Table of Contents. co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern
|
|
|
- Ashlie Joseph
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 outing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2
2 co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern Table of Contents Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An External Router...1 Introduction...1 Important Notes...2 Conventions...4 Network Diagram...4 Configurations...5 Catalyst 3512 XL...5 Cisco 2600 Router Q Configuration on the Router for Cisco IOS Versions Earlier than 12.1(3)T...11 debug and show Commands...13 Sample show Command Output...14 Catalyst 3500XL Switch...14 Cisco 2600 Router...15 Tools Information...17 Related Information...18 i
3 Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An External Router Introduction Important Notes Conventions Network Diagram Configurations Catalyst 3512XL Switch Cisco 2600 Router 802.1Q Configuration on the Router for Cisco IOS Versions Earlier than 12.1(3)T debug and show Commands Sample show Command Output Catalyst 3500XL Switch Cisco 2600 Router Tools Information Related Information Introduction This document provides sample configurations on InterSwitch Link (ISL) and 802.1Q trunking between a Catalyst 3512 XL switch and a Cisco 2600 router; the results of each command are displayed as they are executed. Cisco 3600 and 4500/4700 series routers, or other members of the Cisco 2600 series routers, with FastEthernet interfaces, and any Catalyst 2900XL, 3500XL, or 2950 can be used in the scenarios presented in this document to obtain the same results. Trunking is a way to carry traffic from several VLANs over a point to point link between the two devices. Two ways in which Ethernet trunking can be implemented are: ISL (Cisco proprietary protocol) 802.1Q (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standard) We will create a trunk that will carry traffic from two VLANs (VLAN1 and VLAN2) across a single link between a Catalyst 3500 and a Cisco 2600 router. We are using the Cisco 2600 router to do the Inter VLAN routing between VLAN1 and VLAN2. Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 series switches are Layer 2 (L2) switches, and are not capable of routing or communicating between the VLANs. For further details on Inter VLAN routing, refer to the Routing Between Virtual LANs Overview chapter of the Cisco IOS Switching Services Configuration Guide, Release To create the examples in this document, we used the following switches in a lab environment with cleared
4 configurations: Catalyst 3512XL switch running Cisco IOS 12.0(5.x)XU Cisco 2621 router running Cisco IOS 12.1(3)T Cisco 2621 router running Cisco IOS 12.1(1)T The configurations in this document were implemented in an isolated lab environment. Ensure that you understand the potential impact of any configuration or command on your network before using it. The configurations on all devices were cleared with the write erase command to ensure that they have a default configuration. Important Notes For Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switches: Catalyst 2950 series switches only support 802.1q trunking and do not support ISL trunking. On a 4 MB DRAM Catalyst 2900XL switch, trunking is only supported with the following trunking capable modules: WS X2914 XL V: 4 port 10/100 ISL/802.1Q switch module WS X2922 XL V: 2 port 100BaseFX ISL/802.1Q switch module WS X2924 XL V: 4 port 100BaseFX ISL/802.1Q switch module WS X2931 XL: 1000BaseX uplink for Catalyst 2900 XL WS X2932 XL: 1000BaseT uplink for Catalyst 2900 XL Refer to Table 1 for the current list of switch models that support trunking: Table 1 Switch Models Minimum Release Required for ISL Trunking Minimum Release Required for IEEE 802.1Q Trunking Current Release Required for Trunking (ISL/802.1Q) WS C2916M XL (4 Meg Switch) 11.2(8)SA4 11.2(8)SA5 (Original Edition) 11.2(8.6)SA6 (Original Edition) WS C2912 XL 11.2(8)SA4 11.2(8)SA5 12.0(5)WC(1) or later WS C2924 XL 11.2(8)SA4 11.2(8)SA5 12.0(5)WC(1) or later WS C2924C XL 11.2(8)SA4 11.2(8)SA5 12.0(5)WC(1) or later WS C2924M XL 12.0(5)WC(1) or later
5 WS C2912MF XL 11.2(8)SA4 11.2(8)SA4 11.2(8)SA5 11.2(8)SA5 12.0(5)WC(1) or later WS C2924M XL DC 12.0(5)XU 12.0(5)XU 12.0(5)WC(1) or later WS C3508G XL WS C3512 XL WS C3524 XL WS C3548 XL 11.2(8)SA4 11.2(8)SA4 11.2(8)SA4 12.0(5)XP (Enterprise Edition) 11.2(8)SA5 11.2(8)SA5 (Original Edition) 11.2(8)SA5 12.0(5)XP (Enterprise Edition) 12.0(5)WC(1) or later 12.0(5)WC(1) or later 12.0(5)WC(1) or later 12.0(5)WC(1) or later WS C3524 PWR XL 12.0(5)XU 12.0(5)XU 12.0(5)WC(1) or later WS C ISL Not Supported 12.0(5)WC(1) 12.0(5)WC(1) or later WS C ISL Not Supported 12.0(5)WC(1) 12.0(5)WC(1) or later WS C2950C 24 ISL Not Supported 12.0(5)WC(1) 12.0(5)WC(1) or later WS C2950T 24 ISL Not Supported 12.0(5)WC(1) 12.0(5)WC(1) or later Note: In the above table, only WS C2916M XL is a 4 MB DRAM switch. All the other switches listed are 8 MB DRAM switches. To determine whether your switch has 4 MB or 8 MB of DRAM, enter the user level show version command. For more information, see the "How to Determine the Amount of Switch Memory Using the Command Line Interface" section of Upgrading Software in Catalyst 2900 XL/3500 XL Switches Using the Command Line Interface (CLI). For Cisco 2600 Routers: For 802.1Q trunking, one VLAN