Surface Shape Regions as Manifestations of a Socio-economic Phenomenon
|
|
|
- Ira Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Surface Shape Regions as Manifestations of a Socio-economic Phenomenon a solution to the choropleth mapping problem by John (Jack) Sirles Massey a thesis submitted for the degree of Master of Science in Mathematical & Computer Sciences in the Discipline of Pure Mathematics of the School of Mathematical Sciences The University of Adelaide 25 November 2011
2 dedicated to my wife, partner and friend... Kathleen (Kathie) Egan Massey ii
3 ABSTRACT A choropleth map is a cartographic document. It shows a geographic study area tessellated by a set of polygons that differ in shape and size. Each polygon is depicted by a uniform symbol representing the manifestation of some phenomenon. This thesis focuses on socio-economic phenomena. We want to delineate a set of socio-economic regions within a study area. These regions are used for decision making about the delivery of specific goods and services and/or the provision of specific community infrastructure. However, we have identified three fundamental weaknesses associated with the use of choropleth maps for socio-economic regionalisation. Therefore, as an alternative to the choropleth map if we think explicitly in R 3, then the best representation of the spatial distribution of a socioeconomic phenomenon is a smooth surface. The socio-economic data we use are collected during a national census of population and are summarised for areas, i.e., polygons. To accommodate these data we have developed and applied a method for gridding and smoothing termed regularisation in order to build a smooth surface. We apply Green s theorem and use path integrals with much simplification to compute a smoothed datum for each intersection of a, say, 100 by 100 grid that describes a surface. Mathematically, surface shape is interpreted through the comparison of curvatures. Surface shape analysis involves the measurement of the Gaussian and mean curvatures at the internal intersections of the grid. Curvature measurement requires at least a twice differentiable function. We have invented such a function based on Lagrange interpolation. It is called a Lagrange polynomial in x y. Each internal intersection of the grid is the (2, 2) element of a 3 3 matrix extracted from the grid. We compute a Lagrange polynomial in x y for each 3 3 matrix. Then we use this polynomial to measure the curvatures and classify the shape. Contiguous grid intersections of the same shape class comprise a shape neighbourhoods region interpreted as a specific manifestation of a socio-economic phenomenon. Hence, we have the basis for describing the spatial distribution of the phenomenon. Three investigations into the construction of quadratic polynomials as alternative functions are described. Two of these quadratic polynomials are called exact fit in the sense that the polynomial returns the exact z-datum associated with each xy-pair used in its construction. Construction of a best fit quadratic polynomial based on least squares interpolation comprises the third investigation. We compare the four different types of polynomials and of these we choose the Lagrange polynomial in x y as most appropriate. Given a relatively high density grid, e.g., 250 by 250, regardless of the polynomial used the resulting maps of shape neighbourhoods regions are virtually identical. This surprising convergence in R 2 is explained. Is a map of shape neighbourhoods regions an accurate description of the spatial distribution of a socio-economic phenomenon? We effect an indirect evaluation of a known phenomenon represented by the spatial distribution of f(x, y) = sin x sin y. We compute the true map of shape neighbourhoods regions of this phenomenon. An approximate map of shape neighbourhoods regions is computed by sampling with 100 randomly generated polygons. Comparison implies that the approximate map is an accurate representation of the true map. This conclusion is supported strongly by the results of a study of a nonperiodic nonrandom known phenomenon, based on a combination of exponential functions in x and y. This has a surface similar to that of a socio-economic phenomenon. We review selected geographic studies in which mathematical tools have been used for analytical purposes. Mathematical analysis is gaining broader acceptance in geography. The innovative, high quality Surpop work of British geographers is described, and we comment on the strongly complementary nature of the research presented in this thesis to the Surpop work. We describe 18 future research directions and themes; suggestions are made on how each may be undertaken. Next, we summarise each of the ten results of the research presented in this thesis. The thesis concludes with a statement of the medium-term research directions of the researcher and his acknowledgements. iii
4 CONTENTS Dedication Abstract Contents Statement of Originality and Consent Chapter 1 Justification Introduction An Example Using Choropleth Maps: Weaknesses and Difficulties 6 1) Data collection and summary data geometries 6 2) Complexity of data interpretation 8 3) Homogeneity and discontinuity The Nature of a Socio-Economic Region Thinking in R 3 The Design Principle for a New Mapping Methodology Structure and Content of this Thesis 22 Chapter 2 Regularisation Introduction Gridding and Smoothing Using Green s Theorem 28 1) Description 29 2) Derivation 30 3) Example 31 4) Data representation geometry 34 5) Burnside revisited Epilogue 39 Chapter 3 Classification Introduction Lagrange Polynomial in x y 43 1) A Lagrange Polynomial in x 43 2) A Lagrange Polynomial in x y Shape Neighbourhoods Engine 48 1) Calculating the first and second partial derivatives 48 2) Measuring the Gaussian and mean curvatures 48 3) Classifying the shape in the neighbourhood of an internal grid intersection 49 4) Mapping the shape neighbourhoods regions Simplification of a Lagrange Polynomial in x y 56 iv ii iii iv vii
5 Chapter 4 Approximation Introduction An Exact Fit Quadratic Polynomial A Hybrid Exact Fit Quadratic Polynomial A Best Fit Quadratic Polynomial Approximating Polynomial Functions 79 1) Which function should we use? 79 2) Convergence in R ) Spatial autocorrelation and extraction of overlapping 3 3 matrices 84 Chapter 5 Evaluation Introduction Evaluation Method Terminology and Overview 88 1) Terminology 88 2) Overview Evaluation Method Implementation Nature of the Spatial Distribution and Selection of the Level of Smoothing Evaluation of an Arbitrary Surface 105 1) Introduction 105 2) A mathematical function that describes a nonperiodic nonrandom surface 106 3) Point in polygon calculation of volume, area and average datum of a Voronoi polygon 110 4) Computation of an approximate surface and an approximate shape neighbourhoods map 111 5) Conclusion 111 Chapter 6 Conclusion Introduction Some Studies of Surfaces A Personal Overview 113 1) Some physical geographic studies of surfaces 114 2) Some human geographic studies of surfaces Research Directions 120 1) Markets for socio-economic regionalisation 120 2) Use of socio-economic regionalisation 120 3) Best practice socio-economic regionalisation 120 4) Data collection geometry 121 5) What is a socio-economic region? 121 v
