Document Conventions nc. Page 2-4, 2.1.6: While MCBASE normally points to external RAM, it is permissible to set it up that some or all BDs will actua
|
|
|
- Moris Ray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Application Note AN2289/D Rev. 0, 6/2002 MPC8xx QMC Usage Advisory Heinz Wrobel Freescale GmbH, Munich Part I Introduction QUICC multichannel controller (QMC), support in some of the MPC8xx family members is quite powerful. However, there are a few issues in setting up a working and stable QMC setup that should be well noted. This document should be used in addition to the MC68360 QMC Supplement to MC68360 and MPC860 Users Manuals (MC68MH360UM/D), hereafter referred to as the QMC manual. It will highlight some issues and add clarifications to the manual. The page numbers and chapters mentioned refer to the QMC manual unless otherwise specified. Note that the information contained in this document also applies to the QUICC MC68MH360, even though references are given based on the MPC8xx family. 1.1 Document Conventions In the MPC8xx, PowerPC architecture based microprocessor, the MSB is labeled 0, the LSB is labeled 31. The standard for RAMs, ROMs, etc., is that the MSB is labeled as the highest number, i.e., 31 or 15, and the LSB is labeled 0. The notation x:y is used to denote bits numbered x to y in that order. References to the MPC860 User s Manual refer to the MPC860UM/AD Revision 1. Binary numbers have a 0b prefix. Hex values have a 0x prefix. Part II QMC Manual Clarifications and Corrections Page 2-1, Figure 2-1: For the MPC860, the Parameter RAM refers to the four individual 256 byte pages of the four SCCs, resulting in a total of 1KB. Page 2-2, Figure 2-2: The figure shows correctly how the channel specific parameters start at the Dual-Port RAM base. Note that on the MPC860, you would normally lose I 2 C or SPI when using QMC. If you activate the microcode patch from the Freescale web site to relocate I 2 C/SPI parameters, the channel parameter base will not shift. You will not be able to set up or use channels 0 to 7 or channels 60 to 63. Page 2-3, 2.1.2: The note is not fully correct. QMC only uses 0xAC bytes. You can use the microcode patch to relocate I 2 C/SPI parameters.
2 Document Conventions nc. Page 2-4, 2.1.6: While MCBASE normally points to external RAM, it is permissible to set it up that some or all BDs will actually be placed within free areas of the DPRAM. This may save valuable access time if external memory is slow. Page 2-6, Table 2-1: The description for GRFTHR does not recommend a value. You should normally set it to 1 (one) to get an interrupt per frame received. Page 2-18, Figure 2-9: Where the interrupt table entry is shown, bit 4 should be included in the description of the channel number field. Page 2-22, Table 2-11: Note the description of how to use the POL bit. Be careful to follow it. Page 3-1, Figure 3-1: On the MPC8xx, 64 channels are supported. The channel number actually starts at bit 8. Page 3-2, 3.2: The STOP RECEIVE command is immediate. It will stop the channel right away and in effect freeze activity on this channel. It will not wait for a frame reception to be finished. As the current buffer descriptor can remain open if a reception was in progress, you can get errors on this buffer once you restart reception again. When restarting, set ZDSTATE first and RSTATE afterwards. Page 4-2, Chapter 4: The NOTE is very important but not completely correct. After you have handled a table entry you must make sure to clear everything but the wrap bit. Do not just clear the interrupt bits or you may confuse your own software with incorrect channel interrupts. Page 4-2, 4.1: The fourth paragraph is misleading, stating the CPM crashes due to an overload of serial data. The CPM does not crash in the common sense of the word. Rather, it loses track of the mapping of serial data to QMC channels, so it has to cause a global error and halt QMC activity until the user software intervenes. Note that a problem like this typically indicates a very basic performance related design problem. Note well that latency is very important. Overloading of the QMC via the serial line should not occur if you follow the guidelines in chapter 8 about QMC performance. Page 4-4, Figure 4-2, Table 4-1. Page 4-5, Figure 4-3: In the MPC8xx family, the bits are not 0 to 7, but 8 to 15. The event information is contained in the lower byte of the SCC event and mask registers. Page 4-4, Table 4-1: The IQOV description has a very cryptic last paragraph. This bit should be cleared immediately after reading the SCCE and recognizing this condition by writing a 1 to its location in the SCCE. If this condition occurs, the interrupt last received is lost. It does not overwrite the first entry that is still to be handled by the CPU. The GOV description should refer to an overrun in the SCC s receiver, as it doesn t make sense on the transmitter. Page 4-5, Figure 4-4: The channel number really starts already at bit 4 for the MPC8xx to reflect the 64 channel capability. Page 4-6, Table 4-2: Change the description of bits 4-9 to agree with the changes on the previous page concerning the 64 channel capability. Page 5-1, 5: Please note that the CPM or s the various status bits into the BD. You must clear all the status bits generated by the CPM before (re-)enabling the BD or you may confuse your own software with left over old status values. Page 5-4, 5.1: Please carefully note this page and the last paragraph to avoid overwritten memory beyond the end of a buffer. The documentation is not quite correct, though. The XTRA information shown in Figure 5-2 is written as 32 bit word. Under special, but quite possible circumstances the XTRA data shown in Figure 5-2 will be written four bytes furtther than indicated. This means that you absolutely must allocate MRBLR+8 bytes for each buffer area for 2 MPC8xx QMC Usage Advisory
3 nc. Document Conventions QMC. Again, you need to allocate eight extra bytes rather than only four as described in the manual to be safe. If you do not allocate the extra eight bytes, you risk that these memory area can be overwritten with XTRA info. Page 6-12, 6.2: The QMC examples contain a bad error. The TSA is enabled before the SI-RAM has been set up. Ensure the correct order is used in your code. Page 9-2, 9.2: The first paragraph is not quite correct. It is not possible to route a single timeslot to all four SCCs as shown in Figure 9-1. A timeslot can only be routed to one SCC by one TSA. To route a single timeslot to two SCCs at the same time, you have to connect both TSAs to the same TDM line and set up separate mappings for this timeslot. This allows you to do subchanneling for at most two channels by using two SCCs. Note that as of this writing, the MSC microcode is available for sale and documentation can be found on the Freescale webpage. Please contact your Freescale representative for more information. Part III Notes on QMC Interrupt Handling The recommended method to handle interrupts by the QMC is to first read in the SCCE register. Write back immediately all the bits that you recognize and handle. This clears the respective interrupt events. It is, e.g., incorrect to first handle all the new interrupt table entries and clear GINT afterwards. To avoid deadlocks in your software, you must clear the recognized interrupt bits in the SCCE before actually handling the interrupt entries. Clear only the bits that you handle. Never clear bits for events in the SCCE that you don t handle. This facilitates debugging. When you get a new GINT event, you should always handle all the new entries in the queue, not just a single one. After handling an entry, make sure that the entry is completely cleared out with the exception of the Wrap bit. Any entry that does not have the Valid bit set must be completely cleared out, including the channel number. If you don t clear out all the entries on startup or after handling them, these bits will confuse your software when the entry is used again. QMC will only OR in new bits and numbers. It will not overwrite and clear bits that were set previously. Part IV Notes on QMC Performance and SCC Usage NOTE The information in this chapter is for your information only to illustrate why the QMC behaves in a certain way. Freescale can not recommend that you base actual designs on this information as there are various subtle things that can go wrong if the QMC is used in creative ways. So be careful what you do with the knowledge outlined below. On a 50 MHz 860, QMC is rated for a total of 4.1 Mbps of traffic to be distributed over 64 channels. As a general hint, QMC is best used when each 8 bit timeslot handled by an SCC represents 64 Kbps. To further reduce peak load, spreading the QMC load over two SCCs is recommended as described in chapter 2.3 of the manual to make use of SCC FIFOs to avoid bursts of data to be handled by the CPM. Note that, due to its larger FIFO size and implementation as described below, SCC1 alone performs better in borderline conditions than both SCC2 and SCC3 would perform in a spreaded setup. So in general, SCC1 would be first choice for QMC, and spreading load over the other SCCs would be second choice. MPC8xx QMC Usage Advisory 3
