
Chapter 1: Introduction to Spatial Databases 1.1 Overview 1.2 Application domains 1.3 Compare a SDBMS with a GIS 1.4 Categories of Users 1.5 An example of an SDBMS application 1.6 A Stroll though a spatial
Advanced Data Types and New Applications
 Advanced Data Types and New Applications These slides are a modified version of the slides of the book Database System Concepts (Chapter 24), 5th Ed., McGraw-Hill, by Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan.
Advanced Data Types and New Applications These slides are a modified version of the slides of the book Database System Concepts (Chapter 24), 5th Ed., McGraw-Hill, by Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan.
Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University
 Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University Outline of Today Last week, we learned: Characteristics of spatial data Types of spatial data
Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University Outline of Today Last week, we learned: Characteristics of spatial data Types of spatial data
GIS Data Models. 4/9/ GIS Data Models
 GIS Data Models 1 Conceptual models of the real world The real world can be described using two conceptually different models: 1. As discrete objects, possible to represent as points, lines or polygons.
GIS Data Models 1 Conceptual models of the real world The real world can be described using two conceptually different models: 1. As discrete objects, possible to represent as points, lines or polygons.
Introduction to GIS. Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 9/24/2015. R. Khosla Fall Semester The real world. What in the world is GIS?
 Introduction to GIS Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 What in the world is GIS? GIS is simultaneously the telescope, the microscope, the computer and the Xerox machine of regional analysis and synthesis
Introduction to GIS Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 What in the world is GIS? GIS is simultaneously the telescope, the microscope, the computer and the Xerox machine of regional analysis and synthesis
Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Database Fundaments. Database. Review: Bits and Bytes
 Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Database Fundaments Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University Review: Bits and Bytes Data stored in a computer system is measured in bits
Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Database Fundaments Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University Review: Bits and Bytes Data stored in a computer system is measured in bits
Graphic Display of Vector Object
 What is GIS? GIS stands for Geographic Information Systems, although the term Geographic Information Science is gaining popularity. A GIS is a software platform for storing, organizing, viewing, querying,
What is GIS? GIS stands for Geographic Information Systems, although the term Geographic Information Science is gaining popularity. A GIS is a software platform for storing, organizing, viewing, querying,
Advanced Data Types and New Applications
 Advanced Data Types and New Applications These slides are a modified version of the slides of the book Database System Concepts (Chapter 24), 5th Ed., McGraw-Hill, by Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan.
Advanced Data Types and New Applications These slides are a modified version of the slides of the book Database System Concepts (Chapter 24), 5th Ed., McGraw-Hill, by Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan.
Representing the Real World
 Representing the Real World The theory of representing the real world in a GIS using digital data The nature of digital data and binary notation The discrete object view of the world Entities, data objects,
Representing the Real World The theory of representing the real world in a GIS using digital data The nature of digital data and binary notation The discrete object view of the world Entities, data objects,
Statistical surfaces and interpolation. This is lecture ten
 Statistical surfaces and interpolation This is lecture ten Data models for representation of surfaces So far have considered field and object data models (represented by raster and vector data structures).
Statistical surfaces and interpolation This is lecture ten Data models for representation of surfaces So far have considered field and object data models (represented by raster and vector data structures).
Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS.
 GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
Algorithms for GIS. Spatial data: Models and representation (part I) Laura Toma. Bowdoin College
 Algorithms for GIS Spatial data: Models and representation (part I) Laura Toma Bowdoin College Outline Spatial data in GIS applications Point data Networks Terrains Planar maps and meshes Data structures
Algorithms for GIS Spatial data: Models and representation (part I) Laura Toma Bowdoin College Outline Spatial data in GIS applications Point data Networks Terrains Planar maps and meshes Data structures
L1-Spatial Concepts L1 - Spatial Concepts
 L1 - Spatial Concepts NGEN06(TEK230) Algorithms in Geographical Information Systems Aim Understand the relationship between spatial queries and mathematical concepts. Know how topological relationships
L1 - Spatial Concepts NGEN06(TEK230) Algorithms in Geographical Information Systems Aim Understand the relationship between spatial queries and mathematical concepts. Know how topological relationships
Chapter 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information. 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.