6 6) Spatial cognition thinking in R 2 and R ) Smoothing by regularisation 121 8) Positioning of data collection centroids 121 9) Shape classification using functions describing polygons ) Shape classification using numerical values of Gaussian and mean curvatures ) Grid geometry ) Extraction of matrices from a grid and building of a function for a matrix element ) Polynomials and other functions ) Grid density and amount of smoothing ) Convergence in R ) Value of surfaces ) Evaluation of shape neighbourhoods regions ) Software Summary of Results of the Research 124 1) Weaknesses and difficulties associated with the use of choropleth maps 124 2) The nature of a socio-economic region 124 3) Spatial cognition in R 2 and R ) Gridding and smoothing using Green s theorem regularisation 125 5) Surface shape classification 125 6) Construction of a Lagrange polynomial in x y 125 7) The shape neighbourhoods engine 125 8) Alternative polynomial functions 126 9) Convergence in R ) Accuracy of the maps of shape neighbourhoods regions Conclusion and Acknowledgements 126 Appendices Appendix A 128 Appendix B 129 Appendix C 136 Appendix D 137 References 141 vi
7 STATEMENT OF ORIGINALITY AND CONSENT This work contains no material that has been accepted for the award of any other degree or diploma in any university or tertiary institution to John (Jack) Sirles Massey and, to the best of my knowledge and belief, contains no material previously published or written by another person, except where due reference has been made in the text. I give consent to this copy of my thesis, when deposited in the University Library, being available for loan and photocopying, subject to the provisions of the Copyright Act I also give permission for the digital version of my thesis to be made available on the web, via the University s digital research repository, the Library catalogue, the Australian Digital Theses Program (ADTP) and also through web search engines, unless permission has been granted by the University to restrict access for a period of time. SIGNED: DATE: John (Jack) Sirles Massey vii
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models
 Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
DATA MODELS IN GIS. Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi
 DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
Prentice Hall Pre-Algebra 2004 Correlated to: Hawaii Mathematics Content and Performance Standards (HCPS) II (Grades 9-12)
 Hawaii Mathematics Content and Performance Standards (HCPS) II (Grades 9-12) NUMBER AND OPERATIONS STANDARD 1: Students understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and
Hawaii Mathematics Content and Performance Standards (HCPS) II (Grades 9-12) NUMBER AND OPERATIONS STANDARD 1: Students understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and
Technology for Cadastral Applications. John R. Hacker, Jr. Marketing Manager Geospatial Applications
 Technology for Cadastral Applications John R. Hacker, Jr. Marketing Manager Geospatial Applications Agenda Cadastral Mapping Issues Precision and Accuracy Data Creation Data Management Data Publishing
Technology for Cadastral Applications John R. Hacker, Jr. Marketing Manager Geospatial Applications Agenda Cadastral Mapping Issues Precision and Accuracy Data Creation Data Management Data Publishing
Statistical surfaces and interpolation. This is lecture ten
 Statistical surfaces and interpolation This is lecture ten Data models for representation of surfaces So far have considered field and object data models (represented by raster and vector data structures).
Statistical surfaces and interpolation This is lecture ten Data models for representation of surfaces So far have considered field and object data models (represented by raster and vector data structures).
Contents. I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1
 page v Preface xiii I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1 1 Some model PDEs 3 1.1 Laplace s equation; elliptic BVPs... 3 1.1.1 Physical experiments modeled by Laplace s equation... 5 1.2 Other
page v Preface xiii I The Basic Framework for Stationary Problems 1 1 Some model PDEs 3 1.1 Laplace s equation; elliptic BVPs... 3 1.1.1 Physical experiments modeled by Laplace s equation... 5 1.2 Other
Scope and Sequence for the New Jersey Core Curriculum Content Standards
 Scope and Sequence for the New Jersey Core Curriculum Content Standards The following chart provides an overview of where within Prentice Hall Course 3 Mathematics each of the Cumulative Progress Indicators
Scope and Sequence for the New Jersey Core Curriculum Content Standards The following chart provides an overview of where within Prentice Hall Course 3 Mathematics each of the Cumulative Progress Indicators
Line Generalisation Algorithms Specific Theory
 Line Generalisation Algorithms Specific Theory Digital Generalisation Digital generalisation can be defined as the process of deriving, from a data source, a symbolically or digitally-encoded cartographic
Line Generalisation Algorithms Specific Theory Digital Generalisation Digital generalisation can be defined as the process of deriving, from a data source, a symbolically or digitally-encoded cartographic
PS Geometric Modeling Homework Assignment Sheet I (Due 20-Oct-2017)
 Homework Assignment Sheet I (Due 20-Oct-2017) Assignment 1 Let n N and A be a finite set of cardinality n = A. By definition, a permutation of A is a bijective function from A to A. Prove that there exist
Homework Assignment Sheet I (Due 20-Oct-2017) Assignment 1 Let n N and A be a finite set of cardinality n = A. By definition, a permutation of A is a bijective function from A to A. Prove that there exist
Mathematics Gap Analysis Phase I
 Mathematics Gap Analysis Phase I Organizing Structure: The Standards Compared to the Common Core College and Career Readiness Standards The Mathematics College and Career Readiness Standards (CCRS) are
Mathematics Gap Analysis Phase I Organizing Structure: The Standards Compared to the Common Core College and Career Readiness Standards The Mathematics College and Career Readiness Standards (CCRS) are
Finite Element Method. Chapter 7. Practical considerations in FEM modeling
 Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
Content Standard 1: Numbers, Number Sense, and Computation
 Content Standard 1: Numbers, Number Sense, and Computation Place Value Fractions Comparing and Ordering Counting Facts Estimating and Estimation Strategies Determine an approximate value of radical and
Content Standard 1: Numbers, Number Sense, and Computation Place Value Fractions Comparing and Ordering Counting Facts Estimating and Estimation Strategies Determine an approximate value of radical and
: What is Finite Element Analysis (FEA)?
