EEC 483 Computer Organization
|
|
|
- Daniel Simmons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EEC 48 Computer Organization 5. The Basics of Cache Chansu Yu Caches: The Basic Idea A smaller set of storage locations storing a subset of information from a larger set (memory) Unlike registers or memory, invisible to programmer/isa found (hit) read data from cache Hit time ( cycle) memory reference Is in cache? no (miss) bring data & more (block) from memory into cache Spatial locality Temporal locality Miss penalty (s or s cycles)
2 Cache Block Placement Two issues: How do we know if a data item is in the cache? If it is, how do we find it? Our first example: Block size is 6 bytes of data (x bytes) has 56 bytes (x bytes, x blocks) Cache has 8 bytes (8 blocks) Direct mapped" Direct-mapped Block Placement 6 bytes Address A B C D E F access [xd6] 4 6 bytes Direct-mapped cache Block Index
3 Cache Block Placement Another similar example: Block size is 6 bytes of data (x bytes) has 56 bytes (x bytes, x blocks) Cache has 64 bytes (4 blocks) Direct mapped" 5 Direct-mapped Block Placement 6 bytes Address A B C D E F access [xd6] 6 6 bytes Direct-mapped cache Block Index
4 Decoding Address address [D6] = [ ] offset within the block cache block index ( or ) for identifying the original memory block ( or ) Given the memory address (e.g. D6) Extract the cache block index () Check if the cache block # corresponds to memory D~DF For this, each cache entry remembers the tag data (e.g. ) If tag matches with the first two bits in memory address, HIT Extract the byte within the block with offset address (e.g. 6) 7 Direct-mapped Block Placement 6 bytes Address A B C D E F Block Index access [xd6] 8 6 bytes Direct-mapped cache 4
5 Exercise: Make connections! 6 bytes Address A B C D E F 9 Block Index 6 bytes Direct-mapped cache Exercise: Find them! 6 bytes Address A B C D E F 7 B A D6 Block Index 6 bytes Direct-mapped cache 5
6 Decoding Address Given the memory address (e.g. A) Extract the cache block index () Check if the cache block # corresponds to memory A~AF Since tag is and the first two bits in memory address is, MISS So, what happens when a miss occurs? (see pages ) The current cache block # contains B~BF Read memory A~AF and replace the cache block # Change the to Decoding Address Given the memory address (e.g. B) Extract the cache block index () Check if the cache block # corresponds to memory ~F is and therefore, HIT However, it is possible that = because the cache is initially empty This is not a HIT??? => We need a valid bit! 6
7 Exercise: What is invalid? 6 bytes Address A B C D E F 7 B A D6 Block Index 6 bytes Direct-mapped cache Valid Decoding Address Given the memory address (e.g. D9) Extract the cache block index () Check if the cache block # corresponds to memory D~DF Since = AND valid bit =, HIT Given the memory address (e.g. B) Extract the cache block index () Check if the cache block # corresponds to memory ~F = but valid bit =, MISS So, what happens when a miss occurs? The current cache block # contains an invalid data Read memory ~F and replace the cache block # Change the to and set the valid bit to 4 7
8 Exercise4: What if [D6] is write? 6 bytes Address A B C D E F 7 B A D6 5 Block Index 6 bytes Direct-mapped cache Valid Handling Writes Write strategy (see pages ) When write hit Write through: data is written to both the cache and the memory Write back : data is written only to the cache the modified (dirty) cache block is written to memory when replaced requires dirty bit for each cache block (more complexity) Better performance but semantic problem When write miss Write allocate : fetch-on-write - with Write-back??? No write allocate : write-around - with Write-through??? 6 8
9 Cache Block Placement Two issues: How do we know if a data item is in the cache? If it is, how do we find it? Our first example: block size is 4 words of data "direct mapped" For each item of data in memory, there is exactly one location in the cache where it might be. e.g., lots of items in memory share locations in the cache 7 Single Word Cache Block : Exercise5 address size? (# bits for memory address?) Block size? (# bits for offset?) # blocks? (# bits for block index?) Hit Address (showing bit positions) Byte offset Index Index Valid Data Data address to Cache address # Cache blocks in direct-mapped cache? (# bits for block index?) Which (how many) memory blocks are candidates for cache block #5? size? How memory address is decomposed? 8 9
10 Exercise6 Multiword Cache Block Address (showing bit positions) Hit 6 Byte offset Data Index Block offset 6 bits 8 bits V Data 4K entries 6 Mux 9 Block Identification Ex) Alpha 64 (Direct-mapped cache) -byte Block size : 8KB cache size : Requires 5-bit for block offset 56 (=8KB/B) cache blocks Requires 8-bit for block index 4-bit memory address supports up to 6GB : 5M (=6GB/B) memory blocks Mapping : M (=5M/56) candidates for a cache block (compete with each other) => Requires -bit to identify
11 8 5 Block Address Index Block Offset Byte Byte6 Byte Cache tag Valid bit Cache Index Byte Byte Byte KB cache data Direct-mapped Cache Cache Performance: Tradeoffs () Increasing block size + decreases miss rate, until block gets large (spatial locality) - increases miss penalty () Increasing cache size + decreases miss rate - increases hit time - increases hardware cost To make exact tradeoffs, need to know specific numbers. Calculation & measurement See book for formulae. () Increasing associativity (Section 7.) + increases hit rate - increases hit time - increases hardware cost