 Chapter 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2. Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary What is a Data Model? What
Chapter 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2. Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary What is a Data Model? What
Algorithms for GIS csci3225
 Algorithms for GIS csci3225 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Spatial data types and models Spatial data in GIS satellite imagery planar maps surfaces networks point cloud (LiDAR) Spatial data in GIS satellite
Algorithms for GIS csci3225 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Spatial data types and models Spatial data in GIS satellite imagery planar maps surfaces networks point cloud (LiDAR) Spatial data in GIS satellite
Introduction to GIS 2011
 Introduction to GIS 2011 Digital Elevation Models CREATING A TIN SURFACE FROM CONTOUR LINES 1. Start ArcCatalog from either Desktop or Start Menu. 2. In ArcCatalog, create a new folder dem under your c:\introgis_2011
Introduction to GIS 2011 Digital Elevation Models CREATING A TIN SURFACE FROM CONTOUR LINES 1. Start ArcCatalog from either Desktop or Start Menu. 2. In ArcCatalog, create a new folder dem under your c:\introgis_2011
Longley Chapter 3. Representations
 Longley Chapter 3 Digital Geographic Data Representation Geographic Data Type Data Models Representing Spatial and Temporal Data Attributes The Nature of Geographic Data Representations Are needed to convey
Longley Chapter 3 Digital Geographic Data Representation Geographic Data Type Data Models Representing Spatial and Temporal Data Attributes The Nature of Geographic Data Representations Are needed to convey
Geographic Information Fundamentals Overview
 CEN TC 287 Date: 1998-07 CR 287002:1998 CEN TC 287 Secretariat: AFNOR Geographic Information Fundamentals Overview Geoinformation Übersicht Information géographique Vue d'ensemble ICS: Descriptors: Document
CEN TC 287 Date: 1998-07 CR 287002:1998 CEN TC 287 Secretariat: AFNOR Geographic Information Fundamentals Overview Geoinformation Übersicht Information géographique Vue d'ensemble ICS: Descriptors: Document
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models
 Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
Scope and Sequence for the New Jersey Core Curriculum Content Standards
 Scope and Sequence for the New Jersey Core Curriculum Content Standards The following chart provides an overview of where within Prentice Hall Course 3 Mathematics each of the Cumulative Progress Indicators
Scope and Sequence for the New Jersey Core Curriculum Content Standards The following chart provides an overview of where within Prentice Hall Course 3 Mathematics each of the Cumulative Progress Indicators
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
IST 210. Introduction to Spatial Databases
 Introduction to Spatial Databases Evolution of acronym GIS Geographic Information Systems (1980s) Geographic Information Science (1990s) Geographic Information Services (2000s) GISystems GIServices GIScience
Introduction to Spatial Databases Evolution of acronym GIS Geographic Information Systems (1980s) Geographic Information Science (1990s) Geographic Information Services (2000s) GISystems GIServices GIScience
DATA MODELS IN GIS. Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi
 DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
CPSC 695. Methods for interpolation and analysis of continuing surfaces in GIS Dr. M. Gavrilova
 CPSC 695 Methods for interpolation and analysis of continuing surfaces in GIS Dr. M. Gavrilova Overview Data sampling for continuous surfaces Interpolation methods Global interpolation Local interpolation
CPSC 695 Methods for interpolation and analysis of continuing surfaces in GIS Dr. M. Gavrilova Overview Data sampling for continuous surfaces Interpolation methods Global interpolation Local interpolation
4/7/2009. Model: Abstraction of reality following formal rules e.g. Euclidean space for physical space
 Model: Abstraction of reality following formal rules e.g. Euclidean space for physical space At different levels: mathematical model (Euclidean space) conceptual design model (ER model) data model (design)
Model: Abstraction of reality following formal rules e.g. Euclidean space for physical space At different levels: mathematical model (Euclidean space) conceptual design model (ER model) data model (design)
