Math 4. Class work 2. Algebra. Sets.
|
|
|
- Harry Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 4. Class work 2. Algebra. Sets. I put a skirt, a book, a toothbrush, a coffee mug, and an apple into a bag. Can we call this collection of items a set? Do all these objects have something in common? A set is a collection of objects that have something in common. There are two ways of describing, or specifying, the members of a set. One way is by listing each member of the set: A = {2, 4, 6, 8} B = {d, e, s, k}. The second way is by using a rule: C is the set of four first even natural numbers. D is the set of letters of the word "desk". Venn diagram. Two sets are equal if they contain exactly the same elements. If we look closer on our sets A and C we can see that all elements of set A are the same as elements of set C (same goes for sets B and D). A=C and B=D
2 If set A contains element '2', then we can tell that element '2' belongs to set A. We have a special symbol to write it down in a shorter way: 2 A, 105A. (What does this statement mean?) Let's define several sets. Set W will be the set of all words of the English language. Set N will be the set of all nouns existing in the English language. Set Z will be the set of all English nouns which have only 5 letters. Set T={"table"}. On a Venn diagram below name all these sets: If all elements of one set at the same time belong to another set then we can say that the first set is a subset of the second one. We have another special symbol to write this statement in a shorter way:. T Z Y W If set V is defined as a set of all English verbs, can you draw a diagram for set V on the picture above? Can you tell subset of which set V is? V V V V
3 When several sets are defined it can happened that in accordance with all the rules we have implied several objects can belong to several sets at the same time. For example, on a picture below set S is a set of squares and a set R is a set of red figures. Figures 3 and 4 are squares and they are red, therefore they belong to both sets. Thus we can describe a new set X containing elements that belong to the set S as well as to the set R. The new set was constructed by determining which members of two sets have the features of both sets. This statement also can be written down in a shorter version by using a special symbol. Such set X is called an intersection of sets S and R. X = S R Another new set can be created by combining all elements of either sets (in our case S and R). Using symbol we can easily write the sentence: Set Y contains all elements of set S and set R: Y = S R
4 Such set Y is called a union of set S and R. Set which does not have any element called an empty set in math people use symbol ). element belongs to a set element does not belong to a set one set is a subset of another set one set is not a subset of another set intersection of two sets union of two sets empty set Exercises: 1. A = {a, b, c}, B = {1, 2, 3, 4}. Write the intersection (A B) and the union (A B ) of these two sets. 2. There are 20 students in a Math class. 10 students like apples and 15 students like pears. Show that there are some students who like both apples and pears. Assume that each student likes at least one of the fruits. (This means that each student like either apples, or pears, or both). How many students like both pears and apples? Is it possible to determine if there any students who do not like apples and do not like pears? If yes, explain how you can do it. If no, demonstrate by giving examples.
5 3. The same Math class (with 20 students) forms a soccer team and a basketball team. Every student signs up for at least one team: 12 students play only soccer; 2 students play both soccer and basketball; How many students play basketball only? 4. Students who participated in math coopetition had to solve 2 problems, one in algebra and another in geometry. Among 100 students 65 solved algebra problem, 45 solved geometry problem, 20 students solved both problems. How many students didn t solve any problem at all? students from New-York and Seattle attended a math camp. Of the total number of students, 125 were boys. 65 boys were from New-York. There were 53 girls from Seattle. How many students came from New- York? 6. In 2 boxes there are 160 notebooks altogether. In one box there are 20 more notebooks than in the other. How many notebooks are there in each box? 7. Place parentheses into the following expression so that the statement is true. a = 5 b : 4 = 66 c. 24: = 1 d : 3 = 8 e. 64: = 2 f. 63: = 1 g : = John came to a lemonade stand with a big empty pitcher which can hold 5 liters of lemonade. He wanted to buy only 1 liter of lemonade, but a merchant had jars which can hold 3 liters and 2 liters of liquid. How merchant can measure 1 l. of lemonade if jars do not have any marks on them? Next time when John came to the stand with exactly the same pitcher, the merchant had only 3l and 5l jars. Can he sell to John exactly 4 l of lemonade?
6 Geometry. A definition is a statement of the meaning of a something (term, word, another statement). desk noun noun: desk; plural noun: desks 1. a piece of furniture with a flat or sloped surface and typically with drawers, at which one can read, write, or do other work. o o iting table, bureau, escritoire, secretaire, rolltop desk, carrel, nonyms: orkstation, worktable Music a position in an orchestra at which two players share a music stand. "an extra desk of first and second violins" a counter in a hotel, bank, or airport at which a customer may check in or obtain information. "the reception desk" In mathematics everything (mmm,,,, almost everything) should be very well defined. In our real life it is also very useful and convenient to agree about terms and concepts, to give them a definition, before starting using them just to be sure that everybody knows what they are talking about. Now we move to geometry. Can we give a definition to a point? Can we clearly define what a point is? What a line is? What a plane is? Mathematicians decided do not define terms "point", "straight line", and "plane" and to rely upon intuitive understanding of these terms.
7 Point (an undefined term). In geometry, a point has no dimension (actual size), point is an exact location in space. Although we represent a point with a dot, the point has no length, width, or thickness. Our dot can be very tiny or very large and it still represents a point. A point is usually named with a capital letter. Line (an undefined term). In geometry, a line has no thickness but its length extends in one dimension and goes on forever in both directions. Unless otherwise stated a line is drawn as a straight line with two arrowheads indicating that the line extends without end in both directions (or without them). A line is named by a single lowercase letter, m for example, or by any two points on the line, AB or AB. Plane (an undefined term). In geometry, a plane has no thickness but extends indefinitely in all directions. Planes are usually represented by a shape that looks like a parallelogram. Even though the diagram of a plane has edges, you must remember that the plane has no boundaries. A plane is named by a single letter (plane p) or by three non-collinear points (plane ABC).