4 Document Conventions nc. With the current implementation of the 860 it is possible, but definitely not recommended, to exceed the 4.1Mbps line rate with certain restrictions if, on average, the data rate from the TSA to the SCC does not exceed the upper performance limit for QMC. If you plan to do this anyway, you should definitely contact your Freescale support before proceeding. This can be achieved by having burst data to the SCCs or by spreading out single TSA timeslot routing to have silent times for the SCC to get the required average rate. The SCC FIFOs will take up the data bursts and leave the QMC microcode in the CPM time to actually process the data. Note however, that you can not simply take the FIFO size and assume that data bursts of that size will be handled correctly. There are two FIFOs per SCC to take into account. The RX FIFO could theoretically be filled completely with a burst of data if enough silence follows to have the microcode process the data in the FIFO. The TX FIFO, however, must be treated very carefully. The microcode must always be able to fill data, flags, or idles into the TX FIFO so that there is no FIFO underrun when the FIFO contents are put on the line via the TSA. You can consider the maximum QMC bit rate performance to be the possible fill rate of the TX FIFO by the microcode. One additional issue is that there can be a certain delay of >8 CPU clocks from the start of the microcode until the first data can be handled. If the line rate exceeds the fill rate, you need to be aware of a feature in the QMC called load balancing. Certain operations in the QMC, like opening BDs, may take a significant amount of time as can be seen in chapter 8.3 of the manual. These operations will only be started by the microcode if the TX FIFO is filled beyond a certain threshold. If it is not, the microcode will fill idles or flags instead into the FIFO as configured to keep the channel on the line alive. For the 32 byte FIFO in SCC1, this threshold is set at 16 bytes. For the other SCCs with 16 byte FIFO, the threshold is set at 12 bytes. If these thresholds are not exceeded, the QMC will not open TX BDs and you will only see idles/flags on the line. The QMC works with 32 bit granularity when accessing the FIFO, i.e, it always reads or writes four bytes at a time internally. This granularity is important when thinking about the thresholds. This means that for SCC1 you could theoretically have a burst of 16 bytes length and for the other SCCs a burst of 3 bytes going out to the TSA. Another few bytes would already empty the TX FIFO to the threshold. On the other hand, the microcode will already start to process data after the initial startup while the FIFO data goes. With the microcode start up delay taken into account, this means that, e.g., for a 25MHz CPU and 8Mbps line rate, anything beyond 3 bytes burst on SCC2-4 would not work as expected. On SCC1, there is enough time for the microcode to start data processing in the background for larger bursts. The internal CPM priority handling and execution times mean that you should leave a healthy margin above the thresholds to make sure that the TX side will work and open BDs as you expect it to. Always remember that handling data bursts is not specified in the QMC manual. Freescale does not support this way of operating QMC. 4 MPC8xx QMC Usage Advisory
5 nc. Part V Document Revision History Table 1. Document Revision History Document Conventions Rev. No. Substantive Change(s) 0 Initial release. MPC8xx QMC Usage Advisory 5
6 Document Conventions nc. THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK 6 MPC8xx QMC Usage Advisory
7 nc. THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK Document Conventions MPC8xx QMC Usage Advisory 7
8 nc. AN2289/D
Freescale Semiconductor, I
 Overview 1 QMC Memory Organization 2 QMC Commands 3 QMC Exceptions Buffer Descriptors QMC Initialization Features Deleted in MC68MH360 Performance Multi-Subchannel (MSC) Microcode 68360 Bit Numbering Frequently-Asked
Overview 1 QMC Memory Organization 2 QMC Commands 3 QMC Exceptions Buffer Descriptors QMC Initialization Features Deleted in MC68MH360 Performance Multi-Subchannel (MSC) Microcode 68360 Bit Numbering Frequently-Asked
Freescale Semiconductor, I CPM/CPU INTERACTION
 CPM/CPU INTERACTION Host Commands from CPU Change state of SCC Channel Initialize SCC Channel Consist of microcode routines which change state of microcode or SCC state machine. Buffer Descriptors Give
CPM/CPU INTERACTION Host Commands from CPU Change state of SCC Channel Initialize SCC Channel Consist of microcode routines which change state of microcode or SCC state machine. Buffer Descriptors Give
SECTION 1 QUICC/POWERQUICC DIFFERENCES
 SECTION 1 QUICC/POWERQUICC DIFFERENCES The following section describes how to move applications from the MC68360 QUICC environment to the MPC860 PowerQUICC environment. It is assumed that the user is familiar
SECTION 1 QUICC/POWERQUICC DIFFERENCES The following section describes how to move applications from the MC68360 QUICC environment to the MPC860 PowerQUICC environment. It is assumed that the user is familiar
IMPORTANT DIFFERENCES
 AN2258/D Rev. 0.4, 4/2002 Differences and Additions in the MPC82xx HiP3 and HiP4 Silicon This document provides information for customers who are migrating from the HiP3-process technology PowerQUICC II
AN2258/D Rev. 0.4, 4/2002 Differences and Additions in the MPC82xx HiP3 and HiP4 Silicon This document provides information for customers who are migrating from the HiP3-process technology PowerQUICC II
Fast Communications Controller
 Fast Communications Controller Purpose: The Fast Communications Controller HDLC Protocol module describes the use of the FCC when used in HDLC mode. Objectives: This will provide you with an understanding
Fast Communications Controller Purpose: The Fast Communications Controller HDLC Protocol module describes the use of the FCC when used in HDLC mode. Objectives: This will provide you with an understanding
CS 167 Final Exam Solutions
 CS 167 Final Exam Solutions Spring 2018 Do all questions. 1. [20%] This question concerns a system employing a single (single-core) processor running a Unix-like operating system, in which interrupts are
CS 167 Final Exam Solutions Spring 2018 Do all questions. 1. [20%] This question concerns a system employing a single (single-core) processor running a Unix-like operating system, in which interrupts are
Multi-Channel Controller
 What you will learn What is the? How to interface to a T1 framer What is a super channel? How to initialize SIRAM How the MCC Receives Data How the MCC Transmits Data How the MCC Processes Interrupts 6-1
What you will learn What is the? How to interface to a T1 framer What is a super channel? How to initialize SIRAM How the MCC Receives Data How the MCC Transmits Data How the MCC Processes Interrupts 6-1
PowerQUICC HDLC Support and Example Code
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3966 Rev. 0, 11/2009 PowerQUICC HDLC Support and Example Code High-level data link control (HDLC) is a bit-oriented protocol that falls within
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3966 Rev. 0, 11/2009 PowerQUICC HDLC Support and Example Code High-level data link control (HDLC) is a bit-oriented protocol that falls within
Freescale Semiconductor, I
 nc. MPC8260ESS7UMAD/D 12/2002 Rev. 0.1 Enhanced SS7 Microcode Specification Addendum to MPC8260 RevB ROM Microcode Additions nc. nc. About This Document This document describes additional functionality
nc. MPC8260ESS7UMAD/D 12/2002 Rev. 0.1 Enhanced SS7 Microcode Specification Addendum to MPC8260 RevB ROM Microcode Additions nc. nc. About This Document This document describes additional functionality
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS ABSTRACT
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS ABSTRACT Brief set-up routine for using the automatic turn-around feature for transceiver control when using the RS-485 (sometimes called 9-bit or multi-drop mode) protocol. An interrupt
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS ABSTRACT Brief set-up routine for using the automatic turn-around feature for transceiver control when using the RS-485 (sometimes called 9-bit or multi-drop mode) protocol. An interrupt
Freescale Semiconductor, I
 nc. MC68QH302/D (Motorola Order Number) 11/97 REV 0 MC68QH302 Advance Information MC68QH302 Quad HDLC Integrated Multiprotocol Processor Technical Summary The MC68QH302, quad HDLC integrated multiprotocol
nc. MC68QH302/D (Motorola Order Number) 11/97 REV 0 MC68QH302 Advance Information MC68QH302 Quad HDLC Integrated Multiprotocol Processor Technical Summary The MC68QH302, quad HDLC integrated multiprotocol
Additional Chip Select Allows Another Device to Be Accessed from the ISA Bus. Plug and Play Register Settings Stored in External Low Cost E 2 PROM.
