Module Contact: Dr Pierre Chardaire, CMP Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 1
|
|
|
- Brenda Price
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2015/16 INTRODUCTORY PROGRAMMING CMP-0005B Time allowed: 2 hours. Answer BOTH questions from section A and ONE question from section B. Notes are not permitted in this examination. Do not turn over until you are told to do so by the Invigilator. CMP-0005B Module Contact: Dr Pierre Chardaire, CMP Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 1
2 Page 2 SECTION A 1. (a) The following C++ function contains eight syntax errors. Describe [16 marks] each of them using the line numbers to identify them. If you mention more than eight errors only the first eight will be considered for marking. 1 # include < iostream > 2 #include <vector > 3 4 using namespace std ; 5 6 bool isprime ( i n t n ) 7 { 8 i f ( n == 1) return false ; 9 i f ( n == 2) return true ; 10 double sqx = s q r t ( n ) ; 11 for ( i n t i =2; i =< f l o o r ( sqx ), i ++) 12 i f ( n mod i == 0) 13 return false ; 14 return true void printupto ( i n t n ) 18 { 19 for ( i n t i =2; i <n ; i ++) 20 i f isprime ( i ) 21 cout << i << endl ; i n t main ( ) 25 { 26 i n t n ; 27 cout >> Enter a p o s i t i v e number > ; 28 c i n << n ; 29 n = printupto ( n ) ; 30 return 0; 31
3 Page 3 (b) Trace the execution of the following function for the input n = [8 marks] using the line numbers to indicate when changes in the states of the variables occur. 1 bool t e s t 7 d i v ( i n t n ) 2 { 3 i n t r, q ; 4 while ( n > 0) 5 { 6 r = n % 10; 7 q = n / 10; 8 n = q 2 r ; 9 10 i f ( ( n==0) ( n== 7) ( n== 14) ) 11 return true ; 12 else 13 return false ; 14 (c) What is the following function supposed to do? Clearly justify your [8 marks] answer. You may want to trace the code with some of the inputs BARBER, BAOBAB, BERBER. bool t o i s t a a ( s t r i n g &s ) { i f ( s. l e n g t h ( ) % 2 == 1) return false ; i n t j = s. l e n g t h ( ) / 2 ; for ( i n t i = 0; i < s. length ( ) / 2 ; i ++) i f ( s [ i ]!= s [ i + j ] ) return false ; return true ; TURN OVER
4 Page 4 (d) What is the purpose of the following function? Clearly justify your [8 marks] answer. 1 void j a r j e s t e l l a ( i n t &a, i n t &b, i n t &c ) 2 { 3 i n t temp =0; 4 i f ( b>c ) { temp=b ; b=c ; c=temp ; 5 i f ( a>b ) { temp=a ; a=b ; b=temp ; 6 i f ( b>c ) { temp=b ; b=c ; c=temp ; 7 2. There is no requirement to test for input ranges or carry out other validation in the following parts of this question. Comments should only be included if they are required to add clarity to the code. (a) Write a C++ code fragment to ask the user to enter an integer number, and output all non-negative integer numbers whose squares are less than or equal to the input number. (b) The conversion formulas between temperatures in degrees [15 marks] Fahrenheit (F) and temperatures in degrees Celsius (C) are: F = C 9/ and C = (F 32) 5/9. Write a program that repeatedly ask a user to enter a temperature. The user inputs a number followed by the letter F or by the letter C. After each temperature input the program should output the conversion of the temperature into the other unit. The program should terminate when the same temperature is entered twice in succession.
5 Page 5 (c) A palindrome is a word which reads the same forward and [15 marks] backward. A sentence is called palindromic if after removing spaces, punctuation and changing lower case letters into upper case letters a palindrome is obtained. For example, the sentence Was it a car or a cat I saw? is palindromic. Write one or more functions to determine if a sentence is palindromic. To do so you may want to use the function ispunct that takes a character as input and returns true if the character is a punctuation sign and false otherwise, and the function toupper that returns the upper case letter associated with a letter. TURN OVER
6 Page 6 SECTION B Answer ONE question from this section. 3. A class for storing and returning consecutive primes is declared as [40 marks] follows: #include <vector > using namespace std ; class Primes { public : s t a t i c i n t f i r s t P r i m e ( ) ; s t a t i c i n t nextprime ( ) ; s t a t i c i n t previousprime ( ) ; / / r e t u r n s 0 i f no previous prime private : / / I n i t i a l i s e the data members s t a t i c i n t i n i t P r i m e s ( ) ; / / Adds a new prime t o t h e sequence o f primes s t a t i c void addprime ( ) ; / / Helper f o r addprime : r e t u r n s t r u e i f n i s d i v i s i b l e / / by a prime i n t h e sequence o f primes memorised s t a t i c bool composite ( i n t n ) ; / / memorises consecutive prime numbers 2, 3, 5... s t a t i c v e c t o r <int > primes ; / / index i n v e c t o r primes of the prime l a s t returned / / by a c a l l to f i r s t P r i m e, lastprime or nextprime s t a t i c i n t index ; ;
7 Page 7 For example the class may be used by the following program: # include < iostream > #include " Primes. h " using namespace std ; i n t main ( ) { cout << Primes : : f i r s t P r i m e ( ) ; for ( i n t i =0; i <10; i ++) cout <<, << Primes : : nextprime ( ) ; cout << endl ; the execution of which produces: 2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29,31 Press any key t o continue... The start of the implementation of the class is as follows: vector <int > Primes : : primes ; i n t Primes : : index = Primes : : i n i t P r i m e s ( ) ; Implement the rest of the class. An equal number of marks will be awarded for each of the methods correctly implemented. Reminder: If the first n primes are known, the n + 1 th prime is the first number that follows the n th prime and is not divisible by any of the first n primes. TURN OVER
8 Page 8 4. An integer y is a factor or divisor of an integer x if x/y is an integer number. An integer number is prime if it is greater than one and its only factors are one and itself. Any number can be written as a product of prime factors, called its prime factorization. This product is unique up to the order of the factors. For example = 2 {{ {{ {{ 11 = , = , 143 = , 43 = (a) You are given a function firstprime() that returns the first prime number and a function nextprime() that returns the first prime number that follows the number obtained by the last call to firstprime() or nextprime(). Write a function that takes a non-negative integer n as input and returns the smallest prime greater than n. (b) Write a function that takes two non-negative integers n and p as input and returns true if p is a factor of n and false otherwise. (c) Using the function of question 4b write a function that takes two non-negative integers p and q as input and returns p/q m where m is the largest integer such that q m is a divisor of p and sets an output variable to m. If q is less than two then p should be returned and the output variable set to zero. You are reminded that x 0 = 1 for any integer x.
