and denominators of two fractions. For example, you could use
|
|
|
- Caren Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Learning Goal denominators. Open Question and denominators of two fractions. For example, you could use and 0. Make sure that some of your fractions are improper and some are proper. Make sure that some of your fractions use the same numerator and some do not. Tell which of your fractions is greater and how you know. them. Tell how you know which fraction is greater each time. September 011 Marian Small, 011 Fractions (IS)
2 Think Sheet Pairs of fractions are either equal or one fraction is greater than the other fraction. We can decide which statement is true by using a model, by renaming one or both fractions, or by using benchmarks. Using a Model and, we can use a picture that shows the two fractions lined up, so we can see which extends farther. _ < _ 1 of counters is counters, so of counters is 1 counters. 1 of counters is counters, so of counters is counters. is more than 1, so >. September 011 Marian Small, 011 Fractions (IS)
3 Renaming Fractions To rename a fraction, we can think about how to express the fraction as an equivalent fraction or equivalent decimal. Equivalent Fractions Two fractions are equivalent, or equal, if they take up the same part of a whole or wholes. For example, =. Each section of the model is split into two sections in the model. So, there are twice as many sections in the second model, and twice as many are shaded. The numerator and denominator have both doubled. We can multiply the numerator and denominator by any amount (except 0) and the same thing happens as in the example above. There are more sections shaded and more sections unshaded, but the amount shaded does not change. For example, if we multiply by : = = 9 1. or If we multiply by : = = 0 0. Common Denominators and Common Numerators Renaming fractions to get common denominators or common numerators is helpful when comparing fractions. If we compare fractions with the same denominator, the one with the greater numerator is greater. If we compare fractions with the same numerator, the one with the lesser denominator is greater. To determine if or is more, we might use common denominators: = 1 = 1 = = 9 = 1 = 1 = 1 1 = 1 1 = 1 Since = 1 and = 1, is a common denominator. Since 1 < 1, then <. = 1 = = 9 = 1 = 1 Since = 1 and =, is a common numerator. 1 1 > 1, and >. September 011 Marian Small, 011 Fractions (IS)
4 Decimals Another way to rename a fraction is to represent it as a decimal. For example, =. Using a calculator, we see that = 0. The reason a = a b is because we can imagine a objects, each being shared b by b people. Each person gets one section of each object, so altogether each gets a sections of size 1 b ; that is a b. For example, if four people share three bars each one gets one fourth from each of the whole bars and that is. We can use decimal renaming to compare fractions, such as to. Since = 0. and = 0., we see that <. Using Benchmarks We can use benchmarks to compare fractions. them to 1. For example, 1 1 is more than 1, and 1 is less than 1, so 1 >. greater than one half and one is not. We can mentally rename one half to compare the other fractions to it. For the fraction, since one half is, is more than one half. For the fraction, since one half is, is less than one half. So, >. them to whole numbers other than 1. For the fraction 11, since is, 11 is more than. For the fraction, since is, is less than. So, 11 is more than. 9 September 011 Marian Small, 011 Fractions (IS)
5 1. What fraction comparison is being shown? a) c) d). Draw a picture to show why this statement is true. a) = 1 =. Tell or show why is not equivalent to 9.. a) 9 or 9 9 or 11 September 011 Marian Small, 011 Fractions (IS)
6 . How might you rename one or both fractions as other fractions to make it easier to compare them? Tell how it helps. a) and and 1 c) 9 and 1 1 d) and 1. a) Why does it make sense that 9 = 9? What are the decimal equivalents of and 9? c) How could you use decimal equivalents to compare and 9? 11 September 011 Marian Small, 011 Fractions (IS)
7 . How can each of these fraction pairs be compared without renaming them as other fractions or as decimals? a) and and 1 c) 1 and 1 d) 1 and 9 e) and 9 f) 9 and 1. Describe a real-life situation when you might make each comparison: a) to 1 to 1 9. A fraction with a denominator of is between one fraction with a denominator of and one fraction with a denominator of. Fill in all 9 blanks to show three ways this could be true. < < < < < <. a) List all the fractions with a denominator of between and. List all the fractions with a denominator of between and. c) Is it possible to list all the fractions between and? Explain. 1 September 011 Marian Small, 011 Fractions (IS)
Section 3.2 Comparing and Ordering Fractions and Decimals. 1. Model fractions and/or decimals using blocks, fraction pieces, pattern blocks, etc.
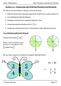 Section 3.2 Comparing and Ordering Fractions and Decimals We will use several methods to compare and order fractions: 1. Model fractions and/or decimals using blocks, fraction pieces, pattern blocks, etc.
Section 3.2 Comparing and Ordering Fractions and Decimals We will use several methods to compare and order fractions: 1. Model fractions and/or decimals using blocks, fraction pieces, pattern blocks, etc.
add and subtract whole numbers with more than 4 digits, including using formal written methods (columnar addition and subtraction)
 I created these worksheets because I think it is useful to have regular practice of calculation methods away from the point of teaching. There are worksheets. Questions are aligned to the Year curriculum,
I created these worksheets because I think it is useful to have regular practice of calculation methods away from the point of teaching. There are worksheets. Questions are aligned to the Year curriculum,
Unit: Rational Number Lesson 3.1: What is a Rational Number? Objectives: Students will compare and order rational numbers.
