Conic Sections. College Algebra
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Young
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Conic Sections College Algebra
2 Conic Sections A conic section, or conic, is a shape resulting from intersecting a right circular cone with a plane. The angle at which the plane intersects the cone determines the shape. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola
3 Ellipses An ellipse is the set of all points x, y in a plane such that the sum of their distances from two fixed points is a constant. Each fixed point is called a focus (plural: foci). Every ellipse has two axes of symmetry. The longer axis is called the major axis, and the shorter axis is called the minor axis. Each endpoint of the major axis is the vertex of the ellipse (plural: vertices), and each endpoint of the minor axis is a co-vertex of the ellipse. The center of an ellipse is the midpoint of both the major and minor axes. The axes are perpendicular at the center. The foci always lie on the major axis, and the sum of the distances from the foci to any point on the ellipse (the constant sum) is greater than the distance between the foci.
4 Ellipses
5 Equation of a Horizontal Ellipse The standard form of the equation of an ellipse with center h, k axis parallel to the x-axis is a > b the length of the major axis is 2a &'( ) * ) +,'- ). ) = 1, where the coordinates of the vertices are h ± a, k the length of the minor axis is 2b the coordinates of the co-vertices are h, k ± b the coordinates of the foci are h ± c, k where c 7 = a 7 b 7 and major
6 Equation of a Vertical Ellipse The standard form of the equation of an ellipse with center h, k axis parallel to the y-axis is a > b the length of the major axis is 2a &'( ). ) +,'- ) * ) = 1, where the coordinates of the vertices are h, k ± a the length of the minor axis is 2b the coordinates of the co-vertices are h ± b, k the coordinates of the foci are h, k ± c where c 7 = a 7 b 7 and major
7 Finding the Equation of an Ellipse Given the vertices and foci of an ellipse not centered at the origin, write its equation in standard form. 1. Determine whether the major axis is parallel to the x-axis (or y-axis) by checking if the y-coordinates (or x-coordinates) of the given vertices and foci are the same, and use the appropriate standard form. 2. Identify the center of the ellipse (h, k) using the midpoint formula and the given coordinates for the vertices.
8 Finding the Equation of an Ellipse (cont.) 3. Find a 7 by solving for the length of the major axis, 2a, which is the distance between the given vertices. 4. Find c 7 using h and k, found in Step 2, along with the given coordinates for the foci. 5. Solve for b 7 using the equation c 7 = a 7 b Substitute the values for h, k, a 7, and b 7 into the standard form of the equation determined in Step 1.
9 Graphs of Ellipses Given an equation of an ellipse in standard form, graph the ellipse. 1. Locate the center at (h, k). 2. Determine the coordinates of the vertices and co-vertices at (h ± a, k) and h, k ± b. 3. Draw a smooth curve to form the ellipse. Example: &;7 ) Center is at ( 2,5). < +,'= ) > = 1 Major axis is parallel to y-axis a = 3, b = 2, so vertices at ( 2,8) and ( 2,2)
10 Equations of an Ellipse Given a general form of an equation of an ellipse, express the equation in standard form. 1. Recognize that an ellipse described by an equation in the form ax 7 + by 7 + cx + dy + e = 0 is in general form. 2. Group terms that contain the same variable and move the constant term to the opposite side of the equation. 3. Factor out the coefficients of the x 7 and y 7 terms. 4. Complete the square for each variable to rewrite the equation as m F x h 7 + m 7 y k 7 = m G where m F, m 7, and m G are constants. 5. Divide both sides of the equation by the constant term m F m 7.
11 Hyperbolas A hyperbola is the set of all points x, y in a plane such that the difference of the distances between x, y and the foci is a positive constant. Every hyperbola has two axes of symmetry. 1. The transverse axis is a line segment that passes through the center of the hyperbola and has vertices as its endpoints. The foci lie on the line that contains the transverse axis. 2. The conjugate axis is perpendicular to the transverse axis and has the co-vertices as its endpoints. The center of a hyperbola is the midpoint of both the transverse and conjugate axes, where they intersect.
12 Hyperbolas Every hyperbola has two asymptotes that pass through its center. As a hyperbola recedes from the center, its branches approach these asymptotes. The central rectangle of the hyperbola is centered at the origin with sides that pass through each vertex and co-vertex.
13 Equation of a Horizontal Hyperbola The standard form of the equation of a hyperbola with center h, k and transverse axis parallel to the x-axis is &'( ) * ),'- ). ) = 1, where the length of the transverse axis is 2a the coordinates of the vertices are h ± a, k the length of the conjugate axis is 2b the coordinates of the co-vertices are h, k ± b the distance between the foci is 2c, where c 7 = a 7 + b 7 the coordinates of the foci are h ± c, k
14 Equation of a Vertical Hyperbola The standard form of the equation of a hyperbola with center h, k and transverse axis parallel to the y-axis is,'- ) * ) &'( ). ) = 1, where the length of the transverse axis is 2a the coordinates of the vertices are h, k ± a the length of the conjugate axis is 2b the coordinates of the co-vertices are h ± b, k the distance between the foci is 2c, where c 7 = a 7 + b 7 the coordinates of the foci are h, k ± c
15 Asymptotes of a Hyperbola The asymptotes of a hyperbola coincide with the diagonals of the central rectangle. For a horizontal hyperbola, the length of the rectangle is 2a and its width is 2b. The slopes of the diagonals are ±., and each diagonal passes * through the center h, k. Using the point-slope formula, it is simple to show that the equations of the asymptotes are y = ±. * x h + k. For a vertical hyperbola, the equations of the asymptotes are y = ± * x h + k..
16 Hyperbolas Not Centered at the Origin
17 Finding the Equation of a Hyperbola Given the vertices and foci of a hyperbola centered at h, k, write its equation in standard form. 1. Determine whether the transverse axis is parallel to the x-axis (or y-axis) by checking if the y-coordinates (or x-coordinates) of the given vertices and foci are the same, and use the appropriate standard form. 2. Identify the center of the hyperbola (h, k) using the midpoint formula and the given coordinates for the vertices.
