So lets start! 8/26/16. Did you register your clicker? Key concept: The COMPUTER does the recipe! Make it as hard, tedious, complex as you want!
|
|
|
- Barrie Summers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Did you register your clicker? Theresa CSE 111 Bio: Program Design I Lecture 2: What is Computer Science Intro to Bio Tanya Berger- Wolf (CS) & Boris Igić (Bio) University of Illinois, Chicago August 25, 2016 Labs: Monday 2249F SEL 1-1:50 (40305), 2-2:50 (40306) Find your lab! TA: Vahid Noroozi Mon 3-5pm 4030 SEL 2 So lets start! Key concept: The COMPUTER does the recipe! Make it as hard, tedious, complex as you want! Crank through a million genomes? No problem! Look through 100,000 documents in a lawsuit to pick out the 17 or the 42,000 containing a par_cular phrase? Easy- peasy! (What the cs111 law course will do) Find one person in a 30,000 student campus? Yawn! Process a million dots on the screen or a bazillion sound samples? (What the media computa_on course will do) 3 1
2 What computers understand It s not text, numbers, mul_media at all. It s unimedia (Nicholas Negroponte) Everything is 0 s and 1 s Computers are exceedingly stupid The only data they understand is 0 s and 1 s They can only do the most simple things with those 0 s and 1 s Move this value here Add, mul_ply, subtract, divide these values Compare these values, and if one is less than the other, go follow this step rather than that one. Key Concept: Encodings But we can interpret these numbers any way we want. We can encode informa_on in those numbers Even the no_on that the computer understands numbers is an interpreta_on We encode the voltages on wires as 0 s and 1 s Which we can, in turn, interpret as a decimal number Tiny detour: Useful terminology The 8 bit byte is the basic unit of memory today. In some sense, a really _ny unit. You more oden see: 1 kilobyte = 1 KB = 1K = 2 10 = 1,024 bytes 1 megabyte = 1 MB = 1M = 2 20 = 1,048,576 bytes 1 gigabyte = 1 GB = 1G = 2 30 = 1,073,741,824 bytes What is a computer? A device that executes a stored program (sequence of instruc_ons). A program is a par_cular wri_ng of a recipe in some par_cular language. (Recipe is likely to be in English or French or Arabic or Hindi; program in a programming language such as C, Java, Visual Basic, or Python) 2
3 All computers consist of 3 components Memory stores program and data (informa_on) Primary: RAM Secondary: hard drive Central Processing Unit (CPU) Control fetch next instruc_on, decode it, execute it ArithmeOc Logic Unit perform simple opera_ons on data (add, compare two for equality, etc.) Input/Output Detour: Specs for a computer Ads for computers typically give: Speed of the CPU (in GHz, say ; recent past in MHz, where 1,000 MHz = 1.0 GHz) Amount of RAM in MB Size of hard drive in GB Which fancy I/O devices (e.g., DVD burner?) Interes_ngly, perceived speed today oden depends mainly on amount of RAM. Moore s Law Heading to Python Programs? Gordon Moore, one of the founders of Intel, made the claim that (essen_ally) computer power doubles for the same dollar every 18 months. This has held true for over 30 years. (Note: some think the end is finally near.) Go ahead! Make your computer do the same thing to all 2.9 billion base pairs of your DNA! It doesn t care! And it won t take much _me either! 2 eggs 1 c milk 1 c sided flour ½ t vanilla extract 12 oz. farmer's cheese 4 oz. cream cheese, sodened ⅓ c sugar 1 t lemon juice 1 t vanilla extract 1 egg yolk Bauer: Combine eggs, milk, salt and vanilla and blend well. Gradually add flour. Beat well. Filling: Combine cheeses, sugar, juice, vanilla and egg yolk in a bowl and mix together un_l smooth. Repeat un_l all the bauer is used: Put a ladleful of bauer into heated greased skillet. Tilt pan to swirl the bauer so it covers the bouom of the skillet. Fry on one side un_l bubbles form, the top is set, and bouom is golden brown. Carefully loosen edges of the crepe and slip it out of the skillet onto a plate. Fill each fried crepe: Place 1 tablespoon of filling on one edge. Roll once to cover filling. Fold sides into the center and con_nue rolling un_l completely closed. Ader all are assembled, heat 2 tablespoons of buuer in the skillet and place each crepe, seam side down, in the skillet and fry 2 minutes on each side, turning once. 3
4 8/26/16 Features of recipe How do you put a giraffe into a fridge? Fixed vocab of words, abbrevia_ons, symbols Syntax: Rules about what can be said & where Sequence of opera_ons to be done in order Some_mes, a repe on of a part Assumed knowledge about context An expected result (yum!) 25 Why use computers for biology? Biology perspecove More and more biological informa_on is available => need for effec_vely accessing and using the informa_on As more detailed informa_on is available different ques_ons can be asked (models of evolu_on) => requires new math Computer science perspecove Excellent applica_on domain Poses special computa_onal challenges Brings computer science closer to scien_fic discovery Currently growing (computa_onal biology, bioinforma_cs, computa_onal ecology, medicine 4
5 VARIABLES STRINGS Theresa Randall Munroe, XKCD xkcd.com/1513/ Introduc_ons: Python Richer syntax allows greater expressiveness! def alifesim(numgens,popsize,numtoselect,network,inhibitorl): """Do an ar_ficial life simula_on for numgens genera_ons with popsize organisms."" fitd={} # get ini_al pop and create popl of (fitness,org) tuples popl=[] for org in createini_alpop(popsize,network,inhibitorl): fitness = org.getfitness() popl.append((fitness,org)) fitd[hash(org)]=fitness topl = gettoporgs(popl, numtoselect) # get top orgs for i in range(numgens): popl=[] for j in range(popsize): toreplicate=random.choice(topl) neworg = toreplicate[1].replicate() # get fitness if hash(neworg) in fitd: fitness=fitd[hash(neworg)] else: fitness=neworg.getfitness() fitd[hash(neworg)]=fitness popl.append((fitness,neworg)) topl = gettoporgs(popl, numtoselect) print "gen:",i,":",topl[0] if i%50==0: fitd.clear() return topl[0] Learning to program is a bit like learning a foreign language! 31 5