is not tagged. This VLAN is called native VLAN. The native VLAN is used for untagged traffic when the port is in 802.1Q trunking mode. While configuring 802.1Q trunking, it is very important to keep in mind that the native VLAN must be configured the same on each side of the trunk link. It is a common mistake not to match the native VLANs while configuring 802.1Q trunking between the router and the switch. For details on native VLANs, refer to the IEEE 802.1Q section, of Bridging Between IEEE 802.1Q VLANs, in New Features in Release 12.1(3)T. In this sample configuration, the native VLAN is VLAN1, by default, on both the Cisco 2621 router and the Catalyst 3512XL switch. Depending on your network needs, you may have to use a native VLAN other than the default VLAN, VLAN1. Commands have been mentioned in the configurations section of this document on how to change the native VLAN on the Cisco 2600 router and Catalyst 3500XL switch. Sample configurations presented in this document can be used on Cisco 2600/3600/4500/4700 series routers with Fast Ethernet interfaces or Fast Ethernet network modules. Also, make sure that you are using the Cisco IOS version that supports ISL/802.1Q VLAN trunking. For a complete list of Cisco 2600/3600/4500/4700 routers that support ISL/802.1Q VLAN trunking and the supported Cisco IOS versions, refer to Table 2. Table 2
6 Router Models Minimum Release Required for ISL Trunking Minimum Release Required for IEEE 802.1Q Trunking Current Release Required for Trunking (ISL/802.1Q) Minimum Required Feature Set (ISL/802.1Q) Cisco (3a)T 12.0(1)T 12.1(5)T, 12.1(5) IP PLUS / IP PLUS Cisco (3a)T 12.0(1)T 12.1(5)T, 12.1(5) IP PLUS / IP PLUS Cisco (3a)T 12.1(3a)T 12.1(5)T, 12.1(5) IP PLUS / IP PLUS Cisco (3a)T 12.1(3a)T 12.1(5)T, 12.1(5) IP PLUS / IP PLUS Cisco (1)T 12.0(1)T 12.1(5)T, 12.1(5) IP PLUS / IP PLUS Cisco (1)T 12.0(1)T 12.1(5)T, 12.1(5a) IP PLUS / IP PLUS Cisco (5)T 12.0(5)T 12.1(5)T, 12.1(5) IP PLUS / IP PLUS Cisco (5)T 12.0(5)T 12.1(5)T, 12.1(5) IP PLUS / IP PLUS Cisco 4500 M Cisco 4700 M Notes: 11.3(1)T 12.0(1)T 12.1(5)T, 12.1(5a) IP PLUS / IP PLUS 11.3(1)T 12.0(1)T 12.1(5)T, 12.1(5a) IP PLUS / IP PLUS Table 2 only lists the minimum or current maintenance/main releases that support this sample configuration. Router models with certain network modules may have different minimum Cisco IOS versions. For a complete list of minimum supported software for any router family, use the Hardware Software Compatibility Matrix and the release notes for that router platform. (For more information on Hardware Software Compatibility Matrix, see the Tools Information section.) For a complete list of other feature sets supported in different Cisco IOS versions and on different platforms, refer to the Feature Navigator tool and the release notes for that router platform. (For more information on Feature Navigator, see the Tools Information section.) The minimum supported release may not necessarily be the recommended release. To determine the best maintenance release for your Cisco product, search for bugs listed by product component in the Bug Navigator. (For more information on Bug Navigator, see the Tools Information section.) Table 2 lists the minimum feature set required to do IP Inter VLAN routing and trunking to support this sample configuration. For a complete list of other feature sets supported in different Cisco IOS versions and on different platforms, use the Feature Navigator tool and the release notes for that router platform. (For more information on Feature Navigator, see the Tools Information section.) Conventions For more information, see the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions. Network Diagram
7 Configurations Catalyst 3512 XL Note: The following screen captures show the commands that were entered on the 3512XL switch. Comments between the commands are added in blue italics to explain certain commands and steps. Set the privileged mode and Telnet password on the switch. switch#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. switch(config)#hostname 3512xl 3512xl(config)#enable password mysecret 3512xl(config)#line vty xl(config line)#login 3512xl(config line)#password mysecret 3512xl(config line)#exit 3512xl(config)#no logging console 3512xl(config)#^Z Set the IP address and default gateway for VLAN1 for management purposes. 3512xl#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
8 3512xl(config)#int vlan xl(config if)#ip address xl(config if)#exit 3512xl(config)#ip default gateway xl(config)#end Set the VTP Mode. In our example, we have set the mode to be transparent. Depending on your network, set the VTP Mode accordingly. For details on VTP, refer to Configuring VTP, VLANs, and VLAN Trunks on Catalyst 2900XL and 3500XL Switches.3512xl#vlan database 3512xl(vlan)#vtp transparent Setting device to VTP TRANSPARENT mode. Adding VLAN2. VLAN1 already exists by default. 3512xl(vlan)#vlan 2 VLAN 2 added: Name: VLAN xl(vlan)#exit APPLY completed. Exiting... Enable trunking on the interface fastethernet 0/ xl#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. 