 Q: What is Finite Element Analysis (FEA)? A1: It is a numerical technique for finding approximate solutions of partial differential equations (PDE) as well as of integral equations. The solution approach
Q: What is Finite Element Analysis (FEA)? A1: It is a numerical technique for finding approximate solutions of partial differential equations (PDE) as well as of integral equations. The solution approach
Content Descriptions Based on the Georgia Performance Standards. GPS Geometry
 Content Descriptions Based on the Georgia Performance Standards GPS Geometry Introduction The State Board of Education is required by Georgia law (A+ Educational Reform Act of 2000, O.C.G.A. 20-2-281)
Content Descriptions Based on the Georgia Performance Standards GPS Geometry Introduction The State Board of Education is required by Georgia law (A+ Educational Reform Act of 2000, O.C.G.A. 20-2-281)
STATISTICS (STAT) Statistics (STAT) 1
 Statistics (STAT) 1 STATISTICS (STAT) STAT 2013 Elementary Statistics (A) Prerequisites: MATH 1483 or MATH 1513, each with a grade of "C" or better; or an acceptable placement score (see placement.okstate.edu).
Statistics (STAT) 1 STATISTICS (STAT) STAT 2013 Elementary Statistics (A) Prerequisites: MATH 1483 or MATH 1513, each with a grade of "C" or better; or an acceptable placement score (see placement.okstate.edu).
Multidimensional Data and Modelling
 Multidimensional Data and Modelling 1 Problems of multidimensional data structures l multidimensional (md-data or spatial) data and their implementation of operations between objects (spatial data practically
Multidimensional Data and Modelling 1 Problems of multidimensional data structures l multidimensional (md-data or spatial) data and their implementation of operations between objects (spatial data practically
Contents. I Basics 1. Copyright by SIAM. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited.
 page v Preface xiii I Basics 1 1 Optimization Models 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Optimization: An Informal Introduction... 4 1.3 Linear Equations... 7 1.4 Linear Optimization... 10 Exercises... 12 1.5
page v Preface xiii I Basics 1 1 Optimization Models 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Optimization: An Informal Introduction... 4 1.3 Linear Equations... 7 1.4 Linear Optimization... 10 Exercises... 12 1.5
Matija Gubec International School Zagreb MYP 0. Mathematics
 Matija Gubec International School Zagreb MYP 0 Mathematics 1 MYP0: Mathematics Unit 1: Natural numbers Through the activities students will do their own research on history of Natural numbers. Students
Matija Gubec International School Zagreb MYP 0 Mathematics 1 MYP0: Mathematics Unit 1: Natural numbers Through the activities students will do their own research on history of Natural numbers. Students
GEOSPATIAL ENGINEERING COMPETENCIES. Geographic Information Science
 GEOSPATIAL ENGINEERING COMPETENCIES Geographic Information Science The character and structure of spatial information, its methods of capture, organisation, classification, qualification, analysis, management,
GEOSPATIAL ENGINEERING COMPETENCIES Geographic Information Science The character and structure of spatial information, its methods of capture, organisation, classification, qualification, analysis, management,
PATTERN CLASSIFICATION AND SCENE ANALYSIS
 PATTERN CLASSIFICATION AND SCENE ANALYSIS RICHARD O. DUDA PETER E. HART Stanford Research Institute, Menlo Park, California A WILEY-INTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane
PATTERN CLASSIFICATION AND SCENE ANALYSIS RICHARD O. DUDA PETER E. HART Stanford Research Institute, Menlo Park, California A WILEY-INTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane
Nonlinear Programming
 Nonlinear Programming SECOND EDITION Dimitri P. Bertsekas Massachusetts Institute of Technology WWW site for book Information and Orders http://world.std.com/~athenasc/index.html Athena Scientific, Belmont,
Nonlinear Programming SECOND EDITION Dimitri P. Bertsekas Massachusetts Institute of Technology WWW site for book Information and Orders http://world.std.com/~athenasc/index.html Athena Scientific, Belmont,
Game Mathematics. (12 Week Lesson Plan)
 Game Mathematics (12 Week Lesson Plan) Lesson 1: Set Theory Textbook: Chapter One (pgs. 1 15) We begin the course by introducing the student to a new vocabulary and set of rules that will be foundational
Game Mathematics (12 Week Lesson Plan) Lesson 1: Set Theory Textbook: Chapter One (pgs. 1 15) We begin the course by introducing the student to a new vocabulary and set of rules that will be foundational
Graphic Display of Vector Object
 What is GIS? GIS stands for Geographic Information Systems, although the term Geographic Information Science is gaining popularity. A GIS is a software platform for storing, organizing, viewing, querying,
What is GIS? GIS stands for Geographic Information Systems, although the term Geographic Information Science is gaining popularity. A GIS is a software platform for storing, organizing, viewing, querying,
MATHEMATICS Curriculum Grades 10 to 12
 MATHEMATICS Curriculum Grades 10 to 12 Grade 10 Number systems Algebraic Expressions expressions Products (Ch. 1) Factorisation Term 1 Exponents (Ch. 2) Number patterns (Ch. 3) (CH.4) Notation, rules,
MATHEMATICS Curriculum Grades 10 to 12 Grade 10 Number systems Algebraic Expressions expressions Products (Ch. 1) Factorisation Term 1 Exponents (Ch. 2) Number patterns (Ch. 3) (CH.4) Notation, rules,
Introduction to optimization methods and line search
 Introduction to optimization methods and line search Jussi Hakanen Post-doctoral researcher jussi.hakanen@jyu.fi How to find optimal solutions? Trial and error widely used in practice, not efficient and
Introduction to optimization methods and line search Jussi Hakanen Post-doctoral researcher jussi.hakanen@jyu.fi How to find optimal solutions? Trial and error widely used in practice, not efficient and
TEACHER CERTIFICATION STUDY GUIDE KNOWLEDGE OF MATHEMATICS THROUGH SOLVING...1
 TABLE OF CONTENTS COMPETENCY/SKILLS PG # COMPETENCY 1 KNOWLEDGE OF MATHEMATICS THROUGH PROBLEM SOLVING...1 Skill 1.1 Skill 1.2 Skill 1.3 Skill 1.4 Identify appropriate mathematical problems from real-world
TABLE OF CONTENTS COMPETENCY/SKILLS PG # COMPETENCY 1 KNOWLEDGE OF MATHEMATICS THROUGH PROBLEM SOLVING...1 Skill 1.1 Skill 1.2 Skill 1.3 Skill 1.4 Identify appropriate mathematical problems from real-world
Introduction to Objective Analysis
 Chapter 4 Introduction to Objective Analysis Atmospheric data are routinely collected around the world but observation sites are located rather randomly from a spatial perspective. On the other hand, most
Chapter 4 Introduction to Objective Analysis Atmospheric data are routinely collected around the world but observation sites are located rather randomly from a spatial perspective. On the other hand, most
COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION
 VOLUME COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION Robert M. Haralick University of Washington Linda G. Shapiro University of Washington A^ ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California
