Section 3.2 Comparing and Ordering Fractions and Decimals. 1. Model fractions and/or decimals using blocks, fraction pieces, pattern blocks, etc.
|
|
|
- Johnathan Jackson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Section 3.2 Comparing and Ordering Fractions and Decimals We will use several methods to compare and order fractions: 1. Model fractions and/or decimals using blocks, fraction pieces, pattern blocks, etc. 2. Cross Multiplying (Butterfly Method) 3. Changing to decimals and comparing using place value 4. Comparing using benchmarks such as 0, or 1 5. Comparing common numerators or denominators using equivalent fractions. Cross Multiplying (Butterfly Method) Consider the fractions and. When we draw models for each fraction, we can easily see that is bigger than. We can easily compare two fractions by using the Butterfly Method > So, 3 4 > 5 8 L. Clemens-Brenton Page 10
2 Example: Using the Butterfly Method, fill in each with >, < or =. c) d) e) f) g) h) i) Changing Fractions to Decimals and Comparing Place Value It is easy to compare decimals using place value. L. Clemens-Brenton Page 11
3 For example, let s order these decimals from least to greatest! Example: Use place value to compare each pair of numbers by placing <, > or = between them c) d) e) f) g) h) L. Clemens-Brenton Page 12
4 We can also compare fractions by first changing them to decimals and then using place value. For example, consider and. Using the methods we learned previously, we know that = and = Example 1: Compare each pair by converting to decimals and writing a <, > or = between them. c) 0.7 L. Clemens-Brenton Page 13
5 d) e) f) g) h) 2.4 i) Example 2: Change the following fractions to decimal form and order from least to greatest.,,, 2,, 3 L. Clemens-Brenton Page 14
6 Using Benchmarks to Compare Fractions We can use the benchmarks 0,,, and 1 to compare and order fractions. For example, would be closer to 0 since the numerator is much smaller than the denominator, whereas is about since 7 is about half of 15. Let s consider, and. Using benchmarks, we can order fractions from least to greatest. We can arrange the fractions from least to greatest on a number line: Example: Use benchmarks and a number line to order each set of numbers from least to greatest.,,, 1 L. Clemens-Brenton Page 15
7 ,, 1, 2 Comparing Common Numerators or Denominators Using Equivalent Fractions What are Equivalent Fractions? Equivalent fractions are fractions that have the same value, even though they may look different. For example, The above fractions are all equivalent fractions. We can easily see that half of the circle is shaded in each diagram, even though the diagrams look a little different. L. Clemens-Brenton Page 16
8 We can make equivalent fractions by multiplying (or dividing) the numerator and denominator by the same number Change the bottom using multiply or divide and the same to the top must be applied! Example 1: Find the missing value in each fraction below. = = c) = d) = e) = f) = g) = h) = i) = L. Clemens-Brenton Page 17
9 We can compare fractions by using equivalent fractions with common numerators or denominators. Common Numerators Let s consider and. We can make both numerators the same simply by multiplying So we have = by 2. We can easily see that is bigger than or When the numerators are the same, the larger fraction has the smaller denominator. Example: Compare the fractions using common numerators and writing a <, > or = between them. c) d) e) f) L. Clemens-Brenton Page 18
10 Common Denominators Let s consider and. We can make both numerators the same simply by multiplying So we have = by 2. We can easily see that or. is bigger than. When the denominators are the same, the larger fraction has the larger numerator. Example 1: Compare the fractions using common numerators and writing a <, > or = between them c) d) e) f) 1 1 L. Clemens-Brenton Page 19
11 Example 2: Order the following fractions from least to greatest using common numerators or denominators:, 9, 2, 2 c),, Example 3: Find a number between each pair of numbers., 8, 8 L. Clemens-Brenton Page 20
12 c), 0.92 d) 0.45,0.46 e) 1, L. Clemens-Brenton Page 21
Section 3.1 Fractions to Decimals
 Section 3.1 Fractions to Decimals A fraction is a part of a whole. For example, it means 1 out of 5 possible pieces. is a fraction; Fractions also illustrate division. For example, also means 1 5 which
Section 3.1 Fractions to Decimals A fraction is a part of a whole. For example, it means 1 out of 5 possible pieces. is a fraction; Fractions also illustrate division. For example, also means 1 5 which
and denominators of two fractions. For example, you could use
 Learning Goal denominators. Open Question and denominators of two fractions. For example, you could use and 0. Make sure that some of your fractions are improper and some are proper. Make sure that some
Learning Goal denominators. Open Question and denominators of two fractions. For example, you could use and 0. Make sure that some of your fractions are improper and some are proper. Make sure that some
Equivalent Fractions R46. Step 1 Make a model to represent 2 _. Step 2 Divide the rectangle from Step 1 in half.
 Lesson. Equivalent Fractions Write two fractions that are equivalent to _. Step Make a model to represent _. The rectangle is divided into equal parts, with parts shaded. Step Divide the rectangle from
Lesson. Equivalent Fractions Write two fractions that are equivalent to _. Step Make a model to represent _. The rectangle is divided into equal parts, with parts shaded. Step Divide the rectangle from
TOPIC 2 DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3
 TOPIC DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3 Association between Fractions and Decimals is a fraction. It means divided by. If we divide by the result is not a whole number. It is a half of whole
TOPIC DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3 Association between Fractions and Decimals is a fraction. It means divided by. If we divide by the result is not a whole number. It is a half of whole
Unit: Rational Number Lesson 3.1: What is a Rational Number? Objectives: Students will compare and order rational numbers.
 Unit: Rational Number Lesson 3.: What is a Rational Number? Objectives: Students will compare and order rational numbers. (9N3) Procedure: This unit will introduce the concept of rational numbers. This
Unit: Rational Number Lesson 3.: What is a Rational Number? Objectives: Students will compare and order rational numbers. (9N3) Procedure: This unit will introduce the concept of rational numbers. This
Vocabulary: Bits and Pieces II
 Vocabulary: Bits and Pieces II Concept Estimation: Students have developed benchmark fractions. They can use these to substitute for all the fractions in a computation. Or they may use a combination of
Vocabulary: Bits and Pieces II Concept Estimation: Students have developed benchmark fractions. They can use these to substitute for all the fractions in a computation. Or they may use a combination of
3.1 Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts. 3.1 Dividing a Set into Fractional Parts. 3.2 Identifying Parts of Wholes.
 . Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts Fraction: represents a part of a whole object or unit Numerator: (top number) represents number of parts of the whole Denominator: (bottom number) represents how
. Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts Fraction: represents a part of a whole object or unit Numerator: (top number) represents number of parts of the whole Denominator: (bottom number) represents how
Decimal Routes. You should record any working out here. Start. End. End. Start at Start and find your way to the
 Decimal Routes Start at Start and find your way to the End left right down. You can only move or up. You can only go into the squares when the answer is or.5.. Shade in your route as you go along. Start
Decimal Routes Start at Start and find your way to the End left right down. You can only move or up. You can only go into the squares when the answer is or.5.. Shade in your route as you go along. Start
TIMSS 2011 Fourth Grade Mathematics Item Descriptions developed during the TIMSS 2011 Benchmarking
 TIMSS 2011 Fourth Grade Mathematics Item Descriptions developed during the TIMSS 2011 Benchmarking Items at Low International Benchmark (400) M01_05 M05_01 M07_04 M08_01 M09_01 M13_01 Solves a word problem
TIMSS 2011 Fourth Grade Mathematics Item Descriptions developed during the TIMSS 2011 Benchmarking Items at Low International Benchmark (400) M01_05 M05_01 M07_04 M08_01 M09_01 M13_01 Solves a word problem
Fractions. Fractions One tenths, two tenths, three tenths
 Recognise, Name and Write Chilli Challenge Count up and down in tenths One tenths, two tenths, three tenths 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Recognise, Name and Write Recognise, Name and Write Recognise that
Recognise, Name and Write Chilli Challenge Count up and down in tenths One tenths, two tenths, three tenths 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Recognise, Name and Write Recognise, Name and Write Recognise that
What is a Fraction? Fractions. One Way To Remember Numerator = North / 16. Example. What Fraction is Shaded? 9/16/16. Fraction = Part of a Whole
 // Fractions Pages What is a Fraction? Fraction Part of a Whole Top Number? Bottom Number? Page Numerator tells how many parts you have Denominator tells how many parts are in the whole Note: the fraction
// Fractions Pages What is a Fraction? Fraction Part of a Whole Top Number? Bottom Number? Page Numerator tells how many parts you have Denominator tells how many parts are in the whole Note: the fraction
Day 4 Percentiles and Box and Whisker.notebook. April 20, 2018
 Day 4 Box & Whisker Plots and Percentiles In a previous lesson, we learned that the median divides a set a data into 2 equal parts. Sometimes it is necessary to divide the data into smaller more precise
Day 4 Box & Whisker Plots and Percentiles In a previous lesson, we learned that the median divides a set a data into 2 equal parts. Sometimes it is necessary to divide the data into smaller more precise
(Type your answer in radians. Round to the nearest hundredth as needed.)
 1. Find the exact value of the following expression within the interval (Simplify your answer. Type an exact answer, using as needed. Use integers or fractions for any numbers in the expression. Type N
1. Find the exact value of the following expression within the interval (Simplify your answer. Type an exact answer, using as needed. Use integers or fractions for any numbers in the expression. Type N
What is a Fraction? A fraction is a part or piece of something. The way we write fractions tells us the size of the piece we are referring to
 October 0, 0 What is a Fraction? A fraction is a part or piece of something. The way we write fractions tells us the size of the piece we are referring to ⅝ is the numerator is the denominator is the whole
October 0, 0 What is a Fraction? A fraction is a part or piece of something. The way we write fractions tells us the size of the piece we are referring to ⅝ is the numerator is the denominator is the whole
Unit 3.2: Fractions, Decimals and Percent Lesson: Comparing and Ordering Fractions and Decimals
 Unit 3.2: Fractions, Decimals and Percent Lesson: Comparing and Ordering Fractions and Decimals Objectives: Students will use benchmarks, place value and equivalent fractions to compare and order fractions
Unit 3.2: Fractions, Decimals and Percent Lesson: Comparing and Ordering Fractions and Decimals Objectives: Students will use benchmarks, place value and equivalent fractions to compare and order fractions
Scheme of work Elementary 1, the maths pathway
 Objective Code Objective Exemplification Links to prior objectives Resources, enrichment, notes E1.1 Multiply and divide numbers by 10, 100 and 1000 including decimals. 6 x 10, 6.5 x 10, 0.65 10 3 x 100,
Objective Code Objective Exemplification Links to prior objectives Resources, enrichment, notes E1.1 Multiply and divide numbers by 10, 100 and 1000 including decimals. 6 x 10, 6.5 x 10, 0.65 10 3 x 100,
Learning Log Title: CHAPTER 3: ARITHMETIC PROPERTIES. Date: Lesson: Chapter 3: Arithmetic Properties
 Chapter 3: Arithmetic Properties CHAPTER 3: ARITHMETIC PROPERTIES Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Arithmetic Properties Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
Chapter 3: Arithmetic Properties CHAPTER 3: ARITHMETIC PROPERTIES Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Arithmetic Properties Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
Introduction to Fractions
 Introduction to Fractions Fractions represent parts of a whole. The top part of a fraction is called the numerator, while the bottom part of a fraction is called the denominator. The denominator states
Introduction to Fractions Fractions represent parts of a whole. The top part of a fraction is called the numerator, while the bottom part of a fraction is called the denominator. The denominator states
Vocabulary: Looking For Pythagoras
 Vocabulary: Looking For Pythagoras Concept Finding areas of squares and other figures by subdividing or enclosing: These strategies for finding areas were developed in Covering and Surrounding. Students
Vocabulary: Looking For Pythagoras Concept Finding areas of squares and other figures by subdividing or enclosing: These strategies for finding areas were developed in Covering and Surrounding. Students
HOW TO DIVIDE: MCC6.NS.2 Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE
 MCC6.NS. Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE Dividend A number that is divided by another number. Divisor A number by which another number
MCC6.NS. Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE Dividend A number that is divided by another number. Divisor A number by which another number
Lesson 1T ~ Greatest Common Factor
 Lesson T ~ Greatest Common Factor Name Period Date List the factors of each number. Decide whether the number is prime or composite.. 9. 9 9 Is 9 prime or composite? Is prime or composite?.. Is prime or
Lesson T ~ Greatest Common Factor Name Period Date List the factors of each number. Decide whether the number is prime or composite.. 9. 9 9 Is 9 prime or composite? Is prime or composite?.. Is prime or
Section 2.3 Rational Numbers. A rational number is a number that may be written in the form a b. for any integer a and any nonzero integer b.