18 Finding the Equation of a Hyperbola (cont.) 3. Find a 7 by solving for the length of the transverse axis, 2a, which is the distance between the given vertices. 4. Find c 7 using h and k, found in Step 2, along with the given coordinates for the foci. 5. Solve b 7 using the equation b 7 = c 7 a Substitute the values for h, k, a 7, and b 7 into the standard form of the equation determined in Step 1.
19 Graphs of Hyperbolas Given an equation of a hyperbola in standard form, graph the hyperbola. 1. Determine the orientation of the transverse axis by comparing the equation to the standard forms for vertical and horizontal hyperbolas. 2. Determine the coordinates of the vertices and co-vertices a. Horizontal hyperbola: at (h ± a, k) and h, k ± b b. Vertical hyperbola: at (h, k ± a) and h ± b, k 3. Sketch the central rectangle and extend the diagonals to show the asymptotes. 4. Draw two smooth curves to form the hyperbola.
20 Desmos Interactive Topic: transformations of hyperbolas
21 Parabolas A parabola is the set of all points x, y in a plane that are the same distance from a fixed line, called the directrix, and a fixed point not on the directrix, called the focus. The axis of symmetry passes through the focus and vertex and is perpendicular to the directrix. The vertex is the midpoint between the directrix and the focus. The line segment that passes through the focus and is parallel to the directrix is called the latus rectum, also called the focal diameter.
22 Parabolas with Vertex at the Origin For a parabola whose axis of symmetry is the x-axis: Standard form equation is y 7 = 4px Focus is at p, 0 and the directrix line is x = p Endpoints of the focal diameter are at p, ±2p If p > 0, the parabola opens right. If p < 0, the parabola opens left. For a parabola whose axis of symmetry is the y-axis: Standard form equation is x 7 = 4py Focus is at 0, p and the directrix line is y = p Endpoints of the focal diameter are at ±2p, p If p > 0, the parabola opens up. If p < 0, the parabola opens down.
23 Graphs of Parabolas with Vertex at the Origin Given a standard form equation for a parabola centered at 0, 0, sketch the graph. 1. Determine which of the standard forms y 7 = 4px or x 7 = 4py applies. 2. Set 4p equal to the coefficient of the first-degree polynomial term to solve for the coordinates of the focus, at p, 0 for horizontal parabolas or at 0, p for vertical parabolas. 3. Find the endpoints of the focal diameter at p, ±2p for horizontal parabolas or at ±2p, p for vertical parabolas. 4. Draw a smooth curve that passes through both endpoints and the vertex at the origin.
24 Desmos Interactive Topic: find the focus, directrix, and endpoints of the focal diameter of a parabola whose vertex is at the origin
25 Parabolas with Vertices Not at the Origin If a parabola is translated h units horizontally and k units vertically, the vertex will be h, k. This translation results in the standard form of the equation with x replaced by x h and y replaced by y k. Horizontal Parabola Vertical Parabola Axis of Symmetry y = k x = h Equation y k 7 = 4p x h x h 7 = 4p y k Focus h + p, k h, k + p Directrix x = h p y = k p Endpoints of Focal Diameter h + p, k ± 2p h ± 2p, k + p
26 Desmos Interactive Topic: find the vertex, axis of symmetry, focus, directrix, and endpoints of the focal diameter of a parabola whose vertex is not at the origin
27 Quick Review What are the three types of conic sections? From the standard form equation of an ellipse, how can you tell if the major axis is a vertical line or a horizontal line? What is the transverse axis of a hyperbola? From the standard form equation of a hyperbola, how do you find the line equations for the asymptotes? What is the focal diameter? What are the coordinates of the vertices and co-vertices of a hyperbola? What is a directrix? How can you tell in which direction a parabola opens?
Chapter 10. Exploring Conic Sections
 Chapter 10 Exploring Conic Sections Conics A conic section is a curve formed by the intersection of a plane and a hollow cone. Each of these shapes are made by slicing the cone and observing the shape
Chapter 10 Exploring Conic Sections Conics A conic section is a curve formed by the intersection of a plane and a hollow cone. Each of these shapes are made by slicing the cone and observing the shape
The point (x, y) lies on the circle of radius r and center (h, k) iff. x h y k r
 NOTES +: ANALYTIC GEOMETRY NAME LESSON. GRAPHS OF EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES (CIRCLES). Standard form of a Circle The point (x, y) lies on the circle of radius r and center (h, k) iff x h y k r Center:
NOTES +: ANALYTIC GEOMETRY NAME LESSON. GRAPHS OF EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES (CIRCLES). Standard form of a Circle The point (x, y) lies on the circle of radius r and center (h, k) iff x h y k r Center:
Unit 12 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork
 Unit 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork Back in Unit 7, we delved into the algebra and geometry of lines. We showed that lines can be written in several forms: a) the general form: Ax + By + C =
Unit 1 Topics in Analytic Geometry - Classwork Back in Unit 7, we delved into the algebra and geometry of lines. We showed that lines can be written in several forms: a) the general form: Ax + By + C =
Multivariable Calculus
 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet
 Name: Period: ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet Algebra II Unit 10 Plan: This plan is subject to change at the teacher s discretion. Section Topic Formative Work Due Date 10.3 Circles
Name: Period: ALGEBRA II UNIT X: Conic Sections Unit Notes Packet Algebra II Unit 10 Plan: This plan is subject to change at the teacher s discretion. Section Topic Formative Work Due Date 10.3 Circles
Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 2 4 x 0
 Pre-Calculus Section 1.1 Completing the Square Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 4 x 0. 3x 3y
Pre-Calculus Section 1.1 Completing the Square Rewrite the equation in the left column into the format in the middle column. The answers are in the third column. 1. y 4y 4x 4 0 y k 4p x h y 4 x 0. 3x 3y
Pre-Calculus. 2) Find the equation of the circle having (2, 5) and (-2, -1) as endpoints of the diameter.
 Pre-Calculus Conic Review Name Block Date Circles: 1) Determine the center and radius of each circle. a) ( x 5) + ( y + 6) = 11 b) x y x y + 6 + 16 + 56 = 0 ) Find the equation of the circle having (,
Pre-Calculus Conic Review Name Block Date Circles: 1) Determine the center and radius of each circle. a) ( x 5) + ( y + 6) = 11 b) x y x y + 6 + 16 + 56 = 0 ) Find the equation of the circle having (,
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students. Francis Joseph H. Campeña, De La Salle University Manila
 KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila January 26, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila January 26, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
Ex. 1-3: Put each circle below in the correct equation form as listed!! above, then determine the center and radius of each circle.