8 A line segment is a part of a straight line between two chosen points. (A set of points of a straight line between two points.) These points are called endpoints. A ray is a part of a straight line consisting of a point (endpoint) and all points of a straight line at one side of an endpoint. Ray is named by endpoint and any other point, ray AB or AB (where A is an endpoint) Exercises: 1. Draw two line segments AB and CD in such way that their intersect a. by a point b. by a segment c. don t intersect at all. 2. Using a ruler draw a straight line, put on it 3 points, A, B, and C so that 2 rays are formed, BC and BA. 3. Draw two rays AB and CD in such way that their intersect d. by a point e. by a segment f. by a ray g. don t intersect at all 4. On the segment AB mark a point M. How many segments do we have on the picture? Mark another point P. How many segments do we have now? Mark a third point F. Count segments. How many segments will be if you mark 5 points? 10 points? 99 points?
Accelerated Math. Class work 1. Algebra. 1. Can you compare Compute by the most convenient way:
 Accelerated Math. Class work 1. Algebra. 1. Can you compare 9 + 19 + 9 + 39 + 47 + 69 200 2. Compute by the most convenient way: a) (179 + 94) + 21 = b) (356 + 849) + (51 + 644) = c) 99 + 99 + 99 + 99
Accelerated Math. Class work 1. Algebra. 1. Can you compare 9 + 19 + 9 + 39 + 47 + 69 200 2. Compute by the most convenient way: a) (179 + 94) + 21 = b) (356 + 849) + (51 + 644) = c) 99 + 99 + 99 + 99
1. Basic Concepts in Geometry
 1. Basic Concepts in Geometry Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of Geometry Introduction: The field of Geometry was developed when ancient mathematicians made efforts to measure the earth. This is how the word
1. Basic Concepts in Geometry Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of Geometry Introduction: The field of Geometry was developed when ancient mathematicians made efforts to measure the earth. This is how the word
Vocabulary Point- Line- Plane- Ray- Line segment- Congruent-
 * Geometry Overview Vocabulary Point- an exact location. It is usually represented as a dot, but it has no size at all. Line- a straight path that extends without end in opposite directions. Plane- a flat
* Geometry Overview Vocabulary Point- an exact location. It is usually represented as a dot, but it has no size at all. Line- a straight path that extends without end in opposite directions. Plane- a flat
Terms, notation, and representation Student Activity Sheet 1; use with Overview
 Student: Class: Date: Student Activity Sheet 1; use with Overview 1. REEVVI IEEW Graph the following points on the coordinate plane. A (1,4) B (-5,0) C (0,8) D (3,-5) E (0,-2) F (-8,-4) G (4,0) H (-7,7)
Student: Class: Date: Student Activity Sheet 1; use with Overview 1. REEVVI IEEW Graph the following points on the coordinate plane. A (1,4) B (-5,0) C (0,8) D (3,-5) E (0,-2) F (-8,-4) G (4,0) H (-7,7)
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships
 Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Points Lines and Planes. Unit 1 Lesson 2
 Unit 1 Lesson 2 Students will be able to: Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, and planes. Identify points, lines, line segments, rays and planes. Know precise definitions of line, and line segment,
Unit 1 Lesson 2 Students will be able to: Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, and planes. Identify points, lines, line segments, rays and planes. Know precise definitions of line, and line segment,
Lesson Plan #001. Class: Geometry Date: Wednesday September 9 th, 2015
 Lesson Plan #001 1 Class: Geometry Date: Wednesday September 9 th, 2015 Topic: Points, lines, and planes Aim: What are points, lines and planes? Objectives: 1) Students will be able to describe what is
Lesson Plan #001 1 Class: Geometry Date: Wednesday September 9 th, 2015 Topic: Points, lines, and planes Aim: What are points, lines and planes? Objectives: 1) Students will be able to describe what is
A point is pictured by a dot. While a dot must have some size, the point it represents has no size. Points are named by capital letters..
 Chapter 1 Points, Lines & Planes s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My guess that you might already be pretty familiar with many
Chapter 1 Points, Lines & Planes s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My guess that you might already be pretty familiar with many
3RD GRADE COMMON CORE VOCABULARY M-Z
 o o o 3RD GRADE COMMON CORE VOCABULARY M-Z mass mass mass The amount of matter in an object. Usually measured by comparing with an object of known mass. While gravity influences weight, it does not affect
o o o 3RD GRADE COMMON CORE VOCABULARY M-Z mass mass mass The amount of matter in an object. Usually measured by comparing with an object of known mass. While gravity influences weight, it does not affect
English 3 rd Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 1/13/14
 English 3 rd Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 1/13/14 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah State
English 3 rd Grade M-Z Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: 1/13/14 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah State
Patterns in Geometry. Polygons. Investigation 1 UNIT. Explore. Vocabulary. Think & Discuss
 UNIT K Patterns in Geometry In this lesson, you will work with two-dimensional geometric figures. You will classify polygons and find angle measures. Explore Inv 1 Polygons 172 How many squares are in
UNIT K Patterns in Geometry In this lesson, you will work with two-dimensional geometric figures. You will classify polygons and find angle measures. Explore Inv 1 Polygons 172 How many squares are in
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships
 Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Euclid. Father of Geometry Euclidean Geometry Euclid s Elements
 Euclid Father of Geometry Euclidean Geometry Euclid s Elements Point Description Indicates a location and has no size. How to Name it You can represent a point by a dot and name it by a capital letter.
Euclid Father of Geometry Euclidean Geometry Euclid s Elements Point Description Indicates a location and has no size. How to Name it You can represent a point by a dot and name it by a capital letter.
Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
Geometry. Students at Dommerich Elementary helped design and construct a mosaic to show parts of their community and local plants and animals.