VOLUME COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION Robert M. Haralick University of Washington Linda G. Shapiro University of Washington A^ ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California
STUDY ON THE USE OF PUBLIC DATA CENTERS FOR IT INFRASTRUCTURE OUTSOURCING IN SRI LANKA
 'LIBRARY SlIJVfcRSlTY Of MORATUWA. SRI IAMIU UORATUWA jlhl»o»{!9cko t l STUDY ON THE USE OF PUBLIC DATA CENTERS FOR IT INFRASTRUCTURE OUTSOURCING IN SRI LANKA THE CASE OFSUNTEL LTD By G.A.A.D. KARAUNARATNE
'LIBRARY SlIJVfcRSlTY Of MORATUWA. SRI IAMIU UORATUWA jlhl»o»{!9cko t l STUDY ON THE USE OF PUBLIC DATA CENTERS FOR IT INFRASTRUCTURE OUTSOURCING IN SRI LANKA THE CASE OFSUNTEL LTD By G.A.A.D. KARAUNARATNE
Precalculus, Quarter 2, Unit 2.1. Trigonometry Graphs. Overview
 13 Precalculus, Quarter 2, Unit 2.1 Trigonometry Graphs Overview Number of instructional days: 12 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Convert between radian and degree measure. Determine the usefulness
13 Precalculus, Quarter 2, Unit 2.1 Trigonometry Graphs Overview Number of instructional days: 12 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Convert between radian and degree measure. Determine the usefulness
17/07/2013 RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES RASTER DATA MODEL& STRUCTURE TIN- TRIANGULAR IRREGULAR NETWORK
 RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES Space is subdivided into regular grids of square grid cells or other forms of polygonal meshes known as picture elements (pixels) the
RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES Space is subdivided into regular grids of square grid cells or other forms of polygonal meshes known as picture elements (pixels) the
The Automatic Design of Batch Processing Systems
 The Automatic Design of Batch Processing Systems by Barry Dwyer, M.A., D.A.E., Grad.Dip. A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Department of Computer Science University of Adelaide
The Automatic Design of Batch Processing Systems by Barry Dwyer, M.A., D.A.E., Grad.Dip. A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Department of Computer Science University of Adelaide
4.0 DIGITIZATION, EDITING AND STRUCTURING OF MAP DATA
 .0 DIGITIZATION, EDITING AND STRUCTURING OF MAP DATA The process of digitizing existing maps is a transformation from one analog) form of information to another digital) form. Data input is the operation
.0 DIGITIZATION, EDITING AND STRUCTURING OF MAP DATA The process of digitizing existing maps is a transformation from one analog) form of information to another digital) form. Data input is the operation
Anoka Hennepin K-12 Curriculum plan
 Anoka Hennepin K-12 Curriculum plan Department: Elementary Math Unit Title: Packages and Polygons (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Triangles and Beyond (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Everyday Math: Volume
Anoka Hennepin K-12 Curriculum plan Department: Elementary Math Unit Title: Packages and Polygons (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Triangles and Beyond (Blue Book, Geo and Measurement) Everyday Math: Volume
statistical mapping outline
 sara irina fabrikant statistical mapping volumetric data outline volumetric data areas: choropleth classification to class or not to class? evaluate classification solution design issues legend color 2
sara irina fabrikant statistical mapping volumetric data outline volumetric data areas: choropleth classification to class or not to class? evaluate classification solution design issues legend color 2
INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT 196 Rosemount, Minnesota Educating our students to reach their full potential
 INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT 196 Rosemount, Minnesota Educating our students to reach their full potential MINNESOTA MATHEMATICS STANDARDS Grades 9, 10, 11 I. MATHEMATICAL REASONING Apply skills of mathematical
INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT 196 Rosemount, Minnesota Educating our students to reach their full potential MINNESOTA MATHEMATICS STANDARDS Grades 9, 10, 11 I. MATHEMATICAL REASONING Apply skills of mathematical
Almost Curvature Continuous Fitting of B-Spline Surfaces
 Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 2 (1998), No. 1, 33 43 Almost Curvature Continuous Fitting of B-Spline Surfaces Márta Szilvási-Nagy Department of Geometry, Mathematical Institute, Technical University
Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 2 (1998), No. 1, 33 43 Almost Curvature Continuous Fitting of B-Spline Surfaces Márta Szilvási-Nagy Department of Geometry, Mathematical Institute, Technical University
Object-Based Classification & ecognition. Zutao Ouyang 11/17/2015
 Object-Based Classification & ecognition Zutao Ouyang 11/17/2015 What is Object-Based Classification The object based image analysis approach delineates segments of homogeneous image areas (i.e., objects)
Object-Based Classification & ecognition Zutao Ouyang 11/17/2015 What is Object-Based Classification The object based image analysis approach delineates segments of homogeneous image areas (i.e., objects)
Spline fitting tool for scientometric applications: estimation of citation peaks and publication time-lags
 Spline fitting tool for scientometric applications: estimation of citation peaks and publication time-lags By: Hicham Sabir Presentation to: 21 STI Conference, September 1th, 21 Description of the problem
Spline fitting tool for scientometric applications: estimation of citation peaks and publication time-lags By: Hicham Sabir Presentation to: 21 STI Conference, September 1th, 21 Description of the problem
Isometries. 1 Identifying Isometries
 Isometries 1 Identifying Isometries 1. Modeling isometries as dynamic maps. 2. GeoGebra files: isoguess1.ggb, isoguess2.ggb, isoguess3.ggb, isoguess4.ggb. 3. Guessing isometries. 4. What can you construct
Isometries 1 Identifying Isometries 1. Modeling isometries as dynamic maps. 2. GeoGebra files: isoguess1.ggb, isoguess2.ggb, isoguess3.ggb, isoguess4.ggb. 3. Guessing isometries. 4. What can you construct
Chapter 7 Practical Considerations in Modeling. Chapter 7 Practical Considerations in Modeling
 CIVL 7/8117 1/43 Chapter 7 Learning Objectives To present concepts that should be considered when modeling for a situation by the finite element method, such as aspect ratio, symmetry, natural subdivisions,
CIVL 7/8117 1/43 Chapter 7 Learning Objectives To present concepts that should be considered when modeling for a situation by the finite element method, such as aspect ratio, symmetry, natural subdivisions,
Point Lattices in Computer Graphics and Visualization how signal processing may help computer graphics
 Point Lattices in Computer Graphics and Visualization how signal processing may help computer graphics Dimitri Van De Ville Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Biomedical Imaging Group dimitri.vandeville@epfl.ch
Point Lattices in Computer Graphics and Visualization how signal processing may help computer graphics Dimitri Van De Ville Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Biomedical Imaging Group dimitri.vandeville@epfl.ch
