Fast evaluation of nonlinear functions using FPGAs
|
|
|
- Jessie Ferguson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Adv. Radio Sci., 6, , 2008 Author(s) This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Advances in Radio Science Fast evaluation of nonlinear functions using FPGAs S. Lachowicz 1 and H.-J. Pfleiderer 2 1 Edith Cowan University, Perth, WA, Australia 2 Ulm University, Ulm, Germany Abstract. The paper presents a novel method of evaluating the square root function in FPGA. The method uses a linear approximation subsystem with a reduced size of a lookup table. The reduction in the size of the lookup table is twofold. Firstly, a simple linear approximation subsystem uses the lookup table only for the node points. Secondly, a concept of a variable step look-up table is introduced, where the node points are not uniformly spaced, but the spacing is determined by how close to the linear function the approximated function is. The proposed method of evaluating nonlinear function and specifically the square root function is practical for word lengths of up to 24 bits. The evaluation is performed in one clock cycle. 1 Introduction Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGA) are becoming widely used in Digital Signal Processing (DSP) systems. Modern FPGAs exhibit very high performance, very large number of IOs and high capacity memory on the chip. The development is rapid and risks are low since the IP can be easily modified. For the low to medium production volume it is not economical to develop an ASIC and, if needed, there are companies like Altera who offer a convenient solution of migration from FPGA to ASIC. The evolution of FPGAs has enabled to implement more and more sophisticated DSP subsystems in the form of dedicated hardware on the device. In late 1990s FPGAs usually had just a few hardware multipliers per chip. In early 2000s, hardwired multipliers in large numbers (up to 500) with clock speeds of up to 100 MHz became available. Mid 2000s saw the DSP algorithms like full FIR filters implemented, and currently, powerful arithmetic, such as fast square root and divide, floating point operations and many more are being implemented. In DSP systems nonlinear functions, such as trigonometric, square root or Bessel functions are often encountered. Correspondence to: S. Lachowicz (s.lachowicz@ecu.edu.au) There are several solutions to this problem, for instance, using a CORDIC core, or look-up tables. A lot of effort is made to reduce the size of the look-up tables because it can become prohibitive for high word lengths. For some functions an existing approach is to create hierarchical lookup tables. In this work we present a different approach to reducing the look-up table size. It is proposed to introduce a variable step of the look-up table, so that the number of entries is higher for more nonlinear segments of the curve and smaller for the parts closer to a linear function. The step length is always a power of 2, hence, 8, 16, 32, etc. The remainder of the paper is organised as follows. Section 2 presents several methods of computation of nonlinear functions. In Sect. 3 the method of linear approximation is described in more detail. Section 4 deals with the nonuniform step lookup table generation and the associated hardware, and presents the experimental results of square root function implementation. It is followed by conclusions. 2 Nonlinear function computation 2.1 Look-up tables In general the look-up tables are used for single precision (Hassler, 1995; Sarma, 1995; Wong, 1995; Ercegovac, 2000). For longer word lengths the size of the table becomes prohibitively large. Sometimes the look-up tables are used with conjunction of linear approximation system which reduces the size of the table considerably. When used, the look-up table method is the fastest, and if the higher precision is required it is used as an initial approximation for iterative methods. 2.2 CORDIC core COordinate Rotation DIgital Computer (CORDIC) is a very popular IP core used for various computations (Volder, 1959). It is based on the iterative rotation of a vector in Cartesian coordinate system (Givens rotations): ( ) x (2) = cos θ x (1) y (1) tan θ, (1a) Published by Copernicus Publications on behalf of the URSI Landesausschuss in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland e.v.
2 234 S. Lachowicz and H.-J. Pfleiderer: Fast evaluation of nonlinear functions using FPGAs Table 1. CORDIC Functions (after DSPedia) Table 1. CORDIC functions (after DSPedia). Table 2. CORDIC accuracy (after DSPedia). Predicted Simulated n/b Figure 1. Piecewise linear approximation of a nonlinear function. Fig. 1. Piecewise linear approximation of a nonlinear function. y (2) = cos θ ( ) y (1) x (1) tan θ. (1b) CORDIC core is widely offered as an IP by the FPGA vendors such as XILINX. Table 1 summarises the functions which can be computed by CORDIC. As the CORDIC is an iterative method, it requires many clock cycles to achieve the required accuracy. Table 2 presents the accuracy depending on n number of iterations and b the number of bits used in the computations. Also, in terms of used resources the number of slices used by the CORDIC in an FPGA chip is quite considerable. 2.3 Series expansion Series expansion is an attractive option of calculating a nonlinear function (Ercegovac, 2000). Some of the more useful functions are shown below: 1 1 x = 1 + x + x2 + x , (2a) Figure 2. Hardware for linear function approximation with a fixed step of a look-up table. Fig. 2. Hardware for linear function approximation with a fixed step of a look-up table. 8 cos x = x x x6 +..., (2b) x + 1 = x 1 8 x x3... (2c) The method is not iterative, therefore, in principle, the implementation does not have to be pipelined. However, usually the number of required multipliers is high, especially for higher accuracy. Also, preprocessing is generally required to make the argument close to 1. It is worth to be noted that Adv. Radio Sci., 6, ,
3 14 S. Lachowicz and H.-J. Pfleiderer: Fast evaluation of nonlinear functions using FPGAs 235 Figure 3. Node points of the look-up table for the cosine function. Fig. 3. Node points of the look-up table for the cosine function. Figure 4. Approximation error for the cosine function. Fig. 4. Approximation error for the cosine function. many multiplications do not need to be large, i.e for double precision. Rectangular multipliers can be used where appropriate. After some preprocessing most of the multiplications are n/2 n/4, where n is the total number of bits. 2.4 Newton-Raphson iteration Newton-Raphson iteration is a rapid convergence method often used for functions such as 1/x and 1/sqrt(x). The general form is: q n+1 = q n f (q n) f (q n ). (3a) The following formulae are applicable to 1/x and 1/sqrt(x), respectively: q n+1 = q n (2 xq n ), q n+1 = 1 2 q n(3 xq 2 n ). Figure 5. Node points of an 11-bit look-up table for the sqrt function. (3b) Fig. 5. Node points of an 11-bit look-up table for the sqrt function. (3c) The method is characterised by quadratic convergence and the number of significant bits roughly doubles with each iteration. 3 Linear approximation with look-up tables One method of reducing the size of the look-up table is to use a linear approximation circuit. Every function can be approximated by a piecewise linear function as presented in Fig. 1. Between the node points the function can be expressed using the line equation: f (x) = y i + y i+1 y i x i+1 x i (x x i ). (4) The hardware mapping is presented in Fig. 2. Here the steps of the look-up table are evenly distributed, so the input word x is 12split into two parts: the more significant part is an address for the look-up table and the less significant part is the increment of x within the current step of the look-up table. The node values y i and y i+1 are read from the look-up table, the increment y is calculated and is subsequently multiplied by the increment x. The shift replaces the division as the difference x i+1 x i is always constant and equal to the number being a power of two. 4 Minimum size look-up table generation Nonlinear functions usually have a different degree of nonlinearity throughout the range of interest. Therefore, to achieve a particular accuracy while using the linear 13 Adv. Radio Sci., 6, , 2008
