Robust Human Body Shape and Pose Tracking
|
|
|
- Mary Oliver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Robust Human Body Shape and Pose Tracking Chun-Hao Huang 1 Edmond Boyer 2 Slobodan Ilic 1 1 Technische Universität München 2 INRIA Grenoble Rhône-Alpes
2 Marker-based motion capture (mocap.) Adventages: precision, reliability little data ( couple of kb/frame for 50 cameras, 5 people) real-time processing, visualization & retargeting. Disadvantages: Attaching, removing, re-attaching markers is tedious. Markers can interfere with the movement. Giant Studios (L.A. Noire set ) Markers prevent the simultaneous acquisition of shape and motion. 2
3 Marker-less mocap. Multiple camera setup is usually required. Accquisition of both motion and shape. 3D dome (CMU) Grimage ( INRIA ) 3
4 Motivation Methods that assume a skeleton usually produce skinning artifacts, require 2 nd stage shape refinement. Degree of freedom (DoF): N J 6 (< 10 2 ) [Vlasic et al. ToG`08] Skeleton-based Purely-surface-based methods handle non-rigid surface deformation better, but do not provide the pose. DoF: N P 6 ( 10 3 ) [Cagniart et al. ECCV`10] Surface-based 4
5 Contribution bone differential coordinate probablistic surface deformation [Straka et al. ECCV`12] [Cagniart et al. ECCV`10] A learning-based outlier rejection scheme. 5
6 Preprocessing step: model Decompose the reference mesh into patches [Cagniart et al. CVPR`10] Shape parameter N, P k k k 1 Θ R c M 0 Pose parameter J N J x j j 1 Rig the skeleton inside the mesh. Each vertex belongs to one body part. [Baran et al. TOG`07] 6
7 Preprocessing step: input data For each time stamp t, visual hull is reconstruced from silhouettes, which serves as our observations 7
8 Pipeline input data t partitioned t filtered t SVM classification filtering M t 1 model Minimizing E(Θ, E(Θ) J) M t 8
9 Pipeline input data t M t 1 model Minimizing E(Θ, E(Θ) J) [Cagniart et al. ECCV`10] M t 9
10 SVM-based body part classification input data partitioned t t SVM classification A multi-class linear SVM is trained on M t 1 t and tested on M t 1 model Feature: 3D coordinate of vertices. Class label: rigid body part label. Good compromise between accuracy and training time. 10
11 Filtering point cloud partitioned t filtered t Bone T b : patches on the bone often move rigidly together. filtering sub-sample the observations. Joint T g : patches on the joint have nonrigid deformation. keep all the observations. Outlier T 0 : abandon all the observations. 11
12 Benefit of SVM classification outlier removal 1 wo outlier removal with outlier removal 0 12
13 Energy minimization filtered t M t 1 model Minimizing E(Θ, J) M t 13
14 Energy function M t 1 E Θ, J filtered t Θ, J Θ Θ Θ, J E E E E data rigid bone E data (Θ) : how well the surface explains the observations. E rigid (Θ) : smooth the motion of neighboring patches. E bone (Θ, J) : keep the relationship between the mesh and the skeleton. 14
15 Data term E data (Θ): how well the surface explains the observations. A probablisitic Iterative Closest Point (ICP) approach. Each observation has a soft assignment to every patch, updated in each iteration. Let observation i correspond to vertex v i k in P k with a soft assigment w i k. E data NT NP1 2 k wi i k vi i1 k1 Θ y x 15
16 A probablistic point of view [Cagniart et al. ECCV`10] Can be interpreted as EM algorithm. The likelihood: Gaussian mixture model E-step: update the soft assignment. P( z k y, Θ) k i i i i N 1 l1 M-step: minimize sum of negative log likelihood (energy). E P P( y z k, Θ) data P( y z l, Θ) i N P i 1 P( y Θ) P( y z k, Θ) i k i i k 1 NT NP1 2 k wi i k vi i1 k1 Θ y x ln( ) 16
17 Rigidity energy [Cagniart et al. CVPR`10] E rigid (Θ) : smooth the motion of neighboring patches P k k x v d l x v P l E rigid N P Θ x x k 1 PN vp P l k k l k v d l v 2 For each patch, the real location and the predicted location should be consistent. Θ is implicitly encoded in x v k and x v l 17
18 Bone-binding energy β coordinate : A relative displacement from patch to bone γ > 1 γ k 0.5 β k c k γ 0 X j(k) Δ k β k = Δ k c k X j_child(k) Δ k = γ k X j(k) + 1 γ k X j_child(k) γ k is computed such that β k is perpendicular to the bone. 18
19 Bone-binding energy E bone (Θ, J) : keep β consistent after transformation. bone N P, E Θ J w β T Θ β k 1 0 k k k k k 2 T k Θ k Δ k 0 N P k 1 w 0 k k k k k Δ T Θ Δ d 2 Δ k d For each patch, Δ k predicted from the patch and Δ k from the bone should be consistent. w k is weighed according to γ k 19
20 Energy function E data (Θ) : how well the surface explains the observations. E E rigid (Θ) : smooth the motion of neighboring patches. E data rigid N N P T N P Θ x x k 1 PN vp P l k k l E bone (Θ, J) : keep the relationship between mesh and joints. 1 Θ w y x i1 k1 k k i i v k v 2 l v 2 regularization terms or deformation prior bone N P, E Θ J w Δ T Θ Δ k 1 0 k k k k k 2 20
21 Minimizing the energy Θ, J Θ Θ Θ, J E E E E d data r rigid b bone λ d =10, λ r =1, and λ b =1 Each term is quadratic in terms of variables. Standard Gauss-Newton optimization is thus feasible. 3-4s per frame (including SVM training time). 21
22 Quantitative results Pose: 70.86mm error in Walking sequence from HumanEvaII benchmark. (error < 80mm typically corresponds to a correct pose [Sigal et al. IJCV`12]). Shape: reprojection error (%) Sequence our surface-based [4] inverse kinematic Handstand 1 [1] Wheel [1] Skirt [1] Dance [1] Crane [2] Handstand 2 [2] Bouncing [2] Free [3] Gall et al. CVPR`09 2. Vlasic et al. ToG`08 3. Starck et al. CGA`07 4.Cagniart et al. ECCV`10 22
23 Qualitative results [Starck et al. 2007] [Vlasic et al. 2008] [Gall et al. 2009] 23
24 Conclusion and future work A method that jointly recovers the pose and the shape of human body has been proposed. We introduce a novel SVM-based classification scheme that filters target point clouds and thus helps better correspondence search. Future directions include alleviating the requirement of background substraction, and exploiting more photometric information. More experiment results in the poster session. 24
25 Thank you! Questions? 25
Robust Human Body Shape and Pose Tracking
 Robust Human Body Shape and Pose Tracking Chun-Hao Huang, Edmond Boyer, Slobodan Ilic To cite this version: Chun-Hao Huang, Edmond Boyer, Slobodan Ilic. Robust Human Body Shape and Pose Tracking. 3DV -
Robust Human Body Shape and Pose Tracking Chun-Hao Huang, Edmond Boyer, Slobodan Ilic To cite this version: Chun-Hao Huang, Edmond Boyer, Slobodan Ilic. Robust Human Body Shape and Pose Tracking. 3DV -
Probabilistic Deformable Surface Tracking from Multiple Videos
 Probabilistic Deformable Surface Tracking from Multiple Videos Cedric Cagniart 1,EdmondBoyer 2, and Slobodan Ilic 1 1 Technische Universität München 2 Grenoble Universités - INRIA Rhône-Alpes {cagniart,slobodan.ilic}@in.tum.de,