3512xl(config)#int fastethernet 0/1 3512xl(config if)#switchport mode trunk Enter the trunking encapsulation as either isl 3512xl(config if)#switchport trunk encapsulation isl or as dot1q: 3512xl(config if)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q In case of 2950 switches, none of the above two commands are used, 2950 switches only support 802.1q encapsulation which is configured automatically, when trunking is enabled on the interface by using switchport mode trunk command. In case of dot1q, you need to make sure that the native VLAN matches across the link. On 3512XL, by default, the native VLAN is 1. Depending on your network needs, you may change the native VLAN to be other than VLAN1, but it is very important that you change the native VLAN on the router accordingly. You may change the native VLAN, if needed, by using the following command: 3512xl(config if)#switchport trunk native vlan <vlan ID> Allow all VLANs on the trunk. 3512xl(config if)#switchport trunk allowed vlan all 3512xl(config if)#exit The following set of commands will place FastEthernet 0/2 into VLAN2 and enable portfast on the interface. 3512xl(config)#int fastethernet 0/2 3512xl(config if)#switchport access vlan xl(config if)#spanning tree portfast 3512xl(config if)#exit FastEthernet 0/3 is already in VLAN1 by default. Enable portfast on the interface.
9 3512xl(config)#int fastethernet 0/3 3512xl(config if)#spanning tree portfast 3512xl(config if)#^z For details on why to enable portfast, refer to: Using Portfast and Other Commands to Fix Workstation Startup Connectivity Delays. Remember to save the configuration. 3512xl#write memory Building configuration xl# 3512xl#show running config Building configuration... Current configuration: version 12.0 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password encryption hostname 3512xl no logging console enable password mysecret ip subnet zero interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport mode trunk If 802.1Q is configured, you will instead see the following output under interface FastEthernet0/1: interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport access vlan 2 spanning tree portfast interface FastEthernet0/3 spanning tree portfast interface FastEthernet0/4 interface FastEthernet0/5 interface FastEthernet0/6 interface FastEthernet0/7
10 interface FastEthernet0/8 interface FastEthernet0/9 interface FastEthernet0/10 interface FastEthernet0/11 interface FastEthernet0/12 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 interface GigabitEthernet0/2 interface VLAN1 ip address no ip directed broadcast no ip route cache ip default gateway line con 0 transport input none stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password mysecret login line vty 5 15 login end Cisco 2600 Router Note: The following screen captures show the commands that were entered on the Cisco 2600 router. Comments between the commands are added in blue italics to explain certain commands and steps. Set the privileged mode and Telnet password on the router. Router#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#hostname c2600 c2600(config)#enable password mysecret c2600(config)#line vty 0 4 c2600(config line)#login c2600(config line)#password mysecret c2600(config line)#exit c2600(config)#no logging console c2600(config)#^z c2600#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Select FastEthernet 0/0 for the trunk configuration. No L2 or Layer 3 (L3) configuration is done here. c2600(config)#int fastethernet 0/0
11 c2600(config if)#no shut c2600(config if)#exit Enable trunking on the sub interface FastEthernet 0/0.1. Note that actual trunks are configured on the sub interfaces. c2600(config)#int fastethernet 0/0.1 Enter the trunking encapsulation as either isl c2600(config subif)#encapsulation isl 1 or as dot1q: In case of dot1q, you need to make sure that the native VLAN matches across the link. On 3512XL, by default, the native VLAN is 1. On the router, configure VLAN1 as the native VLAN. c2600(config subif)#encapsulation dot1q 1? native Make this is native vlan <cr> c2600(config subif)#encapsulation dot1q 1 native On the switch, if you have a native VLAN other than VLAN1, on the router, configure the same VLAN to be the native VLAN, by using the above command. Note: The encapsulation dot1q 1 native command was added in Cisco IOS version 12.1(3)T. If you are using an earlier version of Cisco IOS, then refer to the 802.1Q configuration for Cisco IOS Versions Earlier than 12.1(3)T section of this document, to configure 802.1Q trunking on the router. Configure L3 information on the sub interface 0/0.1. c2600(config subif)#ip address c2600(config subif)#exit Enable trunking on the sub interface FastEthernet 0/0.2. Note that actual trunks are configured on the sub interfaces. c2600(config)#int fastethernet 0/0.2 Enter the trunking encapsulation as either isl c2600(config subif)#encapsulation isl 2 or as dot1q: c2600(config subif)#encapsulation dot1q 2 Configure L3 information on the sub interface 0/0.2. c2600(config subif)#ip address c2600(config subif)#exit c2600(config)#^z Remember to save the configuration. c2600#write memory Building configuration... [OK] c2600# Note: In order to make this setup work, and to successfully ping between workstation1 and workstation2, you need to make sure that the default gateways on the workstations are setup properly. For workstation1, the default gateway should be and for workstation2, the default gateway should be For details on how to set the default gateways on the workstations, refer to their respective sections in this document.
