Volume Worksheets (Chapter 6)
|
|
|
- Joel Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Volume Worksheets (Chapter 6) Name page contents: date AP Free Response Area Between Curves 3-5 Volume b Cross-section with Riemann Sums 6 Volume b Cross-section Homework 7-8 AP Free Response Volume b Cross-Section 9-10 More Volume b Cross-section Homework 11-1 An Wa You Spin It (MVP) Volume b Revolution About x- and -axes with Riemann Sums discs 15 Volume b Revolution About x- and -axes with Integrals 16 Volume b Revolution Homework Chapter 6. Revolution About Other Axes 19 Revolution About Other Axes Homework 0-1 Volume b Revolution with Midpoint Riemann Sums shells Shells Homework 3-4 AP Free Response Volume b Rotation 5-6 Densit
2 AP Free Response Area Between Curves Calculator 1 1.) Let f and g be the functions given b f ( x) sin x and 4 gx ( ) 4 x. Let R be the shaded region in the first quadrant enclosed b the -axis and the graphs of f and g, and let S be the shaded region in the first quadrant enclosed b the graphs of f and g, as shown in the figure. a.) Find the area of R. b.) Find the area of S. AP Free Response No calculator..) The function f is defined b a.) Find f '( x ). f ( x) 5 x for 5 x 5. b.) Write an equation for the line tangent to the graph of f at x = 3. f ( x) 5 x 3 c.) Let g be the function defined b gx ( ) x 7 3 x 5 Is g continuous at x = 3? Use the definition of continuit to explain our answer. d.) Find the value of 5 x 5 x dx 0. page
3 Volume b Cross-section with Riemann Sums 1.) Consider the region enclosed b the graphs of f ( x) x, = 0, and x = 9. a.) Fill in the table. x x b.) Use the values in the table above to draw rectangles on the graph with height and width x. c.) The right side of each slice, the side perpendicular to the x axis and the x- plane, is a square with side length as a function of x. Fill in the table below. x total area of right side x volume of prism d.) Is the total volume an overestimate or an underestimate for the actual volume? Explain using Calculus. We can use Calculus to get a more precise answer if we make the slices infinitel thin and add up an infinite number of them. The limits of integration are the input values from the first slice to the last slice. The integrand represents the area of a slice. e.) Write an integral to find the exact volume of the solid. integral: volume: page 3
4 .) If we make the cross-sections horizontal instead of vertical, do ou think the volume will be the same? Note: We are still using the region enclosed b the graphs of = x, = 0, and x = 9. a.) Fill in the table to find the side length of a square cross section b.) Use the values in the table above to draw rectangles on the graph with height x = f() and width. c.) The bottom side of each slice, the side perpendicular to the axis and the x- plane, is a square with side length x as a function of, x = f(). 0 1 total area of bottom side d.) Write an integral to find the exact volume of the solid. The limits of integration are the input values from the first slice to the last slice. integral: volume: volume of prism e.) Does the exact volume change when the cross-sections change from vertical to horizontal? Explain. page 4
5 3.) Find the area of each shape in terms of. Draw a picture to help ou visualize the answer. a.) a square with side b.) a half-square, cut diagonall, with diagonal c.) a half-square, cut diagonall, with leg d.) an equilateral triangle with side e.) a semicircle with diameter 4.) Complete the chart Function cross sections perpendicular to x-axis Interval Definite integral Volume round or truncate to 3 places after the decimal log x Semi-circle [ 1, 10 ] x Equilateral Triangle [ 0, 9 ] ln x Square [ 1, 6e ] 3 x Half-square Cut diagonall; (hpotenuse is in the x- plane) [ 1, ] page 5
6 Volume b Cross-section Homework For each problem, draw a figure and set up an integral. 1.) (calculator) Find the volume of the solid whose base is bounded b the graphs of x 1 and x 1, with the indicated cross sections taken perpendicular to the x-axis. a.) Squares b.) Rectangles of height.) (no calculator) Find the volume of the solid whose base is bounded b the circle with the indicated cross sections taken perpendicular to the x-axis. a.) Semicircles b.) Equilateral triangles x ) (no calculator) The base of a solid is bounded b x, 0, and x. Find the volume of the solid for each of the following cross sections taken perpendicular to the -axis. a.) Squares b.) Isosceles right triangles with a leg on the base of the solid page 6
7 AP Free Response Volume b Cross-section 1.) no calculator Let R be the region bounded b the graphs of x x and as shown in the figure to the right. The region R is the base of a solid. For this solid, the cross sections perpendicular to the x-axis are squares. Find the volume of this solid..) calculator allowed Let R be the region enclosed b the graph of 4 3 f ( x) x.3x 4 and the horizontal line 4, as shown in the figure to the right. Region R is the base of a solid. For this solid, each cross section perpendicular to the x-axis is an isosceles right triangle with a leg in R. Find the volume of the solid. page 7
8 3.) 1 Let f ( x) x 6x 4 and g( x) 4cos x. Let R be the region bounded b the graphs of f 4 and g, as shown in the figure above. The region R is the base of a solid. For this solid, each cross section perpendicular to the x-axis is a square. Write, but do not evaluate, an integral expression that gives the volume of the solid. 4.) calculator allowed Let R be the region in the first quadrant bounded b the x-axis and the graphs of 5 x, as shown in the figure above. ln x and Region R is the base of a solid. For the solid, each cross section perpendicular to the x-axis is a square. Write, but do not evaluate, an expression involving one or more integrals that gives the volume of the solid. page 8
9 More Volume b Cross-section Homework 1.) Let R be the region in the first quadrant enclosed b the graphs of x and a.) Find the area of R. x. b.) Imagine a vertical line x k which divides the region R into two equal values. Find the value of k. c.) The region R is the base of a solid. For this solid, at each x-value the cross section perpendicular to the x-axis is an equilateral triangle. Find the volume of this solid. d.) Another solid has the same base R. For this solid, the cross sections perpendicular to the - axis are squares. Find the volume of this solid..) Let R be the region bounded b the graphs of sin( x) and x 3 4x. a.) Find the area of R. b.) The region R is the base of a solid. For this solid, each cross section perpendicular to the x- axis is a semi-circle. Find the volume of this solid. c.) The region R is the base of a solid. For this solid, each cross section perpendicular to the x- axis is an isosceles right triangle with the hpotenuse on the base of the solid. Find the volume of this solid. page 9
10 For questions 3-5, sketch a graph of the base. Draw and label a cross section of the solid. Find the volume of the solid. You should be able to evaluate these without a calculator. 3.) The base S is an elliptical region with boundar curve 9x Cross-sections perpendicular to the x-axis are isosceles right triangles with hpotenuse in the base. 4.) The base of S is the region enclosed b the parabola perpendicular to the -axis are squares. 1 x and the x-axis. Cross-sections 5.) The base of S is the region enclosed b the parabola 1 x and the x-axis. Cross-sections perpendicular to the x-axis are isosceles triangles with height equal to the base. page 10
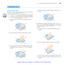
11 An Wa You Spin It (MVP) Perhaps ou have used a potter wheel or a wood lathe. (A lathe is a machine that is used to shape a piece of wood b rotating it rapidl on its axis while a fixed tool is pressed against it. Table legs and wooden pedestals are carved on a wood lathe). You might have plaed with a spinning top or watched a figure skater spin so rapidl she looked like a solid blur. The cla bowl, the table leg, the rotating top and the spinning skater each of these can be modeled as solids of revolution a three dimensional object formed b spinning a two dimensional figure about an axis. Suppose the right triangle shown below is rotating rapidl about the x-axis. Like the spinning skater, a solid image would be formed b the blur of the rotating triangle. 1.) Draw and describe the solid of revolution formed b rotating this triangle about the x-axis..) Find the volume of the solid formed. 3.) What would this figure look like if the triangle rotates rapidl about the -axis? Draw and describe the solid of revolution formed b rotating this triangle about the -axis. 4.) Find the volume of the solid formed. page 11