12 Cache Performance: Tradeoffs Processor Cache DRAM Write Buffer (4) A Write Buffer is needed between the Cache and Processor: writes data into the cache and the write buffer controller: write contents of the buffer to memory Write buffer is just a FIFO: Typical number of entries: 4 Works fine if: Store frequency (w.r.t. time) << / DRAM write cycle system designer s nightmare: Store frequency (w.r.t. time) >> / DRAM write cycle Write buffer saturation Write Buffer Saturation Processor Cache DRAM Write Buffer Store frequency (w.r.t. time) >> / DRAM write cycle If this condition exist for a long period of time (CPU cycle time too quick and/or too many store instructions in a row): Write buffer will overflow no matter how big you make it The CPU Cycle Time <= DRAM Write Cycle Time Solution for write buffer saturation: Use a write back cache Install a second level (L) cache: Processor Cache L Cache DRAM 4 Write Buffer
13 Cache Performance: Tradeoffs (5) Multiple Levels of Caches Emphasize speed: Low hit time Emphasize accuracy: High hit rate Processor Cache Cache larger, slower, cheaper larger line size, higher associativity, more likely to write back Understanding performance is tricky. Use lots of simulation & testing. 5 Cache Performance: Tradeoffs ICache Processor DCache (6) Independent Instruction & Data Caches Possible if locations accessed are independent (different segments) Avoids conflict misses between instructions & data But increases conflict misses among instructions & among data Can be of different sizes & strategies Instructions typically have greater locality ICaches often smaller than DCaches ICaches often don t support writes DCaches often support multiple simultaneous accesses (multi-porting) 6
14 Cache Performance: Tradeoffs (7) organization Make reading multiple words easier by using banks of memory: It can get a lot more complicated... CPU CPU CPU Cache Multiplexor Cache Cache Bus Bus Bus bank bank bank bank b. Wide memory organization c. Interleaved memory organization a. One-word-wide memory organization 7 Cache Performance: Tradeoffs (8) Performance equation Simplified model: execution time = (execution cycles + stall cycles) x cycle time stall cycles = # of instructions x miss ratio x miss penalty Two ways of improving performance: decreasing the miss ratio decreasing the miss penalty What happens if we increase block size? 8 4
15 Performance Increasing the block size tends to decrease miss rate Miss rate 4% 5% % 5% % 5% Use split caches because there is more spatial locality in code % 5% % 4 6 Block size (bytes) 64 KB 8 KB 6 KB KB 56 KB Program Block size in words Instruction miss rate Data miss rate Effective combined miss rate gcc 6.%.% 5.4% 4.%.7%.9% spice.%.%.% 4.%.6%.4% 9 5
Review: Computer Organization
 Review: Computer Organization Cache Chansu Yu Caches: The Basic Idea A smaller set of storage locations storing a subset of information from a larger set. Typically, SRAM for DRAM main memory: Processor
Review: Computer Organization Cache Chansu Yu Caches: The Basic Idea A smaller set of storage locations storing a subset of information from a larger set. Typically, SRAM for DRAM main memory: Processor
Memory Hierarchies. Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev. Fall Lecture 10, October 8, CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology
 Memory Hierarchies Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev Fall 2007 CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology Lecture 10, October 8, 2007 Memories SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast
Memory Hierarchies Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev Fall 2007 CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology Lecture 10, October 8, 2007 Memories SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast
data block 0, word 0 block 0, word 1 block 1, word 0 block 1, word 1 block 2, word 0 block 2, word 1 block 3, word 0 block 3, word 1 Word index cache
 Taking advantage of spatial locality Use block size larger than one word Example: two words Block index tag () () Alternate representations Word index tag block, word block, word block, word block, word
Taking advantage of spatial locality Use block size larger than one word Example: two words Block index tag () () Alternate representations Word index tag block, word block, word block, word block, word
Locality. Cache. Direct Mapped Cache. Direct Mapped Cache
 Locality A principle that makes having a memory hierarchy a good idea If an item is referenced, temporal locality: it will tend to be referenced again soon spatial locality: nearby items will tend to be
Locality A principle that makes having a memory hierarchy a good idea If an item is referenced, temporal locality: it will tend to be referenced again soon spatial locality: nearby items will tend to be
EEC 483 Computer Organization. Chapter 5.3 Measuring and Improving Cache Performance. Chansu Yu
 EEC 483 Computer Organization Chapter 5.3 Measuring and Improving Cache Performance Chansu Yu Cache Performance Performance equation execution time = (execution cycles + stall cycles) x cycle time stall
EEC 483 Computer Organization Chapter 5.3 Measuring and Improving Cache Performance Chansu Yu Cache Performance Performance equation execution time = (execution cycles + stall cycles) x cycle time stall
EEC 170 Computer Architecture Fall Cache Introduction Review. Review: The Memory Hierarchy. The Memory Hierarchy: Why Does it Work?
 EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
Chapter Seven. SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors)
 Chapter Seven emories: Review SRA: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRA (4 to transistors) DRA: value is stored as a charge on capacitor (must be refreshed)
Chapter Seven emories: Review SRA: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRA (4 to transistors) DRA: value is stored as a charge on capacitor (must be refreshed)
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1)
 Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1) 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Depar rtment of Electr rical Engineering,
Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1) 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Depar rtment of Electr rical Engineering,
CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/73/69213006.jpg) CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
Chapter 7 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy. Memory Hierarchy. Locality. Memories: Review
 Memories: Review Chapter 7 Large and Fast: Exploiting Hierarchy DRAM (Dynamic Random Access ): value is stored as a charge on capacitor that must be periodically refreshed, which is why it is called dynamic
Memories: Review Chapter 7 Large and Fast: Exploiting Hierarchy DRAM (Dynamic Random Access ): value is stored as a charge on capacitor that must be periodically refreshed, which is why it is called dynamic
Chapter Seven. Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter Seven Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy 1 Memories: Review SRAM (Static Random Access Memory): value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM DRAM
Chapter Seven Large & Fast: Exploring Memory Hierarchy 1 Memories: Review SRAM (Static Random Access Memory): value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM DRAM
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
 EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
EE 4683/5683: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lecture 6A: Cache Design Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohioedu Agenda 2 Review: Memory Hierarchy Review: Cache Organization Direct-mapped Set- Associative Fully-Associative 1 Major
Course Administration
 Spring 207 EE 363: Computer Organization Chapter 5: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy - Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 4570
Spring 207 EE 363: Computer Organization Chapter 5: Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy - Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 4570
CPU issues address (and data for write) Memory returns data (or acknowledgment for write)
 The Main Memory Unit CPU and memory unit interface Address Data Control CPU Memory CPU issues address (and data for write) Memory returns data (or acknowledgment for write) Memories: Design Objectives
The Main Memory Unit CPU and memory unit interface Address Data Control CPU Memory CPU issues address (and data for write) Memory returns data (or acknowledgment for write) Memories: Design Objectives
Advanced Memory Organizations
 CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
Chapter Seven. Memories: Review. Exploiting Memory Hierarchy CACHE MEMORY AND VIRTUAL MEMORY
 Chapter Seven CACHE MEMORY AND VIRTUAL MEMORY 1 Memories: Review SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors) DRAM: value is stored
Chapter Seven CACHE MEMORY AND VIRTUAL MEMORY 1 Memories: Review SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors) DRAM: value is stored
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 11 SRAM (II), Caches. Announcements
 EECS15 - Digital Design Lecture 11 SRAM (II), Caches September 29, 211 Elad Alon Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http//www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs15 Fall
EECS15 - Digital Design Lecture 11 SRAM (II), Caches September 29, 211 Elad Alon Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http//www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs15 Fall
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (I)
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (I) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2018 Some slides are based on a lecture by David Culler, University of California, Berkley http//www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler/courses/cs252-s05
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (I) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2018 Some slides are based on a lecture by David Culler, University of California, Berkley http//www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~culler/courses/cs252-s05
LECTURE 11. Memory Hierarchy
 LECTURE 11 Memory Hierarchy MEMORY HIERARCHY When it comes to memory, there are two universally desirable properties: Large Size: ideally, we want to never have to worry about running out of memory. Speed
LECTURE 11 Memory Hierarchy MEMORY HIERARCHY When it comes to memory, there are two universally desirable properties: Large Size: ideally, we want to never have to worry about running out of memory. Speed
EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits. Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver. Lecture 19: Caches EE141
 EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver Lecture 19: Caches Cache Introduction 40% of this ARM CPU is devoted to SRAM cache. But the role
EECS151/251A Spring 2018 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: John Wawrzynek and Nick Weaver Lecture 19: Caches Cache Introduction 40% of this ARM CPU is devoted to SRAM cache. But the role
Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science. TDT4255 Memory hierarchies
 TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17: Cache System
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17 System March 17, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http//http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 17 System March 17, 1995 Dave Patterson (patterson@cs) and Shing Kong (shing.kong@eng.sun.com) Slides available on http//http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson
Chapter 6 Caches. Computer System. Alpha Chip Photo. Topics. Memory Hierarchy Locality of Reference SRAM Caches Direct Mapped Associative
 Chapter 6 s Topics Memory Hierarchy Locality of Reference SRAM s Direct Mapped Associative Computer System Processor interrupt On-chip cache s s Memory-I/O bus bus Net cache Row cache Disk cache Memory
Chapter 6 s Topics Memory Hierarchy Locality of Reference SRAM s Direct Mapped Associative Computer System Processor interrupt On-chip cache s s Memory-I/O bus bus Net cache Row cache Disk cache Memory
ארכיטקטורת יחידת עיבוד מרכזי ת
 ארכיטקטורת יחידת עיבוד מרכזי ת (36113741) תשס"ג סמסטר א' July 2, 2008 Hugo Guterman (hugo@ee.bgu.ac.il) Arch. CPU L8 Cache Intr. 1/77 Memory Hierarchy Arch. CPU L8 Cache Intr. 2/77 Why hierarchy works