4 236 S. Lachowicz and H.-J. Pfleiderer: Fast evaluation of nonlinear functions using FPGAs Figure 6. Hardware for a linear function approximation with a variable step look-up table. Fig. 6. Hardware for a linear function approximation with a variable step look-up table. approximation, the distance between the node points in the look-up table can be varied. Where the function is more linear, the distance between the node points can be increased. In the case of the fixed step table, the step corresponding to the most non-linear part of the function has to be maintained throughout the whole look-up table. Figure 3 presents an example of a look-up table generated for the cosine function, in 11-bit resolution and with the accuracy of ±1 bit. It can be observed that where the function exhibits higher degree of nonlinearity, the step of the look-up table is reduced. The look-up table is generated as follows: 1. Each step in the look-up table must be of the length equal to the power of The predetermined accuracy of the linear approximation within one step range is verified for the initial value (large) of the step. 3. If the accuracy is not met then the step is reduced by half and the verification is repeated If the accuracy criterion is met, the algorithm moves to the next step. Figure 7: The address Fig. 7. The decoder address for decoder the circuit forfrom the circuit Fig. 6. from Fig. 6. exact result. Similar table for a 16-bit accuracy has 262 entries. The full look-up tables would require 1024 and entries respectively. The hardware implementing the variable step look-up table linear approximation differs from the fixed-step as it has to split the input word x into variable length address part and the increment x and the fixed shift is replaced by programmable shift dependent on the step of the look-up table. The hardware is shown in Fig. 6. Figure 7 presents the details of the address decoder in the circuit from Fig. 6. An array of comparators determines the current step of the look-up table and splits the input word x into the address part and the increment part. It also controls the number of positions for the shift. The number of comparators in the array is equal to the number of step changes in the look-up table. 5. The next step can be the same length, shorter or longer, however the longer step can only be made if the remaining part of the range is divisible by the new value of the step length. This ensures that the x value can be split into the look-up table address part and the increment part. As an example of accuracy of the proposed method of a lookup table generation, let us consider a cosine function from Fig. 3. The number of entries in the look-up table is 45. The accuracy of the approximation has been compared with the full look-up table of 2048 entries. The RMS error in respect to the accurate (floating point) curve is 0.35 LSB compared with the RMS error of the full look-up table of 0.28 LSB. Figure 4 shows the actual approximation error throughout the input range. Square root is an important function often encountered in DSP. Figure 5 presents the look-up table for 11-bits resolution with ±1 bit accuracy. The look-up table has 21 entries, and for 10-bits the linear approximation circuit generates an Before the input word is presented to the linear approximation circuit the number has to be normalised. For the square root the input number should be within the range {1... 4} for the output within the range {1... 2}. This operation could be referred to as an internally floating-point operation. As an example of application of the linear approximation circuit with variable step look-up table, a 16-bit square root x 2 +y 2 +z 2 has been implemented in Spartan 3/1000. The resources used are 242 slices (3%), 1 block RAM (4%) and 4 hardware multipliers (16%). Three of the multipliers are used to calculate the squares and one in the linear approximation circuit. The on-chip hardware multipliers are 18 18, and for the linear approximation circuit a 9 9 multiplier would be sufficient. Therefore, if the variable word length multiplier was available (Pfaender, 2007), the resources could be further reduced. The same circuit was also implemented in Virtex 2 FPGA and the operation was verified using ChipScope. The circuit exhibits latency of approximately 11 ns. Adv. Radio Sci., 6, , 2008
5 S. Lachowicz and H.-J. Pfleiderer: Fast evaluation of nonlinear functions using FPGAs Conclusions A novel method of nonlinear function computation in FPGA has been developed. The standard linear approximation circuit has been modified in order to use a look-up table with variable step. This allows to minimise the size of the look-up table and therefore the resources needed for the implementation. The method can be used directly for word lengths up to about 24 bits, and can also be used as an initial value generator for Newton-Raphson iterations if a higher accuracy is required. Acknowledgements. The support of the German Academic Exchange Office (DAAD) and Ulm University is gratefully acknowledged. References Ercegovac, M. D., Lang, T., Muller, J.-M., and Tisserand, A.: Reciprocation, Square Root, Inverse Square Root, and Some Elementary Functions Using Small Multipliers, IEEE Trans. Computers, 49(7), , Hassler, H. and Takagi, N.: Function Evaluation by Table Look-Up and Addition, in: Proc. 12th IEEE Symp. Computer Arithmetic, edited by: Knowles, S. and McAllister, W., 10 16, July Pfaender, O. A., Nopper, R., Pfleiderer, H.-J., Zhou, S., and Bermak, A.: Comparison of reconfigurable structures for flexible word-length multiplication, Adv. Radio Sci., 6, Sarma, D. D. and Matula, D. W.: Faithful Bipartite ROM Reciprocal Tables, in: Proc. 12th IEEE Symp. Computer Arithmetic, edited by: Knowles, S. and McAllister, W., 17 28, July Volder, J.: The cordic trigonometric computing technique, IRE Trans. Electron. Comput., 3, , Wong, W. F. and Goto, E.: Fast Evaluation of the Elementary Functions in Single Precision, IEEE Trans. Computers, 44(3), , March Adv. Radio Sci., 6, , 2008
Fast Evaluation of the Square Root and Other Nonlinear Functions in FPGA
 Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Pre. 20 2008 Fast Evaluation of the Square Root and Other Nonlinear Functions in FPGA Stefan Lachowicz Edith Cowan University Hans-Joerg Pfleiderer
Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Pre. 20 2008 Fast Evaluation of the Square Root and Other Nonlinear Functions in FPGA Stefan Lachowicz Edith Cowan University Hans-Joerg Pfleiderer
Vendor Agnostic, High Performance, Double Precision Floating Point Division for FPGAs
 Vendor Agnostic, High Performance, Double Precision Floating Point Division for FPGAs Xin Fang and Miriam Leeser Dept of Electrical and Computer Eng Northeastern University Boston, Massachusetts 02115
Vendor Agnostic, High Performance, Double Precision Floating Point Division for FPGAs Xin Fang and Miriam Leeser Dept of Electrical and Computer Eng Northeastern University Boston, Massachusetts 02115
High Performance Architecture for Reciprocal Function Evaluation on Virtex II FPGA
 EurAsia-ICT 00, Shiraz-Iran, 9-31 Oct. High Performance Architecture for Reciprocal Function Evaluation on Virtex II FPGA M. Anane, H. Bessalah and N. Anane Centre de Développement des Technologies Avancées