12 The following paragraph is only applicable, if you have configured 802.1Q trunking between the router and the switch. If you have followed the configuration steps listed in the above sections, and are still not able to ping across the VLANs (between workstation1 and workstation2), then there is a possibility that you have come across a currently open Caveat:CSCds42715, in which the 802.1Q native VLAN keyword does not function properly when fast switching is enabled. You can check the status and brief description of the bug by using the Bug Navigator tool and entering the bug ID. If you find that the bug is fixed, then it is recommended that you use that version of code. For more information on Bug Navigator, see the Tools Information section. c2600#show running config Building configuration... Current configuration: version 12.1 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password encryption hostname c2600 no logging console enable password mysecret ip subnet zero interface FastEthernet0/0 no ip address duplex auto speed auto interface FastEthernet0/0.1 encapsulation isl 1 ip address no ip redirects If 802.1Q is configured, you will instead see the following output under interface FastEthernet0/0.1: interface FastEthernet0/0.1 encapsulation dot1q 1 native ip address
13 interface FastEthernet0/0.2 encapsulation isl 2 ip address no ip redirects If 802.1Q is configured, you will instead see the following output under interface FastEthernet0/0.2: interface FastEthernet0/0.2 encapsulation dot1q 2 ip address interface FastEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ip classless no ip http server line con 0 transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password mysecret login no scheduler allocate end 802.1Q Configuration on the Router for Cisco IOS Versions Earlier than 12.1(3)T As described earlier in this document, while configuring 802.1Q trunking it is very important to match the native VLAN across the link. In the Cisco IOS software versions earlier than 12.1(3)T, you cannot define the native VLAN explicitly, as the encapsulation dot1q 1 native command under the sub interface is not available. In the earlier Cisco IOS versions, it is important not to configure VLAN1 interface as a sub interface. The router then expects a tag dot1q frame on VLAN1 and the switch is not expecting a tag on VLAN1. As a result, no traffic will pass between VLAN1 on the switch and the router. In the current lab setup, use the following steps to configure the Cisco 2600 router: Set the privileged mode and Telnet password on the router. Router#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#hostname c2600 c2600(config)#enable password mysecret c2600(config)#line vty 0 4 c2600(config line)#login;
14 c2600(config line)#password mysecret c2600(config line)#exit c2600(config)#no logging console c2600(config)#^z c2600#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Select FastEthernet 0/0 for the trunk configuration. c2600(config)#int fastethernet 0/0 c2600(config if)#no shut Note that the IP address for VLAN1 is configured on the main interface, and no encapsulation for VLAN1 will be done under the sub interface. c2600(config if)#ip address c2600(config if)#exit Configure dot1q encapsulation for VLAN 2 on sub interface fastethernet 0/0.2. c2600(config)#int fastethernet 0/0.2 c2600(config subif)#encapsulation dot1q 2 c2600(config subif)# Configuring L3 information on the sub interface 0/0.2. c2600(config subif)#ip address c2600(config subif)#exit c2600(config)#^z Remember to save the configuration. c2600#write memory Building configuration... [OK] c2600# Notes: In order to make this setup work and to successfully ping between workstation1 and workstation2, you need to make sure that the default gateways on the workstations are setup properly. For workstation1, the default gateway should be , and for workstation2, the default gateway should be For details on how to set the default gateways on the workstations, refer to thei respective sections in this document. c2600#show running config Building configuration... Current configuration: version 12.1 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password encryption hostname c2600 no logging console enable password mysecret
15 memory size iomem 7 ip subnet zero interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address duplex auto speed auto interface FastEthernet0/0.2 encapsulation dot1q 2 ip address interface FastEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ip classless no ip http server line con 0 transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password mysecret login no scheduler allocate end c2600# debug and show Commands On the Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 switch, use the following commands: show int {FastEthernet GigabitEthernet} <module/port> switchport show vlan show vtp status On the Cisco 2600 router, use the following commands: show vlan show interface
16 Sample show Command Output Catalyst 3500XL Switch show int {FastEthernet GigabitEthernet} <module/port> switchport This command is used to check the administrative and operational status of the port. It is also used to make sure that the native VLAN matches on both sides of the trunk. The native VLAN is used for untagged traffic when the port is in 802.1Q trunking mode. Refer to Configuring VTP, VLANs, and VLAN Trunks on Catalyst 2900XL and 3500XL Switches for details on native VLANs. 3512xl#show int fastethernet 0/1 switchport Name: Fa0/1 Switchport: Enabled Administrative mode: trunk Operational Mode: trunk Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: isl Operational Trunking Encapsulation: isl Negotiation of Trunking: Disabled Access Mode VLAN: 0 ((Inactive)) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL Trunking VLANs Active: 1,2 Pruning VLANs Enabled: Priority for untagged frames: 0 Override vlan tag priority: FALSE Voice VLAN: none Appliance trust: none Note: For 802.1Q trunking, the output of the above command changes as follows: 3512xl#show int fastethernet 0/1 switchport Name: Fa0/1 Switchport: Enabled Administrative mode: trunk Operational Mode: trunk Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Operational Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Negotiation of Trunking: Disabled Access Mode VLAN: 0 ((Inactive)) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL Trunking VLANs Active: 1,2 Pruning VLANs Enabled: Priority for untagged frames: 0 Override vlan tag priority: FALSE Voice VLAN: none show vlan This command is used to verify that the interfaces (ports) belong to the correct VLAN. In our example, only interface Fa0/2 belongs to VLAN2. The rest are members of VLAN xl#show vlan VLAN Name Status Ports