ארכיטקטורת יחידת עיבוד מרכזי ת (36113741) תשס"ג סמסטר א' July 2, 2008 Hugo Guterman (hugo@ee.bgu.ac.il) Arch. CPU L8 Cache Intr. 1/77 Memory Hierarchy Arch. CPU L8 Cache Intr. 2/77 Why hierarchy works
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design. Lecture 08: Cache Review. Bei Yu
 CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Cache Review Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 A Typical Memory Hierarchy q Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Cache Review Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 A Typical Memory Hierarchy q Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as
CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1
 CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall 2008 Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1 Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson
CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall 2008 Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1 Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson
Memory Hierarchy Design (Appendix B and Chapter 2)
 CS359: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy Design (Appendix B and Chapter 2) Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering 1 Four Memory Hierarchy Questions Q1 (block placement): where
CS359: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy Design (Appendix B and Chapter 2) Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering 1 Four Memory Hierarchy Questions Q1 (block placement): where
Introduction. Memory Hierarchy
 Introduction Why memory subsystem design is important CPU speeds increase 25%-30% per year DRAM speeds increase 2%-11% per year 1 Memory Hierarchy Levels of memory with different sizes & speeds close to
Introduction Why memory subsystem design is important CPU speeds increase 25%-30% per year DRAM speeds increase 2%-11% per year 1 Memory Hierarchy Levels of memory with different sizes & speeds close to
CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/76/74076691.jpg) CSF Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
CSF Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user
ECE ECE4680
 ECE468. -4-7 The otivation for s System ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture DRA Hierarchy System otivation Large memories (DRA) are slow Small memories (SRA) are fast ake the average access time
ECE468. -4-7 The otivation for s System ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture DRA Hierarchy System otivation Large memories (DRA) are slow Small memories (SRA) are fast ake the average access time
CS3350B Computer Architecture
 CS335B Computer Architecture Winter 25 Lecture 32: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy: How? Marc Moreno Maza wwwcsduwoca/courses/cs335b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design, Patterson &
CS335B Computer Architecture Winter 25 Lecture 32: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy: How? Marc Moreno Maza wwwcsduwoca/courses/cs335b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and Design, Patterson &
Page 1. Memory Hierarchies (Part 2)
 Memory Hierarchies (Part ) Outline of Lectures on Memory Systems Memory Hierarchies Cache Memory 3 Virtual Memory 4 The future Increasing distance from the processor in access time Review: The Memory Hierarchy
Memory Hierarchies (Part ) Outline of Lectures on Memory Systems Memory Hierarchies Cache Memory 3 Virtual Memory 4 The future Increasing distance from the processor in access time Review: The Memory Hierarchy
Spring 2018 :: CSE 502. Cache Design Basics. Nima Honarmand
 Cache Design Basics Nima Honarmand Storage Hierarchy Make common case fast: Common: temporal & spatial locality Fast: smaller, more expensive memory Bigger Transfers Registers More Bandwidth Controlled
Cache Design Basics Nima Honarmand Storage Hierarchy Make common case fast: Common: temporal & spatial locality Fast: smaller, more expensive memory Bigger Transfers Registers More Bandwidth Controlled
The levels of a memory hierarchy. Main. Memory. 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms
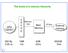 The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
1/19/2009. Data Locality. Exploiting Locality: Caches
 Spring 2009 Prof. Hyesoon Kim Thanks to Prof. Loh & Prof. Prvulovic Data Locality Temporal: if data item needed now, it is likely to be needed again in near future Spatial: if data item needed now, nearby
Spring 2009 Prof. Hyesoon Kim Thanks to Prof. Loh & Prof. Prvulovic Data Locality Temporal: if data item needed now, it is likely to be needed again in near future Spatial: if data item needed now, nearby
ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)]
![ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance. [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)]](/thumbs/72/68075397.jpg) ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] Measuring Cache Performance Assuming cache hit costs are included as part of the normal CPU execution cycle, then CPU
ECE7995 (6) Improving Cache Performance [Adapted from Mary Jane Irwin s slides (PSU)] Measuring Cache Performance Assuming cache hit costs are included as part of the normal CPU execution cycle, then CPU
CS356: Discussion #9 Memory Hierarchy and Caches. Marco Paolieri Illustrations from CS:APP3e textbook
 CS356: Discussion #9 Memory Hierarchy and Caches Marco Paolieri (paolieri@usc.edu) Illustrations from CS:APP3e textbook The Memory Hierarchy So far... We modeled the memory system as an abstract array
CS356: Discussion #9 Memory Hierarchy and Caches Marco Paolieri (paolieri@usc.edu) Illustrations from CS:APP3e textbook The Memory Hierarchy So far... We modeled the memory system as an abstract array
Caches Concepts Review
 Caches Concepts Review What is a block address? Why not bring just what is needed by the processor? What is a set associative cache? Write-through? Write-back? Then we ll see: Block allocation policy on
Caches Concepts Review What is a block address? Why not bring just what is needed by the processor? What is a set associative cache? Write-through? Write-back? Then we ll see: Block allocation policy on
Pick a time window size w. In time span w, are there, Multiple References, to nearby addresses: Spatial Locality
 Pick a time window size w. In time span w, are there, Multiple References, to nearby addresses: Spatial Locality Repeated References, to a set of locations: Temporal Locality Take advantage of behavior
Pick a time window size w. In time span w, are there, Multiple References, to nearby addresses: Spatial Locality Repeated References, to a set of locations: Temporal Locality Take advantage of behavior
Spring 2016 :: CSE 502 Computer Architecture. Caches. Nima Honarmand
 Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
3Introduction. Memory Hierarchy. Chapter 2. Memory Hierarchy Design. Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
registers data 1 registers MEMORY ADDRESS on-chip cache off-chip cache main memory: real address space part of virtual addr. sp.
