Outline. 14. Query, Measurement, and Transformation. Spatial analysis. Definitions. The Snow map. What is spatial analysis?
|
|
|
- Heather Edwards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Outline 14. Query, Measurement, and Transformation What is spatial analysis? Transformations Geographic Information Systems and Science SECOND EDITION Paul A. Longley, Michael F. Goodchild, David J. Maguire, David W. Rhind 2005 John Wiley and Sons, Ltd Spatial analysis Turns raw data into useful information by adding greater informative content and value Reveals patterns, trends, and anomalies that might otherwise be missed Provides a check on human intuition by helping in situations where the eye might deceive Definitions A method of analysis is spatial if the results depend on the locations of the objects being analyzed move the objects and the results change results are not invariant under relocation Spatial analysis requires both attributes and locations of objects a GIS has been designed to store both The Snow map Shows the locations of cholera cases in the Soho area of London during an outbreak in the 1850s. The map shows that the outbreak was centered on a pump in Broad Street, and provided evidence in support of Dr John Snow s hypothesis that contaminated drinking water was causing the outbreak Broad Street Cholera epidemic of London in Led to the discovery of cholera as a water-borne disease. Drastically reduced the incidence of the disease. (Proximity analysis).
2 Spatial Analysis In 1854, a major cholera outbreak in London had already taken nearly six hundred lives when Dr. John Snow, using a handdrawn map, showed that the source of the disease was a contaminated water pump. By plotting each known cholera case on a street map of Soho district (where the outbreak took place), Snow could see that the cases occurred predominantly among those who lived near the Broad Street water pump. This pump belonged to the Southwark and Vauxhall Water Company, which drew water polluted with London sewage from the lower Thames River. The Lambeth Water Company, which had relocated its water source to the upper Thames, escaped the contamination. Snow recommended that the handle of this pump be removed, simple action stopped the outbreak and proved his theory that cholera is transmitted through contaminated drinking water. People could also see on this map that cholera deaths were not confined to the area around a cemetery of plague victims convinced that the infection was not due to vapours coming from it. The exact sequence of events has been challenged Which can first? The theory or the map? Woburn MA, A more recent example In 1979 two of eight water wells serving Woburn, MA, USA were found to be polluted bber/ The Snow map Provides a classic example of the use of location to draw inferences But the same pattern could arise from contagion if the original carrier lived in the center of the outbreak contagion was the hypothesis Snow was trying to refute today, a GIS could be used to show a sequence of maps as the outbreak developed contagion would produce a concentric sequence, drinking water a random sequence Types of spatial analysis There are literally thousands of techniques Six categories are used in this course, each having a distinct conceptual basis: Transformations Descriptive summaries Optimization Hypothesis testing A GIS can respond to queries by presenting data in appropriate views and allowing the user to interact with each view It is often useful to be able to display two or more views at once and to link them together linking views is one important technique of exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA)
3 The catalog view Shows folders, databases, and files on the left, and a preview of the contents of a selected data set on the right. The preview can be used to query the data set s metadata, or to look at a thumbnail map, or at a table of attributes. This example shows ESRI s ArcCatalog. The map view A user can interact with a map view to identify objects and query their attributes, to search for objects meeting specified criteria, or to find the coordinates of objects. This illustration uses ESRI s ArcMap. The table view Here attributes are displayed in the form of a table, linked to a map view. When objects are selected in the table, they are automatically highlighted in the map view, and vice versa. The table view can be used to answer simple queries about objects and their attributes. Many tasks require measurement from maps measurement of distance between two points measurement of area, e.g. the area of a parcel of land Such measurements are tedious and inaccurate if made by hand measurement using GIS tools and digital databases is fast, reliable, and accurate Measurement of length Issues with length measurement A metric is a rule for determining distance from coordinates The Pythagorean metric gives the straightline distance between two points on a flat plane The Great Circle metric gives the shortest distance between two points on a spherical globe given their latitudes and longitudes The length of a true curve is almost always longer than the length of its polyline or polygon representation
4 Issues with length measurement in GIS are often made on horizontal projections of objects length and area may be substantially lower than on a true three-dimensional surface Shape as an indicator of gerrymandering in elections Measurement of shape Shape measures capture the degree of contortedness of areas, relative to the most compact circular shape by comparing perimeter to the square root of area normalized so that the shape of a circle is 1 the more contorted the area, the higher the shape measure The 12 th Congressional District of North Carolina was drawn in 1992 using a GIS, and designed to be a majority-minority district: with a majority of African American voters, it could be expected to return an African American to Congress. This objective was achieved at the cost of a very contorted shape. The U.S. Supreme Court eventually rejected the design. Slope and aspect Calculated from a grid of elevations (a digital elevation model) Slope and aspect are calculated at each point in the grid, by comparing the point s elevation to that of its neighbors usually its eight neighbors but the exact method varies in a scientific study, it is important to know exactly what method is used when calculating slope, and exactly how slope is defined Alternative definitions of slope The ratio of the change in elevation to the horizontal distance traveled, range 0 to infinity The ratio of the change in elevation to the actual distance traveled, range 0 to 1 The angle between the surface and the horizontal, range 0 to 90
5 Transformations Create new objects and attributes, based on simple rules involving geometric construction or calculation may also create new fields, from existing fields or from discrete objects Buffering (dilation) Create a new object consisting of areas within a user-defined distance of an existing object e.g., to determine areas impacted by a proposed highway e.g., to determine the service area of a proposed hospital Feasible in either raster or vector mode Buffering Point-in-polygon transformation Point Polyline Polygon Determine whether a point lies inside or outside a polygon generalization: assign many points to containing polygons used to assign crimes to police precincts, voters to voting districts, accidents to reporting counties The point in polygon algorithm Draw a line from the point to infinity in any direction, and count the number of intersections between this line and each polygon s boundary. The polygon with an odd number of intersections is the containing polygon: all other polygons have an even number of intersections. Polygon overlay Two case: for discrete objects and for fields Discrete object case: find the polygons formed by the intersection of two polygons. There are many related questions, e.g.: do two polygons intersect? where are areas in Polygon A but not in Polygon B?