Proposal of Research Activity. PhD Course in Space Sciences, Technologies and Measurements (STMS)
 Proposal of Research Activity PhD Course in Space Sciences, Technologies and Measurements (STMS) Curriculum: Sciences and Technologies for Aeronautics and Satellite Applications (STASA) XXXIV Cycle PhD
Proposal of Research Activity PhD Course in Space Sciences, Technologies and Measurements (STMS) Curriculum: Sciences and Technologies for Aeronautics and Satellite Applications (STASA) XXXIV Cycle PhD
Fundamentals of Digital Image Processing
 \L\.6 Gw.i Fundamentals of Digital Image Processing A Practical Approach with Examples in Matlab Chris Solomon School of Physical Sciences, University of Kent, Canterbury, UK Toby Breckon School of Engineering,
\L\.6 Gw.i Fundamentals of Digital Image Processing A Practical Approach with Examples in Matlab Chris Solomon School of Physical Sciences, University of Kent, Canterbury, UK Toby Breckon School of Engineering,
Foundation Level Learning Targets Version 2.2
 Milwaukee Public Schools High School Mathematics Foundation Level Learning Targets Version 2.2 Note: Non-Negotiable Learning Targets and descriptors are identified with an *. The specifications aligned
Milwaukee Public Schools High School Mathematics Foundation Level Learning Targets Version 2.2 Note: Non-Negotiable Learning Targets and descriptors are identified with an *. The specifications aligned
4.1.2 Merge Sort Sorting Lower Bound Counting Sort Sorting in Practice Solving Problems by Sorting...
 Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 What is Competitive Programming?... 1 1.1.1 Programming Contests.... 2 1.1.2 Tips for Practicing.... 3 1.2 About This Book... 3 1.3 CSES Problem Set... 5 1.4 Other Resources...
Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 What is Competitive Programming?... 1 1.1.1 Programming Contests.... 2 1.1.2 Tips for Practicing.... 3 1.2 About This Book... 3 1.3 CSES Problem Set... 5 1.4 Other Resources...
What can we represent as a Surface?
 Geography 38/42:376 GIS II Topic 7: Surface Representation and Analysis (Chang: Chapters 13 & 15) DeMers: Chapter 10 What can we represent as a Surface? Surfaces can be used to represent: Continuously
Geography 38/42:376 GIS II Topic 7: Surface Representation and Analysis (Chang: Chapters 13 & 15) DeMers: Chapter 10 What can we represent as a Surface? Surfaces can be used to represent: Continuously
OUTLINE. Quadratic Bezier Curves Cubic Bezier Curves
 BEZIER CURVES 1 OUTLINE Introduce types of curves and surfaces Introduce the types of curves Interpolating Hermite Bezier B-spline Quadratic Bezier Curves Cubic Bezier Curves 2 ESCAPING FLATLAND Until
BEZIER CURVES 1 OUTLINE Introduce types of curves and surfaces Introduce the types of curves Interpolating Hermite Bezier B-spline Quadratic Bezier Curves Cubic Bezier Curves 2 ESCAPING FLATLAND Until
Linear methods for supervised learning
 Linear methods for supervised learning LDA Logistic regression Naïve Bayes PLA Maximum margin hyperplanes Soft-margin hyperplanes Least squares resgression Ridge regression Nonlinear feature maps Sometimes
Linear methods for supervised learning LDA Logistic regression Naïve Bayes PLA Maximum margin hyperplanes Soft-margin hyperplanes Least squares resgression Ridge regression Nonlinear feature maps Sometimes
 Specific Objectives Students will understand that that the family of equation corresponds with the shape of the graph. Students will be able to create a graph of an equation by plotting points. In lesson
Specific Objectives Students will understand that that the family of equation corresponds with the shape of the graph. Students will be able to create a graph of an equation by plotting points. In lesson
Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics
 (Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Lag Mean Distance between pairs of points 1 Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places are related more than distant places Corollary:
(Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Lag Mean Distance between pairs of points 1 Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places are related more than distant places Corollary:
Natural Inclusion of Boundary Points in a Mesh
 http://people.sc.fsu.edu/ jburkardt/presentations/ new orleans 2005.pdf... John 1 Max Gunzburger 2 Hoa Nguyen 2 Yuki Saka 2 1 School of Computational Science Florida State University 2 Department of Mathematics
http://people.sc.fsu.edu/ jburkardt/presentations/ new orleans 2005.pdf... John 1 Max Gunzburger 2 Hoa Nguyen 2 Yuki Saka 2 1 School of Computational Science Florida State University 2 Department of Mathematics
CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 ME 475: Computer-Aided Design of Structures 1-1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Analysis versus Design 1.2 Basic Steps in Analysis 1.3 What is the Finite Element Method? 1.4 Geometrical Representation, Discretization
ME 475: Computer-Aided Design of Structures 1-1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Analysis versus Design 1.2 Basic Steps in Analysis 1.3 What is the Finite Element Method? 1.4 Geometrical Representation, Discretization
APPM/MATH Problem Set 4 Solutions
 APPM/MATH 465 Problem Set 4 Solutions This assignment is due by 4pm on Wednesday, October 16th. You may either turn it in to me in class on Monday or in the box outside my office door (ECOT 35). Minimal
APPM/MATH 465 Problem Set 4 Solutions This assignment is due by 4pm on Wednesday, October 16th. You may either turn it in to me in class on Monday or in the box outside my office door (ECOT 35). Minimal
Extracting Math from PostScript Documents
 Extracting Math from PostScript Documents Michael Yang Univ. Calif., Irvine Richard Fateman Univ. Calif, Berkeley ISSAC-2004 1 Why Extract Math from Documents? The current and recent past publications
Extracting Math from PostScript Documents Michael Yang Univ. Calif., Irvine Richard Fateman Univ. Calif, Berkeley ISSAC-2004 1 Why Extract Math from Documents? The current and recent past publications
Class #2. Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures
 Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Camera Model and Calibration
 Camera Model and Calibration Lecture-10 Camera Calibration Determine extrinsic and intrinsic parameters of camera Extrinsic 3D location and orientation of camera Intrinsic Focal length The size of the
Camera Model and Calibration Lecture-10 Camera Calibration Determine extrinsic and intrinsic parameters of camera Extrinsic 3D location and orientation of camera Intrinsic Focal length The size of the
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 36
 Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 In last class, we have derived element equations for two d elasticity problems
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 36 In last class, we have derived element equations for two d elasticity problems
X Std. Topic Content Expected Learning Outcomes Mode of Transaction
 X Std COMMON SYLLABUS 2009 - MATHEMATICS I. Theory of Sets ii. Properties of operations on sets iii. De Morgan s lawsverification using example Venn diagram iv. Formula for n( AÈBÈ C) v. Functions To revise