 Unit: Rational Number Lesson 3.: What is a Rational Number? Objectives: Students will compare and order rational numbers. (9N3) Procedure: This unit will introduce the concept of rational numbers. This
Unit: Rational Number Lesson 3.: What is a Rational Number? Objectives: Students will compare and order rational numbers. (9N3) Procedure: This unit will introduce the concept of rational numbers. This
Vocabulary: Bits and Pieces II
 Vocabulary: Bits and Pieces II Concept Estimation: Students have developed benchmark fractions. They can use these to substitute for all the fractions in a computation. Or they may use a combination of
Vocabulary: Bits and Pieces II Concept Estimation: Students have developed benchmark fractions. They can use these to substitute for all the fractions in a computation. Or they may use a combination of
What is a Fraction? Fractions. One Way To Remember Numerator = North / 16. Example. What Fraction is Shaded? 9/16/16. Fraction = Part of a Whole
 // Fractions Pages What is a Fraction? Fraction Part of a Whole Top Number? Bottom Number? Page Numerator tells how many parts you have Denominator tells how many parts are in the whole Note: the fraction
// Fractions Pages What is a Fraction? Fraction Part of a Whole Top Number? Bottom Number? Page Numerator tells how many parts you have Denominator tells how many parts are in the whole Note: the fraction
Unit 3.2: Fractions, Decimals and Percent Lesson: Comparing and Ordering Fractions and Decimals
 Unit 3.2: Fractions, Decimals and Percent Lesson: Comparing and Ordering Fractions and Decimals Objectives: Students will use benchmarks, place value and equivalent fractions to compare and order fractions
Unit 3.2: Fractions, Decimals and Percent Lesson: Comparing and Ordering Fractions and Decimals Objectives: Students will use benchmarks, place value and equivalent fractions to compare and order fractions
Gateway Regional School District VERTICAL ARTICULATION OF MATHEMATICS STANDARDS Grades K-4
 NUMBER SENSE & OPERATIONS K.N.1 Count by ones to at least 20. When you count, the last number word you say tells the number of items in the set. Counting a set of objects in a different order does not
NUMBER SENSE & OPERATIONS K.N.1 Count by ones to at least 20. When you count, the last number word you say tells the number of items in the set. Counting a set of objects in a different order does not
1 Addition and Subtraction
 Worsheet for 5.: Operations with Fractions Addition and Subtraction Adding/subtracting when there is a common denominator Draw a picture to work out each problem. Write your answer in lowest terms; if
Worsheet for 5.: Operations with Fractions Addition and Subtraction Adding/subtracting when there is a common denominator Draw a picture to work out each problem. Write your answer in lowest terms; if
Reteaching. Comparing and Ordering Integers
 - Comparing and Ordering Integers The numbers and - are opposites. The numbers 7 and -7 are opposites. Integers are the set of positive whole numbers, their opposites, and zero. 7 6 4 0 negative zero You
- Comparing and Ordering Integers The numbers and - are opposites. The numbers 7 and -7 are opposites. Integers are the set of positive whole numbers, their opposites, and zero. 7 6 4 0 negative zero You
NS6-50 Dividing Whole Numbers by Unit Fractions Pages 16 17
 NS6-0 Dividing Whole Numbers by Unit Fractions Pages 6 STANDARDS 6.NS.A. Goals Students will divide whole numbers by unit fractions. Vocabulary division fraction unit fraction whole number PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
NS6-0 Dividing Whole Numbers by Unit Fractions Pages 6 STANDARDS 6.NS.A. Goals Students will divide whole numbers by unit fractions. Vocabulary division fraction unit fraction whole number PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
The Bracket Strategy
 The Bracket Strategy This strategy will show students how common denominators are actually found. This strategy should be done with fraction bars. Step Create a bracket X Step Fill in the bracket with
The Bracket Strategy This strategy will show students how common denominators are actually found. This strategy should be done with fraction bars. Step Create a bracket X Step Fill in the bracket with
Section 3.1 Fractions to Decimals
 Section 3.1 Fractions to Decimals A fraction is a part of a whole. For example, it means 1 out of 5 possible pieces. is a fraction; Fractions also illustrate division. For example, also means 1 5 which
Section 3.1 Fractions to Decimals A fraction is a part of a whole. For example, it means 1 out of 5 possible pieces. is a fraction; Fractions also illustrate division. For example, also means 1 5 which
What is a Fraction? A fraction is a part or piece of something. The way we write fractions tells us the size of the piece we are referring to
 October 0, 0 What is a Fraction? A fraction is a part or piece of something. The way we write fractions tells us the size of the piece we are referring to ⅝ is the numerator is the denominator is the whole
October 0, 0 What is a Fraction? A fraction is a part or piece of something. The way we write fractions tells us the size of the piece we are referring to ⅝ is the numerator is the denominator is the whole
TOPIC 2 DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3
 TOPIC DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3 Association between Fractions and Decimals is a fraction. It means divided by. If we divide by the result is not a whole number. It is a half of whole
TOPIC DECIMALS (and INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS) WEEK 3 Association between Fractions and Decimals is a fraction. It means divided by. If we divide by the result is not a whole number. It is a half of whole
Gateway Regional School District VERTICAL ALIGNMENT OF MATHEMATICS STANDARDS Grades 3-6
 NUMBER SENSE & OPERATIONS 3.N.1 Exhibit an understanding of the values of the digits in the base ten number system by reading, modeling, writing, comparing, and ordering whole numbers through 9,999. Our
NUMBER SENSE & OPERATIONS 3.N.1 Exhibit an understanding of the values of the digits in the base ten number system by reading, modeling, writing, comparing, and ordering whole numbers through 9,999. Our
Learning Log Title: CHAPTER 2: FRACTIONS AND INTEGER ADDITION. Date: Lesson: Chapter 2: Fractions and Integer Addition
 Chapter : Fractions and Integer Addition CHAPTER : FRACTIONS AND INTEGER ADDITION Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter : Fractions and Integer Addition Date: Lesson:
Chapter : Fractions and Integer Addition CHAPTER : FRACTIONS AND INTEGER ADDITION Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter : Fractions and Integer Addition Date: Lesson:
HOW TO DIVIDE: MCC6.NS.2 Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE
 MCC6.NS. Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE Dividend A number that is divided by another number. Divisor A number by which another number
MCC6.NS. Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. WORD DEFINITION IN YOUR WORDS EXAMPLE Dividend A number that is divided by another number. Divisor A number by which another number
Free Pre-Algebra Lesson 25 page 1
 Free Pre-Algebra Lesson page Lesson The Common Denominator Every fractional amount has many names. The equivalent fraction names for a given amount may make fractions seem a little slippery and difficult
Free Pre-Algebra Lesson page Lesson The Common Denominator Every fractional amount has many names. The equivalent fraction names for a given amount may make fractions seem a little slippery and difficult
Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers
 Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers Strategy note to teachers: Typically students need more practice doing computations with fractions. You may want to consider teaching the sections on
Math 7 Notes Unit Three: Applying Rational Numbers Strategy note to teachers: Typically students need more practice doing computations with fractions. You may want to consider teaching the sections on
Teaching Math thru Big Ideas Focusing on Differentiation. Marian Small April 2017 San Diego, CA
 Teaching Math thru Big Ideas Focusing on Differentiation Marian Small April 2017 San Diego, CA Our focus today Differentiation by focusing on big ideas Formative assessment/feedback Planning lessons/units
Teaching Math thru Big Ideas Focusing on Differentiation Marian Small April 2017 San Diego, CA Our focus today Differentiation by focusing on big ideas Formative assessment/feedback Planning lessons/units
Hi... I am Fractionstein. Did you know that fractions are not as scary as you might think?