 Section 2.3 Rational Numbers A rational number is a number that may be written in the form a b for any integer a and any nonzero integer b. Why is division by zero undefined? For example, we know that
Section 2.3 Rational Numbers A rational number is a number that may be written in the form a b for any integer a and any nonzero integer b. Why is division by zero undefined? For example, we know that
Name Student ID Number. Group Name. Group Members. Fractions
 Name Student ID Number Group Name Group Members Fractions Many people struggle with and even fear working with fractions. Part of the reason people struggle is because they do not know what a fraction
Name Student ID Number Group Name Group Members Fractions Many people struggle with and even fear working with fractions. Part of the reason people struggle is because they do not know what a fraction
 - 0.8.00-0.8. 7 ANSWERS: ) : ) : ) : ) : 8 RATIO WORD PROBLEM EXAMPLES: Ratio Compares two amounts or values; they can be written in ways. As a fraction With a colon : With words to A classroom has girls
- 0.8.00-0.8. 7 ANSWERS: ) : ) : ) : ) : 8 RATIO WORD PROBLEM EXAMPLES: Ratio Compares two amounts or values; they can be written in ways. As a fraction With a colon : With words to A classroom has girls
#1 MATH 6 SOL PRACTICE PACKET #1 Number Sense
 NAME: BLOCK: Due date: #1 MATH 6 SOL PRACTICE PACKET #1 Number Sense do not lose this packet!!! You MUST do EVERY problem. Page 1 of 14 Reporting Category: Number and Number Sense Number of Items: 10 Standards
NAME: BLOCK: Due date: #1 MATH 6 SOL PRACTICE PACKET #1 Number Sense do not lose this packet!!! You MUST do EVERY problem. Page 1 of 14 Reporting Category: Number and Number Sense Number of Items: 10 Standards
Mathematical Practices
 Middletown Public Schools Mathematics Unit Planning Organizer Subject Mathematics -Number and Operations - Fractions Grade 4 Unit 4 Comparing Fractions and Understanding Decimal Notation Duration 0 Instructional
Middletown Public Schools Mathematics Unit Planning Organizer Subject Mathematics -Number and Operations - Fractions Grade 4 Unit 4 Comparing Fractions and Understanding Decimal Notation Duration 0 Instructional
Free Pre-Algebra Lesson 25 page 1
 Free Pre-Algebra Lesson page Lesson The Common Denominator Every fractional amount has many names. The equivalent fraction names for a given amount may make fractions seem a little slippery and difficult
Free Pre-Algebra Lesson page Lesson The Common Denominator Every fractional amount has many names. The equivalent fraction names for a given amount may make fractions seem a little slippery and difficult
Description Reflect and Review Teasers Answers Recall basics of fractions. Review
 1. Revision Recall basics of fractions. are equivalent fractions of. Since Write five equivalent fractions of. 2. Rational Numbers A number is defined as a number which can be represented in the form of,
1. Revision Recall basics of fractions. are equivalent fractions of. Since Write five equivalent fractions of. 2. Rational Numbers A number is defined as a number which can be represented in the form of,
SOLUTION: Because the fractions have a common denominator, compare the numerators. 5 < 3
 Section 1 Practice Problems 1. Because the fractions have a common denominator, compare the numerators. 5 < 3 So,. 2. 0.71 To compare these numbers, write both fractions as a decimal. 0.8 is greater than
Section 1 Practice Problems 1. Because the fractions have a common denominator, compare the numerators. 5 < 3 So,. 2. 0.71 To compare these numbers, write both fractions as a decimal. 0.8 is greater than
Perfect square numbers are formed when we multiply a number (factor) by itself, or square a number. 9 is a perfect square, and 3 is it s factor.
 Math Unit 1: Square Roots and Surface Area. Review from Grade 8: Perfect Squares What is a perfect square? Perfect square numbers are formed when we multiply a number (factor) by itself, or square a number.
Math Unit 1: Square Roots and Surface Area. Review from Grade 8: Perfect Squares What is a perfect square? Perfect square numbers are formed when we multiply a number (factor) by itself, or square a number.
Curriculum Connections (Fractions): K-8 found at under Planning Supports
 Curriculum Connections (Fractions): K-8 found at http://www.edugains.ca/newsite/digitalpapers/fractions/resources.html under Planning Supports Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade
Curriculum Connections (Fractions): K-8 found at http://www.edugains.ca/newsite/digitalpapers/fractions/resources.html under Planning Supports Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade
3.1 Fractions to Decimals
 . Fractions to Decimals Focus Use patterns to convert between decimals and fractions. Numbers can be written in both fraction and decimal form. For example, can be written as and.0. A fraction illustrates
. Fractions to Decimals Focus Use patterns to convert between decimals and fractions. Numbers can be written in both fraction and decimal form. For example, can be written as and.0. A fraction illustrates
Lesson 9: Decimal Expansions of Fractions, Part 1
 Classwork Opening Exercises 1 2 1. a. We know that the fraction can be written as a finite decimal because its denominator is a product of 2 s. Which power of 10 will allow us to easily write the fraction
Classwork Opening Exercises 1 2 1. a. We know that the fraction can be written as a finite decimal because its denominator is a product of 2 s. Which power of 10 will allow us to easily write the fraction
Fifth Grade Math Rubric
 Operations and Algebraic Thinking Support Needed Progressing Meets Writes, solves, and interprets numerical expressions guidance with and/or inconsistently writes, solves, and interprets numerical expressions.