Announcements. Data Sources a list of data files and their sources, an example of what I am looking for:
 Data Announcements Data Sources a list of data files and their sources, an example of what I am looking for: Source Map of Bangor MEGIS NG911 road file for Bangor MEGIS Tax maps for Bangor City Hall, may
Data Announcements Data Sources a list of data files and their sources, an example of what I am looking for: Source Map of Bangor MEGIS NG911 road file for Bangor MEGIS Tax maps for Bangor City Hall, may
Semantics and Ontologies for Geospatial Information. Dr Kristin Stock
 Semantics and Ontologies for Geospatial Information Dr Kristin Stock Introduction The study of semantics addresses the issue of what data means, including: 1. The meaning and nature of basic geospatial
Semantics and Ontologies for Geospatial Information Dr Kristin Stock Introduction The study of semantics addresses the issue of what data means, including: 1. The meaning and nature of basic geospatial
The Computational Geometry Algorithms Library. Andreas Fabri GeometryFactory
 The Computational Geometry Algorithms Library Andreas Fabri GeometryFactory Mission Statement Make the large body of geometric algorithms developed in the field of computational geometry available for
The Computational Geometry Algorithms Library Andreas Fabri GeometryFactory Mission Statement Make the large body of geometric algorithms developed in the field of computational geometry available for
BASE FLOOD ELEVATION DETERMINATION MODULE
 BASE FLOOD ELEVATION DETERMINATION MODULE FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AGENCY PREPARED BY: NOLTE ASSOCIATES, INC. June, 2003 ABSTRACT The FEMA Base Flood Elevation Determination Module is a Visual Basic
BASE FLOOD ELEVATION DETERMINATION MODULE FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AGENCY PREPARED BY: NOLTE ASSOCIATES, INC. June, 2003 ABSTRACT The FEMA Base Flood Elevation Determination Module is a Visual Basic
Introduction to Spatial Database Systems
 Introduction to Spatial Database Systems by Cyrus Shahabi Spatial Databases: A Tour, Shashi Shekhar and Sanjay Chawla * Hart Hartmut Guting s VLDB Journal v3, n4, October 1994 Value of SDBMS Traditional
Introduction to Spatial Database Systems by Cyrus Shahabi Spatial Databases: A Tour, Shashi Shekhar and Sanjay Chawla * Hart Hartmut Guting s VLDB Journal v3, n4, October 1994 Value of SDBMS Traditional
Terms and definitions * keep definitions of processes and terms that may be useful for tests, assignments
 Lecture 1 Core of GIS Thematic layers Terms and definitions * keep definitions of processes and terms that may be useful for tests, assignments Lecture 2 What is GIS? Info: value added data Data to solve
Lecture 1 Core of GIS Thematic layers Terms and definitions * keep definitions of processes and terms that may be useful for tests, assignments Lecture 2 What is GIS? Info: value added data Data to solve
Motion Planning. O Rourke, Chapter 8
 O Rourke, Chapter 8 Outline Translating a polygon Moving a ladder Shortest Path (Point-to-Point) Goal: Given disjoint polygons in the plane, and given positions s and t, find the shortest path from s to
O Rourke, Chapter 8 Outline Translating a polygon Moving a ladder Shortest Path (Point-to-Point) Goal: Given disjoint polygons in the plane, and given positions s and t, find the shortest path from s to
Lecture 2: GIS Data Sources, Data Types and Representation. GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University
 Lecture 2: GIS Data Sources, Data Types and Representation GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University Geographic Data in GIS Can be obtained from various sources in different
Lecture 2: GIS Data Sources, Data Types and Representation GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University Geographic Data in GIS Can be obtained from various sources in different
Spatial Data Models. Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities
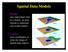 Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Content Standard 1: Numbers, Number Sense, and Computation
 Content Standard 1: Numbers, Number Sense, and Computation Place Value Fractions Comparing and Ordering Counting Facts Estimating and Estimation Strategies Determine an approximate value of radical and
Content Standard 1: Numbers, Number Sense, and Computation Place Value Fractions Comparing and Ordering Counting Facts Estimating and Estimation Strategies Determine an approximate value of radical and