 Hi... I am Fractionstein. Did you know that fractions are not as scary as you might think? Learn along with me and you will be an expert at fractions in no time at all! What are fractions? Fractions are
Hi... I am Fractionstein. Did you know that fractions are not as scary as you might think? Learn along with me and you will be an expert at fractions in no time at all! What are fractions? Fractions are
_ _ _ _ _ _. Add and Subtract Parts of a Whole R54. Name. Justin has 3_. How much cheese does he have in all?
 Lesson 7.1 Add and Subtract Parts of a Whole Justin has 8pound of cheddar cheese and 2_ 8pound of brick cheese. How much cheese does he have in all? Step 1 Use fraction strips to model the problem. Use
Lesson 7.1 Add and Subtract Parts of a Whole Justin has 8pound of cheddar cheese and 2_ 8pound of brick cheese. How much cheese does he have in all? Step 1 Use fraction strips to model the problem. Use
 - 0.8.00-0.8. 7 ANSWERS: ) : ) : ) : ) : 8 RATIO WORD PROBLEM EXAMPLES: Ratio Compares two amounts or values; they can be written in ways. As a fraction With a colon : With words to A classroom has girls
- 0.8.00-0.8. 7 ANSWERS: ) : ) : ) : ) : 8 RATIO WORD PROBLEM EXAMPLES: Ratio Compares two amounts or values; they can be written in ways. As a fraction With a colon : With words to A classroom has girls
Student Success Center Arithmetic Study Guide for the ACCUPLACER (CPT)
 Fractions Terms Numerator: which tells how many parts you have (the number on top) Denominator: which tells how many parts in the whole (the number on the bottom) is parts have a dot out of Proper fraction:
Fractions Terms Numerator: which tells how many parts you have (the number on top) Denominator: which tells how many parts in the whole (the number on the bottom) is parts have a dot out of Proper fraction:
Add and Subtract Parts of a Whole
 Lesson 7. Add and Subtract Parts of a Whole Justin has _ pound of cheddar cheese and 2_ pound of brick cheese. How much cheese does he have in all? Step Use fraction strips to model the problem. Use three
Lesson 7. Add and Subtract Parts of a Whole Justin has _ pound of cheddar cheese and 2_ pound of brick cheese. How much cheese does he have in all? Step Use fraction strips to model the problem. Use three
Topic 3: Fractions. Topic 1 Integers. Topic 2 Decimals. Topic 3 Fractions. Topic 4 Ratios. Topic 5 Percentages. Topic 6 Algebra
 Topic : Fractions Topic Integers Topic Decimals Topic Fractions Topic Ratios Topic Percentages Duration / weeks Content Outline PART (/ week) Introduction Converting Fractions to Decimals Converting Decimals
Topic : Fractions Topic Integers Topic Decimals Topic Fractions Topic Ratios Topic Percentages Duration / weeks Content Outline PART (/ week) Introduction Converting Fractions to Decimals Converting Decimals
GAP CLOSING. Integers. Intermediate / Senior Facilitator s Guide
 GAP CLOSING Integers Intermediate / Senior Facilitator s Guide Topic 3 Integers Diagnostic...5 Administer the diagnostic...5 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions solutions...5 Using Intervention
GAP CLOSING Integers Intermediate / Senior Facilitator s Guide Topic 3 Integers Diagnostic...5 Administer the diagnostic...5 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions solutions...5 Using Intervention
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
 #2081 GLA Guided Learning Activity Multiplying and Dividing Fractions This packet contains background information for GLA 2081a, 2081b, etc. It is intended for student and tutor use as needed. Author:
#2081 GLA Guided Learning Activity Multiplying and Dividing Fractions This packet contains background information for GLA 2081a, 2081b, etc. It is intended for student and tutor use as needed. Author:
Concept Fourth Grade: Second Nine Weeks Readiness Standards Time Key Content Key Vocabulary
 Multiplication by 2-Digit Numbers Concept Fourth Grade: Second Nine Weeks 14-15 Time Key Content Key Vocabulary 4.4C represent the product of 2 two-digit numbers using arrays, area models, or equations,
Multiplication by 2-Digit Numbers Concept Fourth Grade: Second Nine Weeks 14-15 Time Key Content Key Vocabulary 4.4C represent the product of 2 two-digit numbers using arrays, area models, or equations,
Equivalent Fractions R46. Step 1 Make a model to represent 2 _. Step 2 Divide the rectangle from Step 1 in half.
 Lesson. Equivalent Fractions Write two fractions that are equivalent to _. Step Make a model to represent _. The rectangle is divided into equal parts, with parts shaded. Step Divide the rectangle from
Lesson. Equivalent Fractions Write two fractions that are equivalent to _. Step Make a model to represent _. The rectangle is divided into equal parts, with parts shaded. Step Divide the rectangle from
GAP CLOSING. Grade 9. Facilitator s Guide
 GAP CLOSING Grade 9 Facilitator s Guide Topic 3 Integers Diagnostic...5 Administer the diagnostic...5 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions solutions... 5 Using Intervention Materials...8
GAP CLOSING Grade 9 Facilitator s Guide Topic 3 Integers Diagnostic...5 Administer the diagnostic...5 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions solutions... 5 Using Intervention Materials...8
3.1 Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts. 3.1 Dividing a Set into Fractional Parts. 3.2 Identifying Parts of Wholes.
 . Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts Fraction: represents a part of a whole object or unit Numerator: (top number) represents number of parts of the whole Denominator: (bottom number) represents how
. Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts Fraction: represents a part of a whole object or unit Numerator: (top number) represents number of parts of the whole Denominator: (bottom number) represents how
Topic: Topic 1-Numeration
 Suggested Blocks of Instruction: 10 days /September Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. 3.NBT.1. Use place value understanding to round whole numbers
Suggested Blocks of Instruction: 10 days /September Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. 3.NBT.1. Use place value understanding to round whole numbers
For more information, see the Math Notes box in Lesson of the Core Connections, Course 1 text.
 Number TYPES OF NUMBERS When two or more integers are multiplied together, each number is a factor of the product. Nonnegative integers that have eactly two factors, namely, one and itself, are called
Number TYPES OF NUMBERS When two or more integers are multiplied together, each number is a factor of the product. Nonnegative integers that have eactly two factors, namely, one and itself, are called
Fifth Grade Math Rubric
 Operations and Algebraic Thinking Support Needed Progressing Meets Writes, solves, and interprets numerical expressions guidance with and/or inconsistently writes, solves, and interprets numerical expressions.
Operations and Algebraic Thinking Support Needed Progressing Meets Writes, solves, and interprets numerical expressions guidance with and/or inconsistently writes, solves, and interprets numerical expressions.
Lesson 12: Order and Compare with Benchmarks
 Lesson 12: Order and Compare with Benchmarks Objective By the end of the lesson, students will be able to order and compare fractions with like and unlike denominators, using the definition for equivalent
Lesson 12: Order and Compare with Benchmarks Objective By the end of the lesson, students will be able to order and compare fractions with like and unlike denominators, using the definition for equivalent
TIMSS 2011 Fourth Grade Mathematics Item Descriptions developed during the TIMSS 2011 Benchmarking
 TIMSS 2011 Fourth Grade Mathematics Item Descriptions developed during the TIMSS 2011 Benchmarking Items at Low International Benchmark (400) M01_05 M05_01 M07_04 M08_01 M09_01 M13_01 Solves a word problem
TIMSS 2011 Fourth Grade Mathematics Item Descriptions developed during the TIMSS 2011 Benchmarking Items at Low International Benchmark (400) M01_05 M05_01 M07_04 M08_01 M09_01 M13_01 Solves a word problem
MAFS.5.NF.2.5. Interpret multiplication as rescaling.
 MAFS.5.NF.2.5 Interpret multiplication as rescaling. Understand that multiplying a fraction > 1 and a given number results in a product > either factor. Examples: 2 x 5/4 = 10/4 or 2½; 10/4 > 2 or 2½ >
MAFS.5.NF.2.5 Interpret multiplication as rescaling. Understand that multiplying a fraction > 1 and a given number results in a product > either factor. Examples: 2 x 5/4 = 10/4 or 2½; 10/4 > 2 or 2½ >
Simpson Elementary School Curriculum Prioritization and Mapping 3rd Grade Math
 Timeline Topic Priority Standard Learning Checks Unit 1 August/ September E E 3.NBT.1: Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. 3.NBT.2: Fluently add and subtract
Timeline Topic Priority Standard Learning Checks Unit 1 August/ September E E 3.NBT.1: Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. 3.NBT.2: Fluently add and subtract
Dublin Unified School District Suggested Pacing Guide for Grade 2 Text: Scott Foresman-Addison Wesley envision Math
 Trimester 1 8 Topic 1: Understanding Addition and Subtraction 1 1-1: s: Writing Addition Sentences, 1 1-2: s: Stories About Joining AF 1.0,, 1 1-3: s: Writing Subtraction Sentences, 1 1-4: s: Stories About
Trimester 1 8 Topic 1: Understanding Addition and Subtraction 1 1-1: s: Writing Addition Sentences, 1 1-2: s: Stories About Joining AF 1.0,, 1 1-3: s: Writing Subtraction Sentences, 1 1-4: s: Stories About
Mathematics. Name: Class: Transforming Life chances
 Mathematics Name: Class: Transforming Life chances Children first- Aspire- Challenge- Achieve Aspire: To be the best I can be in everything that I try to do. To use the adults and resources available both
Mathematics Name: Class: Transforming Life chances Children first- Aspire- Challenge- Achieve Aspire: To be the best I can be in everything that I try to do. To use the adults and resources available both
Module 1 - Applications: Visually Modeling Fractions
 Applications: Visually Modeling Fractions Inquire: How to Model Fraction Operations Overview When learning, it can be said that we forget more when we focus on memorizing steps over making sense of our
Applications: Visually Modeling Fractions Inquire: How to Model Fraction Operations Overview When learning, it can be said that we forget more when we focus on memorizing steps over making sense of our
Mississippi College and Career Readiness Standards for Mathematics Scaffolding Document. Grade 5
 Mississippi College and Career Readiness Standards for Mathematics Scaffolding Document Grade 5 Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Write and interpret numerical expressions 5.OA.1 Use parentheses,
Mississippi College and Career Readiness Standards for Mathematics Scaffolding Document Grade 5 Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Write and interpret numerical expressions 5.OA.1 Use parentheses,
What s Half of a Half of a Half?
 Overview Activity ID: 8606 Math Concepts Materials Students will use a physical model to determine what happens fractions TI-0XS when they repeatedly halve a piece of paper, and then they decimals MultiView
Overview Activity ID: 8606 Math Concepts Materials Students will use a physical model to determine what happens fractions TI-0XS when they repeatedly halve a piece of paper, and then they decimals MultiView
Rational Number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 10.
 PA Ch 5 Rational Expressions Rational Number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 0. Since decimals are special
PA Ch 5 Rational Expressions Rational Number is a number that can be written as a quotient of two integers. DECIMALS are special fractions whose denominators are powers of 0. Since decimals are special
NF5-21 Multiplying Unit Fractions Pages 13 14
 NF- Multiplying Unit Fractions Pages STANDARDS.NF.B. Goals Students will develop and apply the formula for multiplying unit fractions by unit fractions. Vocabulary denominator numerator of (to mean multiply
NF- Multiplying Unit Fractions Pages STANDARDS.NF.B. Goals Students will develop and apply the formula for multiplying unit fractions by unit fractions. Vocabulary denominator numerator of (to mean multiply
(Type your answer in radians. Round to the nearest hundredth as needed.)