 Order this document by P/D Product Brief Passive ISDN Protocol Engine The Passive ISDN Protocol Engine (PIPE) is a communication controller optimized for ISDN passive cards, with an ISA PNP interface and
Order this document by P/D Product Brief Passive ISDN Protocol Engine The Passive ISDN Protocol Engine (PIPE) is a communication controller optimized for ISDN passive cards, with an ISA PNP interface and
Architectural Differences nc. DRAM devices are accessed with a multiplexed address scheme. Each unit of data is accessed by first selecting its row ad
 nc. Application Note AN1801 Rev. 0.2, 11/2003 Performance Differences between MPC8240 and the Tsi106 Host Bridge Top Changwatchai Roy Jenevein risc10@email.sps.mot.com CPD Applications This paper discusses
nc. Application Note AN1801 Rev. 0.2, 11/2003 Performance Differences between MPC8240 and the Tsi106 Host Bridge Top Changwatchai Roy Jenevein risc10@email.sps.mot.com CPD Applications This paper discusses
Rev /99. MPC8xx ATM Supplement to the MPC860/MPC850 PowerQUICC User s Manual
 Rev. 1.4 09/99 MPC8xx ATM Supplement to the MPC860/MPC850 PowerQUICC User s Manual Motorola Inc. 1998. All rights reserved. Portions hereof International Business Machines Corp. 1991 1998. All rights reserved.
Rev. 1.4 09/99 MPC8xx ATM Supplement to the MPC860/MPC850 PowerQUICC User s Manual Motorola Inc. 1998. All rights reserved. Portions hereof International Business Machines Corp. 1991 1998. All rights reserved.
BOOST YOUR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE USING THE ZILOG ESCC CONTROLLER
 BOOST YOUR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE USING THE ZILOG ESCC CONTROLLER AN030001-0509 For greater testability, larger interface flexibility, and increased CPU/ DMA offloading, replace the SCC with the ESCC Controller...
BOOST YOUR SYSTEM PERFORMANCE USING THE ZILOG ESCC CONTROLLER AN030001-0509 For greater testability, larger interface flexibility, and increased CPU/ DMA offloading, replace the SCC with the ESCC Controller...
Freescale Semiconductor, I. EKB Applications MC Document Location: EKB Datacomms Server / Product Info / MC68302 Info / Power Measurements
 K e l v i n I n d. E s t a t e. E a s t K i l b r i d e, S c o t l a n d. G 7 5 0 T G. EKB Applications Power Measurements on the MC68302 Document ID: Power Measurements on the MC68302 Document Location:
K e l v i n I n d. E s t a t e. E a s t K i l b r i d e, S c o t l a n d. G 7 5 0 T G. EKB Applications Power Measurements on the MC68302 Document ID: Power Measurements on the MC68302 Document Location:
MCS-51 Serial Port A T 8 9 C 5 2 1
 MCS-51 Serial Port AT89C52 1 Introduction to Serial Communications Serial vs. Parallel transfer of data Simplex, Duplex and half-duplex modes Synchronous, Asynchronous UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter.
MCS-51 Serial Port AT89C52 1 Introduction to Serial Communications Serial vs. Parallel transfer of data Simplex, Duplex and half-duplex modes Synchronous, Asynchronous UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter.
G Robert Grimm New York University
 G22.3250-001 Receiver Livelock Robert Grimm New York University Altogether Now: The Three Questions What is the problem? What is new or different? What are the contributions and limitations? Motivation
G22.3250-001 Receiver Livelock Robert Grimm New York University Altogether Now: The Three Questions What is the problem? What is new or different? What are the contributions and limitations? Motivation
Operating System Concepts
 Chapter 9: Virtual-Memory Management 9.1 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2005 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped
Chapter 9: Virtual-Memory Management 9.1 Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2005 Chapter 9: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped
ETH. Ethernet MAC with Timestamp Extension. TCD30xx User Guide. Revision July 17, 2015
 TCD30xx User Guide ETH Ethernet MAC with Timestamp Extension Revision 1.0.0-41582 July 17, 2015 Copyright 2015, TC Applied Technologies. All rights reserved. LIST OF TABLES... 16-3 LIST OF FIGURES... 16-4
TCD30xx User Guide ETH Ethernet MAC with Timestamp Extension Revision 1.0.0-41582 July 17, 2015 Copyright 2015, TC Applied Technologies. All rights reserved. LIST OF TABLES... 16-3 LIST OF FIGURES... 16-4
CPU ERRATA CPU1. Bus Error Not Fully Supported by the Data Cache on a Burst
 MPC823 Device Errata MPC823 Silicon Revision B.0 Mask Set 0H97G March 30, 2000 (Version 5) These errata apply to the MPC823 Revision B.0 (CDR2) silicon. Those errata that are currently scheduled to be
MPC823 Device Errata MPC823 Silicon Revision B.0 Mask Set 0H97G March 30, 2000 (Version 5) These errata apply to the MPC823 Revision B.0 (CDR2) silicon. Those errata that are currently scheduled to be
Application Note, V1.0, Jul AP XC16x. Interfacing the XC16x Microcontroller to a Serial SPI EEPROM. Microcontrollers
 Application Note, V1.0, Jul. 2006 AP16095 XC16x Interfacing the XC16x Microcontroller to a Serial SPI EEPROM Microcontrollers Edition 2006-07-10 Published by Infineon Technologies AG 81726 München, Germany
Application Note, V1.0, Jul. 2006 AP16095 XC16x Interfacing the XC16x Microcontroller to a Serial SPI EEPROM Microcontrollers Edition 2006-07-10 Published by Infineon Technologies AG 81726 München, Germany
1.1 MPC860T PowerQUICC Key Features
 nc. Technical Summary MPC860TTS/D Rev. 0.1, 12/2001 MPC860T PowerQUICC Technical Summary Advance Information MPC860T Fast Ethernet PowerQUICC Technical Summary The MPC860T Fast Ethernet communication controller
nc. Technical Summary MPC860TTS/D Rev. 0.1, 12/2001 MPC860T PowerQUICC Technical Summary Advance Information MPC860T Fast Ethernet PowerQUICC Technical Summary The MPC860T Fast Ethernet communication controller
MT8952B. ISO-CMOS ST-BUS FAMILY HDLC Protocol Controller. Features. Description. Applications
 ISO-CMOS ST-BUS FAMILY HDLC Protocol Controller Features Formats data as per X.25 (CCITT) level-2 standards Go-Ahead sequence generation and detection Single byte address recognition Microprocessor port
ISO-CMOS ST-BUS FAMILY HDLC Protocol Controller Features Formats data as per X.25 (CCITT) level-2 standards Go-Ahead sequence generation and detection Single byte address recognition Microprocessor port
Errata and Clarifications to the PCI-X Addendum, Revision 1.0a. Update 3/12/01 Rev P
 Errata and Clarifications to the PCI-X Addendum, Revision 1.0a Update 3/12/01 Rev P REVISION REVISION HISTORY DATE P E1a-E6a, C1a-C12a 3/12/01 2 Table of Contents Table of Contents...3 Errata to PCI-X
Errata and Clarifications to the PCI-X Addendum, Revision 1.0a Update 3/12/01 Rev P REVISION REVISION HISTORY DATE P E1a-E6a, C1a-C12a 3/12/01 2 Table of Contents Table of Contents...3 Errata to PCI-X
FPQ9 - MPC8360E implementation
 Training MPC8360E implementation: This course covers PowerQUICC II Pro MPC8360E - PowerPC processors: NXP Power CPUs FPQ9 - MPC8360E implementation This course covers PowerQUICC II Pro MPC8360E Objectives
Training MPC8360E implementation: This course covers PowerQUICC II Pro MPC8360E - PowerPC processors: NXP Power CPUs FPQ9 - MPC8360E implementation This course covers PowerQUICC II Pro MPC8360E Objectives
DLD VIDYA SAGAR P. potharajuvidyasagar.wordpress.com. Vignana Bharathi Institute of Technology UNIT 1 DLD P VIDYA SAGAR