Probabilistic Deformable Surface Tracking from Multiple Videos Cedric Cagniart 1,EdmondBoyer 2, and Slobodan Ilic 1 1 Technische Universität München 2 Grenoble Universités - INRIA Rhône-Alpes {cagniart,slobodan.ilic}@in.tum.de,
Free-Form Mesh Tracking: a Patch-Based Approach
 Free-Form Mesh Tracking: a Patch-Based Approach Cedric Cagniart 1, Edmond Boyer 2, Slobodan Ilic 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Technical University of Munich 2 Grenoble Universités, INRIA Rhône-Alpes
Free-Form Mesh Tracking: a Patch-Based Approach Cedric Cagniart 1, Edmond Boyer 2, Slobodan Ilic 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Technical University of Munich 2 Grenoble Universités, INRIA Rhône-Alpes
Video based Animation Synthesis with the Essential Graph. Adnane Boukhayma, Edmond Boyer MORPHEO INRIA Grenoble Rhône-Alpes
 Video based Animation Synthesis with the Essential Graph Adnane Boukhayma, Edmond Boyer MORPHEO INRIA Grenoble Rhône-Alpes Goal Given a set of 4D models, how to generate realistic motion from user specified
Video based Animation Synthesis with the Essential Graph Adnane Boukhayma, Edmond Boyer MORPHEO INRIA Grenoble Rhône-Alpes Goal Given a set of 4D models, how to generate realistic motion from user specified
3D Imaging from Video and Planar Radiography
 3D Imaging from Video and Planar Radiography Julien Pansiot and Edmond Boyer Morpheo, Inria Grenoble Rhône-Alpes, France International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention
3D Imaging from Video and Planar Radiography Julien Pansiot and Edmond Boyer Morpheo, Inria Grenoble Rhône-Alpes, France International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention
Real-time 3D reconstruction: applications to collision detection and surgical workflow monitoring
 Real-time 3D reconstruction: applications to collision detection and surgical workflow monitoring Nassir Navab! Alexander Ladikos, Nicolas Padoy, Diana Mateus and Cedric Cagniart! Presented by Nicolas
Real-time 3D reconstruction: applications to collision detection and surgical workflow monitoring Nassir Navab! Alexander Ladikos, Nicolas Padoy, Diana Mateus and Cedric Cagniart! Presented by Nicolas
Dynamic Geometry Processing
 Dynamic Geometry Processing EG 2012 Tutorial Will Chang, Hao Li, Niloy Mitra, Mark Pauly, Michael Wand Tutorial: Dynamic Geometry Processing 1 Articulated Global Registration Introduction and Overview
Dynamic Geometry Processing EG 2012 Tutorial Will Chang, Hao Li, Niloy Mitra, Mark Pauly, Michael Wand Tutorial: Dynamic Geometry Processing 1 Articulated Global Registration Introduction and Overview
Introduction to Computer Graphics. Animation (1) May 19, 2016 Kenshi Takayama
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Animation (1) May 19, 2016 Kenshi Takayama Skeleton-based animation Simple Intuitive Low comp. cost https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsonab58qva 2 Representing a pose using
Introduction to Computer Graphics Animation (1) May 19, 2016 Kenshi Takayama Skeleton-based animation Simple Intuitive Low comp. cost https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsonab58qva 2 Representing a pose using
Cage-based Motion Recovery using Manifold Learning
 Cage-based Motion Recovery using Manifold Learning Estelle Duveau Simon Courtemanche Lionel Reveret Edmond Boyer LJK, INRIA Grenoble Rhône-Alpes, France Abstract We present a flexible model-based approach
Cage-based Motion Recovery using Manifold Learning Estelle Duveau Simon Courtemanche Lionel Reveret Edmond Boyer LJK, INRIA Grenoble Rhône-Alpes, France Abstract We present a flexible model-based approach
Progressive Shape Models
 Progressive Shape Models Antoine Letouzey, Edmond Boyer To cite this version: Antoine Letouzey, Edmond Boyer. Progressive Shape Models. CVPR - Computer Vision and Patern Recognition - 2012, Jun 2012, Providence,
Progressive Shape Models Antoine Letouzey, Edmond Boyer To cite this version: Antoine Letouzey, Edmond Boyer. Progressive Shape Models. CVPR - Computer Vision and Patern Recognition - 2012, Jun 2012, Providence,
SCAPE: Shape Completion and Animation of People
 SCAPE: Shape Completion and Animation of People By Dragomir Anguelov, Praveen Srinivasan, Daphne Koller, Sebastian Thrun, Jim Rodgers, James Davis From SIGGRAPH 2005 Presentation for CS468 by Emilio Antúnez
SCAPE: Shape Completion and Animation of People By Dragomir Anguelov, Praveen Srinivasan, Daphne Koller, Sebastian Thrun, Jim Rodgers, James Davis From SIGGRAPH 2005 Presentation for CS468 by Emilio Antúnez
Animations. Hakan Bilen University of Edinburgh. Computer Graphics Fall Some slides are courtesy of Steve Marschner and Kavita Bala
 Animations Hakan Bilen University of Edinburgh Computer Graphics Fall 2017 Some slides are courtesy of Steve Marschner and Kavita Bala Animation Artistic process What are animators trying to do? What tools
Animations Hakan Bilen University of Edinburgh Computer Graphics Fall 2017 Some slides are courtesy of Steve Marschner and Kavita Bala Animation Artistic process What are animators trying to do? What tools
Human body animation. Computer Animation. Human Body Animation. Skeletal Animation
 Computer Animation Aitor Rovira March 2010 Human body animation Based on slides by Marco Gillies Human Body Animation Skeletal Animation Skeletal Animation (FK, IK) Motion Capture Motion Editing (retargeting,
Computer Animation Aitor Rovira March 2010 Human body animation Based on slides by Marco Gillies Human Body Animation Skeletal Animation Skeletal Animation (FK, IK) Motion Capture Motion Editing (retargeting,
Iterative Mesh Deformation for Dense Surface Tracking
 Iterative Mesh Deformation for Dense Surface Tracking Cedric Cagniart CAMP TU Munich & Deutsche Telekom Laboratories cedric.cagniart@in.tum.de Edmond Boyer INRIA Alpes Grenoble edmond.boyer@inrialpes.fr
Iterative Mesh Deformation for Dense Surface Tracking Cedric Cagniart CAMP TU Munich & Deutsche Telekom Laboratories cedric.cagniart@in.tum.de Edmond Boyer INRIA Alpes Grenoble edmond.boyer@inrialpes.fr
Inverse Kinematics II and Motion Capture
 Mathematical Foundations of Computer Graphics and Vision Inverse Kinematics II and Motion Capture Luca Ballan Institute of Visual Computing Comparison 0 1 A B 2 C 3 Fake exponential map Real exponential
Mathematical Foundations of Computer Graphics and Vision Inverse Kinematics II and Motion Capture Luca Ballan Institute of Visual Computing Comparison 0 1 A B 2 C 3 Fake exponential map Real exponential
Rapid Skin: Estimating the 3D Human Pose and Shape in Real-Time
 Rapid Skin: Estimating the 3D Human Pose and Shape in Real-Time Matthias Straka, Stefan Hauswiesner, Matthias Rüther, and Horst Bischof Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision Graz University of Technology,