TOWARDS A 3D SPATIAL QUERY LANGUAGE FOR BUILDING INFORMATION MODELS
 TOWARDS A D SPATIAL QUERY LANGUAGE FOR BUILDING INFORMATION MODELS André Borrmann 1, Christoph van Treeck 1, and Ernst Rank 1 ABSTRACT The paper introduces the concept of a spatial query language for building
TOWARDS A D SPATIAL QUERY LANGUAGE FOR BUILDING INFORMATION MODELS André Borrmann 1, Christoph van Treeck 1, and Ernst Rank 1 ABSTRACT The paper introduces the concept of a spatial query language for building
v SMS 11.1 Tutorial SRH-2D Prerequisites None Time minutes Requirements Map Module Mesh Module Scatter Module Generic Model SRH-2D
 v. 11.1 SMS 11.1 Tutorial SRH-2D Objectives This lesson will teach you how to prepare an unstructured mesh, run the SRH-2D numerical engine and view the results all within SMS. You will start by reading
v. 11.1 SMS 11.1 Tutorial SRH-2D Objectives This lesson will teach you how to prepare an unstructured mesh, run the SRH-2D numerical engine and view the results all within SMS. You will start by reading
17/07/2013 RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES RASTER DATA MODEL& STRUCTURE TIN- TRIANGULAR IRREGULAR NETWORK
 RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES Space is subdivided into regular grids of square grid cells or other forms of polygonal meshes known as picture elements (pixels) the
RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES Space is subdivided into regular grids of square grid cells or other forms of polygonal meshes known as picture elements (pixels) the
Map Library ArcView Version 1 02/20/03 Page 1 of 12. ArcView GIS
 Map Library ArcView Version 1 02/20/03 Page 1 of 12 1. Introduction 1 ArcView GIS ArcView is the most popular desktop GIS analysis and map presentation software package.. With ArcView GIS you can create
Map Library ArcView Version 1 02/20/03 Page 1 of 12 1. Introduction 1 ArcView GIS ArcView is the most popular desktop GIS analysis and map presentation software package.. With ArcView GIS you can create
GEOSPATIAL ENGINEERING COMPETENCIES. Geographic Information Science
 GEOSPATIAL ENGINEERING COMPETENCIES Geographic Information Science The character and structure of spatial information, its methods of capture, organisation, classification, qualification, analysis, management,
GEOSPATIAL ENGINEERING COMPETENCIES Geographic Information Science The character and structure of spatial information, its methods of capture, organisation, classification, qualification, analysis, management,
Geometric and Thematic Integration of Spatial Data into Maps
 Geometric and Thematic Integration of Spatial Data into Maps Mark McKenney Department of Computer Science, Texas State University mckenney@txstate.edu Abstract The map construction problem (MCP) is defined
Geometric and Thematic Integration of Spatial Data into Maps Mark McKenney Department of Computer Science, Texas State University mckenney@txstate.edu Abstract The map construction problem (MCP) is defined
LECTURE 2 SPATIAL DATA MODELS
 LECTURE 2 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Computers and GIS cannot directly be applied to the real world: a data gathering step comes first. Digital computers operate in numbers and characters held internally as binary
LECTURE 2 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Computers and GIS cannot directly be applied to the real world: a data gathering step comes first. Digital computers operate in numbers and characters held internally as binary
CSG obj. oper3. obj1 obj2 obj3. obj5. obj4
 Solid Modeling Solid: Boundary + Interior Volume occupied by geometry Solid representation schemes Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) Boundary representations (B-reps) Space-partition representations Operations
Solid Modeling Solid: Boundary + Interior Volume occupied by geometry Solid representation schemes Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) Boundary representations (B-reps) Space-partition representations Operations
v TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics SMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisites Overview Tutorial
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial TUFLOW-2D Hydrodynamics Objectives This tutorial describes the generation of a TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. This project utilizes only the two dimensional flow calculation
Feature Enhancements by Release