9 Page 9 (d) Using the functions of questions 4a and 4c write a main program that repeatedly ask for an integer number until a zero or a one is entered. For each number entered the program should output its prime factorisation, representing consecutive primes with their exponents as consecutive pairs. An example of execution is as follows: Enter number > = ( 2, 2 ) ( 3, 4 ) ( 1 1, 2 ) Enter number > = ( 2, 7 ) ( 3, 3 ) Enter number > 0 Press any key t o continue... END OF PAPER
Module Contact: Dr Pierre Chardaire, CMP Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 1
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2014/15 INTRODUCTORY PROGRAMMING CMP-0005B Time allowed: 2 hours. Answer BOTH questions from section A and ONE question
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2014/15 INTRODUCTORY PROGRAMMING CMP-0005B Time allowed: 2 hours. Answer BOTH questions from section A and ONE question
Module Contact: Dr Pierre Chardaire, CMP Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 1
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2016-17 INTRODUCTORY PROGRAMMING CMP-0005A Time allowed: 2 hours Answer BOTH questions from Section A and ONE question
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2016-17 INTRODUCTORY PROGRAMMING CMP-0005A Time allowed: 2 hours Answer BOTH questions from Section A and ONE question
Answer BOTH questions from Section A and ONE question from Section B.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013/14 INTRODUCTORY PROGRAMMING CMP-0005B Time allowed: 2 hours Answer BOTH questions from Section A and ONE question
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013/14 INTRODUCTORY PROGRAMMING CMP-0005B Time allowed: 2 hours Answer BOTH questions from Section A and ONE question
1- Write a single C++ statement that: A. Calculates the sum of the two integrates 11 and 12 and outputs the sum to the consol.
 1- Write a single C++ statement that: A. Calculates the sum of the two integrates 11 and 12 and outputs the sum to the consol. B. Outputs to the console a floating point number f1 in scientific format
1- Write a single C++ statement that: A. Calculates the sum of the two integrates 11 and 12 and outputs the sum to the consol. B. Outputs to the console a floating point number f1 in scientific format
Other operators. Some times a simple comparison is not enough to determine if our criteria has been met.
 Lecture 6 Other operators Some times a simple comparison is not enough to determine if our criteria has been met. For example: (and operation) If a person wants to login to bank account, the user name
Lecture 6 Other operators Some times a simple comparison is not enough to determine if our criteria has been met. For example: (and operation) If a person wants to login to bank account, the user name
1. a) What #include statement do you put at the top of a program that does uses cin, cout or endl?
 Exercises with solutions. 1. a) What #include statement do you put at the top of a program that does uses cin, cout or endl? #include b) What using statement do you always put at the top of
Exercises with solutions. 1. a) What #include statement do you put at the top of a program that does uses cin, cout or endl? #include b) What using statement do you always put at the top of
University of Dublin
 University of Dublin TRINITY COLLEGE Faculty of Enginering & Systems Sciences School of Engineering Junior Freshman Engineering Trinity Term 2015 Computer Engineering I (1E3) Date Location Time Dr L. Hederman
University of Dublin TRINITY COLLEGE Faculty of Enginering & Systems Sciences School of Engineering Junior Freshman Engineering Trinity Term 2015 Computer Engineering I (1E3) Date Location Time Dr L. Hederman
Multiple Choice (Questions 1 13) 26 Points Select all correct answers (multiple correct answers are possible)
 Name Closed notes, book and neighbor. If you have any questions ask them. Notes: Segment of code necessary C++ statements to perform the action described not a complete program Program a complete C++ program
Name Closed notes, book and neighbor. If you have any questions ask them. Notes: Segment of code necessary C++ statements to perform the action described not a complete program Program a complete C++ program
C++ for Everyone, 2e, Cay Horstmann, Copyright 2012 John Wiley and Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Using a Debugger WE5.
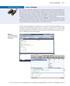 Using a Debugger WE5 W o r k E D E x a m p l e 5.2 Using a Debugger As you have undoubtedly realized by now, computer programs rarely run perfectly the first time. At times, it can be quite frustrating
Using a Debugger WE5 W o r k E D E x a m p l e 5.2 Using a Debugger As you have undoubtedly realized by now, computer programs rarely run perfectly the first time. At times, it can be quite frustrating
Lab Instructor : Jean Lai
 Lab Instructor : Jean Lai Group related statements to perform a specific task. Structure the program (No duplicate codes!) Must be declared before used. Can be invoked (called) as any number of times.
Lab Instructor : Jean Lai Group related statements to perform a specific task. Structure the program (No duplicate codes!) Must be declared before used. Can be invoked (called) as any number of times.
Module Contact: Dr Gavin Cawley, CMP Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 1
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-18 PROGRAMMING 1 CMP-4008Y Time allowed: 2 hours Answer FOUR questions. All questions carry equal weight. Notes are
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-18 PROGRAMMING 1 CMP-4008Y Time allowed: 2 hours Answer FOUR questions. All questions carry equal weight. Notes are
Review: Exam 1. Your First C++ Program. Declaration Statements. Tells the compiler. Examples of declaration statements
 Review: Exam 1 9/20/06 CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 1 Your First C++ Program 1 //*********************************************************** 2 // File name: hello.cpp 3 // Author: Shereen Khoja
Review: Exam 1 9/20/06 CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 1 Your First C++ Program 1 //*********************************************************** 2 // File name: hello.cpp 3 // Author: Shereen Khoja
Review Questions for Final Exam
 CS 102 / ECE 206 Spring 11 Review Questions for Final Exam The following review questions are similar to the kinds of questions you will be expected to answer on the Final Exam, which will cover LCR, chs.
CS 102 / ECE 206 Spring 11 Review Questions for Final Exam The following review questions are similar to the kinds of questions you will be expected to answer on the Final Exam, which will cover LCR, chs.
Week 3. Function Definitions. Example: Function. Function Call, Return Statement. Functions & Arrays. Gaddis: Chapters 6 and 7.