 Geometry Describing and analyzing two-dimensional shapes Students at Dommerich Elementary helped design and construct a mosaic to show parts of their community and local plants and animals. 479 Make a
Geometry Describing and analyzing two-dimensional shapes Students at Dommerich Elementary helped design and construct a mosaic to show parts of their community and local plants and animals. 479 Make a
Geometry - Chapter 1 - Corrective #1
 Class: Date: Geometry - Chapter 1 - Corrective #1 Short Answer 1. Sketch a figure that shows two coplanar lines that do not intersect, but one of the lines is the intersection of two planes. 2. Name two
Class: Date: Geometry - Chapter 1 - Corrective #1 Short Answer 1. Sketch a figure that shows two coplanar lines that do not intersect, but one of the lines is the intersection of two planes. 2. Name two
Definition 1 (Hand-shake model). A hand shake model is an incidence geometry for which every line has exactly two points.
 Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe Name: All3181\3181_spr13t1.tex 1 Solution of Test I Definition 1 (Hand-shake model). A hand shake model is an incidence geometry for which every line has exactly two points. Definition
Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe Name: All3181\3181_spr13t1.tex 1 Solution of Test I Definition 1 (Hand-shake model). A hand shake model is an incidence geometry for which every line has exactly two points. Definition
Geometry 1-1. Non-collinear Points not on the same line. Need at least 3 points to be non-collinear since two points are always collinear
 Name Geometry 1-1 Undefined terms terms which cannot be defined only described. Point, line, plane Point a location in space Line a series of points that extends indefinitely in opposite directions. It
Name Geometry 1-1 Undefined terms terms which cannot be defined only described. Point, line, plane Point a location in space Line a series of points that extends indefinitely in opposite directions. It
Describe Plane Shapes
 Lesson 12.1 Describe Plane Shapes You can use math words to describe plane shapes. point an exact position or location line endpoints line segment ray a straight path that goes in two directions without
Lesson 12.1 Describe Plane Shapes You can use math words to describe plane shapes. point an exact position or location line endpoints line segment ray a straight path that goes in two directions without
Summer Review for incoming Geometry students (all levels)
 Name: 2017-2018 Mathematics Teacher: Summer Review for incoming Geometry students (all levels) Please complete this review packet for the FIRST DAY OF CLASS. The problems included in this packet will provide
Name: 2017-2018 Mathematics Teacher: Summer Review for incoming Geometry students (all levels) Please complete this review packet for the FIRST DAY OF CLASS. The problems included in this packet will provide
4 Mathematics Curriculum. Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1. Topic B: Angle Measurement... 4.B.1
 New York State Common Core 4 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E Table of Contents GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Angle Measure and Plane Figures GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1
New York State Common Core 4 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E Table of Contents GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Angle Measure and Plane Figures GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1
Geometric Constructions
 HISTORY OF MATHEMATICS Spring 2005 Geometric Constructions Notes, activities, assignment; #3 in a series. Note: I m not giving a specific due date for this somewhat vague assignment. The idea is that it
HISTORY OF MATHEMATICS Spring 2005 Geometric Constructions Notes, activities, assignment; #3 in a series. Note: I m not giving a specific due date for this somewhat vague assignment. The idea is that it
 Tools of Geometry 1. X + 9 = 24 2. 25 X = 15 3. X + 3 = -2X -10 4. 3X + 4Y = 2 Place in slope intercept form. 5. Y = ½ X 2 What is the slope? What is the Y- Intercept? Inductive Reasoning is reasoning
Tools of Geometry 1. X + 9 = 24 2. 25 X = 15 3. X + 3 = -2X -10 4. 3X + 4Y = 2 Place in slope intercept form. 5. Y = ½ X 2 What is the slope? What is the Y- Intercept? Inductive Reasoning is reasoning
Definitions. You can represent a point by a dot and name it by a capital letter.
 Definitions Name Block Term Definition Notes Sketch Notation Point A location in space that is represented by a dot and has no dimension You can represent a point by a dot and name it by a capital letter.
Definitions Name Block Term Definition Notes Sketch Notation Point A location in space that is represented by a dot and has no dimension You can represent a point by a dot and name it by a capital letter.
GEOMETRY BASIC GEOMETRICAL IDEAS. 3) A point has no dimensions (length, breadth or thickness).
 CLASS 6 - GEOMETRY BASIC GEOMETRICAL IDEAS Geo means Earth and metron means Measurement. POINT 1) The most basic shape in geometry is the Point. 2) A point determines a location. 3) A point has no dimensions
CLASS 6 - GEOMETRY BASIC GEOMETRICAL IDEAS Geo means Earth and metron means Measurement. POINT 1) The most basic shape in geometry is the Point. 2) A point determines a location. 3) A point has no dimensions
Commutative property. Associative property. Distributive property
 Math 4. Class work 4. Algebra Addition Multiplication a+b=b+a Commutative a b=b a a+(b+c)=(a+b)+c Associative a (b c)=(a b) c Distributive a (b+c)=a b + a c a (b c)=a b a c Commutative and associative
Math 4. Class work 4. Algebra Addition Multiplication a+b=b+a Commutative a b=b a a+(b+c)=(a+b)+c Associative a (b c)=(a b) c Distributive a (b+c)=a b + a c a (b c)=a b a c Commutative and associative
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 7th Grade Unit 8
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 7th Grade Unit 8 Unit 8 Geometry Math 708 Geometry Introduction 3 1. Basic Geometry 5 Introduction to Geometry 5 Special Pairs of Angles 12 Polygons 20 Circles 27 Self Test 1: Basic Geometry
MATH STUDENT BOOK 7th Grade Unit 8 Unit 8 Geometry Math 708 Geometry Introduction 3 1. Basic Geometry 5 Introduction to Geometry 5 Special Pairs of Angles 12 Polygons 20 Circles 27 Self Test 1: Basic Geometry
Angles, Polygons, Circles
 Page 1 of 5 Part One Last week we learned about the angle properties of circles and used them to solve a simple puzzle. This week brings a new puzzle that will make us use our algebra a bit more. But first,
Page 1 of 5 Part One Last week we learned about the angle properties of circles and used them to solve a simple puzzle. This week brings a new puzzle that will make us use our algebra a bit more. But first,
Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms
 Unit 1 asics of Geometry Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms 1. Point has no dimension, geometrically looks
Unit 1 asics of Geometry Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms 1. Point has no dimension, geometrically looks
Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions
 Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Variable is a letter or symbol that represents a number. Variable (algebraic)
Objective- Students will be able to use the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions. Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Variable is a letter or symbol that represents a number. Variable (algebraic)
Day 1. I m greeting at the door. They come in and something is waiting for them. This sets the year off right as far as I m concerned.