12 5.) What about the following two-dimensional figure? Draw and describe the solid of revolution formed b rotating this figure about the x-axis. 6.) Draw a cross section of the solid of revolution formed b this figure if the plane cutting the solid is the plane containing the coordinate axes. 7.) Draw some cross sections of the solid of revolution formed b the figure if the planes cutting the solid are perpendicular to the x- axis and the plane containing the coordinate axes. Draw the cross sections when the intersecting planes are located at x = 5, x = 10, and x = ) How could ou use the cross-sections to estimate the volume? page 1
13 Volume b Revolution About x- and -axes with Riemann Sums - Discs 1.) = x a.) Fill in the table. x x b.) If we rotate the area under the curve in the first quadrant around the x-axis we form a solid. If we make vertical cuts perpendicular to the x-axis, the cross-sections will be circles. We will estimate the volume with four cuts, making four clinders. Each height,, is the radius of a circle and x is the width of the clinder. Use the values in the table above to draw four rectangles on the graph to represent the part of the solid that is in the x- plane. c.) The left side of each clinder, the side perpendicular to the x axis, is a circle with radius. Fill in the table below. x area of left side x 0 π8 18π 4 6 total volume of clinder We can use Calculus to get a more precise answer if we make the slices infinitel thin and add up an infinite number of them. The limits of integration are the input values from the first slice to the last slice. The integrand represents the area of a slice. d.) Write an integral to find the exact volume of the solid. integral: volume: page 13
14 .) If we rotate the area under the curve in the first quadrant around the -axis and make the cross-sections horizontal instead of vertical, do ou think the volume will be the same? = x a.) Fill in the table. x b.) Each height x f ( ), is the radius of a circle and is the width of a clinder. Use the values in the table above to draw rectangles on the graph to represent the part of the solid that is in the x- plane. c.) The bottom side of the clinder, the side perpendicular to the axis, is a circle with radius x f ( ). Fill in the table below. area of bottom side total d.) Write an integral to find the exact volume of the solid. The limits of integration are the input values from the first slice to the last slice. integral: volume: volume of clinder e.) Does the exact volume change when the cross-sections change from vertical to horizontal? Explain. page 14
15 Volume b Revolution About x- and -axes with Integrals 3.) Use Calculus to find the volume of this cone. 4.) Find the volume of the solid generated b rotating x about the x-axis from x 0 to x 1. 5.) Find the volume of the solid generated b 3 rotating x about the -axis from 0 to 8. 6.) Find the volume of the solid bounded b x and x rotated about the x-axis. page 15
16 Volume b Revolution Homework no calculator Find the volume of the solid obtained b rotating the region bounded b the given curves about the specified line. Sketch the region, the solid, and a tpical disc or washer. 1.) 1 x, 0 ; about the x-axis.) 5 x, 0, x, x 4 ; about the x-axis 3.) x, x 0 ; about the -axis 4.) 1 4 x, 5 x ; about the x-axis 5.) 1 4 x, x, 0 ; about the -axis page 16
17 Chapter 6. Revolution about Other Axes Let S be the region in the first Quadrant bounded b the graphs of the -axis. (calculator allowed) x, 1 0,5 x, and Example 1: Find the volume of the solid generated when S is revolved about the line. Example : Find the volume of the solid generated when S is revolved about the line 3. Example3: Find the volume of the solid generated when S is revolved about the line x 3. page 17
18 Example 4: Find the volume of the solid generated when S is rotated about the line x 1. Let Q be the region in the first quadrant between the -axis and the graph of ( 3) 9 x Example 5: Find the volume of the solid generated when Q is revolved about the line x 10.. page 18
19 Revolution About Other Axes Homework For questions 1 4, find the volume of the solid obtained b rotating the region bounded b the given curves about the specified line. Sketch the region, the solid, and a tpical disc or washer. Calculator allowed. 1.) x, x ; about 1.) 1 sec x on the interval [.5,.5], 3 ; about 1 3.) x, 1 x ; about x 1 4.) x, x ; about x 1 For questions 5-6, set up, but do not evaluate, an integral for the volume of the solid obtained b rotating the region bounded b the given curves about the specified line. 5.) 3 tan x, 1, x 0 ; about 1 6.) 0, sin x, 0 x ; about 1 page 19
20 Volume b Revolution with Midpoint Riemann Sums Shells 1.) = x a.) Fill in the table. x x b.) If we rotate the area under the curve in the first quadrant around the -axis we form a solid. We can slice the solid into vertical clinders (some hollow). Use the values in the table above to draw rectangles on the graph to represent the part of each of the four clinders that is in the x- plane. Color can be useful to show the different sections. clinder dimensions radius: x Height: c.) Fill in the table below. x lateral area rh x volume of clinder 1 π(1)(7.875) 31.5π total We can use Calculus to get a more precise answer if we make the slices infinitel thin and add up an infinite number of them. The limits of integration are the input values from the first slice to the last slice. The integrand represents the area of a slice. d.) Write an integral to find the exact volume of the solid. integral: volume: page 0
21 .) = x a) Fill in the table with positive values. x b.) If we rotate the area under the curve in the first quadrant around the x-axis we form a solid. We can slice the solid into horizontal clinders (some hollow). Use the values in the table above to draw rectangles on the graph to represent the part of each clinder that is in the x- plane. c.) hollow clinder dimensions radius: Height: x f ( ) d lateral area rh total volume clinder d.) Compare our estimate with our estimate from page 13 #1c. e.) Write an integral to find the exact volume of the solid. The limits of integration are the input values from the first slice to the last slice. integral: volume:. page 1
22 Shells Homework For question 1-3, use the method of clindrical shells to find the volume generated b rotating the region bounded b the given curves about the -axis. Sketch the region of a tpical shell. 1.) 1 x, 0, x 1, x.), 4, x 0 x, 0 x 3.) (calculator allowed) 4 x, x x 4 7 Use the method of clindrical shells to set up an integral to find the volume generated b rotating the region bounded b the given curves about the x-axis. Sketch the region of a tpical shell. (calculator) 4.) 3 x, 8, 0 x 5.) x 1, x 6.) If the region shown in the figure is rotated about the -axis to form a solid use the Midpoint Rule with n 5 to estimate the volume of the solid. page
23 AP Free Response Volume b Rotation 1.) calculator 4 3 Let R be the region enclosed b the graph of f ( x) x.3x 4 and the horizontal line 4, as shown in the figure to the left. Find the volume of the solid generated when R is rotated about the horizontal line..) no calculator Let R be the region bounded b the graphs of x and, x as shown in the figure to the left. Write, but do not evaluate, an integral expression that gives the volume of the solid generated when R is rotated about the -axis. 3.) no calculator Let f(x) = x 6x + 4 and g(x) = 4cos ( 1 πx). Let R be 4 the region bounded b the graphs of f and g, as shown in the figure to the left. Write, but do not evaluate, an integral expression that gives the volume of the solid generated when R is rotated about the horizontal line = 4. page 3
24 4.) calculator Let R be the region in the first quadrant bounded b the x-axis and the graphs of ln x and 5 x, as shown in the figure to the left. Write but do not evaluate an integral expression for the volume of the solid generated when R is rotated about the vertical line x 1. 5.) The tide removes sand from Sand Point Beach at a rate modeled b the function R, given b 4 t Rt ( ) 5sin 5 A pumping station adds sand to the beach at a rate modeled b the function S, given b 15t St () 1 3t Both R(t)and S(t) have units of cubic ards per hour and t is measured in hours for 0 t 6. At time t = 0, the beach contains 500 cubic ards of sand. (calculator allowed) a.) How much sand will the tide remove from the beach during this 6-hour period? Indicate units of measure. b.) Write an expression for Yt (), the total number of cubic ards of sand on the beach at time t. c.) Find the rate at which the total amount of sand on the beach is changing at time t 4. d.) For 0 t 6, at what time t is the amount of sand on the beach a minimum? What is the minimum value? Justif our answers. page 4