 Autodesk Map Feature Enhancements by Release This document highlights the feature enhancements that have occurred with each release of Autodesk Map software from Release 4 (2000i) through the current 2004
Autodesk Map Feature Enhancements by Release This document highlights the feature enhancements that have occurred with each release of Autodesk Map software from Release 4 (2000i) through the current 2004
v Introduction to WMS Become familiar with the WMS interface WMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisite Tutorials None
 s v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Read files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
s v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Read files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
CS-235 Computational Geometry
 CS-235 Computational Geometry Computer Science Department Fall Quarter 2002. Computational Geometry Study of algorithms for geometric problems. Deals with discrete shapes: points, lines, polyhedra, polygonal
CS-235 Computational Geometry Computer Science Department Fall Quarter 2002. Computational Geometry Study of algorithms for geometric problems. Deals with discrete shapes: points, lines, polyhedra, polygonal
Anoka Hennepin K-12 Curriculum plan
 Anoka Hennepin K-12 Curriculum plan Department: Elementary Math Unit Title: Packages and Polygons (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Triangles and Beyond (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Everyday Math: Volume
Anoka Hennepin K-12 Curriculum plan Department: Elementary Math Unit Title: Packages and Polygons (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Triangles and Beyond (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Everyday Math: Volume
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe
 CHAPTER 26 Enhanced Data Models: Introduction to Active, Temporal, Spatial, Multimedia, and Deductive Databases 26.1 Active Database Concepts and Triggers Database systems implement rules that specify
CHAPTER 26 Enhanced Data Models: Introduction to Active, Temporal, Spatial, Multimedia, and Deductive Databases 26.1 Active Database Concepts and Triggers Database systems implement rules that specify
UTM Geo Map APP Quick Start (Version 1.2)
 UTM Geo Map APP Quick Start (Version 1.2) Measure Points (Marker) You can measure points of coordinate base on GPS or position on the Maps and save marker into database for unlimited number using Real-time
UTM Geo Map APP Quick Start (Version 1.2) Measure Points (Marker) You can measure points of coordinate base on GPS or position on the Maps and save marker into database for unlimited number using Real-time
Chapter 7 Spatial Operation
 7.1 Introduction Chapter 7 Spatial Operation Q: What is spatial operation? A: Spatial operation is computational manipulation of spatial objects that deepen our understanding of spatial phenomena. In spatial
7.1 Introduction Chapter 7 Spatial Operation Q: What is spatial operation? A: Spatial operation is computational manipulation of spatial objects that deepen our understanding of spatial phenomena. In spatial
Course Number: Course Title: Geometry
 Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
GIS in agriculture scale farm level - used in agricultural applications - managing crop yields, monitoring crop rotation techniques, and estimate
 Types of Input GIS in agriculture scale farm level - used in agricultural applications - managing crop yields, monitoring crop rotation techniques, and estimate soil loss from individual farms or agricultural
Types of Input GIS in agriculture scale farm level - used in agricultural applications - managing crop yields, monitoring crop rotation techniques, and estimate soil loss from individual farms or agricultural
Objectives This tutorial will introduce how to prepare and run a basic ADH model using the SMS interface.
 v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will introduce how to prepare and run a basic ADH model using the SMS interface. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements ADH Mesh Module Scatter
v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will introduce how to prepare and run a basic ADH model using the SMS interface. Prerequisites Overview Tutorial Requirements ADH Mesh Module Scatter
Unit 4: Vector Overlay Analysis. Lecture Outline. Possible background reading material: McHarg, Ian 1992 Design with Nature. Wiley and Sons, New York.