 Day 1 Conics - Circles Equation of a Circle The circle with center (h, k) and radius r is the set of all points (x, y) that satisfies!! (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 Ex. 1-3: Put each circle below in the correct
Day 1 Conics - Circles Equation of a Circle The circle with center (h, k) and radius r is the set of all points (x, y) that satisfies!! (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2 Ex. 1-3: Put each circle below in the correct
Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics. A circle is
 Name: Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics Section Circles A circle is _ Example 1 Write an equation for the circle with center (3, ) and radius 5. To do this, we ll need the x1 y y1 distance formula:
Name: Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics Section Circles A circle is _ Example 1 Write an equation for the circle with center (3, ) and radius 5. To do this, we ll need the x1 y y1 distance formula:
1.) Write the equation of a circle in standard form with radius 3 and center (-3,4). Then graph the circle.
 Welcome to the world of conic sections! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bfonicn4bbg Some examples of conics in the real world: Parabolas Ellipse Hyperbola Your Assignment: Circle -Find at least four pictures
Welcome to the world of conic sections! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bfonicn4bbg Some examples of conics in the real world: Parabolas Ellipse Hyperbola Your Assignment: Circle -Find at least four pictures
Standard Equation of a Circle
 Math 335 Trigonometry Conics We will study all 4 types of conic sections, which are curves that result from the intersection of a right circular cone and a plane that does not contain the vertex. (If the
Math 335 Trigonometry Conics We will study all 4 types of conic sections, which are curves that result from the intersection of a right circular cone and a plane that does not contain the vertex. (If the
9.3 Hyperbolas and Rotation of Conics
 9.3 Hyperbolas and Rotation of Conics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Write equations of hyperbolas in standard form. Find asymptotes of and graph hyperbolas. Use
9.3 Hyperbolas and Rotation of Conics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Write equations of hyperbolas in standard form. Find asymptotes of and graph hyperbolas. Use
Unit 5: Quadratic Functions
 Unit 5: Quadratic Functions LESSON #5: THE PARABOLA GEOMETRIC DEFINITION DIRECTRIX FOCUS LATUS RECTUM Geometric Definition of a Parabola Quadratic Functions Geometrically, a parabola is the set of all
Unit 5: Quadratic Functions LESSON #5: THE PARABOLA GEOMETRIC DEFINITION DIRECTRIX FOCUS LATUS RECTUM Geometric Definition of a Parabola Quadratic Functions Geometrically, a parabola is the set of all
Math 155, Lecture Notes- Bonds
 Math 155, Lecture Notes- Bonds Name Section 10.1 Conics and Calculus In this section, we will study conic sections from a few different perspectives. We will consider the geometry-based idea that conics
Math 155, Lecture Notes- Bonds Name Section 10.1 Conics and Calculus In this section, we will study conic sections from a few different perspectives. We will consider the geometry-based idea that conics
CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS
 CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Writing equations of conic sections ) Graphing equations of conic sections 3) Solving quadratic systems Section: Essential Question 8-1 Apply
CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Writing equations of conic sections ) Graphing equations of conic sections 3) Solving quadratic systems Section: Essential Question 8-1 Apply
We start by looking at a double cone. Think of this as two pointy ice cream cones that are connected at the small tips:
 Math 1330 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text. We start
Math 1330 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text. We start
Algebra II. Slide 1 / 181. Slide 2 / 181. Slide 3 / 181. Conic Sections Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 181 Algebra II Slide 2 / 181 Conic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 181 Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Introduction
Slide 1 / 181 Algebra II Slide 2 / 181 Conic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 181 Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Introduction
Chapter 8.1 Conic Sections/Parabolas. Honors Pre-Calculus Rogers High School
 Chapter 8.1 Conic Sections/Parabolas Honors Pre-Calculus Rogers High School Introduction to Conic Sections Conic sections are defined geometrically as the result of the intersection of a plane with a right
Chapter 8.1 Conic Sections/Parabolas Honors Pre-Calculus Rogers High School Introduction to Conic Sections Conic sections are defined geometrically as the result of the intersection of a plane with a right
Mid-Chapter Quiz: Lessons 7-1 through 7-3
 Write an equation for and graph a parabola with the given focus F and vertex V 1. F(1, 5), V(1, 3) Because the focus and vertex share the same x coordinate, the graph is vertical. The focus is (h, k +
Write an equation for and graph a parabola with the given focus F and vertex V 1. F(1, 5), V(1, 3) Because the focus and vertex share the same x coordinate, the graph is vertical. The focus is (h, k +
Algebra II Lesson 10-5: Hyperbolas Mrs. Snow, Instructor
 Algebra II Lesson 10-5: Hyperbolas Mrs. Snow, Instructor In this section, we will look at the hyperbola. A hyperbola is a set of points P in a plane such that the absolute value of the difference between
Algebra II Lesson 10-5: Hyperbolas Mrs. Snow, Instructor In this section, we will look at the hyperbola. A hyperbola is a set of points P in a plane such that the absolute value of the difference between
Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry
 Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9.1 The Ellipse 9.2 The Hyperbola 9.3 The Parabola 9.4 Rotation of Axes 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Conic
Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9.1 The Ellipse 9.2 The Hyperbola 9.3 The Parabola 9.4 Rotation of Axes 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Conic
Figures adapted from Mathworld.wolfram.com and vectosite.net.
 MTH 11 CONIC SECTIONS 1 The four basic types of conic sections we will discuss are: circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas. They were named conic by the Greeks who used them to describe the intersection
MTH 11 CONIC SECTIONS 1 The four basic types of conic sections we will discuss are: circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas. They were named conic by the Greeks who used them to describe the intersection
2.) Write the standard form of the equation of a circle whose endpoints of diameter are (4, 7) and (2,3).