 Day 1 1. Pick a seat. Any seat. 2. Get a sheet. The circle sheet. 3. Cut out the circle. 4. Draw your face on the circle. 5. Hurry. We use time well in this class. I m greeting at the door. They come in
Day 1 1. Pick a seat. Any seat. 2. Get a sheet. The circle sheet. 3. Cut out the circle. 4. Draw your face on the circle. 5. Hurry. We use time well in this class. I m greeting at the door. They come in
Reporting Category 3. Geometry and Measurement BINGO
 Reporting Category 3 Geometry and Measurement BINGO names an exact location in space, named by a capital letter Has NO width, length, or depth. 2 a straight path with 2 endpoints, has a definite beginning
Reporting Category 3 Geometry and Measurement BINGO names an exact location in space, named by a capital letter Has NO width, length, or depth. 2 a straight path with 2 endpoints, has a definite beginning
PLANE GEOMETRY SKILL BUILDER ELEVEN
 PLANE GEOMETRY SKILL BUILDER ELEVEN Lines, Segments, and Rays The following examples should help you distinguish between lines, segments, and rays. The three undefined terms in geometry are point, line,
PLANE GEOMETRY SKILL BUILDER ELEVEN Lines, Segments, and Rays The following examples should help you distinguish between lines, segments, and rays. The three undefined terms in geometry are point, line,
1 Appendix to notes 2, on Hyperbolic geometry:
 1230, notes 3 1 Appendix to notes 2, on Hyperbolic geometry: The axioms of hyperbolic geometry are axioms 1-4 of Euclid, plus an alternative to axiom 5: Axiom 5-h: Given a line l and a point p not on l,
1230, notes 3 1 Appendix to notes 2, on Hyperbolic geometry: The axioms of hyperbolic geometry are axioms 1-4 of Euclid, plus an alternative to axiom 5: Axiom 5-h: Given a line l and a point p not on l,
1.1 Points, Lines, and Planes
 1.1 Points, Lines, and Planes Identify and model points, lines and planes. Identify collinear, and coplanar points and intersecting lines and planes in the space. Vocabulary Point, line, plane, collinear,
1.1 Points, Lines, and Planes Identify and model points, lines and planes. Identify collinear, and coplanar points and intersecting lines and planes in the space. Vocabulary Point, line, plane, collinear,
Lesson 2: Basic Concepts of Geometry
 : Basic Concepts of Geometry Learning Target I can identify the difference between a figure notation and its measurements I can list collinear and non collinear points I can find the distance / length
: Basic Concepts of Geometry Learning Target I can identify the difference between a figure notation and its measurements I can list collinear and non collinear points I can find the distance / length
Basics of Geometry Unit 1 - Notes. Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes.
 asics of Geometry Unit 1 - Notes Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms 1. Point has no dimension, geometrically
asics of Geometry Unit 1 - Notes Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms 1. Point has no dimension, geometrically
Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 7 Geometry First Edition
 Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 7 Geometry First Edition Lesson 1 Basic Geometric Concepts and Figures TOPICS 7.1.1 Figures in 1 and 2 Dimensions 1 Identify and define points, lines, line segments,
Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 7 Geometry First Edition Lesson 1 Basic Geometric Concepts and Figures TOPICS 7.1.1 Figures in 1 and 2 Dimensions 1 Identify and define points, lines, line segments,
(2 1) What does evaluate to? What does evaluate to? What does evaluate to?
 Order of Operations (Time 20 minutes) Math is a language, just like English, Spanish, or any other language. We use nouns, like "bread", "tomato", "mustard" and "cheese" to describe physical objects. Math
Order of Operations (Time 20 minutes) Math is a language, just like English, Spanish, or any other language. We use nouns, like "bread", "tomato", "mustard" and "cheese" to describe physical objects. Math
Mrs. Daniel s Geometry Vocab List
 Mrs. Daniel s Geometry Vocab List Geometry Definition: a branch of mathematics concerned with questions of shape, size, relative position of figures, and the properties of space. Reflectional Symmetry
Mrs. Daniel s Geometry Vocab List Geometry Definition: a branch of mathematics concerned with questions of shape, size, relative position of figures, and the properties of space. Reflectional Symmetry
TOPIC 2 Building Blocks of Geometry. Good Luck To
 Good Luck To Period Date PART I DIRECTIONS: Use the Terms (page 2), Definitions (page 3), and Diagrams (page 4) to complete the table Term (capital letters) 1. Chord 2. Definition (roman numerals) Pictures
Good Luck To Period Date PART I DIRECTIONS: Use the Terms (page 2), Definitions (page 3), and Diagrams (page 4) to complete the table Term (capital letters) 1. Chord 2. Definition (roman numerals) Pictures
Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry
 Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Goals: 1) learn to draw conclusions based on patterns 2) learn the building blocks for the structure of geometry 3) learn to measure line segments and angles 4) understand the
Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry Goals: 1) learn to draw conclusions based on patterns 2) learn the building blocks for the structure of geometry 3) learn to measure line segments and angles 4) understand the