25 Densit A.) What is Densit? In Phsics: Population: B.) Problem with Constant Densit C.) Problems with changing Densit (there are infinite examples here are just a few) 1.) Amount of Soot on a road. The Springfield chemical plant is putting soot onto a road that runs West to East from both sides of the plant. Let x be the distance from the plant in km. The densit of soot put onto the road, in mg per kilometer, each da, is given b d 500(1 x ). Write, and evaluate (with a calculator), a definite integral which stands for the total amount of soot put onto the road each da..) Number of tents in a campground. A campground is in the shape of a rectangle measuring 1000 ds b 600 ds with a river running along one side of the longer sides. At a distance of x ds from the river, the densit of tents per square d is given b d x on a Fourth of Jul weekend. Find the number of tents in the campground. 3.) Cit population: Circle Cit, a tpical metropolis, is ver densel populated near its center, and its population graduall thins out toward the cit limits. In fact, its population densit is 10000(3 r) people per square mile at a distance r from the center. What is the total population of the cit? page 5
26 Densit Homework (calculator allowed on all problems except #3) 1.) A cit in the shape of a circle of radius 10 miles is growing. Its population densit is a function of the distance from the center of the cit. At a distance of r miles from the cit 5000 center its population densit is d people per square mile. 1 r a.) Write a definite integral which stands for the number of people within miles of the cit center. Evaluate this definite integral. b.) Write a definite integral which stands for the number of people who live between 5 and 10 miles from the cit center. Evaluate this definite integral..) The densit of cars (in cars per mile) down a stretch of Route 3 (the highwa that connects Boston and Cape Cod) on a Frida afternoon at 5:00pm can be approximated b the function d 83 34cos(0.5 x) where x represents the distance in miles from the Boston. Write a definite integral which stands for the number of cars on the 10-mile stretch. Evaluate our integral. 3.) A state forest is in the shape of a rectangle measuring 8 miles b 0 miles, with a highwa running along one of the 0 mile sides. Deer in the forest are more numerous awa from the highwa. In fact, the densit of their population is expressed b the function D 0.5x 1 where D is the number of deer per square mile at distance x from the highwa. Write a definite integral which stands for the total number of deer in the forest. Evaluate our integral algebraicall. (no calculator) 4.) An hour after starting the Walk for Hunger, the number of walkers per mile a distance x 3 miles from the start of the walk was given (approximatel) b W 0.17x 3.1x 14. 8x. Assume all walkers are walking along a straight, thin path. a.) Write a definite integral which stands for the number of walkers between 3 and 4 miles from the start. Evaluate our definite integral. b.) Write a definite integral which stands for the number of walkers who are within 0-5 miles of the start. Evaluate our definite integral. page 6
Chapter 8: Applications of Definite Integrals
 Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 8: Applications of Definite Integrals v v Sections: 8.1 Integral as Net Change 8.2 Areas in the Plane v 8.3 Volumes HW Sets Set A (Section 8.1) Pages
Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 8: Applications of Definite Integrals v v Sections: 8.1 Integral as Net Change 8.2 Areas in the Plane v 8.3 Volumes HW Sets Set A (Section 8.1) Pages
AP CALCULUS BC PACKET 2 FOR UNIT 4 SECTIONS 6.1 TO 6.3 PREWORK FOR UNIT 4 PT 2 HEIGHT UNDER A CURVE
 AP CALCULUS BC PACKET FOR UNIT 4 SECTIONS 6. TO 6.3 PREWORK FOR UNIT 4 PT HEIGHT UNDER A CURVE Find an expression for the height of an vertical segment that can be drawn into the shaded region... = x =
AP CALCULUS BC PACKET FOR UNIT 4 SECTIONS 6. TO 6.3 PREWORK FOR UNIT 4 PT HEIGHT UNDER A CURVE Find an expression for the height of an vertical segment that can be drawn into the shaded region... = x =
Aim: How do we find the volume of a figure with a given base? Get Ready: The region R is bounded by the curves. y = x 2 + 1
 Get Ready: The region R is bounded by the curves y = x 2 + 1 y = x + 3. a. Find the area of region R. b. The region R is revolved around the horizontal line y = 1. Find the volume of the solid formed.
Get Ready: The region R is bounded by the curves y = x 2 + 1 y = x + 3. a. Find the area of region R. b. The region R is revolved around the horizontal line y = 1. Find the volume of the solid formed.
Name Date Period. Worksheet 6.3 Volumes Show all work. No calculator unless stated. Multiple Choice
 Name Date Period Worksheet 6. Volumes Show all work. No calculator unless stated. Multiple Choice. (Calculator Permitted) The base of a solid S is the region enclosed by the graph of y ln x, the line x
Name Date Period Worksheet 6. Volumes Show all work. No calculator unless stated. Multiple Choice. (Calculator Permitted) The base of a solid S is the region enclosed by the graph of y ln x, the line x
AP Calculus. Areas and Volumes. Student Handout
 AP Calculus Areas and Volumes Student Handout 016-017 EDITION Use the following link or scan the QR code to complete the evaluation for the Study Session https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/s_sss Copyright
AP Calculus Areas and Volumes Student Handout 016-017 EDITION Use the following link or scan the QR code to complete the evaluation for the Study Session https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/s_sss Copyright
Find the volume of a solid with regular cross sections whose base is the region between two functions
 Area Volume Big Ideas Find the intersection point(s) of the graphs of two functions Find the area between the graph of a function and the x-axis Find the area between the graphs of two functions Find the
Area Volume Big Ideas Find the intersection point(s) of the graphs of two functions Find the area between the graph of a function and the x-axis Find the area between the graphs of two functions Find the
Area and Volume. where x right and x left are written in terms of y.
 Area and Volume Area between two curves Sketch the region and determine the points of intersection. Draw a small strip either as dx or dy slicing. Use the following templates to set up a definite integral:
Area and Volume Area between two curves Sketch the region and determine the points of intersection. Draw a small strip either as dx or dy slicing. Use the following templates to set up a definite integral:
If ( ) is approximated by a left sum using three inscribed rectangles of equal width on the x-axis, then the approximation is
 More Integration Page 1 Directions: Solve the following problems using the available space for scratchwork. Indicate your answers on the front page. Do not spend too much time on any one problem. Note:
More Integration Page 1 Directions: Solve the following problems using the available space for scratchwork. Indicate your answers on the front page. Do not spend too much time on any one problem. Note:
Unit #13 : Integration to Find Areas and Volumes, Volumes of Revolution
 Unit #13 : Integration to Find Areas and Volumes, Volumes of Revolution Goals: Beabletoapplyaslicingapproachtoconstructintegralsforareasandvolumes. Be able to visualize surfaces generated by rotating functions
Unit #13 : Integration to Find Areas and Volumes, Volumes of Revolution Goals: Beabletoapplyaslicingapproachtoconstructintegralsforareasandvolumes. Be able to visualize surfaces generated by rotating functions
The base of a solid is the region in the first quadrant bounded above by the line y = 2, below by
 Chapter 7 1) (AB/BC, calculator) The base of a solid is the region in the first quadrant bounded above by the line y =, below by y sin 1 x, and to the right by the line x = 1. For this solid, each cross-section
Chapter 7 1) (AB/BC, calculator) The base of a solid is the region in the first quadrant bounded above by the line y =, below by y sin 1 x, and to the right by the line x = 1. For this solid, each cross-section
In this chapter, we will investigate what have become the standard applications of the integral:
 Chapter 8 Overview: Applications of Integrals Calculus, like most mathematical fields, began with trying to solve everyday problems. The theory and operations were formalized later. As early as 70 BC,
Chapter 8 Overview: Applications of Integrals Calculus, like most mathematical fields, began with trying to solve everyday problems. The theory and operations were formalized later. As early as 70 BC,
AP Calculus BC. Find a formula for the area. B. The cross sections are squares with bases in the xy -plane.