17 1 default active Fa0/3, Fa0/4, Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12, Gi0/1, Gi0/2 2 VLAN0002 active Fa0/ fddi default active 1003 token ring default active 1004 fddinet default active 1005 trnet default active...(output suppressed) show vtp status This command is used to check the VLAN trunking protocol (VTP) configuration on the switch. In our example, we have used transparent mode. The correct VTP mode depends on the topology of your network. For details on VTP, refer to Configuring VTP, VLANs, and VLAN Trunks on Catalyst 2900XL and 3500XL Switches. 3512xl#show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 0 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 254 Number of existing VLANs : 6 VTP Operating Mode : Transparent VTP Domain Name : VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled VTP V2 Mode : Disabled VTP Traps Generation : Disabled MD5 digest : 0xC3 0x71 0xF9 0x77 0x2B 0xAC 0x5C 0x97 Configuration last modified by at :00:00 Cisco 2600 Router show vlan This command tells you what L2 or L3 information is configured for each VLAN. c2600#show vlan Virtual LAN ID: 1 (Inter Switch Link Encapsulation) vlan Trunk Interface: FastEthernet0/0.1 Protocols Configured: Address: Received: Transmitted: IP Virtual LAN ID: 2 (Inter Switch Link Encapsulation) vlan Trunk Interface: FastEthernet0/0.2 Protocols Configured: Address: Received: Transmitted: IP Note: For 802.1Q trunking, the output of the above command changes as follows: c2600#show vlan
18 Virtual LAN ID: 1 (IEEE 802.1Q Encapsulation) vlan Trunk Interface: FastEthernet0/0.1 This is configured as native Vlan for the following interface(s): FastEthernet0/0 Protocols Configured: Address: Received: Transmitted: IP Virtual LAN ID: 2 (IEEE 802.1Q Encapsulation) vlan Trunk Interface: FastEthernet0/0.2 Protocols Configured: Address: Received: Transmitted: IP Note: For 802.1Q trunking, with Cisco IOS versions earlier then 12.1(3)T, the output of the command changes as follows: c2600#show vlan Virtual LAN ID: 2 (IEEE 802.1Q Encapsulation) vlan Trunk Interface: FastEthernet0/0.2 Protocols Configured: Address: Received: Transmitted: IP Note: No IEEE 802.1Q encapsulation is displayed for VLAN1 on any of the sub interfaces. show interface This command is used to check the administrative and operational status of the interface. c2600#show interfaces fastethernet 0/0 FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is AmdFE, address is 0003.e36f.41e0 (bia 0003.e36f.41e0) MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit, DLY 100 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) Full duplex, 100Mb/s, 100BaseTX/FX ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:07, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue 0/40, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 1 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 217 packets input, bytes Received 217 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored 0 watchdog 0 input packets with dribble condition detected 45 packets output, 6211 bytes, 0 underruns(0/0/0) 0 output errors, 0 collisions, 4 interface resets 0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred 0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier 0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
19 c2600#show interfaces fastethernet 0/0.1 FastEthernet0/0.1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is AmdFE, address is 0003.e36f.41e0 (bia 0003.e36f.41e0) Internet address is /24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit, DLY 100 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ISL Virtual LAN, Color 1. ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 c2600#show interfaces fastethernet 0/0.2 FastEthernet0/0.2 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is AmdFE, address is 0003.e36f.41e0 (bia 0003.e36f.41e0) Internet address is /24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit, DLY 100 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ISL Virtual LAN, Color 2. ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Note: For 802.1Q trunking, the output of the above command changes as follows: c2600#show interfaces fastethernet 0/0.1 FastEthernet0/0.1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is AmdFE, address is 0003.e36f.41e0 (bia 0003.e36f.41e0) Internet address is /24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit, DLY 100 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation 802.1Q Virtual LAN, Vlan ID 1. ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 c2600#show interfaces fastethernet 0/0.2 FastEthernet0/0.2 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is AmdFE, address is 0003.e36f.41e0 (bia 0003.e36f.41e0) Internet address is /24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit, DLY 100 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation 802.1Q Virtual LAN, Vlan ID 2. ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Tools Information To use the troubleshooting tools described below, you must be a registered user and you must be logged in. Feature Navigator use this tool for a complete list of feature sets supported in the different Cisco IOS versions and on different platforms. Bug Navigator use this tool to search for known bugs based on software version, feature set, and keywords. Hardware Software Compatibility Matrix use this tool for a complete list of minimum supported software for any router family.