 UNIT I Digital Systems: Binary Numbers, Octal, Hexa Decimal and other base numbers, Number base conversions, complements, signed binary numbers, Floating point number representation, binary codes, error
UNIT I Digital Systems: Binary Numbers, Octal, Hexa Decimal and other base numbers, Number base conversions, complements, signed binary numbers, Floating point number representation, binary codes, error
Application Note, V1.0, November AP XC2000/XE166 family. ADC Result Handling on XC2000/XE166 family of Microcontrollers.
 Application Note, V1.0, November. 2008 AP16155 XC2000/XE166 family ADC Result Handling on XC2000/XE166 family of Microcontrollers Microcontrollers Edition 2008-11-11 Published by Infineon Technologies
Application Note, V1.0, November. 2008 AP16155 XC2000/XE166 family ADC Result Handling on XC2000/XE166 family of Microcontrollers Microcontrollers Edition 2008-11-11 Published by Infineon Technologies
Virtual Memory Outline
 Virtual Memory Outline Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations Operating-System Examples
Virtual Memory Outline Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating Kernel Memory Other Considerations Operating-System Examples
1. Introduction. Be sure to read the release notes in section 10 before operating the Unit.
 1. Introduction This manual describes the ways of configuring and monitoring the operation of the PROFINET IO Controller CJ1W-PNT Sample Version V0.00 V67.06 V0.00 (Internal release V6.29). Be sure to
1. Introduction This manual describes the ways of configuring and monitoring the operation of the PROFINET IO Controller CJ1W-PNT Sample Version V0.00 V67.06 V0.00 (Internal release V6.29). Be sure to
CS370 Operating Systems
 CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2017 Lecture 23 Virtual memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 FAQ Is a page replaces when
CS370 Operating Systems Colorado State University Yashwant K Malaiya Fall 2017 Lecture 23 Virtual memory Slides based on Text by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Various sources 1 1 FAQ Is a page replaces when
MSC8156 Ethernet Interface
 June 21, 2010 MSC8156 Ethernet Interface QUICC Engine Ethernet Programming Andrew Temple NMG DSP Applications Reg. U.S. Pat. & Tm. Off. BeeKit, BeeStack, CoreNet, the Energy Efficient Solutions logo, Flexis,
June 21, 2010 MSC8156 Ethernet Interface QUICC Engine Ethernet Programming Andrew Temple NMG DSP Applications Reg. U.S. Pat. & Tm. Off. BeeKit, BeeStack, CoreNet, the Energy Efficient Solutions logo, Flexis,
Winford Engineering ETH32 Protocol Reference
 Winford Engineering ETH32 Protocol Reference Table of Contents 1 1 Overview 1 Connection 1 General Structure 2 Communications Summary 2 Port Numbers 4 No-reply Commands 4 Set Port Value 4 Set Port Direction
Winford Engineering ETH32 Protocol Reference Table of Contents 1 1 Overview 1 Connection 1 General Structure 2 Communications Summary 2 Port Numbers 4 No-reply Commands 4 Set Port Value 4 Set Port Direction
Receive Livelock. Robert Grimm New York University
 Receive Livelock Robert Grimm New York University The Three Questions What is the problem? What is new or different? What are the contributions and limitations? Motivation Interrupts work well when I/O
Receive Livelock Robert Grimm New York University The Three Questions What is the problem? What is new or different? What are the contributions and limitations? Motivation Interrupts work well when I/O
TMS320C672x DSP Dual Data Movement Accelerator (dmax) Reference Guide
 TMS320C672x DSP Dual Data Movement Accelerator (dmax) Reference Guide Literature Number: SPRU795D November 2005 Revised October 2007 2 SPRU795D November 2005 Revised October 2007 Contents Preface... 11
TMS320C672x DSP Dual Data Movement Accelerator (dmax) Reference Guide Literature Number: SPRU795D November 2005 Revised October 2007 2 SPRU795D November 2005 Revised October 2007 Contents Preface... 11
Freescale Semiconductor, I
 nc. Technical Summary MPC860SAR/D Rev. 0.1, 12/2001 MPC860SAR PowerQUICC Technical Summary Advance Information MPC860SAR Communication Controller Technical Summary The MPC860SAR ATM communication controller
nc. Technical Summary MPC860SAR/D Rev. 0.1, 12/2001 MPC860SAR PowerQUICC Technical Summary Advance Information MPC860SAR Communication Controller Technical Summary The MPC860SAR ATM communication controller
Congestion control in TCP
 Congestion control in TCP If the transport entities on many machines send too many packets into the network too quickly, the network will become congested, with performance degraded as packets are delayed
Congestion control in TCP If the transport entities on many machines send too many packets into the network too quickly, the network will become congested, with performance degraded as packets are delayed
W25X05CL/10CL/20CL 2.5 / 3 / 3.3 V 512K / 1M / 2M-BIT SERIAL FLASH MEMORY WITH 4KB SECTORS AND DUAL I/O SPI
 2.5 / 3 / 3.3 V 512K / 1M / 2M-BIT SERIAL FLASH MEMORY WITH 4KB SECTORS AND DUAL I/O SPI - 1 - Revision B Table of Contents 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION...4 2. FEATURES...4 3. PIN CONFIGURATION SOIC 150-MIL,
2.5 / 3 / 3.3 V 512K / 1M / 2M-BIT SERIAL FLASH MEMORY WITH 4KB SECTORS AND DUAL I/O SPI - 1 - Revision B Table of Contents 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION...4 2. FEATURES...4 3. PIN CONFIGURATION SOIC 150-MIL,
Midterm II December 4 th, 2006 CS162: Operating Systems and Systems Programming
 Fall 2006 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Computer Science Division EECS John Kubiatowicz Midterm II December 4 th, 2006 CS162: Operating Systems and Systems Programming Your
Fall 2006 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Computer Science Division EECS John Kubiatowicz Midterm II December 4 th, 2006 CS162: Operating Systems and Systems Programming Your
DatasheetDirect.com. Visit to get your free datasheets. This datasheet has been downloaded by
 DatasheetDirect.com Your dedicated source for free downloadable datasheets. Over one million datasheets Optimized search function Rapid quote option Free unlimited downloads Visit www.datasheetdirect.com
DatasheetDirect.com Your dedicated source for free downloadable datasheets. Over one million datasheets Optimized search function Rapid quote option Free unlimited downloads Visit www.datasheetdirect.com
Operating Systems. Overview Virtual memory part 2. Page replacement algorithms. Lecture 7 Memory management 3: Virtual memory
 Operating Systems Lecture 7 Memory management : Virtual memory Overview Virtual memory part Page replacement algorithms Frame allocation Thrashing Other considerations Memory over-allocation Efficient
Operating Systems Lecture 7 Memory management : Virtual memory Overview Virtual memory part Page replacement algorithms Frame allocation Thrashing Other considerations Memory over-allocation Efficient
TMS320VC5503/5507/5509/5510 DSP Direct Memory Access (DMA) Controller Reference Guide
 TMS320VC5503/5507/5509/5510 DSP Direct Memory Access (DMA) Controller Reference Guide Literature Number: January 2007 This page is intentionally left blank. Preface About This Manual Notational Conventions
TMS320VC5503/5507/5509/5510 DSP Direct Memory Access (DMA) Controller Reference Guide Literature Number: January 2007 This page is intentionally left blank. Preface About This Manual Notational Conventions
1.1 MPC855T Key Features
 nc. Advance Information MPC855TTS/D Rev. 0.1, 11/2001 MPC855T Communications Controller Technical Summary The MPC855T communications controller is a member of the MPC8xx family targeted at cost sensitive