X Std COMMON SYLLABUS 2009 - MATHEMATICS I. Theory of Sets ii. Properties of operations on sets iii. De Morgan s lawsverification using example Venn diagram iv. Formula for n( AÈBÈ C) v. Functions To revise
IMPROVED MESOSCALE MATERIAL PROPERTY BOUNDS BASED ON VORONOI TESSELLATION OF STATISTICAL VOLUME ELEMENTS
 Meccanica dei Materiali e delle Strutture Vol. VI (216), no.1, pp. 179-186 ISSN: 235-679X Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile, Ambientale, Aerospaziale, Dei Materiali DICAM IMPROVED MESOSCALE MATERIAL PROPERTY
Meccanica dei Materiali e delle Strutture Vol. VI (216), no.1, pp. 179-186 ISSN: 235-679X Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile, Ambientale, Aerospaziale, Dei Materiali DICAM IMPROVED MESOSCALE MATERIAL PROPERTY
Introduction to Geospatial Analysis
 Introduction to Geospatial Analysis Introduction to Geospatial Analysis 1 Descriptive Statistics Descriptive statistics. 2 What and Why? Descriptive Statistics Quantitative description of data Why? Allow
Introduction to Geospatial Analysis Introduction to Geospatial Analysis 1 Descriptive Statistics Descriptive statistics. 2 What and Why? Descriptive Statistics Quantitative description of data Why? Allow
Spatial Interpolation - Geostatistics 4/3/2018
 Spatial Interpolation - Geostatistics 4/3/201 (Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Distance between pairs of points Lag Mean Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places
Spatial Interpolation - Geostatistics 4/3/201 (Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Distance between pairs of points Lag Mean Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places
Lecture 8. Divided Differences,Least-Squares Approximations. Ceng375 Numerical Computations at December 9, 2010
 Lecture 8, Ceng375 Numerical Computations at December 9, 2010 Computer Engineering Department Çankaya University 8.1 Contents 1 2 3 8.2 : These provide a more efficient way to construct an interpolating
Lecture 8, Ceng375 Numerical Computations at December 9, 2010 Computer Engineering Department Çankaya University 8.1 Contents 1 2 3 8.2 : These provide a more efficient way to construct an interpolating
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 24
 Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 24 So in today s class, we will look at quadrilateral elements; and we will
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 24 So in today s class, we will look at quadrilateral elements; and we will
Getting Started with Spatial Analyst. Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham
 Getting Started with Spatial Analyst Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham Workshop Overview Fundamentals of using Spatial Analyst What analysis capabilities exist and where to find them How to build a simple site
Getting Started with Spatial Analyst Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham Workshop Overview Fundamentals of using Spatial Analyst What analysis capabilities exist and where to find them How to build a simple site
GTPS Curriculum Mathematics Grade 8
 4.2.8.B2 Use iterative procedures to generate geometric patterns: Fractals (e.g., the Koch Snowflake); Self-similarity; Construction of initial stages; Patterns in successive stages (e.g., number of triangles
4.2.8.B2 Use iterative procedures to generate geometric patterns: Fractals (e.g., the Koch Snowflake); Self-similarity; Construction of initial stages; Patterns in successive stages (e.g., number of triangles
A C 2 Four-Point Subdivision Scheme with Fourth Order Accuracy and its Extensions
 A C 2 Four-Point Subdivision Scheme with Fourth Order Accuracy and its Extensions Nira Dyn School of Mathematical Sciences Tel Aviv University Michael S. Floater Department of Informatics University of
A C 2 Four-Point Subdivision Scheme with Fourth Order Accuracy and its Extensions Nira Dyn School of Mathematical Sciences Tel Aviv University Michael S. Floater Department of Informatics University of
Mathematics NC Math 3 Scope and Sequence 176 Instructional Days (Traditional) 88 Instructional Days (Block) 9 Units
 Mathematics NC Math 3 Scope and Sequence 176 Instructional () 88 Instructional () 9 Units Unit 1: Functions and Their Inverses NC.M3.F-BF.4a Understand the inverse relationship between exponential and
Mathematics NC Math 3 Scope and Sequence 176 Instructional () 88 Instructional () 9 Units Unit 1: Functions and Their Inverses NC.M3.F-BF.4a Understand the inverse relationship between exponential and
Introduction to Computer Graphics. Modeling (3) April 27, 2017 Kenshi Takayama
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Modeling (3) April 27, 2017 Kenshi Takayama Solid modeling 2 Solid models Thin shapes represented by single polygons Unorientable Clear definition of inside & outside
Introduction to Computer Graphics Modeling (3) April 27, 2017 Kenshi Takayama Solid modeling 2 Solid models Thin shapes represented by single polygons Unorientable Clear definition of inside & outside
240AR059 - Geometric Fundamentals for Robot Design
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 240 - ETSEIB - Barcelona School of Industrial Engineering 707 - ESAII - Department of Automatic Control MASTER'S DEGREE IN AUTOMATIC
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 240 - ETSEIB - Barcelona School of Industrial Engineering 707 - ESAII - Department of Automatic Control MASTER'S DEGREE IN AUTOMATIC
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems
 1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
Northern York County School District Curriculum
 Course Name Keystone Geometry (1.03 / 1.06 / 1.10) Grade Level Grade 10 Northern York County School District Curriculum Module Instructional Procedures Module 1: Geometric Properties and Reasoning Course
Course Name Keystone Geometry (1.03 / 1.06 / 1.10) Grade Level Grade 10 Northern York County School District Curriculum Module Instructional Procedures Module 1: Geometric Properties and Reasoning Course
Integration of Textural and Material Information Into Existing BIM Using IR Sensing. A research by: Asem Zabin Baha Khalil
 Integration of Textural and Material Information Into Existing BIM Using IR Sensing A research by: Asem Zabin Baha Khalil Asem Zabin Senior BIM Engineer at itech Management Consultancy Master of Science
Integration of Textural and Material Information Into Existing BIM Using IR Sensing A research by: Asem Zabin Baha Khalil Asem Zabin Senior BIM Engineer at itech Management Consultancy Master of Science
Force density method for simultaneous optimization of geometry and topology of spatial trusses
 25-28th September, 217, Hamburg, Germany Annette Bögle, Manfred Grohmann (eds.) Force density method for simultaneous optimization of geometry and topology of spatial trusses Kazuki Hayashi*, Makoto Ohsaki
25-28th September, 217, Hamburg, Germany Annette Bögle, Manfred Grohmann (eds.) Force density method for simultaneous optimization of geometry and topology of spatial trusses Kazuki Hayashi*, Makoto Ohsaki
CAN THE SUN S DIRECTION BE ESTIMATED PRIOR TO THE DETERMINATION OF SHAPE?