Operations and Algebraic Thinking Support Needed Progressing Meets Writes, solves, and interprets numerical expressions guidance with and/or inconsistently writes, solves, and interprets numerical expressions.
Fractions Decimals Percents
 1 Fractions Decimals Percents Name TAG 2 Fractions to Decimals There are ways to convert fractions to decimals. 1. Use place value 2. Using equivalent fractions with denominators of,, 0, etc.. Use long
1 Fractions Decimals Percents Name TAG 2 Fractions to Decimals There are ways to convert fractions to decimals. 1. Use place value 2. Using equivalent fractions with denominators of,, 0, etc.. Use long
Integers and Rational Numbers
 A A Family Letter: Integers Dear Family, The student will be learning about integers and how these numbers relate to the coordinate plane. The set of integers includes the set of whole numbers (0, 1,,,...)
A A Family Letter: Integers Dear Family, The student will be learning about integers and how these numbers relate to the coordinate plane. The set of integers includes the set of whole numbers (0, 1,,,...)
SNAP Centre Workshop. Graphing Lines
 SNAP Centre Workshop Graphing Lines 45 Graphing a Line Using Test Values A simple way to linear equation involves finding test values, plotting the points on a coordinate plane, and connecting the points.
SNAP Centre Workshop Graphing Lines 45 Graphing a Line Using Test Values A simple way to linear equation involves finding test values, plotting the points on a coordinate plane, and connecting the points.
~IC Subtract 208 from the product:
 TEKSas Target Practice Student Answer Sheet set A How many tens? hundreds? thousands? Value of tens? hundreds? thousands? -- What number is 10 more? 100 more? B Write the number in words: ----------- C
TEKSas Target Practice Student Answer Sheet set A How many tens? hundreds? thousands? Value of tens? hundreds? thousands? -- What number is 10 more? 100 more? B Write the number in words: ----------- C
Two Plus You. Unit. National PASS Center 2013
 Two Plus You Unit National PASS Center 0 National PASS Center Geneseo Migrant Center Mt. Morris-Leicester Road Leicester, NY 44 () 6-7960 () 6-7969 (fax) www.migrant.net/pass Authors: Editor: Proofer:
Two Plus You Unit National PASS Center 0 National PASS Center Geneseo Migrant Center Mt. Morris-Leicester Road Leicester, NY 44 () 6-7960 () 6-7969 (fax) www.migrant.net/pass Authors: Editor: Proofer:
Relate Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
 Domain 1 Lesson 1 Relate Fractions, Decimals, and Percents Common Core Standard: 7.RP.3 Getting the Idea Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed in the form a, where a and b are b integers and
Domain 1 Lesson 1 Relate Fractions, Decimals, and Percents Common Core Standard: 7.RP.3 Getting the Idea Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed in the form a, where a and b are b integers and
Section 4.1 Investigating Circles
 Section 4.1 Investigating Circles A circle is formed when all the points in a plane that are the same distance away from a center point. The distance from the center of the circle to any point on the edge
Section 4.1 Investigating Circles A circle is formed when all the points in a plane that are the same distance away from a center point. The distance from the center of the circle to any point on the edge
I can statements for NBT 1-7 1st attempt 2nd attempt mastered
 MATH NAME: I can statements for OA1-3 1st attempt Date 2nd attempt Date Mastered statement I can write expressions using parenthesis, brackets and braces based on wording such as add 5 and then divide
MATH NAME: I can statements for OA1-3 1st attempt Date 2nd attempt Date Mastered statement I can write expressions using parenthesis, brackets and braces based on wording such as add 5 and then divide
Functional Skills Mathematics
 Functional Skills Mathematics Level Learning Resource Fractions N/L. N/L. LEVEL Contents Numerator and Denominator N/L. Page Equivalent Fractions N/L. Pages - Comparing Fractions N/L. Pages - Improper
Functional Skills Mathematics Level Learning Resource Fractions N/L. N/L. LEVEL Contents Numerator and Denominator N/L. Page Equivalent Fractions N/L. Pages - Comparing Fractions N/L. Pages - Improper
Grade 4. Number Strand. Achievement Indicators. 1. Represent and describe whole numbers to , pictorially and symbolically.
 Number Strand Outcomes 1. Represent and describe whole numbers to 10 000, pictorially and symbolically. Grade 4 Achievement Indicators Read a four-digit numeral without using the word and (e.g., 5321 is
Number Strand Outcomes 1. Represent and describe whole numbers to 10 000, pictorially and symbolically. Grade 4 Achievement Indicators Read a four-digit numeral without using the word and (e.g., 5321 is
TABLE OF CONTENTS. About Finish Line PA Core Math 5. UNIT 1: Big Ideas from Grade 7 7 UNIT 1 REVIEW 38. UNIT 2: The Number System 43 UNIT 2 REVIEW 58
 TABLE OF CONTENTS About Finish Line PA Core Math 5 UNIT 1: Big Ideas from Grade 7 7 LESSON 1 CC..1.7.D.1 Understanding Proportional Relationships [connects to CC...8.B.] 8 LESSON CC..1.7.E.1 Operations
TABLE OF CONTENTS About Finish Line PA Core Math 5 UNIT 1: Big Ideas from Grade 7 7 LESSON 1 CC..1.7.D.1 Understanding Proportional Relationships [connects to CC...8.B.] 8 LESSON CC..1.7.E.1 Operations
What s Half of a Half of a Half?