 1. Find the exact value of the following expression within the interval (Simplify your answer. Type an exact answer, using as needed. Use integers or fractions for any numbers in the expression. Type N
1. Find the exact value of the following expression within the interval (Simplify your answer. Type an exact answer, using as needed. Use integers or fractions for any numbers in the expression. Type N
Grade 4. Number Strand. Achievement Indicators. 1. Represent and describe whole numbers to , pictorially and symbolically.
 Number Strand Outcomes 1. Represent and describe whole numbers to 10 000, pictorially and symbolically. Grade 4 Achievement Indicators Read a four-digit numeral without using the word and (e.g., 5321 is
Number Strand Outcomes 1. Represent and describe whole numbers to 10 000, pictorially and symbolically. Grade 4 Achievement Indicators Read a four-digit numeral without using the word and (e.g., 5321 is
4th grade Math (3rd grade CAP)
 Davison Community Schools ADVISORY CURRICULUM COUNCIL Phase II, April 20, 2015 Julie Crockett, Matt Lobban 4th grade Math (3rd grade CAP) Course Essential Questions (from Phase I report): How do we multiply/divide
Davison Community Schools ADVISORY CURRICULUM COUNCIL Phase II, April 20, 2015 Julie Crockett, Matt Lobban 4th grade Math (3rd grade CAP) Course Essential Questions (from Phase I report): How do we multiply/divide
Year 5 PROMPT sheet. Negative numbers 4 7 = -3. l l l l l l l l l Place value in numbers to 1million = 4
 Year PROMPT sheet Place value in numbers to million The position of the digit gives its size Millions Hundred thousands Ten thousands thousands hundreds tens units 7 Negative numbers A number line is very
Year PROMPT sheet Place value in numbers to million The position of the digit gives its size Millions Hundred thousands Ten thousands thousands hundreds tens units 7 Negative numbers A number line is very
First Trimester Second Trimester Third Trimester
 STANDARD 1 Number Sense: Develop number sense and use numbers and number relationships in problem-solving situations and communicate the reasoning used in solving these problems. (Aligned to Everyday Mathematics
STANDARD 1 Number Sense: Develop number sense and use numbers and number relationships in problem-solving situations and communicate the reasoning used in solving these problems. (Aligned to Everyday Mathematics
Unit 1: Numeration I Can Statements
 Unit 1: Numeration I can write a number using proper spacing without commas. e.g., 934 567. I can write a number to 1 000 000 in words. I can show my understanding of place value in a given number. I can
Unit 1: Numeration I can write a number using proper spacing without commas. e.g., 934 567. I can write a number to 1 000 000 in words. I can show my understanding of place value in a given number. I can
Answers Investigation 1
 Answers Investigation Applications. ; Possible explanation: 9 9 more than. is, so 0 9 is. ; Possible explanation: Since 8 6 =, 9 6 is close to.. ; Possible explanation: 6 is only 6 less than whole. 4.
Answers Investigation Applications. ; Possible explanation: 9 9 more than. is, so 0 9 is. ; Possible explanation: Since 8 6 =, 9 6 is close to.. ; Possible explanation: 6 is only 6 less than whole. 4.
Exploration: Multiplying Fractions & Decimals Using an Area Model
 Exploration: Multiplying Fractions & Decimals Using an Area Model REPRESENT MULTIPLICATION SITUATIONS INVOLVING FRACTIONS & DECIMALS WITH MODELS INCLUDING PICTURES IDENTIFY FACTORS OF POSITIVE INTEGERS
Exploration: Multiplying Fractions & Decimals Using an Area Model REPRESENT MULTIPLICATION SITUATIONS INVOLVING FRACTIONS & DECIMALS WITH MODELS INCLUDING PICTURES IDENTIFY FACTORS OF POSITIVE INTEGERS
Two Plus You. Unit. National PASS Center 2013
 Two Plus You Unit National PASS Center 0 National PASS Center Geneseo Migrant Center Mt. Morris-Leicester Road Leicester, NY 44 () 6-7960 () 6-7969 (fax) www.migrant.net/pass Authors: Editor: Proofer:
Two Plus You Unit National PASS Center 0 National PASS Center Geneseo Migrant Center Mt. Morris-Leicester Road Leicester, NY 44 () 6-7960 () 6-7969 (fax) www.migrant.net/pass Authors: Editor: Proofer:
Accuplacer Arithmetic Study Guide
 Accuplacer Arithmetic Study Guide I. Terms Numerator: which tells how many parts you have (the number on top) Denominator: which tells how many parts in the whole (the number on the bottom) Example: parts
Accuplacer Arithmetic Study Guide I. Terms Numerator: which tells how many parts you have (the number on top) Denominator: which tells how many parts in the whole (the number on the bottom) Example: parts
Concept Fourth Grade: Second Nine Weeks *Revised 5/21/15 Readiness Standards Time Key Content Key Vocabulary
 Multiplication by 2-Digit Numbers Concept Fourth Grade: Second Nine Weeks 2015-2016 *Revised 5/21/15 Readiness Standards Time Key Content Key Vocabulary Supporting Standards 4.4C represent the product
Multiplication by 2-Digit Numbers Concept Fourth Grade: Second Nine Weeks 2015-2016 *Revised 5/21/15 Readiness Standards Time Key Content Key Vocabulary Supporting Standards 4.4C represent the product
Rational Numbers CHAPTER Introduction
 RATIONAL NUMBERS Rational Numbers CHAPTER. Introduction In Mathematics, we frequently come across simple equations to be solved. For example, the equation x + () is solved when x, because this value of
RATIONAL NUMBERS Rational Numbers CHAPTER. Introduction In Mathematics, we frequently come across simple equations to be solved. For example, the equation x + () is solved when x, because this value of
3. Mr. White does not wear white, so he is wearing the blue shirt. 4. Then Mr. Red wears a white shirt.
 5A METHOD 1: Strategy: Use reasoning. 1. Mr. Red and Mr. White are older than the man in gray. Neither Mr. Red nor Mr. White wears gray. Mr. Gray does not wear gray. So Mr. Blue wears the gray shirt. 2.