 CAN THE SUN S DIRECTION BE ESTIMATED PRIOR TO THE DETERMINATION OF SHAPE? WOJCIECH CHOJNACKI MICHAEL J. BROOKS Department of Computer Science, University of Adelaide Adelaide, SA 5005, Australia and DANIEL
CAN THE SUN S DIRECTION BE ESTIMATED PRIOR TO THE DETERMINATION OF SHAPE? WOJCIECH CHOJNACKI MICHAEL J. BROOKS Department of Computer Science, University of Adelaide Adelaide, SA 5005, Australia and DANIEL
MEI Desmos Tasks for AS Pure
 Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x² 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Select the points of intersection of the line and the curve. What
Task 1: Coordinate Geometry Intersection of a line and a curve 1. Add a quadratic curve, e.g. y = x² 4x + 1 2. Add a line, e.g. y = x 3 3. Select the points of intersection of the line and the curve. What
Geo372 Vertiefung GIScience. Spatial Interpolation
 Geo372 Vertiefung GIScience Spatial Interpolation Herbstsemester Ross Purves Last week We looked at data quality and integration We saw how uncertainty could be introduced by the concepts we chose, by
Geo372 Vertiefung GIScience Spatial Interpolation Herbstsemester Ross Purves Last week We looked at data quality and integration We saw how uncertainty could be introduced by the concepts we chose, by
1. Introduction. 2. Parametrization of General CCSSs. 3. One-Piece through Interpolation. 4. One-Piece through Boolean Operations
 Subdivision Surface based One-Piece Representation Shuhua Lai Department of Computer Science, University of Kentucky Outline. Introduction. Parametrization of General CCSSs 3. One-Piece through Interpolation
Subdivision Surface based One-Piece Representation Shuhua Lai Department of Computer Science, University of Kentucky Outline. Introduction. Parametrization of General CCSSs 3. One-Piece through Interpolation
Shape Modeling and Geometry Processing
 252-0538-00L, Spring 2018 Shape Modeling and Geometry Processing Discrete Differential Geometry Differential Geometry Motivation Formalize geometric properties of shapes Roi Poranne # 2 Differential Geometry
252-0538-00L, Spring 2018 Shape Modeling and Geometry Processing Discrete Differential Geometry Differential Geometry Motivation Formalize geometric properties of shapes Roi Poranne # 2 Differential Geometry
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images
 Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Investigation and Justification (Proof) Thread
 Concept Category 3 (CC3): Triangle Trigonometry Grounded in students study of similar triangles in CC2, students consider slope triangles in CC3 to learn about the relationship between the angles and the
Concept Category 3 (CC3): Triangle Trigonometry Grounded in students study of similar triangles in CC2, students consider slope triangles in CC3 to learn about the relationship between the angles and the
A numerical grid and grid less (Mesh less) techniques for the solution of 2D Laplace equation
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2014, 5(1):150-155 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC A numerical grid and grid less (Mesh less) techniques for
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2014, 5(1):150-155 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC A numerical grid and grid less (Mesh less) techniques for
CHAPTER 6 DETECTION OF MASS USING NOVEL SEGMENTATION, GLCM AND NEURAL NETWORKS
 130 CHAPTER 6 DETECTION OF MASS USING NOVEL SEGMENTATION, GLCM AND NEURAL NETWORKS A mass is defined as a space-occupying lesion seen in more than one projection and it is described by its shapes and margin
130 CHAPTER 6 DETECTION OF MASS USING NOVEL SEGMENTATION, GLCM AND NEURAL NETWORKS A mass is defined as a space-occupying lesion seen in more than one projection and it is described by its shapes and margin
Image Analysis - Lecture 5
 Texture Segmentation Clustering Review Image Analysis - Lecture 5 Texture and Segmentation Magnus Oskarsson Lecture 5 Texture Segmentation Clustering Review Contents Texture Textons Filter Banks Gabor
Texture Segmentation Clustering Review Image Analysis - Lecture 5 Texture and Segmentation Magnus Oskarsson Lecture 5 Texture Segmentation Clustering Review Contents Texture Textons Filter Banks Gabor
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
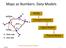 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
HS Geometry Mathematics CC
 Course Description This course involves the integration of logical reasoning and spatial visualization skills. It includes a study of deductive proofs and applications from Algebra, an intense study of
Course Description This course involves the integration of logical reasoning and spatial visualization skills. It includes a study of deductive proofs and applications from Algebra, an intense study of
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Quizzes Lab 8? WEEK EIGHT Lecture INTERPOLATION & SPATIAL ESTIMATION Joe Wheaton READING FOR TODAY WHAT CAN WE COLLECT AT POINTS?
HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Quizzes Lab 8? WEEK EIGHT Lecture INTERPOLATION & SPATIAL ESTIMATION Joe Wheaton READING FOR TODAY WHAT CAN WE COLLECT AT POINTS?
Correlation of the ALEKS courses Algebra 1 and High School Geometry to the Wyoming Mathematics Content Standards for Grade 11
 Correlation of the ALEKS courses Algebra 1 and High School Geometry to the Wyoming Mathematics Content Standards for Grade 11 1: Number Operations and Concepts Students use numbers, number sense, and number
Correlation of the ALEKS courses Algebra 1 and High School Geometry to the Wyoming Mathematics Content Standards for Grade 11 1: Number Operations and Concepts Students use numbers, number sense, and number
Conjectures concerning the geometry of 2-point Centroidal Voronoi Tessellations
 Conjectures concerning the geometry of 2-point Centroidal Voronoi Tessellations Emma Twersky May 2017 Abstract This paper is an exploration into centroidal Voronoi tessellations, or CVTs. A centroidal
Conjectures concerning the geometry of 2-point Centroidal Voronoi Tessellations Emma Twersky May 2017 Abstract This paper is an exploration into centroidal Voronoi tessellations, or CVTs. A centroidal
Assessment for all units is ongoing and continuous consisting of tests, assignments and reports. Most units have a final two-hour examination.
 Diploma of Computing Course Outline (T3, 2017) Campus Intake CRICOS Course Duration Teaching Methods Assessment Course Structure Units Melbourne Burwood Campus / Jakarta Campus, Indonesia March, June,
Diploma of Computing Course Outline (T3, 2017) Campus Intake CRICOS Course Duration Teaching Methods Assessment Course Structure Units Melbourne Burwood Campus / Jakarta Campus, Indonesia March, June,
MODERN DESCRIPTIVE GEOMETRY SUPPORTED BY 3D COMPUTER MODELLING
 International Conference on Mathematics Textbook Research and Development 2014 () 29-31 July 2014, University of Southampton, UK MODERN DESCRIPTIVE GEOMETRY SUPPORTED BY 3D COMPUTER MODELLING Petra Surynková
International Conference on Mathematics Textbook Research and Development 2014 () 29-31 July 2014, University of Southampton, UK MODERN DESCRIPTIVE GEOMETRY SUPPORTED BY 3D COMPUTER MODELLING Petra Surynková
05 - Surfaces. Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung. CSCI-GA Geometric Modeling - Daniele Panozzo
 05 - Surfaces Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung Reminder Curves Turning Number Theorem Continuous world Discrete world k: Curvature is scale dependent is scale-independent Discrete Curvature Integrated
05 - Surfaces Acknowledgements: Olga Sorkine-Hornung Reminder Curves Turning Number Theorem Continuous world Discrete world k: Curvature is scale dependent is scale-independent Discrete Curvature Integrated
Model-based segmentation and recognition from range data
 Model-based segmentation and recognition from range data Jan Boehm Institute for Photogrammetry Universität Stuttgart Germany Keywords: range image, segmentation, object recognition, CAD ABSTRACT This
Model-based segmentation and recognition from range data Jan Boehm Institute for Photogrammetry Universität Stuttgart Germany Keywords: range image, segmentation, object recognition, CAD ABSTRACT This
Simplified Voronoi diagrams for motion planning of quadratically-solvable Gough-Stewart platforms
 Simplified Voronoi diagrams for motion planning of quadratically-solvable Gough-Stewart platforms Rubén Vaca, Joan Aranda, and Federico Thomas Abstract The obstacles in Configuration Space of quadratically-solvable
Simplified Voronoi diagrams for motion planning of quadratically-solvable Gough-Stewart platforms Rubén Vaca, Joan Aranda, and Federico Thomas Abstract The obstacles in Configuration Space of quadratically-solvable
1. Introduction. performance of numerical methods. complexity bounds. structural convex optimization. course goals and topics
 1. Introduction EE 546, Univ of Washington, Spring 2016 performance of numerical methods complexity bounds structural convex optimization course goals and topics 1 1 Some course info Welcome to EE 546!
1. Introduction EE 546, Univ of Washington, Spring 2016 performance of numerical methods complexity bounds structural convex optimization course goals and topics 1 1 Some course info Welcome to EE 546!
Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision
 Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision Prasanna Sahoo Department of Mathematics University of Louisville 1 Structure Computation Lecture 18 March 22, 2005 2 3D Reconstruction The goal of 3D reconstruction
Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision Prasanna Sahoo Department of Mathematics University of Louisville 1 Structure Computation Lecture 18 March 22, 2005 2 3D Reconstruction The goal of 3D reconstruction
An introduction to interpolation and splines
 An introduction to interpolation and splines Kenneth H. Carpenter, EECE KSU November 22, 1999 revised November 20, 2001, April 24, 2002, April 14, 2004 1 Introduction Suppose one wishes to draw a curve
An introduction to interpolation and splines Kenneth H. Carpenter, EECE KSU November 22, 1999 revised November 20, 2001, April 24, 2002, April 14, 2004 1 Introduction Suppose one wishes to draw a curve
TEKS Clarification Document. Mathematics Precalculus
 TEKS Clarification Document Mathematics Precalculus 2012 2013 111.31. Implementation of Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Mathematics, Grades 9-12. Source: The provisions of this 111.31 adopted
TEKS Clarification Document Mathematics Precalculus 2012 2013 111.31. Implementation of Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Mathematics, Grades 9-12. Source: The provisions of this 111.31 adopted
SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015
 SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 GIS Data Organization The basics Data can be organized in a variety of ways Spatial location, content (attributes), frequency of use Come up with a system
SPATIAL DATA MODELS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 GIS Data Organization The basics Data can be organized in a variety of ways Spatial location, content (attributes), frequency of use Come up with a system
Segmentation and Grouping
 Segmentation and Grouping How and what do we see? Fundamental Problems ' Focus of attention, or grouping ' What subsets of pixels do we consider as possible objects? ' All connected subsets? ' Representation
Segmentation and Grouping How and what do we see? Fundamental Problems ' Focus of attention, or grouping ' What subsets of pixels do we consider as possible objects? ' All connected subsets? ' Representation