 AP Calculus BC Find a formula for the area Homework Problems Section 7. Ax of the cross sections of the solid that are perpendicular to the x -axis. 1. The solid lies between the planes perpendicular to
AP Calculus BC Find a formula for the area Homework Problems Section 7. Ax of the cross sections of the solid that are perpendicular to the x -axis. 1. The solid lies between the planes perpendicular to
AP * Calculus Review. Area and Volume
 AP * Calculus Review Area and Volume Student Packet Advanced Placement and AP are registered trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Board was not involved in the production of,
AP * Calculus Review Area and Volume Student Packet Advanced Placement and AP are registered trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Board was not involved in the production of,
5.2 Any Way You Spin It
 SECONDARY MATH III // MODULE 5 MODELING WITH GEOMETRY 5.2 Perhaps you have used a pottery wheel or a wood lathe. (A lathe is a machine that is used to shape a piece of wood by rotating it rapidly on its
SECONDARY MATH III // MODULE 5 MODELING WITH GEOMETRY 5.2 Perhaps you have used a pottery wheel or a wood lathe. (A lathe is a machine that is used to shape a piece of wood by rotating it rapidly on its
Chapter 7 curve. 3. x=y-y 2, x=0, about the y axis. 6. y=x, y= x,about y=1
 Chapter 7 curve Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the region bounded by the given cures about the specified line. Sketch the region, the solid, and a typical disk or washer.. y-/, =, =;
Chapter 7 curve Find the volume of the solid obtained by rotating the region bounded by the given cures about the specified line. Sketch the region, the solid, and a typical disk or washer.. y-/, =, =;
AB Student Notes: Area and Volume
 AB Student Notes: Area and Volume An area and volume problem has appeared on every one of the free response sections of the AP Calculus exam AB since year 1. They are straightforward and only occasionally
AB Student Notes: Area and Volume An area and volume problem has appeared on every one of the free response sections of the AP Calculus exam AB since year 1. They are straightforward and only occasionally
Topic 6: Calculus Integration Volume of Revolution Paper 2
 Topic 6: Calculus Integration Standard Level 6.1 Volume of Revolution Paper 1. Let f(x) = x ln(4 x ), for < x
Topic 6: Calculus Integration Standard Level 6.1 Volume of Revolution Paper 1. Let f(x) = x ln(4 x ), for < x
Volume by Slicing (Disks & Washers)
 Volume by Slicing (Disks & Washers) SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: As you work through the problems listed below, you should reference Chapter 6.2 of the recommended textbook (or the equivalent chapter
Volume by Slicing (Disks & Washers) SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: As you work through the problems listed below, you should reference Chapter 6.2 of the recommended textbook (or the equivalent chapter
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral
 Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral More on Area More on Area Integrating the vertical separation gives Riemann Sums of the form More on Area Example Find the area A of the set shaded in Figure
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral More on Area More on Area Integrating the vertical separation gives Riemann Sums of the form More on Area Example Find the area A of the set shaded in Figure
Volume by Slicing (Disks & Washers)
 Volume by Slicing Disks & Washers) SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: As you work through the problems listed below, you should reference Chapter 6. of the recommended textbook or the equivalent chapter in
Volume by Slicing Disks & Washers) SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: As you work through the problems listed below, you should reference Chapter 6. of the recommended textbook or the equivalent chapter in
LECTURE 3-1 AREA OF A REGION BOUNDED BY CURVES
 7 CALCULUS II DR. YOU 98 LECTURE 3- AREA OF A REGION BOUNDED BY CURVES If y = f(x) and y = g(x) are continuous on an interval [a, b] and f(x) g(x) for all x in [a, b], then the area of the region between
7 CALCULUS II DR. YOU 98 LECTURE 3- AREA OF A REGION BOUNDED BY CURVES If y = f(x) and y = g(x) are continuous on an interval [a, b] and f(x) g(x) for all x in [a, b], then the area of the region between
Volumes of Rotation with Solids of Known Cross Sections
 Volumes of Rotation with Solids of Known Cross Sections In this lesson we are going to learn how to find the volume of a solid which is swept out by a curve revolving about an ais. There are three main
Volumes of Rotation with Solids of Known Cross Sections In this lesson we are going to learn how to find the volume of a solid which is swept out by a curve revolving about an ais. There are three main
Section 7.2 Volume: The Disk Method
 Section 7. Volume: The Disk Method White Board Challenge Find the volume of the following cylinder: No Calculator 6 ft 1 ft V 3 1 108 339.9 ft 3 White Board Challenge Calculate the volume V of the solid
Section 7. Volume: The Disk Method White Board Challenge Find the volume of the following cylinder: No Calculator 6 ft 1 ft V 3 1 108 339.9 ft 3 White Board Challenge Calculate the volume V of the solid
AREA OF A SURFACE OF REVOLUTION
 AREA OF A SURFACE OF REVOLUTION h cut r πr h A surface of revolution is formed when a curve is rotated about a line. Such a surface is the lateral boundar of a solid of revolution of the tpe discussed
AREA OF A SURFACE OF REVOLUTION h cut r πr h A surface of revolution is formed when a curve is rotated about a line. Such a surface is the lateral boundar of a solid of revolution of the tpe discussed
5 Applications of Definite Integrals
 5 Applications of Definite Integrals The previous chapter introduced the concepts of a definite integral as an area and as a limit of Riemann sums, demonstrated some of the properties of integrals, introduced
5 Applications of Definite Integrals The previous chapter introduced the concepts of a definite integral as an area and as a limit of Riemann sums, demonstrated some of the properties of integrals, introduced
Volume by Disk/Washers - Classwork
 Volume by Disk/Washers - Classwork Example 1) Find the volume if the region enclosing y = x, y = 0, x = 3 is rotated about the a) x-axis b) the line y = 6 c) the line y = 8 d) the y-axis e) the line x
Volume by Disk/Washers - Classwork Example 1) Find the volume if the region enclosing y = x, y = 0, x = 3 is rotated about the a) x-axis b) the line y = 6 c) the line y = 8 d) the y-axis e) the line x
Lecture 11 (Application of Integration) Areas between Curves Let and be continuous and on. Let s look at the region between and on.