nc. Advance Information MPC855TTS/D Rev. 0.1, 11/2001 MPC855T Communications Controller Technical Summary The MPC855T communications controller is a member of the MPC8xx family targeted at cost sensitive
In 8086 Carry flag, Parity flag, Auxiliary carry flag, Zero flag, Overflow flag, Trace flag, Interrupt flag, Direction flag, and Sign flag.
 What is a Microprocessor? Microprocessor is a program-controlled device, which fetches the instructions from memory, decodes and executes the instructions. Most Micro Processor are single- chip devices.
What is a Microprocessor? Microprocessor is a program-controlled device, which fetches the instructions from memory, decodes and executes the instructions. Most Micro Processor are single- chip devices.
TPMC810. Isolated 2x CAN Bus. Version 1.1. User Manual. Issue June 2009
 The Embedded I/O Company TPMC810 Isolated 2x CAN Bus Version 1.1 User Manual Issue 1.1.6 June 2009 TEWS TECHNOLOGIES GmbH Am Bahnhof 7 25469 Halstenbek / Germany Phone: +49-(0)4101-4058-0 Fax: +49-(0)4101-4058-19
The Embedded I/O Company TPMC810 Isolated 2x CAN Bus Version 1.1 User Manual Issue 1.1.6 June 2009 TEWS TECHNOLOGIES GmbH Am Bahnhof 7 25469 Halstenbek / Germany Phone: +49-(0)4101-4058-0 Fax: +49-(0)4101-4058-19
CS Introduction to Data Structures How to Parse Arithmetic Expressions
 CS3901 - Introduction to Data Structures How to Parse Arithmetic Expressions Lt Col Joel Young One of the common task required in implementing programming languages, calculators, simulation systems, and
CS3901 - Introduction to Data Structures How to Parse Arithmetic Expressions Lt Col Joel Young One of the common task required in implementing programming languages, calculators, simulation systems, and
smxnand RTOS Innovators Flash Driver General Features
 smxnand Flash Driver RTOS Innovators The smxnand flash driver makes NAND flash memory appear to a file system like a disk drive. It supports single-level cell (SLC) and multi-level cell (MLC) NAND flash.
smxnand Flash Driver RTOS Innovators The smxnand flash driver makes NAND flash memory appear to a file system like a disk drive. It supports single-level cell (SLC) and multi-level cell (MLC) NAND flash.
Installing the Software
 Logic User s Guide Note: this is a new version to support the 1.1.0+ software. Please let us know if you can t find what you re looking for http://www.saleae.com/contact Contents Installing the Software...
Logic User s Guide Note: this is a new version to support the 1.1.0+ software. Please let us know if you can t find what you re looking for http://www.saleae.com/contact Contents Installing the Software...
Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Embedded Software. Lab 1 Tower Serial Communications
 Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Subject: 48434 Embedded Software Assessment Number: 1 Assessment Title: Lab 1 Tower Serial Communications Tutorial Group: Students Name(s) and Number(s)
Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology Subject: 48434 Embedded Software Assessment Number: 1 Assessment Title: Lab 1 Tower Serial Communications Tutorial Group: Students Name(s) and Number(s)
Quality of Service (QoS)
 Quality of Service (QoS) The Internet was originally designed for best-effort service without guarantee of predictable performance. Best-effort service is often sufficient for a traffic that is not sensitive
Quality of Service (QoS) The Internet was originally designed for best-effort service without guarantee of predictable performance. Best-effort service is often sufficient for a traffic that is not sensitive
Memory Management Outline. Operating Systems. Motivation. Paging Implementation. Accessing Invalid Pages. Performance of Demand Paging
 Memory Management Outline Operating Systems Processes (done) Memory Management Basic (done) Paging (done) Virtual memory Virtual Memory (Chapter.) Motivation Logical address space larger than physical
Memory Management Outline Operating Systems Processes (done) Memory Management Basic (done) Paging (done) Virtual memory Virtual Memory (Chapter.) Motivation Logical address space larger than physical
Freescale Semiconductor, I. SECTION 13 CAN 2.0B CONTROLLER MODULE (TouCAN)
 nc. SECTION 13 CAN 2.0B CONTROLLER MODULE (TouCAN) This section is an overview of the TouCAN module. Refer to D.10 TouCAN Module for information concerning TouCAN address map and register structure. 13.1
nc. SECTION 13 CAN 2.0B CONTROLLER MODULE (TouCAN) This section is an overview of the TouCAN module. Refer to D.10 TouCAN Module for information concerning TouCAN address map and register structure. 13.1
Documents. Configuration. Important Dependent Parameters (Approximate) Version 2.3 (Wed, Dec 1, 2010, 1225 hours)
 1 of 7 12/2/2010 11:31 AM Version 2.3 (Wed, Dec 1, 2010, 1225 hours) Notation And Abbreviations preliminaries TCP Experiment 2 TCP Experiment 1 Remarks How To Design A TCP Experiment KB (KiloBytes = 1,000
1 of 7 12/2/2010 11:31 AM Version 2.3 (Wed, Dec 1, 2010, 1225 hours) Notation And Abbreviations preliminaries TCP Experiment 2 TCP Experiment 1 Remarks How To Design A TCP Experiment KB (KiloBytes = 1,000
Multichannel Communication Controller HDLC Superchannel Mode on the MPC8560
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3541 Rev. 0, 1/2008 Multichannel Communication Controller HDLC Superchannel Mode on the MPC8560 by Michael Johnston Networking and Multimedia
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3541 Rev. 0, 1/2008 Multichannel Communication Controller HDLC Superchannel Mode on the MPC8560 by Michael Johnston Networking and Multimedia
Swapping. Operating Systems I. Swapping. Motivation. Paging Implementation. Demand Paging. Active processes use more physical memory than system has
 Swapping Active processes use more physical memory than system has Operating Systems I Address Binding can be fixed or relocatable at runtime Swap out P P Virtual Memory OS Backing Store (Swap Space) Main
Swapping Active processes use more physical memory than system has Operating Systems I Address Binding can be fixed or relocatable at runtime Swap out P P Virtual Memory OS Backing Store (Swap Space) Main
Chapter 10 Sections 1,2,9,10 Dr. Iyad Jafar
 Starting with Serial Chapter 10 Sections 1,2,9,10 Dr. Iyad Jafar Outline Introduction Synchronous Serial Communication Asynchronous Serial Communication Physical Limitations Overview of PIC 16 Series The
Starting with Serial Chapter 10 Sections 1,2,9,10 Dr. Iyad Jafar Outline Introduction Synchronous Serial Communication Asynchronous Serial Communication Physical Limitations Overview of PIC 16 Series The
16 Sharing Main Memory Segmentation and Paging
 Operating Systems 64 16 Sharing Main Memory Segmentation and Paging Readings for this topic: Anderson/Dahlin Chapter 8 9; Siberschatz/Galvin Chapter 8 9 Simple uniprogramming with a single segment per
Operating Systems 64 16 Sharing Main Memory Segmentation and Paging Readings for this topic: Anderson/Dahlin Chapter 8 9; Siberschatz/Galvin Chapter 8 9 Simple uniprogramming with a single segment per
Freescale Semiconductor, I
 Advance Information MPC852TTS/D Rev. 1.3, 4/2003 MPC852T PowerQUICC Technical Summary This document provides an overview of the MPC852T PowerQUICC device, describing major functions and features. The MPC852T