 Week 3 Functions & Arrays Gaddis: Chapters 6 and 7 CS 5301 Fall 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Function Definitions! Function definition pattern: datatype identifier (parameter1, parameter2,...) { statements... Where
Week 3 Functions & Arrays Gaddis: Chapters 6 and 7 CS 5301 Fall 2015 Jill Seaman 1 Function Definitions! Function definition pattern: datatype identifier (parameter1, parameter2,...) { statements... Where
C++ Quick Reference. switch Statements
 C++ Quick Reference if Statements switch Statements Array/Initializer if (condition) if (condition) else if (condition1) else if (condition2) else Loop Statements while (condition) do while (condition);
C++ Quick Reference if Statements switch Statements Array/Initializer if (condition) if (condition) else if (condition1) else if (condition2) else Loop Statements while (condition) do while (condition);
Total 100. The American University in Cairo Computer Science & Engineering Department CSCE 106. Instructor: Final Exam Fall Section No.
 The American University in Cairo Computer Science & Engineering Department CSCE 106 Instructor: Final Exam Fall 2010 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Section No.: EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS * Do not
The American University in Cairo Computer Science & Engineering Department CSCE 106 Instructor: Final Exam Fall 2010 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Section No.: EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS * Do not
CSCE Practice Midterm. Data Types
 CSCE 2004 - Practice Midterm This midterm exam was given in class several years ago. Work each of the following questions on your own. Once you are done, check your answers. For any questions whose answers
CSCE 2004 - Practice Midterm This midterm exam was given in class several years ago. Work each of the following questions on your own. Once you are done, check your answers. For any questions whose answers
Midterm Exam. Sample Solutions
 Name: CS 410 Introduction to Software Engineering Fall 2016 Instructor: Marc Pomplun Midterm Exam Sample Solutions No books, no notes, and no calculators are allowed. Question 1: out of points Question
Name: CS 410 Introduction to Software Engineering Fall 2016 Instructor: Marc Pomplun Midterm Exam Sample Solutions No books, no notes, and no calculators are allowed. Question 1: out of points Question
Total 100. The American University in Cairo Computer Science & Engineering Department CSCE 106. Dr. Khalil Exam II Fall 2011
 The American University in Cairo Computer Science & Engineering Department CSCE 106 Dr. Khalil Exam II Fall 2011 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Form I Section No.: ( ) EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS *
The American University in Cairo Computer Science & Engineering Department CSCE 106 Dr. Khalil Exam II Fall 2011 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Form I Section No.: ( ) EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS *
A Freshman C++ Programming Course
 A Freshman C++ Programming Course Dr. Ali H. Al-Saedi Al-Mustansiria University, Baghdad, Iraq January 2, 2018 1 Number Systems and Base Conversions Before studying any programming languages, students
A Freshman C++ Programming Course Dr. Ali H. Al-Saedi Al-Mustansiria University, Baghdad, Iraq January 2, 2018 1 Number Systems and Base Conversions Before studying any programming languages, students
! A program is a set of instructions that the. ! It must be translated. ! Variable: portion of memory that stores a value. char
 Week 1 Operators, Data Types & I/O Gaddis: Chapters 1, 2, 3 CS 5301 Fall 2016 Jill Seaman Programming A program is a set of instructions that the computer follows to perform a task It must be translated
Week 1 Operators, Data Types & I/O Gaddis: Chapters 1, 2, 3 CS 5301 Fall 2016 Jill Seaman Programming A program is a set of instructions that the computer follows to perform a task It must be translated
The American University in Cairo Computer Science & Engineering Department CSCE Dr. KHALIL Exam II Spring 2010
 The American University in Cairo Computer Science & Engineering Department CSCE 106-08 Dr. KHALIL Exam II Spring 2010 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Form - I EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS * Do not turn
The American University in Cairo Computer Science & Engineering Department CSCE 106-08 Dr. KHALIL Exam II Spring 2010 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Form - I EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS * Do not turn
Computer Programming : C++
 The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2003 Muath i.alnabris Computer Programming : C++ Experiment #1 Basics Contents Structure of a program
The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2003 Muath i.alnabris Computer Programming : C++ Experiment #1 Basics Contents Structure of a program
(6) The specification of a name with its type in a program. (7) Some memory that holds a value of a given type.
 CS 7A - Fall 2016 - Midterm 1 10/20/16 Write responses to questions 1 and 2 on this paper or attach additional sheets, as necessary For all subsequent problems, use separate paper Do not use a computer
CS 7A - Fall 2016 - Midterm 1 10/20/16 Write responses to questions 1 and 2 on this paper or attach additional sheets, as necessary For all subsequent problems, use separate paper Do not use a computer
CSC 126 FINAL EXAMINATION FINAL Spring 2012 B. Name (last, First) Instructor. Total Possible. Received
 CSC 126 FINAL EXAMINATION FINAL Spring 2012 B Name (last, First) Instructor Question # Total Possible Total Received 1. 8 2. 8 3. 8 4. 14 5. 18 6. 10 7. 16 8. 18 TOTAL 100 Final Exam/ Page 2 1) (8 points)
CSC 126 FINAL EXAMINATION FINAL Spring 2012 B Name (last, First) Instructor Question # Total Possible Total Received 1. 8 2. 8 3. 8 4. 14 5. 18 6. 10 7. 16 8. 18 TOTAL 100 Final Exam/ Page 2 1) (8 points)
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Third Edition
 C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Third Edition Chapter 2: Basic Elements of C++ Objectives (continued) Become familiar with the use of increment and decrement operators Examine
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Third Edition Chapter 2: Basic Elements of C++ Objectives (continued) Become familiar with the use of increment and decrement operators Examine
CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ C++ Basics
 CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ C++ Basics Integers Basic Types Can be short, long, or just plain int C++ does not define the size of them other than short
CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ C++ Basics Integers Basic Types Can be short, long, or just plain int C++ does not define the size of them other than short
do { statements } while (condition);
 Topic 4 1. The while loop 2. Problem solving: hand-tracing 3. The for loop 4. The do loop 5. Processing input 6. Problem solving: storyboards 7. Common loop algorithms 8. Nested loops 9. Problem solving:
Topic 4 1. The while loop 2. Problem solving: hand-tracing 3. The for loop 4. The do loop 5. Processing input 6. Problem solving: storyboards 7. Common loop algorithms 8. Nested loops 9. Problem solving:
A SHORT COURSE ON C++
 Introduction to A SHORT COURSE ON School of Mathematics Semester 1 2008 Introduction to OUTLINE 1 INTRODUCTION TO 2 FLOW CONTROL AND FUNCTIONS If Else Looping Functions Cmath Library Prototyping Introduction
Introduction to A SHORT COURSE ON School of Mathematics Semester 1 2008 Introduction to OUTLINE 1 INTRODUCTION TO 2 FLOW CONTROL AND FUNCTIONS If Else Looping Functions Cmath Library Prototyping Introduction
Exam 1 Practice CSE 232 Summer 2018 (1) DO NOT OPEN YOUR EXAM BOOKLET UNTIL YOU HAVE BEEN TOLD TO BEGIN.