 Lecture 11 (Application of Integration) Areas between Curves Let and be continuous and on. Let s look at the region between and on. Definition: The area of the region bounded by the curves and, and the
Lecture 11 (Application of Integration) Areas between Curves Let and be continuous and on. Let s look at the region between and on. Definition: The area of the region bounded by the curves and, and the
The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations
 1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
1. The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve C with parametric equations x = 5t 4, y = t(9 t ) The curve C cuts the x-axis at the points A and B. (a) Find the x-coordinate at the point A and the x-coordinate
CHAPTER 6: APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRALS
 (Exercises for Section 6.1: Area) E.6.1 CHAPTER 6: APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRALS SECTION 6.1: AREA 1) For parts a) and b) below, in the usual xy-plane i) Sketch the region R bounded by the graphs of the given
(Exercises for Section 6.1: Area) E.6.1 CHAPTER 6: APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRALS SECTION 6.1: AREA 1) For parts a) and b) below, in the usual xy-plane i) Sketch the region R bounded by the graphs of the given
Log1 Contest Round 2 Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons. 4 points each
 Name: Units do not have to be included. 016 017 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it
Name: Units do not have to be included. 016 017 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it
y = 4x + 2, 0 x 1 Name: Class: Date: 1 Find the area of the region that lies under the given curve:
 Name: Class: Date: 1 Find the area of the region that lies under the given curve: y = 4x + 2, 0 x 1 Select the correct answer. The choices are rounded to the nearest thousandth. 8 Find the volume of the
Name: Class: Date: 1 Find the area of the region that lies under the given curve: y = 4x + 2, 0 x 1 Select the correct answer. The choices are rounded to the nearest thousandth. 8 Find the volume of the
MA 114 Worksheet #17: Average value of a function
 Spring 2019 MA 114 Worksheet 17 Thursday, 7 March 2019 MA 114 Worksheet #17: Average value of a function 1. Write down the equation for the average value of an integrable function f(x) on [a, b]. 2. Find
Spring 2019 MA 114 Worksheet 17 Thursday, 7 March 2019 MA 114 Worksheet #17: Average value of a function 1. Write down the equation for the average value of an integrable function f(x) on [a, b]. 2. Find
Math 2260 Exam #1 Practice Problem Solutions
 Math 6 Exam # Practice Problem Solutions. What is the area bounded by the curves y x and y x + 7? Answer: As we can see in the figure, the line y x + 7 lies above the parabola y x in the region we care
Math 6 Exam # Practice Problem Solutions. What is the area bounded by the curves y x and y x + 7? Answer: As we can see in the figure, the line y x + 7 lies above the parabola y x in the region we care
MATH 31A HOMEWORK 9 (DUE 12/6) PARTS (A) AND (B) SECTION 5.4. f(x) = x + 1 x 2 + 9, F (7) = 0
 FROM ROGAWSKI S CALCULUS (2ND ED.) SECTION 5.4 18.) Express the antiderivative F (x) of f(x) satisfying the given initial condition as an integral. f(x) = x + 1 x 2 + 9, F (7) = 28.) Find G (1), where
FROM ROGAWSKI S CALCULUS (2ND ED.) SECTION 5.4 18.) Express the antiderivative F (x) of f(x) satisfying the given initial condition as an integral. f(x) = x + 1 x 2 + 9, F (7) = 28.) Find G (1), where
Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates
 Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates. A flat plate is in the shape of the region in the first quadrant ling between the circles + and +. The densit of the plate at point, is + kilograms per square meter
Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates. A flat plate is in the shape of the region in the first quadrant ling between the circles + and +. The densit of the plate at point, is + kilograms per square meter
VOLUME OF A REGION CALCULATOR EBOOK
 19 March, 2018 VOLUME OF A REGION CALCULATOR EBOOK Document Filetype: PDF 390.92 KB 0 VOLUME OF A REGION CALCULATOR EBOOK How do you calculate volume. A solid of revolution is a solid formed by revolving
19 March, 2018 VOLUME OF A REGION CALCULATOR EBOOK Document Filetype: PDF 390.92 KB 0 VOLUME OF A REGION CALCULATOR EBOOK How do you calculate volume. A solid of revolution is a solid formed by revolving
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1
 P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
Notice that the height of each rectangle is and the width of each rectangle is.
 Math 1410 Worksheet #40: Section 6.3 Name: In some cases, computing the volume of a solid of revolution with cross-sections can be difficult or even impossible. Is there another way to compute volumes
Math 1410 Worksheet #40: Section 6.3 Name: In some cases, computing the volume of a solid of revolution with cross-sections can be difficult or even impossible. Is there another way to compute volumes
x=2 26. y 3x Use calculus to find the area of the triangle with the given vertices. y sin x cos 2x dx 31. y sx 2 x dx
 4 CHAPTER 6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION 6. EXERCISES 4 Find the area of the shaded region.. =5-. (4, 4) =. 4. = - = (_, ) = -4 =œ + = + =.,. sin,. cos, sin,, 4. cos, cos, 5., 6., 7.,, 4, 8., 8, 4 4, =_
4 CHAPTER 6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION 6. EXERCISES 4 Find the area of the shaded region.. =5-. (4, 4) =. 4. = - = (_, ) = -4 =œ + = + =.,. sin,. cos, sin,, 4. cos, cos, 5., 6., 7.,, 4, 8., 8, 4 4, =_
x + 2 = 0 or Our limits of integration will apparently be a = 2 and b = 4.
 QUIZ ON CHAPTER 6 - SOLUTIONS APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRALS; MATH 15 SPRING 17 KUNIYUKI 15 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 1 POINTS = 1% Note: The functions here are continuous on the intervals of interest. This guarantees
QUIZ ON CHAPTER 6 - SOLUTIONS APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRALS; MATH 15 SPRING 17 KUNIYUKI 15 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 1 POINTS = 1% Note: The functions here are continuous on the intervals of interest. This guarantees
Applications of Integration. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Applications of Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Volume: The Disk Method Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Find the volume of a solid of revolution
Applications of Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Volume: The Disk Method Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Find the volume of a solid of revolution
5/27/12. Objectives 7.1. Area of a Region Between Two Curves. Find the area of a region between two curves using integration.
 Objectives 7.1 Find the area of a region between two curves using integration. Find the area of a region between intersecting curves using integration. Describe integration as an accumulation process.
Objectives 7.1 Find the area of a region between two curves using integration. Find the area of a region between intersecting curves using integration. Describe integration as an accumulation process.
Math 113 Exam 1 Practice
 Math Exam Practice January 6, 00 Exam will cover sections 6.-6.5 and 7.-7.5 This sheet has three sections. The first section will remind you about techniques and formulas that you should know. The second
Math Exam Practice January 6, 00 Exam will cover sections 6.-6.5 and 7.-7.5 This sheet has three sections. The first section will remind you about techniques and formulas that you should know. The second
Exam 3 SCORE. MA 114 Exam 3 Spring Section and/or TA:
 MA 114 Exam 3 Spring 217 Exam 3 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test.
MA 114 Exam 3 Spring 217 Exam 3 Name: Section and/or TA: Last Four Digits of Student ID: Do not remove this answer page you will return the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test.