Advance Information MPC852TTS/D Rev. 1.3, 4/2003 MPC852T PowerQUICC Technical Summary This document provides an overview of the MPC852T PowerQUICC device, describing major functions and features. The MPC852T
W25X40CL 2.5/3/3.3 V 4M-BIT SERIAL FLASH MEMORY WITH 4KB SECTORS AND DUAL I/O SPI. Publication Release Date: October 15, Revision E
 2.5/3/3.3 V 4M-BIT SERIAL FLASH MEMORY WITH 4KB SECTORS AND DUAL I/O SPI - 1 - Revision E Table of Contents 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 4 2. FEATURES... 4 3. PIN CONFIGURATION SOIC 208-MIL, SOIC 150-MIL
2.5/3/3.3 V 4M-BIT SERIAL FLASH MEMORY WITH 4KB SECTORS AND DUAL I/O SPI - 1 - Revision E Table of Contents 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 4 2. FEATURES... 4 3. PIN CONFIGURATION SOIC 208-MIL, SOIC 150-MIL
The SPI supports data bus widths of 32 bits.
 19. SPI Controller November 2012 av_54019-1.2 av_54019-1.2 The hard processor system (HPS) provides two serial peripheral interface (SPI) masters and two SPI slaves. The SPI masters and slaves are instances
19. SPI Controller November 2012 av_54019-1.2 av_54019-1.2 The hard processor system (HPS) provides two serial peripheral interface (SPI) masters and two SPI slaves. The SPI masters and slaves are instances
Chapter 13: I/O Systems
 Chapter 13: I/O Systems DM510-14 Chapter 13: I/O Systems I/O Hardware Application I/O Interface Kernel I/O Subsystem Transforming I/O Requests to Hardware Operations STREAMS Performance 13.2 Objectives
Chapter 13: I/O Systems DM510-14 Chapter 13: I/O Systems I/O Hardware Application I/O Interface Kernel I/O Subsystem Transforming I/O Requests to Hardware Operations STREAMS Performance 13.2 Objectives
CHECKPOINT 3 Wireless Transceiver
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE CHECKPOINT 3 Wireless Transceiver 1.0 MOTIVATION The wireless, radio-frequency (RF)
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE CHECKPOINT 3 Wireless Transceiver 1.0 MOTIVATION The wireless, radio-frequency (RF)
Understanding the basic building blocks of a microcontroller device in general. Knows the terminologies like embedded and external memory devices,
 Understanding the basic building blocks of a microcontroller device in general. Knows the terminologies like embedded and external memory devices, CISC and RISC processors etc. Knows the architecture and
Understanding the basic building blocks of a microcontroller device in general. Knows the terminologies like embedded and external memory devices, CISC and RISC processors etc. Knows the architecture and
Pretty Good Protocol - Design Specification
 Document # Date effective October 23, 2006 Author(s) Ryan Herbst Supersedes Draft Revision 0.02 January 12, 2007 Document Title Pretty Good Protocol - Design Specification CHANGE HISTORY LOG Revision Effective
Document # Date effective October 23, 2006 Author(s) Ryan Herbst Supersedes Draft Revision 0.02 January 12, 2007 Document Title Pretty Good Protocol - Design Specification CHANGE HISTORY LOG Revision Effective
Integrated Device Technology, Inc Stender Way, Santa Clara, CA Phone #: (408) Fax #: (408) Errata Notification
 Integrated Device Technology, Inc. 2975 Stender Way, Santa Clara, CA - 95054 Phone #: (408) 727-6116 Fax #: (408) 727-2328 Errata Notification EN #: IEN01-02 Errata Revision #: 11/5/01 Issue Date: December
Integrated Device Technology, Inc. 2975 Stender Way, Santa Clara, CA - 95054 Phone #: (408) 727-6116 Fax #: (408) 727-2328 Errata Notification EN #: IEN01-02 Errata Revision #: 11/5/01 Issue Date: December
Page Replacement Algorithms
 Page Replacement Algorithms MIN, OPT (optimal) RANDOM evict random page FIFO (first-in, first-out) give every page equal residency LRU (least-recently used) MRU (most-recently used) 1 9.1 Silberschatz,
Page Replacement Algorithms MIN, OPT (optimal) RANDOM evict random page FIFO (first-in, first-out) give every page equal residency LRU (least-recently used) MRU (most-recently used) 1 9.1 Silberschatz,
Heuristic Evaluation Project
 INFSCI 2470: Interactive System Design Heuristic Evaluation Project Evaluated System: Course Agent http://wwwsispittedu/~cagent Group Members Abdul Raqeeb Abdul Azeez Arash Farsi Sriranjani Mandayam Denis
INFSCI 2470: Interactive System Design Heuristic Evaluation Project Evaluated System: Course Agent http://wwwsispittedu/~cagent Group Members Abdul Raqeeb Abdul Azeez Arash Farsi Sriranjani Mandayam Denis
Chapter 8: Virtual Memory. Operating System Concepts
 Chapter 8: Virtual Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Chapter 8: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating
Chapter 8: Virtual Memory Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Chapter 8: Virtual Memory Background Demand Paging Copy-on-Write Page Replacement Allocation of Frames Thrashing Memory-Mapped Files Allocating
µtasker Document Controller Area Netwok (CAN)
 Embedding it better... µtasker Document Controller Area Netwok (CAN) utaskercan.doc/1.01 Copyright 2014 M.J.Butcher Consulting Table of Contents 1. Introduction...3 2. CAN Bit Timing...4 3. CAN Frame Format...5
Embedding it better... µtasker Document Controller Area Netwok (CAN) utaskercan.doc/1.01 Copyright 2014 M.J.Butcher Consulting Table of Contents 1. Introduction...3 2. CAN Bit Timing...4 3. CAN Frame Format...5
DS Wire Digital Thermometer and Thermostat
 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Temperature measurements require no external components with ±1 C accuracy Measures temperatures from -55 C to +125 C; Fahrenheit equivalent is -67 F to +257 F Temperature resolution
www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Temperature measurements require no external components with ±1 C accuracy Measures temperatures from -55 C to +125 C; Fahrenheit equivalent is -67 F to +257 F Temperature resolution
Migrating from the MPC852T to the MPC875
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2584 Rev. 1, 1/2007 Migrating from the MPC852T to the MPC875 by Ned Reinhold NCSD Applications Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX This
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2584 Rev. 1, 1/2007 Migrating from the MPC852T to the MPC875 by Ned Reinhold NCSD Applications Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX This
AN Reduce CPU overhead with Intelligence Interrupt Arbitration (I2A) feature. Document information
 Reduce CPU overhead with Intelligence Interrupt Arbitration (I2A) feature Rev. 01 25 June 2004 Application note Document information Info Content Keywords I2A, Interrupt Arbitration, Arbitration Abstract
Reduce CPU overhead with Intelligence Interrupt Arbitration (I2A) feature Rev. 01 25 June 2004 Application note Document information Info Content Keywords I2A, Interrupt Arbitration, Arbitration Abstract
Congestion. Can t sustain input rate > output rate Issues: - Avoid congestion - Control congestion - Prioritize who gets limited resources
 Congestion Source 1 Source 2 10-Mbps Ethernet 100-Mbps FDDI Router 1.5-Mbps T1 link Destination Can t sustain input rate > output rate Issues: - Avoid congestion - Control congestion - Prioritize who gets
Congestion Source 1 Source 2 10-Mbps Ethernet 100-Mbps FDDI Router 1.5-Mbps T1 link Destination Can t sustain input rate > output rate Issues: - Avoid congestion - Control congestion - Prioritize who gets
Table 1: Cross Reference of Applicable Products
 Standard Product Enable the Ethernet MAC Controller Module Application Note September 29, 2017 The most important thing we build is trust Table 1: Cross Reference of Applicable Products PRODUCT NAME MANUFACTURER