EurAsia-ICT 00, Shiraz-Iran, 9-31 Oct. High Performance Architecture for Reciprocal Function Evaluation on Virtex II FPGA M. Anane, H. Bessalah and N. Anane Centre de Développement des Technologies Avancées
FPGA Design, Implementation and Analysis of Trigonometric Generators using Radix 4 CORDIC Algorithm
 International Journal of Microcircuits and Electronic. ISSN 0974-2204 Volume 4, Number 1 (2013), pp. 1-9 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com FPGA Design, Implementation and
International Journal of Microcircuits and Electronic. ISSN 0974-2204 Volume 4, Number 1 (2013), pp. 1-9 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com FPGA Design, Implementation and
Vendor Agnostic, High Performance, Double Precision Floating Point Division for FPGAs
 Vendor Agnostic, High Performance, Double Precision Floating Point Division for FPGAs Presented by Xin Fang Advisor: Professor Miriam Leeser ECE Department Northeastern University 1 Outline Background
Vendor Agnostic, High Performance, Double Precision Floating Point Division for FPGAs Presented by Xin Fang Advisor: Professor Miriam Leeser ECE Department Northeastern University 1 Outline Background
Implementation of Optimized CORDIC Designs
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 3 August 2014 ISSN(online) : 2349-6010 Implementation of Optimized CORDIC Designs Bibinu Jacob M Tech Student
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 3 August 2014 ISSN(online) : 2349-6010 Implementation of Optimized CORDIC Designs Bibinu Jacob M Tech Student
Efficient Double-Precision Cosine Generation
 Efficient Double-Precision Cosine Generation Derek Nowrouzezahrai Brian Decker William Bishop dnowrouz@uwaterloo.ca bjdecker@uwaterloo.ca wdbishop@uwaterloo.ca Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Efficient Double-Precision Cosine Generation Derek Nowrouzezahrai Brian Decker William Bishop dnowrouz@uwaterloo.ca bjdecker@uwaterloo.ca wdbishop@uwaterloo.ca Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Modified CORDIC Architecture for Fixed Angle Rotation
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology EISSN 2277 4106, PISSN 2347 5161 2015INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Binu M
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology EISSN 2277 4106, PISSN 2347 5161 2015INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Binu M
High Speed Radix 8 CORDIC Processor
 High Speed Radix 8 CORDIC Processor Smt. J.M.Rudagi 1, Dr. Smt. S.S ubbaraman 2 1 Associate Professor, K.L.E CET, Chikodi, karnataka, India. 2 Professor, W C E Sangli, Maharashtra. 1 js_itti@yahoo.co.in
High Speed Radix 8 CORDIC Processor Smt. J.M.Rudagi 1, Dr. Smt. S.S ubbaraman 2 1 Associate Professor, K.L.E CET, Chikodi, karnataka, India. 2 Professor, W C E Sangli, Maharashtra. 1 js_itti@yahoo.co.in
Implementation of CORDIC Algorithms in FPGA
 Summer Project Report Implementation of CORDIC Algorithms in FPGA Sidharth Thomas Suyash Mahar under the guidance of Dr. Bishnu Prasad Das May 2017 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
Summer Project Report Implementation of CORDIC Algorithms in FPGA Sidharth Thomas Suyash Mahar under the guidance of Dr. Bishnu Prasad Das May 2017 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multistage Pipelined Adder Based CORDIC Structure for Large Operand Word Lengths
 International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2012] 105 ISSN 2047-3338 FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multistage Pipelined Adder Based CORDIC Structure for
International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2012] 105 ISSN 2047-3338 FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multistage Pipelined Adder Based CORDIC Structure for
Sine/Cosine using CORDIC Algorithm
 Sine/Cosine using CORDIC Algorithm Prof. Kris Gaj Gaurav Doshi, Hiren Shah Outlines Introduction Basic Idea CORDIC Principles Hardware Implementation FPGA & ASIC Results Conclusion Introduction CORDIC
Sine/Cosine using CORDIC Algorithm Prof. Kris Gaj Gaurav Doshi, Hiren Shah Outlines Introduction Basic Idea CORDIC Principles Hardware Implementation FPGA & ASIC Results Conclusion Introduction CORDIC
High Speed Special Function Unit for Graphics Processing Unit
 High Speed Special Function Unit for Graphics Processing Unit Abd-Elrahman G. Qoutb 1, Abdullah M. El-Gunidy 1, Mohammed F. Tolba 1, and Magdy A. El-Moursy 2 1 Electrical Engineering Department, Fayoum
High Speed Special Function Unit for Graphics Processing Unit Abd-Elrahman G. Qoutb 1, Abdullah M. El-Gunidy 1, Mohammed F. Tolba 1, and Magdy A. El-Moursy 2 1 Electrical Engineering Department, Fayoum
FPGA Implementation of the Complex Division in Digital Predistortion Linearizer
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(10): 5028-5037, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 FPGA Implementation of the Complex Division in Digital Predistortion Linearizer Somayeh Mohammady, Pooria Varahram,
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(10): 5028-5037, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 FPGA Implementation of the Complex Division in Digital Predistortion Linearizer Somayeh Mohammady, Pooria Varahram,
A CORDIC Algorithm with Improved Rotation Strategy for Embedded Applications
 A CORDIC Algorithm with Improved Rotation Strategy for Embedded Applications Kui-Ting Chen Research Center of Information, Production and Systems, Waseda University, Fukuoka, Japan Email: nore@aoni.waseda.jp
A CORDIC Algorithm with Improved Rotation Strategy for Embedded Applications Kui-Ting Chen Research Center of Information, Production and Systems, Waseda University, Fukuoka, Japan Email: nore@aoni.waseda.jp
FPGA Implementation of Discrete Fourier Transform Using CORDIC Algorithm
 AMSE JOURNALS-AMSE IIETA publication-2017-series: Advances B; Vol. 60; N 2; pp 332-337 Submitted Apr. 04, 2017; Revised Sept. 25, 2017; Accepted Sept. 30, 2017 FPGA Implementation of Discrete Fourier Transform
AMSE JOURNALS-AMSE IIETA publication-2017-series: Advances B; Vol. 60; N 2; pp 332-337 Submitted Apr. 04, 2017; Revised Sept. 25, 2017; Accepted Sept. 30, 2017 FPGA Implementation of Discrete Fourier Transform
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF CORDIC ALGORITHM ARCHITECTURE
 FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF CORDIC ALGORITHM ARCHITECTURE Ramanpreet Kaur 1, Parminder Singh Jassal 2 Department of Electronics And Communication Engineering, Punjabi University Yadavindra College of Engineering,
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF CORDIC ALGORITHM ARCHITECTURE Ramanpreet Kaur 1, Parminder Singh Jassal 2 Department of Electronics And Communication Engineering, Punjabi University Yadavindra College of Engineering,
Introduction to Field Programmable Gate Arrays
 Introduction to Field Programmable Gate Arrays Lecture 2/3 CERN Accelerator School on Digital Signal Processing Sigtuna, Sweden, 31 May 9 June 2007 Javier Serrano, CERN AB-CO-HT Outline Digital Signal
Introduction to Field Programmable Gate Arrays Lecture 2/3 CERN Accelerator School on Digital Signal Processing Sigtuna, Sweden, 31 May 9 June 2007 Javier Serrano, CERN AB-CO-HT Outline Digital Signal
Advanced FPGA Design Methodologies with Xilinx Vivado
 Advanced FPGA Design Methodologies with Xilinx Vivado Lecturer: Alexander Jäger Course of studies: Technische Informatik Student number: 3158849 Date: 30.01.2015 30/01/15 Advanced FPGA Design Methodologies
Advanced FPGA Design Methodologies with Xilinx Vivado Lecturer: Alexander Jäger Course of studies: Technische Informatik Student number: 3158849 Date: 30.01.2015 30/01/15 Advanced FPGA Design Methodologies
Performance Analysis of CORDIC Architectures Targeted by FPGA Devices
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Performance Analysis of CORDIC Architectures Targeted by FPGA Devices Guddeti Nagarjuna Reddy 1, R.Jayalakshmi 2, Dr.K.Umapathy