Rapid Skin: Estimating the 3D Human Pose and Shape in Real-Time Matthias Straka, Stefan Hauswiesner, Matthias Rüther, and Horst Bischof Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision Graz University of Technology,
Robust Non-rigid Motion Tracking and Surface Reconstruction Using L 0 Regularization
 Robust Non-rigid Motion Tracking and Surface Reconstruction Using L 0 Regularization Kaiwen Guo 1,2, Feng Xu 1,3, Yangang Wang 4, Yebin Liu 1,2, Qionghai Dai 1,2 1 Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information
Robust Non-rigid Motion Tracking and Surface Reconstruction Using L 0 Regularization Kaiwen Guo 1,2, Feng Xu 1,3, Yangang Wang 4, Yebin Liu 1,2, Qionghai Dai 1,2 1 Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information
ACQUIRING 3D models of deforming objects in real-life is
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VISUALIZATION AND COMPUTER GRAPHICS 1 Robust Non-rigid Motion Tracking and Surface Reconstruction Using L 0 Regularization Kaiwen Guo, Feng Xu, Yangang Wang, Yebin Liu, Member, IEEE
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VISUALIZATION AND COMPUTER GRAPHICS 1 Robust Non-rigid Motion Tracking and Surface Reconstruction Using L 0 Regularization Kaiwen Guo, Feng Xu, Yangang Wang, Yebin Liu, Member, IEEE
Animation. CS 465 Lecture 22
 Animation CS 465 Lecture 22 Animation Industry production process leading up to animation What animation is How animation works (very generally) Artistic process of animation Further topics in how it works
Animation CS 465 Lecture 22 Animation Industry production process leading up to animation What animation is How animation works (very generally) Artistic process of animation Further topics in how it works
CSE452 Computer Graphics
 CSE452 Computer Graphics Lecture 19: From Morphing To Animation Capturing and Animating Skin Deformation in Human Motion, Park and Hodgins, SIGGRAPH 2006 CSE452 Lecture 19: From Morphing to Animation 1
CSE452 Computer Graphics Lecture 19: From Morphing To Animation Capturing and Animating Skin Deformation in Human Motion, Park and Hodgins, SIGGRAPH 2006 CSE452 Lecture 19: From Morphing to Animation 1
Motion Capture Using Joint Skeleton Tracking and Surface Estimation
 Motion Capture Using Joint Skeleton Tracking and Surface Estimation Juergen Gall 1,2, Carsten Stoll 2, Edilson de Aguiar 2, Christian Theobalt 3, Bodo Rosenhahn 4, and Hans-Peter Seidel 2 1 BIWI, ETH Zurich
Motion Capture Using Joint Skeleton Tracking and Surface Estimation Juergen Gall 1,2, Carsten Stoll 2, Edilson de Aguiar 2, Christian Theobalt 3, Bodo Rosenhahn 4, and Hans-Peter Seidel 2 1 BIWI, ETH Zurich
Nonrigid Surface Modelling. and Fast Recovery. Department of Computer Science and Engineering. Committee: Prof. Leo J. Jia and Prof. K. H.
 Nonrigid Surface Modelling and Fast Recovery Zhu Jianke Supervisor: Prof. Michael R. Lyu Committee: Prof. Leo J. Jia and Prof. K. H. Wong Department of Computer Science and Engineering May 11, 2007 1 2
Nonrigid Surface Modelling and Fast Recovery Zhu Jianke Supervisor: Prof. Michael R. Lyu Committee: Prof. Leo J. Jia and Prof. K. H. Wong Department of Computer Science and Engineering May 11, 2007 1 2
CS 523: Computer Graphics, Spring Shape Modeling. Skeletal deformation. Andrew Nealen, Rutgers, /12/2011 1
 CS 523: Computer Graphics, Spring 2011 Shape Modeling Skeletal deformation 4/12/2011 1 Believable character animation Computers games and movies Skeleton: intuitive, low-dimensional subspace Clip courtesy
CS 523: Computer Graphics, Spring 2011 Shape Modeling Skeletal deformation 4/12/2011 1 Believable character animation Computers games and movies Skeleton: intuitive, low-dimensional subspace Clip courtesy
Grasp Recognition using a 3D Articulated Model and Infrared Images
 Grasp Recognition using a 3D Articulated Model and Infrared Images Koichi Ogawara Institute of Industrial Science, Univ. of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan Jun Takamatsu Institute of Industrial Science, Univ. of Tokyo,
Grasp Recognition using a 3D Articulated Model and Infrared Images Koichi Ogawara Institute of Industrial Science, Univ. of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan Jun Takamatsu Institute of Industrial Science, Univ. of Tokyo,
Articulated Pose Estimation with Flexible Mixtures-of-Parts
 Articulated Pose Estimation with Flexible Mixtures-of-Parts PRESENTATION: JESSE DAVIS CS 3710 VISUAL RECOGNITION Outline Modeling Special Cases Inferences Learning Experiments Problem and Relevance Problem:
Articulated Pose Estimation with Flexible Mixtures-of-Parts PRESENTATION: JESSE DAVIS CS 3710 VISUAL RECOGNITION Outline Modeling Special Cases Inferences Learning Experiments Problem and Relevance Problem:
CS 775: Advanced Computer Graphics. Lecture 17 : Motion Capture
 CS 775: Advanced Computer Graphics Lecture 17 : History Study of human motion Leonardo da Vinci (1452 1519) History Study of human motion Edward J. Muybridge, 1830 1904 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/eadweard_muybridge
CS 775: Advanced Computer Graphics Lecture 17 : History Study of human motion Leonardo da Vinci (1452 1519) History Study of human motion Edward J. Muybridge, 1830 1904 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/eadweard_muybridge
Skeletal deformation
 CS 523: Computer Graphics, Spring 2009 Shape Modeling Skeletal deformation 4/22/2009 1 Believable character animation Computers games and movies Skeleton: intuitive, low dimensional subspace Clip courtesy
CS 523: Computer Graphics, Spring 2009 Shape Modeling Skeletal deformation 4/22/2009 1 Believable character animation Computers games and movies Skeleton: intuitive, low dimensional subspace Clip courtesy
10 - ARAP and Linear Blend Skinning
 10 - ARAP and Linear Blend Skinning Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung As Rigid As Possible Demo Libigl demo 405 As-Rigid-As-Possible Deformation Preserve shape of cells covering the surface Ask each
10 - ARAP and Linear Blend Skinning Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung As Rigid As Possible Demo Libigl demo 405 As-Rigid-As-Possible Deformation Preserve shape of cells covering the surface Ask each
Multi-View 3D-Reconstruction
 Multi-View 3D-Reconstruction Cedric Cagniart Computer Aided Medical Procedures (CAMP) Technische Universität München, Germany 1 Problem Statement Given several calibrated views of an object... can we automatically
Multi-View 3D-Reconstruction Cedric Cagniart Computer Aided Medical Procedures (CAMP) Technische Universität München, Germany 1 Problem Statement Given several calibrated views of an object... can we automatically
Tracking Articulated Bodies using Generalized Expectation Maximization