 Cache associativity Cache and performance 12 1 CMPE110 Spring 2005 A. Di Blas 110 Spring 2005 CMPE Cache Direct-mapped cache Reads and writes Textbook Edition: 7.1 to 7.3 Second Third Edition: 7.1 to 7.3
Cache associativity Cache and performance 12 1 CMPE110 Spring 2005 A. Di Blas 110 Spring 2005 CMPE Cache Direct-mapped cache Reads and writes Textbook Edition: 7.1 to 7.3 Second Third Edition: 7.1 to 7.3
Memory Hierarchy. Maurizio Palesi. Maurizio Palesi 1
 Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Logical Diagram of a Set-associative Cache Accessing a Cache
 Introduction Memory Hierarchy Why memory subsystem design is important CPU speeds increase 25%-30% per year DRAM speeds increase 2%-11% per year Levels of memory with different sizes & speeds close to
Introduction Memory Hierarchy Why memory subsystem design is important CPU speeds increase 25%-30% per year DRAM speeds increase 2%-11% per year Levels of memory with different sizes & speeds close to
EN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 06: Memory System
 EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
Caches. Samira Khan March 23, 2017
 Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Agenda Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Agenda Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
Q3: Block Replacement. Replacement Algorithms. ECE473 Computer Architecture and Organization. Memory Hierarchy: Set Associative Cache
 Fundamental Questions Computer Architecture and Organization Hierarchy: Set Associative Q: Where can a block be placed in the upper level? (Block placement) Q: How is a block found if it is in the upper
Fundamental Questions Computer Architecture and Organization Hierarchy: Set Associative Q: Where can a block be placed in the upper level? (Block placement) Q: How is a block found if it is in the upper
Computer Organization and Structure. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
Caches 3/23/17. Agenda. The Dataflow Model (of a Computer)
 Agenda Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
Agenda Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
14:332:331. Week 13 Basics of Cache
 14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Fall 2003 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Lec20.1 Fall 2003 Head
14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Fall 2003 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Lec20.1 Fall 2003 Head
Why memory hierarchy
 Why memory hierarchy (3 rd Ed: p.468-487, 4 th Ed: p. 452-470) users want unlimited fast memory fast memory expensive, slow memory cheap cache: small, fast memory near CPU large, slow memory (main memory,
Why memory hierarchy (3 rd Ed: p.468-487, 4 th Ed: p. 452-470) users want unlimited fast memory fast memory expensive, slow memory cheap cache: small, fast memory near CPU large, slow memory (main memory,
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory
 EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache optimization Virtual memory Case study AMD Opteron Summary 2 Memory hierarchy 3 Cache
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache optimization Virtual memory Case study AMD Opteron Summary 2 Memory hierarchy 3 Cache
Memory Hierarchy. Maurizio Palesi. Maurizio Palesi 1
 Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
Caching Basics. Memory Hierarchies
 Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
14:332:331. Week 13 Basics of Cache
 14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Spring 2006 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Week131 Spring 2006
14:332:331 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Spring 2006 Week 13 Basics of Cache [Adapted from Dave Patterson s UCB CS152 slides and Mary Jane Irwin s PSU CSE331 slides] 331 Week131 Spring 2006
Registers. Instruction Memory A L U. Data Memory C O N T R O L M U X A D D A D D. Sh L 2 M U X. Sign Ext M U X ALU CTL INSTRUCTION FETCH
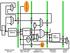 PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O T R O L ALU CTL ISTRUCTIO FETCH ISTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMOR ACCESS WRITE BACK A D D A D D A L U
PC Instruction Memory 4 M U X Registers Sign Ext M U X Sh L 2 Data Memory M U X C O T R O L ALU CTL ISTRUCTIO FETCH ISTR DECODE REG FETCH EXECUTE/ ADDRESS CALC MEMOR ACCESS WRITE BACK A D D A D D A L U
Levels in memory hierarchy
 CS1C Cache Memory Lecture 1 March 1, 1999 Dave Patterson (http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs1c/schedule.html Review 1/: Memory Hierarchy Pyramid Upper Levels in memory hierarchy
CS1C Cache Memory Lecture 1 March 1, 1999 Dave Patterson (http.cs.berkeley.edu/~patterson) www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs1c/schedule.html Review 1/: Memory Hierarchy Pyramid Upper Levels in memory hierarchy
LECTURE 10: Improving Memory Access: Direct and Spatial caches
 EECS 318 CAD Computer Aided Design LECTURE 10: Improving Memory Access: Direct and Spatial caches Instructor: Francis G. Wolff wolff@eecs.cwru.edu Case Western Reserve University This presentation uses
EECS 318 CAD Computer Aided Design LECTURE 10: Improving Memory Access: Direct and Spatial caches Instructor: Francis G. Wolff wolff@eecs.cwru.edu Case Western Reserve University This presentation uses
Memory Hierarchy. Mehran Rezaei
 Memory Hierarchy Mehran Rezaei What types of memory do we have? Registers Cache (Static RAM) Main Memory (Dynamic RAM) Disk (Magnetic Disk) Option : Build It Out of Fast SRAM About 5- ns access Decoders
Memory Hierarchy Mehran Rezaei What types of memory do we have? Registers Cache (Static RAM) Main Memory (Dynamic RAM) Disk (Magnetic Disk) Option : Build It Out of Fast SRAM About 5- ns access Decoders
CPE 631 Lecture 04: CPU Caches