 Ch 10: Conic Sections Name: Objectives: Students will be able to: -graph parabolas, hyperbolas and ellipses and answer characteristic questions about these graphs. -write equations of conic sections Dec
Ch 10: Conic Sections Name: Objectives: Students will be able to: -graph parabolas, hyperbolas and ellipses and answer characteristic questions about these graphs. -write equations of conic sections Dec
Conics. By: Maya, Dietrich, and Jesse
 Conics By: Maya, Dietrich, and Jesse Exploring Conics (This is basically the summary too) A conic section curve formed by intersection of a plane and double cone: by changing plane, one can create parabola,
Conics By: Maya, Dietrich, and Jesse Exploring Conics (This is basically the summary too) A conic section curve formed by intersection of a plane and double cone: by changing plane, one can create parabola,
Geometry: Conic Sections
 Conic Sections Introduction When a right circular cone is intersected by a plane, as in figure 1 below, a family of four types of curves results. Because of their relationship to the cone, they are called
Conic Sections Introduction When a right circular cone is intersected by a plane, as in figure 1 below, a family of four types of curves results. Because of their relationship to the cone, they are called
Summary of Formulas: see
 To review the Conic Sections, Identify them and sketch them from the given equations, watch the following set of YouTube videos. They are followed by several practice problems for you to try, covering
To review the Conic Sections, Identify them and sketch them from the given equations, watch the following set of YouTube videos. They are followed by several practice problems for you to try, covering
Substituting a 2 b 2 for c 2 and using a little algebra, we can then derive the standard equation for an ellipse centred at the origin,
 Conics onic sections are the curves which result from the intersection of a plane with a cone. These curves were studied and revered by the ancient Greeks, and were written about extensively by both Euclid
Conics onic sections are the curves which result from the intersection of a plane with a cone. These curves were studied and revered by the ancient Greeks, and were written about extensively by both Euclid
8.5 Graph and Write Equations of Hyperbolas p.518 What are the parts of a hyperbola? What are the standard form equations of a hyperbola?
 8.5 Graph and Write Equations of Hyperbolas p.518 What are the parts of a hyperbola? What are the standard form equations of a hyperbola? How do you know which way it opens? Given a & b, how do you find
8.5 Graph and Write Equations of Hyperbolas p.518 What are the parts of a hyperbola? What are the standard form equations of a hyperbola? How do you know which way it opens? Given a & b, how do you find
Study Guide and Review
 Graph the hyperbola given by each equation. 30. = 1 The equation is in standard form, and h = 6 and k = 3. Because a 2 = 30 and b 2 = 8, a = 5.5 and b =. The values of a and b can be used to find c. c
Graph the hyperbola given by each equation. 30. = 1 The equation is in standard form, and h = 6 and k = 3. Because a 2 = 30 and b 2 = 8, a = 5.5 and b =. The values of a and b can be used to find c. c
Unit 8, Ongoing Activity, Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties
 Unit 8, Ongoing Activity, Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties Unit 8 Conic Sections 8.1 Circle write the definition, provide examples of both the standard
Unit 8, Ongoing Activity, Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties Little Black Book of Algebra II Properties Unit 8 Conic Sections 8.1 Circle write the definition, provide examples of both the standard
We start by looking at a double cone. Think of this as two pointy ice cream cones that are connected at the small tips:
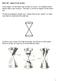 Math 1330 Chapter 8 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text.
Math 1330 Chapter 8 Conic Sections In this chapter, we will study conic sections (or conics). It is helpful to know exactly what a conic section is. This topic is covered in Chapter 8 of the online text.
Acc. Pre Calculus Day 5 - Parabolas Notesheet PARABOLAS
 Acc. Pre Calculus Day 5 - Parabolas Notesheet Name Date Block 1) Complete these truths about parabolas: * Parabolas are - shaped. PARABOLAS * Parabolas have a line of. * Parabolas are the graphs of functions.
Acc. Pre Calculus Day 5 - Parabolas Notesheet Name Date Block 1) Complete these truths about parabolas: * Parabolas are - shaped. PARABOLAS * Parabolas have a line of. * Parabolas are the graphs of functions.
13.1 2/20/2018. Conic Sections. Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles
 13 Conic Sections 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles 13.2 Conic Sections: Ellipses 13.3 Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 13.4 Nonlinear Systems of Equations 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles
13 Conic Sections 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles 13.2 Conic Sections: Ellipses 13.3 Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 13.4 Nonlinear Systems of Equations 13.1 Conic Sections: Parabolas and Circles
Algebra II. Midpoint and Distance Formula. Slide 1 / 181 Slide 2 / 181. Slide 3 / 181. Slide 4 / 181. Slide 6 / 181. Slide 5 / 181.
 Slide 1 / 181 Slide 2 / 181 lgebra II onic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 181 Slide 4 / 181 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and istance Formulas
Slide 1 / 181 Slide 2 / 181 lgebra II onic Sections 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 181 Slide 4 / 181 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and istance Formulas
Module 3: Stand Up Conics
 MATH55 Module 3: Stand Up Conics Main Math concepts: Conic Sections (i.e. Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas), nd degree equations Auxilliary ideas: Analytic vs. Co-ordinate-free Geometry, Parameters, Calculus.
MATH55 Module 3: Stand Up Conics Main Math concepts: Conic Sections (i.e. Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas), nd degree equations Auxilliary ideas: Analytic vs. Co-ordinate-free Geometry, Parameters, Calculus.
8.2 Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas
 8.2 Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas Where is the focus and directrix compared to the vertex? How do you know what direction a parabola opens? How do you write the equation of a parabola given the
8.2 Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas Where is the focus and directrix compared to the vertex? How do you know what direction a parabola opens? How do you write the equation of a parabola given the
Algebra II Chapter 10 Conics Notes Packet. Student Name Teacher Name
 Algebra II Chapter 10 Conics Notes Packet Student Name Teacher Name 1 Conic Sections 2 Identifying Conics Ave both variables squared?' No PARABOLA y = a(x- h)z + k x = a(y- k)z + h YEs Put l'h squared!'erms
Algebra II Chapter 10 Conics Notes Packet Student Name Teacher Name 1 Conic Sections 2 Identifying Conics Ave both variables squared?' No PARABOLA y = a(x- h)z + k x = a(y- k)z + h YEs Put l'h squared!'erms
7. r = r = r = r = r = 2 5
 Exercise a: I. Write the equation in standard form of each circle with its center at the origin and the given radius.. r = 4. r = 6 3. r = 7 r = 5 5. r = 6. r = 6 7. r = 0.3 8. r =.5 9. r = 4 0. r = 3.