 Tracking Articulated Bodies using Generalized Expectation Maximization A. Fossati CVLab EPFL, Switzerland andrea.fossati@epfl.ch E. Arnaud Université Joseph Fourier INRIA Rhone-Alpes, France elise.arnaud@inrialpes.fr
Tracking Articulated Bodies using Generalized Expectation Maximization A. Fossati CVLab EPFL, Switzerland andrea.fossati@epfl.ch E. Arnaud Université Joseph Fourier INRIA Rhone-Alpes, France elise.arnaud@inrialpes.fr
Kinematics. CS 448D: Character Animation Prof. Vladlen Koltun Stanford University
 Kinematics CS 448D: Character Animation Prof. Vladlen Koltun Stanford University Kinematics Kinematics: The science of pure motion, considered without reference to the matter of objects moved, or to the
Kinematics CS 448D: Character Animation Prof. Vladlen Koltun Stanford University Kinematics Kinematics: The science of pure motion, considered without reference to the matter of objects moved, or to the
PERFORMANCE CAPTURE FROM SPARSE MULTI-VIEW VIDEO
 Stefan Krauß, Juliane Hüttl SE, SoSe 2011, HU-Berlin PERFORMANCE CAPTURE FROM SPARSE MULTI-VIEW VIDEO 1 Uses of Motion/Performance Capture movies games, virtual environments biomechanics, sports science,
Stefan Krauß, Juliane Hüttl SE, SoSe 2011, HU-Berlin PERFORMANCE CAPTURE FROM SPARSE MULTI-VIEW VIDEO 1 Uses of Motion/Performance Capture movies games, virtual environments biomechanics, sports science,
Part I: HumanEva-I dataset and evaluation metrics
 Part I: HumanEva-I dataset and evaluation metrics Leonid Sigal Michael J. Black Department of Computer Science Brown University http://www.cs.brown.edu/people/ls/ http://vision.cs.brown.edu/humaneva/ Motivation
Part I: HumanEva-I dataset and evaluation metrics Leonid Sigal Michael J. Black Department of Computer Science Brown University http://www.cs.brown.edu/people/ls/ http://vision.cs.brown.edu/humaneva/ Motivation
CS 775: Advanced Computer Graphics. Lecture 8 : Motion Capture
 CS 775: Advanced Computer Graphics Lecture 8 : History Study of human motion Leonardo da Vinci (1452 1519) History Study of human motion Edward J. Muybridge, 1830 1904 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/eadweard_muybridge
CS 775: Advanced Computer Graphics Lecture 8 : History Study of human motion Leonardo da Vinci (1452 1519) History Study of human motion Edward J. Muybridge, 1830 1904 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/eadweard_muybridge
Repeatable Local Coordinate Frames for 3D Human Motion Tracking: from Rigid to Non-Rigid
 Repeatable Local Coordinate Frames for 3D Human Motion Tracking: from Rigid to Non-Rigid Chun-Hao Huang 1 Federico Tombari 1,2 Nassir Navab 1,3 1 Technische Universität München, 2 Università di Bologna,
Repeatable Local Coordinate Frames for 3D Human Motion Tracking: from Rigid to Non-Rigid Chun-Hao Huang 1 Federico Tombari 1,2 Nassir Navab 1,3 1 Technische Universität München, 2 Università di Bologna,
Optimal motion trajectories. Physically based motion transformation. Realistic character animation with control. Highly dynamic motion
 Realistic character animation with control Optimal motion trajectories Physically based motion transformation, Popovi! and Witkin Synthesis of complex dynamic character motion from simple animation, Liu
Realistic character animation with control Optimal motion trajectories Physically based motion transformation, Popovi! and Witkin Synthesis of complex dynamic character motion from simple animation, Liu
Game Programming. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Game Programming Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Character Motion Hierarchical Modeling Character Animation Motion Editing 1 Hierarchical Modeling Connected primitives 2 3D Example: A robot arm
Game Programming Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Character Motion Hierarchical Modeling Character Animation Motion Editing 1 Hierarchical Modeling Connected primitives 2 3D Example: A robot arm
Rigging / Skinning. based on Taku Komura, Jehee Lee and Charles B.Own's slides
 Rigging / Skinning based on Taku Komura, Jehee Lee and Charles B.Own's slides Skeletal Animation Victoria 2 CSE 872 Dr. Charles B. Owen Advanced Computer Graphics Skinning http://www.youtube.com/watch?
Rigging / Skinning based on Taku Komura, Jehee Lee and Charles B.Own's slides Skeletal Animation Victoria 2 CSE 872 Dr. Charles B. Owen Advanced Computer Graphics Skinning http://www.youtube.com/watch?
Predicting 3D People from 2D Pictures
 Predicting 3D People from 2D Pictures Leonid Sigal Michael J. Black Department of Computer Science Brown University http://www.cs.brown.edu/people/ls/ CIAR Summer School August 15-20, 2006 Leonid Sigal
Predicting 3D People from 2D Pictures Leonid Sigal Michael J. Black Department of Computer Science Brown University http://www.cs.brown.edu/people/ls/ CIAR Summer School August 15-20, 2006 Leonid Sigal
Example-Based Skeleton Extraction. Scott Schaefer Can Yuksel
 Example-Based Skeleton Extraction Scott Schaefer Can Yuksel Example-Based Deformation Examples Previous Work Mesh-based Inverse Kinematics [Sumner et al. 2005], [Der et al. 2006] Example-based deformation
Example-Based Skeleton Extraction Scott Schaefer Can Yuksel Example-Based Deformation Examples Previous Work Mesh-based Inverse Kinematics [Sumner et al. 2005], [Der et al. 2006] Example-based deformation
Accurate 3D Face and Body Modeling from a Single Fixed Kinect
 Accurate 3D Face and Body Modeling from a Single Fixed Kinect Ruizhe Wang*, Matthias Hernandez*, Jongmoo Choi, Gérard Medioni Computer Vision Lab, IRIS University of Southern California Abstract In this
Accurate 3D Face and Body Modeling from a Single Fixed Kinect Ruizhe Wang*, Matthias Hernandez*, Jongmoo Choi, Gérard Medioni Computer Vision Lab, IRIS University of Southern California Abstract In this
Homework 2 Questions? Animation, Motion Capture, & Inverse Kinematics. Velocity Interpolation. Handing Free Surface with MAC
 Homework 2 Questions? Animation, Motion Capture, & Inverse Kinematics Velocity Interpolation Original image from Foster & Metaxas, 1996 In 2D: For each axis, find the 4 closest face velocity samples: Self-intersecting
Homework 2 Questions? Animation, Motion Capture, & Inverse Kinematics Velocity Interpolation Original image from Foster & Metaxas, 1996 In 2D: For each axis, find the 4 closest face velocity samples: Self-intersecting
TEXTURE OVERLAY ONTO NON-RIGID SURFACE USING COMMODITY DEPTH CAMERA
 TEXTURE OVERLAY ONTO NON-RIGID SURFACE USING COMMODITY DEPTH CAMERA Tomoki Hayashi 1, Francois de Sorbier 1 and Hideo Saito 1 1 Graduate School of Science and Technology, Keio University, 3-14-1 Hiyoshi,
TEXTURE OVERLAY ONTO NON-RIGID SURFACE USING COMMODITY DEPTH CAMERA Tomoki Hayashi 1, Francois de Sorbier 1 and Hideo Saito 1 1 Graduate School of Science and Technology, Keio University, 3-14-1 Hiyoshi,