 Overview Activity ID: 8606 Math Concepts Materials Students will use a physical model to determine what happens fractions TI-0XS when they repeatedly halve a piece of paper, and then they decimals MultiView
Overview Activity ID: 8606 Math Concepts Materials Students will use a physical model to determine what happens fractions TI-0XS when they repeatedly halve a piece of paper, and then they decimals MultiView
North Thurston Public Schools Sixth Grade Math Power Standard 1 Unit Assessment #1 and #3
 Math Power Standard 1 Unit Assessment #1 and #3 PS 1 - Estimate products and quotients of fractions and decimals (6.1.C) Big Idea: Estimating helps us decide if our answers make sense. Essential Questions:
Math Power Standard 1 Unit Assessment #1 and #3 PS 1 - Estimate products and quotients of fractions and decimals (6.1.C) Big Idea: Estimating helps us decide if our answers make sense. Essential Questions:
Step 1 The number name given in the question is five and sixty-eight-hundredths. We know that
 Answers (1) 5.68 The number name given in the question is five and sixty-eight-hundredths. We know that hundredths can be represented as 1. So, we can write five and sixty-eight-hundredths as 5 and 68
Answers (1) 5.68 The number name given in the question is five and sixty-eight-hundredths. We know that hundredths can be represented as 1. So, we can write five and sixty-eight-hundredths as 5 and 68
February 23, Chapter 1. and Surface Area
 Chapter 1 and Surface Area 1. By tracing lines on the 1 cm graph paper provided, create three different sized squares. 2. Label the area of each square 3. Label the side length of each square How many
Chapter 1 and Surface Area 1. By tracing lines on the 1 cm graph paper provided, create three different sized squares. 2. Label the area of each square 3. Label the side length of each square How many
Fractions / 8 / / 10 1 ½ / 12
 Fractions / 8 / 60 / ½ / 0 / What is a fraction? Loosely speaking, a fraction is a quantity that cannot be represented by a whole number. Why do we need fractions? Consider the following scenario. Can
Fractions / 8 / 60 / ½ / 0 / What is a fraction? Loosely speaking, a fraction is a quantity that cannot be represented by a whole number. Why do we need fractions? Consider the following scenario. Can
Activity 1 Look at the pattern on the number line and find the missing numbers. Model. (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) (d)
 Lesson Look at the pattern on the number line and find the missing numbers. Model (a) (b) (c) 9 Answers: (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) 00 00. (a) (b) 00. (c) 0 0 (a) (b) (c) Use the number
Lesson Look at the pattern on the number line and find the missing numbers. Model (a) (b) (c) 9 Answers: (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) 00 00. (a) (b) 00. (c) 0 0 (a) (b) (c) Use the number
NF5-21 Multiplying Unit Fractions Pages 13 14
 NF- Multiplying Unit Fractions Pages STANDARDS.NF.B. Goals Students will develop and apply the formula for multiplying unit fractions by unit fractions. Vocabulary denominator numerator of (to mean multiply
NF- Multiplying Unit Fractions Pages STANDARDS.NF.B. Goals Students will develop and apply the formula for multiplying unit fractions by unit fractions. Vocabulary denominator numerator of (to mean multiply
Classwork. Exercises Use long division to determine the decimal expansion of. NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 8 7
 Classwork Exercises 1 5 1. Use long division to determine the decimal expansion of. 2. Use long division to determine the decimal expansion of. 3. Use long division to determine the decimal expansion of.
Classwork Exercises 1 5 1. Use long division to determine the decimal expansion of. 2. Use long division to determine the decimal expansion of. 3. Use long division to determine the decimal expansion of.
Basic and Intermediate Math Vocabulary Spring 2017 Semester
 Digit A symbol for a number (1-9) Whole Number A number without fractions or decimals. Place Value The value of a digit that depends on the position in the number. Even number A natural number that is
Digit A symbol for a number (1-9) Whole Number A number without fractions or decimals. Place Value The value of a digit that depends on the position in the number. Even number A natural number that is
add and subtract whole numbers with more than 4 digits, including using formal written methods (columnar addition and subtraction)
 I created these worksheets because I think it is useful to have regular practice of calculation methods away from the point of teaching. There are worksheets. Questions are aligned to the Year curriculum,
I created these worksheets because I think it is useful to have regular practice of calculation methods away from the point of teaching. There are worksheets. Questions are aligned to the Year curriculum,
Exploring Adding and Subtracting Decimals. :i + Ml = HH. d) = e) f) = d) = e}
 3.1 Exploring Adding and Subtracting Decimals Add and subtract decimals using mental math. 1. Rewrite these number sentences using near numbers, to make them easier to estimate. Then calculate. The first
3.1 Exploring Adding and Subtracting Decimals Add and subtract decimals using mental math. 1. Rewrite these number sentences using near numbers, to make them easier to estimate. Then calculate. The first
Rational numbers as decimals and as integer fractions
 Rational numbers as decimals and as integer fractions Given a rational number expressed as an integer fraction reduced to the lowest terms, the quotient of that fraction will be: an integer, if the denominator
Rational numbers as decimals and as integer fractions Given a rational number expressed as an integer fraction reduced to the lowest terms, the quotient of that fraction will be: an integer, if the denominator
To be able to count up and down in tenths
 Progression Grid: Year Year 2 Year 3 Year Year Year 6 Counting in Fractional steps To be able to count in fractions up to 0, starting from any number and using the/2 and 2/ equivalence on the number line
Progression Grid: Year Year 2 Year 3 Year Year Year 6 Counting in Fractional steps To be able to count in fractions up to 0, starting from any number and using the/2 and 2/ equivalence on the number line
Ce qui est important dans l'enseignement des mathématiques. Marian Small novembre 2017
 Ce qui est important dans l'enseignement des mathématiques Marian Small novembre 2017 Playing with math Uae your linking cubes. Show that the mean of 4, 7 and 7 is 6. Playing with math Uae your linking
Ce qui est important dans l'enseignement des mathématiques Marian Small novembre 2017 Playing with math Uae your linking cubes. Show that the mean of 4, 7 and 7 is 6. Playing with math Uae your linking
Gateway Regional School District VERTICAL ALIGNMENT OF MATHEMATICS STANDARDS Grades 3-6
