Computer Vision for VLFeat and more...
|
|
|
- Godfrey Ford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computer Vision for VLFeat and more... Holistic Methods Francisco Escolano, PhD Associate Professor University of Alicante, Spain
2 Contents PCA/Karhunen-Loeve (slides appart) GIST and Spatial Evelope Image Complexity
3 GIST and Spatial Envelopes
4 Discrete Fourier Transform Maps a signal (1D) to a new domain. The domain of frequencies. The inverse mapping returns the original signal: fft and ifft MATLAB commands Converts a sequence x(1)...x(n) of real numbers into a combination of (complex) sinusoids ordered by their frequencies. Euler s formula
5 Image Fourier Transform Maps a gray image (2D) to a domain of x and y frequencies: fft2 and ifft2 MATLAB commands F(p,q) is a sample of the continuous transform F(w1, w2). Magnitude and Phase. q MATLAB: F = fft2(f,256,256); F2 = fftshift(f); imshow(log(abs(f2)),[-1 5]); colormap(jet); colorbar p
6 Image Fourier Transform Binary images (gray=1) Hamming window Reduces boundary effects Amplitude vs Phase: Amplitude spectrum Phase function
7 Image Fourier Transform Amplitude gives unlocalized information about image structure. Represents spatial frequencies spread everywhere. Thus informs us about orientation, smoothness, length and width of the contours forming the image. The squared magnitude of the FT (energy spectrum) gives the distribution of the signal s energy among the different spatial frequencies.
8 Image Fourier Transform Phase represents information relative to local properties of the image. It contains information relative to the form and position of the image components. Windowed FT. Defined around a given (x,y) with a radius associated to the window. Since the energy spectrum captures global things this allows us to localize image properties: Spectrogram Computed at 8x8 overlapped blocks of diameter 64 pixels. Now more localized if the radius is small.
9 PCAs of FTs Energy spectrum can be decomposed in terms of PCA/KL basis and similarly with the spectrogram PCA of global energy spectrum N*N samples for PCA PCA of the spectrogram 64*N*N samples for PCA Rearrange the samples of enegy spectrum or spectrogram in a column vector Ni (training images) << N^2 Compute expectations along the image database and then Cov matrix and eigenvectors Reduce the number of samples of A (log-polar sampling)
10 PCAs of FTs Log-polar sampling: Sample A(fx,fy) with: Gaussians arranged in a log-polar array and calculated by rotating and scaling where f0=0.02, 0.04, 0.08, 0.16 and 0.32 (5 frequencies) and 12 orientations are considered. L<<Ni log-polar transform Compose from solving Eigenvectors Eigenvalues Approximations
11 PCAs of FTs First 6 principal components of the energy spectrum First 6 principal components of the spectrogram. 4x4 blocks used. Each sub-image to the local energy spectrum Redundant representations, spectrogram enough!
12 % Load image img = imread('demo2.jpg'); GIST in MATLAB % GIST Parameters: clear param % number of orientations per scale (from HF to LF) param.orientationsperscale = [ ]; param.numberblocks = 4; param.fc_prefilt = 4; % Computing gist: [gist, param] = LMgist(img, '', param); % Visualization figure subplot(121) imshow(img) title('input image') subplot(122) showgist(gist, param) title('descriptor') Re-normalize image demogist #Filters x #Cells From only one image: 512=(8x4)x(4*4) is given by the filter bank BUT the code is ready for multiple images
13 Spatial Envelope The PCs of Energy spectrum (ES) and spectrogram (SG) define a feature space into which scene can be projected. However we must modify such space so that each dimension has a semantic meaning: openness, roughness, naturalness, etc. Specific templates must be learnt. Skyscraper=low expansion, little bit of rouhgness and low openness
14 Spatial Envelope Estimation of spatial evelope attributes s from image-based featues (v and w) after PCA/KL can be done with linear regression. Global DST we must learn di Windowed DST
15 Spatial Envelope Learning the d parameters: 1. Training set: (link v, w with s values) 2. Assume a linear model: 3. Solve by least squares: Column Inverse, ill conditioned if NG or NL are too high!
16 Spatial Envelope What are the image features leading to a given spatial envelope propery? Look the templates! Separating positive and negative parts Opponent energy image
17 Spatial Envelope What is the contribution of each spatial location? Look the windowed templates! Localized filters x,y in 8x8 Opponent energy image Use Hanning window
18 Spatial Envelope DST h_(x,y) h+(x,y) WDST(x,y,fx,fy) at 4x4 Localized filters x,y in 8x8 Naturalness: Images (top), DST*global spectrum (middle), opposed image (bottom)
19 DST Openness for Natural (a) and Man-made (b) Spatial Envelope Ruggedness for Natural (c) Expansion for Man-made (d) Roughness for Natural (e) and Man-made (f) h_(x,y) h+(x,y)
20 Spatial Envelope WDST Openness Ruggedness Roughness Natural Man Made
21 Spatial Envelope Ruggedness: deviation of the ground wrt horizon (horizon covered) Roughness: Size of the major components
22 Spatial Envelope Distance between images: WDST=more detail
23 Properties Spatial Envelope Errors
24 To do: false alarms Spatial Envelope Too global! But Scene centered representations predict false alarms
Statistics of Natural Image Categories
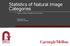 Statistics of Natural Image Categories Authors: Antonio Torralba and Aude Oliva Presented by: Sebastian Scherer Experiment Please estimate the average depth from the camera viewpoint to all locations(pixels)
Statistics of Natural Image Categories Authors: Antonio Torralba and Aude Oliva Presented by: Sebastian Scherer Experiment Please estimate the average depth from the camera viewpoint to all locations(pixels)
Digital Image Processing. Image Enhancement in the Frequency Domain
 Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement in the Frequency Domain Topics Frequency Domain Enhancements Fourier Transform Convolution High Pass Filtering in Frequency Domain Low Pass Filtering in Frequency
Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement in the Frequency Domain Topics Frequency Domain Enhancements Fourier Transform Convolution High Pass Filtering in Frequency Domain Low Pass Filtering in Frequency
GIST. GPU Implementation. Prakhar Jain ( ) Ejaz Ahmed ( ) 3 rd May, 2009
 GIST GPU Implementation Prakhar Jain ( 200601066 ) Ejaz Ahmed ( 200601028 ) 3 rd May, 2009 International Institute Of Information Technology, Hyderabad Table of Contents S. No. Topic Page No. 1 Abstract
GIST GPU Implementation Prakhar Jain ( 200601066 ) Ejaz Ahmed ( 200601028 ) 3 rd May, 2009 International Institute Of Information Technology, Hyderabad Table of Contents S. No. Topic Page No. 1 Abstract
Computer Vision I. Announcements. Fourier Tansform. Efficient Implementation. Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 13.
 Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Lecture 8 Object Descriptors
 Lecture 8 Object Descriptors Azadeh Fakhrzadeh Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University 2 Reading instructions Chapter 11.1 11.4 in G-W Azadeh Fakhrzadeh
Lecture 8 Object Descriptors Azadeh Fakhrzadeh Centre for Image Analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University 2 Reading instructions Chapter 11.1 11.4 in G-W Azadeh Fakhrzadeh
Image processing in frequency Domain
 Image processing in frequency Domain Introduction to Frequency Domain Deal with images in: -Spatial domain -Frequency domain Frequency Domain In the frequency or Fourier domain, the value and location
Image processing in frequency Domain Introduction to Frequency Domain Deal with images in: -Spatial domain -Frequency domain Frequency Domain In the frequency or Fourier domain, the value and location
Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images. Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009
 Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009 Traditional ways of inferring depth Binocular disparity Structure from motion Defocus Given a single monocular image, how to infer
Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009 Traditional ways of inferring depth Binocular disparity Structure from motion Defocus Given a single monocular image, how to infer
Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks
 Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks Computer Vision James Hays, Brown Slides: Hoiem and others Reminder Project due Friday Fourier Bases Teases away fast vs. slow changes in the image. This change
Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks Computer Vision James Hays, Brown Slides: Hoiem and others Reminder Project due Friday Fourier Bases Teases away fast vs. slow changes in the image. This change
Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB
 Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB Chapter 18 Feature extraction and representation What will we learn? What is feature extraction and why is it a critical step in most computer vision and
Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB Chapter 18 Feature extraction and representation What will we learn? What is feature extraction and why is it a critical step in most computer vision and
9 length of contour = no. of horizontal and vertical components + ( 2 no. of diagonal components) diameter of boundary B
 8. Boundary Descriptor 8.. Some Simple Descriptors length of contour : simplest descriptor - chain-coded curve 9 length of contour no. of horiontal and vertical components ( no. of diagonal components
8. Boundary Descriptor 8.. Some Simple Descriptors length of contour : simplest descriptor - chain-coded curve 9 length of contour no. of horiontal and vertical components ( no. of diagonal components
Schedule for Rest of Semester
 Schedule for Rest of Semester Date Lecture Topic 11/20 24 Texture 11/27 25 Review of Statistics & Linear Algebra, Eigenvectors 11/29 26 Eigenvector expansions, Pattern Recognition 12/4 27 Cameras & calibration
Schedule for Rest of Semester Date Lecture Topic 11/20 24 Texture 11/27 25 Review of Statistics & Linear Algebra, Eigenvectors 11/29 26 Eigenvector expansions, Pattern Recognition 12/4 27 Cameras & calibration
LOCAL AND GLOBAL DESCRIPTORS FOR PLACE RECOGNITION IN ROBOTICS
 8th International DAAAM Baltic Conference "INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING - 19-21 April 2012, Tallinn, Estonia LOCAL AND GLOBAL DESCRIPTORS FOR PLACE RECOGNITION IN ROBOTICS Shvarts, D. & Tamre, M. Abstract: The
8th International DAAAM Baltic Conference "INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING - 19-21 April 2012, Tallinn, Estonia LOCAL AND GLOBAL DESCRIPTORS FOR PLACE RECOGNITION IN ROBOTICS Shvarts, D. & Tamre, M. Abstract: The
ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Spring 2014 TTh 14:30-15:45 CBC C313 Lecture 06 Image Structures 13/02/06 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Spring 2014 TTh 14:30-15:45 CBC C313 Lecture 06 Image Structures 13/02/06 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/
Tutorial of Origin 7.0. Chuang Tan, Zheyun Liu
 Tutorial of Origin 7.0 Chuang Tan, Zheyun Liu Origin is a kind of powerful software for numerical manipulation and data analysis. Here is a brief tutorial that explains how to do the numerical Fourier
Tutorial of Origin 7.0 Chuang Tan, Zheyun Liu Origin is a kind of powerful software for numerical manipulation and data analysis. Here is a brief tutorial that explains how to do the numerical Fourier
Computer Vision and Graphics (ee2031) Digital Image Processing I
 Computer Vision and Graphics (ee203) Digital Image Processing I Dr John Collomosse J.Collomosse@surrey.ac.uk Centre for Vision, Speech and Signal Processing University of Surrey Learning Outcomes After
Computer Vision and Graphics (ee203) Digital Image Processing I Dr John Collomosse J.Collomosse@surrey.ac.uk Centre for Vision, Speech and Signal Processing University of Surrey Learning Outcomes After
ECE 176 Digital Image Processing Handout #14 Pamela Cosman 4/29/05 TEXTURE ANALYSIS
 ECE 176 Digital Image Processing Handout #14 Pamela Cosman 4/29/ TEXTURE ANALYSIS Texture analysis is covered very briefly in Gonzalez and Woods, pages 66 671. This handout is intended to supplement that
ECE 176 Digital Image Processing Handout #14 Pamela Cosman 4/29/ TEXTURE ANALYSIS Texture analysis is covered very briefly in Gonzalez and Woods, pages 66 671. This handout is intended to supplement that
Image Transformation Techniques Dr. Rajeev Srivastava Dept. of Computer Engineering, ITBHU, Varanasi