International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Performance Analysis of CORDIC Architectures Targeted by FPGA Devices Guddeti Nagarjuna Reddy 1, R.Jayalakshmi 2, Dr.K.Umapathy
Low Power and Memory Efficient FFT Architecture Using Modified CORDIC Algorithm
 Low Power and Memory Efficient FFT Architecture Using Modified CORDIC Algorithm 1 A.Malashri, 2 C.Paramasivam 1 PG Student, Department of Electronics and Communication K S Rangasamy College Of Technology,
Low Power and Memory Efficient FFT Architecture Using Modified CORDIC Algorithm 1 A.Malashri, 2 C.Paramasivam 1 PG Student, Department of Electronics and Communication K S Rangasamy College Of Technology,
A FLOATING POINT DIVISION UNIT BASED ON TAYLOR-SERIES EXPANSION ALGORITHM AND ITERATIVE LOGARITHMIC MULTIPLIER
 A FLOATING POINT DIVISION UNIT BASED ON TAYLOR-SERIES EXPANSION ALGORITHM AND ITERATIVE LOGARITHMIC MULTIPLIER Riyansh K. Karani, Akash K. Rana, Dhruv H. Reshamwala, Kishore Saldanha Electronics Department,
A FLOATING POINT DIVISION UNIT BASED ON TAYLOR-SERIES EXPANSION ALGORITHM AND ITERATIVE LOGARITHMIC MULTIPLIER Riyansh K. Karani, Akash K. Rana, Dhruv H. Reshamwala, Kishore Saldanha Electronics Department,
Performance Evaluation of a Novel Direct Table Lookup Method and Architecture With Application to 16-bit Integer Functions
 Performance Evaluation of a Novel Direct Table Lookup Method and Architecture With Application to 16-bit nteger Functions L. Li, Alex Fit-Florea, M. A. Thornton, D. W. Matula Southern Methodist University,
Performance Evaluation of a Novel Direct Table Lookup Method and Architecture With Application to 16-bit nteger Functions L. Li, Alex Fit-Florea, M. A. Thornton, D. W. Matula Southern Methodist University,
Signal Processing Algorithms into Fixed Point FPGA Hardware Dennis Silage ECE Temple University
 Signal Processing Algorithms into Fixed Point FPGA Hardware Dennis Silage silage@temple.edu ECE Temple University www.temple.edu/scdl Signal Processing Algorithms into Fixed Point FPGA Hardware Motivation
Signal Processing Algorithms into Fixed Point FPGA Hardware Dennis Silage silage@temple.edu ECE Temple University www.temple.edu/scdl Signal Processing Algorithms into Fixed Point FPGA Hardware Motivation
Model-Based Design for effective HW/SW Co-Design Alexander Schreiber Senior Application Engineer MathWorks, Germany
 Model-Based Design for effective HW/SW Co-Design Alexander Schreiber Senior Application Engineer MathWorks, Germany 2013 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Agenda Model-Based Design of embedded Systems Software Implementation
Model-Based Design for effective HW/SW Co-Design Alexander Schreiber Senior Application Engineer MathWorks, Germany 2013 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 Agenda Model-Based Design of embedded Systems Software Implementation
A Modified CORDIC Processor for Specific Angle Rotation based Applications
 IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 4, Issue 2, Ver. II (Mar-Apr. 2014), PP 29-37 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 A Modified CORDIC Processor for Specific Angle Rotation
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 4, Issue 2, Ver. II (Mar-Apr. 2014), PP 29-37 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 A Modified CORDIC Processor for Specific Angle Rotation
Second Order Function Approximation Using a Single Multiplication on FPGAs
 Second Order Function Approximation Using a Single Multiplication on FPGAs Jérémie Detrey and Florent de Dinechin Laboratoire de l Informatique du Parallélisme École Normale Supérieure de Lyon 46, allée
Second Order Function Approximation Using a Single Multiplication on FPGAs Jérémie Detrey and Florent de Dinechin Laboratoire de l Informatique du Parallélisme École Normale Supérieure de Lyon 46, allée
Pipelined Quadratic Equation based Novel Multiplication Method for Cryptographic Applications
 , Vol 7(4S), 34 39, April 204 ISSN (Print): 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Pipelined Quadratic Equation based Novel Multiplication Method for Cryptographic Applications B. Vignesh *, K. P. Sridhar
, Vol 7(4S), 34 39, April 204 ISSN (Print): 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Pipelined Quadratic Equation based Novel Multiplication Method for Cryptographic Applications B. Vignesh *, K. P. Sridhar
Xilinx Based Simulation of Line detection Using Hough Transform
 Xilinx Based Simulation of Line detection Using Hough Transform Vijaykumar Kawde 1 Assistant Professor, Department of EXTC Engineering, LTCOE, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India 1 ABSTRACT: In auto focusing
Xilinx Based Simulation of Line detection Using Hough Transform Vijaykumar Kawde 1 Assistant Professor, Department of EXTC Engineering, LTCOE, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India 1 ABSTRACT: In auto focusing
Three Dimensional CORDIC with reduced iterations
 Three Dimensional CORDIC with reduced iterations C.T. Clarke and G.R. Nudd Department of Computer Science University of Warwick Coventry CV4 7AL United Kingdom Abstract This paper describes a modification
Three Dimensional CORDIC with reduced iterations C.T. Clarke and G.R. Nudd Department of Computer Science University of Warwick Coventry CV4 7AL United Kingdom Abstract This paper describes a modification
A Single/Double Precision Floating-Point Reciprocal Unit Design for Multimedia Applications
 A Single/Double Precision Floating-Point Reciprocal Unit Design for Multimedia Applications Metin Mete Özbilen 1 and Mustafa Gök 2 1 Mersin University, Engineering Faculty, Department of Computer Science,
A Single/Double Precision Floating-Point Reciprocal Unit Design for Multimedia Applications Metin Mete Özbilen 1 and Mustafa Gök 2 1 Mersin University, Engineering Faculty, Department of Computer Science,
Agenda. Introduction FPGA DSP platforms Design challenges New programming models for FPGAs
 New Directions in Programming FPGAs for DSP Dr. Jim Hwang Xilinx, Inc. Agenda Introduction FPGA DSP platforms Design challenges New programming models for FPGAs System Generator Getting your math into
New Directions in Programming FPGAs for DSP Dr. Jim Hwang Xilinx, Inc. Agenda Introduction FPGA DSP platforms Design challenges New programming models for FPGAs System Generator Getting your math into
FPGA Implementation of the CORDIC Algorithm for Fingerprints Recognition Systems
 FPGA Implementation of the CORDIC Algorithm for Fingerprints Recognition Systems Nihel Neji, Anis Boudabous, Wajdi Kharrat, Nouri Masmoudi University of Sfax, Electronics and Information Technology Laboratory,
FPGA Implementation of the CORDIC Algorithm for Fingerprints Recognition Systems Nihel Neji, Anis Boudabous, Wajdi Kharrat, Nouri Masmoudi University of Sfax, Electronics and Information Technology Laboratory,
Realization of Hardware Architectures for Householder Transformation based QR Decomposition using Xilinx System Generator Block Sets
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 2 Issue 08 February 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Realization of Hardware Architectures for Householder Transformation based QR
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 2 Issue 08 February 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Realization of Hardware Architectures for Householder Transformation based QR
Chapter 5: ASICs Vs. PLDs
 Chapter 5: ASICs Vs. PLDs 5.1 Introduction A general definition of the term Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) is virtually every type of chip that is designed to perform a dedicated task.
Chapter 5: ASICs Vs. PLDs 5.1 Introduction A general definition of the term Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) is virtually every type of chip that is designed to perform a dedicated task.
NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Graduate School of Engineering. Approved for Thesis Requirements of the Master of Science Degree
 NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Graduate School of Engineering Thesis Title: Variable Precision Floating Point Reciprocal, Division and Square Root for Major FPGA vendors Author: Xin Fang Department: Electrical
NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Graduate School of Engineering Thesis Title: Variable Precision Floating Point Reciprocal, Division and Square Root for Major FPGA vendors Author: Xin Fang Department: Electrical
Baseline V IRAM Trimedia. Cycles ( x 1000 ) N
 CS 252 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE MAY 2000 An Investigation of the QR Decomposition Algorithm on Parallel Architectures Vito Dai and Brian Limketkai Abstract This paper presents an implementation of a QR decomposition
CS 252 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE MAY 2000 An Investigation of the QR Decomposition Algorithm on Parallel Architectures Vito Dai and Brian Limketkai Abstract This paper presents an implementation of a QR decomposition
Linköping University Post Print. Analysis of Twiddle Factor Memory Complexity of Radix-2^i Pipelined FFTs
 Linköping University Post Print Analysis of Twiddle Factor Complexity of Radix-2^i Pipelined FFTs Fahad Qureshi and Oscar Gustafsson N.B.: When citing this work, cite the original article. 200 IEEE. Personal
Linköping University Post Print Analysis of Twiddle Factor Complexity of Radix-2^i Pipelined FFTs Fahad Qureshi and Oscar Gustafsson N.B.: When citing this work, cite the original article. 200 IEEE. Personal
Compact Clock Skew Scheme for FPGA based Wave- Pipelined Circuits
 International Journal of Communication Engineering and Technology. ISSN 2277-3150 Volume 3, Number 1 (2013), pp. 13-22 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Compact Clock Skew Scheme
International Journal of Communication Engineering and Technology. ISSN 2277-3150 Volume 3, Number 1 (2013), pp. 13-22 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Compact Clock Skew Scheme
An FPGA Implementation of the Powering Function with Single Precision Floating-Point Arithmetic
 An FPGA Implementation of the Powering Function with Single Precision Floating-Point Arithmetic Pedro Echeverría, Marisa López-Vallejo Department of Electronic Engineering, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid
An FPGA Implementation of the Powering Function with Single Precision Floating-Point Arithmetic Pedro Echeverría, Marisa López-Vallejo Department of Electronic Engineering, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid
Binary Adders. Ripple-Carry Adder
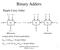 Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
INTRODUCTION TO FPGA ARCHITECTURE
 3/3/25 INTRODUCTION TO FPGA ARCHITECTURE DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN (BASIC TECHNIQUES) a b a y 2input Black Box y b Functional Schematic a b y a b y a b y 2 Truth Table (AND) Truth Table (OR) Truth Table (XOR)
3/3/25 INTRODUCTION TO FPGA ARCHITECTURE DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN (BASIC TECHNIQUES) a b a y 2input Black Box y b Functional Schematic a b y a b y a b y 2 Truth Table (AND) Truth Table (OR) Truth Table (XOR)
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF FLOATING POINT ADDER AND MULTIPLIER UNDER ROUND TO NEAREST
 FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF FLOATING POINT ADDER AND MULTIPLIER UNDER ROUND TO NEAREST SAKTHIVEL Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, Coimbatore Institute of Engineering and Technology Abstract- FPGA is
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF FLOATING POINT ADDER AND MULTIPLIER UNDER ROUND TO NEAREST SAKTHIVEL Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, Coimbatore Institute of Engineering and Technology Abstract- FPGA is
FPGA Implementation of Matrix Inversion Using QRD-RLS Algorithm
 FPGA Implementation of Matrix Inversion Using QRD-RLS Algorithm Marjan Karkooti, Joseph R. Cavallaro Center for imedia Communication, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering MS-366, Rice University,
FPGA Implementation of Matrix Inversion Using QRD-RLS Algorithm Marjan Karkooti, Joseph R. Cavallaro Center for imedia Communication, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering MS-366, Rice University,
Bipartite Modular Multiplication
 Bipartite Modular Multiplication Marcelo E. Kaihara and Naofumi Takagi Department of Information Engineering, Nagoya University, Nagoya, 464-8603, Japan {mkaihara, ntakagi}@takagi.nuie.nagoya-u.ac.jp Abstract.
Bipartite Modular Multiplication Marcelo E. Kaihara and Naofumi Takagi Department of Information Engineering, Nagoya University, Nagoya, 464-8603, Japan {mkaihara, ntakagi}@takagi.nuie.nagoya-u.ac.jp Abstract.
Digital Integrated Circuits
 Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 9 Jaeyong Chung Robust Systems Laboratory Incheon National University DIGITAL DESIGN FLOW Chung EPC6055 2 FPGA vs. ASIC FPGA (A programmable Logic Device) Faster time-to-market
Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 9 Jaeyong Chung Robust Systems Laboratory Incheon National University DIGITAL DESIGN FLOW Chung EPC6055 2 FPGA vs. ASIC FPGA (A programmable Logic Device) Faster time-to-market
FPGA architecture and design technology
 CE 435 Embedded Systems Spring 2017 FPGA architecture and design technology Nikos Bellas Computer and Communications Engineering Department University of Thessaly 1 FPGA fabric A generic island-style FPGA
CE 435 Embedded Systems Spring 2017 FPGA architecture and design technology Nikos Bellas Computer and Communications Engineering Department University of Thessaly 1 FPGA fabric A generic island-style FPGA
EFFICIENT RECURSIVE IMPLEMENTATION OF A QUADRATIC PERMUTATION POLYNOMIAL INTERLEAVER FOR LONG TERM EVOLUTION SYSTEMS
 Rev. Roum. Sci. Techn. Électrotechn. et Énerg. Vol. 61, 1, pp. 53 57, Bucarest, 016 Électronique et transmission de l information EFFICIENT RECURSIVE IMPLEMENTATION OF A QUADRATIC PERMUTATION POLYNOMIAL
Rev. Roum. Sci. Techn. Électrotechn. et Énerg. Vol. 61, 1, pp. 53 57, Bucarest, 016 Électronique et transmission de l information EFFICIENT RECURSIVE IMPLEMENTATION OF A QUADRATIC PERMUTATION POLYNOMIAL
Computations Of Elementary Functions Based On Table Lookup And Interpolation
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Computations Of Elementary Functions Based On Table Lookup And Interpolation Syed Aliasgar 1, Dr.V.Thrimurthulu 2, G Dillirani 3 1 Assistant Professor, Dept.of ECE, CREC, Tirupathi,
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Computations Of Elementary Functions Based On Table Lookup And Interpolation Syed Aliasgar 1, Dr.V.Thrimurthulu 2, G Dillirani 3 1 Assistant Professor, Dept.of ECE, CREC, Tirupathi,
FPGAs: FAST TRACK TO DSP
 FPGAs: FAST TRACK TO DSP Revised February 2009 ABSRACT: Given the prevalence of digital signal processing in a variety of industry segments, several implementation solutions are available depending on
FPGAs: FAST TRACK TO DSP Revised February 2009 ABSRACT: Given the prevalence of digital signal processing in a variety of industry segments, several implementation solutions are available depending on
Construction of digital integer arithmetic
 Construction of digital integer arithmetic FPGA implementation of high throughput pipelined division circuit Johan Arthur Øvergaard Master of Science in Electronics Submission date: June 2009 Supervisor:
Construction of digital integer arithmetic FPGA implementation of high throughput pipelined division circuit Johan Arthur Øvergaard Master of Science in Electronics Submission date: June 2009 Supervisor:
THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLEDGE
 THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLEDGE Design and Implementation of Optimized Floating Point Matrix Multiplier Based on FPGA Maruti L. Doddamani IV Semester, M.Tech (Digital Electronics), Department
THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLEDGE Design and Implementation of Optimized Floating Point Matrix Multiplier Based on FPGA Maruti L. Doddamani IV Semester, M.Tech (Digital Electronics), Department
High Level Abstractions for Implementation of Software Radios
 High Level Abstractions for Implementation of Software Radios J. B. Evans, Ed Komp, S. G. Mathen, and G. Minden Information and Telecommunication Technology Center University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS 66044-7541
High Level Abstractions for Implementation of Software Radios J. B. Evans, Ed Komp, S. G. Mathen, and G. Minden Information and Telecommunication Technology Center University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS 66044-7541
ECEn 621 Computer Arithmetic Project #3. CORDIC History
 ECEn 621 Computer Arithmetic Project #3 CORDIC Algorithms Slide #1 CORDIC History Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer Invented in late 1950 s Based on the observation that: if you rotate a unit-length
ECEn 621 Computer Arithmetic Project #3 CORDIC Algorithms Slide #1 CORDIC History Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer Invented in late 1950 s Based on the observation that: if you rotate a unit-length
Implementation of Area Efficient Multiplexer Based Cordic
 Implementation of Area Efficient Multiplexer Based Cordic M. Madhava Rao 1, G. Suresh 2 1 M.Tech student M.L.E College, S. Konda, Prakasam (DIST), India 2 Assoc.prof in ECE Department, M.L.E College, S.
Implementation of Area Efficient Multiplexer Based Cordic M. Madhava Rao 1, G. Suresh 2 1 M.Tech student M.L.E College, S. Konda, Prakasam (DIST), India 2 Assoc.prof in ECE Department, M.L.E College, S.