 Lecture 04 CPU Caches Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville Outline Memory Hierarchy Four Questions for Memory Hierarchy Cache Performance 26/01/2004 UAH- 2 1 Processor-DR
Lecture 04 CPU Caches Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville Outline Memory Hierarchy Four Questions for Memory Hierarchy Cache Performance 26/01/2004 UAH- 2 1 Processor-DR
Computer Architecture CS372 Exam 3
 Name: Computer Architecture CS372 Exam 3 This exam has 7 pages. Please make sure you have all of them. Write your name on this page and initials on every other page now. You may only use the green card
Name: Computer Architecture CS372 Exam 3 This exam has 7 pages. Please make sure you have all of them. Write your name on this page and initials on every other page now. You may only use the green card
Introduction to cache memories
 Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Introduction to cache memories Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Summary Summary Main goal Spatial and temporal
Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Introduction to cache memories Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Summary Summary Main goal Spatial and temporal
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2
 EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache performance optimization Bandwidth increase Reduce hit time Reduce miss penalty Reduce miss
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache performance optimization Bandwidth increase Reduce hit time Reduce miss penalty Reduce miss
Memory Technology. Caches 1. Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Magnetic disk. Ideal memory. 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB
 Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Textbook: Burdea and Coiffet, Virtual Reality Technology, 2 nd Edition, Wiley, Textbook web site:
 Textbook: Burdea and Coiffet, Virtual Reality Technology, 2 nd Edition, Wiley, 2003 Textbook web site: www.vrtechnology.org 1 Textbook web site: www.vrtechnology.org Laboratory Hardware 2 Topics 14:332:331
Textbook: Burdea and Coiffet, Virtual Reality Technology, 2 nd Edition, Wiley, 2003 Textbook web site: www.vrtechnology.org 1 Textbook web site: www.vrtechnology.org Laboratory Hardware 2 Topics 14:332:331
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350):
 The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350): Motivation for The Memory Hierarchy: { CPU/Memory Performance Gap The Principle Of Locality Cache $$$$$ Cache Basics:
The Memory Hierarchy & Cache Review of Memory Hierarchy & Cache Basics (from 350): Motivation for The Memory Hierarchy: { CPU/Memory Performance Gap The Principle Of Locality Cache $$$$$ Cache Basics:
Why memory hierarchy? Memory hierarchy. Memory hierarchy goals. CS2410: Computer Architecture. L1 cache design. Sangyeun Cho
 Why memory hierarchy? L1 cache design Sangyeun Cho Computer Science Department Memory hierarchy Memory hierarchy goals Smaller Faster More expensive per byte CPU Regs L1 cache L2 cache SRAM SRAM To provide
Why memory hierarchy? L1 cache design Sangyeun Cho Computer Science Department Memory hierarchy Memory hierarchy goals Smaller Faster More expensive per byte CPU Regs L1 cache L2 cache SRAM SRAM To provide
CS 136: Advanced Architecture. Review of Caches
 1 / 30 CS 136: Advanced Architecture Review of Caches 2 / 30 Why Caches? Introduction Basic goal: Size of cheapest memory... At speed of most expensive Locality makes it work Temporal locality: If you
1 / 30 CS 136: Advanced Architecture Review of Caches 2 / 30 Why Caches? Introduction Basic goal: Size of cheapest memory... At speed of most expensive Locality makes it work Temporal locality: If you
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design. Lecture 08: Memory - I. Bei Yu
 CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Memory - I Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 Outline q Why Memory Hierarchy q How Memory Hierarchy? SRAM (Cache) & DRAM (main memory) Memory System
CENG 3420 Computer Organization and Design Lecture 08: Memory - I Bei Yu CEG3420 L08.1 Spring 2016 Outline q Why Memory Hierarchy q How Memory Hierarchy? SRAM (Cache) & DRAM (main memory) Memory System
EN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 06: Memory System
 EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
The University of Adelaide, School of Computer Science 13 September 2018
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Sixth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more expensive per
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Sixth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more expensive per
CPUs. Caching: The Basic Idea. Cache : MainMemory :: Window : Caches. Memory management. CPU performance. 1. Door 2. Bigger Door 3. The Great Outdoors
 CPUs Caches. Memory management. CPU performance. Cache : MainMemory :: Window : 1. Door 2. Bigger Door 3. The Great Outdoors 4. Horizontal Blinds 18% 9% 64% 9% Door Bigger Door The Great Outdoors Horizontal
CPUs Caches. Memory management. CPU performance. Cache : MainMemory :: Window : 1. Door 2. Bigger Door 3. The Great Outdoors 4. Horizontal Blinds 18% 9% 64% 9% Door Bigger Door The Great Outdoors Horizontal
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Key Point. What are Cache lines
 Caching 1 Key Point What are Cache lines Tags Index offset How do we find data in the cache? How do we tell if it s the right data? What decisions do we need to make in designing a cache? What are possible
Caching 1 Key Point What are Cache lines Tags Index offset How do we find data in the cache? How do we tell if it s the right data? What decisions do we need to make in designing a cache? What are possible
Reducing Hit Times. Critical Influence on cycle-time or CPI. small is always faster and can be put on chip