5A METHOD 1: Strategy: Use reasoning. 1. Mr. Red and Mr. White are older than the man in gray. Neither Mr. Red nor Mr. White wears gray. Mr. Gray does not wear gray. So Mr. Blue wears the gray shirt. 2.
Maths Key Objectives Check list Year 1
 Maths Key Objectives Check list Year 1 Count to and across 100 from any number. Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals. Read and write mathematical symbols +, - and =. Identify one more and one
Maths Key Objectives Check list Year 1 Count to and across 100 from any number. Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals. Read and write mathematical symbols +, - and =. Identify one more and one
For Exercises 1 5, the whole is one hundredths grid. Write fraction and decimal names for the shaded part.
 Applications For Exercises, the whole is one hundredths grid. Write fraction and decimal names for the shaded part...... 6. Name three fractions whose decimal equivalent is 0.. Explain how you know each
Applications For Exercises, the whole is one hundredths grid. Write fraction and decimal names for the shaded part...... 6. Name three fractions whose decimal equivalent is 0.. Explain how you know each
Fractions and Decimals
 FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS 9 Fractions and Decimals Chapter. INTRODUCTION You have learnt fractions and decimals in earlier classes. The study of fractions included proper, improper and mixed fractions as
FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS 9 Fractions and Decimals Chapter. INTRODUCTION You have learnt fractions and decimals in earlier classes. The study of fractions included proper, improper and mixed fractions as
Using Equivalent Fractions to Solve Problems
 Using Equivalent Fractions to Solve Problems Home Link -1 1 Fill in the equivalent fractions in the table below. Multi ply Both the Numerator and Denominator by: Fraction 6 1 _ 6_ 6_ 9 1 16 10_ 1 6_ 1
Using Equivalent Fractions to Solve Problems Home Link -1 1 Fill in the equivalent fractions in the table below. Multi ply Both the Numerator and Denominator by: Fraction 6 1 _ 6_ 6_ 9 1 16 10_ 1 6_ 1
Big Mathematical Ideas and Understandings
 Big Mathematical Ideas and Understandings A Big Idea is a statement of an idea that is central to the learning of mathematics, one that links numerous mathematical understandings into a coherent whole.
Big Mathematical Ideas and Understandings A Big Idea is a statement of an idea that is central to the learning of mathematics, one that links numerous mathematical understandings into a coherent whole.
5. NSBT.1 I can understand and explain the value of digits in a number.
 5. NSBT.1 I can understand and explain the value of digits in a number. 5. NSBT.1 I can relate the place value system to the base ten system and realize that a digit in one place represents 10 times what
5. NSBT.1 I can understand and explain the value of digits in a number. 5. NSBT.1 I can relate the place value system to the base ten system and realize that a digit in one place represents 10 times what
Question. What is a fraction? Answer: A topic that scares many of our students
 Question What is a fraction? Answer: A topic that scares many of our students More seriously: Please write down your definition of a fraction. Then briefly discuss with a neighbor. FRACTIONS are numbers
Question What is a fraction? Answer: A topic that scares many of our students More seriously: Please write down your definition of a fraction. Then briefly discuss with a neighbor. FRACTIONS are numbers
Learning Log Title: CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS. Date: Lesson: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers
 Chapter 3: Portions and Integers CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
Chapter 3: Portions and Integers CHAPTER 3: PORTIONS AND INTEGERS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 3: Portions and Integers Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title:
Name Period Date. UNIT 3: EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS WEEK 12: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT : EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS WEEK 2: Student Packet 2. Inputs and Outputs Use tables, graphs, equations, and words to solve problems. Informally introduce the slope-intercept form
Name Period Date UNIT : EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS WEEK 2: Student Packet 2. Inputs and Outputs Use tables, graphs, equations, and words to solve problems. Informally introduce the slope-intercept form
Working with Fractions on the TI-73 Graphing Calculator
 Working with Fractions on the TI-7 Graphing Calculator The TI-7 graphing calculator has as a major feature the ability to handle working with fractions without the need to translate them into decimals.
Working with Fractions on the TI-7 Graphing Calculator The TI-7 graphing calculator has as a major feature the ability to handle working with fractions without the need to translate them into decimals.