6 8/26/16 Ader all, there are thousands of languages to choose from! Why? Hello World Rela_vely nice syntax Emerging as language of choice in many fields Packages for graphics, audio, scien_fic compu_ng, Python: print Hello World! Java: class HelloWorld { sta_c public void main( String args[] ) { System.out.println( "Hello World!" ); } } C++: #include <iostream.h> main() { cout << "Hello World!" << endl; return 0; } Ook: Befunge: Image: University of Florida Python Demo 34 6
7 Genome Sizes Carsonella ruddii, 160,000 base pairs (bp) porcine (pig) circovirus 1.7Kbp, ssdna cowpea mosaic virus, 9.4Kbp, ssrna phi29 (Bacillus phage) 19Kbp, dsdna humans? Genome Sizes Carsonella ruddii, 160,000 base pairs (bp) porcine (pig) circovirus 1.7Kbp, ssdna cowpea mosaic virus, 9.4Kbp, ssrna phi29 (Bacillus phage) 19Kbp, dsdna humans? Largest genome: (A) Human, (B) Fish, (C) Amoeba, (D) Flowering plant, (E) Don t know Genome Sizes Carsonella ruddii, 160,000 base pairs (bp) porcine (pig) circovirus 1.7Kbp, ssdna cowpea mosaic virus, 9.4Kbp, ssrna phi29 (Bacillus phage) 19Kbp, dsdna Paris japonica, 150Gbp Protopterus aethiopicus, 130Gbp Amoeba dubia, 670Gbp Come to the lab: Install Python+VC Learn to use it For next class Write first programs (first assignment yippee!) Read the textbook: Post something on PIazza 39 7
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer Science and Media Computation
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer Science and Media Computation Story What is computer science about? What computers really understand, and where Programming Languages fit in Media Computation: Why digitize
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer Science and Media Computation Story What is computer science about? What computers really understand, and where Programming Languages fit in Media Computation: Why digitize
CS 1124 Media Computation. Steve Harrison Lecture 1.2 (August 27, 2008)
 CS 1124 Media Computation Steve Harrison Lecture 1.2 (August 27, 2008) Today Computer science Look at Jython Look at some cool image things Pixels Why study CS? What is computer science about? What do
CS 1124 Media Computation Steve Harrison Lecture 1.2 (August 27, 2008) Today Computer science Look at Jython Look at some cool image things Pixels Why study CS? What is computer science about? What do
CSE 201 Java Programming I. Smart Coding School website:
 CSE 201 Java Programming I Smart Coding School website: http://www.smartcodingschool.com Definition: A named group of statements public static void methodname() { statements Usage: 1. denotes the structure
CSE 201 Java Programming I Smart Coding School website: http://www.smartcodingschool.com Definition: A named group of statements public static void methodname() { statements Usage: 1. denotes the structure
Admin CS41B MACHINE. Midterm topics. Admin 2/11/16. Midterm next Thursday in-class (2/18) SML. recursion. math. David Kauchak CS 52 Spring 2016
 Admin! Assignment 3! due Monday at :59pm! Academic honesty CS4B MACHINE David Kauchak CS 5 Spring 6 Admin Midterm next Thursday in-class (/8)! Comprehensive! Closed books, notes, computers, etc.! Except,
Admin! Assignment 3! due Monday at :59pm! Academic honesty CS4B MACHINE David Kauchak CS 5 Spring 6 Admin Midterm next Thursday in-class (/8)! Comprehensive! Closed books, notes, computers, etc.! Except,
Admin. ! Assignment 3. ! due Monday at 11:59pm! one small error in 5b (fast division) that s been fixed. ! Midterm next Thursday in-class (10/1)
 Admin CS4B MACHINE David Kauchak CS 5 Fall 5! Assignment 3! due Monday at :59pm! one small error in 5b (fast division) that s been fixed! Midterm next Thursday in-class (/)! Comprehensive! Closed books,
Admin CS4B MACHINE David Kauchak CS 5 Fall 5! Assignment 3! due Monday at :59pm! one small error in 5b (fast division) that s been fixed! Midterm next Thursday in-class (/)! Comprehensive! Closed books,
CS 177 Recitation. Week 1 Intro to Java
 CS 177 Recitation Week 1 Intro to Java Questions? Computers Computers can do really complex stuff. How? By manipulating data according to lists of instructions. Fundamentally, this is all that a computer
CS 177 Recitation Week 1 Intro to Java Questions? Computers Computers can do really complex stuff. How? By manipulating data according to lists of instructions. Fundamentally, this is all that a computer
The Programming Process Summer 2010 Margaret Reid-Miller
 The Programming Process 15-110 Margaret Reid-Miller Hardware Components Central Processing Unit (CPU) Program control Arithmetic/logical operations Coordinates data movement between memory and registers
The Programming Process 15-110 Margaret Reid-Miller Hardware Components Central Processing Unit (CPU) Program control Arithmetic/logical operations Coordinates data movement between memory and registers
CSE 111 Bio: Program Design I Lecture 3: Python Basics & More Bio
 Theresa McCracken @McHumor.com CSE 111 Bio: Program Design I Lecture 3: Python Basics & More Bio Robert Sloan (CS) & Rachel Poretsky (Bio) University of Illinois, Chicago August 31, 2017 DNA sequencing
Theresa McCracken @McHumor.com CSE 111 Bio: Program Design I Lecture 3: Python Basics & More Bio Robert Sloan (CS) & Rachel Poretsky (Bio) University of Illinois, Chicago August 31, 2017 DNA sequencing
Discussion. Why do we use Base 10?