Exercise a: I. Write the equation in standard form of each circle with its center at the origin and the given radius.. r = 4. r = 6 3. r = 7 r = 5 5. r = 6. r = 6 7. r = 0.3 8. r =.5 9. r = 4 0. r = 3.
PreCalculus Chapter 9 Practice Test Name:
 This ellipse has foci 0,, and therefore has a vertical major axis. The standard form for an ellipse with a vertical major axis is: 1 Note: graphs of conic sections for problems 1 to 1 were made with the
This ellipse has foci 0,, and therefore has a vertical major axis. The standard form for an ellipse with a vertical major axis is: 1 Note: graphs of conic sections for problems 1 to 1 were made with the
Chapter 10 Test Review
 Name: Class: Date: Chapter 10 Test Review Short Answer 1. Write an equation of a parabola with a vertex at the origin and a focus at ( 2, 0). 2. Write an equation of a parabola with a vertex at the origin
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 10 Test Review Short Answer 1. Write an equation of a parabola with a vertex at the origin and a focus at ( 2, 0). 2. Write an equation of a parabola with a vertex at the origin
Name. Center axis. Introduction to Conic Sections
 Name Introduction to Conic Sections Center axis This introduction to conic sections is going to focus on what they some of the skills needed to work with their equations and graphs. year, we will only
Name Introduction to Conic Sections Center axis This introduction to conic sections is going to focus on what they some of the skills needed to work with their equations and graphs. year, we will only
CK 12 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1
 10.1 Parabolas with Vertex at the Origin Answers 1. up 2. left 3. down 4.focus: (0, 0.5), directrix: y = 0.5 5.focus: (0.0625, 0), directrix: x = 0.0625 6.focus: ( 1.25, 0), directrix: x = 1.25 7.focus:
10.1 Parabolas with Vertex at the Origin Answers 1. up 2. left 3. down 4.focus: (0, 0.5), directrix: y = 0.5 5.focus: (0.0625, 0), directrix: x = 0.0625 6.focus: ( 1.25, 0), directrix: x = 1.25 7.focus:
Chapter 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry
 Chapter 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry What You ll Learn: 9.1 Introduction to Conics: Parabolas 9.2 Ellipses 9.3 Hyperbolas 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Polar Coordinates 9.7 Graphs of Polar Equations 9.1
Chapter 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry What You ll Learn: 9.1 Introduction to Conics: Parabolas 9.2 Ellipses 9.3 Hyperbolas 9.5 Parametric Equations 9.6 Polar Coordinates 9.7 Graphs of Polar Equations 9.1
Name: Class: Date: Conics Multiple Choice Pre-Test. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Conics Multiple Choice Pre-Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Graph the equation x 2 + y 2 = 36. Then describe the
Name: Class: Date: Conics Multiple Choice Pre-Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Graph the equation x 2 + y 2 = 36. Then describe the
= ( )= To find the domain, we look at the vertical asymptote(s) (where denominator equals zero) , =0
 Precalculus College Algebra Review for Final Name It is also a good idea to go back through your old tests and quizzes to review. 1. Find (+1) given ()=3 +1 2. Determine () given ()=+2 and ()= (+1)=3(+1)
Precalculus College Algebra Review for Final Name It is also a good idea to go back through your old tests and quizzes to review. 1. Find (+1) given ()=3 +1 2. Determine () given ()=+2 and ()= (+1)=3(+1)
OpenStax-CNX module: m The Ellipse. OpenStax College. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49438 1 The Ellipse OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you will: Write equations
OpenStax-CNX module: m49438 1 The Ellipse OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you will: Write equations
What you will learn today
 What you will learn today Conic Sections (in 2D coordinates) Cylinders (3D) Quadric Surfaces (3D) Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/24 Parabolas ellipses Hyperbolas Shifted Conics Conic sections result
What you will learn today Conic Sections (in 2D coordinates) Cylinders (3D) Quadric Surfaces (3D) Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/24 Parabolas ellipses Hyperbolas Shifted Conics Conic sections result
, minor axis of length 12. , asymptotes y 2x. 16y
 Math 4 Midterm 1 Review CONICS [1] Find the equations of the following conics. If the equation corresponds to a circle find its center & radius. If the equation corresponds to a parabola find its focus
Math 4 Midterm 1 Review CONICS [1] Find the equations of the following conics. If the equation corresponds to a circle find its center & radius. If the equation corresponds to a parabola find its focus
Put your initials on the top of every page, in case the pages become separated.
 Math 1201, Fall 2016 Name (print): Dr. Jo Nelson s Calculus III Practice for 1/2 of Final, Midterm 1 Material Time Limit: 90 minutes DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. This exam contains
Math 1201, Fall 2016 Name (print): Dr. Jo Nelson s Calculus III Practice for 1/2 of Final, Midterm 1 Material Time Limit: 90 minutes DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. This exam contains
10.2: Parabolas. Chapter 10: Conic Sections. Conic sections are plane figures formed by the intersection of a double-napped cone and a plane.