Section Graphs and Lines
 Section 1.1 - Graphs and Lines The first chapter of this text is a review of College Algebra skills that you will need as you move through the course. This is a review, so you should have some familiarity
Section 1.1 - Graphs and Lines The first chapter of this text is a review of College Algebra skills that you will need as you move through the course. This is a review, so you should have some familiarity
Ce qui est important dans l'enseignement des mathématiques. Marian Small novembre 2017
 Ce qui est important dans l'enseignement des mathématiques Marian Small novembre 2017 Playing with math Uae your linking cubes. Show that the mean of 4, 7 and 7 is 6. Playing with math Uae your linking
Ce qui est important dans l'enseignement des mathématiques Marian Small novembre 2017 Playing with math Uae your linking cubes. Show that the mean of 4, 7 and 7 is 6. Playing with math Uae your linking
Answer Key Lesson 5: Area Problems
 Answer Key Lesson 5: Problems Student Guide Problems (SG pp. 186 187) Questions 1 3 1. Shapes will vary. Sample shape with an area of 12 sq cm: Problems Here are 12 square centimeters. A square centimeter
Answer Key Lesson 5: Problems Student Guide Problems (SG pp. 186 187) Questions 1 3 1. Shapes will vary. Sample shape with an area of 12 sq cm: Problems Here are 12 square centimeters. A square centimeter
FRACTIONS, DECIMALS, & PERCENTS
 FRACTIONS, DECIMALS, & PERCENTS ggre Math Preparation Guide This book provides an in-depth look at the array of GRE questions that test knowledge of Fractions, Decimals, and Percents. Learn to see the
FRACTIONS, DECIMALS, & PERCENTS ggre Math Preparation Guide This book provides an in-depth look at the array of GRE questions that test knowledge of Fractions, Decimals, and Percents. Learn to see the
Math 6 Pre-assessment
 Name: lass: ate: I: Math 6 Pre-assessment Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the four-step plan to solve each problem.. omplete the pattern:,,
Name: lass: ate: I: Math 6 Pre-assessment Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the four-step plan to solve each problem.. omplete the pattern:,,
Stage 5 PROMPT sheet. 5/3 Negative numbers 4 7 = -3. l l l l l l l l l /1 Place value in numbers to 1million = 4
 Stage PROMPT sheet / Place value in numbers to million The position of the digit gives its size / Negative numbers A number line is very useful for negative numbers. The number line below shows: 7 - l
Stage PROMPT sheet / Place value in numbers to million The position of the digit gives its size / Negative numbers A number line is very useful for negative numbers. The number line below shows: 7 - l
Answer Key. Name. Here is a birthday cake cut into pieces. How many pieces do you see? ANSWER: 24 pieces
 Here is a birthday cake cut into pieces. How many pieces do you see? ANSWER: pieces COMMENTS & EXTENSIONS: Trace your hand on graph paper. How many of the graph paper squares does your hand cover? Which
Here is a birthday cake cut into pieces. How many pieces do you see? ANSWER: pieces COMMENTS & EXTENSIONS: Trace your hand on graph paper. How many of the graph paper squares does your hand cover? Which
Year 4 term 3&4 Points in italics are either where statements have been moved from other year groups or to support progression where no statement is
 Oral and Mental calculation Read and write numbers with one decimal place up to 10,000. Count on and back in 1s, 10 s or 100 s from any number up to 10,000. Count forwards and backwards in equal steps
Oral and Mental calculation Read and write numbers with one decimal place up to 10,000. Count on and back in 1s, 10 s or 100 s from any number up to 10,000. Count forwards and backwards in equal steps
4.3 Rational Thinking
 RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS & FUNCTIONS -4.3 4.3 Rational Thinking A Solidify Understanding Task The broad category of functions that contains the function!(#) = & ' is called rational functions. A rational number
RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS & FUNCTIONS -4.3 4.3 Rational Thinking A Solidify Understanding Task The broad category of functions that contains the function!(#) = & ' is called rational functions. A rational number
Stage 5 PROMPT sheet. 5/3 Negative numbers 4 7 = -3. l l l l l l l l l /1 Place value in numbers to 1million = 4
 Millions Hundred thousands Ten thousands Thousands Hundreds Tens Ones Stage PROMPT sheet / Place value in numbers to million The position of the digit gives its size / Negative numbers A number line is
Millions Hundred thousands Ten thousands Thousands Hundreds Tens Ones Stage PROMPT sheet / Place value in numbers to million The position of the digit gives its size / Negative numbers A number line is
Everyday Math and the Indiana Academic Standards for Grade 4 Mathematics
 Unit One 1.2-1.3 Identify, describe, and draw rays, right angles, acute angles, 4.4.1 Geometry Right Time Geometry obtuse angles and straight angles using appropriate mathematical tools and technology.
Unit One 1.2-1.3 Identify, describe, and draw rays, right angles, acute angles, 4.4.1 Geometry Right Time Geometry obtuse angles and straight angles using appropriate mathematical tools and technology.
Days (5) Essential Knowledge and Skills Suggested Instructional Activities Add. Info. Blooms: Essential Questions and Understandings
 First Six Weeks Curriculum Guide Subject: Math 6 Virginia SOL 6.3 The student will a. identify and represent integers; b. order and compare integers; and c. identify and describe absolute value of integers.
First Six Weeks Curriculum Guide Subject: Math 6 Virginia SOL 6.3 The student will a. identify and represent integers; b. order and compare integers; and c. identify and describe absolute value of integers.
To be able to count up and down in tenths
 Progression Grid: Year Year 2 Year 3 Year Year Year 6 Counting in Fractional steps To be able to count in fractions up to 0, starting from any number and using the/2 and 2/ equivalence on the number line
Progression Grid: Year Year 2 Year 3 Year Year Year 6 Counting in Fractional steps To be able to count in fractions up to 0, starting from any number and using the/2 and 2/ equivalence on the number line
ADDING FRACTIONS Teacher Notes
 ADDING FRACTIONS Teacher Notes References Foundation Foundation Plus Higher Higher Plus Introduction N3.1 Fractions N6.1 Adding and subtracting fractions N2.1 Adding and subtracting fractions N1.5 Fraction
ADDING FRACTIONS Teacher Notes References Foundation Foundation Plus Higher Higher Plus Introduction N3.1 Fractions N6.1 Adding and subtracting fractions N2.1 Adding and subtracting fractions N1.5 Fraction
Formative Benchmark 1
 Key Section 1: Lessons 1-10 2-Digit Numbers & Place Value, Elapsed Time, Data Collection & Display, Odd & Even Numbers between 0 and August to Formative Benchmark 1 November 13-20, 2013 Section 2: Lessons
Key Section 1: Lessons 1-10 2-Digit Numbers & Place Value, Elapsed Time, Data Collection & Display, Odd & Even Numbers between 0 and August to Formative Benchmark 1 November 13-20, 2013 Section 2: Lessons
CONTENTS. Functional Maths and Numeracy study guide Name 1) THE FOUR RULES OF ARITHMETIC 6) ROUNDING 2) MEASURES, SHAPE AND SPACE 8) NEGATIVE NUMBERS
 Name CONTENTS 1) THE FOUR RULES OF ARITHMETIC Addition (page 2) Addition of decimals (page 4) Subtraction (page 5) Subtraction of decimals (page 8) Subtraction other methods (page 9) Multiplication (page
Name CONTENTS 1) THE FOUR RULES OF ARITHMETIC Addition (page 2) Addition of decimals (page 4) Subtraction (page 5) Subtraction of decimals (page 8) Subtraction other methods (page 9) Multiplication (page
GEOMETRY. slide #3. 6th Grade Math Unit 7. 6th Grade Unit 7: GEOMETRY. Name: Table of Contents. Area of Rectangles
 Name: 6th Grade Math Unit 7 GEOMETRY 2012 10 17 www.njctl.org 1 Table of Contents Area of Rectangles Area of Parallelograms Area of Triangles Area of Trapezoids Mixed Review Area of Irregular Figures Area
Name: 6th Grade Math Unit 7 GEOMETRY 2012 10 17 www.njctl.org 1 Table of Contents Area of Rectangles Area of Parallelograms Area of Triangles Area of Trapezoids Mixed Review Area of Irregular Figures Area
DIRECTIONS + ANSWER KEY
 * Full credit will be provided to students answers that are not reduced to lowest terms in order to assess the standard. Measurement and Data 2: Make a line plot to display a data set of measurements in
* Full credit will be provided to students answers that are not reduced to lowest terms in order to assess the standard. Measurement and Data 2: Make a line plot to display a data set of measurements in
Section 2.3 Rational Numbers. A rational number is a number that may be written in the form a b. for any integer a and any nonzero integer b.