6 Polygon overlay, discrete object case A B In this example, two polygons are intersected to form 9 new polygons. One is formed from both input polygons; four are formed by Polygon A and not Polygon B; and four are formed by Polygon B and not Polygon A. Polygon overlay, field case Two complete layers of polygons are input, representing two classifications of the same area e.g., soil type and land ownership The layers are overlaid, and all intersections are computed creating a new layer each polygon in the new layer has both a soil type and a land ownership the attributes are said to be concatenated The task is often performed in raster Polygon overlay, field case Owner X Owner Y Public Map Overlay for Interpolation Census Block data Digital Ortho Photo or Satellite Image Data A layer representing a field of land ownership (colors) is overlaid on a layer of soil type (layers offset for emphasis). The result after overlay will be a single layer with 5 polygons, each with a land ownership value and a soil type. Overlay Higher level of positional accuracy Spurious or sliver polygons In any two such layers there will almost certainly be boundaries that are common to both layers e.g. following rivers The two versions of such boundaries will not be coincident As a result large numbers of small sliver polygons will be created these must somehow be removed this is normally done using a user-defined tolerance Transformation Cartograms distort area or distance in order to achieve a specific objective Dasymetric maps use the intersection of two datasets (or layers in the same dataset) to obtain more precise estimates of a spatial distribution
7 Cartogram Central A USGS supported site Site created by Ian Bortins and Steve Demers under the direction of Dr. Keith Clarke, hosted and maintained by NCGIA. Other cartogram links SPATIAL ANALYSIS Six categories: Transformations Descriptive summaries Optimization Hypothesis testing
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis. GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University
 Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WATS 4930/6920 WHERE WE RE GOING WATS 6915 welcome to tag along for any, all or none WEEK FIVE Lecture VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton HOUSEKEEPING
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WATS 4930/6920 WHERE WE RE GOING WATS 6915 welcome to tag along for any, all or none WEEK FIVE Lecture VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton HOUSEKEEPING
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 ADVANCED GIS
 Slides by Wheaton et al. (2009-2014) are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 ADVANCED GIS VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton
Slides by Wheaton et al. (2009-2014) are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 ADVANCED GIS VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton
GIS Data Models. 4/9/ GIS Data Models
 GIS Data Models 1 Conceptual models of the real world The real world can be described using two conceptually different models: 1. As discrete objects, possible to represent as points, lines or polygons.
GIS Data Models 1 Conceptual models of the real world The real world can be described using two conceptually different models: 1. As discrete objects, possible to represent as points, lines or polygons.
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models Feature Types and Data Models How Does a GIS Work? - a GIS operates on the premise that all of the features in the real world can
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 02: Feature Types and Data Models Feature Types and Data Models How Does a GIS Work? - a GIS operates on the premise that all of the features in the real world can
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling
 Spatial Analysis in GIS (cont d) GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling - the basic types of analysis that can be accomplished with a GIS are outlined in The Esri Guide to GIS Analysis
Spatial Analysis in GIS (cont d) GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 18: Spatial Modeling - the basic types of analysis that can be accomplished with a GIS are outlined in The Esri Guide to GIS Analysis
ERROR PROPAGATION MODELING IN GIS POLYGON OVERLAY
 ERROR PROPAGATION MODELING IN GIS POLYGON OVERLAY Jinda Sae-Jung, Xiao Yong Chen, Do Minh Phuong Department of Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems, Asian Institute of Technology, Thailand
ERROR PROPAGATION MODELING IN GIS POLYGON OVERLAY Jinda Sae-Jung, Xiao Yong Chen, Do Minh Phuong Department of Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems, Asian Institute of Technology, Thailand
Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models
 Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary Learning Objectives Learning
Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary Learning Objectives Learning
Lecture 7 Digitizing. Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017
 Lecture 7 Digitizing Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017 Model of the course Using and making maps Navigating GIS maps Map design Working with spatial data Geoprocessing Spatial data infrastructure Digitizing File
Lecture 7 Digitizing Dr. Zhang Spring, 2017 Model of the course Using and making maps Navigating GIS maps Map design Working with spatial data Geoprocessing Spatial data infrastructure Digitizing File
9. GIS Data Collection
 9. GIS Data Collection Geographic Information Systems and Science SECOND EDITION Paul A. Longley, Michael F. Goodchild, David J. Maguire, David W. Rhind 2005 John Wiley and Sons, Ltd Overview Introduction
9. GIS Data Collection Geographic Information Systems and Science SECOND EDITION Paul A. Longley, Michael F. Goodchild, David J. Maguire, David W. Rhind 2005 John Wiley and Sons, Ltd Overview Introduction
Greenville County Internet Mapping System User s Guide
 Greenville County Internet Mapping System User s Guide Version 2.0 Greenville County Geographic Information Systems May 30, 2006 Table of Contents NAVIGATING TO THE ONLINE MAPPING APPLICATIONS...- 3 -
Greenville County Internet Mapping System User s Guide Version 2.0 Greenville County Geographic Information Systems May 30, 2006 Table of Contents NAVIGATING TO THE ONLINE MAPPING APPLICATIONS...- 3 -