 Unit 4: Vector Overlay Analysis Lecture Outline Possible background reading material: McHarg, Ian 1992 Design with Nature. Wiley and Sons, New York. Introduction: The idea of overlay originated when maps
Unit 4: Vector Overlay Analysis Lecture Outline Possible background reading material: McHarg, Ian 1992 Design with Nature. Wiley and Sons, New York. Introduction: The idea of overlay originated when maps
Computational Geometry Algorithms Library. Geographic information Systems
 Computational Geometry Algorithms Library in Geographic information Systems Edward Verbree, Peter van Oosterom and Wilko Quak TU Delft, Department of Geodesy, Thijsseweg 11, 2629 JA Delft, the Netherlands
Computational Geometry Algorithms Library in Geographic information Systems Edward Verbree, Peter van Oosterom and Wilko Quak TU Delft, Department of Geodesy, Thijsseweg 11, 2629 JA Delft, the Netherlands
Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks Objectives Import survey data in an XYZ format. Digitize elevation points using contour imagery. Edit
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks Objectives Import survey data in an XYZ format. Digitize elevation points using contour imagery. Edit
Roadway Design using GeoTools
 Roadway Design using GeoTools Introduction GeoTools is a general-purpose productivity tool for users of all types of geographic data. In the Civil Tools section, there are many tools for Civil engineering
Roadway Design using GeoTools Introduction GeoTools is a general-purpose productivity tool for users of all types of geographic data. In the Civil Tools section, there are many tools for Civil engineering
Solid Modelling. Graphics Systems / Computer Graphics and Interfaces COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF PORTO
 Solid Modelling Graphics Systems / Computer Graphics and Interfaces 1 Solid Modelling In 2D, one set 2D line segments or curves does not necessarily form a closed area. In 3D, a collection of surfaces
Solid Modelling Graphics Systems / Computer Graphics and Interfaces 1 Solid Modelling In 2D, one set 2D line segments or curves does not necessarily form a closed area. In 3D, a collection of surfaces
Object modeling and geodatabases. GEOG 419: Advanced GIS
 Object modeling and geodatabases GEOG 419: Advanced GIS CAD Data Model 1960s and 1970s Geographic data stored as points, lines, and areas No attributes; each feature type stored on a different layer No
Object modeling and geodatabases GEOG 419: Advanced GIS CAD Data Model 1960s and 1970s Geographic data stored as points, lines, and areas No attributes; each feature type stored on a different layer No
DETERMINATION OF THE OPTIMUM PATH ON THE EARTH S SURFACE. (extended abstract) Abstract
 Proceedings of the 17th International Cartographic Association Conference, Barcelona, Spain, September 1995. DETERMINATION OF THE OPTIMUM PATH ON THE EARTH S SURFACE (extended abstract) Marinos Kavouras
Proceedings of the 17th International Cartographic Association Conference, Barcelona, Spain, September 1995. DETERMINATION OF THE OPTIMUM PATH ON THE EARTH S SURFACE (extended abstract) Marinos Kavouras
Tiling Three-Dimensional Space with Simplices. Shankar Krishnan AT&T Labs - Research
 Tiling Three-Dimensional Space with Simplices Shankar Krishnan AT&T Labs - Research What is a Tiling? Partition of an infinite space into pieces having a finite number of distinct shapes usually Euclidean
Tiling Three-Dimensional Space with Simplices Shankar Krishnan AT&T Labs - Research What is a Tiling? Partition of an infinite space into pieces having a finite number of distinct shapes usually Euclidean
Spatial data and QGIS