 Conic sections are plane figures formed b the intersection of a double-napped cone and a plane. Chapter 10: Conic Sections Ellipse Hperbola The conic sections ma be defined as the sets of points in the
Conic sections are plane figures formed b the intersection of a double-napped cone and a plane. Chapter 10: Conic Sections Ellipse Hperbola The conic sections ma be defined as the sets of points in the
Practice Test - Chapter 7
 Write an equation for an ellipse with each set of characteristics. 1. vertices (7, 4), ( 3, 4); foci (6, 4), ( 2, 4) The distance between the vertices is 2a. 2a = 7 ( 3) a = 5; a 2 = 25 The distance between
Write an equation for an ellipse with each set of characteristics. 1. vertices (7, 4), ( 3, 4); foci (6, 4), ( 2, 4) The distance between the vertices is 2a. 2a = 7 ( 3) a = 5; a 2 = 25 The distance between
Conic Sections: Parabolas
 Conic Sections: Parabolas Why are the graphs of parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas called 'conic sections'? Because if you pass a plane through a double cone, the intersection of the plane and the cone
Conic Sections: Parabolas Why are the graphs of parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas called 'conic sections'? Because if you pass a plane through a double cone, the intersection of the plane and the cone
P.5 Rational Expressions
 P.5 Rational Expressions I Domain Domain: Rational expressions : Finding domain a. polynomials: b. Radicals: keep it real! i. sqrt(x-2) x>=2 [2, inf) ii. cubert(x-2) all reals since cube rootscan be positive
P.5 Rational Expressions I Domain Domain: Rational expressions : Finding domain a. polynomials: b. Radicals: keep it real! i. sqrt(x-2) x>=2 [2, inf) ii. cubert(x-2) all reals since cube rootscan be positive
Conic Sections. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Conic Sections MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department o Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction The conic sections include the parabola, the ellipse, and the hyperbola. y y y x x x Parabola A
Conic Sections MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department o Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction The conic sections include the parabola, the ellipse, and the hyperbola. y y y x x x Parabola A
Chapter 11. Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates
 Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ayman H. Sakka Chapter 11 Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates In this chapter we study new ways to define curves in the plane, give geometric definitions of parabolas, ellipses,
Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ayman H. Sakka Chapter 11 Parametric Equations And Polar Coordinates In this chapter we study new ways to define curves in the plane, give geometric definitions of parabolas, ellipses,
Common Core Cluster. Experiment with transformations in the plane. Unpacking What does this standard mean that a student will know and be able to do?
 Congruence G.CO Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Congruence G.CO Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Accelerated Pre-Calculus Unit 1 Task 1: Our Only Focus: Circles & Parabolas Review
 Accelerated Pre-Calculus Unit 1 Task 1: Our Only Focus: Circles & Parabolas Review Name: Date: Period: For most students, you last learned about conic sections in Analytic Geometry, which was a while ago.
Accelerated Pre-Calculus Unit 1 Task 1: Our Only Focus: Circles & Parabolas Review Name: Date: Period: For most students, you last learned about conic sections in Analytic Geometry, which was a while ago.
Common Core Specifications for Geometry
 1 Common Core Specifications for Geometry Examples of how to read the red references: Congruence (G-Co) 2-03 indicates this spec is implemented in Unit 3, Lesson 2. IDT_C indicates that this spec is implemented
1 Common Core Specifications for Geometry Examples of how to read the red references: Congruence (G-Co) 2-03 indicates this spec is implemented in Unit 3, Lesson 2. IDT_C indicates that this spec is implemented
Warm-Up. Write the standard equation of the circle with the given radius and center. 1) 9; (0,0) 2) 1; (0,5) 3) 4; (-8,-1) 4) 5; (4,2)
 Warm-Up Write the standard equation of the circle with the given radius and center. 1) 9; (0,0) ) 1; (0,5) 3) 4; (-8,-1) 4) 5; (4,) 8.4 Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses What are the major parts of
Warm-Up Write the standard equation of the circle with the given radius and center. 1) 9; (0,0) ) 1; (0,5) 3) 4; (-8,-1) 4) 5; (4,) 8.4 Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses What are the major parts of
Practice Test - Chapter 9
 Find the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints at the given coordinates 1 (8, 3), ( 4, 9) Substitute 8, 4, 3 and 9 for x 1, x 2, y 1 and y 2 respectively in the midpoint formula Find the distance
Find the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints at the given coordinates 1 (8, 3), ( 4, 9) Substitute 8, 4, 3 and 9 for x 1, x 2, y 1 and y 2 respectively in the midpoint formula Find the distance
Find the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints at the given coordinates. 1. (8, 3), ( 4, 9) SOLUTION: Substitute 8, 4, 3 and 9 for x 1
 Find the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints at the given coordinates. 1. (8, 3), ( 4, 9) Substitute 8, 4, 3 and 9 for x 1, x 2, y 1 and y 2 respectively in the midpoint formula. 2. Substitute
Find the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints at the given coordinates. 1. (8, 3), ( 4, 9) Substitute 8, 4, 3 and 9 for x 1, x 2, y 1 and y 2 respectively in the midpoint formula. 2. Substitute
Each point P in the xy-plane corresponds to an ordered pair (x, y) of real numbers called the coordinates of P.
 Lecture 7, Part I: Section 1.1 Rectangular Coordinates Rectangular or Cartesian coordinate system Pythagorean theorem Distance formula Midpoint formula Lecture 7, Part II: Section 1.2 Graph of Equations
Lecture 7, Part I: Section 1.1 Rectangular Coordinates Rectangular or Cartesian coordinate system Pythagorean theorem Distance formula Midpoint formula Lecture 7, Part II: Section 1.2 Graph of Equations