Announcements: Quiz. Animation, Motion Capture, & Inverse Kinematics. Last Time? Today: How do we Animate? Keyframing. Procedural Animation
 Announcements: Quiz Animation, Motion Capture, & Inverse Kinematics On Friday (3/1), in class One 8.5x11 sheet of notes allowed Sample quiz (from a previous year) on website Focus on reading comprehension
Announcements: Quiz Animation, Motion Capture, & Inverse Kinematics On Friday (3/1), in class One 8.5x11 sheet of notes allowed Sample quiz (from a previous year) on website Focus on reading comprehension
Computational Design. Stelian Coros
 Computational Design Stelian Coros Schedule for presentations February 3 5 10 12 17 19 24 26 March 3 5 10 12 17 19 24 26 30 April 2 7 9 14 16 21 23 28 30 Send me: ASAP: 3 choices for dates + approximate
Computational Design Stelian Coros Schedule for presentations February 3 5 10 12 17 19 24 26 March 3 5 10 12 17 19 24 26 30 April 2 7 9 14 16 21 23 28 30 Send me: ASAP: 3 choices for dates + approximate
Real-Time Human Pose Recognition in Parts from Single Depth Images
 Real-Time Human Pose Recognition in Parts from Single Depth Images Jamie Shotton, Andrew Fitzgibbon, Mat Cook, Toby Sharp, Mark Finocchio, Richard Moore, Alex Kipman, Andrew Blake CVPR 2011 PRESENTER:
Real-Time Human Pose Recognition in Parts from Single Depth Images Jamie Shotton, Andrew Fitzgibbon, Mat Cook, Toby Sharp, Mark Finocchio, Richard Moore, Alex Kipman, Andrew Blake CVPR 2011 PRESENTER:
Style-based Inverse Kinematics
 Style-based Inverse Kinematics Keith Grochow, Steven L. Martin, Aaron Hertzmann, Zoran Popovic SIGGRAPH 04 Presentation by Peter Hess 1 Inverse Kinematics (1) Goal: Compute a human body pose from a set
Style-based Inverse Kinematics Keith Grochow, Steven L. Martin, Aaron Hertzmann, Zoran Popovic SIGGRAPH 04 Presentation by Peter Hess 1 Inverse Kinematics (1) Goal: Compute a human body pose from a set
Markerless Motion Capture with Multi-view Structured Light
 Markerless Motion Capture with Multi-view Structured Light Ricardo R. Garcia, Avideh Zakhor; UC Berkeley; Berkeley, CA (a) (c) Figure 1: Using captured partial scans of (a) front and (b) back to generate
Markerless Motion Capture with Multi-view Structured Light Ricardo R. Garcia, Avideh Zakhor; UC Berkeley; Berkeley, CA (a) (c) Figure 1: Using captured partial scans of (a) front and (b) back to generate
Animation. CS 4620 Lecture 33. Cornell CS4620 Fall Kavita Bala
 Animation CS 4620 Lecture 33 Cornell CS4620 Fall 2015 1 Announcements Grading A5 (and A6) on Monday after TG 4621: one-on-one sessions with TA this Friday w/ prior instructor Steve Marschner 2 Quaternions
Animation CS 4620 Lecture 33 Cornell CS4620 Fall 2015 1 Announcements Grading A5 (and A6) on Monday after TG 4621: one-on-one sessions with TA this Friday w/ prior instructor Steve Marschner 2 Quaternions
Surface Registration. Gianpaolo Palma
 Surface Registration Gianpaolo Palma The problem 3D scanning generates multiple range images Each contain 3D points for different parts of the model in the local coordinates of the scanner Find a rigid
Surface Registration Gianpaolo Palma The problem 3D scanning generates multiple range images Each contain 3D points for different parts of the model in the local coordinates of the scanner Find a rigid
HUMAN motion capture has been under investigation for many
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VISUALIZATION AND COMPUTER GRAPHICS, VOL., NO., JANUARY 2015 1 Markerless Motion Capture with Multi-view Structured Light Ricardo R. Garcia, Student Member, IEEE, and Avideh Zakhor,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VISUALIZATION AND COMPUTER GRAPHICS, VOL., NO., JANUARY 2015 1 Markerless Motion Capture with Multi-view Structured Light Ricardo R. Garcia, Student Member, IEEE, and Avideh Zakhor,
Markerless human motion capture through visual hull and articulated ICP
 Markerless human motion capture through visual hull and articulated ICP Lars Mündermann lmuender@stanford.edu Stefano Corazza Stanford, CA 93405 stefanoc@stanford.edu Thomas. P. Andriacchi Bone and Joint
Markerless human motion capture through visual hull and articulated ICP Lars Mündermann lmuender@stanford.edu Stefano Corazza Stanford, CA 93405 stefanoc@stanford.edu Thomas. P. Andriacchi Bone and Joint
Animation of 3D surfaces
 Animation of 3D surfaces 2013-14 Motivations When character animation is controlled by skeleton set of hierarchical joints joints oriented by rotations the character shape still needs to be visible: visible
Animation of 3D surfaces 2013-14 Motivations When character animation is controlled by skeleton set of hierarchical joints joints oriented by rotations the character shape still needs to be visible: visible
Data-driven Approaches to Simulation (Motion Capture)
 1 Data-driven Approaches to Simulation (Motion Capture) Ting-Chun Sun tingchun.sun@usc.edu Preface The lecture slides [1] are made by Jessica Hodgins [2], who is a professor in Computer Science Department
1 Data-driven Approaches to Simulation (Motion Capture) Ting-Chun Sun tingchun.sun@usc.edu Preface The lecture slides [1] are made by Jessica Hodgins [2], who is a professor in Computer Science Department
An Efficient Volumetric Framework for Shape Tracking
 An Efficient Volumetric Framework for Shape Tracking Benjamin Allain Jean-Sébastien Franco Inria Grenoble Rhône-Alpes - LJK Grenoble Universities, France firstname.lastname@inria.fr Edmond Boyer Abstract
An Efficient Volumetric Framework for Shape Tracking Benjamin Allain Jean-Sébastien Franco Inria Grenoble Rhône-Alpes - LJK Grenoble Universities, France firstname.lastname@inria.fr Edmond Boyer Abstract
Character animation Christian Miller CS Fall 2011
 Character animation Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 Exam 2 grades Avg = 74.4, std. dev. = 14.4, min = 42, max = 99 Characters Everything is important in an animation But people are especially sensitive
Character animation Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 Exam 2 grades Avg = 74.4, std. dev. = 14.4, min = 42, max = 99 Characters Everything is important in an animation But people are especially sensitive
Supplemental Material: Detailed, accurate, human shape estimation from clothed 3D scan sequences
 Supplemental Material: Detailed, accurate, human shape estimation from clothed 3D scan sequences Chao Zhang 1,2, Sergi Pujades 1, Michael Black 1, and Gerard Pons-Moll 1 1 MPI for Intelligent Systems,
Supplemental Material: Detailed, accurate, human shape estimation from clothed 3D scan sequences Chao Zhang 1,2, Sergi Pujades 1, Michael Black 1, and Gerard Pons-Moll 1 1 MPI for Intelligent Systems,
Model-based Motion Capture for Crash Test Video Analysis