 Spatial data and QGIS Xue Jingbo IT Center 2017.08.07 A GIS consists of: Spatial Data. Computer Hardware. Computer Software. Longitude Latitude Disease Date 26.870436-31.909519 Mumps 13/12/2008 26.868682-31.909259
Spatial data and QGIS Xue Jingbo IT Center 2017.08.07 A GIS consists of: Spatial Data. Computer Hardware. Computer Software. Longitude Latitude Disease Date 26.870436-31.909519 Mumps 13/12/2008 26.868682-31.909259
Study on Delaunay Triangulation with the Islets Constraints
 Intelligent Information Management, 2010, 2, 375-379 doi:10.4236/iim.2010.26045 Published Online June 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/iim) Study on Delaunay Triangulation with the Islets Constraints
Intelligent Information Management, 2010, 2, 375-379 doi:10.4236/iim.2010.26045 Published Online June 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/iim) Study on Delaunay Triangulation with the Islets Constraints
Consistent Query Answering under Spatial Semantic Constraints
 Consistent Query Answering under Spatial Semantic Constraints M. Andrea Rodríguez Universidad de Concepción, Chile andrea@udec.cl Mónica Caniupán Universidad del Bío-Bío, Chile mcaniupa@ubiobio.cl Leopoldo
Consistent Query Answering under Spatial Semantic Constraints M. Andrea Rodríguez Universidad de Concepción, Chile andrea@udec.cl Mónica Caniupán Universidad del Bío-Bío, Chile mcaniupa@ubiobio.cl Leopoldo
LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY
 LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce and explore surface data analysis using a vector data model: TIN. We
LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce and explore surface data analysis using a vector data model: TIN. We
Spa$al Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University
 Spa$al Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University Class Outlines Spatial Point Pattern Regional Data (Areal Data) Continuous Spatial Data (Geostatistical
Spa$al Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University Class Outlines Spatial Point Pattern Regional Data (Areal Data) Continuous Spatial Data (Geostatistical
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images
 Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
automatic digitization. In the context of ever increasing population worldwide and thereby
 Chapter 1 Introduction In the recent time, many researchers had thrust upon developing various improvised methods of automatic digitization. In the context of ever increasing population worldwide and thereby
Chapter 1 Introduction In the recent time, many researchers had thrust upon developing various improvised methods of automatic digitization. In the context of ever increasing population worldwide and thereby
Outline of the presentation
 Surface Reconstruction Petra Surynková Charles University in Prague Faculty of Mathematics and Physics petra.surynkova@mff.cuni.cz Outline of the presentation My work up to now Surfaces of Building Practice
Surface Reconstruction Petra Surynková Charles University in Prague Faculty of Mathematics and Physics petra.surynkova@mff.cuni.cz Outline of the presentation My work up to now Surfaces of Building Practice
Mathematics Curriculum
 6 G R A D E Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 5 Table of Contents 1... 1 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)... 11 Lesson 1: The Area of Parallelograms Through Rectangle Facts...
6 G R A D E Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 5 Table of Contents 1... 1 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)... 11 Lesson 1: The Area of Parallelograms Through Rectangle Facts...