20 Related Information Configuring VTP, VLANs, and VLAN Trunks on Catalyst 2900XL and 3500XL Switches Creating and Maintaining VLANs on Catalyst 2950 Switches Using Portfast and Other Commands to Fix Workstation Startup Connectivity Delays Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL, Cisco IOS Desktop Switching Command Reference Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Command Reference Cisco IOS Switching Services Configuration Guide (12.1) Cisco IOS Switching Services Command Reference (12.1) LAN Technologies Technical Tips LAN Technologies Top Issues All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems Inc. All rights reserved. Important Notices and Privacy Statement.
IEEE 802.1Q Configuration
 CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
1 of :22
 Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router (InterVLAN Routing)
 Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
Table of Contents. isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ
 king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
Application Guide. VLANs for improved Q-SYS performance
 Application Guide Rev. A, 6 June 2018 OPTIMIZE Q-SYS PERFORMANCE: CREATE DEDICATED VLANS. One way to greatly ensure the reliability and performance of a Q-SYS network is putting Q-SYS traffic on one or
Application Guide Rev. A, 6 June 2018 OPTIMIZE Q-SYS PERFORMANCE: CREATE DEDICATED VLANS. One way to greatly ensure the reliability and performance of a Q-SYS network is putting Q-SYS traffic on one or
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol.
 CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
If this is your first time configuring the switch, you will notice that the Switch IOS is almost identical to Router IOS.
 Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card
 CHAPTER 34 Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card This chapter applies to the ML-MR-10 card and describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh
CHAPTER 34 Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card This chapter applies to the ML-MR-10 card and describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh
Lab Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination
CS IT ports switch basic configuration. Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee.
 Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Agenda 24 ports switch basic configuration Switch remote configuration peer2peer star network clients/server star network
Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Agenda 24 ports switch basic configuration Switch remote configuration peer2peer star network clients/server star network
BASIC CONFIGURATION CISCO SWITCH
 BASIC CONFIGURATION CISCO SWITCH switch#show running-config ( prikaz trenutne konfiguracije ) switch#show startup-config ( prikaz startne konfiguracije ) switch#configure terminal ( ulaz u global config
BASIC CONFIGURATION CISCO SWITCH switch#show running-config ( prikaz trenutne konfiguracije ) switch#show startup-config ( prikaz startne konfiguracije ) switch#configure terminal ( ulaz u global config
configuring and connecting 24
 Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch
 Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lab Configuring Basic Switch Settings (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic Switch Configuration
 Topology NOTE TO USER: This activity is a variation of Lab 2.5.1. Packet Tracer may not support all the tasks specified in the hands-on lab. This activity should not be considered equivalent to completing
Topology NOTE TO USER: This activity is a variation of Lab 2.5.1. Packet Tracer may not support all the tasks specified in the hands-on lab. This activity should not be considered equivalent to completing
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues
 Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device
 Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration file for a new networking device, or a device that you have
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration file for a new networking device, or a device that you have
CCNA Practice test. 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage? A. NTP B. WCCP C. Telnet D. SNMP Answer: D
 1. Which network would support at least 30 hosts? A. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 B. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.240 C. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 D. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage?
1. Which network would support at least 30 hosts? A. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 B. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.240 C. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 D. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage?
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
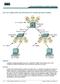 Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software
 Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software Document ID: 8759 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Theory Important
Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software Document ID: 8759 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Theory Important
Configuring IRB. Integrated Routing and Bridging CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure integrated routing and bridging (IRB) for the ML-Series card. For more information about the Cisco IOS commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure integrated routing and bridging (IRB) for the ML-Series card. For more information about the Cisco IOS commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device
 Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device First Published: August 9, 2005 Last Updated: December 3, 2010 Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device First Published: August 9, 2005 Last Updated: December 3, 2010 Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing
 Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing This document describes how the IEEE 802.3ad link bundling and load balancing leverages the EtherChannel infrastructure within Cisco software to
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing This document describes how the IEEE 802.3ad link bundling and load balancing leverages the EtherChannel infrastructure within Cisco software to
Configuring Interfaces on the ML-Series Card
 5 CHAPTER This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and running. Advanced packet-over-sonet (POS) interface configuration is covered
5 CHAPTER This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and running. Advanced packet-over-sonet (POS) interface configuration is covered
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series
 Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Switch configuration. By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch.
 By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch. 4 SESSION OVERVIEW... 2 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS... 3 WHY CONFIGURE SWITCHES?... 4 CONSOLE PORT...