Calculators ARE NOT Permitted On This Portion Of The Exam 28 Questions - 55 Minutes
 1 of 11 1) Give f(g(1)), given that Calculators ARE NOT Permitted On This Portion Of The Exam 28 Questions - 55 Minutes 2) Find the slope of the tangent line to the graph of f at x = 4, given that 3) Determine
1 of 11 1) Give f(g(1)), given that Calculators ARE NOT Permitted On This Portion Of The Exam 28 Questions - 55 Minutes 2) Find the slope of the tangent line to the graph of f at x = 4, given that 3) Determine
AP Calculus. Slide 1 / 95. Slide 2 / 95. Slide 3 / 95. Applications of Definite Integrals
 Slide 1 / 95 Slide 2 / 95 AP Calculus Applications of Definite Integrals 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 95 Particle Movement Area Between Curves Volume: Known Cross Sections Volume:
Slide 1 / 95 Slide 2 / 95 AP Calculus Applications of Definite Integrals 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 95 Particle Movement Area Between Curves Volume: Known Cross Sections Volume:
Name Class. (a) (b) (c) 2. Find the volume of the solid formed by revolving the region bounded by the graphs of
 Applications of Integration Test Form A. Determine the area of the region bounded by the graphs of y x 4x and y x 4. (a) 9 9 (b) 6 (c). Find the volume of the solid formed by revolving the region bounded
Applications of Integration Test Form A. Determine the area of the region bounded by the graphs of y x 4x and y x 4. (a) 9 9 (b) 6 (c). Find the volume of the solid formed by revolving the region bounded
4. Describe the correlation shown by the scatter plot. 8. Find the distance between the lines with the equations and.
 Integrated Math III Summer Review Packet DUE THE FIRST DAY OF SCHOOL The problems in this packet are designed to help you review topics from previous mathematics courses that are essential to your success
Integrated Math III Summer Review Packet DUE THE FIRST DAY OF SCHOOL The problems in this packet are designed to help you review topics from previous mathematics courses that are essential to your success
= f (a, b) + (hf x + kf y ) (a,b) +
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
2.2 Volumes of Solids of Revolution
 2.2 Volumes of Solids of Revolution We know how to find volumes of well-established solids such as a cylinder or rectangular box. What happens when the volume can t be found quite as easily nice or when
2.2 Volumes of Solids of Revolution We know how to find volumes of well-established solids such as a cylinder or rectangular box. What happens when the volume can t be found quite as easily nice or when
Volumes of Solids of Revolution Lecture #6 a
 Volumes of Solids of Revolution Lecture #6 a Sphereoid Parabaloid Hyperboloid Whateveroid Volumes Calculating 3-D Space an Object Occupies Take a cross-sectional slice. Compute the area of the slice. Multiply
Volumes of Solids of Revolution Lecture #6 a Sphereoid Parabaloid Hyperboloid Whateveroid Volumes Calculating 3-D Space an Object Occupies Take a cross-sectional slice. Compute the area of the slice. Multiply
Unit 4 End-of-Unit Assessment Study Guide
 Circles Unit 4 End-of-Unit Assessment Study Guide Definitions Radius (r) = distance from the center of a circle to the circle s edge Diameter (d) = distance across a circle, from edge to edge, through
Circles Unit 4 End-of-Unit Assessment Study Guide Definitions Radius (r) = distance from the center of a circle to the circle s edge Diameter (d) = distance across a circle, from edge to edge, through
For Test #1 study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework.
 Mth 74 - Review Problems for Test Test covers Sections 6.-6.5, 7. and 7. For Test # study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework.. The base of a solid is the region inside the circle
Mth 74 - Review Problems for Test Test covers Sections 6.-6.5, 7. and 7. For Test # study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework.. The base of a solid is the region inside the circle
Volumes of Solids of Revolution
 Volumes of Solids of Revolution Farid Aliniaeifard York University http://math.yorku.ca/ faridanf April 27, 2016 Overview What is a solid of revolution? Method of Rings or Method of Disks Method of Cylindrical
Volumes of Solids of Revolution Farid Aliniaeifard York University http://math.yorku.ca/ faridanf April 27, 2016 Overview What is a solid of revolution? Method of Rings or Method of Disks Method of Cylindrical
Applications of Integration
 Week 12. Applications of Integration 12.1.Areas Between Curves Example 12.1. Determine the area of the region enclosed by y = x 2 and y = x. Solution. First you need to find the points where the two functions
Week 12. Applications of Integration 12.1.Areas Between Curves Example 12.1. Determine the area of the region enclosed by y = x 2 and y = x. Solution. First you need to find the points where the two functions
EXERCISES 6.1. Cross-Sectional Areas. 6.1 Volumes by Slicing and Rotation About an Axis 405
 6. Volumes b Slicing and Rotation About an Ais 5 EXERCISES 6. Cross-Sectional Areas In Eercises and, find a formula for te area A() of te crosssections of te solid perpendicular to te -ais.. Te solid lies
6. Volumes b Slicing and Rotation About an Ais 5 EXERCISES 6. Cross-Sectional Areas In Eercises and, find a formula for te area A() of te crosssections of te solid perpendicular to te -ais.. Te solid lies
Math 116 First Midterm February 6, 2012
 Math 6 First Midterm Februar 6, 202 Name: Instructor: Section:. Do not open this exam until ou are told to do so. 2. This exam has 0 pages including this cover. There are 9 problems. Note that the problems
Math 6 First Midterm Februar 6, 202 Name: Instructor: Section:. Do not open this exam until ou are told to do so. 2. This exam has 0 pages including this cover. There are 9 problems. Note that the problems
APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION
 6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION The volume of a sphere is the limit of sums of volumes of approimating clinders. In this chapter we eplore some of the applications of the definite integral b using it to
6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION The volume of a sphere is the limit of sums of volumes of approimating clinders. In this chapter we eplore some of the applications of the definite integral b using it to
MATH 104 Sample problems for first exam - Fall MATH 104 First Midterm Exam - Fall (d) 256 3
 MATH 14 Sample problems for first exam - Fall 1 MATH 14 First Midterm Exam - Fall 1. Find the area between the graphs of y = 9 x and y = x + 1. (a) 4 (b) (c) (d) 5 (e) 4 (f) 81. A solid has as its base
MATH 14 Sample problems for first exam - Fall 1 MATH 14 First Midterm Exam - Fall 1. Find the area between the graphs of y = 9 x and y = x + 1. (a) 4 (b) (c) (d) 5 (e) 4 (f) 81. A solid has as its base
V = 2πx(1 x) dx. x 2 dx. 3 x3 0
 Wednesday, September 3, 215 Page 462 Problem 1 Problem. Use the shell method to set up and evaluate the integral that gives the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region (y = x, y =, x = 2)
Wednesday, September 3, 215 Page 462 Problem 1 Problem. Use the shell method to set up and evaluate the integral that gives the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region (y = x, y =, x = 2)
1) Find. a) b) c) d) e) 2) The function g is defined by the formula. Find the slope of the tangent line at x = 1. a) b) c) e) 3) Find.
 1 of 7 1) Find 2) The function g is defined by the formula Find the slope of the tangent line at x = 1. 3) Find 5 1 The limit does not exist. 4) The given function f has a removable discontinuity at x
1 of 7 1) Find 2) The function g is defined by the formula Find the slope of the tangent line at x = 1. 3) Find 5 1 The limit does not exist. 4) The given function f has a removable discontinuity at x
minutes/question 26 minutes
 st Set Section I (Multiple Choice) Part A (No Graphing Calculator) 3 problems @.96 minutes/question 6 minutes. What is 3 3 cos cos lim? h hh (D) - The limit does not exist.. At which of the five points
st Set Section I (Multiple Choice) Part A (No Graphing Calculator) 3 problems @.96 minutes/question 6 minutes. What is 3 3 cos cos lim? h hh (D) - The limit does not exist.. At which of the five points
Mathematics 134 Calculus 2 With Fundamentals Exam 2 Answers/Solutions for Sample Questions March 2, 2018
 Sample Exam Questions Mathematics 1 Calculus 2 With Fundamentals Exam 2 Answers/Solutions for Sample Questions March 2, 218 Disclaimer: The actual exam questions may be organized differently and ask questions
Sample Exam Questions Mathematics 1 Calculus 2 With Fundamentals Exam 2 Answers/Solutions for Sample Questions March 2, 218 Disclaimer: The actual exam questions may be organized differently and ask questions
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com January 2007 2. Figure 1 A a θ α A uniform solid right circular cone has base radius a and semi-vertical angle α, where 1 tanα = 3. The cone is freely suspended by a string attached
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com January 2007 2. Figure 1 A a θ α A uniform solid right circular cone has base radius a and semi-vertical angle α, where 1 tanα = 3. The cone is freely suspended by a string attached
12 m. 30 m. The Volume of a sphere is 36 cubic units. Find the length of the radius.