Class #2. Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures
 Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Unit 3: Proximity Analysis and Buffering. Lecture Outline
 Unit 3: Proximity Analysis and Buffering Lecture Outline I. Vector-Based Proximity 1. Proximity involves the calculation of distance between features in a single layer, or between features in multiple
Unit 3: Proximity Analysis and Buffering Lecture Outline I. Vector-Based Proximity 1. Proximity involves the calculation of distance between features in a single layer, or between features in multiple
Contents of Lecture. Surface (Terrain) Data Models. Terrain Surface Representation. Sampling in Surface Model DEM
 Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
GIS Basics for Urban Studies
 GIS Basics for Urban Studies Date: March 21, 2018 Contacts: Mehdi Aminipouri, Graduate Peer GIS Faciliator, SFU Library (maminipo@sfu.ca) Keshav Mukunda, GIS & Map Librarian Librarian for Geography (kmukunda@sfu.ca)
GIS Basics for Urban Studies Date: March 21, 2018 Contacts: Mehdi Aminipouri, Graduate Peer GIS Faciliator, SFU Library (maminipo@sfu.ca) Keshav Mukunda, GIS & Map Librarian Librarian for Geography (kmukunda@sfu.ca)
Probability An Example
 Probability An Example For example, suppose we have a data set where in six cities, we count the number of malls located in that city present: Each count of the # of malls in a city is an event # of Malls
Probability An Example For example, suppose we have a data set where in six cities, we count the number of malls located in that city present: Each count of the # of malls in a city is an event # of Malls
Mapping Distance and Density
 Mapping Distance and Density Distance functions allow you to determine the nearest location of something or the least-cost path to a particular destination. Density functions, on the other hand, allow
Mapping Distance and Density Distance functions allow you to determine the nearest location of something or the least-cost path to a particular destination. Density functions, on the other hand, allow
Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS.
 GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CONTOURS! Self-Paced Lab Due Friday! WEEK SIX Lecture RASTER ANALYSES Joe Wheaton YOUR EXCERCISE Integer Elevations Rounded up
HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CONTOURS! Self-Paced Lab Due Friday! WEEK SIX Lecture RASTER ANALYSES Joe Wheaton YOUR EXCERCISE Integer Elevations Rounded up
The Death Map. Hollins University Visitors 25 October / 63
 The Death Map John Burkardt Information Technology Department Virginia Tech... http://people.sc.fsu.edu/ jburkardt/presentations/,,, death map 2007 vt.pdf Hollins University Visitors 25 October 2007 1
The Death Map John Burkardt Information Technology Department Virginia Tech... http://people.sc.fsu.edu/ jburkardt/presentations/,,, death map 2007 vt.pdf Hollins University Visitors 25 October 2007 1
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri. [10] Spring 2018 GIS Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri Spatial Analyst
![Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri. [10] Spring 2018 GIS Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri Spatial Analyst Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri. [10] Spring 2018 GIS Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri Spatial Analyst](/thumbs/80/81171101.jpg) Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri 1 Preface POINTS, LINES, and POLYGONS are good at representing geographic objects with distinct shapes They are less good
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri 1 Preface POINTS, LINES, and POLYGONS are good at representing geographic objects with distinct shapes They are less good
GIS Workbook #1. GIS Basics and the ArcGIS Environment. Helen Goodchild
 GIS Basics and the ArcGIS Environment Helen Goodchild Overview of Geographic Information Systems Geographical Information Systems (GIS) are used to display, manipulate and analyse spatial data (data that
GIS Basics and the ArcGIS Environment Helen Goodchild Overview of Geographic Information Systems Geographical Information Systems (GIS) are used to display, manipulate and analyse spatial data (data that
Geodatabase over Taita Hills, Kenya
 Geodatabase over Taita Hills, Kenya Anna Broberg & Antero Keskinen Abstract This article introduces the basics of geographical information systems (GIS) and explains how the Taita Hills project can benefit
Geodatabase over Taita Hills, Kenya Anna Broberg & Antero Keskinen Abstract This article introduces the basics of geographical information systems (GIS) and explains how the Taita Hills project can benefit
[Figure about here]
![[Figure about here] [Figure about here]](/thumbs/78/77444676.jpg) CHAPTER 3.6: SPATIAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Michael F. Goodchild University of California, Santa Barbara 3.6.1 Introduction In the previous chapters we have seen how a wide variety of types of geographic
CHAPTER 3.6: SPATIAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Michael F. Goodchild University of California, Santa Barbara 3.6.1 Introduction In the previous chapters we have seen how a wide variety of types of geographic
Chapter 1: Introduction to Spatial Databases
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Spatial Databases 1.1 Overview 1.2 Application domains 1.3 Compare a SDBMS with a GIS 1.4 Categories of Users 1.5 An example of an SDBMS application 1.6 A Stroll though a spatial
Chapter 1: Introduction to Spatial Databases 1.1 Overview 1.2 Application domains 1.3 Compare a SDBMS with a GIS 1.4 Categories of Users 1.5 An example of an SDBMS application 1.6 A Stroll though a spatial
ArcGIS 9. ArcGIS Survey Analyst Tutorial
 ArcGIS 9 ArcGIS Survey Analyst Tutorial Copyright 00 008 ESRI All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. The information contained in this document is the exclusive property of ESRI.
ArcGIS 9 ArcGIS Survey Analyst Tutorial Copyright 00 008 ESRI All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. The information contained in this document is the exclusive property of ESRI.
RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O
 RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O TOPICS COVERED Spatial Analyst basics Raster / Vector conversion Raster data
RASTER ANALYSIS S H A W N L. P E N M A N E A R T H D A T A A N A LY S I S C E N T E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F N E W M E X I C O TOPICS COVERED Spatial Analyst basics Raster / Vector conversion Raster data
User Guide. ExploreHRM ICT BIDS. 0 P a g e
 User Guide ICT BIDS 0 P a g e Contents Introduction... 2 Top Left Panel Navigation and Search Widgets... 3 Search... 3 Zoom In/Out... 3 Home... 3 Zoom Extent... 3 Right Panel Information and Print Widgets...
User Guide ICT BIDS 0 P a g e Contents Introduction... 2 Top Left Panel Navigation and Search Widgets... 3 Search... 3 Zoom In/Out... 3 Home... 3 Zoom Extent... 3 Right Panel Information and Print Widgets...
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations,
 Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introduction to 3D Data: Modeling with ArcGIS 3D Analyst and Google Earth CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 3D Data: Modeling with ArcGIS 3D Analyst and Google Earth Introduction to 3D Data is a self - study tutorial workbook that teaches you how to create data and maps with ESRI s
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 3D Data: Modeling with ArcGIS 3D Analyst and Google Earth Introduction to 3D Data is a self - study tutorial workbook that teaches you how to create data and maps with ESRI s
INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE
 111 Mulford Hall, College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley (510) 643-4539 INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE This exercise is a survey of some GIS and spatial analysis tools for ecological and natural
111 Mulford Hall, College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley (510) 643-4539 INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE This exercise is a survey of some GIS and spatial analysis tools for ecological and natural
Spatial data and QGIS
 Spatial data and QGIS Xue Jingbo IT Center 2017.08.07 A GIS consists of: Spatial Data. Computer Hardware. Computer Software. Longitude Latitude Disease Date 26.870436-31.909519 Mumps 13/12/2008 26.868682-31.909259
Spatial data and QGIS Xue Jingbo IT Center 2017.08.07 A GIS consists of: Spatial Data. Computer Hardware. Computer Software. Longitude Latitude Disease Date 26.870436-31.909519 Mumps 13/12/2008 26.868682-31.909259
layers in a raster model
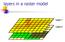 layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
Assimilating GIS-Based Voter Districting Processes in Maricopa County, Arizona
 Assimilating GIS-Based Voter Districting Processes in Maricopa County, Arizona Tim Johnson Geographic Information Systems Manager Maricopa County Recorder/Elections Department Abstract Accurate district
Assimilating GIS-Based Voter Districting Processes in Maricopa County, Arizona Tim Johnson Geographic Information Systems Manager Maricopa County Recorder/Elections Department Abstract Accurate district
1. Start ArcMap by going to the Start menu > All Programs > ArcGIS > ArcMap.
 Learning ArcGIS: Introduction to ArcMap 10.1 The Map Document Feature Manipulation Navigating ArcMap Map Documents, Layers, and Features Shapes, Location, and Attribute Data Symbology Zoom, Pan and Map
Learning ArcGIS: Introduction to ArcMap 10.1 The Map Document Feature Manipulation Navigating ArcMap Map Documents, Layers, and Features Shapes, Location, and Attribute Data Symbology Zoom, Pan and Map
Peoria County Front Desk Map Application
 Peoria County Front Desk Map Application Quick Guide, 2017 At a First Glance This guide will tell users all they need to know about the Peoria County Front Desk application which can be found on the Peoria
Peoria County Front Desk Map Application Quick Guide, 2017 At a First Glance This guide will tell users all they need to know about the Peoria County Front Desk application which can be found on the Peoria
M. Andrea Rodríguez-Tastets. I Semester 2008
 M. -Tastets Universidad de Concepción,Chile andrea@udec.cl I Semester 2008 Outline refers to data with a location on the Earth s surface. Examples Census data Administrative boundaries of a country, state
M. -Tastets Universidad de Concepción,Chile andrea@udec.cl I Semester 2008 Outline refers to data with a location on the Earth s surface. Examples Census data Administrative boundaries of a country, state
Guidelines for Creating Historical Geospatial Boundary Data
 Tsering Wangyal Shawa * Guidelines for Creating Historical Geospatial Boundary Data Keywords: image enhancing; georeferencing; historical boundary data; vectorisation Summary: Princeton University Library
Tsering Wangyal Shawa * Guidelines for Creating Historical Geospatial Boundary Data Keywords: image enhancing; georeferencing; historical boundary data; vectorisation Summary: Princeton University Library
Suitability Modeling with GIS
 Developed and Presented by Juniper GIS 1/33 Course Objectives What is Suitability Modeling? The Suitability Modeling Process Cartographic Modeling GIS Tools for Suitability Modeling Demonstrations of Models
Developed and Presented by Juniper GIS 1/33 Course Objectives What is Suitability Modeling? The Suitability Modeling Process Cartographic Modeling GIS Tools for Suitability Modeling Demonstrations of Models
Explore some of the new functionality in ArcMap 10
 Explore some of the new functionality in ArcMap 10 Scenario In this exercise, imagine you are a GIS analyst working for Old Dominion University. Construction will begin shortly on renovation of the new
Explore some of the new functionality in ArcMap 10 Scenario In this exercise, imagine you are a GIS analyst working for Old Dominion University. Construction will begin shortly on renovation of the new
Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3
 Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3 Practical: Creating and Editing Shapefiles Using Straight, AutoComplete and Cut Polygon Tools Use ArcCatalog to copy data files from:
Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Lecture_3 Practical: Creating and Editing Shapefiles Using Straight, AutoComplete and Cut Polygon Tools Use ArcCatalog to copy data files from:
MODFLOW Conceptual Model Approach II Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques
 v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques 00 Objectives The conceptual model approach involves using the GIS tools in the Map module to develop
v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques 00 Objectives The conceptual model approach involves using the GIS tools in the Map module to develop
Information Visualization. SWE 432, Fall 2016 Design and Implementation of Software for the Web
 Information Visualization SWE 432, Fall 2016 Design and Implementation of Software for the Web Today What types of information visualization are there? Which one should you choose? What does usability
Information Visualization SWE 432, Fall 2016 Design and Implementation of Software for the Web Today What types of information visualization are there? Which one should you choose? What does usability
Module 4. Stereographic projection: concept and application. Lecture 4. Stereographic projection: concept and application
 Module 4 Stereographic projection: concept and application Lecture 4 Stereographic projection: concept and application 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials
Module 4 Stereographic projection: concept and application Lecture 4 Stereographic projection: concept and application 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials
VECTOR ANALYSIS: QUERIES, MEASUREMENTS & TRANSFORMATIONS
 VECTOR ANALYSIS: QUERIES, MEASUREMENTS & TRANSFORMATIONS GIS Analysis Winter 2016 Spatial Analysis Operations performed on spatial data that add value Can reveal things that might otherwise be invisible
VECTOR ANALYSIS: QUERIES, MEASUREMENTS & TRANSFORMATIONS GIS Analysis Winter 2016 Spatial Analysis Operations performed on spatial data that add value Can reveal things that might otherwise be invisible
CSAP Achievement Levels Mathematics Grade 6 March, 2006
 Advanced Performance Level 4 (Score range: 589 to 830) Students demonstrate equivalency among fractions decimals, and percents; apply number sense; solve real-world problems using geometric and numeric
Advanced Performance Level 4 (Score range: 589 to 830) Students demonstrate equivalency among fractions decimals, and percents; apply number sense; solve real-world problems using geometric and numeric
IST 210. Introduction to Spatial Databases
 Introduction to Spatial Databases Evolution of acronym GIS Geographic Information Systems (1980s) Geographic Information Science (1990s) Geographic Information Services (2000s) GISystems GIServices GIScience
Introduction to Spatial Databases Evolution of acronym GIS Geographic Information Systems (1980s) Geographic Information Science (1990s) Geographic Information Services (2000s) GISystems GIServices GIScience
Lab 1: Exploring ArcMap and ArcCatalog In this lab, you will explore the ArcGIS applications ArcCatalog and ArcMap. You will learn how to use
 Lab 1: Exploring ArcMap and ArcCatalog In this lab, you will explore the ArcGIS applications ArcCatalog and ArcMap. You will learn how to use ArcCatalog to find maps and data and how to display maps in
Lab 1: Exploring ArcMap and ArcCatalog In this lab, you will explore the ArcGIS applications ArcCatalog and ArcMap. You will learn how to use ArcCatalog to find maps and data and how to display maps in
CSTools Guide (for ArcGIS version 10.2 and 10.3)
 CSTools Guide (for ArcGIS version 10.2 and 10.3) 1. Why to use Orientation Analysis and Cross section tools (CSTools) in ArcGIS? 2 2. Data format 2 2.1 Coordinate Systems 2 3. How to get the tools into
CSTools Guide (for ArcGIS version 10.2 and 10.3) 1. Why to use Orientation Analysis and Cross section tools (CSTools) in ArcGIS? 2 2. Data format 2 2.1 Coordinate Systems 2 3. How to get the tools into
Building and Analyzing Topology in Autodesk Map GI21-1
 December 2-5, 2003 MGM Grand Hotel Las Vegas Building and Analyzing Topology in Autodesk Map GI21-1 Alex Penney ISD Training Content Manager, Autodesk Professional Services, Autodesk Inc. Topology is one
December 2-5, 2003 MGM Grand Hotel Las Vegas Building and Analyzing Topology in Autodesk Map GI21-1 Alex Penney ISD Training Content Manager, Autodesk Professional Services, Autodesk Inc. Topology is one
Alaska Department of Transportation Roads to Resources Project LiDAR & Imagery Quality Assurance Report Juneau Access South Corridor
 Alaska Department of Transportation Roads to Resources Project LiDAR & Imagery Quality Assurance Report Juneau Access South Corridor Written by Rick Guritz Alaska Satellite Facility Nov. 24, 2015 Contents
Alaska Department of Transportation Roads to Resources Project LiDAR & Imagery Quality Assurance Report Juneau Access South Corridor Written by Rick Guritz Alaska Satellite Facility Nov. 24, 2015 Contents
Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
I. An Intro to ArcMap Version 9.3 and 10. 1) Arc Map is basically a build your own Google map
 I. An Intro to ArcMap Version 9.3 and 10 What is Arc Map? 1) Arc Map is basically a build your own Google map a. Display and manage geo-spatial data (maps, images, points that have a geographic location)
I. An Intro to ArcMap Version 9.3 and 10 What is Arc Map? 1) Arc Map is basically a build your own Google map a. Display and manage geo-spatial data (maps, images, points that have a geographic location)