By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch. 4 SESSION OVERVIEW... 2 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS... 3 WHY CONFIGURE SWITCHES?... 4 CONSOLE PORT...
Lab Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.1 Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure Inter-VLAN routing using a switch with an internal route processor. The network
Lab 5.3.4.1 Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure Inter-VLAN routing using a switch with an internal route processor. The network
Cisco Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam. Practice Test. Version 2.2. https://certkill.com
 Cisco 640-821 640-821 Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam Practice Test Version 2.2 QUESTION NO: 1 Refer to the exhibit. Why was this message received? A. No VTY password has been set B.
Cisco 640-821 640-821 Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam Practice Test Version 2.2 QUESTION NO: 1 Refer to the exhibit. Why was this message received? A. No VTY password has been set B.
Management IP Interface
 The management interface is used for the video control plane messages, such as session creation and deletion, between the Logical Edge Devices (LED) and the external Edge Resource Manager (ERM) server.
The management interface is used for the video control plane messages, such as session creation and deletion, between the Logical Edge Devices (LED) and the external Edge Resource Manager (ERM) server.
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example
 EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example Document ID: 82288 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions EtherSwitch Modules Concepts Configure
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example Document ID: 82288 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions EtherSwitch Modules Concepts Configure
The configuration of the router at the initial stage was fairly simple (quoting only significant commands, not the entire config):
 Gentlemen, As was to be expected, Joseph was correct on all accounts. My testbed consisted of a 2811 router running 12.4(24)T4 Advanced IP Services, and two PCs connected to it. One PC was used as the
Gentlemen, As was to be expected, Joseph was correct on all accounts. My testbed consisted of a 2811 router running 12.4(24)T4 Advanced IP Services, and two PCs connected to it. One PC was used as the
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Basic Router Configuration
 This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Question 5.1. Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain.
 Question 5.1 Q 5.1.1 Number of Collision Domains: = 14 Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain. Number of Broadcast Domains: = 5 Every port on a router
Question 5.1 Q 5.1.1 Number of Collision Domains: = 14 Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain. Number of Broadcast Domains: = 5 Every port on a router
Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF).
 Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers
 Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Troubleshoot Methodology Troubleshoot Examples Introduction This document describes troubleshoot
Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Troubleshoot Methodology Troubleshoot Examples Introduction This document describes troubleshoot
Lab Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
Lab Viewing Network Device MAC Addresses
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Configure Devices
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Configure Devices
VLANs. Traditional Campus Networks. Performance Issues. Broadcast Issues. Bridges terminate collision domains
 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 6 The chapter applies to the ML-Series (ML100T-2, ML100X-8, ML1000-2 cards. This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and
CHAPTER 6 The chapter applies to the ML-Series (ML100T-2, ML100X-8, ML1000-2 cards. This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing
 Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup
 Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
Lab Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Note: Use two 2960 switches for ALS1 and ALS2 and two 3560 switches for DLS1 and DLS2
 LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
Configuring Catalyst Switches for Polycom Conference Phones
 Configuring Catalyst Switches for Polycom Conference Phones Document ID: 97229 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Background Information Configure
Configuring Catalyst Switches for Polycom Conference Phones Document ID: 97229 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Background Information Configure
PT Activity 4.4.1: Basic VTP Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13 255.255.255.0
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13 255.255.255.0
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network
 IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. VLANs, Trunking, & VTP. VLANs Overview
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2
 Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Lab Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Configure VTP Part 2: Configure DTP Table Heading Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Configure VTP Part 2: Configure DTP Table Heading Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0
Lab 6.4.1: Basic Inter-VLAN Routing
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1
All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example
 All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 81682 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 81682 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS
 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. This chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Configuration, page 9-2 Using the Interface,
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. This chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Configuration, page 9-2 Using the Interface,
Supported Platforms for Unique MAC Address Configuration on VLAN or L3 Interfaces for Catalyst Switches
 Supported Platforms for Unique Configuration on VLAN or L3 Interfaces for Catalyst Switches Document ID: 41263 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Difference Between
Supported Platforms for Unique Configuration on VLAN or L3 Interfaces for Catalyst Switches Document ID: 41263 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Difference Between
Lab Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test
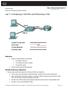 Lab 7.1.6 Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test Objectives Analyze a sample test plan to determine: The subject of the test The methods and tools for testing The potential results Perform the test
Lab 7.1.6 Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test Objectives Analyze a sample test plan to determine: The subject of the test The methods and tools for testing The potential results Perform the test
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example
 GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1
 CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
Lab 1. CLI Navigation. Scenario. Initial Configuration for R1
 Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
 This chapter explains how to configure the Gigabit Ethernet (GE) interface on the Cisco ASR 901 router. Configuring the Interface, page 1 Setting the Speed and Duplex Mode, page 2 Enabling the Interface,