And Now From a New Angle Special Angles and Postulates LEARNING GOALS
 And Now From a New Angle Special Angles and Postulates LEARNING GOALS KEY TERMS. In this lesson, you will: Calculate the complement and supplement of an angle. Classify adjacent angles, linear pairs, and
And Now From a New Angle Special Angles and Postulates LEARNING GOALS KEY TERMS. In this lesson, you will: Calculate the complement and supplement of an angle. Classify adjacent angles, linear pairs, and
Euclid s Muse Directions
 Euclid s Muse Directions First: Draw and label three columns on your chart paper as shown below. Name Picture Definition Tape your cards to the chart paper (3 per page) in the appropriate columns. Name
Euclid s Muse Directions First: Draw and label three columns on your chart paper as shown below. Name Picture Definition Tape your cards to the chart paper (3 per page) in the appropriate columns. Name
9. MATHEMATICIANS ARE FOND OF COLLECTIONS
 get the complete book: http://wwwonemathematicalcatorg/getfulltextfullbookhtm 9 MATHEMATICIANS ARE FOND OF COLLECTIONS collections Collections are extremely important in life: when we group together objects
get the complete book: http://wwwonemathematicalcatorg/getfulltextfullbookhtm 9 MATHEMATICIANS ARE FOND OF COLLECTIONS collections Collections are extremely important in life: when we group together objects
GEOMETRY HONORS COORDINATE GEOMETRY PACKET
 GEOMETRY HONORS COORDINATE GEOMETRY PACKET Name Period 1 Day 1 - Directed Line Segments DO NOW Distance formula 1 2 1 2 2 2 D x x y y Midpoint formula x x, y y 2 2 M 1 2 1 2 Slope formula y y m x x 2 1
GEOMETRY HONORS COORDINATE GEOMETRY PACKET Name Period 1 Day 1 - Directed Line Segments DO NOW Distance formula 1 2 1 2 2 2 D x x y y Midpoint formula x x, y y 2 2 M 1 2 1 2 Slope formula y y m x x 2 1
PRINCIPLES FROM PATTERNS Geometry - Algebra II - Trigonometry
 Integrating Geometry - Algebra II - Trigonometry 1 PRINCIPLES FROM PATTERNS Geometry - Algebra II - Trigonometry by David Quine Final Draft October 2010 Chapter 1 2 Principles from Patterns CHAPTER Section
Integrating Geometry - Algebra II - Trigonometry 1 PRINCIPLES FROM PATTERNS Geometry - Algebra II - Trigonometry by David Quine Final Draft October 2010 Chapter 1 2 Principles from Patterns CHAPTER Section
2 Sets. 2.1 Notation. last edited January 26, 2016
 2 Sets Sets show up in virtually every topic in mathematics, and so understanding their basics is a necessity for understanding advanced mathematics. As far as we re concerned, the word set means what
2 Sets Sets show up in virtually every topic in mathematics, and so understanding their basics is a necessity for understanding advanced mathematics. As far as we re concerned, the word set means what
3.1. 3x 4y = 12 3(0) 4y = 12. 3x 4y = 12 3x 4(0) = y = x 0 = 12. 4y = 12 y = 3. 3x = 12 x = 4. The Rectangular Coordinate System
 3. The Rectangular Coordinate System Interpret a line graph. Objectives Interpret a line graph. Plot ordered pairs. 3 Find ordered pairs that satisfy a given equation. 4 Graph lines. 5 Find x- and y-intercepts.
3. The Rectangular Coordinate System Interpret a line graph. Objectives Interpret a line graph. Plot ordered pairs. 3 Find ordered pairs that satisfy a given equation. 4 Graph lines. 5 Find x- and y-intercepts.
1.1 IDENTIFY POINTS, LINES AND PLANES
 1.1 IDENTIFY POINTS, LINES AND PLANES OBJECTIVE I WILL KNOW THESE DEFINITIONS AND BE ABLE TO SKETCH THEM: POINT LINE PLANE RAY OPPOSITE RAY COLLINEAR AND COPLANAR POINTS INTERSECTIONS OF TWO LINES AND
1.1 IDENTIFY POINTS, LINES AND PLANES OBJECTIVE I WILL KNOW THESE DEFINITIONS AND BE ABLE TO SKETCH THEM: POINT LINE PLANE RAY OPPOSITE RAY COLLINEAR AND COPLANAR POINTS INTERSECTIONS OF TWO LINES AND
Unit 1: Tools of Geometry / Reasoning and Proof
 Date Period Unit 1: Tools of Geometry / Reasoning and Proof Day Topic 1 Points, Lines and Planes 2 Segments, Rays, Parallel Lines and Planes 3 Measuring Segments 4 Measuring Angles Basic Constructions
Date Period Unit 1: Tools of Geometry / Reasoning and Proof Day Topic 1 Points, Lines and Planes 2 Segments, Rays, Parallel Lines and Planes 3 Measuring Segments 4 Measuring Angles Basic Constructions
Geometry CP. Unit 1 Notes
 Geometry CP Unit 1 Notes 1.1 The Building Blocks of Geometry The three most basic figures of geometry are: Points Shown as dots. No size. Named by capital letters. Are collinear if a single line can contain
Geometry CP Unit 1 Notes 1.1 The Building Blocks of Geometry The three most basic figures of geometry are: Points Shown as dots. No size. Named by capital letters. Are collinear if a single line can contain
Building Blocks of Geometry
 Practice A Building Blocks of Geometry Name each geometric figure. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Use the diagram to choose the correct answer. 7. Which of the following does not name a line on the diagram? A Line
Practice A Building Blocks of Geometry Name each geometric figure. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Use the diagram to choose the correct answer. 7. Which of the following does not name a line on the diagram? A Line
Does a group of parallel line segments need to be the same length?