Introduction to GIS 2011
 Introduction to GIS 2011 Digital Elevation Models CREATING A TIN SURFACE FROM CONTOUR LINES 1. Start ArcCatalog from either Desktop or Start Menu. 2. In ArcCatalog, create a new folder dem under your c:\introgis_2011
Introduction to GIS 2011 Digital Elevation Models CREATING A TIN SURFACE FROM CONTOUR LINES 1. Start ArcCatalog from either Desktop or Start Menu. 2. In ArcCatalog, create a new folder dem under your c:\introgis_2011
Blacksburg, VA July 24 th 30 th, 2010 Georeferencing images and scanned maps Page 1. Georeference
 George McLeod Prepared by: With support from: NSF DUE-0903270 in partnership with: Geospatial Technician Education Through Virginia s Community Colleges (GTEVCC) Georeference The process of defining how
George McLeod Prepared by: With support from: NSF DUE-0903270 in partnership with: Geospatial Technician Education Through Virginia s Community Colleges (GTEVCC) Georeference The process of defining how
An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) using ArcGIS 9.2
 An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) using ArcGIS 9.2 by Marcel Fortin, GIS and Map Librarian, University of Toronto Libraries, 2009 gis.maps@utoronto.ca http://www.library.utoronto.ca/maplib/
An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) using ArcGIS 9.2 by Marcel Fortin, GIS and Map Librarian, University of Toronto Libraries, 2009 gis.maps@utoronto.ca http://www.library.utoronto.ca/maplib/
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment
 Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World Rotation Differential Scaling Distortion Skew Translation 1 The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World Rotation Differential Scaling Distortion Skew Translation 1 The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either
GMS 10.0 Tutorial MODFLOW Conceptual Model Approach II Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques
 v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques 00 Objectives The conceptual model approach involves using the GIS tools in the Map Module to develop
v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial Build a multi-layer MODFLOW model using advanced conceptual model techniques 00 Objectives The conceptual model approach involves using the GIS tools in the Map Module to develop
Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing. David Eppstein
 Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine School of Information and Computer Science (including joint work with Marshall Bern from WADS 01 and SODA 03) Outline
Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine School of Information and Computer Science (including joint work with Marshall Bern from WADS 01 and SODA 03) Outline
LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8
 LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8 Outline Introduction Purpose Lab Basics o About the Computers o About the software o Additional information Data ArcGIS Applications o Starting ArcGIS o o o Conclusion To
LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8 Outline Introduction Purpose Lab Basics o About the Computers o About the software o Additional information Data ArcGIS Applications o Starting ArcGIS o o o Conclusion To
Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS
 Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS An ESRI White Paper August 2003 ESRI 380 New York St., Redlands, CA 92373-8100, USA TEL 909-793-2853 FAX 909-793-5953 E-MAIL info@esri.com WEB www.esri.com Copyright 2003
Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS An ESRI White Paper August 2003 ESRI 380 New York St., Redlands, CA 92373-8100, USA TEL 909-793-2853 FAX 909-793-5953 E-MAIL info@esri.com WEB www.esri.com Copyright 2003
4.0 DIGITIZATION, EDITING AND STRUCTURING OF MAP DATA
 .0 DIGITIZATION, EDITING AND STRUCTURING OF MAP DATA The process of digitizing existing maps is a transformation from one analog) form of information to another digital) form. Data input is the operation
.0 DIGITIZATION, EDITING AND STRUCTURING OF MAP DATA The process of digitizing existing maps is a transformation from one analog) form of information to another digital) form. Data input is the operation
Nearest Neighbor Predictors
 Nearest Neighbor Predictors September 2, 2018 Perhaps the simplest machine learning prediction method, from a conceptual point of view, and perhaps also the most unusual, is the nearest-neighbor method,
Nearest Neighbor Predictors September 2, 2018 Perhaps the simplest machine learning prediction method, from a conceptual point of view, and perhaps also the most unusual, is the nearest-neighbor method,
GPS/GIS Activities Summary
 GPS/GIS Activities Summary Group activities Outdoor activities Use of GPS receivers Use of computers Calculations Relevant to robotics Relevant to agriculture 1. Information technologies in agriculture
GPS/GIS Activities Summary Group activities Outdoor activities Use of GPS receivers Use of computers Calculations Relevant to robotics Relevant to agriculture 1. Information technologies in agriculture
4/7/2009. Model: Abstraction of reality following formal rules e.g. Euclidean space for physical space
 Model: Abstraction of reality following formal rules e.g. Euclidean space for physical space At different levels: mathematical model (Euclidean space) conceptual design model (ER model) data model (design)
Model: Abstraction of reality following formal rules e.g. Euclidean space for physical space At different levels: mathematical model (Euclidean space) conceptual design model (ER model) data model (design)
Chapter 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information. 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.