3. Solve the following. Round to the nearest thousandth.
 This review does NOT cover everything! Be sure to go over all notes, homework, and tests that were given throughout the semester. 1. Given g ( x) i, h( x) x 4x x, f ( x) x, evaluate the following: a) f
This review does NOT cover everything! Be sure to go over all notes, homework, and tests that were given throughout the semester. 1. Given g ( x) i, h( x) x 4x x, f ( x) x, evaluate the following: a) f
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
1.8 Coordinate Geometry. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 1.8 Coordinate Geometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives The Coordinate Plane The Distance and Midpoint Formulas Graphs of Equations in Two Variables Intercepts Circles Symmetry
1.8 Coordinate Geometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives The Coordinate Plane The Distance and Midpoint Formulas Graphs of Equations in Two Variables Intercepts Circles Symmetry
Log1 Contest Round 2 Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons. 4 points each
 Name: Units do not have to be included. 016 017 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it
Name: Units do not have to be included. 016 017 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it
1. Answer: x or x. Explanation Set up the two equations, then solve each equation. x. Check
 Thinkwell s Placement Test 5 Answer Key If you answered 7 or more Test 5 questions correctly, we recommend Thinkwell's Algebra. If you answered fewer than 7 Test 5 questions correctly, we recommend Thinkwell's
Thinkwell s Placement Test 5 Answer Key If you answered 7 or more Test 5 questions correctly, we recommend Thinkwell's Algebra. If you answered fewer than 7 Test 5 questions correctly, we recommend Thinkwell's
MATH 110 analytic geometry Conics. The Parabola
 1 MATH 11 analytic geometry Conics The graph of a second-degree equation in the coordinates x and y is called a conic section or, more simply, a conic. This designation derives from the fact that the curve
1 MATH 11 analytic geometry Conics The graph of a second-degree equation in the coordinates x and y is called a conic section or, more simply, a conic. This designation derives from the fact that the curve
) 2 + (y 2. x 1. y c x2 = y
 Graphing Parabola Parabolas A parabola is a set of points P whose distance from a fixed point, called the focus, is equal to the perpendicular distance from P to a line, called the directrix. Since this
Graphing Parabola Parabolas A parabola is a set of points P whose distance from a fixed point, called the focus, is equal to the perpendicular distance from P to a line, called the directrix. Since this
Chapter 10. Homework
 Chapter 0 Homework Lesson 0- pages 538 5 Exercises. 2. Hyperbola: center (0, 0), y-intercepts at ±, no x-intercepts, the lines of symmetry are the x- and y-axes; domain: all real numbers, range: y 5 3
Chapter 0 Homework Lesson 0- pages 538 5 Exercises. 2. Hyperbola: center (0, 0), y-intercepts at ±, no x-intercepts, the lines of symmetry are the x- and y-axes; domain: all real numbers, range: y 5 3
Mathematics High School Geometry
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Algebra II. 6 th Six Weeks
 Algebra II 6 th Six Weeks 0 1 Chapter 9 Test Review 7 Circles HW: PP 1-4 Circles WS EXTRA GRAPH PP37-38 4 Ellipses 8 Parabolas HW: PP 5-7 Parabolas WS 1 5 Ellipses CW: Chapter 9 Test Review Sheet 9 Parabolas
Algebra II 6 th Six Weeks 0 1 Chapter 9 Test Review 7 Circles HW: PP 1-4 Circles WS EXTRA GRAPH PP37-38 4 Ellipses 8 Parabolas HW: PP 5-7 Parabolas WS 1 5 Ellipses CW: Chapter 9 Test Review Sheet 9 Parabolas
Honors Precalculus: Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically. Page 1
 Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically 1. Plot points on the Cartesian coordinate plane. P.1 2. Represent data graphically using scatter plots, bar graphs, & line graphs. P.1
Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically 1. Plot points on the Cartesian coordinate plane. P.1 2. Represent data graphically using scatter plots, bar graphs, & line graphs. P.1
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Pre-Calculus Mid Term Review. January 2014 Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Use the graph of the function f, plotted with a solid
Pre-Calculus Mid Term Review. January 2014 Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Use the graph of the function f, plotted with a solid
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Precalculus Fall 204 Midterm Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find an equation in standard form for the hyperbola that
Precalculus Fall 204 Midterm Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find an equation in standard form for the hyperbola that
3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS
 3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Finding the Zeros of a Quadratic Function Examples 1 and and more Find the zeros of f(x) = x x 6. Solution by Factoring f(x) = x x 6 = (x 3)(x + )
3.1 INTRODUCTION TO THE FAMILY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS Finding the Zeros of a Quadratic Function Examples 1 and and more Find the zeros of f(x) = x x 6. Solution by Factoring f(x) = x x 6 = (x 3)(x + )
9.1: GRAPHING QUADRATICS ALGEBRA 1
 9.1: GRAPHING QUADRATICS ALGEBRA 1 OBJECTIVES I will be able to graph quadratics: Given in Standard Form Given in Vertex Form Given in Intercept Form What does the graph of a quadratic look like? https://www.desmos.com/calculator
9.1: GRAPHING QUADRATICS ALGEBRA 1 OBJECTIVES I will be able to graph quadratics: Given in Standard Form Given in Vertex Form Given in Intercept Form What does the graph of a quadratic look like? https://www.desmos.com/calculator
Geometry. Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 G.CO.2. Common Core Institute
 Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
Geometry Cluster: Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of
Assignment Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Assignment.1-.3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) The arch beneath a bridge is semi-elliptical, a one-way
Assignment.1-.3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) The arch beneath a bridge is semi-elliptical, a one-way
Geometry Common Core State Standard (CCSS) Math
 = ntroduced R=Reinforced/Reviewed HGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY MATH STANDARDS 1 2 3 4 Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line,
= ntroduced R=Reinforced/Reviewed HGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY MATH STANDARDS 1 2 3 4 Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line,
Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended. Mathematics. Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c
 Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended Mathematics Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c Most Complex Least Complex Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions
Ohio s Learning Standards-Extended Mathematics Congruence Standards Complexity a Complexity b Complexity c Most Complex Least Complex Experiment with transformations in the plane G.CO.1 Know precise definitions
Z+z 1 X2 Y2. or y, Graph / 4 25 jj y=±x. x2+y 2=
 Conic Sections Understanding the graphs of conic sections is made easier if you first begin with the simplest form of a conic section. These would be the graphs that are centered at the origin. If we can
Conic Sections Understanding the graphs of conic sections is made easier if you first begin with the simplest form of a conic section. These would be the graphs that are centered at the origin. If we can