 Name: Section: INSTRUCTIONS: (1) DO NOT OPEN YOUR EXAM BOOKLET UNTIL YOU HAVE BEEN TOLD TO BEGIN. (2) The total for the exam is 100 points (3) There are 8 pages with 32 problem; 15 multiple-choice, 15
Name: Section: INSTRUCTIONS: (1) DO NOT OPEN YOUR EXAM BOOKLET UNTIL YOU HAVE BEEN TOLD TO BEGIN. (2) The total for the exam is 100 points (3) There are 8 pages with 32 problem; 15 multiple-choice, 15
The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineeringt CSCI &09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2009
 The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineeringt CSCI 106-05&09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2009 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Form I Section No.: EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS
The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineeringt CSCI 106-05&09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2009 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Form I Section No.: EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS
Computer Science II Lecture 1 Introduction and Background
 Computer Science II Lecture 1 Introduction and Background Discussion of Syllabus Instructor, TAs, office hours Course web site, http://www.cs.rpi.edu/courses/fall04/cs2, will be up soon Course emphasis,
Computer Science II Lecture 1 Introduction and Background Discussion of Syllabus Instructor, TAs, office hours Course web site, http://www.cs.rpi.edu/courses/fall04/cs2, will be up soon Course emphasis,
Chapter 3 Problem Solving and the Computer
 Chapter 3 Problem Solving and the Computer An algorithm is a step-by-step operations that the CPU must execute in order to solve a problem, or to perform that task. A program is the specification of an
Chapter 3 Problem Solving and the Computer An algorithm is a step-by-step operations that the CPU must execute in order to solve a problem, or to perform that task. A program is the specification of an
Local and Global Variables
 Lecture 10 Local and Global Variables Nearly every programming language has a concept of local variable. As long as two functions mind their own data, as it were, they won t interfere with each other.
Lecture 10 Local and Global Variables Nearly every programming language has a concept of local variable. As long as two functions mind their own data, as it were, they won t interfere with each other.
Module Contact: Dr Anthony J. Bagnall, CMP Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 2
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2014/15 PROGRAMMING 2 CMP-5015Y Time allowed: 2 hours Answer four questions. All questions carry equal weight. Notes are
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2014/15 PROGRAMMING 2 CMP-5015Y Time allowed: 2 hours Answer four questions. All questions carry equal weight. Notes are
Module Contact: Dr Geoff McKeown, CMP Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 2
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2012-13 PROGRAMMING 1 CMPC1M0Y Time allowed: 2 hours Section A (Attempt all questions: 80 marks) Section B (Attempt one
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2012-13 PROGRAMMING 1 CMPC1M0Y Time allowed: 2 hours Section A (Attempt all questions: 80 marks) Section B (Attempt one
The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineering CSCI &09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2011
 The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineering CSCI 106-07&09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2011 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Form I Section No.: EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS
The American University in Cairo Department of Computer Science & Engineering CSCI 106-07&09 Dr. KHALIL Exam-I Fall 2011 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:... Form I Section No.: EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS
Perfect square. #include<iostream> using namespace std; int main(){ int a=1; int square; while(true){ } cout<<square<<endl; }
 Lab 3 Kaikai Bian Perfect square #include using namespace std; int main(){ int a=1; int square; while(true){ } cout
Lab 3 Kaikai Bian Perfect square #include using namespace std; int main(){ int a=1; int square; while(true){ } cout
The American University in Cairo Computer Science & Engineering Department CSCE 106 Fundamentals of Computer Science
 The American University in Cairo Computer Science & Engineering Department CSCE 106 Fundamentals of Computer Science Instructor: Dr. Howaida Ismail Final Exam Spring 2013 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:...
The American University in Cairo Computer Science & Engineering Department CSCE 106 Fundamentals of Computer Science Instructor: Dr. Howaida Ismail Final Exam Spring 2013 Last Name :... ID:... First Name:...
Study Guide for Test 2
 Study Guide for Test 2 Topics: decisions, loops, arrays, c-strings, linux Material Selected from: Chapters 4, 5, 6, 7, 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.4 Examples 14 33 Assignments 4 8 Any syntax errors are unintentional
Study Guide for Test 2 Topics: decisions, loops, arrays, c-strings, linux Material Selected from: Chapters 4, 5, 6, 7, 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.4 Examples 14 33 Assignments 4 8 Any syntax errors are unintentional
CS 101 Computer Programming and utilization. Dr Deepak B Phatak Subrao Nilekani Chair Professor Department of CSE, Kanwal Rekhi Building IIT Bombay
 CS 101 Computer Programming and utilization Dr Deepak B Phatak Subrao Nilekani Chair Professor Department of CSE, Kanwal Rekhi Building Bombay Lecture 4, Conditional execution of instructions Friday, August
CS 101 Computer Programming and utilization Dr Deepak B Phatak Subrao Nilekani Chair Professor Department of CSE, Kanwal Rekhi Building Bombay Lecture 4, Conditional execution of instructions Friday, August
VARIABLE, OPERATOR AND EXPRESSION [SET 1]
![VARIABLE, OPERATOR AND EXPRESSION [SET 1] VARIABLE, OPERATOR AND EXPRESSION [SET 1]](/thumbs/77/74785529.jpg) VARIABLE, OPERATOR AND EXPRESSION Question 1 Write a program to print HELLO WORLD on screen. Write a program to display the following output using a single cout statement. Subject Marks Mathematics 90
VARIABLE, OPERATOR AND EXPRESSION Question 1 Write a program to print HELLO WORLD on screen. Write a program to display the following output using a single cout statement. Subject Marks Mathematics 90
Jordan University of Science & Technology Department of Computer Science CS 211 Exam #1 (23/10/2010) -- Form A
 Jordan University of Science & Technology Department of Computer Science CS 211 Exam #1 (23/10/2010) -- Form A Name: ID#: Section #: Day & Time: Instructor: Answer all questions as indicated. Closed book/closed
Jordan University of Science & Technology Department of Computer Science CS 211 Exam #1 (23/10/2010) -- Form A Name: ID#: Section #: Day & Time: Instructor: Answer all questions as indicated. Closed book/closed
CS 105 Lab As a review of what we did last week a. What are two ways in which the Python shell is useful to us?