Fixed Point LMS Adaptive Filter with Low Adaptation Delay
 Fixed Point LMS Adaptive Filter with Low Adaptation Delay INGUDAM CHITRASEN MEITEI Electronics and Communication Engineering Vel Tech Multitech Dr RR Dr SR Engg. College Chennai, India MR. P. BALAVENKATESHWARLU
Fixed Point LMS Adaptive Filter with Low Adaptation Delay INGUDAM CHITRASEN MEITEI Electronics and Communication Engineering Vel Tech Multitech Dr RR Dr SR Engg. College Chennai, India MR. P. BALAVENKATESHWARLU
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN. 5 th Edition. The Hardware/Software Interface. Chapter 3. Arithmetic for Computers Implementation
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers Implementation Today Review representations (252/352 recap) Floating point Addition: Ripple
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 3 Arithmetic for Computers Implementation Today Review representations (252/352 recap) Floating point Addition: Ripple
An Efficient Hardwired Realization of Embedded Neural Controller on System-On-Programmable-Chip (SOPC)
 An Efficient Hardwired Realization of Embedded Neural Controller on System-On-Programmable-Chip (SOPC) Karan Goel, Uday Arun, A. K. Sinha ABES Engineering College, Department of Computer Science & Engineering,
An Efficient Hardwired Realization of Embedded Neural Controller on System-On-Programmable-Chip (SOPC) Karan Goel, Uday Arun, A. K. Sinha ABES Engineering College, Department of Computer Science & Engineering,
High-Performance Linear Algebra Processor using FPGA
 High-Performance Linear Algebra Processor using FPGA J. R. Johnson P. Nagvajara C. Nwankpa 1 Extended Abstract With recent advances in FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) technology it is now feasible
High-Performance Linear Algebra Processor using FPGA J. R. Johnson P. Nagvajara C. Nwankpa 1 Extended Abstract With recent advances in FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) technology it is now feasible
Parallel FIR Filters. Chapter 5
 Chapter 5 Parallel FIR Filters This chapter describes the implementation of high-performance, parallel, full-precision FIR filters using the DSP48 slice in a Virtex-4 device. ecause the Virtex-4 architecture
Chapter 5 Parallel FIR Filters This chapter describes the implementation of high-performance, parallel, full-precision FIR filters using the DSP48 slice in a Virtex-4 device. ecause the Virtex-4 architecture
Method We follow- How to Get Entry Pass in SEMICODUCTOR Industries for 3rd year engineering. Winter/Summer Training
 Method We follow- How to Get Entry Pass in SEMICODUCTOR Industries for 3rd year engineering Winter/Summer Training Level 2 continues. 3 rd Year 4 th Year FIG-3 Level 1 (Basic & Mandatory) & Level 1.1 and
Method We follow- How to Get Entry Pass in SEMICODUCTOR Industries for 3rd year engineering Winter/Summer Training Level 2 continues. 3 rd Year 4 th Year FIG-3 Level 1 (Basic & Mandatory) & Level 1.1 and
Towards a Dynamically Reconfigurable System-on-Chip Platform for Video Signal Processing
 Towards a Dynamically Reconfigurable System-on-Chip Platform for Video Signal Processing Walter Stechele, Stephan Herrmann, Andreas Herkersdorf Technische Universität München 80290 München Germany Walter.Stechele@ei.tum.de
Towards a Dynamically Reconfigurable System-on-Chip Platform for Video Signal Processing Walter Stechele, Stephan Herrmann, Andreas Herkersdorf Technische Universität München 80290 München Germany Walter.Stechele@ei.tum.de
A fast and area-efficient FPGA-based architecture for high accuracy logarithm approximation
 A ast and area-eicient FPGA-based architecture or high accuracy logarithm approximation Dimitris Bariamis, Dimitris Maroulis, Dimitris K. Iakovidis Department o Inormatics and Telecommunications University
A ast and area-eicient FPGA-based architecture or high accuracy logarithm approximation Dimitris Bariamis, Dimitris Maroulis, Dimitris K. Iakovidis Department o Inormatics and Telecommunications University
ENERGY-EFFICIENT VLSI REALIZATION OF BINARY64 DIVISION WITH REDUNDANT NUMBER SYSTEMS 1 AVANIGADDA. NAGA SANDHYA RANI
 ENERGY-EFFICIENT VLSI REALIZATION OF BINARY64 DIVISION WITH REDUNDANT NUMBER SYSTEMS 1 AVANIGADDA. NAGA SANDHYA RANI 2 BALA KRISHNA.KONDA M.Tech, Assistant Professor 1,2 Eluru College Of Engineering And
ENERGY-EFFICIENT VLSI REALIZATION OF BINARY64 DIVISION WITH REDUNDANT NUMBER SYSTEMS 1 AVANIGADDA. NAGA SANDHYA RANI 2 BALA KRISHNA.KONDA M.Tech, Assistant Professor 1,2 Eluru College Of Engineering And
FPGA Based FIR Filter using Parallel Pipelined Structure
 FPGA Based FIR Filter using Parallel Pipelined Structure Rajesh Mehra, SBL Sachan Electronics & Communication Engineering Department National Institute of Technical Teachers Training & Research Chandigarh,
FPGA Based FIR Filter using Parallel Pipelined Structure Rajesh Mehra, SBL Sachan Electronics & Communication Engineering Department National Institute of Technical Teachers Training & Research Chandigarh,
Power and Area Optimization for Pipelined CORDIC Processor
 Power and Area Optimization for Pipelined CORDIC Processor Architecture in VLSI G.Sandhya**, Syed Inthiyaz*, Dr. Fazal Noor Basha*** ** (M.Tech VLSI student, Department of ECE, KL University, and Vijayawada)
Power and Area Optimization for Pipelined CORDIC Processor Architecture in VLSI G.Sandhya**, Syed Inthiyaz*, Dr. Fazal Noor Basha*** ** (M.Tech VLSI student, Department of ECE, KL University, and Vijayawada)
Efficient computation of source magnetic scalar potential
 Adv. Radio Sci., 4, 59 63, 2006 Author(s) 2006. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Advances in Radio Science Efficient computation of source magnetic scalar potential W. Hafla, A.
Adv. Radio Sci., 4, 59 63, 2006 Author(s) 2006. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Advances in Radio Science Efficient computation of source magnetic scalar potential W. Hafla, A.
COPY RIGHT. To Secure Your Paper As Per UGC Guidelines We Are Providing A Electronic Bar Code
 COPY RIGHT 2018IJIEMR.Personal use of this material is permitted. Permission from IJIEMR must be obtained for all other uses, in any current or future media, including reprinting/republishing this material
COPY RIGHT 2018IJIEMR.Personal use of this material is permitted. Permission from IJIEMR must be obtained for all other uses, in any current or future media, including reprinting/republishing this material
Copyright 2007 Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE (Proc. SPIE Vol.