 Reducing Hit Times Critical Influence on cycle-time or CPI Keep L1 small and simple small is always faster and can be put on chip interesting compromise is to keep the tags on chip and the block data off
Reducing Hit Times Critical Influence on cycle-time or CPI Keep L1 small and simple small is always faster and can be put on chip interesting compromise is to keep the tags on chip and the block data off
CS/CoE 1541 Exam 2 (Spring 2019).
 CS/CoE 1541 Exam 2 (Spring 2019) Name: Question 1 (5+5+5=15 points): Show the content of each of the caches shown below after the two memory references 35, 44 Use the notation [tag, M(address),] to describe
CS/CoE 1541 Exam 2 (Spring 2019) Name: Question 1 (5+5+5=15 points): Show the content of each of the caches shown below after the two memory references 35, 44 Use the notation [tag, M(address),] to describe
registers data 1 registers MEMORY ADDRESS on-chip cache off-chip cache main memory: real address space part of virtual addr. sp.
 13 1 CMPE110 Computer Architecture, Winter 2009 Andrea Di Blas 110 Winter 2009 CMPE Cache Direct-mapped cache Reads and writes Cache associativity Cache and performance Textbook Edition: 7.1 to 7.3 Third
13 1 CMPE110 Computer Architecture, Winter 2009 Andrea Di Blas 110 Winter 2009 CMPE Cache Direct-mapped cache Reads and writes Cache associativity Cache and performance Textbook Edition: 7.1 to 7.3 Third
exercise 4 byte blocks, 4 sets index valid tag value 00
 Caching (part 2) 1 exercise 3 address (hex) result 00000000 (00) 00000001 (01) 01100011 (63) 01100001 (61) 01100010 (62) 00000000 (00) 01100100 (64) 4 byte blocks, 4 sets index valid tag value 00 01 10
Caching (part 2) 1 exercise 3 address (hex) result 00000000 (00) 00000001 (01) 01100011 (63) 01100001 (61) 01100010 (62) 00000000 (00) 01100100 (64) 4 byte blocks, 4 sets index valid tag value 00 01 10
Page 1. Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash )
 Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
MIPS) ( MUX
 Memory What do we use for accessing small amounts of data quickly? Registers (32 in MIPS) Why not store all data and instructions in registers? Too much overhead for addressing; lose speed advantage Register
Memory What do we use for accessing small amounts of data quickly? Registers (32 in MIPS) Why not store all data and instructions in registers? Too much overhead for addressing; lose speed advantage Register
Memory Technologies. Technology Trends
 . 5 Technologies Random access technologies Random good access time same for all locations DRAM Dynamic Random Access High density, low power, cheap, but slow Dynamic need to be refreshed regularly SRAM
. 5 Technologies Random access technologies Random good access time same for all locations DRAM Dynamic Random Access High density, low power, cheap, but slow Dynamic need to be refreshed regularly SRAM
Memory Hierarchies &
 Memory Hierarchies & Cache Memory CSE 410, Spring 2009 Computer Systems http://www.cs.washington.edu/410 4/26/2009 cse410-13-cache 2006-09 Perkins, DW Johnson and University of Washington 1 Reading and
Memory Hierarchies & Cache Memory CSE 410, Spring 2009 Computer Systems http://www.cs.washington.edu/410 4/26/2009 cse410-13-cache 2006-09 Perkins, DW Johnson and University of Washington 1 Reading and
ECEC 355: Cache Design
 ECEC 355: Cache Design November 28, 2007 Terminology Let us first define some general terms applicable to caches. Cache block or line. The minimum unit of information (in bytes) that can be either present
ECEC 355: Cache Design November 28, 2007 Terminology Let us first define some general terms applicable to caches. Cache block or line. The minimum unit of information (in bytes) that can be either present
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2
 EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache performance optimization Bandwidth increase Reduce hit time Reduce miss penalty Reduce miss
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache performance optimization Bandwidth increase Reduce hit time Reduce miss penalty Reduce miss
CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems. Cache $$$$$
 CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems Cache $$$$$ Memory Systems! How can we supply the CPU with enough data to keep it busy?! We will focus on memory issues,! which are frequently bottlenecks
CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems Cache $$$$$ Memory Systems! How can we supply the CPU with enough data to keep it busy?! We will focus on memory issues,! which are frequently bottlenecks
Computer Architecture Spring 2016
 Computer Architecture Spring 2016 Lecture 02: Introduction II Shuai Wang Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University Pipeline Hazards Major hurdle to pipelining: hazards prevent the
Computer Architecture Spring 2016 Lecture 02: Introduction II Shuai Wang Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University Pipeline Hazards Major hurdle to pipelining: hazards prevent the
Chapter Seven Morgan Kaufmann Publishers
 Chapter Seven Memories: Review SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors) DRAM: value is stored as a charge on capacitor (must be
Chapter Seven Memories: Review SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors) DRAM: value is stored as a charge on capacitor (must be
Slide Set 9. for ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01. Steve Norman, PhD, PEng
 Slide Set 9 for ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary March 2018 ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01
Slide Set 9 for ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary March 2018 ENCM 369 Winter 2018 Section 01
Improving our Simple Cache
 Improving our Simple Cache SI232 Slide Set #17: More More (Hierarchy) (Chapter 7) 1. How to handle a write? 2.Efficient Bit Manipulation 3.How to handle a miss? 4.How to eliminate even more conflicts?