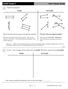 1 Parallel Line Segments Parallel t Parallel What is the same about the groups of parallel line segments? They are always the same distance apart. They do not intersect each other. If you extend the line
1 Parallel Line Segments Parallel t Parallel What is the same about the groups of parallel line segments? They are always the same distance apart. They do not intersect each other. If you extend the line
6th Grade Graphing
 1 6th Grade Graphing 2015-12-02 www.njctl.org 2 Graphing 6th Grade Topics Cartesian Plane Click on the topic to go to that section Graphing Ordered Pairs Polygons in the Coordinate Plane Cartesian Plane
1 6th Grade Graphing 2015-12-02 www.njctl.org 2 Graphing 6th Grade Topics Cartesian Plane Click on the topic to go to that section Graphing Ordered Pairs Polygons in the Coordinate Plane Cartesian Plane
Little Piece of Random
 Miss C's Little Piece of Random Is this figure possible with a straight arrow and a solid board? Use the toothpick and slip of paper on your desk help you figure out the answer. Announcements Take-Home
Miss C's Little Piece of Random Is this figure possible with a straight arrow and a solid board? Use the toothpick and slip of paper on your desk help you figure out the answer. Announcements Take-Home
Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK
 Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK [acute angle] [acute triangle] [adjacent interior angle] [alternate exterior angles] [alternate interior angles] [altitude] [angle] [angle_addition_postulate]
Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK [acute angle] [acute triangle] [adjacent interior angle] [alternate exterior angles] [alternate interior angles] [altitude] [angle] [angle_addition_postulate]
2x + 3x = 180 5x = (5x) = 1 5 (180) x = 36. Angle 1: 2(36) = 72 Angle 2: 3(36) = 108
 GRADE 7 MODULE 6 TOPIC A LESSONS 1 4 KEY CONCEPT OVERVIEW In this topic, students return to using equations to find unknown angle measures. Students write equations to model various angle relationships
GRADE 7 MODULE 6 TOPIC A LESSONS 1 4 KEY CONCEPT OVERVIEW In this topic, students return to using equations to find unknown angle measures. Students write equations to model various angle relationships
Unit 1. Word Definition Picture. The number s distance from 0 on the number line. The symbol that means a number is greater than the second number.
 Unit 1 Word Definition Picture Absolute Value The number s distance from 0 on the number line. -3 =3 Greater Than The symbol that means a number is greater than the second number. > Greatest to Least To
Unit 1 Word Definition Picture Absolute Value The number s distance from 0 on the number line. -3 =3 Greater Than The symbol that means a number is greater than the second number. > Greatest to Least To
Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes
 Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My guess
Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My guess
Working with Transformations on the Coordinate Plane
 Working with Transformations on the Coordinate Plane Movies create the illusion of movement by showing us 24 images per second. When the human eye processes 24 images per second it is interpreted in our
Working with Transformations on the Coordinate Plane Movies create the illusion of movement by showing us 24 images per second. When the human eye processes 24 images per second it is interpreted in our
5-Minute Check Solve.
 5-Minute Check (over Chapter 9) Use with Lesson 10-1 Solve. 1. There are 12 balls in a hat and 3 are red. What is the probability of drawing a red ball? 2. Use the Fundamental Counting Principle to find
5-Minute Check (over Chapter 9) Use with Lesson 10-1 Solve. 1. There are 12 balls in a hat and 3 are red. What is the probability of drawing a red ball? 2. Use the Fundamental Counting Principle to find
Sets 1. The things in a set are called the elements of it. If x is an element of the set S, we say
 Sets 1 Where does mathematics start? What are the ideas which come first, in a logical sense, and form the foundation for everything else? Can we get a very small number of basic ideas? Can we reduce it
Sets 1 Where does mathematics start? What are the ideas which come first, in a logical sense, and form the foundation for everything else? Can we get a very small number of basic ideas? Can we reduce it
Department: Course: Chapter 1
 Department: Course: 2016-2017 Term, Phrase, or Expression Simple Definition Chapter 1 Comprehension Support Point Line plane collinear coplanar A location in space. It does not have a size or shape The
Department: Course: 2016-2017 Term, Phrase, or Expression Simple Definition Chapter 1 Comprehension Support Point Line plane collinear coplanar A location in space. It does not have a size or shape The
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Section 1: Introduction to Geometry Points, Lines, and Planes
 Section 1: Introduction to Geometry Points, Lines, and Planes Topic 1: Basics of Geometry - Part 1... 3 Topic 2: Basics of Geometry Part 2... 5 Topic 3: Midpoint and Distance in the Coordinate Plane Part
Section 1: Introduction to Geometry Points, Lines, and Planes Topic 1: Basics of Geometry - Part 1... 3 Topic 2: Basics of Geometry Part 2... 5 Topic 3: Midpoint and Distance in the Coordinate Plane Part
Math 3A Meadows or Malls? Review
 Math 3A Meadows or Malls? Review Name Linear Programming w/o Graphing (2 variables) 1. A manufacturer makes digital watches and analogue (non-digital) watches. It cost $15 to make digital watch and $20
Math 3A Meadows or Malls? Review Name Linear Programming w/o Graphing (2 variables) 1. A manufacturer makes digital watches and analogue (non-digital) watches. It cost $15 to make digital watch and $20
Section 1.1 Notes. Points - have no size or dimension and named using capital letters A
 Section 1.1 Notes Building Blocks of Geometry Undefined Terms: Points - have no size or dimension and named using capital letters A Lines - have no thickness (1D) and extend forever. Named using 2 points
Section 1.1 Notes Building Blocks of Geometry Undefined Terms: Points - have no size or dimension and named using capital letters A Lines - have no thickness (1D) and extend forever. Named using 2 points
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
B ABC is mapped into A'B'C'
 h. 00 Transformations Sec. 1 Mappings & ongruence Mappings Moving a figure around a plane is called mapping. In the figure below, was moved (mapped) to a new position in the plane and the new triangle
h. 00 Transformations Sec. 1 Mappings & ongruence Mappings Moving a figure around a plane is called mapping. In the figure below, was moved (mapped) to a new position in the plane and the new triangle
Building a Geometry Vocabulary
 7-4127_EZGeoCh1-4 1/21/09 2:25 PM Page 1 1 Building a Geometry Vocabulary WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Studying geometry is very different from studying elementary algebra. In geometry we are concerned with developing
7-4127_EZGeoCh1-4 1/21/09 2:25 PM Page 1 1 Building a Geometry Vocabulary WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Studying geometry is very different from studying elementary algebra. In geometry we are concerned with developing
Analytic Geometry Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Important Notes for Teachers:
 Analytic Geometry Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file reflect the vocabulary students taking Coordinate Algebra will need to know and be able
Analytic Geometry Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file reflect the vocabulary students taking Coordinate Algebra will need to know and be able
Section 1-1 Points, Lines, and Planes
 Section 1-1 Points, Lines, and Planes I CAN. Identify and model points, lines, and planes. Identify collinear and coplanar points and intersecting lines and planes in space. Undefined Term- Words, usually
Section 1-1 Points, Lines, and Planes I CAN. Identify and model points, lines, and planes. Identify collinear and coplanar points and intersecting lines and planes in space. Undefined Term- Words, usually
Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes
 Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Terms: A point has no size but is often represented by a dot and usually named by a capital letter.. A A line extends in two directions without ending. Lines
Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Terms: A point has no size but is often represented by a dot and usually named by a capital letter.. A A line extends in two directions without ending. Lines
Acute Angle. Angle. An angle that measures greater than 0 and less than 90. A figure formed by two line segments or rays that share the same endpoint.
 Acute Angle An angle that measures greater than 0 and less than 90. Geometry Angle A figure formed by two line segments or rays that share the same endpoint. 5 Geometry Area The number of square units
Acute Angle An angle that measures greater than 0 and less than 90. Geometry Angle A figure formed by two line segments or rays that share the same endpoint. 5 Geometry Area The number of square units
DAY 1 DEFINITION OF ANGLES
 DAY 1 DEFINITION OF ANGLES INTRODUCTION In daily life we encounter patterns, designs and a variety of shapes. Roads, furniture, vehicles and houses, among others, are designed by accurate use of angles
DAY 1 DEFINITION OF ANGLES INTRODUCTION In daily life we encounter patterns, designs and a variety of shapes. Roads, furniture, vehicles and houses, among others, are designed by accurate use of angles
Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes
 Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My
Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My
UNIT 1: TOOLS OF GEOMETRY POINTS,LINES, & PLANES Geometry is a mathematical system built on accepted facts, basic terms, and definitions.
 UNIT 1: TOOLS OF GEOMETRY POINTS,LINES, & PLANES Geometry is a mathematical system built on accepted facts, basic terms, and definitions. Point, line, and plane are all undefined terms. They are the basic
UNIT 1: TOOLS OF GEOMETRY POINTS,LINES, & PLANES Geometry is a mathematical system built on accepted facts, basic terms, and definitions. Point, line, and plane are all undefined terms. They are the basic
Number/Computation. addend Any number being added. digit Any one of the ten symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9
 14 Number/Computation addend Any number being added algorithm A step-by-step method for computing array A picture that shows a number of items arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle associative
14 Number/Computation addend Any number being added algorithm A step-by-step method for computing array A picture that shows a number of items arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle associative
Mill Hill School. 13+ Entrance Examination Mathematics. January Time: 1 hour. School: Mark: Materials required for examination
 Name: School: Mark: Mill Hill School 13+ Entrance Examination Mathematics January 2014 Time: 1 hour Materials required for examination Ruler, protractor, compasses, pen, pencil, eraser Calculators must
Name: School: Mark: Mill Hill School 13+ Entrance Examination Mathematics January 2014 Time: 1 hour Materials required for examination Ruler, protractor, compasses, pen, pencil, eraser Calculators must
Basic Triangle Congruence Lesson Plan
 Basic Triangle Congruence Lesson Plan Developed by CSSMA Staff Drafted August 2015 Prescribed Learning Outcomes: Introduce students to the concept of triangle congruence and teach them about the congruency
Basic Triangle Congruence Lesson Plan Developed by CSSMA Staff Drafted August 2015 Prescribed Learning Outcomes: Introduce students to the concept of triangle congruence and teach them about the congruency
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 10: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
2. Getting Started When you start GeoGebra, you will see a version of the following window. 1
 Math 5335 Fall 2018 Lab #0: Installing and using GeoGebra This semester you will have a number of lab assignments which require you to use GeoGebra, a dynamic geometry program. GeoGebra lets you explore
Math 5335 Fall 2018 Lab #0: Installing and using GeoGebra This semester you will have a number of lab assignments which require you to use GeoGebra, a dynamic geometry program. GeoGebra lets you explore
OHS GEOMETRY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT
 OHS GEOMETRY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Name: Date Started: Complete each of the following exercises in this formative assessment. To receive full credit for this assignment, you must show your work in this packet,
OHS GEOMETRY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Name: Date Started: Complete each of the following exercises in this formative assessment. To receive full credit for this assignment, you must show your work in this packet,
Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls. Ideas for everyday use of a Word Wall to develop vocabulary knowledge and fluency by the students
 Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core Georgia Performance Standards. The cards are arranged alphabetically. Each card has three sections. o Section 1 is
Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core Georgia Performance Standards. The cards are arranged alphabetically. Each card has three sections. o Section 1 is
Unit 1 Transformations in the Coordinate Plane
 Unit 1 Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Table of Contents Title Page # Formula Sheet...2 Lesson 1 1: Introduction to Transformations and Rotations 3 Lesson 1 2: Reflections and Translations..9 Lesson
Unit 1 Transformations in the Coordinate Plane Table of Contents Title Page # Formula Sheet...2 Lesson 1 1: Introduction to Transformations and Rotations 3 Lesson 1 2: Reflections and Translations..9 Lesson
Lesson 1. Unit 2 Practice Problems. Problem 2. Problem 1. Solution 1, 4, 5. Solution. Problem 3
 Unit 2 Practice Problems Lesson 1 Problem 1 Rectangle measures 12 cm by 3 cm. Rectangle is a scaled copy of Rectangle. Select all of the measurement pairs that could be the dimensions of Rectangle. 1.
Unit 2 Practice Problems Lesson 1 Problem 1 Rectangle measures 12 cm by 3 cm. Rectangle is a scaled copy of Rectangle. Select all of the measurement pairs that could be the dimensions of Rectangle. 1.