 NUMBER SENSE & OPERATIONS 3.N.1 Exhibit an understanding of the values of the digits in the base ten number system by reading, modeling, writing, comparing, and ordering whole numbers through 9,999. Our
NUMBER SENSE & OPERATIONS 3.N.1 Exhibit an understanding of the values of the digits in the base ten number system by reading, modeling, writing, comparing, and ordering whole numbers through 9,999. Our
Concept Fourth Grade: Second Nine Weeks Readiness Standards Time Key Content Key Vocabulary
 Multiplication by 2-Digit Numbers Concept Fourth Grade: Second Nine Weeks 14-15 Time Key Content Key Vocabulary 4.4C represent the product of 2 two-digit numbers using arrays, area models, or equations,
Multiplication by 2-Digit Numbers Concept Fourth Grade: Second Nine Weeks 14-15 Time Key Content Key Vocabulary 4.4C represent the product of 2 two-digit numbers using arrays, area models, or equations,
1 Addition and Subtraction
 Worsheet for 5.: Operations with Fractions Addition and Subtraction Adding/subtracting when there is a common denominator Draw a picture to work out each problem. Write your answer in lowest terms; if
Worsheet for 5.: Operations with Fractions Addition and Subtraction Adding/subtracting when there is a common denominator Draw a picture to work out each problem. Write your answer in lowest terms; if
Mathematics Background
 Finding Area and Distance Students work in this Unit develops a fundamentally important relationship connecting geometry and algebra: the Pythagorean Theorem. The presentation of ideas in the Unit reflects
Finding Area and Distance Students work in this Unit develops a fundamentally important relationship connecting geometry and algebra: the Pythagorean Theorem. The presentation of ideas in the Unit reflects
Lesson 1: THE DECIMAL SYSTEM
 Lesson 1: THE DECIMAL SYSTEM The word DECIMAL comes from a Latin word, which means "ten. The Decimal system uses the following ten digits to write a number: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. Each time
Lesson 1: THE DECIMAL SYSTEM The word DECIMAL comes from a Latin word, which means "ten. The Decimal system uses the following ten digits to write a number: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. Each time
Know how to use fractions to describe part of something Write an improper fraction as a mixed number Write a mixed number as an improper fraction
 . Fractions Know how to use fractions to describe part of something Write an improper fraction as a mixed number Write a mixed number as an improper fraction Key words fraction denominator numerator proper
. Fractions Know how to use fractions to describe part of something Write an improper fraction as a mixed number Write a mixed number as an improper fraction Key words fraction denominator numerator proper
1. Let n be a positive number. a. When we divide a decimal number, n, by 10, how are the numeral and the quotient related?
 Black Converting between Fractions and Decimals Unit Number Patterns and Fractions. Let n be a positive number. When we divide a decimal number, n, by 0, how are the numeral and the quotient related?.
Black Converting between Fractions and Decimals Unit Number Patterns and Fractions. Let n be a positive number. When we divide a decimal number, n, by 0, how are the numeral and the quotient related?.
Rev Name Date. . Round-off error is the answer to the question How wrong is the rounded answer?
 Name Date TI-84+ GC 7 Avoiding Round-off Error in Multiple Calculations Objectives: Recall the meaning of exact and approximate Observe round-off error and learn to avoid it Perform calculations using
Name Date TI-84+ GC 7 Avoiding Round-off Error in Multiple Calculations Objectives: Recall the meaning of exact and approximate Observe round-off error and learn to avoid it Perform calculations using
Fractions and Decimals
 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS 9 Fractions and Decimals Chapter. INTRODUCTION You have learnt fractions and decimals in earlier classes. The study of fractions included proper, improper and mixed fractions as
FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS 9 Fractions and Decimals Chapter. INTRODUCTION You have learnt fractions and decimals in earlier classes. The study of fractions included proper, improper and mixed fractions as
In this class, we addressed problem 14 from Chapter 2. So first step, we expressed the problem in STANDARD FORM:
 In this class, we addressed problem 14 from Chapter 2. So first step, we expressed the problem in STANDARD FORM: Now that we have done that, we want to plot our constraint lines, so we can find our feasible
In this class, we addressed problem 14 from Chapter 2. So first step, we expressed the problem in STANDARD FORM: Now that we have done that, we want to plot our constraint lines, so we can find our feasible
Student Success Center Arithmetic Study Guide for the ACCUPLACER (CPT)
 Fractions Terms Numerator: which tells how many parts you have (the number on top) Denominator: which tells how many parts in the whole (the number on the bottom) is parts have a dot out of Proper fraction:
Fractions Terms Numerator: which tells how many parts you have (the number on top) Denominator: which tells how many parts in the whole (the number on the bottom) is parts have a dot out of Proper fraction:
Topic 3: Fractions. Topic 1 Integers. Topic 2 Decimals. Topic 3 Fractions. Topic 4 Ratios. Topic 5 Percentages. Topic 6 Algebra
 Topic : Fractions Topic Integers Topic Decimals Topic Fractions Topic Ratios Topic Percentages Duration / weeks Content Outline PART (/ week) Introduction Converting Fractions to Decimals Converting Decimals
Topic : Fractions Topic Integers Topic Decimals Topic Fractions Topic Ratios Topic Percentages Duration / weeks Content Outline PART (/ week) Introduction Converting Fractions to Decimals Converting Decimals
OA: Operations and Algebraic Thinking
 OA: Operations and Algebraic Thinking I can write and explain the meaning of a multiplication equation. 4.OA.1 I can create and solve multiplication equations that compare two sets. 4.OA.1 I can represent
OA: Operations and Algebraic Thinking I can write and explain the meaning of a multiplication equation. 4.OA.1 I can create and solve multiplication equations that compare two sets. 4.OA.1 I can represent
Chapter 1 Section 1 Lesson: Solving Linear Equations
 Introduction Linear equations are the simplest types of equations to solve. In a linear equation, all variables are to the first power only. All linear equations in one variable can be reduced to the form
Introduction Linear equations are the simplest types of equations to solve. In a linear equation, all variables are to the first power only. All linear equations in one variable can be reduced to the form