Standard Product Enable the Ethernet MAC Controller Module Application Note September 29, 2017 The most important thing we build is trust Table 1: Cross Reference of Applicable Products PRODUCT NAME MANUFACTURER
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER BASED SYSTEMS
 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER BASED SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO 8085 8085 Microprocessor - Architecture and its operation, Concept of instruction execution and timing diagrams, fundamentals of
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER BASED SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO 8085 8085 Microprocessor - Architecture and its operation, Concept of instruction execution and timing diagrams, fundamentals of
How & Why We Subnet Lab Workbook
 i How & Why We Subnet Lab Workbook ii CertificationKits.com How & Why We Subnet Workbook Copyright 2013 CertificationKits LLC All rights reserved. No part of this book maybe be reproduced or transmitted
i How & Why We Subnet Lab Workbook ii CertificationKits.com How & Why We Subnet Workbook Copyright 2013 CertificationKits LLC All rights reserved. No part of this book maybe be reproduced or transmitted
Cache Coherence Tutorial
 Cache Coherence Tutorial The cache coherence protocol described in the book is not really all that difficult and yet a lot of people seem to have troubles when it comes to using it or answering an assignment
Cache Coherence Tutorial The cache coherence protocol described in the book is not really all that difficult and yet a lot of people seem to have troubles when it comes to using it or answering an assignment
MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
 DATA SHEET MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT µpd6708 IEBus (Inter Equipment Bus ) PROTOCOL CONTROL LSI DESCRIPTION The µpd6708 is a peripheral LSI for microcontrollers that controls the protocol of the IEBus. This
DATA SHEET MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT µpd6708 IEBus (Inter Equipment Bus ) PROTOCOL CONTROL LSI DESCRIPTION The µpd6708 is a peripheral LSI for microcontrollers that controls the protocol of the IEBus. This
1 Detecting Boot Mode
 Application Note nc. AN2442/D Rev. 0, 1/2003 Booting the MSC8102 Device Through TDM by Barbara Johnson CONTENTS 1 Detecting Boot Mode... 1 2 Synchronizing the Boot Signals... 1 3 Initializing the TDM...
Application Note nc. AN2442/D Rev. 0, 1/2003 Booting the MSC8102 Device Through TDM by Barbara Johnson CONTENTS 1 Detecting Boot Mode... 1 2 Synchronizing the Boot Signals... 1 3 Initializing the TDM...
EGON FAMILY PROGRAMMING NOTES
 EGON FAMILY PROGRAMMING NOTES REV. January 2013 Welcome Thank you for choosing NAVIOP EGON Series products. We invite you to read this manual in full before proceeding to use the product. The purpose of
EGON FAMILY PROGRAMMING NOTES REV. January 2013 Welcome Thank you for choosing NAVIOP EGON Series products. We invite you to read this manual in full before proceeding to use the product. The purpose of
Chapter 3 Memory Management: Virtual Memory
 Memory Management Where we re going Chapter 3 Memory Management: Virtual Memory Understanding Operating Systems, Fourth Edition Disadvantages of early schemes: Required storing entire program in memory
Memory Management Where we re going Chapter 3 Memory Management: Virtual Memory Understanding Operating Systems, Fourth Edition Disadvantages of early schemes: Required storing entire program in memory
Chapter 12: I/O Systems
 Chapter 12: I/O Systems Chapter 12: I/O Systems I/O Hardware! Application I/O Interface! Kernel I/O Subsystem! Transforming I/O Requests to Hardware Operations! STREAMS! Performance! Silberschatz, Galvin
Chapter 12: I/O Systems Chapter 12: I/O Systems I/O Hardware! Application I/O Interface! Kernel I/O Subsystem! Transforming I/O Requests to Hardware Operations! STREAMS! Performance! Silberschatz, Galvin
Chapter 13: I/O Systems
 Chapter 13: I/O Systems Chapter 13: I/O Systems I/O Hardware Application I/O Interface Kernel I/O Subsystem Transforming I/O Requests to Hardware Operations STREAMS Performance Silberschatz, Galvin and
Chapter 13: I/O Systems Chapter 13: I/O Systems I/O Hardware Application I/O Interface Kernel I/O Subsystem Transforming I/O Requests to Hardware Operations STREAMS Performance Silberschatz, Galvin and
Chapter 12: I/O Systems. Operating System Concepts Essentials 8 th Edition
 Chapter 12: I/O Systems Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2011 Chapter 12: I/O Systems I/O Hardware Application I/O Interface Kernel I/O Subsystem Transforming I/O Requests to Hardware Operations STREAMS
Chapter 12: I/O Systems Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2011 Chapter 12: I/O Systems I/O Hardware Application I/O Interface Kernel I/O Subsystem Transforming I/O Requests to Hardware Operations STREAMS
Application Note. Before you begin. Introduction. Setting Up a Routed PPP Over a DSL Link Model 3224
 Application Note Setting Up a Routed PPP Over a DSL Link Model 3224 Before you begin There are several hardware requirements for this procedure. You must have: One Patton 3224 unit A PC or a laptop with
Application Note Setting Up a Routed PPP Over a DSL Link Model 3224 Before you begin There are several hardware requirements for this procedure. You must have: One Patton 3224 unit A PC or a laptop with
CY7C Errata Revision: *A. June 25, 2004 Errata Document for CY7C Part Numbers Affected. CY7C67200 Qualification Status
 Errata Revision: *A June 25, 2004 for This document describes the errata for the. Details include errata trigger conditions, available workarounds, and silicon revision applicability. This document should
Errata Revision: *A June 25, 2004 for This document describes the errata for the. Details include errata trigger conditions, available workarounds, and silicon revision applicability. This document should
AN-895 APPLICATION NOTE
 APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 9106 Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.4700 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com ADuC702x MicroConverter I 2 C -Compatible Interface by Michael Looney
APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 9106 Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.4700 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com ADuC702x MicroConverter I 2 C -Compatible Interface by Michael Looney
CP/M-86 Compatibility Guide For CP/M-80 Users
 CCGFCU.WS4 ---------- CP/M-86 Compatibility Guide For CP/M-80 Users (= CCGFCU...) Copyright (c) 1980 Digital Research Pacific Grove, California (Revision of 10/21/80) (= 21 October 1980) (Retyped by Emmanuel
CCGFCU.WS4 ---------- CP/M-86 Compatibility Guide For CP/M-80 Users (= CCGFCU...) Copyright (c) 1980 Digital Research Pacific Grove, California (Revision of 10/21/80) (= 21 October 1980) (Retyped by Emmanuel
8051 Serial Communication
 8051 Serial Communication Basics of serial communication Parallel: transfers eight bits of data simultaneously over eight data lines expensive - short distance fast Serial : one bit at a time is transferred
8051 Serial Communication Basics of serial communication Parallel: transfers eight bits of data simultaneously over eight data lines expensive - short distance fast Serial : one bit at a time is transferred
In the HEW, open a new project by selecting New workspace from the main menu.