 MEASURING DATA Data (the plural of datum) are anything in a form suitable for use with a computer. Whatever a computer receives as an input is data. Data are raw facts without any clear meaning. Computers
MEASURING DATA Data (the plural of datum) are anything in a form suitable for use with a computer. Whatever a computer receives as an input is data. Data are raw facts without any clear meaning. Computers
CMSC 104 -Lecture 2 John Y. Park, adapted by C Grasso
 CMSC 104 -Lecture 2 John Y. Park, adapted by C Grasso 1 Topics Major Computer Components Bits, Bytes, and Words The Decimal Number System The Binary Number System Converting from Binary to Decimal Converting
CMSC 104 -Lecture 2 John Y. Park, adapted by C Grasso 1 Topics Major Computer Components Bits, Bytes, and Words The Decimal Number System The Binary Number System Converting from Binary to Decimal Converting
Worksheet - Storing Data
 Unit 1 Lesson 12 Name(s) Period Date Worksheet - Storing Data At the smallest scale in the computer, information is stored as bits and bytes. In this section, we'll look at how that works. Bit Bit, like
Unit 1 Lesson 12 Name(s) Period Date Worksheet - Storing Data At the smallest scale in the computer, information is stored as bits and bytes. In this section, we'll look at how that works. Bit Bit, like
CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java
 CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java Course Information Introductions Website Syllabus Computers First Java Program Text Editor Helpful Commands Java Download Intro to CSC116 Instructors Course Instructor:
CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java Course Information Introductions Website Syllabus Computers First Java Program Text Editor Helpful Commands Java Download Intro to CSC116 Instructors Course Instructor:
Java Programming. What is a program? Programs Recipes. Programs as Recipes 8/16/12. Pancakes In one bowl. mix: 1½ cup flour
 What is a program? Java Programming CS 160, Fall Semester 2012 TOPICS Computer Programs Using Eclipse Program Program Components Definition: a sequence of instructions telling a computer what to do Analogy:
What is a program? Java Programming CS 160, Fall Semester 2012 TOPICS Computer Programs Using Eclipse Program Program Components Definition: a sequence of instructions telling a computer what to do Analogy:
[301] Bits and Memory. Tyler Caraza-Harter
![[301] Bits and Memory. Tyler Caraza-Harter [301] Bits and Memory. Tyler Caraza-Harter](/thumbs/88/116370212.jpg) [301] Bits and Memory Tyler Caraza-Harter Ones and Zeros 01111111110101011000110010011011000010010001100110101101 01000101110110000000110011101011101111000110101010010011 00011000100110001010111010110001010011101000100110100000
[301] Bits and Memory Tyler Caraza-Harter Ones and Zeros 01111111110101011000110010011011000010010001100110101101 01000101110110000000110011101011101111000110101010010011 00011000100110001010111010110001010011101000100110100000
CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1. What is CS150? Who Are We? CS150 is a programming course You will learn
 CS 150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 Professor: Shereen Khoja shereen@pacificu.edu 1 What is CS150? CS150 is a programming course You will learn o The mechanics of writing programs in C++ o How to
CS 150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 Professor: Shereen Khoja shereen@pacificu.edu 1 What is CS150? CS150 is a programming course You will learn o The mechanics of writing programs in C++ o How to
The diagram below is only partially complete. Use the terms in the word list to complete the empty boxes. Make dinner
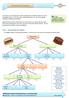 Decomposing Problems As we have seen, decomposition means breaking down a difficult problem into more manageable pieces. A common way to tackle this process is to use a tree diagram showing increasing
Decomposing Problems As we have seen, decomposition means breaking down a difficult problem into more manageable pieces. A common way to tackle this process is to use a tree diagram showing increasing
Elements of Computers and Programming Dr. William C. Bulko. What is a Computer?
 Elements of Computers and Programming Dr. William C. Bulko What is a Computer? 2017 What is a Computer? A typical computer consists of: a CPU memory a hard disk a monitor and one or more communication
Elements of Computers and Programming Dr. William C. Bulko What is a Computer? 2017 What is a Computer? A typical computer consists of: a CPU memory a hard disk a monitor and one or more communication
计算机信息表达. Information Representation 刘志磊天津大学智能与计算学部
 计算机信息表达 刘志磊天津大学智能与计算学部 Bits & Bytes Bytes & Letters More Bytes Bit ( 位 ) the smallest unit of storage Everything in a computer is 0 s and 1 s Bits why? Computer Hardware Chip uses electricity 0/1 states
计算机信息表达 刘志磊天津大学智能与计算学部 Bits & Bytes Bytes & Letters More Bytes Bit ( 位 ) the smallest unit of storage Everything in a computer is 0 s and 1 s Bits why? Computer Hardware Chip uses electricity 0/1 states
CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java
 CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java Intro to CSC116 Course Information Introductions Website Syllabus Computers First Java Program Text Editor Helpful Commands Java Download Course Instructor: Instructors
CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java Intro to CSC116 Course Information Introductions Website Syllabus Computers First Java Program Text Editor Helpful Commands Java Download Course Instructor: Instructors
CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics. COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction
 CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction Announcements Did you miss the first lecture? Come talk to me after class. If you want
CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction Announcements Did you miss the first lecture? Come talk to me after class. If you want
The x86 Microprocessors. Introduction. The 80x86 Microprocessors. 1.1 Assembly Language
 The x86 Microprocessors Introduction 1.1 Assembly Language Numbering and Coding Systems Human beings use the decimal system (base 10) Decimal digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 Computer systems use the
The x86 Microprocessors Introduction 1.1 Assembly Language Numbering and Coding Systems Human beings use the decimal system (base 10) Decimal digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 Computer systems use the
CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java
 CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java Course Information Introductions Website Syllabus Schedule Computing Environment AFS (Andrew File System) Linux/Unix Commands Helpful Tricks Computers First Java
CSC116: Introduction to Computing - Java Course Information Introductions Website Syllabus Schedule Computing Environment AFS (Andrew File System) Linux/Unix Commands Helpful Tricks Computers First Java
Homeschool Enrichment. The System Unit: Processing & Memory
 Homeschool Enrichment The System Unit: Processing & Memory Overview This chapter covers: How computers represent data and programs How the CPU, memory, and other components are arranged inside the system
Homeschool Enrichment The System Unit: Processing & Memory Overview This chapter covers: How computers represent data and programs How the CPU, memory, and other components are arranged inside the system
Introduc)on to Compu)ng (SE- 101)
 Introduc)on to Compu)ng (SE- 101) Ali Ameer Gondal Assistant Professor So?ware Engineering Department University Of Engineering & Technology Taxila, Pakistan ali.ameer@uettaxila.edu.pk Introducing Computer
Introduc)on to Compu)ng (SE- 101) Ali Ameer Gondal Assistant Professor So?ware Engineering Department University Of Engineering & Technology Taxila, Pakistan ali.ameer@uettaxila.edu.pk Introducing Computer
CSC 101: Lab Manual#9 Machine Language and the CPU (largely based on the work of Prof. William Turkett) Lab due date: 5:00pm, day after lab session
 CSC 101: Lab Manual#9 Machine Language and the CPU (largely based on the work of Prof. William Turkett) Lab due date: 5:00pm, day after lab session Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to gain additional
CSC 101: Lab Manual#9 Machine Language and the CPU (largely based on the work of Prof. William Turkett) Lab due date: 5:00pm, day after lab session Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to gain additional
Introduc)on to Compu)ng. Heng Sovannarith
 Introduc)on to Compu)ng Heng Sovannarith heng_sovannarith@yahoo.com Introduc)on Computers play an increasingly important and nearly indispensable role in everyday life. Computers are used all over the
Introduc)on to Compu)ng Heng Sovannarith heng_sovannarith@yahoo.com Introduc)on Computers play an increasingly important and nearly indispensable role in everyday life. Computers are used all over the
CSE 1310: Introduction Mariottini UT Arlington
 Kind of obvious, but a computer is something that does computa0on. What is interes8ng in it is what is going to be computed. In the 1960 s, when computers were becoming popular, they were commonly called
Kind of obvious, but a computer is something that does computa0on. What is interes8ng in it is what is going to be computed. In the 1960 s, when computers were becoming popular, they were commonly called
Introduction. A Look Inside a Laptop Computer. What is inside a laptop computer? What is Inside a Laptop Computer?
 What is inside a laptop computer? Introduction What is Inside a Laptop Computer? Watch the video (3:44). Need help? Have you ever looked inside a desktop computer case before? There is a lot of extra room
What is inside a laptop computer? Introduction What is Inside a Laptop Computer? Watch the video (3:44). Need help? Have you ever looked inside a desktop computer case before? There is a lot of extra room
CS1 Lecture 3 Jan. 18, 2019
 CS1 Lecture 3 Jan. 18, 2019 Office hours for Prof. Cremer and for TAs have been posted. Locations will change check class website regularly First homework assignment will be available Monday evening, due
CS1 Lecture 3 Jan. 18, 2019 Office hours for Prof. Cremer and for TAs have been posted. Locations will change check class website regularly First homework assignment will be available Monday evening, due
 WELCOME TO CS 24! Problem Solving with Computers-II https://ucsb-cs24-s18.github.io/ Read the syllabus. Know what s required. Know how to get help. Enrollment status: 117/105 2 About me Diba Mirza (diba@ucsb.edu)
WELCOME TO CS 24! Problem Solving with Computers-II https://ucsb-cs24-s18.github.io/ Read the syllabus. Know what s required. Know how to get help. Enrollment status: 117/105 2 About me Diba Mirza (diba@ucsb.edu)
WELCOME TO CS 24! Enrollment status: 105/105, Read the syllabus. Know what s required. Know how to get help. Problem Solving with Computers-II
 WELCOME TO CS 24! Problem Solving with Computers-II Read the syllabus. Know what s required. Know how to get help. Enrollment status: 105/105, !2 About me Diba Mirza (diba@ucsb.edu) Faculty, Computer Science
WELCOME TO CS 24! Problem Solving with Computers-II Read the syllabus. Know what s required. Know how to get help. Enrollment status: 105/105, !2 About me Diba Mirza (diba@ucsb.edu) Faculty, Computer Science
Electricity: Voltage. Gate: A signal enters the gate at a certain voltage. The gate performs operations on it, and sends it out was a new signal.
 Hardware CSCE 101 Electricity: Voltage Gate: A signal enters the gate at a certain voltage. The gate performs operations on it, and sends it out was a new signal. The signals voltage will either be between
Hardware CSCE 101 Electricity: Voltage Gate: A signal enters the gate at a certain voltage. The gate performs operations on it, and sends it out was a new signal. The signals voltage will either be between
Introduction. Look Inside a Desktop Computer. What is inside a desktop computer? What is Inside a Desktop Computer?
 What is inside a desktop computer? Introduction What is Inside a Desktop Computer? Watch the video (3:44). Need help? Have you ever looked inside a computer case before? Or seen pictures of the inside
What is inside a desktop computer? Introduction What is Inside a Desktop Computer? Watch the video (3:44). Need help? Have you ever looked inside a computer case before? Or seen pictures of the inside
Chapter 1: Why Program? Computers and Programming. Why Program?
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Programming 1.1 Why Program? Why Program? Computer programmable machine designed to follow instructions Program instructions in computer memory to make it do something
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computers and Programming 1.1 Why Program? Why Program? Computer programmable machine designed to follow instructions Program instructions in computer memory to make it do something
Computers Are Your Future
 Computers Are Your Future 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Inside the System Unit 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Slide 2 What You Will Learn... Understand how computers represent
Computers Are Your Future 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Inside the System Unit 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Slide 2 What You Will Learn... Understand how computers represent
h7ps://bit.ly/citustutorial
 Before We Start Setup a Citus Cloud account for the exercises: h7ps://bit.ly/citustutorial Designing a Mul
Before We Start Setup a Citus Cloud account for the exercises: h7ps://bit.ly/citustutorial Designing a Mul
CS 150 Introduction to Computer Science 1. August 31, 2009
 CS 150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 Professor: Douglas J. Ryan August 31, 2009 CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 8/30/09 Douglas J. Ryan http://zeus.cs.pacificu.edu/ryand ryandj@pacificu.edu
CS 150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 Professor: Douglas J. Ryan August 31, 2009 CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 8/30/09 Douglas J. Ryan http://zeus.cs.pacificu.edu/ryand ryandj@pacificu.edu
Computer Basics PC-100
 Computer Basics PC-100 Course Group Overview PC-100 Computer Basics PC-101 Intro to Operating Systems and Window s Basics PC-102 Computer Programs and File Management PC-103 Computer Security PC-104 The
Computer Basics PC-100 Course Group Overview PC-100 Computer Basics PC-101 Intro to Operating Systems and Window s Basics PC-102 Computer Programs and File Management PC-103 Computer Security PC-104 The
CISC 110 Week 1. An Introduction to Computer Graphics and Scripting
 CISC 110 Week 1 An Introduction to Computer Graphics and Scripting Emese Somogyvari Office: Goodwin 235 E-mail: somogyva@cs.queensu.ca Please use proper email etiquette! Office hours: TBD Course website:
CISC 110 Week 1 An Introduction to Computer Graphics and Scripting Emese Somogyvari Office: Goodwin 235 E-mail: somogyva@cs.queensu.ca Please use proper email etiquette! Office hours: TBD Course website:
REPRESENTING INFORMATION:
 REPRESENTING INFORMATION: BINARY, HEX, ASCII CORRESPONDING READING: WELL, NONE IN YOUR TEXT. SO LISTEN CAREFULLY IN LECTURE (BECAUSE IT WILL BE ON THE EXAM(S))! CMSC 150: Fall 2015 Controlling Information
REPRESENTING INFORMATION: BINARY, HEX, ASCII CORRESPONDING READING: WELL, NONE IN YOUR TEXT. SO LISTEN CAREFULLY IN LECTURE (BECAUSE IT WILL BE ON THE EXAM(S))! CMSC 150: Fall 2015 Controlling Information
CSCE150A. Administrivia. Overview. Hardware. Software. Example. Program. Pseudocode. Flowchart. Control Structures. Hello World Program CSCE150A
 Computer Science & Engineering 150A Problem Solving Using Computers Lecture 01 - Course Introduction Stephen Scott (Adapted from Christopher M. Bourke) Roll Syllabus Course Webpage: http://cse.unl.edu/~sscott/teach/classes/cse150af09/
Computer Science & Engineering 150A Problem Solving Using Computers Lecture 01 - Course Introduction Stephen Scott (Adapted from Christopher M. Bourke) Roll Syllabus Course Webpage: http://cse.unl.edu/~sscott/teach/classes/cse150af09/
Computer Science & Engineering 150A Problem Solving Using Computers
 Computer Science & Engineering 150A Problem Solving Using Computers Lecture 01 - Course Introduction Stephen Scott (Adapted from Christopher M. Bourke) 1 / 43 Fall 2009 Roll Syllabus Course Webpage: http://cse.unl.edu/~sscott/teach/classes/cse150af09/
Computer Science & Engineering 150A Problem Solving Using Computers Lecture 01 - Course Introduction Stephen Scott (Adapted from Christopher M. Bourke) 1 / 43 Fall 2009 Roll Syllabus Course Webpage: http://cse.unl.edu/~sscott/teach/classes/cse150af09/
Announcements. 1. Forms to return today after class:
 Announcements Handouts (3) to pick up 1. Forms to return today after class: Pretest (take during class later) Laptop information form (fill out during class later) Academic honesty form (must sign) 2.
Announcements Handouts (3) to pick up 1. Forms to return today after class: Pretest (take during class later) Laptop information form (fill out during class later) Academic honesty form (must sign) 2.
Systems Architecture
 Systems Architecture Friday, 27 April 2018 Systems Architecture Today s Objectives: 1. To be able to explain the purposes and uses of embedded systems. 2. To be able to describe how the CPU executes instructions
Systems Architecture Friday, 27 April 2018 Systems Architecture Today s Objectives: 1. To be able to explain the purposes and uses of embedded systems. 2. To be able to describe how the CPU executes instructions
Computer Memory. Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 SP 18 - KASEY CHAMPION 1
 Computer Memory Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 SP 18 - KASEY CHAMPION 1 Warm Up public int sum1(int n, int m, int[][] table) { int output = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j
Computer Memory Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 SP 18 - KASEY CHAMPION 1 Warm Up public int sum1(int n, int m, int[][] table) { int output = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j
COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction. CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics
 COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics Last Class Solving many little problems to avoid thinking about too much at once! A tiny
COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics Last Class Solving many little problems to avoid thinking about too much at once! A tiny
Week One: Introduction A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, AND ALGORITHM DEVELOPMENT
 Week One: Introduction A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, AND ALGORITHM DEVELOPMENT Outline In this chapter you will learn: About computer hardware, software and programming How to write and execute
Week One: Introduction A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, AND ALGORITHM DEVELOPMENT Outline In this chapter you will learn: About computer hardware, software and programming How to write and execute
COMP1400 Programming for Designers. Claude Sammut
 COMP1400 Programming for Designers Claude Sammut Contacts Lecturer in Charge: Claude Sammut Web pages: http://blogs.unsw.edu.au/comp1400/ Email: cs1400@cse.unsw.edu.au Subject admin: Tim Wiley Tutor: Tim
COMP1400 Programming for Designers Claude Sammut Contacts Lecturer in Charge: Claude Sammut Web pages: http://blogs.unsw.edu.au/comp1400/ Email: cs1400@cse.unsw.edu.au Subject admin: Tim Wiley Tutor: Tim
Unit 2: Data Storage CS 101, Fall 2018
 Unit 2: Data Storage CS 101, Fall 2018 Learning Objectives After completing this unit, you should be able to: Evaluate digital circuits that use AND, OR, XOR, and NOT. Convert binary integers to/from decimal,
Unit 2: Data Storage CS 101, Fall 2018 Learning Objectives After completing this unit, you should be able to: Evaluate digital circuits that use AND, OR, XOR, and NOT. Convert binary integers to/from decimal,
CSSE232 Computer Architecture. Introduc5on
 CSSE232 Computer Architecture Introduc5on Reading Be:er for you if done before class For today: Ch 1 (esp 1.1-3, 10) App. C Sec5ons 2.4, 3.1-2 Outline Introduc5ons Class details Syllabus, website, schedule
CSSE232 Computer Architecture Introduc5on Reading Be:er for you if done before class For today: Ch 1 (esp 1.1-3, 10) App. C Sec5ons 2.4, 3.1-2 Outline Introduc5ons Class details Syllabus, website, schedule
CS1 Lecture 3 Jan. 22, 2018
 CS1 Lecture 3 Jan. 22, 2018 Office hours for me and for TAs have been posted, locations will change check class website regularly First homework available, due Mon., 9:00am. Discussion sections tomorrow
CS1 Lecture 3 Jan. 22, 2018 Office hours for me and for TAs have been posted, locations will change check class website regularly First homework available, due Mon., 9:00am. Discussion sections tomorrow
Advanced Placement Computer Science Principles The Information Age
 08/20/18 Advanced Placement Computer Science Principles The Information Age Where is it heading? How big is the information? Lesson 0-2 Journal Entry 08/20/18 How do you think computers and technology
08/20/18 Advanced Placement Computer Science Principles The Information Age Where is it heading? How big is the information? Lesson 0-2 Journal Entry 08/20/18 How do you think computers and technology
Chapter 1. Introduction to Computers and Programming. M hiwa ahmad aziz
 . Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers and Programming www.raparinweb.com M hiwa ahmad aziz 1 Ch 1 - Introduction to Computers and Programming Hardware Terminology Main Memory Auxiliary Memory Drives Writing
. Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers and Programming www.raparinweb.com M hiwa ahmad aziz 1 Ch 1 - Introduction to Computers and Programming Hardware Terminology Main Memory Auxiliary Memory Drives Writing
COMPUTATIONAL THINKING
 Computational Concepts sequence loops parallelism events conditionals operators variables lists COMPUTATIONAL THINKING PROGRAMMING AS PROBLEM SOLVING Computational Practices incremental/iterative testing/debugging
Computational Concepts sequence loops parallelism events conditionals operators variables lists COMPUTATIONAL THINKING PROGRAMMING AS PROBLEM SOLVING Computational Practices incremental/iterative testing/debugging
Today. An Animated Introduction to Programming. Prerequisites. Computer programming
 Today 1 2 3 4 Computer programming What is this course about? We re making several assumptions about you as a student. In particular, we assume that you have: Never taken a programming course before. Have
Today 1 2 3 4 Computer programming What is this course about? We re making several assumptions about you as a student. In particular, we assume that you have: Never taken a programming course before. Have
COMP Data Structures
 Shahin Kamali Topic 1 - Introductions University of Manitoba Based on notes by S. Durocher. 1 / 35 Introduction Introduction 1 / 35 Introduction In a Glance... Data structures are building blocks for designing
Shahin Kamali Topic 1 - Introductions University of Manitoba Based on notes by S. Durocher. 1 / 35 Introduction Introduction 1 / 35 Introduction In a Glance... Data structures are building blocks for designing
COMP Data Structures
 COMP 2140 - Data Structures Shahin Kamali Topic 1 - Introductions University of Manitoba Based on notes by S. Durocher. COMP 2140 - Data Structures 1 / 35 Introduction COMP 2140 - Data Structures 1 / 35
COMP 2140 - Data Structures Shahin Kamali Topic 1 - Introductions University of Manitoba Based on notes by S. Durocher. COMP 2140 - Data Structures 1 / 35 Introduction COMP 2140 - Data Structures 1 / 35
Programming with Arrays Intro to Pointers CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #11
 Programming with Arrays Intro to Pointers CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #11 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Thursday, 5/17 in this classroom Starts at 2:00 PM **SHARP** Please
Programming with Arrays Intro to Pointers CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #11 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Thursday, 5/17 in this classroom Starts at 2:00 PM **SHARP** Please
Microprocessors I MICROCOMPUTERS AND MICROPROCESSORS
 Microprocessors I Outline of the Lecture Microcomputers and Microprocessors Evolution of Intel 80x86 Family Microprocessors Binary and Hexadecimal Number Systems MICROCOMPUTERS AND MICROPROCESSORS There
Microprocessors I Outline of the Lecture Microcomputers and Microprocessors Evolution of Intel 80x86 Family Microprocessors Binary and Hexadecimal Number Systems MICROCOMPUTERS AND MICROPROCESSORS There
Darrell Bethea May 10, MTWRF 9:45-11:15 AM Sitterson 011
 Darrell Bethea May 10, 2011 MTWRF 9:45-11:15 AM Sitterson 011 1 Office hours: MW 1-2 PM If you still cannot make it to either office hour, email me to set up an appointment if you need help with an assignment.
Darrell Bethea May 10, 2011 MTWRF 9:45-11:15 AM Sitterson 011 1 Office hours: MW 1-2 PM If you still cannot make it to either office hour, email me to set up an appointment if you need help with an assignment.
W1005 Intro to CS and Programming in MATLAB. Brief History of Compu?ng. Fall 2014 Instructor: Ilia Vovsha. hip://www.cs.columbia.
 W1005 Intro to CS and Programming in MATLAB Brief History of Compu?ng Fall 2014 Instructor: Ilia Vovsha hip://www.cs.columbia.edu/~vovsha/w1005 Computer Philosophy Computer is a (electronic digital) device
W1005 Intro to CS and Programming in MATLAB Brief History of Compu?ng Fall 2014 Instructor: Ilia Vovsha hip://www.cs.columbia.edu/~vovsha/w1005 Computer Philosophy Computer is a (electronic digital) device
o MAC (6/18 or 33%) o WIN (17/18 or 94%) o Unix (0/18 or 0%)
 Computer OS: Feel comfortable with these operating systems o MAC (6/18 or 33%) o WIN (17/18 or 94%) o Unix (0/18 or 0%) CS120 The Information Era LECTURE 2 TOPICS:, Review, Computer Basics, Computer History,
Computer OS: Feel comfortable with these operating systems o MAC (6/18 or 33%) o WIN (17/18 or 94%) o Unix (0/18 or 0%) CS120 The Information Era LECTURE 2 TOPICS:, Review, Computer Basics, Computer History,
An Introduc+on to Computers and Java CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal
 An Introduc+on to Computers and Java CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the basic terminology of a computer system Understand the basics of high level languages, including Java Understand
An Introduc+on to Computers and Java CSC 121 Spring 2017 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Learn the basic terminology of a computer system Understand the basics of high level languages, including Java Understand
CS 465 Final Review. Fall 2017 Prof. Daniel Menasce
 CS 465 Final Review Fall 2017 Prof. Daniel Menasce Ques@ons What are the types of hazards in a datapath and how each of them can be mi@gated? State and explain some of the methods used to deal with branch
CS 465 Final Review Fall 2017 Prof. Daniel Menasce Ques@ons What are the types of hazards in a datapath and how each of them can be mi@gated? State and explain some of the methods used to deal with branch
! Learn how to think like a computer scientist. ! Learn problem solving. ! Read and write code. ! Understand object oriented programming
 1 TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE AND PROGRAMMING Topic 1 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming Notes adapted from Introduction to Computing and Programming with Java: A Multimedia
1 TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE AND PROGRAMMING Topic 1 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming Notes adapted from Introduction to Computing and Programming with Java: A Multimedia
CMSC 1513 Lecture 1.2
 Key Point: A computer is an electronic device that stores and processes data. Hardware Software Hardware comprises the visible, physical elements of the computer. Software provides the invisible instructions
Key Point: A computer is an electronic device that stores and processes data. Hardware Software Hardware comprises the visible, physical elements of the computer. Software provides the invisible instructions
CS 150 Introduction to Computer Science 1
 CS 150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 Professor: Chadd Williams CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 Chadd Williams http://zeus.cs.pacificu.edu/chadd chadd@pacificu.edu Office 202 Strain Office
CS 150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 Professor: Chadd Williams CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 Chadd Williams http://zeus.cs.pacificu.edu/chadd chadd@pacificu.edu Office 202 Strain Office
CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms. Memory and Locality. Autumn Shrirang (Shri) Mare
 CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms Memory and Locality Autumn 2018 Shrirang (Shri) Mare shri@cs.washington.edu Thanks to Kasey Champion, Ben Jones, Adam Blank, Michael Lee, Evan McCarty, Robbie Weber,
CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms Memory and Locality Autumn 2018 Shrirang (Shri) Mare shri@cs.washington.edu Thanks to Kasey Champion, Ben Jones, Adam Blank, Michael Lee, Evan McCarty, Robbie Weber,
CS 121 Intro to Programming:Java - Lecture 2. Professor Robert Moll (+ TAs) CS BLDG
 CS 121 Intro to Programming:Java - Lecture 2 Course home page: Professor Robert Moll (+ TAs) CS BLDG 276-545-4315 moll@cs.umass.edu http://twiki-edlab.cs.umass.edu/bin/view/moll121/webhome First OWL assignment
CS 121 Intro to Programming:Java - Lecture 2 Course home page: Professor Robert Moll (+ TAs) CS BLDG 276-545-4315 moll@cs.umass.edu http://twiki-edlab.cs.umass.edu/bin/view/moll121/webhome First OWL assignment
Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. PaHerson hhp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa10. Fall Lecture #1. Agenda
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. PaHerson hhp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa10 1 Agenda Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Administrivia
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. PaHerson hhp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa10 1 Agenda Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Administrivia
Class List. Java Must Have. Class Goals. Class Goals. Schedule
 Class List Accelerated Introduction to CS Using Java 5 2004 Illinois Institute of Technology Schedule CS -201-071 M 06:25-09:05PM Rice Campus - Wheaton Room RI 148 LAB W 06:25-09:05PM CS -201-392 MW 06:25-09:05PM
Class List Accelerated Introduction to CS Using Java 5 2004 Illinois Institute of Technology Schedule CS -201-071 M 06:25-09:05PM Rice Campus - Wheaton Room RI 148 LAB W 06:25-09:05PM CS -201-392 MW 06:25-09:05PM
Computers Are Your Future
 Computers Are Your Future Twelfth Edition Chapter 2: Inside the System Unit Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 Inside the Computer System Copyright 2012 Pearson Education,
Computers Are Your Future Twelfth Edition Chapter 2: Inside the System Unit Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 Inside the Computer System Copyright 2012 Pearson Education,
CC411: Introduction To Microprocessors
 CC411: Introduction To Microprocessors OBJECTIVES this chapter enables the student to: Use number { base 2, base 10, or base 16 }. Add and subtract binary/hex numbers. Represent any binary number in 2
CC411: Introduction To Microprocessors OBJECTIVES this chapter enables the student to: Use number { base 2, base 10, or base 16 }. Add and subtract binary/hex numbers. Represent any binary number in 2
Introduction to C Programming 計算機程式設計
 Introduction to C Programming 計算機程式設計 2/22/2012 朱浩華 Today s Do List Course Overview (20 minutes) Setup computer accounts Hello world! CodeBlocks program (30 minutes) Overviews of Computers and Programming
Introduction to C Programming 計算機程式設計 2/22/2012 朱浩華 Today s Do List Course Overview (20 minutes) Setup computer accounts Hello world! CodeBlocks program (30 minutes) Overviews of Computers and Programming
what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored?
 Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
Parts are adapted from Windows 98 by Mark Twain Media, Inc. A Computer System has Hardware and Software
 Parts are adapted from Windows 98 by Mark Twain Media, Inc. A Computer System has Hardware and Software All the parts--monitor, printer, hard drive, etc.-- cables, cabinets, and programs that make a computer
Parts are adapted from Windows 98 by Mark Twain Media, Inc. A Computer System has Hardware and Software All the parts--monitor, printer, hard drive, etc.-- cables, cabinets, and programs that make a computer
COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction. CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics
 COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics Last Class Solving many little problems to avoid thinking about too much at once! A tiny
COMP-202 Unit 1: Introduction CONTENTS: What Is Programming? How a Computer Works Programming Languages Java Basics Last Class Solving many little problems to avoid thinking about too much at once! A tiny
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Computers and Java
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Computers and Java Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken NJ Chapter Topics Chapter 1 discusses the following main topics: Why Program? Computer Systems: Hardware and
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Computers and Java Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken NJ Chapter Topics Chapter 1 discusses the following main topics: Why Program? Computer Systems: Hardware and
A Unicorn Named Sparkle Word Search. A New Friend for Sparkle Coloring Sheet. A Unicorn Named Sparkle s First Christmas Coloring Sheet
 Table of Contents Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Page 6 Page 7 Pages 8 9 Page 10 Page 11 Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Name Tags A Unicorn Named Sparkle Word Search Draw and Name Your Unicorn Connect
Table of Contents Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5 Page 6 Page 7 Pages 8 9 Page 10 Page 11 Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Name Tags A Unicorn Named Sparkle Word Search Draw and Name Your Unicorn Connect
CSC 015: FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER SCIENCE I
 CSC 015: FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER SCIENCE I Lecture 1: Class Introduction DR. BO TANG ASSISTANT PROFESSOR HOFSTRA UNIVERSITY 1 9/7/16 CSC15 - Python OUTLINE What is Computer Science? What is this Class
CSC 015: FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER SCIENCE I Lecture 1: Class Introduction DR. BO TANG ASSISTANT PROFESSOR HOFSTRA UNIVERSITY 1 9/7/16 CSC15 - Python OUTLINE What is Computer Science? What is this Class
Lecture 1: What is a Computer? Lecture for CPSC 2105 Computer Organization by Edward Bosworth, Ph.D.
 Lecture 1: What is a Computer? Lecture for CPSC 2105 Computer Organization by Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. An Older Computer The figure at right is an older computer, called a PDP-11/20. It was designed in the
Lecture 1: What is a Computer? Lecture for CPSC 2105 Computer Organization by Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. An Older Computer The figure at right is an older computer, called a PDP-11/20. It was designed in the
Basic Computer Programming for ISNE. Santi Phithakkitnukoon ผศ.ดร.ส นต พ ท กษ ก จน ก ร
 269102 Basic Computer Programming for ISNE Santi Phithakkitnukoon ผศ.ดร.ส นต พ ท กษ ก จน ก ร Syllabus Instructor: Asst. Prof. Dr. Santi Phithakkitnukoon ผศ.ดร.ส นต พ ท กษ ก จน ก ร (อ.เอ ม) Office room:
269102 Basic Computer Programming for ISNE Santi Phithakkitnukoon ผศ.ดร.ส นต พ ท กษ ก จน ก ร Syllabus Instructor: Asst. Prof. Dr. Santi Phithakkitnukoon ผศ.ดร.ส นต พ ท กษ ก จน ก ร (อ.เอ ม) Office room:
Java Programming. What is a program? Programs as Recipes. Programs Recipes 8/20/15. Pancakes In one bowl
 What is a program? Java Programming CS 160, Fall Semester 2012 TOPICS Computer Programs Using Eclipse Program Program Components Definition: a sequence of instructions telling a computer what to do Analogy:
What is a program? Java Programming CS 160, Fall Semester 2012 TOPICS Computer Programs Using Eclipse Program Program Components Definition: a sequence of instructions telling a computer what to do Analogy:
IT 252 Computer Organization and Architecture. Introduction. Chia-Chi Teng
 IT 252 Computer Organization and Architecture Introduction Chia-Chi Teng What is computer architecture about? Computer architecture is the study of building computer systems. IT 252 is roughly split into
IT 252 Computer Organization and Architecture Introduction Chia-Chi Teng What is computer architecture about? Computer architecture is the study of building computer systems. IT 252 is roughly split into
The computer is a universal machine. It s a mind-set, not a skill-set. Brilliance helps, but is not required. Instead, adopt these mantras: be
 The computer is a universal machine. It s a mind-set, not a skill-set. Brilliance helps, but is not required. Instead, adopt these mantras: be stubborn, bossy, lazy, obsessive, cynical, plodding, and importunate.
The computer is a universal machine. It s a mind-set, not a skill-set. Brilliance helps, but is not required. Instead, adopt these mantras: be stubborn, bossy, lazy, obsessive, cynical, plodding, and importunate.
Func+on applica+ons (calls, invoca+ons)
 Func%ons in Racket Racket Functions: most important building block in Racket (and 25) Functions/procedures/methods/subroutines abstract over computations Like Java methods, Python functions have arguments
Func%ons in Racket Racket Functions: most important building block in Racket (and 25) Functions/procedures/methods/subroutines abstract over computations Like Java methods, Python functions have arguments
last time in cs recitations. computer commands. today s topics.
 last time in cs1007... recitations. course objectives policies academic integrity resources WEB PAGE: http://www.columbia.edu/ cs1007 NOTE CHANGES IN ASSESSMENT 5 EXTRA CREDIT POINTS ADDED sign up for
last time in cs1007... recitations. course objectives policies academic integrity resources WEB PAGE: http://www.columbia.edu/ cs1007 NOTE CHANGES IN ASSESSMENT 5 EXTRA CREDIT POINTS ADDED sign up for
What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? 1-1
 What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did the computer become known as the stored-program computer? Do they all have the same
What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did the computer become known as the stored-program computer? Do they all have the same
Chapter. Focus of the Course. Object-Oriented Software Development. program design, implementation, and testing
 Introduction 1 Chapter 5 TH EDITION Lewis & Loftus java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Focus of the Course Object-Oriented Software Development
Introduction 1 Chapter 5 TH EDITION Lewis & Loftus java Software Solutions Foundations of Program Design 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Focus of the Course Object-Oriented Software Development
Information Communications Technology (CE-ICT) 6 th Class
 Information Communications Technology (CE-ICT) 6 th Class Lecture 2: Computer Concepts (Part A) Lecturer: Objectives Hardware Concepts Types of Computer Components of a Computer System Computer Performance
Information Communications Technology (CE-ICT) 6 th Class Lecture 2: Computer Concepts (Part A) Lecturer: Objectives Hardware Concepts Types of Computer Components of a Computer System Computer Performance
Design and Debug: Essen.al Concepts CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #8
 Design and Debug: Essen.al Concepts CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #8 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Outline Midterm# 1 Grades Review of key concepts Loop design help Ch.
Design and Debug: Essen.al Concepts CS 16: Solving Problems with Computers I Lecture #8 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Outline Midterm# 1 Grades Review of key concepts Loop design help Ch.
Agenda. Old School CS61c. Agenda. New School CS61c 8/26/10. CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures)
 Agenda CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. PaHerson hhp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa10 1 Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Administrivia
Agenda CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture (Machine Structures) Instructors: Randy H. Katz David A. PaHerson hhp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa10 1 Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Administrivia
COMP Summer 2015 (A01) Jim (James) Young jimyoung.ca
 COMP 1010- Summer 2015 (A01) Jim (James) Young young@cs.umanitoba.ca jimyoung.ca Hello! James (Jim) Young young@cs.umanitoba.ca jimyoung.ca office hours T / Th: 17:00 18:00 EITC-E2-582 (or by appointment,
COMP 1010- Summer 2015 (A01) Jim (James) Young young@cs.umanitoba.ca jimyoung.ca Hello! James (Jim) Young young@cs.umanitoba.ca jimyoung.ca office hours T / Th: 17:00 18:00 EITC-E2-582 (or by appointment,
CP122 CS I. Hello, World!
 CP122 CS I Hello, World! Introductions Webpage and Syllabus cs.coloradocollege.edu/~mwhitehead Tech News! AlphaGo Zero defeats AlphaGo 100 games to 0. Tech News! AlphaGo Zero defeats AlphaGo 100 games
CP122 CS I Hello, World! Introductions Webpage and Syllabus cs.coloradocollege.edu/~mwhitehead Tech News! AlphaGo Zero defeats AlphaGo 100 games to 0. Tech News! AlphaGo Zero defeats AlphaGo 100 games
Information Science 1
 Information Science 1 -Basic Concepts of Computers: Opera4on, Architecture, Memory- Week 02 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Today s lecture outline l Recall the previous
Information Science 1 -Basic Concepts of Computers: Opera4on, Architecture, Memory- Week 02 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Today s lecture outline l Recall the previous
Computer Architecture and System Software Lecture 02: Overview of Computer Systems & Start of Chapter 2
 Computer Architecture and System Software Lecture 02: Overview of Computer Systems & Start of Chapter 2 Instructor: Rob Bergen Applied Computer Science University of Winnipeg Announcements Website is up
Computer Architecture and System Software Lecture 02: Overview of Computer Systems & Start of Chapter 2 Instructor: Rob Bergen Applied Computer Science University of Winnipeg Announcements Website is up
COMP 273 Winter physical vs. virtual mem Mar. 15, 2012
 Virtual Memory The model of MIPS Memory that we have been working with is as follows. There is your MIPS program, including various functions and data used by this program, and there are some kernel programs
Virtual Memory The model of MIPS Memory that we have been working with is as follows. There is your MIPS program, including various functions and data used by this program, and there are some kernel programs
Welcome to COMPSCI111/111G!
 Welcome to COMPSCI111/111G! Today s class Introduction to COMPSCI111/111G People Assessment Labs Test and exam Introduction to computer hardware https://www.cs.auckland.ac.nz/courses/compsci111s1c/ Lecturers
Welcome to COMPSCI111/111G! Today s class Introduction to COMPSCI111/111G People Assessment Labs Test and exam Introduction to computer hardware https://www.cs.auckland.ac.nz/courses/compsci111s1c/ Lecturers
Intentionally Blank 0
 Intentionally Blank 0 Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 1 Understanding Your Computer: Computers are Data Processing Devices Perform four major functions Input:
Intentionally Blank 0 Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 1 Understanding Your Computer: Computers are Data Processing Devices Perform four major functions Input:
CP122 CS I. Chapter 1: Introduction
 CP122 CS I Chapter 1: Introduction Introductions Webpage and Syllabus cs.coloradocollege.edu/~mwhitehead Hacker's Tip of the Day Hacker A person interested in how things work. A critical thinker, an endless
CP122 CS I Chapter 1: Introduction Introductions Webpage and Syllabus cs.coloradocollege.edu/~mwhitehead Hacker's Tip of the Day Hacker A person interested in how things work. A critical thinker, an endless