Improving our Simple Cache SI232 Slide Set #17: More More (Hierarchy) (Chapter 7) 1. How to handle a write? 2.Efficient Bit Manipulation 3.How to handle a miss? 4.How to eliminate even more conflicts?
COMP 3221: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems
 COMP 3: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems Lectures 7: Cache Memory - III http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs3 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session, 5 Outline Fully Associative Cache N-Way Associative Cache Block Replacement
COMP 3: Microprocessors and Embedded Systems Lectures 7: Cache Memory - III http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs3 Lecturer: Hui Wu Session, 5 Outline Fully Associative Cache N-Way Associative Cache Block Replacement
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
The Memory Hierarchy. Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2)
 The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
Cache Memory: Instruction Cache, HW/SW Interaction. Admin
 Cache Memory Instruction Cache, HW/SW Interaction Computer Science 104 Admin Project Due Dec 7 Homework #5 Due November 19, in class What s Ahead Finish Caches Virtual Memory Input/Output (1 homework)
Cache Memory Instruction Cache, HW/SW Interaction Computer Science 104 Admin Project Due Dec 7 Homework #5 Due November 19, in class What s Ahead Finish Caches Virtual Memory Input/Output (1 homework)
EEC 170 Computer Architecture Fall Improving Cache Performance. Administrative. Review: The Memory Hierarchy. Review: Principle of Locality
 Administrative EEC 7 Computer Architecture Fall 5 Improving Cache Performance Problem #6 is posted Last set of homework You should be able to answer each of them in -5 min Quiz on Wednesday (/7) Chapter
Administrative EEC 7 Computer Architecture Fall 5 Improving Cache Performance Problem #6 is posted Last set of homework You should be able to answer each of them in -5 min Quiz on Wednesday (/7) Chapter
12 Cache-Organization 1
 12 Cache-Organization 1 Caches Memory, 64M, 500 cycles L1 cache 64K, 1 cycles 1-5% misses L2 cache 4M, 10 cycles 10-20% misses L3 cache 16M, 20 cycles Memory, 256MB, 500 cycles 2 Improving Miss Penalty
12 Cache-Organization 1 Caches Memory, 64M, 500 cycles L1 cache 64K, 1 cycles 1-5% misses L2 cache 4M, 10 cycles 10-20% misses L3 cache 16M, 20 cycles Memory, 256MB, 500 cycles 2 Improving Miss Penalty
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Cache Memory - II. Some of the slides are adopted from David Patterson (UCB)
 Cache Memory - II Some of the slides are adopted from David Patterson (UCB) Outline Direct-Mapped Cache Types of Cache Misses A (long) detailed example Peer - to - peer education example Block Size Tradeoff
Cache Memory - II Some of the slides are adopted from David Patterson (UCB) Outline Direct-Mapped Cache Types of Cache Misses A (long) detailed example Peer - to - peer education example Block Size Tradeoff
Lecture 14: Cache Innovations and DRAM. Today: cache access basics and innovations, DRAM (Sections )
 Lecture 14: Cache Innovations and DRAM Today: cache access basics and innovations, DRAM (Sections 5.1-5.3) 1 Reducing Miss Rate Large block size reduces compulsory misses, reduces miss penalty in case
Lecture 14: Cache Innovations and DRAM Today: cache access basics and innovations, DRAM (Sections 5.1-5.3) 1 Reducing Miss Rate Large block size reduces compulsory misses, reduces miss penalty in case
Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University
 Caches Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns
Caches Jin-Soo Kim (jinsookim@skku.edu) Computer Systems Laboratory Sungkyunkwan University http://csl.skku.edu Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns