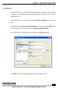 1.1 Introduction Renesas s HEW 4.0 is used for developing application programs. Each program is opened as a separate project and the related files are stored in the relevant project directory. In the HEW,
1.1 Introduction Renesas s HEW 4.0 is used for developing application programs. Each program is opened as a separate project and the related files are stored in the relevant project directory. In the HEW,
User Guide. K V1 7/05 Rev A
 NAVIGATOR REPORTER User Guide K10321-1V1 7/05 Rev A Table of Contents Conventions Used in This Manual... iii SECTION 1: General Description... 1-1 About Navigator Reporter...1-1 About User Manager...1-1
NAVIGATOR REPORTER User Guide K10321-1V1 7/05 Rev A Table of Contents Conventions Used in This Manual... iii SECTION 1: General Description... 1-1 About Navigator Reporter...1-1 About User Manager...1-1
Errata to the MPC8280 PowerQUICC II Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1
 Freescale Semiconductor Addendum Document Number: MPC8280RMAD Rev. 1.5, 12/2010 Errata to the MPC8280 PowerQUICC II Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1 This errata document describes corrections to the MPC8280
Freescale Semiconductor Addendum Document Number: MPC8280RMAD Rev. 1.5, 12/2010 Errata to the MPC8280 PowerQUICC II Family Reference Manual, Rev. 1 This errata document describes corrections to the MPC8280
ECEN Final Exam Fall Instructor: Srinivas Shakkottai
 ECEN 424 - Final Exam Fall 2013 Instructor: Srinivas Shakkottai NAME: Problem maximum points your points Problem 1 10 Problem 2 10 Problem 3 20 Problem 4 20 Problem 5 20 Problem 6 20 total 100 1 2 Midterm
ECEN 424 - Final Exam Fall 2013 Instructor: Srinivas Shakkottai NAME: Problem maximum points your points Problem 1 10 Problem 2 10 Problem 3 20 Problem 4 20 Problem 5 20 Problem 6 20 total 100 1 2 Midterm
Section 6 Blackfin ADSP-BF533 Memory
 Section 6 Blackfin ADSP-BF533 Memory 6-1 a ADSP-BF533 Block Diagram Core Timer 64 L1 Instruction Memory Performance Monitor JTAG/ Debug Core Processor LD0 32 LD1 32 L1 Data Memory SD32 DMA Mastered 32
Section 6 Blackfin ADSP-BF533 Memory 6-1 a ADSP-BF533 Block Diagram Core Timer 64 L1 Instruction Memory Performance Monitor JTAG/ Debug Core Processor LD0 32 LD1 32 L1 Data Memory SD32 DMA Mastered 32
Much Faster Networking
 Much Faster Networking David Riddoch driddoch@solarflare.com Copyright 2016 Solarflare Communications, Inc. All rights reserved. What is kernel bypass? The standard receive path The standard receive path
Much Faster Networking David Riddoch driddoch@solarflare.com Copyright 2016 Solarflare Communications, Inc. All rights reserved. What is kernel bypass? The standard receive path The standard receive path
Tasks. Task Implementation and management
 Tasks Task Implementation and management Tasks Vocab Absolute time - real world time Relative time - time referenced to some event Interval - any slice of time characterized by start & end times Duration
Tasks Task Implementation and management Tasks Vocab Absolute time - real world time Relative time - time referenced to some event Interval - any slice of time characterized by start & end times Duration
Linux Network Tuning Guide for AMD EPYC Processor Based Servers
 Linux Network Tuning Guide for AMD EPYC Processor Application Note Publication # 56224 Revision: 1.00 Issue Date: November 2017 Advanced Micro Devices 2017 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
Linux Network Tuning Guide for AMD EPYC Processor Application Note Publication # 56224 Revision: 1.00 Issue Date: November 2017 Advanced Micro Devices 2017 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
INTRODUCTION TO MICROPROCESSORS
 INTRODUCTION TO MICROPROCESSORS Richa Upadhyay Prabhu NMIMS s MPSTME richa.upadhyay@nmims.edu January 7, 2016 Richa Upadhyay Prabhu (MPSTME) INTRODUCTION January 7, 2016 1 / 63 Course Design Prerequisite:
INTRODUCTION TO MICROPROCESSORS Richa Upadhyay Prabhu NMIMS s MPSTME richa.upadhyay@nmims.edu January 7, 2016 Richa Upadhyay Prabhu (MPSTME) INTRODUCTION January 7, 2016 1 / 63 Course Design Prerequisite:
M68HC08 Microcontroller The MC68HC908GP32. General Description. MCU Block Diagram CPU08 1
 M68HC08 Microcontroller The MC68HC908GP32 Babak Kia Adjunct Professor Boston University College of Engineering Email: bkia -at- bu.edu ENG SC757 - Advanced Microprocessor Design General Description The
M68HC08 Microcontroller The MC68HC908GP32 Babak Kia Adjunct Professor Boston University College of Engineering Email: bkia -at- bu.edu ENG SC757 - Advanced Microprocessor Design General Description The
TCP. CSU CS557, Spring 2018 Instructor: Lorenzo De Carli (Slides by Christos Papadopoulos, remixed by Lorenzo De Carli)
 TCP CSU CS557, Spring 2018 Instructor: Lorenzo De Carli (Slides by Christos Papadopoulos, remixed by Lorenzo De Carli) 1 Sources Fall and Stevens, TCP/IP Illustrated Vol. 1, 2nd edition Congestion Avoidance
TCP CSU CS557, Spring 2018 Instructor: Lorenzo De Carli (Slides by Christos Papadopoulos, remixed by Lorenzo De Carli) 1 Sources Fall and Stevens, TCP/IP Illustrated Vol. 1, 2nd edition Congestion Avoidance