 1 CS 105 Lab 3 The purpose of this lab is to practice the techniques of making choices and looping. Before you begin, please be sure that you understand the following concepts that we went over in class:
1 CS 105 Lab 3 The purpose of this lab is to practice the techniques of making choices and looping. Before you begin, please be sure that you understand the following concepts that we went over in class:
6.096 Introduction to C++ January (IAP) 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.096 Introduction to C++ January (IAP) 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Welcome to 6.096 Lecture
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.096 Introduction to C++ January (IAP) 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Welcome to 6.096 Lecture
Agenda. The main body and cout. Fundamental data types. Declarations and definitions. Control structures
 The main body and cout Agenda 1 Fundamental data types Declarations and definitions Control structures References, pass-by-value vs pass-by-references The main body and cout 2 C++ IS AN OO EXTENSION OF
The main body and cout Agenda 1 Fundamental data types Declarations and definitions Control structures References, pass-by-value vs pass-by-references The main body and cout 2 C++ IS AN OO EXTENSION OF
o Counter and sentinel controlled loops o Formatting output o Type casting o Top-down, stepwise refinement
 Last Time Let s all Repeat Together 10/3/05 CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 1 We covered o Counter and sentinel controlled loops o Formatting output Today we will o Type casting o Top-down, stepwise
Last Time Let s all Repeat Together 10/3/05 CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 1 We covered o Counter and sentinel controlled loops o Formatting output Today we will o Type casting o Top-down, stepwise
Class 2: Variables and Memory. Laura Marik Spring 2012 C++ Course Notes (Provided by Jason Minski)
 Class 2: Variables and Memory Variables A variable is a value that is stored in memory It can be numeric or a character C++ needs to be told what type it is before it can store it in memory It also needs
Class 2: Variables and Memory Variables A variable is a value that is stored in memory It can be numeric or a character C++ needs to be told what type it is before it can store it in memory It also needs
Programming Language. Functions. Eng. Anis Nazer First Semester
 Programming Language Functions Eng. Anis Nazer First Semester 2016-2017 Definitions Function : a set of statements that are written once, and can be executed upon request Functions are separate entities
Programming Language Functions Eng. Anis Nazer First Semester 2016-2017 Definitions Function : a set of statements that are written once, and can be executed upon request Functions are separate entities
6. Control Statements II
 Visibility Declaration in a block is not visible outside of the block. 6. Control Statements II Visibility, Local Variables, While Statement, Do Statement, Jump Statements main block int main () int i
Visibility Declaration in a block is not visible outside of the block. 6. Control Statements II Visibility, Local Variables, While Statement, Do Statement, Jump Statements main block int main () int i
Title As It Is In the Proceedings Include Only If Paper Has a Subtitle. F. Author S. Another Freie Universität Berlin
 Title As It Is In the Proceedings Include Only If Paper Has a Subtitle F. Author S. Another Freie Universität Berlin Conference on Fabulous Presentations 2003 Outline Motivation The Basic Problem That
Title As It Is In the Proceedings Include Only If Paper Has a Subtitle F. Author S. Another Freie Universität Berlin Conference on Fabulous Presentations 2003 Outline Motivation The Basic Problem That
CSC 126 FINAL EXAMINATION Spring Total Possible TOTAL 100
 CSC 126 FINAL EXAMINATION Spring 2011 Version A Name (Last, First) Your Instructor Question # Total Possible 1. 10 Total Received 2. 15 3. 15 4. 10 5. 10 6. 10 7. 10 8. 20 TOTAL 100 Name: Sp 11 Page 2
CSC 126 FINAL EXAMINATION Spring 2011 Version A Name (Last, First) Your Instructor Question # Total Possible 1. 10 Total Received 2. 15 3. 15 4. 10 5. 10 6. 10 7. 10 8. 20 TOTAL 100 Name: Sp 11 Page 2
CSCE 110 Dr. Amr Goneid Exercise Sheet (7): Exercises on Recursion (Solutions)
 CSCE 110 Dr. Amr Goneid Exercise Sheet (7): Exercises on Recursion (Solutions) Consider the following recursive function: int what ( int x, int y) if (x > y) return what (x-y, y); else if (y > x) return
CSCE 110 Dr. Amr Goneid Exercise Sheet (7): Exercises on Recursion (Solutions) Consider the following recursive function: int what ( int x, int y) if (x > y) return what (x-y, y); else if (y > x) return
Multiple Choice (Questions 1 13) 26 Points Select all correct answers (multiple correct answers are possible)
 Name Closed notes, book and neighbor. If you have any questions ask them. Notes: Segment of code necessary C++ statements to perform the action described not a complete program Program a complete C++ program
Name Closed notes, book and neighbor. If you have any questions ask them. Notes: Segment of code necessary C++ statements to perform the action described not a complete program Program a complete C++ program
Module Contact: Dr Dan Smith, CMP Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 1
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2015/16 INFORMATION RETRIEVAL CMP-5036A/CMP-6008A Time allowed: 2 hours Answer any TWO questions. Notes are not permitted
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2015/16 INFORMATION RETRIEVAL CMP-5036A/CMP-6008A Time allowed: 2 hours Answer any TWO questions. Notes are not permitted
CSCI 111 Midterm 1, version A Exam Fall Solutions 09.00am 09.50am, Tuesday, October 13, 2015
 QUEENS COLLEGE Department of Computer Science CSCI 111 Midterm 1, version A Exam Fall 2015 10.13.15 Solutions 09.00am 09.50am, Tuesday, October 13, 2015 Problem 1 Write a complete C++ program that does
QUEENS COLLEGE Department of Computer Science CSCI 111 Midterm 1, version A Exam Fall 2015 10.13.15 Solutions 09.00am 09.50am, Tuesday, October 13, 2015 Problem 1 Write a complete C++ program that does
By the end of this section you should: Understand what the variables are and why they are used. Use C++ built in data types to create program
 1 By the end of this section you should: Understand what the variables are and why they are used. Use C++ built in data types to create program variables. Apply C++ syntax rules to declare variables, initialize
1 By the end of this section you should: Understand what the variables are and why they are used. Use C++ built in data types to create program variables. Apply C++ syntax rules to declare variables, initialize
Superior University. Department of Electrical Engineering CS-115. Computing Fundamentals. Experiment No.6
 Superior University Department of Electrical Engineering CS-115 Computing Fundamentals Experiment No.6 Pre-Defined Functions, User-Defined Function: Value Returning Functions Prepared for By: Name: ID:
Superior University Department of Electrical Engineering CS-115 Computing Fundamentals Experiment No.6 Pre-Defined Functions, User-Defined Function: Value Returning Functions Prepared for By: Name: ID:
Basic program The following is a basic program in C++; Basic C++ Source Code Compiler Object Code Linker (with libraries) Executable
 Basic C++ Overview C++ is a version of the older C programming language. This is a language that is used for a wide variety of applications and which has a mature base of compilers and libraries. C++ is
Basic C++ Overview C++ is a version of the older C programming language. This is a language that is used for a wide variety of applications and which has a mature base of compilers and libraries. C++ is
Module Contact: Dr Geoff McKeown, CMP Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 1
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013-14 PROGRAMMING FOR NON-SPECIALISTS CMPC2X02 Time allowed: 2 hours Section A (Attempt all questions: 80 marks) Section
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013-14 PROGRAMMING FOR NON-SPECIALISTS CMPC2X02 Time allowed: 2 hours Section A (Attempt all questions: 80 marks) Section
Subprograms. Introduction to Programming (in C++) Subprograms: procedures and functions. Subprograms. Subprograms. Functions are defined as follows:
 Introduction to Programming (in C++) : procedures and functions Programming languages, in particular C++, not only provide a set of basic operations and statements, but also a means to define our own operations
Introduction to Programming (in C++) : procedures and functions Programming languages, in particular C++, not only provide a set of basic operations and statements, but also a means to define our own operations
CSci 1113, Fall 2015 Lab Exercise 4 (Week 5): Write Your Own Functions. User Defined Functions
 CSci 1113, Fall 2015 Lab Exercise 4 (Week 5): Write Your Own Functions User Defined Functions In previous labs, you've encountered useful functions, such as sqrt() and pow(), that were created by other
CSci 1113, Fall 2015 Lab Exercise 4 (Week 5): Write Your Own Functions User Defined Functions In previous labs, you've encountered useful functions, such as sqrt() and pow(), that were created by other
Module Operator Overloading and Type Conversion. Table of Contents
 1 Module - 33 Operator Overloading and Type Conversion Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Operator Overloading 3. this pointer 4. Overloading Unary Operators 5. Overloading Binary Operators 6. Overloading
1 Module - 33 Operator Overloading and Type Conversion Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Operator Overloading 3. this pointer 4. Overloading Unary Operators 5. Overloading Binary Operators 6. Overloading
CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS. Dr. Shady Yehia Elmashad
 CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Dr. Shady Yehia Elmashad Outline 1. Introduction 2. Program Components in C++ 3. Math Library Functions 4. Functions 5. Function Definitions 6. Function Prototypes 7. Header Files 8.
CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Dr. Shady Yehia Elmashad Outline 1. Introduction 2. Program Components in C++ 3. Math Library Functions 4. Functions 5. Function Definitions 6. Function Prototypes 7. Header Files 8.
Introduction to Programming I COS1511 School of Computing Revision Notes
 Introduction to Programming I COS1511 School of Computing Revision Notes UNISA 2018 1 Introduction Some key basic principles to remember: Apply the BODMAS rules of Mathematics for all calculations; The
Introduction to Programming I COS1511 School of Computing Revision Notes UNISA 2018 1 Introduction Some key basic principles to remember: Apply the BODMAS rules of Mathematics for all calculations; The
CMSC 202 Midterm Exam 1 Fall 2015
 1. (15 points) There are six logic or syntax errors in the following program; find five of them. Circle each of the five errors you find and write the line number and correction in the space provided below.
1. (15 points) There are six logic or syntax errors in the following program; find five of them. Circle each of the five errors you find and write the line number and correction in the space provided below.
CSCE Practice Midterm. Data Types
 CSCE 2004 - Practice Midterm This midterm exam was given in class several years ago. Work each of the following questions on your own. Once you are done, check your answers. For any questions whose answers
CSCE 2004 - Practice Midterm This midterm exam was given in class several years ago. Work each of the following questions on your own. Once you are done, check your answers. For any questions whose answers
Module Contact: Dr Geoff McKeown, CMP Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 1
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2015-16 PROGRAMMING 1 CMP-4008Y Time allowed: 2 hours Section A (Attempt all questions: 80 marks) Section B (Attempt one
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2015-16 PROGRAMMING 1 CMP-4008Y Time allowed: 2 hours Section A (Attempt all questions: 80 marks) Section B (Attempt one
Addis Ababa University, Amist Kilo July 5, 2011 Algorithms and Programming for High Schoolers. Lab 2
 Addis Ababa University, Amist Kilo July 5, 2011 Algorithms and Programming for High Schoolers Lab 2 Exercise 1: In my high school, students were given letter grades based on their numerical scores. Here
Addis Ababa University, Amist Kilo July 5, 2011 Algorithms and Programming for High Schoolers Lab 2 Exercise 1: In my high school, students were given letter grades based on their numerical scores. Here
6.1. Chapter 6: What Is A Function? Why Functions? Introduction to Functions
 Chapter 6: 6.1 Functions Introduction to Functions What Is A Function? Why Functions? We ve been using functions ( e.g. main() ). C++ program consists of one or more functions Function: a collection of
Chapter 6: 6.1 Functions Introduction to Functions What Is A Function? Why Functions? We ve been using functions ( e.g. main() ). C++ program consists of one or more functions Function: a collection of
Programming. C++ Basics
 Programming C++ Basics Introduction to C++ C is a programming language developed in the 1970s with the UNIX operating system C programs are efficient and portable across different hardware platforms C++
Programming C++ Basics Introduction to C++ C is a programming language developed in the 1970s with the UNIX operating system C programs are efficient and portable across different hardware platforms C++
Function Overloading
 Function Overloading C++ supports writing more than one function with the same name but different argument lists How does the compiler know which one the programmer is calling? They have different signatures
Function Overloading C++ supports writing more than one function with the same name but different argument lists How does the compiler know which one the programmer is calling? They have different signatures
BEng (Hons) Electronic Engineering. BEng (Hons) Telecommunications. Examinations for / Semester 2
 BEng (Hons) Electronic Engineering BEng (Hons) Telecommunications Cohort: BEE/16B/FT & BTEL/16B/FT Examinations for 2016-2017 / Semester 2 Resit Examinations for BTEL/15B/FT, BEE/13B/FT, BTEL/14B/FT &
BEng (Hons) Electronic Engineering BEng (Hons) Telecommunications Cohort: BEE/16B/FT & BTEL/16B/FT Examinations for 2016-2017 / Semester 2 Resit Examinations for BTEL/15B/FT, BEE/13B/FT, BTEL/14B/FT &
5.1. Chapter 5: The Increment and Decrement Operators. The Increment and Decrement Operators. The Increment and Decrement Operators
 Chapter 5: 5.1 Looping The Increment and Decrement Operators The Increment and Decrement Operators The Increment and Decrement Operators ++ is the increment operator. It adds one to a variable. val++;
Chapter 5: 5.1 Looping The Increment and Decrement Operators The Increment and Decrement Operators The Increment and Decrement Operators ++ is the increment operator. It adds one to a variable. val++;
Functions. Function Prototypes. Function prototype is needed if the function call comes before the function definition in the program.