 Chapter 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2. Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary What is a Data Model? What
Chapter 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2. Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary What is a Data Model? What
DATA MODELS IN GIS. Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi
 DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
Introduction. Product List. Design and Functionality 1/10/2013. GIS Seminar Series 2012 Division of Spatial Information Science
 Introduction Open GEODA GIS Seminar Series 2012 Division of Spatial Information Science University of Tsukuba H.Malinda Siriwardana The GeoDa Center for Geospatial Analysis and Computation develops state
Introduction Open GEODA GIS Seminar Series 2012 Division of Spatial Information Science University of Tsukuba H.Malinda Siriwardana The GeoDa Center for Geospatial Analysis and Computation develops state
(Refer Slide Time: 00:02:00)
 Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 18 Polyfill - Scan Conversion of a Polygon Today we will discuss the concepts
Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 18 Polyfill - Scan Conversion of a Polygon Today we will discuss the concepts
Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2)
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Today: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), Topographic functions (surface analysis): slope, aspect hillshade, viewshed,
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Today: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), Topographic functions (surface analysis): slope, aspect hillshade, viewshed,
Easily add Maps and Geo Analytics in MicroStrategy
 Easily add Maps and Geo Analytics in MicroStrategy Agenda Introduction Configure to use Maps in MicroStrategy MicroStrategy Geo Analysis Capabilities and Examples Key Takeaways and Q&A Why Geospatial Analysis
Easily add Maps and Geo Analytics in MicroStrategy Agenda Introduction Configure to use Maps in MicroStrategy MicroStrategy Geo Analysis Capabilities and Examples Key Takeaways and Q&A Why Geospatial Analysis
Georeferencing. Georeferencing: = linking a layer or dataset with spatial coordinates. Registration: = lining up layers with each other
 Georeferencing How do we make sure all our data layers line up? Georeferencing: = linking a layer or dataset with spatial coordinates Registration: = lining up layers with each other Rectification: The
Georeferencing How do we make sure all our data layers line up? Georeferencing: = linking a layer or dataset with spatial coordinates Registration: = lining up layers with each other Rectification: The
Geodatabases. Dr. Zhang SPRING 2016 GISC /03/2016
 Geodatabases Dr. Zhang SPRING 2016 GISC 1401 10/03/2016 Using and making maps Navigating GIS maps Map design Working with spatial data Spatial data infrastructure Interactive maps Map Animations Map layouts
Geodatabases Dr. Zhang SPRING 2016 GISC 1401 10/03/2016 Using and making maps Navigating GIS maps Map design Working with spatial data Spatial data infrastructure Interactive maps Map Animations Map layouts
MainStreetMaps Web GIS User Guide
 MainStreetMaps Web GIS User Guide by MainStreetGIS, LLC www.mainstreetgis.com Updated 11/11/2017 Web GIS User Guide - Copyright MainStreetGIS, LLC - www.mainstreetgis.com Page 1 of 15 Table of Contents
MainStreetMaps Web GIS User Guide by MainStreetGIS, LLC www.mainstreetgis.com Updated 11/11/2017 Web GIS User Guide - Copyright MainStreetGIS, LLC - www.mainstreetgis.com Page 1 of 15 Table of Contents
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment 2/13/2018
 Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment The Problem Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment The Problem Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in
PDHonline Course L154G (5 PDH) Data in GIS. Instructor: Steve Ramroop, Ph.D. PDH Online PDH Center
 PDHonline Course L154G (5 PDH) Data in GIS Instructor: Steve Ramroop, Ph.D. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088 www.pdhonline.org www.pdhcenter.com
PDHonline Course L154G (5 PDH) Data in GIS Instructor: Steve Ramroop, Ph.D. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088 www.pdhonline.org www.pdhcenter.com
Civil 3D Introduction
 Civil 3D Introduction Points Overview Points are data collected by surveyors which represent existing site conditions (elevations, boundaries, utilities, etc.). Each point is numbered (or named) and has
Civil 3D Introduction Points Overview Points are data collected by surveyors which represent existing site conditions (elevations, boundaries, utilities, etc.). Each point is numbered (or named) and has
The Problem. Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment. Nature Of The Problem: For Example: Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment 9/20/2016
 Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in
US Geo-Explorer User s Guide. Web:
 US Geo-Explorer User s Guide Web: http://usgeoexplorer.org Updated on October 26, 2016 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 3 1. System Interface... 5 2. Administrative Unit... 7 2.1 Region Selection... 7
US Geo-Explorer User s Guide Web: http://usgeoexplorer.org Updated on October 26, 2016 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 3 1. System Interface... 5 2. Administrative Unit... 7 2.1 Region Selection... 7
Remote Sensing in an
 Chapter 2: Adding Data to a Map Document Remote Sensing in an ArcMap Environment Remote Sensing Analysis in an ArcMap Environment Tammy E. Parece Image source: landsat.usgs.gov Tammy Parece James Campbell
Chapter 2: Adding Data to a Map Document Remote Sensing in an ArcMap Environment Remote Sensing Analysis in an ArcMap Environment Tammy E. Parece Image source: landsat.usgs.gov Tammy Parece James Campbell
Lab Assignment 4 Basics of ArcGIS Server. Due Date: 01/19/2012
 Lab Assignment 4 Basics of ArcGIS Server Due Date: 01/19/2012 Overview This lab assignment is designed to help you develop a good understanding about the basics of ArcGIS Server and how it works. You will
Lab Assignment 4 Basics of ArcGIS Server Due Date: 01/19/2012 Overview This lab assignment is designed to help you develop a good understanding about the basics of ArcGIS Server and how it works. You will
The Problem. Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment. Nature of the problem: For Example: Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment 2/4/2014
 Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to a GIS The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in geographical
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to a GIS The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either raster or vector, made to align with data that exist in geographical
points are stationed arbitrarily close to one corner of the square ( n+1
 1 Intro We ve seen previously that we can construct networks based on the regular triangular, rectangular and hexagonal lattices where the total network length is linear in n and the R-statistic for the
1 Intro We ve seen previously that we can construct networks based on the regular triangular, rectangular and hexagonal lattices where the total network length is linear in n and the R-statistic for the
Making Topographic Maps
 T O P O Applications N Making Topographic Maps M A P S Making Topographic Maps with TNTmips page 1 Before Getting Started TNTmips provides a variety of tools for working with map data and making topographic