 Section 2.3 Rational Numbers A rational number is a number that may be written in the form a b for any integer a and any nonzero integer b. Why is division by zero undefined? For example, we know that
Section 2.3 Rational Numbers A rational number is a number that may be written in the form a b for any integer a and any nonzero integer b. Why is division by zero undefined? For example, we know that
Fraction Skills. I can understand that fractions have to have parts or pieces of equal sizes.
 Fraction Skills I can understand and define fractions. I can name fraction models. I can draw fraction models. I can understand that fractions have to have parts or pieces of equal sizes. I can plot and
Fraction Skills I can understand and define fractions. I can name fraction models. I can draw fraction models. I can understand that fractions have to have parts or pieces of equal sizes. I can plot and
Chapter 6 Rational Numbers and Proportional Reasoning
 Chapter 6 Rational Numbers and Proportional Reasoning Students should build their understanding of fractions as parts of a whole and as division. They will need to see and explore a variety of models of
Chapter 6 Rational Numbers and Proportional Reasoning Students should build their understanding of fractions as parts of a whole and as division. They will need to see and explore a variety of models of
Equations and Problem Solving with Fractions. Variable. Expression. Equation. A variable is a letter used to represent a number.
 MAT 040: Basic Math Equations and Problem Solving with Fractions Variable A variable is a letter used to represent a number. Expression An algebraic expression is a combination of variables and/or numbers
MAT 040: Basic Math Equations and Problem Solving with Fractions Variable A variable is a letter used to represent a number. Expression An algebraic expression is a combination of variables and/or numbers
PROGRESSION IS HIGHLIGHTED IN THE FOLLOWING DOCUMENT VIA BOLDED TEXT. MATHEMATICAL PROCESSES
 Alberta's Program of Studies (Curriculum) - Mathematics - Number (Strand with Achievement Outcomes) Note: These strands are not intended to be discrete units of instruction. The integration of outcomes
Alberta's Program of Studies (Curriculum) - Mathematics - Number (Strand with Achievement Outcomes) Note: These strands are not intended to be discrete units of instruction. The integration of outcomes
Supporting our children to aim high!
 Reach for the Sky Supporting our children to aim high! St Mary s CE School Maths Support Resources Parents often ask us, how can I help my child in maths? Firstly, we provide parents with the expectations
Reach for the Sky Supporting our children to aim high! St Mary s CE School Maths Support Resources Parents often ask us, how can I help my child in maths? Firstly, we provide parents with the expectations
Released December Year. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 2 - Fractions
 Released December 07 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block - Fractions Year 5 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Equivalent fractions Improper fractions to mixed numbers Mixed
Released December 07 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block - Fractions Year 5 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Equivalent fractions Improper fractions to mixed numbers Mixed
2.1 Transforming Linear Functions
 2.1 Transforming Linear Functions Before we begin looking at transforming linear functions, let s take a moment to review how to graph linear equations using slope intercept form. This will help us because
2.1 Transforming Linear Functions Before we begin looking at transforming linear functions, let s take a moment to review how to graph linear equations using slope intercept form. This will help us because
Name Student ID Number. Group Name. Group Members. Fractions
 Name Student ID Number Group Name Group Members Fractions Many people struggle with and even fear working with fractions. Part of the reason people struggle is because they do not know what a fraction
Name Student ID Number Group Name Group Members Fractions Many people struggle with and even fear working with fractions. Part of the reason people struggle is because they do not know what a fraction
Know how to use fractions to describe part of something Write an improper fraction as a mixed number Write a mixed number as an improper fraction
 . Fractions Know how to use fractions to describe part of something Write an improper fraction as a mixed number Write a mixed number as an improper fraction Key words fraction denominator numerator proper
. Fractions Know how to use fractions to describe part of something Write an improper fraction as a mixed number Write a mixed number as an improper fraction Key words fraction denominator numerator proper
Rational number operations can often be simplified by converting mixed numbers to improper fractions Add EXAMPLE:
 Rational number operations can often be simplified by converting mixed numbers to improper fractions Add ( 2) EXAMPLE: 2 Multiply 1 Negative fractions can be written with the negative number in the numerator
Rational number operations can often be simplified by converting mixed numbers to improper fractions Add ( 2) EXAMPLE: 2 Multiply 1 Negative fractions can be written with the negative number in the numerator
Equivalent fractions are
 MATHEMATICS 8 CHAPTER FRACTION OPERATIONS REVIEW: EQUIVALENT FRACTIONS AND IMPROPER FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS Date The numerator is The denominator is A proper fraction is An improper fraction is A mixed
MATHEMATICS 8 CHAPTER FRACTION OPERATIONS REVIEW: EQUIVALENT FRACTIONS AND IMPROPER FRACTIONS AND MIXED NUMBERS Date The numerator is The denominator is A proper fraction is An improper fraction is A mixed
Revision on fractions and decimals
 Revision on fractions and decimals Fractions 1. Addition and subtraction of fractions (i) For same denominator, only need to add the numerators, then simplify the fraction Example 1: " + $ " = &$ " (they
Revision on fractions and decimals Fractions 1. Addition and subtraction of fractions (i) For same denominator, only need to add the numerators, then simplify the fraction Example 1: " + $ " = &$ " (they