 NAME DATE PER. REVIEW #18: SPHERES, COMPOSITE FIGURES, & CHANGING DIMENSIONS PART 1: SURFACE AREA & VOLUME OF SPHERES Find the measure(s) indicated. Answers to even numbered problems should be rounded
NAME DATE PER. REVIEW #18: SPHERES, COMPOSITE FIGURES, & CHANGING DIMENSIONS PART 1: SURFACE AREA & VOLUME OF SPHERES Find the measure(s) indicated. Answers to even numbered problems should be rounded
I IS II. = 2y"\ V= n{ay 2 l 3 -\y 2 )dy. Jo n [fy 5 ' 3 1
 r Exercises 5.2 Figure 530 (a) EXAMPLE'S The region in the first quadrant bounded by the graphs of y = i* and y = 2x is revolved about the y-axis. Find the volume of the resulting solid. SOLUTON The region
r Exercises 5.2 Figure 530 (a) EXAMPLE'S The region in the first quadrant bounded by the graphs of y = i* and y = 2x is revolved about the y-axis. Find the volume of the resulting solid. SOLUTON The region
Unit 4. Applications of integration
 Unit 4. Applications of integration 4A. Areas between curves. 4A-1 Find the area between the following curves a) y = 2x 2 and y = 3x 1 b) y = x 3 and y = ax; assume a > 0 c) y = x + 1/x and y = 5/2. d)
Unit 4. Applications of integration 4A. Areas between curves. 4A-1 Find the area between the following curves a) y = 2x 2 and y = 3x 1 b) y = x 3 and y = ax; assume a > 0 c) y = x + 1/x and y = 5/2. d)
Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections
 Geometry A Unit Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections Name Date Objectives In this lesson, you will: visualize three-dimensional objects from different perspectives be able to create a projection
Geometry A Unit Answer Key: Three-Dimensional Cross Sections Name Date Objectives In this lesson, you will: visualize three-dimensional objects from different perspectives be able to create a projection
Unit 4. Applications of integration
 18.01 EXERCISES Unit 4. Applications of integration 4A. Areas between curves. 4A-1 Find the area between the following curves a) y = 2x 2 and y = 3x 1 b) y = x 3 and y = ax; assume a > 0 c) y = x + 1/x
18.01 EXERCISES Unit 4. Applications of integration 4A. Areas between curves. 4A-1 Find the area between the following curves a) y = 2x 2 and y = 3x 1 b) y = x 3 and y = ax; assume a > 0 c) y = x + 1/x
6.2 Volumes by Disks, Washers, and Cross-Sections
 6.2 Volumes by Disks, Washers, and Cross-Sections General Principle: Disks Take slices PERPENDICULAR to axis of rotation and rotate around that axis. About x-axis: About y-axis: 1 Examples: Set up integrals
6.2 Volumes by Disks, Washers, and Cross-Sections General Principle: Disks Take slices PERPENDICULAR to axis of rotation and rotate around that axis. About x-axis: About y-axis: 1 Examples: Set up integrals
Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework. SA of Prisms & Pyramids Pg. 441 # 1, 3, 5a, 7b, 11bc, 16. Surface Area of Cylinders WS 6.6
 UNIT 6 MEASUREMENT Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework May 6.1 8.1 May 4 6. 8. The Pythagorean Theorem Pg. 4 # 1ac, ac, ab, 4ac, 5, 7, 8, 10 Perimeter and Area (NO CIRCLES) Pg. 4 # 1acde, abdf,, 4, 11, 14,
UNIT 6 MEASUREMENT Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework May 6.1 8.1 May 4 6. 8. The Pythagorean Theorem Pg. 4 # 1ac, ac, ab, 4ac, 5, 7, 8, 10 Perimeter and Area (NO CIRCLES) Pg. 4 # 1acde, abdf,, 4, 11, 14,
Maximum and Minimum Problems
 Maximum and Minimum Problems Numbers 1. The sum of two positive numbers is 20. Find the two numbers such that a) the sum of the square is minimum, b) the product of one and the square of the other is maximum.
Maximum and Minimum Problems Numbers 1. The sum of two positive numbers is 20. Find the two numbers such that a) the sum of the square is minimum, b) the product of one and the square of the other is maximum.
USING THE DEFINITE INTEGRAL
 Print this page Chapter Eight USING THE DEFINITE INTEGRAL 8.1 AREAS AND VOLUMES In Chapter 5, we calculated areas under graphs using definite integrals. We obtained the integral by slicing up the region,
Print this page Chapter Eight USING THE DEFINITE INTEGRAL 8.1 AREAS AND VOLUMES In Chapter 5, we calculated areas under graphs using definite integrals. We obtained the integral by slicing up the region,
Geometry Second Semester Final Exam Review
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Geometry Second Semester Final Exam Review 1. Find the length of the leg of this right triangle. Give an approximation to 3 decimal places. 2. Find the length of the leg of this
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Geometry Second Semester Final Exam Review 1. Find the length of the leg of this right triangle. Give an approximation to 3 decimal places. 2. Find the length of the leg of this
B.Stat / B.Math. Entrance Examination 2017
 B.Stat / B.Math. Entrance Examination 017 BOOKLET NO. TEST CODE : UGA Forenoon Questions : 0 Time : hours Write your Name, Registration Number, Test Centre, Test Code and the Number of this Booklet in
B.Stat / B.Math. Entrance Examination 017 BOOKLET NO. TEST CODE : UGA Forenoon Questions : 0 Time : hours Write your Name, Registration Number, Test Centre, Test Code and the Number of this Booklet in
8/6/2010 Assignment Previewer
 8//2010 Assignment Previewer Week 8 Friday Homework (1324223) Question 12345789101112131415117181920 1. Question Detailsscalcet 3.9.ae.05.nva [129124] EXAMPLE 5 A man walks along a straight path at a speed
8//2010 Assignment Previewer Week 8 Friday Homework (1324223) Question 12345789101112131415117181920 1. Question Detailsscalcet 3.9.ae.05.nva [129124] EXAMPLE 5 A man walks along a straight path at a speed
S P. Geometry Final Exam Review. Name R S P Q P S. Chapter 7 1. If you reflect the point (2, -6) in the x-axis, the coordinates of the image would be:
 Geometry Final Exam Review Chapter 7 1. If you reflect the point (2, -6) in the x-axis, the coordinates of the image would be: Name 6. Use the graph below to complete the sentence. 2. If you reflect the
Geometry Final Exam Review Chapter 7 1. If you reflect the point (2, -6) in the x-axis, the coordinates of the image would be: Name 6. Use the graph below to complete the sentence. 2. If you reflect the
STRAND E: Measurement. UNIT 13 Areas Student Text Contents. Section Squares, Rectangles and Triangles Area and Circumference of Circles
 UNIT 13 Areas Student Text Contents STRAND E: Measurement Unit 13 Areas Student Text Contents Section 13.1 Squares, Rectangles and Triangles 13. Area and Circumference of Circles 13.3 Sector Areas and
UNIT 13 Areas Student Text Contents STRAND E: Measurement Unit 13 Areas Student Text Contents Section 13.1 Squares, Rectangles and Triangles 13. Area and Circumference of Circles 13.3 Sector Areas and
Name Period Teacher 1
 Name Period Teacher 1 Geometr Pre-AP Westside High School 6 th Si Weeks all dates subject to change (8 das) 01-015 Monda Tuesda Wednesda Thursda Frida April 6 9. Rotations 7 Rotations about a point not
Name Period Teacher 1 Geometr Pre-AP Westside High School 6 th Si Weeks all dates subject to change (8 das) 01-015 Monda Tuesda Wednesda Thursda Frida April 6 9. Rotations 7 Rotations about a point not
Indiana State Math Contest Geometry
 Indiana State Math Contest 018 Geometry This test was prepared by faculty at Indiana University - Purdue University Columbus Do not open this test booklet until you have been advised to do so by the test
Indiana State Math Contest 018 Geometry This test was prepared by faculty at Indiana University - Purdue University Columbus Do not open this test booklet until you have been advised to do so by the test