 Model-based Motion Capture for Crash Test Video Analysis Juergen Gall 1, Bodo Rosenhahn 1, Stefan Gehrig 2, and Hans-Peter Seidel 1 1 Max-Planck-Institute for Computer Science, Campus E1 4, 66123 Saarbrücken,
Model-based Motion Capture for Crash Test Video Analysis Juergen Gall 1, Bodo Rosenhahn 1, Stefan Gehrig 2, and Hans-Peter Seidel 1 1 Max-Planck-Institute for Computer Science, Campus E1 4, 66123 Saarbrücken,
Multiview Stereo COSC450. Lecture 8
 Multiview Stereo COSC450 Lecture 8 Stereo Vision So Far Stereo and epipolar geometry Fundamental matrix captures geometry 8-point algorithm Essential matrix with calibrated cameras 5-point algorithm Intersect
Multiview Stereo COSC450 Lecture 8 Stereo Vision So Far Stereo and epipolar geometry Fundamental matrix captures geometry 8-point algorithm Essential matrix with calibrated cameras 5-point algorithm Intersect
Animation by Adaptation Tales of Motion Use and Re-Use
 Animation by Adaptation Tales of Motion Use and Re-Use Michael Gleicher And the UW Graphics Gang Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison http://www.cs.wisc.edu/graphics Tales of
Animation by Adaptation Tales of Motion Use and Re-Use Michael Gleicher And the UW Graphics Gang Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison http://www.cs.wisc.edu/graphics Tales of
Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images. Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009
 Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009 Traditional ways of inferring depth Binocular disparity Structure from motion Defocus Given a single monocular image, how to infer
Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009 Traditional ways of inferring depth Binocular disparity Structure from motion Defocus Given a single monocular image, how to infer
Online Interactive 4D Character Animation
 Online Interactive 4D Character Animation Marco Volino, Peng Huang and Adrian Hilton Web3D 2015 Outline 4D Performance Capture - 3D Reconstruction, Alignment, Texture Maps Animation - Parametric Motion
Online Interactive 4D Character Animation Marco Volino, Peng Huang and Adrian Hilton Web3D 2015 Outline 4D Performance Capture - 3D Reconstruction, Alignment, Texture Maps Animation - Parametric Motion
Skeleton-Based Shape Deformation using Simplex Transformations
 Computer Graphics International 2006 Skeleton-Based Shape Deformation using Simplex Transformations Han-Bing Yan, Shi-Min Hu and Ralph Martin Outline Motivation Introduction Mesh segmentation using skeleton
Computer Graphics International 2006 Skeleton-Based Shape Deformation using Simplex Transformations Han-Bing Yan, Shi-Min Hu and Ralph Martin Outline Motivation Introduction Mesh segmentation using skeleton
Chapter 5 Human Performance Capture Using Multiple Handheld Kinects
 Chapter 5 Human Performance Capture Using Multiple Handheld Kinects Yebin Liu, Genzhi Ye, Yangang Wang, Qionghai Dai and Christian Theobalt Abstract Capturing real performances of human actors has been
Chapter 5 Human Performance Capture Using Multiple Handheld Kinects Yebin Liu, Genzhi Ye, Yangang Wang, Qionghai Dai and Christian Theobalt Abstract Capturing real performances of human actors has been
Deformation Transfer for Triangle Meshes
 Deformation Transfer for Triangle Meshes a Paper (SIGGRAPH 2004) by Robert W. Sumner & Jovan Popovic presented by Roni Oeschger Deformation Transfer Source deformed Target deformed 1 Outline of my presentation
Deformation Transfer for Triangle Meshes a Paper (SIGGRAPH 2004) by Robert W. Sumner & Jovan Popovic presented by Roni Oeschger Deformation Transfer Source deformed Target deformed 1 Outline of my presentation
Character Animation COS 426
 Character Animation COS 426 Syllabus I. Image processing II. Modeling III. Rendering IV. Animation Image Processing (Rusty Coleman, CS426, Fall99) Rendering (Michael Bostock, CS426, Fall99) Modeling (Dennis
Character Animation COS 426 Syllabus I. Image processing II. Modeling III. Rendering IV. Animation Image Processing (Rusty Coleman, CS426, Fall99) Rendering (Michael Bostock, CS426, Fall99) Modeling (Dennis
Cage-based Tracking for Performance Animation
 Cage-based Tracking for Performance Animation Yann Savoye, Jean-Sébastien Franco To cite this version: Yann Savoye, Jean-Sébastien Franco. Cage-based Tracking for Performance Animation. ACCV 10 :the Tenth
Cage-based Tracking for Performance Animation Yann Savoye, Jean-Sébastien Franco To cite this version: Yann Savoye, Jean-Sébastien Franco. Cage-based Tracking for Performance Animation. ACCV 10 :the Tenth
Skinning Mesh Animations
 Doug L. James, Christopher D. Twigg Carnegie Mellon University presented by Johannes Schmid 1 Outline Introduction & Motivation Overview & Details Results Discussion 2 Introduction Mesh sequence: 3 General
Doug L. James, Christopher D. Twigg Carnegie Mellon University presented by Johannes Schmid 1 Outline Introduction & Motivation Overview & Details Results Discussion 2 Introduction Mesh sequence: 3 General
Dynamic 3D Shape From Multi-viewpoint Images Using Deformable Mesh Model
 Dynamic 3D Shape From Multi-viewpoint Images Using Deformable Mesh Model Shohei Nobuhara Takashi Matsuyama Graduate School of Informatics, Kyoto University Sakyo, Kyoto, 606-8501, Japan {nob, tm}@vision.kuee.kyoto-u.ac.jp
Dynamic 3D Shape From Multi-viewpoint Images Using Deformable Mesh Model Shohei Nobuhara Takashi Matsuyama Graduate School of Informatics, Kyoto University Sakyo, Kyoto, 606-8501, Japan {nob, tm}@vision.kuee.kyoto-u.ac.jp
Image Processing and Computer Vision
 1 / 1 Image Processing and Computer Vision Detecting primitives and rigid objects in Images Martin de La Gorce martin.de-la-gorce@enpc.fr February 2015 Detecting lines 2 / 1 How can we detect simple primitive
1 / 1 Image Processing and Computer Vision Detecting primitives and rigid objects in Images Martin de La Gorce martin.de-la-gorce@enpc.fr February 2015 Detecting lines 2 / 1 How can we detect simple primitive
Learning 6D Object Pose Estimation and Tracking
 Learning 6D Object Pose Estimation and Tracking Carsten Rother presented by: Alexander Krull 21/12/2015 6D Pose Estimation Input: RGBD-image Known 3D model Output: 6D rigid body transform of object 21/12/2015
Learning 6D Object Pose Estimation and Tracking Carsten Rother presented by: Alexander Krull 21/12/2015 6D Pose Estimation Input: RGBD-image Known 3D model Output: 6D rigid body transform of object 21/12/2015
Animation, Motion Capture, & Inverse Kinematics. Announcements: Quiz
 Animation, Motion Capture, & Inverse Kinematics Announcements: Quiz On Tuesday (3/10), in class One 8.5x11 sheet of notes allowed Sample quiz (from a previous year) on website Focus on reading comprehension
Animation, Motion Capture, & Inverse Kinematics Announcements: Quiz On Tuesday (3/10), in class One 8.5x11 sheet of notes allowed Sample quiz (from a previous year) on website Focus on reading comprehension
Monocular Human Motion Capture with a Mixture of Regressors. Ankur Agarwal and Bill Triggs GRAVIR-INRIA-CNRS, Grenoble, France
 Monocular Human Motion Capture with a Mixture of Regressors Ankur Agarwal and Bill Triggs GRAVIR-INRIA-CNRS, Grenoble, France IEEE Workshop on Vision for Human-Computer Interaction, 21 June 2005 Visual
Monocular Human Motion Capture with a Mixture of Regressors Ankur Agarwal and Bill Triggs GRAVIR-INRIA-CNRS, Grenoble, France IEEE Workshop on Vision for Human-Computer Interaction, 21 June 2005 Visual
CS 231. Inverse Kinematics Intro to Motion Capture. 3D characters. Representation. 1) Skeleton Origin (root) Joint centers/ bones lengths
 CS Inverse Kinematics Intro to Motion Capture Representation D characters ) Skeleton Origin (root) Joint centers/ bones lengths ) Keyframes Pos/Rot Root (x) Joint Angles (q) Kinematics study of static
CS Inverse Kinematics Intro to Motion Capture Representation D characters ) Skeleton Origin (root) Joint centers/ bones lengths ) Keyframes Pos/Rot Root (x) Joint Angles (q) Kinematics study of static
Pose Space Deformation A unified Approach to Shape Interpolation and Skeleton-Driven Deformation
 Pose Space Deformation A unified Approach to Shape Interpolation and Skeleton-Driven Deformation J.P. Lewis Matt Cordner Nickson Fong Presented by 1 Talk Outline Character Animation Overview Problem Statement
Pose Space Deformation A unified Approach to Shape Interpolation and Skeleton-Driven Deformation J.P. Lewis Matt Cordner Nickson Fong Presented by 1 Talk Outline Character Animation Overview Problem Statement
TEXTURE OVERLAY ONTO NON-RIGID SURFACE USING COMMODITY DEPTH CAMERA
 TEXTURE OVERLAY ONTO NON-RIGID SURFACE USING COMMODITY DEPTH CAMERA Tomoki Hayashi, Francois de Sorbier and Hideo Saito Graduate School of Science and Technology, Keio University, 3-14-1 Hiyoshi, Kohoku-ku,
TEXTURE OVERLAY ONTO NON-RIGID SURFACE USING COMMODITY DEPTH CAMERA Tomoki Hayashi, Francois de Sorbier and Hideo Saito Graduate School of Science and Technology, Keio University, 3-14-1 Hiyoshi, Kohoku-ku,
Hartley - Zisserman reading club. Part I: Hartley and Zisserman Appendix 6: Part II: Zhengyou Zhang: Presented by Daniel Fontijne
 Hartley - Zisserman reading club Part I: Hartley and Zisserman Appendix 6: Iterative estimation methods Part II: Zhengyou Zhang: A Flexible New Technique for Camera Calibration Presented by Daniel Fontijne
Hartley - Zisserman reading club Part I: Hartley and Zisserman Appendix 6: Iterative estimation methods Part II: Zhengyou Zhang: A Flexible New Technique for Camera Calibration Presented by Daniel Fontijne
Introduction to Mobile Robotics
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Clustering Wolfram Burgard Cyrill Stachniss Giorgio Grisetti Maren Bennewitz Christian Plagemann Clustering (1) Common technique for statistical data analysis (machine learning,
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Clustering Wolfram Burgard Cyrill Stachniss Giorgio Grisetti Maren Bennewitz Christian Plagemann Clustering (1) Common technique for statistical data analysis (machine learning,
Advanced Graphics and Animation
 Advanced Graphics and Animation Character Marco Gillies and Dan Jones Goldsmiths Aims and objectives By the end of the lecture you will be able to describe How 3D characters are animated Skeletal animation
Advanced Graphics and Animation Character Marco Gillies and Dan Jones Goldsmiths Aims and objectives By the end of the lecture you will be able to describe How 3D characters are animated Skeletal animation
Learning Articulated Skeletons From Motion
 Learning Articulated Skeletons From Motion Danny Tarlow University of Toronto, Machine Learning with David Ross and Richard Zemel (and Brendan Frey) August 6, 2007 Point Light Displays It's easy for humans
Learning Articulated Skeletons From Motion Danny Tarlow University of Toronto, Machine Learning with David Ross and Richard Zemel (and Brendan Frey) August 6, 2007 Point Light Displays It's easy for humans
CS 231. Basics of Computer Animation
 CS 231 Basics of Computer Animation Animation Techniques Keyframing Motion capture Physics models Keyframe animation Highest degree of control, also difficult Interpolation affects end result Timing must
CS 231 Basics of Computer Animation Animation Techniques Keyframing Motion capture Physics models Keyframe animation Highest degree of control, also difficult Interpolation affects end result Timing must
CMSC 425: Lecture 10 Skeletal Animation and Skinning
 CMSC 425: Lecture 10 Skeletal Animation and Skinning Reading: Chapt 11 of Gregory, Game Engine Architecture. Recap: Last time we introduced the principal elements of skeletal models and discussed forward
CMSC 425: Lecture 10 Skeletal Animation and Skinning Reading: Chapt 11 of Gregory, Game Engine Architecture. Recap: Last time we introduced the principal elements of skeletal models and discussed forward
International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Vol. XXXIV-5/W10
 BUNDLE ADJUSTMENT FOR MARKERLESS BODY TRACKING IN MONOCULAR VIDEO SEQUENCES Ali Shahrokni, Vincent Lepetit, Pascal Fua Computer Vision Lab, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL) ali.shahrokni,vincent.lepetit,pascal.fua@epfl.ch
BUNDLE ADJUSTMENT FOR MARKERLESS BODY TRACKING IN MONOCULAR VIDEO SEQUENCES Ali Shahrokni, Vincent Lepetit, Pascal Fua Computer Vision Lab, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL) ali.shahrokni,vincent.lepetit,pascal.fua@epfl.ch
Multiple Model Estimation : The EM Algorithm & Applications
 Multiple Model Estimation : The EM Algorithm & Applications Princeton University COS 429 Lecture Dec. 4, 2008 Harpreet S. Sawhney hsawhney@sarnoff.com Plan IBR / Rendering applications of motion / pose
Multiple Model Estimation : The EM Algorithm & Applications Princeton University COS 429 Lecture Dec. 4, 2008 Harpreet S. Sawhney hsawhney@sarnoff.com Plan IBR / Rendering applications of motion / pose
Nonrigid Registration using Free-Form Deformations
 Nonrigid Registration using Free-Form Deformations Hongchang Peng April 20th Paper Presented: Rueckert et al., TMI 1999: Nonrigid registration using freeform deformations: Application to breast MR images
Nonrigid Registration using Free-Form Deformations Hongchang Peng April 20th Paper Presented: Rueckert et al., TMI 1999: Nonrigid registration using freeform deformations: Application to breast MR images
Scanning Real World Objects without Worries 3D Reconstruction
 Scanning Real World Objects without Worries 3D Reconstruction 1. Overview Feng Li 308262 Kuan Tian 308263 This document is written for the 3D reconstruction part in the course Scanning real world objects
Scanning Real World Objects without Worries 3D Reconstruction 1. Overview Feng Li 308262 Kuan Tian 308263 This document is written for the 3D reconstruction part in the course Scanning real world objects
Multi-Frame Scene-Flow Estimation Using a Patch Model and Smooth Motion Prior
 POPHAM, BHALERAO, WILSON: MULTI-FRAME SCENE-FLOW ESTIMATION 1 Multi-Frame Scene-Flow Estimation Using a Patch Model and Smooth Motion Prior Thomas Popham tpopham@dcs.warwick.ac.uk Abhir Bhalerao abhir@dcs.warwick.ac.uk
POPHAM, BHALERAO, WILSON: MULTI-FRAME SCENE-FLOW ESTIMATION 1 Multi-Frame Scene-Flow Estimation Using a Patch Model and Smooth Motion Prior Thomas Popham tpopham@dcs.warwick.ac.uk Abhir Bhalerao abhir@dcs.warwick.ac.uk
Tracking human joint motion for turntable-based static model reconstruction
 joint angles Tracking human joint motion for turntable-based static model reconstruction Neil Birkbeck Dana Cobzas Martin Jagersand University of Alberta Edmonton, Alberta, CA {birkbeck,dana,jag}@cs.ualberta.ca
joint angles Tracking human joint motion for turntable-based static model reconstruction Neil Birkbeck Dana Cobzas Martin Jagersand University of Alberta Edmonton, Alberta, CA {birkbeck,dana,jag}@cs.ualberta.ca
Geometric Registration for Deformable Shapes 1.1 Introduction
 Geometric Registration for Deformable Shapes 1.1 Introduction Overview Data Sources and Applications Problem Statement Overview Presenters Will Chang University of California at San Diego, USA Hao Li ETH
Geometric Registration for Deformable Shapes 1.1 Introduction Overview Data Sources and Applications Problem Statement Overview Presenters Will Chang University of California at San Diego, USA Hao Li ETH
Three-Dimensional Sensors Lecture 6: Point-Cloud Registration
 Three-Dimensional Sensors Lecture 6: Point-Cloud Registration Radu Horaud INRIA Grenoble Rhone-Alpes, France Radu.Horaud@inria.fr http://perception.inrialpes.fr/ Point-Cloud Registration Methods Fuse data
Three-Dimensional Sensors Lecture 6: Point-Cloud Registration Radu Horaud INRIA Grenoble Rhone-Alpes, France Radu.Horaud@inria.fr http://perception.inrialpes.fr/ Point-Cloud Registration Methods Fuse data
3D Human Motion Analysis and Manifolds
 D E P A R T M E N T O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E U N I V E R S I T Y O F C O P E N H A G E N 3D Human Motion Analysis and Manifolds Kim Steenstrup Pedersen DIKU Image group and E-Science center Motivation
D E P A R T M E N T O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E U N I V E R S I T Y O F C O P E N H A G E N 3D Human Motion Analysis and Manifolds Kim Steenstrup Pedersen DIKU Image group and E-Science center Motivation
Animation Lecture 10 Slide Fall 2003
 Animation Lecture 10 Slide 1 6.837 Fall 2003 Conventional Animation Draw each frame of the animation great control tedious Reduce burden with cel animation layer keyframe inbetween cel panoramas (Disney
Animation Lecture 10 Slide 1 6.837 Fall 2003 Conventional Animation Draw each frame of the animation great control tedious Reduce burden with cel animation layer keyframe inbetween cel panoramas (Disney
3D Face Modeling. Lacey Best- Rowden, Joseph Roth Feb. 18, MSU
 3D Face Modeling Lacey Best- Rowden, Joseph Roth Feb. 18, MSU Outline ApplicaDon / Benefits 3D ReconstrucDon Techniques o Range Scanners o Single Image! 3DMM o MulDple Image! Shape from stereo! Photometric
3D Face Modeling Lacey Best- Rowden, Joseph Roth Feb. 18, MSU Outline ApplicaDon / Benefits 3D ReconstrucDon Techniques o Range Scanners o Single Image! 3DMM o MulDple Image! Shape from stereo! Photometric
Patch-based Non-rigid 3D Reconstruction from a Single Depth Stream
 Patch-based Non-rigid 3D Reconstruction from a Single Depth Stream Carmel Kozlov Miroslava Slavcheva Slobodan Ilic Technische Universität München Siemens Corporate Technology Abstract We propose an approach
Patch-based Non-rigid 3D Reconstruction from a Single Depth Stream Carmel Kozlov Miroslava Slavcheva Slobodan Ilic Technische Universität München Siemens Corporate Technology Abstract We propose an approach
Intrinsic3D: High-Quality 3D Reconstruction by Joint Appearance and Geometry Optimization with Spatially-Varying Lighting
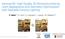 Intrinsic3D: High-Quality 3D Reconstruction by Joint Appearance and Geometry Optimization with Spatially-Varying Lighting R. Maier 1,2, K. Kim 1, D. Cremers 2, J. Kautz 1, M. Nießner 2,3 Fusion Ours 1
Intrinsic3D: High-Quality 3D Reconstruction by Joint Appearance and Geometry Optimization with Spatially-Varying Lighting R. Maier 1,2, K. Kim 1, D. Cremers 2, J. Kautz 1, M. Nießner 2,3 Fusion Ours 1
Clothed and Naked Human Shapes Estimation from a Single Image
 Clothed and Naked Human Shapes Estimation from a Single Image Yu Guo, Xiaowu Chen, Bin Zhou, and Qinping Zhao State Key Laboratory of Virtual Reality Technology and Systems School of Computer Science and
Clothed and Naked Human Shapes Estimation from a Single Image Yu Guo, Xiaowu Chen, Bin Zhou, and Qinping Zhao State Key Laboratory of Virtual Reality Technology and Systems School of Computer Science and
Gesture Recognition: Hand Pose Estimation. Adrian Spurr Ubiquitous Computing Seminar FS
 Gesture Recognition: Hand Pose Estimation Adrian Spurr Ubiquitous Computing Seminar FS2014 27.05.2014 1 What is hand pose estimation? Input Computer-usable form 2 Augmented Reality Gaming Robot Control
Gesture Recognition: Hand Pose Estimation Adrian Spurr Ubiquitous Computing Seminar FS2014 27.05.2014 1 What is hand pose estimation? Input Computer-usable form 2 Augmented Reality Gaming Robot Control
Motion Control (wheeled robots)
 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground Definition of required motion -> speed control,
Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground Definition of required motion -> speed control,
Geometric Registration for Deformable Shapes 3.3 Advanced Global Matching
 Geometric Registration for Deformable Shapes 3.3 Advanced Global Matching Correlated Correspondences [ASP*04] A Complete Registration System [HAW*08] In this session Advanced Global Matching Some practical
Geometric Registration for Deformable Shapes 3.3 Advanced Global Matching Correlated Correspondences [ASP*04] A Complete Registration System [HAW*08] In this session Advanced Global Matching Some practical
CS 532: 3D Computer Vision 7 th Set of Notes
 1 CS 532: 3D Computer Vision 7 th Set of Notes Instructor: Philippos Mordohai Webpage: www.cs.stevens.edu/~mordohai E-mail: Philippos.Mordohai@stevens.edu Office: Lieb 215 Logistics No class on October
1 CS 532: 3D Computer Vision 7 th Set of Notes Instructor: Philippos Mordohai Webpage: www.cs.stevens.edu/~mordohai E-mail: Philippos.Mordohai@stevens.edu Office: Lieb 215 Logistics No class on October