T O P O Applications N Making Topographic Maps M A P S Making Topographic Maps with TNTmips page 1 Before Getting Started TNTmips provides a variety of tools for working with map data and making topographic
Metadata or "data about data" describe the content, quality, condition, and other characteristics of data. The Federal Geographic Data Committee
 Metadata or "data about data" describe the content, quality, condition, and other characteristics of data. The Federal Geographic Data Committee (http://www.fgdc.gov/) approved the Content Standard for
Metadata or "data about data" describe the content, quality, condition, and other characteristics of data. The Federal Geographic Data Committee (http://www.fgdc.gov/) approved the Content Standard for
Metadata or "data about data" describe the content, quality, condition, and other characteristics of data. The Federal Geographic Data Committee
 Metadata or "data about data" describe the content, quality, condition, and other characteristics of data. The Federal Geographic Data Committee (http://www.fgdc.gov/) approved the Content Standard for
Metadata or "data about data" describe the content, quality, condition, and other characteristics of data. The Federal Geographic Data Committee (http://www.fgdc.gov/) approved the Content Standard for
Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
Gaston County GIS. Interactive Mapping Website
 Gaston County GIS Interactive Mapping Website The Gaston County GIS mapping website optimizes the available window viewing area and has interactive tools, collapsible menus and movable windows. This map
Gaston County GIS Interactive Mapping Website The Gaston County GIS mapping website optimizes the available window viewing area and has interactive tools, collapsible menus and movable windows. This map
GIS DATA MODELS AND SPATIAL DATA STRUCTURE
 UNIT 5 GIS DATA MODELS AND SPATIAL DATA STRUCTURE GIS Data Models and Spatial Data 5.1 Introduction Objectives 5.2 GIS Data Models Raster Data Models Vector Data Models Comparison of Raster and Vector
UNIT 5 GIS DATA MODELS AND SPATIAL DATA STRUCTURE GIS Data Models and Spatial Data 5.1 Introduction Objectives 5.2 GIS Data Models Raster Data Models Vector Data Models Comparison of Raster and Vector
Algorithms for GIS csci3225
 Algorithms for GIS csci3225 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Spatial data types and models Spatial data in GIS satellite imagery planar maps surfaces networks point cloud (LiDAR) Spatial data in GIS satellite
Algorithms for GIS csci3225 Laura Toma Bowdoin College Spatial data types and models Spatial data in GIS satellite imagery planar maps surfaces networks point cloud (LiDAR) Spatial data in GIS satellite
Chapter 7 Spatial Operation
 7.1 Introduction Chapter 7 Spatial Operation Q: What is spatial operation? A: Spatial operation is computational manipulation of spatial objects that deepen our understanding of spatial phenomena. In spatial
7.1 Introduction Chapter 7 Spatial Operation Q: What is spatial operation? A: Spatial operation is computational manipulation of spatial objects that deepen our understanding of spatial phenomena. In spatial
LAB REFLECTION FROM A PLANE MIRROR
 Name (printed) LAB REFLECTION FROM A PLANE MIRROR INTRODUCTION It s true that plane mirrors produce simpler images than curved mirrors, but they certainly aren t trivial. Ask a group of people who have
Name (printed) LAB REFLECTION FROM A PLANE MIRROR INTRODUCTION It s true that plane mirrors produce simpler images than curved mirrors, but they certainly aren t trivial. Ask a group of people who have
Geographic Information Systems. using QGIS
 Geographic Information Systems using QGIS 1 - INTRODUCTION Generalities A GIS (Geographic Information System) consists of: -Computer hardware -Computer software - Digital Data Generalities GIS softwares
Geographic Information Systems using QGIS 1 - INTRODUCTION Generalities A GIS (Geographic Information System) consists of: -Computer hardware -Computer software - Digital Data Generalities GIS softwares
Lecture 2: GIS Data Sources, Data Types and Representation. GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University
 Lecture 2: GIS Data Sources, Data Types and Representation GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University Geographic Data in GIS Can be obtained from various sources in different
Lecture 2: GIS Data Sources, Data Types and Representation GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University Geographic Data in GIS Can be obtained from various sources in different
Introduction to GIS. Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 9/24/2015. R. Khosla Fall Semester The real world. What in the world is GIS?
 Introduction to GIS Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 What in the world is GIS? GIS is simultaneously the telescope, the microscope, the computer and the Xerox machine of regional analysis and synthesis
Introduction to GIS Geographic Information Systems SOCR-377 What in the world is GIS? GIS is simultaneously the telescope, the microscope, the computer and the Xerox machine of regional analysis and synthesis
Integrated Algebra/Geometry 1
 *Ability to add, subtract, multiply and divide integers (without the use of a calculator) Ability to make statements about information presented in: tables and graphs concept maps identify and extend patterns
*Ability to add, subtract, multiply and divide integers (without the use of a calculator) Ability to make statements about information presented in: tables and graphs concept maps identify and extend patterns
Dijkstra's Algorithm
 Shortest Path Algorithm Dijkstra's Algorithm To find the shortest path from the origin node to the destination node No matrix calculation Floyd s Algorithm To find all the shortest paths from the nodes
Shortest Path Algorithm Dijkstra's Algorithm To find the shortest path from the origin node to the destination node No matrix calculation Floyd s Algorithm To find all the shortest paths from the nodes
The GIS Spatial Data Model
 The GIS Spatial Data Model Introduction: Spatial data are what drive a GIS. Every piece of functionality that makes a GIS separate from another analytical environment is rooted in the spatially explicit
The GIS Spatial Data Model Introduction: Spatial data are what drive a GIS. Every piece of functionality that makes a GIS separate from another analytical environment is rooted in the spatially explicit
8 th Grade Pre-Integrated Math
 Use order of operations Evaluate expressions Use integers and absolute value Add integers Subtract integers Use inductive reasoning Multiply and divide integers Use properties of numbers Simplify variable
Use order of operations Evaluate expressions Use integers and absolute value Add integers Subtract integers Use inductive reasoning Multiply and divide integers Use properties of numbers Simplify variable
FOUR ADVANCES IN HANDLING UNCERTAINTIES IN SPATIAL DATA AND ANALYSIS
 FOUR ADVANCES IN HANDLING UNCERTAINTIES IN SPATIAL DATA AND ANALYSIS Wenzhong Shi Advanced Research Centre for Spatial Information Technology Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatics The Hong Kong
FOUR ADVANCES IN HANDLING UNCERTAINTIES IN SPATIAL DATA AND ANALYSIS Wenzhong Shi Advanced Research Centre for Spatial Information Technology Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatics The Hong Kong