 Copyright 2007 Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE (Proc. SPIE Vol. 6937, 69370N, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/12.784572 ) and is made
Copyright 2007 Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE (Proc. SPIE Vol. 6937, 69370N, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/12.784572 ) and is made
COPROCESSOR APPROACH TO ACCELERATING MULTIMEDIA APPLICATION [CLAUDIO BRUNELLI, JARI NURMI ] Processor Design
![COPROCESSOR APPROACH TO ACCELERATING MULTIMEDIA APPLICATION [CLAUDIO BRUNELLI, JARI NURMI ] Processor Design COPROCESSOR APPROACH TO ACCELERATING MULTIMEDIA APPLICATION [CLAUDIO BRUNELLI, JARI NURMI ] Processor Design](/thumbs/80/81947289.jpg) COPROCESSOR APPROACH TO ACCELERATING MULTIMEDIA APPLICATION [CLAUDIO BRUNELLI, JARI NURMI ] Processor Design Lecture Objectives Background Need for Accelerator Accelerators and different type of parallelizm
COPROCESSOR APPROACH TO ACCELERATING MULTIMEDIA APPLICATION [CLAUDIO BRUNELLI, JARI NURMI ] Processor Design Lecture Objectives Background Need for Accelerator Accelerators and different type of parallelizm
Implementation Of Quadratic Rotation Decomposition Based Recursive Least Squares Algorithm
 157 Implementation Of Quadratic Rotation Decomposition Based Recursive Least Squares Algorithm Manpreet Singh 1, Sandeep Singh Gill 2 1 University College of Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala-India
157 Implementation Of Quadratic Rotation Decomposition Based Recursive Least Squares Algorithm Manpreet Singh 1, Sandeep Singh Gill 2 1 University College of Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala-India
A SIMULINK-TO-FPGA MULTI-RATE HIERARCHICAL FIR FILTER DESIGN
 A SIMULINK-TO-FPGA MULTI-RATE HIERARCHICAL FIR FILTER DESIGN Xiaoying Li 1 Fuming Sun 2 Enhua Wu 1, 3 1 University of Macau, Macao, China 2 University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China
A SIMULINK-TO-FPGA MULTI-RATE HIERARCHICAL FIR FILTER DESIGN Xiaoying Li 1 Fuming Sun 2 Enhua Wu 1, 3 1 University of Macau, Macao, China 2 University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China
Carry-Free Radix-2 Subtractive Division Algorithm and Implementation of the Divider
 Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 3, No., pp. 29-255 (2000) 29 Carry-Free Radix-2 Subtractive Division Algorithm and Implementation of the Divider Jen-Shiun Chiang, Hung-Da Chung and Min-Show
Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 3, No., pp. 29-255 (2000) 29 Carry-Free Radix-2 Subtractive Division Algorithm and Implementation of the Divider Jen-Shiun Chiang, Hung-Da Chung and Min-Show
The DSP Primer 8. FPGA Technology. DSPprimer Home. DSPprimer Notes. August 2005, University of Strathclyde, Scotland, UK
 The DSP Primer 8 FPGA Technology Return DSPprimer Home Return DSPprimer Notes August 2005, University of Strathclyde, Scotland, UK For Academic Use Only THIS SLIDE IS BLANK August 2005, For Academic Use
The DSP Primer 8 FPGA Technology Return DSPprimer Home Return DSPprimer Notes August 2005, University of Strathclyde, Scotland, UK For Academic Use Only THIS SLIDE IS BLANK August 2005, For Academic Use
VHDL Implementation of DIT-FFT using CORDIC
 Available online www.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 2015, 2(6): 98-102 Research Article ISSN: 2394-658X VHDL Implementation of DIT-FFT using CORDIC M Paavani 1, A
Available online www.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 2015, 2(6): 98-102 Research Article ISSN: 2394-658X VHDL Implementation of DIT-FFT using CORDIC M Paavani 1, A
Hardware efficient architecture for compressed imaging
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.11, No.14, 1 12 Hardware efficient architecture for compressed imaging Jun Luo, Qijun Huang a), Sheng Chang, and Hao Wang Department of Electronic Science and Technology,
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.11, No.14, 1 12 Hardware efficient architecture for compressed imaging Jun Luo, Qijun Huang a), Sheng Chang, and Hao Wang Department of Electronic Science and Technology,
An Efficient Carry Select Adder with Less Delay and Reduced Area Application
 An Efficient Carry Select Adder with Less Delay and Reduced Area Application Pandu Ranga Rao #1 Priyanka Halle #2 # Associate Professor Department of ECE Sreyas Institute of Engineering and Technology,
An Efficient Carry Select Adder with Less Delay and Reduced Area Application Pandu Ranga Rao #1 Priyanka Halle #2 # Associate Professor Department of ECE Sreyas Institute of Engineering and Technology,
Honors Precalculus: Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically. Page 1
 Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically 1. Plot points on the Cartesian coordinate plane. P.1 2. Represent data graphically using scatter plots, bar graphs, & line graphs. P.1
Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically 1. Plot points on the Cartesian coordinate plane. P.1 2. Represent data graphically using scatter plots, bar graphs, & line graphs. P.1
Synthesis of VHDL Code for FPGA Design Flow Using Xilinx PlanAhead Tool
 Synthesis of VHDL Code for FPGA Design Flow Using Xilinx PlanAhead Tool Md. Abdul Latif Sarker, Moon Ho Lee Division of Electronics & Information Engineering Chonbuk National University 664-14 1GA Dekjin-Dong
Synthesis of VHDL Code for FPGA Design Flow Using Xilinx PlanAhead Tool Md. Abdul Latif Sarker, Moon Ho Lee Division of Electronics & Information Engineering Chonbuk National University 664-14 1GA Dekjin-Dong
OPTIMIZATION OF AREA COMPLEXITY AND DELAY USING PRE-ENCODED NR4SD MULTIPLIER.
 OPTIMIZATION OF AREA COMPLEXITY AND DELAY USING PRE-ENCODED NR4SD MULTIPLIER. A.Anusha 1 R.Basavaraju 2 anusha201093@gmail.com 1 basava430@gmail.com 2 1 PG Scholar, VLSI, Bharath Institute of Engineering
OPTIMIZATION OF AREA COMPLEXITY AND DELAY USING PRE-ENCODED NR4SD MULTIPLIER. A.Anusha 1 R.Basavaraju 2 anusha201093@gmail.com 1 basava430@gmail.com 2 1 PG Scholar, VLSI, Bharath Institute of Engineering
VLSI Design Of a Novel Pre Encoding Multiplier Using DADDA Multiplier. Guntur(Dt),Pin:522017
 VLSI Design Of a Novel Pre Encoding Multiplier Using DADDA Multiplier 1 Katakam Hemalatha,(M.Tech),Email Id: hema.spark2011@gmail.com 2 Kundurthi Ravi Kumar, M.Tech,Email Id: kundurthi.ravikumar@gmail.com
VLSI Design Of a Novel Pre Encoding Multiplier Using DADDA Multiplier 1 Katakam Hemalatha,(M.Tech),Email Id: hema.spark2011@gmail.com 2 Kundurthi Ravi Kumar, M.Tech,Email Id: kundurthi.ravikumar@gmail.com
IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ADAPTIVE FIR FILTER USING HIGH SPEED DISTRIBUTED ARITHMETIC
 IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ADAPTIVE FIR FILTER USING HIGH SPEED DISTRIBUTED ARITHMETIC Thangamonikha.A 1, Dr.V.R.Balaji 2 1 PG Scholar, Department OF ECE, 2 Assitant Professor, Department of ECE 1, 2 Sri Krishna
IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ADAPTIVE FIR FILTER USING HIGH SPEED DISTRIBUTED ARITHMETIC Thangamonikha.A 1, Dr.V.R.Balaji 2 1 PG Scholar, Department OF ECE, 2 Assitant Professor, Department of ECE 1, 2 Sri Krishna
DIGITAL IMPLEMENTATION OF THE SIGMOID FUNCTION FOR FPGA CIRCUITS
 DIGITAL IMPLEMENTATION OF THE SIGMOID FUNCTION FOR FPGA CIRCUITS Alin TISAN, Stefan ONIGA, Daniel MIC, Attila BUCHMAN Electronic and Computer Department, North University of Baia Mare, Baia Mare, Romania
DIGITAL IMPLEMENTATION OF THE SIGMOID FUNCTION FOR FPGA CIRCUITS Alin TISAN, Stefan ONIGA, Daniel MIC, Attila BUCHMAN Electronic and Computer Department, North University of Baia Mare, Baia Mare, Romania
Advanced FPGA Design Methodologies with Xilinx Vivado
 Advanced FPGA Design Methodologies with Xilinx Vivado Alexander Jäger Computer Architecture Group Heidelberg University, Germany Abstract With shrinking feature sizes in the ASIC manufacturing technology,