Grades 7 & 8 Pre-Algebra/Course 3,
 Grades 7 & 8 Pre-Algebra/Course 3, TERM 1 - AUGUST/SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER Algebra Tools Solving Equations Integers Solving Multi-Step Equations and Inequalities TERM 2 NOVEMBER/DECEMBER/JANUARY Functions &
Grades 7 & 8 Pre-Algebra/Course 3, TERM 1 - AUGUST/SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER Algebra Tools Solving Equations Integers Solving Multi-Step Equations and Inequalities TERM 2 NOVEMBER/DECEMBER/JANUARY Functions &
Chapter 12 Solid Modeling. Disadvantages of wireframe representations
 Chapter 12 Solid Modeling Wireframe, surface, solid modeling Solid modeling gives a complete and unambiguous definition of an object, describing not only the shape of the boundaries but also the object
Chapter 12 Solid Modeling Wireframe, surface, solid modeling Solid modeling gives a complete and unambiguous definition of an object, describing not only the shape of the boundaries but also the object
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models Feature Types and Data Models How Does a GIS Work? - a GIS operates on the premise that all of the features in the real world can
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models Feature Types and Data Models How Does a GIS Work? - a GIS operates on the premise that all of the features in the real world can
Multidimensional Indexes [14]
![Multidimensional Indexes [14] Multidimensional Indexes [14]](/thumbs/88/117268268.jpg) CMSC 661, Principles of Database Systems Multidimensional Indexes [14] Dr. Kalpakis http://www.csee.umbc.edu/~kalpakis/courses/661 Motivation Examined indexes when search keys are in 1-D space Many interesting
CMSC 661, Principles of Database Systems Multidimensional Indexes [14] Dr. Kalpakis http://www.csee.umbc.edu/~kalpakis/courses/661 Motivation Examined indexes when search keys are in 1-D space Many interesting
Navigation and Metric Path Planning
 Navigation and Metric Path Planning October 4, 2011 Minerva tour guide robot (CMU): Gave tours in Smithsonian s National Museum of History Example of Minerva s occupancy map used for navigation Objectives
Navigation and Metric Path Planning October 4, 2011 Minerva tour guide robot (CMU): Gave tours in Smithsonian s National Museum of History Example of Minerva s occupancy map used for navigation Objectives
Lecture overview. Visualisatie BMT. Fundamental algorithms. Visualization pipeline. Structural classification - 1. Structural classification - 2
 Visualisatie BMT Fundamental algorithms Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl Lecture overview Classification of algorithms Scalar algorithms Vector algorithms Tensor algorithms Modeling algorithms 1 2 Visualization
Visualisatie BMT Fundamental algorithms Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl Lecture overview Classification of algorithms Scalar algorithms Vector algorithms Tensor algorithms Modeling algorithms 1 2 Visualization
DISCRETE DOMAIN REPRESENTATION FOR SHAPE CONCEPTUALIZATION
 DISCRETE DOMAIN REPRESENTATION FOR SHAPE CONCEPTUALIZATION Zoltán Rusák, Imre Horváth, György Kuczogi, Joris S.M. Vergeest, Johan Jansson Department of Design Engineering Delft University of Technology
DISCRETE DOMAIN REPRESENTATION FOR SHAPE CONCEPTUALIZATION Zoltán Rusák, Imre Horváth, György Kuczogi, Joris S.M. Vergeest, Johan Jansson Department of Design Engineering Delft University of Technology
Data Representation in Visualisation
 Data Representation in Visualisation Visualisation Lecture 4 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Taku Komura Data Representation 1 Data Representation We have
Data Representation in Visualisation Visualisation Lecture 4 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Taku Komura Data Representation 1 Data Representation We have
Constrained Delaunay Triangulations (CDT)
 Constrained Delaunay Triangulations (CDT) Recall: Definition 1 (Constrained triangulation). A triangulation with prespecified edges or breaklines between nodes. Motivation: Geological faults in oil recovery
Constrained Delaunay Triangulations (CDT) Recall: Definition 1 (Constrained triangulation). A triangulation with prespecified edges or breaklines between nodes. Motivation: Geological faults in oil recovery
Scalar Visualization
 Scalar Visualization Visualizing scalar data Popular scalar visualization techniques Color mapping Contouring Height plots outline Recap of Chap 4: Visualization Pipeline 1. Data Importing 2. Data Filtering
Scalar Visualization Visualizing scalar data Popular scalar visualization techniques Color mapping Contouring Height plots outline Recap of Chap 4: Visualization Pipeline 1. Data Importing 2. Data Filtering
Multidimensional (spatial) Data and Modelling (3)
 Multidimensional (spatial) Data and Modelling (3) 1 GIS-centric approach l Focus on management of spatial data l Goal: Creation of a solely spatial data representation like maps (spatial partition, map
Multidimensional (spatial) Data and Modelling (3) 1 GIS-centric approach l Focus on management of spatial data l Goal: Creation of a solely spatial data representation like maps (spatial partition, map