 Functions Functions are defined as follows: return-value-type function-name( parameter-list ) { local declarations and statements Example: int square( int y ) { return y * y; 1 Function Prototypes Function
Functions Functions are defined as follows: return-value-type function-name( parameter-list ) { local declarations and statements Example: int square( int y ) { return y * y; 1 Function Prototypes Function
Introduction to Programming EC-105. Lecture 2
 Introduction to Programming EC-105 Lecture 2 Input and Output A data stream is a sequence of data - Typically in the form of characters or numbers An input stream is data for the program to use - Typically
Introduction to Programming EC-105 Lecture 2 Input and Output A data stream is a sequence of data - Typically in the form of characters or numbers An input stream is data for the program to use - Typically
1) What of the following sets of values for A, B, C, and D would cause the string "one" to be printed?
 Instructions: This homework assignment focuses primarily on some of the basic syntax and semantics of C++. The answers to the following questions can be determined from Chapters 6 and 7 of the lecture
Instructions: This homework assignment focuses primarily on some of the basic syntax and semantics of C++. The answers to the following questions can be determined from Chapters 6 and 7 of the lecture
UNIVERSITY OF SWAZILAND SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION, JULY 2013
 UNIVERSITY OF SWAZILAND SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION, JULY 2013 Title of Paper : STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING - I Course number: CS243 Time allowed Instructions : Three (3) hours. : (1) Read all the questions in
UNIVERSITY OF SWAZILAND SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION, JULY 2013 Title of Paper : STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING - I Course number: CS243 Time allowed Instructions : Three (3) hours. : (1) Read all the questions in
UCT Algorithm Circle: Number Theory
 UCT Algorithm Circle: 7 April 2011 Outline Primes and Prime Factorisation 1 Primes and Prime Factorisation 2 3 4 Some revision (hopefully) What is a prime number? An integer greater than 1 whose only factors
UCT Algorithm Circle: 7 April 2011 Outline Primes and Prime Factorisation 1 Primes and Prime Factorisation 2 3 4 Some revision (hopefully) What is a prime number? An integer greater than 1 whose only factors
Module Contact: Dr Geoff McKeown, CMP Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 1
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2015-16 PROGRAMMING FOR APPLICATIONS CMP-4009B Time allowed: 2 hours Section A (Attempt all questions: 80 marks) Section
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2015-16 PROGRAMMING FOR APPLICATIONS CMP-4009B Time allowed: 2 hours Section A (Attempt all questions: 80 marks) Section
2.1. Chapter 2: Parts of a C++ Program. Parts of a C++ Program. Introduction to C++ Parts of a C++ Program
 Chapter 2: Introduction to C++ 2.1 Parts of a C++ Program Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley 2-1 Parts of a C++ Program Parts of a C++ Program // sample C++ program
Chapter 2: Introduction to C++ 2.1 Parts of a C++ Program Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley 2-1 Parts of a C++ Program Parts of a C++ Program // sample C++ program
Multiple Choice (Questions 1 14) 28 Points Select all correct answers (multiple correct answers are possible)
 Name Closed notes, book and neighbor. If you have any questions ask them. Notes: Segment of code necessary C++ statements to perform the action described not a complete program Program a complete C++ program
Name Closed notes, book and neighbor. If you have any questions ask them. Notes: Segment of code necessary C++ statements to perform the action described not a complete program Program a complete C++ program
Fundamentals of Programming CS-110. Lecture 2
 Fundamentals of Programming CS-110 Lecture 2 Last Lab // Example program #include using namespace std; int main() { cout
Fundamentals of Programming CS-110 Lecture 2 Last Lab // Example program #include using namespace std; int main() { cout
CSCS 261 Programming Concepts Exam 2 Fall EXAM 2 VERSION 1 Fall Points. Absolutely no electronic devices may be used during this exam.