2. The Wheel of Theodorus in Problem 4.1 includes only the first 11 triangles in the wheel. The wheel can go on forever.
 A C E Applications Connections Extensions Applications 1. The hypotenuse of a right triangle is 15 centimeters long. One leg is 9 centimeters long. How long is the other leg? 2. The Wheel of Theodorus
A C E Applications Connections Extensions Applications 1. The hypotenuse of a right triangle is 15 centimeters long. One leg is 9 centimeters long. How long is the other leg? 2. The Wheel of Theodorus
3. Mr. White does not wear white, so he is wearing the blue shirt. 4. Then Mr. Red wears a white shirt.
 5A METHOD 1: Strategy: Use reasoning. 1. Mr. Red and Mr. White are older than the man in gray. Neither Mr. Red nor Mr. White wears gray. Mr. Gray does not wear gray. So Mr. Blue wears the gray shirt. 2.
5A METHOD 1: Strategy: Use reasoning. 1. Mr. Red and Mr. White are older than the man in gray. Neither Mr. Red nor Mr. White wears gray. Mr. Gray does not wear gray. So Mr. Blue wears the gray shirt. 2.
Fractions with a denominator of 10, 100 or can be written as decimals. A decimal is any number which has a decimal comma.
 101 Unit 8 Decimals Fractions with a denominator of 10, or 1 000 can be written as decimals. A decimal is any number which has a decimal comma. A decimal comma separates whole numbers from tenths, hundredths
101 Unit 8 Decimals Fractions with a denominator of 10, or 1 000 can be written as decimals. A decimal is any number which has a decimal comma. A decimal comma separates whole numbers from tenths, hundredths
Multiplying and Dividing by Powers of 10
 Multiplying and Dividing by Powers of 10 1.) Complete stations A-F around the room. Copy each problem and answer it below. Problem A B C D E F Answer = = = = = = 2.) Where is the decimal point in a whole
Multiplying and Dividing by Powers of 10 1.) Complete stations A-F around the room. Copy each problem and answer it below. Problem A B C D E F Answer = = = = = = 2.) Where is the decimal point in a whole
Chapter 1 Performing Operations and Evaluating Expressions Section 3 Operations with Fractions and Proportions; Converting Units
 Math 167 Pre-Statistics Chapter 1 Performing Operations and Evaluating Expressions Section 3 Operations with Fractions and Proportions; Converting Units Objectives 1. Describe the meaning of a fraction.
Math 167 Pre-Statistics Chapter 1 Performing Operations and Evaluating Expressions Section 3 Operations with Fractions and Proportions; Converting Units Objectives 1. Describe the meaning of a fraction.
Place Value to Thousands
 Place Value to Thousands You can show,0 in a place-value chart. The value of each digit in a number depends on its place in the number. In,0 the value of: is hundred thousand or 00,000. is ten thousands
Place Value to Thousands You can show,0 in a place-value chart. The value of each digit in a number depends on its place in the number. In,0 the value of: is hundred thousand or 00,000. is ten thousands
Fractions. There are several terms that are commonly used when working with fractions.
 Chapter 0 Review of Arithmetic Fractions There are several terms that are commonly used when working with fractions. Fraction: The ratio of two numbers. We use a division bar to show this ratio. The number
Chapter 0 Review of Arithmetic Fractions There are several terms that are commonly used when working with fractions. Fraction: The ratio of two numbers. We use a division bar to show this ratio. The number
Add the fractions by first finding. f + D U C
 Add the fractions by first finding the LCD. U + C U C (Circle the LCD) Rewrite the fractions using the LCD and then add. Remember to reduce the answer if you can. Add the fractions by first finding M the
Add the fractions by first finding the LCD. U + C U C (Circle the LCD) Rewrite the fractions using the LCD and then add. Remember to reduce the answer if you can. Add the fractions by first finding M the
Module 1 - Applications: Visually Modeling Fractions
 Applications: Visually Modeling Fractions Inquire: How to Model Fraction Operations Overview When learning, it can be said that we forget more when we focus on memorizing steps over making sense of our
Applications: Visually Modeling Fractions Inquire: How to Model Fraction Operations Overview When learning, it can be said that we forget more when we focus on memorizing steps over making sense of our
MATHEMATICS UTAH CORE GUIDES GRADE 4
 MATHEMATICS UTAH CORE GUIDES GRADE 4 UTAH STATE BOARD OF EDUCATION 250 EAST 500 SOUTH P.O. BOX 144200 SALT LAKE CITY, UTAH 84114-4200 SYDNEE DICKSON, Ed.D., STATE SUPERINTENDENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION Operations
MATHEMATICS UTAH CORE GUIDES GRADE 4 UTAH STATE BOARD OF EDUCATION 250 EAST 500 SOUTH P.O. BOX 144200 SALT LAKE CITY, UTAH 84114-4200 SYDNEE DICKSON, Ed.D., STATE SUPERINTENDENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION Operations
8 7 Solving Inequalities by Adding and Subtracting. Daily Do from last class Homework Answers 8 6
 Daily Do from last class Homework Answers 8 6 1. Graph the inequality: x 5 2. Write the inequality for this graph below 31 32 33 34 1. s>30 2. h
Daily Do from last class Homework Answers 8 6 1. Graph the inequality: x 5 2. Write the inequality for this graph below 31 32 33 34 1. s>30 2. h
Learning Log Title: CHAPTER 2: FRACTIONS AND INTEGER ADDITION. Date: Lesson: Chapter 2: Fractions and Integer Addition
 Chapter : Fractions and Integer Addition CHAPTER : FRACTIONS AND INTEGER ADDITION Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter : Fractions and Integer Addition Date: Lesson:
Chapter : Fractions and Integer Addition CHAPTER : FRACTIONS AND INTEGER ADDITION Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter : Fractions and Integer Addition Date: Lesson:
5th Grade Mathematics Essential Standards
 Standard 1 Number Sense (10-20% of ISTEP/Acuity) Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the
Standard 1 Number Sense (10-20% of ISTEP/Acuity) Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the
Teaching Math thru Big Ideas Focusing on Differentiation. Marian Small April 2017 San Diego, CA