 Image Transformation Techniques Dr. Rajeev Srivastava Dept. of Computer Engineering, ITBHU, Varanasi 1. Introduction The choice of a particular transform in a given application depends on the amount of
Image Transformation Techniques Dr. Rajeev Srivastava Dept. of Computer Engineering, ITBHU, Varanasi 1. Introduction The choice of a particular transform in a given application depends on the amount of
Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications
 Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications B14 Image Analysis Michaelmas 2017 Dr. M. Fallon Fourier transforms and spatial frequencies in 2D Definition and meaning The Convolution Theorem Applications
Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications B14 Image Analysis Michaelmas 2017 Dr. M. Fallon Fourier transforms and spatial frequencies in 2D Definition and meaning The Convolution Theorem Applications
Biomedical Image Processing
 Biomedical Image Processing Jason Thong Gabriel Grant 1 2 Motivation from the Medical Perspective MRI, CT and other biomedical imaging devices were designed to assist doctors in their diagnosis and treatment
Biomedical Image Processing Jason Thong Gabriel Grant 1 2 Motivation from the Medical Perspective MRI, CT and other biomedical imaging devices were designed to assist doctors in their diagnosis and treatment
Digital Image Processing Chapter 11: Image Description and Representation
 Digital Image Processing Chapter 11: Image Description and Representation Image Representation and Description? Objective: To represent and describe information embedded in an image in other forms that
Digital Image Processing Chapter 11: Image Description and Representation Image Representation and Description? Objective: To represent and describe information embedded in an image in other forms that
Computer Vision. Fourier Transform. 20 January Copyright by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved
 Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision Computer Vision Fourier Transform 20 January 2017 Copyright 2001 2017 by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved j.van.de.loosdrecht@nhl.nl,
Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision Computer Vision Fourier Transform 20 January 2017 Copyright 2001 2017 by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved j.van.de.loosdrecht@nhl.nl,
Interlude: Solving systems of Equations
 Interlude: Solving systems of Equations Solving Ax = b What happens to x under Ax? The singular value decomposition Rotation matrices Singular matrices Condition number Null space Solving Ax = 0 under
Interlude: Solving systems of Equations Solving Ax = b What happens to x under Ax? The singular value decomposition Rotation matrices Singular matrices Condition number Null space Solving Ax = 0 under
Texture. Outline. Image representations: spatial and frequency Fourier transform Frequency filtering Oriented pyramids Texture representation
 Texture Outline Image representations: spatial and frequency Fourier transform Frequency filtering Oriented pyramids Texture representation 1 Image Representation The standard basis for images is the set
Texture Outline Image representations: spatial and frequency Fourier transform Frequency filtering Oriented pyramids Texture representation 1 Image Representation The standard basis for images is the set
The 2D Fourier transform & image filtering
 Luleå University of Technology Matthew Thurley and Johan Carlson Last revision: Oct 27, 2011 Industrial Image Analysis E0005E Product Development Phase 6 The 2D Fourier transform & image filtering Contents
Luleå University of Technology Matthew Thurley and Johan Carlson Last revision: Oct 27, 2011 Industrial Image Analysis E0005E Product Development Phase 6 The 2D Fourier transform & image filtering Contents
Computer Vision 2. SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung. Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier
 Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
Lecture 14 Shape. ch. 9, sec. 1-8, of Machine Vision by Wesley E. Snyder & Hairong Qi. Spring (CMU RI) : BioE 2630 (Pitt)
 Lecture 14 Shape ch. 9, sec. 1-8, 12-14 of Machine Vision by Wesley E. Snyder & Hairong Qi Spring 2018 16-725 (CMU RI) : BioE 2630 (Pitt) Dr. John Galeotti The content of these slides by John Galeotti,
Lecture 14 Shape ch. 9, sec. 1-8, 12-14 of Machine Vision by Wesley E. Snyder & Hairong Qi Spring 2018 16-725 (CMU RI) : BioE 2630 (Pitt) Dr. John Galeotti The content of these slides by John Galeotti,
The HPEC Challenge Benchmark Suite
 The HPEC Challenge Benchmark Suite Ryan Haney, Theresa Meuse, Jeremy Kepner and James Lebak Massachusetts Institute of Technology Lincoln Laboratory HPEC 2005 This work is sponsored by the Defense Advanced
The HPEC Challenge Benchmark Suite Ryan Haney, Theresa Meuse, Jeremy Kepner and James Lebak Massachusetts Institute of Technology Lincoln Laboratory HPEC 2005 This work is sponsored by the Defense Advanced
Modeling the Shape of the Scene: A Holistic Representation of the Spatial Envelope
 International Journal of Computer Vision 42(3), 145 175, 2001 c 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Modeling the Shape of the Scene: A Holistic Representation of the Spatial
International Journal of Computer Vision 42(3), 145 175, 2001 c 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Modeling the Shape of the Scene: A Holistic Representation of the Spatial
Lecture 6: Edge Detection
 #1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
#1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
Boundary descriptors. Representation REPRESENTATION & DESCRIPTION. Descriptors. Moore boundary tracking
 Representation REPRESENTATION & DESCRIPTION After image segmentation the resulting collection of regions is usually represented and described in a form suitable for higher level processing. Most important
Representation REPRESENTATION & DESCRIPTION After image segmentation the resulting collection of regions is usually represented and described in a form suitable for higher level processing. Most important
Edge Detection. Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City
 Edge Detection Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City Previous two classes: Image Filtering Spatial domain Smoothing, sharpening, measuring texture * = FFT FFT Inverse FFT = Frequency domain Denoising,
Edge Detection Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City Previous two classes: Image Filtering Spatial domain Smoothing, sharpening, measuring texture * = FFT FFT Inverse FFT = Frequency domain Denoising,
Digital Image Processing. Lecture 6
 Digital Image Processing Lecture 6 (Enhancement in the Frequency domain) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 2016 Image Enhancement In The Frequency Domain Outline Jean Baptiste Joseph
Digital Image Processing Lecture 6 (Enhancement in the Frequency domain) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 2016 Image Enhancement In The Frequency Domain Outline Jean Baptiste Joseph
Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong)
 Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong) References: [1] http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/hipr2/index.htm [2] http://www.cs.wisc.edu/~dyer/cs540/notes/vision.html
Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong) References: [1] http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/hipr2/index.htm [2] http://www.cs.wisc.edu/~dyer/cs540/notes/vision.html
TEXTURE ANALYSIS USING GABOR FILTERS
 TEXTURE ANALYSIS USING GABOR FILTERS Texture Types Definition of Texture Texture types Synthetic Natural Stochastic < Prev Next > Texture Definition Texture: the regular repetition of an element or pattern
TEXTURE ANALYSIS USING GABOR FILTERS Texture Types Definition of Texture Texture types Synthetic Natural Stochastic < Prev Next > Texture Definition Texture: the regular repetition of an element or pattern
Image representation. 1. Introduction
 Image representation Introduction Representation schemes Chain codes Polygonal approximations The skeleton of a region Boundary descriptors Some simple descriptors Shape numbers Fourier descriptors Moments
Image representation Introduction Representation schemes Chain codes Polygonal approximations The skeleton of a region Boundary descriptors Some simple descriptors Shape numbers Fourier descriptors Moments
Tutorial 5. Jun Xu, Teaching Asistant March 2, COMP4134 Biometrics Authentication
 Tutorial 5 Jun Xu, Teaching Asistant nankaimathxujun@gmail.com COMP4134 Biometrics Authentication March 2, 2017 Table of Contents Problems Problem 1: Answer The Questions Problem 2: Indeterminate Region
Tutorial 5 Jun Xu, Teaching Asistant nankaimathxujun@gmail.com COMP4134 Biometrics Authentication March 2, 2017 Table of Contents Problems Problem 1: Answer The Questions Problem 2: Indeterminate Region
Computer Vision I. Announcement. Corners. Edges. Numerical Derivatives f(x) Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 11
 Announcement Edge and Corner Detection Slides are posted HW due Friday CSE5A Lecture 11 Edges Corners Edge is Where Change Occurs: 1-D Change is measured by derivative in 1D Numerical Derivatives f(x)
Announcement Edge and Corner Detection Slides are posted HW due Friday CSE5A Lecture 11 Edges Corners Edge is Where Change Occurs: 1-D Change is measured by derivative in 1D Numerical Derivatives f(x)
TEXTURE ANALYSIS USING GABOR FILTERS FIL
 TEXTURE ANALYSIS USING GABOR FILTERS Texture Types Definition of Texture Texture types Synthetic ti Natural Stochastic < Prev Next > Texture Definition Texture: the regular repetition of an element or
TEXTURE ANALYSIS USING GABOR FILTERS Texture Types Definition of Texture Texture types Synthetic ti Natural Stochastic < Prev Next > Texture Definition Texture: the regular repetition of an element or
Image and Multidimensional Signal Processing
 Image and Multidimensional Signal Processing Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ Representation and Description 2 Representation and
Image and Multidimensional Signal Processing Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ Representation and Description 2 Representation and
Lecture 3 - Intensity transformation
 Computer Vision Lecture 3 - Intensity transformation Instructor: Ha Dai Duong duonghd@mta.edu.vn 22/09/2015 1 Today s class 1. Gray level transformations 2. Bit-plane slicing 3. Arithmetic/logic operators
Computer Vision Lecture 3 - Intensity transformation Instructor: Ha Dai Duong duonghd@mta.edu.vn 22/09/2015 1 Today s class 1. Gray level transformations 2. Bit-plane slicing 3. Arithmetic/logic operators
Digital Image Processing. Lecture # 3 Image Enhancement
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Image Enhancement 1 Image Enhancement Image Enhancement 3 Image Enhancement 4 Image Enhancement Process an image so that the result is more suitable than the original
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Image Enhancement 1 Image Enhancement Image Enhancement 3 Image Enhancement 4 Image Enhancement Process an image so that the result is more suitable than the original
CS143 Introduction to Computer Vision Homework assignment 1.
 CS143 Introduction to Computer Vision Homework assignment 1. Due: Problem 1 & 2 September 23 before Class Assignment 1 is worth 15% of your total grade. It is graded out of a total of 100 (plus 15 possible
CS143 Introduction to Computer Vision Homework assignment 1. Due: Problem 1 & 2 September 23 before Class Assignment 1 is worth 15% of your total grade. It is graded out of a total of 100 (plus 15 possible
Local Image preprocessing (cont d)
 Local Image preprocessing (cont d) 1 Outline - Edge detectors - Corner detectors - Reading: textbook 5.3.1-5.3.5 and 5.3.10 2 What are edges? Edges correspond to relevant features in the image. An edge
Local Image preprocessing (cont d) 1 Outline - Edge detectors - Corner detectors - Reading: textbook 5.3.1-5.3.5 and 5.3.10 2 What are edges? Edges correspond to relevant features in the image. An edge
Image Processing. Image Features
 Image Processing Image Features Preliminaries 2 What are Image Features? Anything. What they are used for? Some statements about image fragments (patches) recognition Search for similar patches matching
Image Processing Image Features Preliminaries 2 What are Image Features? Anything. What they are used for? Some statements about image fragments (patches) recognition Search for similar patches matching
A Fast Personal Palm print Authentication based on 3D-Multi Wavelet Transformation
 A Fast Personal Palm print Authentication based on 3D-Multi Wavelet Transformation * A. H. M. Al-Helali, * W. A. Mahmmoud, and * H. A. Ali * Al- Isra Private University Email: adnan_hadi@yahoo.com Abstract:
A Fast Personal Palm print Authentication based on 3D-Multi Wavelet Transformation * A. H. M. Al-Helali, * W. A. Mahmmoud, and * H. A. Ali * Al- Isra Private University Email: adnan_hadi@yahoo.com Abstract:
Assignment 3: Edge Detection
 Assignment 3: Edge Detection - EE Affiliate I. INTRODUCTION This assignment looks at different techniques of detecting edges in an image. Edge detection is a fundamental tool in computer vision to analyse
Assignment 3: Edge Detection - EE Affiliate I. INTRODUCTION This assignment looks at different techniques of detecting edges in an image. Edge detection is a fundamental tool in computer vision to analyse
AK Computer Vision Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors
 AK Computer Vision Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors 1 Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors: Motivation 2 Step 1: Detect local features should be invariant to scale and rotation, or perspective
AK Computer Vision Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors 1 Feature Point Detectors and Descriptors: Motivation 2 Step 1: Detect local features should be invariant to scale and rotation, or perspective
Algorithms for Recognition of Low Quality Iris Images. Li Peng Xie University of Ottawa
 Algorithms for Recognition of Low Quality Iris Images Li Peng Xie University of Ottawa Overview Iris Recognition Eyelash detection Accurate circular localization Covariance feature with LDA Fourier magnitude
Algorithms for Recognition of Low Quality Iris Images Li Peng Xie University of Ottawa Overview Iris Recognition Eyelash detection Accurate circular localization Covariance feature with LDA Fourier magnitude
Principal Component Image Interpretation A Logical and Statistical Approach
 Principal Component Image Interpretation A Logical and Statistical Approach Md Shahid Latif M.Tech Student, Department of Remote Sensing, Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra Ranchi, Jharkhand-835215 Abstract
Principal Component Image Interpretation A Logical and Statistical Approach Md Shahid Latif M.Tech Student, Department of Remote Sensing, Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra Ranchi, Jharkhand-835215 Abstract
Other Linear Filters CS 211A
 Other Linear Filters CS 211A Slides from Cornelia Fermüller and Marc Pollefeys Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin
Other Linear Filters CS 211A Slides from Cornelia Fermüller and Marc Pollefeys Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin
Segmentation and Grouping
 Segmentation and Grouping How and what do we see? Fundamental Problems ' Focus of attention, or grouping ' What subsets of pixels do we consider as possible objects? ' All connected subsets? ' Representation
Segmentation and Grouping How and what do we see? Fundamental Problems ' Focus of attention, or grouping ' What subsets of pixels do we consider as possible objects? ' All connected subsets? ' Representation
Intensity Transformation and Spatial Filtering
 Intensity Transformation and Spatial Filtering Outline of the Lecture Introduction. Intensity Transformation Functions. Piecewise-Linear Transformation Functions. Introduction Definition: Image enhancement
Intensity Transformation and Spatial Filtering Outline of the Lecture Introduction. Intensity Transformation Functions. Piecewise-Linear Transformation Functions. Introduction Definition: Image enhancement
Topic 6 Representation and Description
 Topic 6 Representation and Description Background Segmentation divides the image into regions Each region should be represented and described in a form suitable for further processing/decision-making Representation
Topic 6 Representation and Description Background Segmentation divides the image into regions Each region should be represented and described in a form suitable for further processing/decision-making Representation
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 10 130221 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Canny Edge Detector Hough Transform Feature-Based
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 10 130221 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Canny Edge Detector Hough Transform Feature-Based
Statistical Image Compression using Fast Fourier Coefficients
 Statistical Image Compression using Fast Fourier Coefficients M. Kanaka Reddy Research Scholar Dept.of Statistics Osmania University Hyderabad-500007 V. V. Haragopal Professor Dept.of Statistics Osmania
Statistical Image Compression using Fast Fourier Coefficients M. Kanaka Reddy Research Scholar Dept.of Statistics Osmania University Hyderabad-500007 V. V. Haragopal Professor Dept.of Statistics Osmania
Texture. Texture is a description of the spatial arrangement of color or intensities in an image or a selected region of an image.
 Texture Texture is a description of the spatial arrangement of color or intensities in an image or a selected region of an image. Structural approach: a set of texels in some regular or repeated pattern
Texture Texture is a description of the spatial arrangement of color or intensities in an image or a selected region of an image. Structural approach: a set of texels in some regular or repeated pattern
Digital Image Processing, 2nd ed. Digital Image Processing, 2nd ed. The principal objective of enhancement
 Chapter 3 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain The principal objective of enhancement to process an image so that the result is more suitable than the original image for a specific application. Enhancement
Chapter 3 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain The principal objective of enhancement to process an image so that the result is more suitable than the original image for a specific application. Enhancement
CoE4TN4 Image Processing
 CoE4TN4 Image Processing Chapter 11 Image Representation & Description Image Representation & Description After an image is segmented into regions, the regions are represented and described in a form suitable
CoE4TN4 Image Processing Chapter 11 Image Representation & Description Image Representation & Description After an image is segmented into regions, the regions are represented and described in a form suitable
SURF. Lecture6: SURF and HOG. Integral Image. Feature Evaluation with Integral Image
 SURF CSED441:Introduction to Computer Vision (2015S) Lecture6: SURF and HOG Bohyung Han CSE, POSTECH bhhan@postech.ac.kr Speed Up Robust Features (SURF) Simplified version of SIFT Faster computation but
SURF CSED441:Introduction to Computer Vision (2015S) Lecture6: SURF and HOG Bohyung Han CSE, POSTECH bhhan@postech.ac.kr Speed Up Robust Features (SURF) Simplified version of SIFT Faster computation but
An Intuitive Explanation of Fourier Theory
 An Intuitive Explanation of Fourier Theory Steven Lehar slehar@cns.bu.edu Fourier theory is pretty complicated mathematically. But there are some beautifully simple holistic concepts behind Fourier theory
An Intuitive Explanation of Fourier Theory Steven Lehar slehar@cns.bu.edu Fourier theory is pretty complicated mathematically. But there are some beautifully simple holistic concepts behind Fourier theory
Accurate Image Registration from Local Phase Information
 Accurate Image Registration from Local Phase Information Himanshu Arora, Anoop M. Namboodiri, and C.V. Jawahar Center for Visual Information Technology, IIIT, Hyderabad, India { himanshu@research., anoop@,
Accurate Image Registration from Local Phase Information Himanshu Arora, Anoop M. Namboodiri, and C.V. Jawahar Center for Visual Information Technology, IIIT, Hyderabad, India { himanshu@research., anoop@,
Single-view 3D Reconstruction
 Single-view 3D Reconstruction 10/12/17 Computational Photography Derek Hoiem, University of Illinois Some slides from Alyosha Efros, Steve Seitz Notes about Project 4 (Image-based Lighting) You can work
Single-view 3D Reconstruction 10/12/17 Computational Photography Derek Hoiem, University of Illinois Some slides from Alyosha Efros, Steve Seitz Notes about Project 4 (Image-based Lighting) You can work
Image Processing Fundamentals. Nicolas Vazquez Principal Software Engineer National Instruments
 Image Processing Fundamentals Nicolas Vazquez Principal Software Engineer National Instruments Agenda Objectives and Motivations Enhancing Images Checking for Presence Locating Parts Measuring Features
Image Processing Fundamentals Nicolas Vazquez Principal Software Engineer National Instruments Agenda Objectives and Motivations Enhancing Images Checking for Presence Locating Parts Measuring Features
Local Features: Detection, Description & Matching
 Local Features: Detection, Description & Matching Lecture 08 Computer Vision Material Citations Dr George Stockman Professor Emeritus, Michigan State University Dr David Lowe Professor, University of British
Local Features: Detection, Description & Matching Lecture 08 Computer Vision Material Citations Dr George Stockman Professor Emeritus, Michigan State University Dr David Lowe Professor, University of British
Face Detection and Recognition in an Image Sequence using Eigenedginess
 Face Detection and Recognition in an Image Sequence using Eigenedginess B S Venkatesh, S Palanivel and B Yegnanarayana Department of Computer Science and Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
Face Detection and Recognition in an Image Sequence using Eigenedginess B S Venkatesh, S Palanivel and B Yegnanarayana Department of Computer Science and Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Third Edition Rafael C. Gonzalez University of Tennessee Richard E. Woods MedData Interactive PEARSON Prentice Hall Pearson Education International Contents Preface xv Acknowledgments
Digital Image Processing Third Edition Rafael C. Gonzalez University of Tennessee Richard E. Woods MedData Interactive PEARSON Prentice Hall Pearson Education International Contents Preface xv Acknowledgments
Lecture 5: Frequency Domain Transformations
 #1 Lecture 5: Frequency Domain Transformations Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu From Last Lecture Spatial Domain Transformation Point Processing for Enhancement Area/Mask Processing Transformations Image
#1 Lecture 5: Frequency Domain Transformations Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu From Last Lecture Spatial Domain Transformation Point Processing for Enhancement Area/Mask Processing Transformations Image
Laboratory of Applied Robotics
 Laboratory of Applied Robotics OpenCV: Shape Detection Paolo Bevilacqua RGB (Red-Green-Blue): Color Spaces RGB and HSV Color defined in relation to primary colors Correlated channels, information on both
Laboratory of Applied Robotics OpenCV: Shape Detection Paolo Bevilacqua RGB (Red-Green-Blue): Color Spaces RGB and HSV Color defined in relation to primary colors Correlated channels, information on both
IMAGING. Images are stored by capturing the binary data using some electronic devices (SENSORS)
 IMAGING Film photography Digital photography Images are stored by capturing the binary data using some electronic devices (SENSORS) Sensors: Charge Coupled Device (CCD) Photo multiplier tube (PMT) The
IMAGING Film photography Digital photography Images are stored by capturing the binary data using some electronic devices (SENSORS) Sensors: Charge Coupled Device (CCD) Photo multiplier tube (PMT) The
Lab 1: Basic operations on images in Matlab
 Lab 1: Basic operations on images in Matlab Maria Magnusson with contributions by Michael Felsberg, 2017, Computer Vision Laboratory, Department of Electrical Engineering, Linköping University 1 Introduction
Lab 1: Basic operations on images in Matlab Maria Magnusson with contributions by Michael Felsberg, 2017, Computer Vision Laboratory, Department of Electrical Engineering, Linköping University 1 Introduction
Review of Filtering. Filtering in frequency domain
 Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert image and filter to fft (fft2
Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert image and filter to fft (fft2
CS 787: Assignment 4, Stereo Vision: Block Matching and Dynamic Programming Due: 12:00noon, Fri. Mar. 30, 2007.
 CS 787: Assignment 4, Stereo Vision: Block Matching and Dynamic Programming Due: 12:00noon, Fri. Mar. 30, 2007. In this assignment you will implement and test some simple stereo algorithms discussed in
CS 787: Assignment 4, Stereo Vision: Block Matching and Dynamic Programming Due: 12:00noon, Fri. Mar. 30, 2007. In this assignment you will implement and test some simple stereo algorithms discussed in
BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging
 1 Lucas Parra, CCNY BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging Lecture 11 Point Spread Function, Inverse Filtering, Wiener Filtering, Sharpening,... Lucas C. Parra, parra@ccny.cuny.edu Blackboard: http://cityonline.ccny.cuny.edu/
1 Lucas Parra, CCNY BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging Lecture 11 Point Spread Function, Inverse Filtering, Wiener Filtering, Sharpening,... Lucas C. Parra, parra@ccny.cuny.edu Blackboard: http://cityonline.ccny.cuny.edu/
COSC160: Detection and Classification. Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor
 COSC160: Detection and Classification Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Problem I. Strategies II. Features for training III. Using spatial information? IV. Reducing dimensionality
COSC160: Detection and Classification Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Problem I. Strategies II. Features for training III. Using spatial information? IV. Reducing dimensionality
3. Image formation, Fourier analysis and CTF theory. Paula da Fonseca
 3. Image formation, Fourier analysis and CTF theory Paula da Fonseca EM course 2017 - Agenda - Overview of: Introduction to Fourier analysis o o o o Sine waves Fourier transform (simple examples of 1D
3. Image formation, Fourier analysis and CTF theory Paula da Fonseca EM course 2017 - Agenda - Overview of: Introduction to Fourier analysis o o o o Sine waves Fourier transform (simple examples of 1D
Image Pyramids and Applications
 Image Pyramids and Applications Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech Golconda, René Magritte, 1953 Administrative stuffs HW 1 will be posted tonight, due 11:59 PM Sept 25 Anonymous feedback Previous
Image Pyramids and Applications Computer Vision Jia-Bin Huang, Virginia Tech Golconda, René Magritte, 1953 Administrative stuffs HW 1 will be posted tonight, due 11:59 PM Sept 25 Anonymous feedback Previous
Sherlock 7 Technical Resource. Search Geometric
 Sherlock 7 Technical Resource DALSA Corp., Industrial Products (IPD) www.goipd.com 978.670.2002 (U.S.A.) Document Revision: September 24, 2007 Search Geometric Search utilities A common task in machine
Sherlock 7 Technical Resource DALSA Corp., Industrial Products (IPD) www.goipd.com 978.670.2002 (U.S.A.) Document Revision: September 24, 2007 Search Geometric Search utilities A common task in machine
Anno accademico 2006/2007. Davide Migliore
 Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Image Compression with Singular Value Decomposition & Correlation: a Graphical Analysis
 ISSN -7X Volume, Issue June 7 Image Compression with Singular Value Decomposition & Correlation: a Graphical Analysis Tamojay Deb, Anjan K Ghosh, Anjan Mukherjee Tripura University (A Central University),
ISSN -7X Volume, Issue June 7 Image Compression with Singular Value Decomposition & Correlation: a Graphical Analysis Tamojay Deb, Anjan K Ghosh, Anjan Mukherjee Tripura University (A Central University),
Dietrich Paulus Joachim Hornegger. Pattern Recognition of Images and Speech in C++
 Dietrich Paulus Joachim Hornegger Pattern Recognition of Images and Speech in C++ To Dorothea, Belinda, and Dominik In the text we use the following names which are protected, trademarks owned by a company
Dietrich Paulus Joachim Hornegger Pattern Recognition of Images and Speech in C++ To Dorothea, Belinda, and Dominik In the text we use the following names which are protected, trademarks owned by a company
Feature Extraction and Image Processing, 2 nd Edition. Contents. Preface
 , 2 nd Edition Preface ix 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 Human and Computer Vision 1 1.3 The Human Vision System 3 1.3.1 The Eye 4 1.3.2 The Neural System 7 1.3.3 Processing 7 1.4 Computer Vision
, 2 nd Edition Preface ix 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 Human and Computer Vision 1 1.3 The Human Vision System 3 1.3.1 The Eye 4 1.3.2 The Neural System 7 1.3.3 Processing 7 1.4 Computer Vision
Chapter 3: Intensity Transformations and Spatial Filtering
 Chapter 3: Intensity Transformations and Spatial Filtering 3.1 Background 3.2 Some basic intensity transformation functions 3.3 Histogram processing 3.4 Fundamentals of spatial filtering 3.5 Smoothing
Chapter 3: Intensity Transformations and Spatial Filtering 3.1 Background 3.2 Some basic intensity transformation functions 3.3 Histogram processing 3.4 Fundamentals of spatial filtering 3.5 Smoothing
Denoising and Edge Detection Using Sobelmethod
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Denoising and Edge Detection Using Sobelmethod P. Sravya 1, T. Rupa devi 2, M. Janardhana Rao 3, K. Sai Jagadeesh 4, K. Prasanna
International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Denoising and Edge Detection Using Sobelmethod P. Sravya 1, T. Rupa devi 2, M. Janardhana Rao 3, K. Sai Jagadeesh 4, K. Prasanna
Theoretically Perfect Sensor
 Sampling 1/67 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Sampling 1/67 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Training-Free, Generic Object Detection Using Locally Adaptive Regression Kernels
 Training-Free, Generic Object Detection Using Locally Adaptive Regression Kernels IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIENCE, VOL.32, NO.9, SEPTEMBER 2010 Hae Jong Seo, Student Member,
Training-Free, Generic Object Detection Using Locally Adaptive Regression Kernels IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIENCE, VOL.32, NO.9, SEPTEMBER 2010 Hae Jong Seo, Student Member,
Classification of Hyperspectral Breast Images for Cancer Detection. Sander Parawira December 4, 2009
 1 Introduction Classification of Hyperspectral Breast Images for Cancer Detection Sander Parawira December 4, 2009 parawira@stanford.edu In 2009 approximately one out of eight women has breast cancer.
1 Introduction Classification of Hyperspectral Breast Images for Cancer Detection Sander Parawira December 4, 2009 parawira@stanford.edu In 2009 approximately one out of eight women has breast cancer.
Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking
 Image Matching Image Retrieval Object Recognition Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking Example: Mosiacing (Panorama) M. Brown and D. G. Lowe. Recognising Panoramas. ICCV 2003 Example 3D Reconstruction
Image Matching Image Retrieval Object Recognition Motion Estimation and Optical Flow Tracking Example: Mosiacing (Panorama) M. Brown and D. G. Lowe. Recognising Panoramas. ICCV 2003 Example 3D Reconstruction
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING DS7201 ADVANCED DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING II M.E (C.S) QUESTION BANK UNIT I 1. Write the differences between photopic and scotopic vision? 2. What
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING DS7201 ADVANCED DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING II M.E (C.S) QUESTION BANK UNIT I 1. Write the differences between photopic and scotopic vision? 2. What
CSE 252A Computer Vision Homework 3 Instructor: Ben Ochoa Due : Monday, November 21, 2016, 11:59 PM
 CSE 252A Computer Vision Homework 3 Instructor: Ben Ochoa Due : Monday, November 21, 2016, 11:59 PM Instructions: Homework 3 has to be submitted in groups of 3. Review the academic integrity and collaboration
CSE 252A Computer Vision Homework 3 Instructor: Ben Ochoa Due : Monday, November 21, 2016, 11:59 PM Instructions: Homework 3 has to be submitted in groups of 3. Review the academic integrity and collaboration
Augmented Reality VU. Computer Vision 3D Registration (2) Prof. Vincent Lepetit
 Augmented Reality VU Computer Vision 3D Registration (2) Prof. Vincent Lepetit Feature Point-Based 3D Tracking Feature Points for 3D Tracking Much less ambiguous than edges; Point-to-point reprojection
Augmented Reality VU Computer Vision 3D Registration (2) Prof. Vincent Lepetit Feature Point-Based 3D Tracking Feature Points for 3D Tracking Much less ambiguous than edges; Point-to-point reprojection
Chapter 11 Representation & Description
 Chapter 11 Representation & Description The results of segmentation is a set of regions. Regions have then to be represented and described. Two main ways of representing a region: - external characteristics
Chapter 11 Representation & Description The results of segmentation is a set of regions. Regions have then to be represented and described. Two main ways of representing a region: - external characteristics
Spatializing GIS Commands with Self-Organizing Maps. Jochen Wendel Barbara P. Buttenfield Roland J. Viger Jeremy M. Smith
 Spatializing GIS Commands with Self-Organizing Maps Jochen Wendel Barbara P. Buttenfield Roland J. Viger Jeremy M. Smith Outline Introduction Characterizing GIS Commands Implementation Interpretation of
Spatializing GIS Commands with Self-Organizing Maps Jochen Wendel Barbara P. Buttenfield Roland J. Viger Jeremy M. Smith Outline Introduction Characterizing GIS Commands Implementation Interpretation of
Image restoration. Lecture 14. Milan Gavrilovic Centre for Image Analysis Uppsala University
 Image restoration Lecture 14 Milan Gavrilovic milan@cb.uu.se Centre for Image Analysis Uppsala University Computer Assisted Image Analysis 2009-05-08 M. Gavrilovic (Uppsala University) L14 Image restoration
Image restoration Lecture 14 Milan Gavrilovic milan@cb.uu.se Centre for Image Analysis Uppsala University Computer Assisted Image Analysis 2009-05-08 M. Gavrilovic (Uppsala University) L14 Image restoration
Dense Image-based Motion Estimation Algorithms & Optical Flow
 Dense mage-based Motion Estimation Algorithms & Optical Flow Video A video is a sequence of frames captured at different times The video data is a function of v time (t) v space (x,y) ntroduction to motion
Dense mage-based Motion Estimation Algorithms & Optical Flow Video A video is a sequence of frames captured at different times The video data is a function of v time (t) v space (x,y) ntroduction to motion
Theoretically Perfect Sensor
 Sampling 1/60 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Sampling 1/60 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Spectral modeling of musical sounds
 Spectral modeling of musical sounds Xavier Serra Audiovisual Institute, Pompeu Fabra University http://www.iua.upf.es xserra@iua.upf.es 1. Introduction Spectral based analysis/synthesis techniques offer
Spectral modeling of musical sounds Xavier Serra Audiovisual Institute, Pompeu Fabra University http://www.iua.upf.es xserra@iua.upf.es 1. Introduction Spectral based analysis/synthesis techniques offer
Outlines. Medical Image Processing Using Transforms. 4. Transform in image space
 Medical Image Processing Using Transforms Hongmei Zhu, Ph.D Department of Mathematics & Statistics York University hmzhu@yorku.ca Outlines Image Quality Gray value transforms Histogram processing Transforms
Medical Image Processing Using Transforms Hongmei Zhu, Ph.D Department of Mathematics & Statistics York University hmzhu@yorku.ca Outlines Image Quality Gray value transforms Histogram processing Transforms
Motivation. Gray Levels
 Motivation Image Intensity and Point Operations Dr. Edmund Lam Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering The University of Hong ong A digital image is a matrix of numbers, each corresponding
Motivation Image Intensity and Point Operations Dr. Edmund Lam Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering The University of Hong ong A digital image is a matrix of numbers, each corresponding
Basic relations between pixels (Chapter 2)
 Basic relations between pixels (Chapter 2) Lecture 3 Basic Relationships Between Pixels Definitions: f(x,y): digital image Pixels: q, p (p,q f) A subset of pixels of f(x,y): S A typology of relations:
Basic relations between pixels (Chapter 2) Lecture 3 Basic Relationships Between Pixels Definitions: f(x,y): digital image Pixels: q, p (p,q f) A subset of pixels of f(x,y): S A typology of relations:
Computer Assisted Image Analysis TF 3p and MN1 5p Lecture 1, (GW 1, )
 Centre for Image Analysis Computer Assisted Image Analysis TF p and MN 5p Lecture, 422 (GW, 2.-2.4) 2.4) 2 Why put the image into a computer? A digital image of a rat. A magnification of the rat s nose.
Centre for Image Analysis Computer Assisted Image Analysis TF p and MN 5p Lecture, 422 (GW, 2.-2.4) 2.4) 2 Why put the image into a computer? A digital image of a rat. A magnification of the rat s nose.