Problem #3 Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page Mark Sparks 2012
 Problem # Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 490 Mark Sparks 01 Finding Anti-derivatives of Polynomial-Type Functions If you had to explain to someone how to find
Problem # Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 490 Mark Sparks 01 Finding Anti-derivatives of Polynomial-Type Functions If you had to explain to someone how to find
Final Exam May 2, 2017
 Math 07 Calculus II Name: Final Exam May, 07 Circle the name of your instructor and, in the appropriate column, the name of your recitation leader. The second row is the time of your lecture. Radu Ledder
Math 07 Calculus II Name: Final Exam May, 07 Circle the name of your instructor and, in the appropriate column, the name of your recitation leader. The second row is the time of your lecture. Radu Ledder
Geometry Vocabulary Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
We imagine the egg being the three dimensional solid defined by rotating this ellipse around the x-axis:
 CHAPTER 6. INTEGRAL APPLICATIONS 7 Example. Imagine we want to find the volume of hard boiled egg. We could put the egg in a measuring cup and measure how much water it displaces. But we suppose we want
CHAPTER 6. INTEGRAL APPLICATIONS 7 Example. Imagine we want to find the volume of hard boiled egg. We could put the egg in a measuring cup and measure how much water it displaces. But we suppose we want
Log1 Contest Round 1 Theta Circles & Polygons. 4 points each. 5 points each
 014 015 Log1 Contest Round 1 Theta Circles & Polygons 1 Find the area, in square inches, enclosed by a circle whose diameter is 8 inches. A rectangle has sides of length 4 and 6. Find the area enclosed
014 015 Log1 Contest Round 1 Theta Circles & Polygons 1 Find the area, in square inches, enclosed by a circle whose diameter is 8 inches. A rectangle has sides of length 4 and 6. Find the area enclosed
Questions Q1. (a) Find the values of the constants A, B and C. (4) b) Hence find
 Questions Q1. (a) Find the values of the constants A, B and C. (4) b) Hence find (ii) Find, leaving your answer in the form a + ln b, where a and b are constants. (6) (Total 10 marks) Q2. (a) Find the
Questions Q1. (a) Find the values of the constants A, B and C. (4) b) Hence find (ii) Find, leaving your answer in the form a + ln b, where a and b are constants. (6) (Total 10 marks) Q2. (a) Find the
3. Draw the orthographic projection (front, right, and top) for the following solid. Also, state how many cubic units the volume is.
 PAP Geometry Unit 7 Review Name: Leave your answers as exact answers unless otherwise specified. 1. Describe the cross sections made by the intersection of the plane and the solids. Determine if the shape
PAP Geometry Unit 7 Review Name: Leave your answers as exact answers unless otherwise specified. 1. Describe the cross sections made by the intersection of the plane and the solids. Determine if the shape
6. Find the equation of the plane that passes through the point (-1,2,1) and contains the line x = y = z.
 Week 1 Worksheet Sections from Thomas 13 th edition: 12.4, 12.5, 12.6, 13.1 1. A plane is a set of points that satisfies an equation of the form c 1 x + c 2 y + c 3 z = c 4. (a) Find any three distinct
Week 1 Worksheet Sections from Thomas 13 th edition: 12.4, 12.5, 12.6, 13.1 1. A plane is a set of points that satisfies an equation of the form c 1 x + c 2 y + c 3 z = c 4. (a) Find any three distinct
Study Guide for Test 2
 Study Guide for Test Math 6: Calculus October, 7. Overview Non-graphing calculators will be allowed. You will need to know the following:. Set Pieces 9 4.. Trigonometric Substitutions (Section 7.).. Partial
Study Guide for Test Math 6: Calculus October, 7. Overview Non-graphing calculators will be allowed. You will need to know the following:. Set Pieces 9 4.. Trigonometric Substitutions (Section 7.).. Partial
AP Calculus AB Worksheet Areas, Volumes, and Arc Lengths
 WorksheetAreasVolumesArcLengths.n 1 AP Calculus AB Worksheet Areas, Volumes, and Arc Lengths Areas To find the area etween the graph of f(x) and the x-axis from x = a to x = we first determine if the function
WorksheetAreasVolumesArcLengths.n 1 AP Calculus AB Worksheet Areas, Volumes, and Arc Lengths Areas To find the area etween the graph of f(x) and the x-axis from x = a to x = we first determine if the function
Multivariable Calculus
 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
The Geometry of Solids
 CONDENSED LESSON 10.1 The Geometry of Solids In this lesson you will Learn about polyhedrons, including prisms and pyramids Learn about solids with curved surfaces, including cylinders, cones, and spheres
CONDENSED LESSON 10.1 The Geometry of Solids In this lesson you will Learn about polyhedrons, including prisms and pyramids Learn about solids with curved surfaces, including cylinders, cones, and spheres
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide
 Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Birkdale High School - Higher Scheme of Work
 Birkdale High School - Higher Scheme of Work Module 1 - Integers and Decimals Understand and order integers (assumed) Use brackets and hierarchy of operations (BODMAS) Add, subtract, multiply and divide
Birkdale High School - Higher Scheme of Work Module 1 - Integers and Decimals Understand and order integers (assumed) Use brackets and hierarchy of operations (BODMAS) Add, subtract, multiply and divide
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Name Date Period. Multiple Choice
 Name Date Period Worksheet 3.6 Optimization Show all work. Calculator permitted. Show all set-ups and analysis. Report all answers to 3 decimals and avoid intermediate rounding error. Multiple Choice 1.
Name Date Period Worksheet 3.6 Optimization Show all work. Calculator permitted. Show all set-ups and analysis. Report all answers to 3 decimals and avoid intermediate rounding error. Multiple Choice 1.
Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review
 Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review G-GPE.7 I can use the distance formula to compute perimeter and area of triangles and rectangles. Name Period Date 3. Find the area and perimeter of the triangle with
Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review G-GPE.7 I can use the distance formula to compute perimeter and area of triangles and rectangles. Name Period Date 3. Find the area and perimeter of the triangle with
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Convert the angle to decimal degrees and round to the nearest hundredth of a degree. 1)
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Convert the angle to decimal degrees and round to the nearest hundredth of a degree. 1)
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Review for Test 2 MATH 116 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the right triangle. If two sides are given, give angles in degrees and
Review for Test 2 MATH 116 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the right triangle. If two sides are given, give angles in degrees and
Unit Circle. Project Response Sheet
 NAME: PROJECT ACTIVITY: Trigonometry TOPIC Unit Circle GOALS MATERIALS Explore Degree and Radian Measure Explore x- and y- coordinates on the Unit Circle Investigate Odd and Even functions Investigate
NAME: PROJECT ACTIVITY: Trigonometry TOPIC Unit Circle GOALS MATERIALS Explore Degree and Radian Measure Explore x- and y- coordinates on the Unit Circle Investigate Odd and Even functions Investigate