 Teaching Math thru Big Ideas Focusing on Differentiation Marian Small April 2017 San Diego, CA Our focus today Differentiation by focusing on big ideas Formative assessment/feedback Planning lessons/units
Teaching Math thru Big Ideas Focusing on Differentiation Marian Small April 2017 San Diego, CA Our focus today Differentiation by focusing on big ideas Formative assessment/feedback Planning lessons/units
The Bracket Strategy
 The Bracket Strategy This strategy will show students how common denominators are actually found. This strategy should be done with fraction bars. Step Create a bracket X Step Fill in the bracket with
The Bracket Strategy This strategy will show students how common denominators are actually found. This strategy should be done with fraction bars. Step Create a bracket X Step Fill in the bracket with
Lesson 2 Fractions on a Number Line
 Lesson Fractions on a Number Line Think A paper tape is marked so that there are equal parts between each meter. The tape is used to measure the length of two ribbons. 0 m m A B C D E F 0 (c) (d) (e) What
Lesson Fractions on a Number Line Think A paper tape is marked so that there are equal parts between each meter. The tape is used to measure the length of two ribbons. 0 m m A B C D E F 0 (c) (d) (e) What
SPRINGBOARD UNIT 6 DATA ANALYSIS AND PROBABILITY
 SPRINGBOARD UNIT 6 DATA ANALYSIS AND PROBABILITY 6. Theoretical and Experimental Probability Probability = number of ways to get outcome number of possible outcomes Theoretical Probability the probability
SPRINGBOARD UNIT 6 DATA ANALYSIS AND PROBABILITY 6. Theoretical and Experimental Probability Probability = number of ways to get outcome number of possible outcomes Theoretical Probability the probability
Fraction Addition & Subtraction
 Fraction Addition & Subtraction Question: Why is the answer to 1/2 + 1/3 not 2/5? Possible answers to the question are: 1. Are you sure that the answer is not 2/5? Seems sensible that 2/5 is the answer
Fraction Addition & Subtraction Question: Why is the answer to 1/2 + 1/3 not 2/5? Possible answers to the question are: 1. Are you sure that the answer is not 2/5? Seems sensible that 2/5 is the answer
Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Academic Standards Mathematics
 5 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions,
5 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions,
College Prep Algebra II Summer Packet
 Name: College Prep Algebra II Summer Packet This packet is an optional review which is highly recommended before entering CP Algebra II. It provides practice for necessary Algebra I topics. Remember: When
Name: College Prep Algebra II Summer Packet This packet is an optional review which is highly recommended before entering CP Algebra II. It provides practice for necessary Algebra I topics. Remember: When
Class 4 Decimals. Answer the questions. For more such worksheets visit
 ID : in-4-decimals [1] Class 4 Decimals For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) What is the place value of 4 in 365.704? (2) Write two and five-tenths as a decimal fraction.
ID : in-4-decimals [1] Class 4 Decimals For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) What is the place value of 4 in 365.704? (2) Write two and five-tenths as a decimal fraction.
Grade 4 Fractions. Answer the questions. For more such worksheets visit (1) Convert into a mixed fraction. (2) Convert
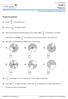 ID : aefractions [1] Grade Fractions For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Convert 63 13 (2) Convert 6 7 12 into a mixed fraction. to improper fraction. (3) Aleser had
ID : aefractions [1] Grade Fractions For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Convert 63 13 (2) Convert 6 7 12 into a mixed fraction. to improper fraction. (3) Aleser had
Appendix 14C: TIMSS 2015 Eighth Grade Mathematics Item Descriptions Developed During the TIMSS 2015 Benchmarking
 Appendix 14C: TIMSS 2015 Eighth Grade Mathematics Item Descriptions Developed During the TIMSS 2015 Benchmarking Items at Low International Benchmark (400) Number M04_01 M07_01 Recognizes a 7-digit number
Appendix 14C: TIMSS 2015 Eighth Grade Mathematics Item Descriptions Developed During the TIMSS 2015 Benchmarking Items at Low International Benchmark (400) Number M04_01 M07_01 Recognizes a 7-digit number
6.3 ADDING and SUBTRACTING Rational Expressions REVIEW. When you ADD rational numbers (fractions): 1) Write each number with common denominator
 6.3 ADDING and SUBTRACTING Rational REVIEW When you ADD rational numbers (fractions): 1) Write each number with common denominator 4 5 + 10 12 = 6.3 ADDING and SUBTRACTING Rational 4 5 + 10 12 = REVIEW
6.3 ADDING and SUBTRACTING Rational REVIEW When you ADD rational numbers (fractions): 1) Write each number with common denominator 4 5 + 10 12 = 6.3 ADDING and SUBTRACTING Rational 4 5 + 10 12 = REVIEW
Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers
 Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers Strategy note to teachers: Typically students need more practice doing computations with fractions. You may want to consider teaching the sections on
Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers Strategy note to teachers: Typically students need more practice doing computations with fractions. You may want to consider teaching the sections on
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source:
 Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
Properties of a Circle Diagram Source: http://www.ricksmath.com/circles.html Definitions: Circumference (c): The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference Diameter (d): Any straight line drawn
or 5.00 or 5.000, and so on You can expand the decimal places of a number that already has digits to the right of the decimal point.
 1 LESSON Understanding Rational and Irrational Numbers UNDERSTAND All numbers can be written with a For example, you can rewrite 22 and 5 with decimal points without changing their values. 22 5 22.0 or
1 LESSON Understanding Rational and Irrational Numbers UNDERSTAND All numbers can be written with a For example, you can rewrite 22 and 5 with decimal points without changing their values. 22 5 22.0 or