Advanced FPGA Design Methodologies with Xilinx Vivado Alexander Jäger Computer Architecture Group Heidelberg University, Germany Abstract With shrinking feature sizes in the ASIC manufacturing technology,
Novel design of multiplier-less FFT processors
 Signal Processing 8 (00) 140 140 www.elsevier.com/locate/sigpro Novel design of multiplier-less FFT processors Yuan Zhou, J.M. Noras, S.J. Shepherd School of EDT, University of Bradford, Bradford, West
Signal Processing 8 (00) 140 140 www.elsevier.com/locate/sigpro Novel design of multiplier-less FFT processors Yuan Zhou, J.M. Noras, S.J. Shepherd School of EDT, University of Bradford, Bradford, West
System Verification of Hardware Optimization Based on Edge Detection
 Circuits and Systems, 2013, 4, 293-298 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/cs.2013.43040 Published Online July 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs) System Verification of Hardware Optimization Based on Edge Detection
Circuits and Systems, 2013, 4, 293-298 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/cs.2013.43040 Published Online July 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs) System Verification of Hardware Optimization Based on Edge Detection
A Ripple Carry Adder based Low Power Architecture of LMS Adaptive Filter
 A Ripple Carry Adder based Low Power Architecture of LMS Adaptive Filter A.S. Sneka Priyaa PG Scholar Government College of Technology Coimbatore ABSTRACT The Least Mean Square Adaptive Filter is frequently
A Ripple Carry Adder based Low Power Architecture of LMS Adaptive Filter A.S. Sneka Priyaa PG Scholar Government College of Technology Coimbatore ABSTRACT The Least Mean Square Adaptive Filter is frequently
Series Expansion based Efficient Architectures for Double Precision Floating Point Division
 DOI 0.007/s00034-04-98-8 Series Expansion based Efficient Architectures for Double Precision Floating Point Division Manish Kumar Jaiswal Ray C.C. Cheung M. Balakrishnan Kolin Paul Received: 28 October
DOI 0.007/s00034-04-98-8 Series Expansion based Efficient Architectures for Double Precision Floating Point Division Manish Kumar Jaiswal Ray C.C. Cheung M. Balakrishnan Kolin Paul Received: 28 October
REVIEW OF CORDIC ARCHITECTURES
 REVIEW OF CORDIC ARCHITECTURES T.SUBHA SRI #1, K.SESHU KUMAR #2, R. MUTTAIAH #3 School of Computing, M.Tech VLSI design, SASTRA University Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, 613401, India luckysanju8@gmail.com #1
REVIEW OF CORDIC ARCHITECTURES T.SUBHA SRI #1, K.SESHU KUMAR #2, R. MUTTAIAH #3 School of Computing, M.Tech VLSI design, SASTRA University Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, 613401, India luckysanju8@gmail.com #1
Parallelized Radix-4 Scalable Montgomery Multipliers
 Parallelized Radix-4 Scalable Montgomery Multipliers Nathaniel Pinckney and David Money Harris 1 1 Harvey Mudd College, 301 Platt. Blvd., Claremont, CA, USA e-mail: npinckney@hmc.edu ABSTRACT This paper
Parallelized Radix-4 Scalable Montgomery Multipliers Nathaniel Pinckney and David Money Harris 1 1 Harvey Mudd College, 301 Platt. Blvd., Claremont, CA, USA e-mail: npinckney@hmc.edu ABSTRACT This paper
A Parametric Error Analysis of Goldschmidt s Division Algorithm
 A Parametric Error Analysis of Goldschmidt s Division Algorithm - EXTENDED ABSTRACT - Guy Even Dept of Electrical Engineering Systems Tel-Aviv University Tel-Aviv 678 Israel guy@engtauacil Warren E Ferguson
A Parametric Error Analysis of Goldschmidt s Division Algorithm - EXTENDED ABSTRACT - Guy Even Dept of Electrical Engineering Systems Tel-Aviv University Tel-Aviv 678 Israel guy@engtauacil Warren E Ferguson
TSEA44 - Design for FPGAs
 2015-11-24 Now for something else... Adapting designs to FPGAs Why? Clock frequency Area Power Target FPGA architecture: Xilinx FPGAs with 4 input LUTs (such as Virtex-II) Determining the maximum frequency
2015-11-24 Now for something else... Adapting designs to FPGAs Why? Clock frequency Area Power Target FPGA architecture: Xilinx FPGAs with 4 input LUTs (such as Virtex-II) Determining the maximum frequency
PROJECT REPORT IMPLEMENTATION OF LOGARITHM COMPUTATION DEVICE AS PART OF VLSI TOOLS COURSE
 PROJECT REPORT ON IMPLEMENTATION OF LOGARITHM COMPUTATION DEVICE AS PART OF VLSI TOOLS COURSE Project Guide Prof Ravindra Jayanti By Mukund UG3 (ECE) 200630022 Introduction The project was implemented
PROJECT REPORT ON IMPLEMENTATION OF LOGARITHM COMPUTATION DEVICE AS PART OF VLSI TOOLS COURSE Project Guide Prof Ravindra Jayanti By Mukund UG3 (ECE) 200630022 Introduction The project was implemented
The Xilinx XC6200 chip, the software tools and the board development tools
 The Xilinx XC6200 chip, the software tools and the board development tools What is an FPGA? Field Programmable Gate Array Fully programmable alternative to a customized chip Used to implement functions
The Xilinx XC6200 chip, the software tools and the board development tools What is an FPGA? Field Programmable Gate Array Fully programmable alternative to a customized chip Used to implement functions
Design of a Multiplier Architecture Based on LUT and VHBCSE Algorithm For FIR Filter
 African Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences 9 (1): 53-58, 2017 ISSN 2079-2034 IDOSI Publications, 2017 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ajbas.2017.53.58 Design of a Multiplier Architecture Based on LUT and VHBCSE Algorithm
African Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences 9 (1): 53-58, 2017 ISSN 2079-2034 IDOSI Publications, 2017 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ajbas.2017.53.58 Design of a Multiplier Architecture Based on LUT and VHBCSE Algorithm
AT Arithmetic. Integer addition
 AT Arithmetic Most concern has gone into creating fast implementation of (especially) FP Arith. Under the AT (area-time) rule, area is (almost) as important. So it s important to know the latency, bandwidth
AT Arithmetic Most concern has gone into creating fast implementation of (especially) FP Arith. Under the AT (area-time) rule, area is (almost) as important. So it s important to know the latency, bandwidth
YEAR 12 Core 1 & 2 Maths Curriculum (A Level Year 1)
 YEAR 12 Core 1 & 2 Maths Curriculum (A Level Year 1) Algebra and Functions Quadratic Functions Equations & Inequalities Binomial Expansion Sketching Curves Coordinate Geometry Radian Measures Sine and
YEAR 12 Core 1 & 2 Maths Curriculum (A Level Year 1) Algebra and Functions Quadratic Functions Equations & Inequalities Binomial Expansion Sketching Curves Coordinate Geometry Radian Measures Sine and
Lecture 7: Introduction to Co-synthesis Algorithms
 Design & Co-design of Embedded Systems Lecture 7: Introduction to Co-synthesis Algorithms Sharif University of Technology Computer Engineering Dept. Winter-Spring 2008 Mehdi Modarressi Topics for today
Design & Co-design of Embedded Systems Lecture 7: Introduction to Co-synthesis Algorithms Sharif University of Technology Computer Engineering Dept. Winter-Spring 2008 Mehdi Modarressi Topics for today
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering. Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666
 UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666 Part 8 Division through Multiplication Israel Koren ECE666/Koren Part.8.1 Division by Convergence
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Digital Computer Arithmetic ECE 666 Part 8 Division through Multiplication Israel Koren ECE666/Koren Part.8.1 Division by Convergence
Computing the Discrete Fourier Transform on FPGA Based Systolic Arrays
 Computing the Discrete Fourier Transform on FPGA Based Systolic Arrays Chris Dick School of Electronic Engineering La Trobe University Melbourne 3083, Australia Abstract Reconfigurable logic arrays allow
Computing the Discrete Fourier Transform on FPGA Based Systolic Arrays Chris Dick School of Electronic Engineering La Trobe University Melbourne 3083, Australia Abstract Reconfigurable logic arrays allow