Use the Move tool to drag A around and see how the automatically constructed objects (like G or the perpendicular and parallel lines) are updated.
 Math 5335 Fall 2015 Lab #0: Installing and using GeoGebra This semester you will have a number of lab assignments which require you to use GeoGebra, a dynamic geometry program. GeoGebra lets you explore
Math 5335 Fall 2015 Lab #0: Installing and using GeoGebra This semester you will have a number of lab assignments which require you to use GeoGebra, a dynamic geometry program. GeoGebra lets you explore
Boardworks Ltd KS3 Mathematics. S1 Lines and Angles
 1 KS3 Mathematics S1 Lines and Angles 2 Contents S1 Lines and angles S1.1 Labelling lines and angles S1.2 Parallel and perpendicular lines S1.3 Calculating angles S1.4 Angles in polygons 3 Lines In Mathematics,
1 KS3 Mathematics S1 Lines and Angles 2 Contents S1 Lines and angles S1.1 Labelling lines and angles S1.2 Parallel and perpendicular lines S1.3 Calculating angles S1.4 Angles in polygons 3 Lines In Mathematics,
Math-in-CTE Lesson Plan Template
 Lesson Development Math-in-CTE Lesson Plan Template Lesson Title: Basic Geometric Concepts Lesson # Author(s): Phone Number(s): E-mail Address(es): Juan Carlos Martínez jcmartinez@dadeschoolsnet Bergman
Lesson Development Math-in-CTE Lesson Plan Template Lesson Title: Basic Geometric Concepts Lesson # Author(s): Phone Number(s): E-mail Address(es): Juan Carlos Martínez jcmartinez@dadeschoolsnet Bergman
Dynamic-Geometry Activities with GeoGebra for Virtual Math Teams VMT Project Team The Math Forum at Drexel University
 Dynamic-Geometry Activities with GeoGebra for Virtual Math Teams VMT Project Team The Math Forum at Drexel University Draft for review only page 1 Tuesday, May 1, 2012 Introduction Dynamic-Geometry Activities
Dynamic-Geometry Activities with GeoGebra for Virtual Math Teams VMT Project Team The Math Forum at Drexel University Draft for review only page 1 Tuesday, May 1, 2012 Introduction Dynamic-Geometry Activities
Algebra I Summer Math Packet
 01 Algebra I Summer Math Packet DHondtT Grosse Pointe Public Schools 5/0/01 Evaluate the power. 1.. 4. when = Write algebraic epressions and algebraic equations. Use as the variable. 4. 5. 6. the quotient
01 Algebra I Summer Math Packet DHondtT Grosse Pointe Public Schools 5/0/01 Evaluate the power. 1.. 4. when = Write algebraic epressions and algebraic equations. Use as the variable. 4. 5. 6. the quotient
Course Guide (/8/teachers/teacher_course_guide.html) Print (/8/teachers/print_materials.html) LMS (/8
 (http://openupresources.org)menu Close OUR Curriculum (http://openupresources.org) Professional Development (http://openupresources.org/illustrative-mathematics-professional-development) Implementation
(http://openupresources.org)menu Close OUR Curriculum (http://openupresources.org) Professional Development (http://openupresources.org/illustrative-mathematics-professional-development) Implementation
B ABC is mapped into A'B'C'
 h. 00 Transformations Sec. 1 Mappings & ongruence Mappings Moving a figure around a plane is called mapping. In the figure below, was moved (mapped) to a new position in the plane and the new triangle
h. 00 Transformations Sec. 1 Mappings & ongruence Mappings Moving a figure around a plane is called mapping. In the figure below, was moved (mapped) to a new position in the plane and the new triangle
Name Period Date GRADE 7: MATHEMATICS COMMON CORE SUPPLEMENT ANGLES, DRAWINGS, AND ALGEBRAIC CONNECTIONS
 Name Period Date 7-CORE3.1 Geometric Figures Measure and draw angles using a protractor. Review facts about interior angles of triangles and quadrilaterals. Find missing angle measures in geometric diagrams.
Name Period Date 7-CORE3.1 Geometric Figures Measure and draw angles using a protractor. Review facts about interior angles of triangles and quadrilaterals. Find missing angle measures in geometric diagrams.
August 3 - August 31
 Mathematics Georgia Standards of Excellence Geometry Parent Guide Unit 1 A All About Our Unit of Study Transformations in the Coordinate Plane August 3 - August 31 In this unit students will perform transformations
Mathematics Georgia Standards of Excellence Geometry Parent Guide Unit 1 A All About Our Unit of Study Transformations in the Coordinate Plane August 3 - August 31 In this unit students will perform transformations
Euclid s Axioms. 1 There is exactly one line that contains any two points.
 11.1 Basic Notions Euclid s Axioms 1 There is exactly one line that contains any two points. Euclid s Axioms 1 There is exactly one line that contains any two points. 2 If two points line in a plane then
11.1 Basic Notions Euclid s Axioms 1 There is exactly one line that contains any two points. Euclid s Axioms 1 There is exactly one line that contains any two points. 2 If two points line in a plane then
BACK TO THE BASICS: GEOMETRY
 BACK TO THE BASICS: GEOMETRY Grade Level or Special Area: 4 th Grade Written by: Amy Beling, Littleton Academy, Littleton, Colorado Length of Unit: Five lessons (approximately five days, one day = 45 minutes)
BACK TO THE BASICS: GEOMETRY Grade Level or Special Area: 4 th Grade Written by: Amy Beling, Littleton Academy, Littleton, Colorado Length of Unit: Five lessons (approximately five days, one day = 45 minutes)
Unit 6: Connecting Algebra and Geometry Through Coordinates
 Unit 6: Connecting Algebra and Geometry Through Coordinates The focus of this unit is to have students analyze and prove geometric properties by applying algebraic concepts and skills on a coordinate plane.
Unit 6: Connecting Algebra and Geometry Through Coordinates The focus of this unit is to have students analyze and prove geometric properties by applying algebraic concepts and skills on a coordinate plane.