Assignment 3/17/15. Section 10.2(p 568) 2 12 (E) (E)
 Section 10.2 Warm Up Assignment 3/17/15 Section 10.2(p 568) 2 12 (E) 24 40 (E) Objective We are going to find equations for parabolas identify the vertex, focus, and directrix of a parabola The parabola
Section 10.2 Warm Up Assignment 3/17/15 Section 10.2(p 568) 2 12 (E) 24 40 (E) Objective We are going to find equations for parabolas identify the vertex, focus, and directrix of a parabola The parabola
Polynomial and Rational Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.1 Quadratic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Analyze graphs of quadratic
2 Polynomial and Rational Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.1 Quadratic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Analyze graphs of quadratic
x y 2 2 CONIC SECTIONS Problem 1
 CONIC SECTIONS Problem For the equations below, identify each conic section If it s a parabola, specify its vertex, focus and directrix If it s an ellipse, specify its center, vertices and foci If it s
CONIC SECTIONS Problem For the equations below, identify each conic section If it s a parabola, specify its vertex, focus and directrix If it s an ellipse, specify its center, vertices and foci If it s
Math104 General Mathematics 2. Prof. Messaoud Bounkhel Department of Mathematics King Saud University
 Math104 General Mathematics 2 Prof. Messaoud Bounkhel Department of Mathematics King Saud University Office Number: 2A184 Building4 Tel. Number: 4676526 01 Email: bounkhel@ksu.edu.sa Webpage: http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/bounkhel
Math104 General Mathematics 2 Prof. Messaoud Bounkhel Department of Mathematics King Saud University Office Number: 2A184 Building4 Tel. Number: 4676526 01 Email: bounkhel@ksu.edu.sa Webpage: http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/bounkhel
Chapter. Implicit Function Graphs
 Chapter 14 Implicit Function Graphs You can graph any one of the following types of implicit functions using the calculator s built-in functions. Parabolic graph Circle graph Elliptical graph Hyperbolic
Chapter 14 Implicit Function Graphs You can graph any one of the following types of implicit functions using the calculator s built-in functions. Parabolic graph Circle graph Elliptical graph Hyperbolic
Grade 9 Math Terminology
 Unit 1 Basic Skills Review BEDMAS a way of remembering order of operations: Brackets, Exponents, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction Collect like terms gather all like terms and simplify as
Unit 1 Basic Skills Review BEDMAS a way of remembering order of operations: Brackets, Exponents, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction Collect like terms gather all like terms and simplify as
Name: Date: 1. Match the equation with its graph. Page 1
 Name: Date: 1. Match the equation with its graph. y 6x A) C) Page 1 D) E) Page . Match the equation with its graph. ( x3) ( y3) A) C) Page 3 D) E) Page 4 3. Match the equation with its graph. ( x ) y 1
Name: Date: 1. Match the equation with its graph. y 6x A) C) Page 1 D) E) Page . Match the equation with its graph. ( x3) ( y3) A) C) Page 3 D) E) Page 4 3. Match the equation with its graph. ( x ) y 1
K-12 Geometry Standards
 Geometry K.G Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1. Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes, and describe
Geometry K.G Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1. Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes, and describe
To sketch the graph we need to evaluate the parameter t within the given interval to create our x and y values.
 Module 10 lesson 6 Parametric Equations. When modeling the path of an object, it is useful to use equations called Parametric equations. Instead of using one equation with two variables, we will use two
Module 10 lesson 6 Parametric Equations. When modeling the path of an object, it is useful to use equations called Parametric equations. Instead of using one equation with two variables, we will use two
Section Graphs and Lines
 Section 1.1 - Graphs and Lines The first chapter of this text is a review of College Algebra skills that you will need as you move through the course. This is a review, so you should have some familiarity
Section 1.1 - Graphs and Lines The first chapter of this text is a review of College Algebra skills that you will need as you move through the course. This is a review, so you should have some familiarity
Graph and Write Equations of Hyperbolas
 TEKS 9.5 a.5, 2A.5.B, 2A.5.C Graph and Write Equations of Hperbolas Before You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas, circles, and ellipses. Now You will graph and write equations of hperbolas. Wh?
TEKS 9.5 a.5, 2A.5.B, 2A.5.C Graph and Write Equations of Hperbolas Before You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas, circles, and ellipses. Now You will graph and write equations of hperbolas. Wh?
Unit #3: Quadratic Functions Lesson #13: The Almighty Parabola. Day #1
 Algebra I Unit #3: Quadratic Functions Lesson #13: The Almighty Parabola Name Period Date Day #1 There are some important features about the graphs of quadratic functions we are going to explore over the
Algebra I Unit #3: Quadratic Functions Lesson #13: The Almighty Parabola Name Period Date Day #1 There are some important features about the graphs of quadratic functions we are going to explore over the
MATH 1020 WORKSHEET 10.1 Parametric Equations
 MATH WORKSHEET. Parametric Equations If f and g are continuous functions on an interval I, then the equations x ft) and y gt) are called parametric equations. The parametric equations along with the graph
MATH WORKSHEET. Parametric Equations If f and g are continuous functions on an interval I, then the equations x ft) and y gt) are called parametric equations. The parametric equations along with the graph
Topics in Two-Dimensional Analytic Geometry
 Chapter Topics in Two-Dimensional Analytic Geometry In this chapter we look at topics in analytic geometry so we can use our calculus in many new settings. Most of the discussion will involve developing
Chapter Topics in Two-Dimensional Analytic Geometry In this chapter we look at topics in analytic geometry so we can use our calculus in many new settings. Most of the discussion will involve developing
HYPERBOLA. Going off on a TANGENT!
 HYPERBOLA Going off on a TANGENT! RECALL THAT THE HYPERBOLA IS A CONIC SECTION A LAMP CASTS A HYPERBOLIC BEAM OF LIGHT NUCLEAR COOLING TOWERS TORNADO TOWER, QATAR KOBE PORT TOWER, JAPAN RULED HYPERBOLOID
HYPERBOLA Going off on a TANGENT! RECALL THAT THE HYPERBOLA IS A CONIC SECTION A LAMP CASTS A HYPERBOLIC BEAM OF LIGHT NUCLEAR COOLING TOWERS TORNADO TOWER, QATAR KOBE PORT TOWER, JAPAN RULED HYPERBOLOID
Math 136 Exam 1 Practice Problems
 Math Exam Practice Problems. Find the surface area of the surface of revolution generated by revolving the curve given by around the x-axis? To solve this we use the equation: In this case this translates
Math Exam Practice Problems. Find the surface area of the surface of revolution generated by revolving the curve given by around the x-axis? To solve this we use the equation: In this case this translates
Exam 2 Review. 2. What the difference is between an equation and an expression?
 Exam 2 Review Chapter 1 Section1 Do You Know: 1. What does it mean to solve an equation? 2. What the difference is between an equation and an expression? 3. How to tell if an equation is linear? 4. How
Exam 2 Review Chapter 1 Section1 Do You Know: 1. What does it mean to solve an equation? 2. What the difference is between an equation and an expression? 3. How to tell if an equation is linear? 4. How