 Name: Print legibly! Section: COMPUTER SCIENCE 261 PROGRAMMING CONCEPTS EXAM 2 VERSION 1 Fall 2014 150 Points Absolutely no electronic devices may be used during this exam. 1. No cell phones, computers,
Name: Print legibly! Section: COMPUTER SCIENCE 261 PROGRAMMING CONCEPTS EXAM 2 VERSION 1 Fall 2014 150 Points Absolutely no electronic devices may be used during this exam. 1. No cell phones, computers,
A First Program - Greeting.cpp
 C++ Basics A First Program - Greeting.cpp Preprocessor directives Function named main() indicates start of program // Program: Display greetings #include using namespace std; int main() { cout
C++ Basics A First Program - Greeting.cpp Preprocessor directives Function named main() indicates start of program // Program: Display greetings #include using namespace std; int main() { cout
Unit 3. Constants and Expressions
 1 Unit 3 Constants and Expressions 2 Review C Integer Data Types Integer Types (signed by default unsigned with optional leading keyword) C Type Bytes Bits Signed Range Unsigned Range [unsigned] char 1
1 Unit 3 Constants and Expressions 2 Review C Integer Data Types Integer Types (signed by default unsigned with optional leading keyword) C Type Bytes Bits Signed Range Unsigned Range [unsigned] char 1
Exam 2. CSI 201: Computer Science 1 Fall 2016 Professors: Shaun Ramsey and Kyle Wilson. Question Points Score Total: 80
 Exam 2 CSI 201: Computer Science 1 Fall 2016 Professors: Shaun Ramsey and Kyle Wilson Question Points Score 1 18 2 29 3 18 4 15 Total: 80 I understand that this exam is closed book and closed note and
Exam 2 CSI 201: Computer Science 1 Fall 2016 Professors: Shaun Ramsey and Kyle Wilson Question Points Score 1 18 2 29 3 18 4 15 Total: 80 I understand that this exam is closed book and closed note and
Problem Solving: Storyboards for User Interaction
 Topic 6 1. The while loop 2. Problem solving: hand-tracing 3. The for loop 4. The do loop 5. Processing input 6. Problem solving: storyboards 7. Common loop algorithms 8. Nested loops 9. Problem solving:
Topic 6 1. The while loop 2. Problem solving: hand-tracing 3. The for loop 4. The do loop 5. Processing input 6. Problem solving: storyboards 7. Common loop algorithms 8. Nested loops 9. Problem solving:
CSCS 261 Programming Concepts Exam 2 Fall EXAM 2 VERSION 1 Fall Points. Absolutely no electronic devices may be used during this exam.
 Name: Print legibly! Section: COMPUTER SCIENCE 261 PROGRAMMING CONCEPTS EXAM 2 VERSION 1 Fall 2014 150 Points Absolutely no electronic devices may be used during this exam. 1. No cell phones, computers,
Name: Print legibly! Section: COMPUTER SCIENCE 261 PROGRAMMING CONCEPTS EXAM 2 VERSION 1 Fall 2014 150 Points Absolutely no electronic devices may be used during this exam. 1. No cell phones, computers,
ME240 Computation for Mechanical Engineering. Lecture 4. C++ Data Types
 ME240 Computation for Mechanical Engineering Lecture 4 C++ Data Types Introduction In this lecture we will learn some fundamental elements of C++: Introduction Data Types Identifiers Variables Constants
ME240 Computation for Mechanical Engineering Lecture 4 C++ Data Types Introduction In this lecture we will learn some fundamental elements of C++: Introduction Data Types Identifiers Variables Constants
CSCE121: Introduction to Program Design and Concepts Practice Questions for Midterm 3
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING CSCE121: Introduction to Program Design and Concepts Practice Questions for Midterm 3 March 27, 2019 Question 1: Printing a histogram of letters Question 2:
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING CSCE121: Introduction to Program Design and Concepts Practice Questions for Midterm 3 March 27, 2019 Question 1: Printing a histogram of letters Question 2:
The following is a typical execution run of this program:
 et181:endterm test, fall 2010 (200 points) name: Closed notes, open book, two hour test. You may use any graded program of your choice. There are four sections on eight pages. Each section is worth 50
et181:endterm test, fall 2010 (200 points) name: Closed notes, open book, two hour test. You may use any graded program of your choice. There are four sections on eight pages. Each section is worth 50
Module Contact: Dr Geoff McKeown, CMP Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 1
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2015-16 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS CMP-5014Y Time allowed: 3 hours Section A (Attempt any 4 questions: 60 marks) Section
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2015-16 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS CMP-5014Y Time allowed: 3 hours Section A (Attempt any 4 questions: 60 marks) Section
Computer Programming
 Computer Programming Dr. Deepak B Phatak Dr. Supratik Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering Session: Character Strings Dr. Deepak B. Phatak & Dr. Supratik Chakraborty, 1 Quick Recap
Computer Programming Dr. Deepak B Phatak Dr. Supratik Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering Session: Character Strings Dr. Deepak B. Phatak & Dr. Supratik Chakraborty, 1 Quick Recap
CSci 1113 Final. Name: Student ID:
 CSci 1113 Final Name: Student ID: Instructions: Please pick and answer any 10 of the 12 problems for a total of 100 points. If you answer more than 10 problems, only the first 10 will be graded. The time
CSci 1113 Final Name: Student ID: Instructions: Please pick and answer any 10 of the 12 problems for a total of 100 points. If you answer more than 10 problems, only the first 10 will be graded. The time
Chapter 2: Overview of C++
 Chapter 2: Overview of C++ Problem Solving, Abstraction, and Design using C++ 6e by Frank L. Friedman and Elliot B. Koffman C++ Background Introduced by Bjarne Stroustrup of AT&T s Bell Laboratories in
Chapter 2: Overview of C++ Problem Solving, Abstraction, and Design using C++ 6e by Frank L. Friedman and Elliot B. Koffman C++ Background Introduced by Bjarne Stroustrup of AT&T s Bell Laboratories in
Laboratory 0 Week 0 Advanced Structured Programming An Introduction to Visual Studio and C++
 Laboratory 0 Week 0 Advanced Structured Programming An Introduction to Visual Studio and C++ 0.1 Introduction This is a session to familiarize working with the Visual Studio development environment. It
Laboratory 0 Week 0 Advanced Structured Programming An Introduction to Visual Studio and C++ 0.1 Introduction This is a session to familiarize working with the Visual Studio development environment. It
Scientific Computing
 Scientific Computing Martin Lotz School of Mathematics The University of Manchester Lecture 1, September 22, 2014 Outline Course Overview Programming Basics The C++ Programming Language Outline Course
Scientific Computing Martin Lotz School of Mathematics The University of Manchester Lecture 1, September 22, 2014 Outline Course Overview Programming Basics The C++ Programming Language Outline Course
Computer Programming. Basic Control Flow - Loops. Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons
 Computer Programming Basic Control Flow - Loops Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons Objectives To learn about the three types of loops: while for do To avoid infinite
Computer Programming Basic Control Flow - Loops Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons Objectives To learn about the three types of loops: while for do To avoid infinite
Discussion 1H Notes (Week 3, April 14) TA: Brian Choi Section Webpage:
 Discussion 1H Notes (Week 3, April 14) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs31 More on Arithmetic Expressions The following two are equivalent:! x = x + 5;
Discussion 1H Notes (Week 3, April 14) TA: Brian Choi (schoi@cs.ucla.edu) Section Webpage: http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~schoi/cs31 More on Arithmetic Expressions The following two are equivalent:! x = x + 5;