This chapter explains how to configure the Gigabit Ethernet (GE) interface on the Cisco ASR 901 router. Configuring the Interface, page 1 Setting the Speed and Duplex Mode, page 2 Enabling the Interface,
Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE
 Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE Document ID: 4105 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations
Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE Document ID: 4105 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations
Lab - Exploring Router Physical Characteristics
 Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Router External Characteristics Part 2: Examine Router Internal Characteristics Using Show Commands Background / Scenario In this lab, you will examine the outside of
Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Router External Characteristics Part 2: Examine Router Internal Characteristics Using Show Commands Background / Scenario In this lab, you will examine the outside of
Configuring EtherChannel Between Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL Switches and CatOS Switches
 Configuring EtherChannel Between Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL Switches and CatOS Switches Document ID: 14974 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Configuring EtherChannel Between Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL Switches and CatOS Switches Document ID: 14974 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Lab Exploring Cisco IOS and Configuring Basic Switch Settings
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Cable
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Cable
Address Resolution Protocol
 The (ARP) feature performs a required function in IP routing. ARP finds the hardware address, also known as Media Access Control (MAC) address, of a host from its known IP address. ARP maintains a cache
The (ARP) feature performs a required function in IP routing. ARP finds the hardware address, also known as Media Access Control (MAC) address, of a host from its known IP address. ARP maintains a cache
RealCiscoLAB.com. Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network. Hot
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network. Hot
SWITCH Lab Guide Labs powered by
 SWITCH Lab Guide 300-115 ii SWITCH 300-115 Lab Guide LM20170908/BV1.0 iii 25 C e n tur y Blvd., S te. 5 0 0, N a s hvill e, T N 37214 B o s o n.c o m To perform the labs referenced in this book, please
SWITCH Lab Guide 300-115 ii SWITCH 300-115 Lab Guide LM20170908/BV1.0 iii 25 C e n tur y Blvd., S te. 5 0 0, N a s hvill e, T N 37214 B o s o n.c o m To perform the labs referenced in this book, please
Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection
 Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection This chapter describes the tasks for configuring Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED), distributed WRED (DWRED), flow-based WRED, and DiffServ Compliant WRED
Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection This chapter describes the tasks for configuring Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED), distributed WRED (DWRED), flow-based WRED, and DiffServ Compliant WRED
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
For information about configuring these settings from Cluster Management Suite (CMS), refer to the online help.
 Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Modular Ethernet Line Card
 Configuring the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Modular Ethernet Line Card This chapter provides information about configuring the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Modular Ethernet Line Card on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers.
Configuring the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Modular Ethernet Line Card This chapter provides information about configuring the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Modular Ethernet Line Card on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers.
Buy full file at
 14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS
 Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
CONFIGURATION DU SWITCH
 Current configuration : 2037 bytes version 12.2 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname Switch no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero
Current configuration : 2037 bytes version 12.2 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname Switch no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CCIE Foundation. WorkBooks.com. Narbik Kocharians CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP. 3550/3560 Switching. Answers
 CCIE Foundation The GAP from CCNP to CCIE WWW.Net WorkBooks.com Narbik Kocharians CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP 3550/3560 Switching Answers CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 1 of
CCIE Foundation The GAP from CCNP to CCIE WWW.Net WorkBooks.com Narbik Kocharians CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP 3550/3560 Switching Answers CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 1 of
Lab 5: Basic VLAN Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Table of Contents. Cisco Configuring Jumbo/Giant Frame Support on Catalyst Switches
 Table of Contents Jumbo/Giant Frame Support on Catalyst Switches Configuration Example...1 Document ID: 24048...1 Introduction...1 Conventions...1 Background Theory...2 Catalyst Supports for Maximum Frame
Table of Contents Jumbo/Giant Frame Support on Catalyst Switches Configuration Example...1 Document ID: 24048...1 Introduction...1 Conventions...1 Background Theory...2 Catalyst Supports for Maximum Frame
Configuring 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet WAN Optical Services Modules
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet WAN Optical Services Modules This chapter provides an overview of the features supported on the 4-port Gigabit Ethernet WAN Optical Services Modules (OSM-2+4GE-WAN+
CHAPTER 4 Configuring 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet WAN Optical Services Modules This chapter provides an overview of the features supported on the 4-port Gigabit Ethernet WAN Optical Services Modules (OSM-2+4GE-WAN+
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring Weighted Random Early Detection
 Feature History Release Cisco IOS Modification For information about feature support in Cisco IOS software, use Cisco Feature Navigator. This module describes the tasks for configuring Weighted Random
Feature History Release Cisco IOS Modification For information about feature support in Cisco IOS software, use Cisco Feature Navigator. This module describes the tasks for configuring Weighted Random
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
Basic switch configuration
 Basic switch configuration Cisco IOS Basic switch functions, names and passwords The switch name is tool to let us see what device we are connected to. The prompt will display the name of the switch so
Basic switch configuration Cisco IOS Basic switch functions, names and passwords The switch name is tool to let us see what device we are connected to. The prompt will display the name of the switch so
Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol
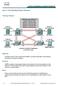 Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Diagram Objective Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault tolerant routing to the internal network. Scenario Step 1 HSRP provides
Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Diagram Objective Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault tolerant routing to the internal network. Scenario Step 1 HSRP provides
Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller
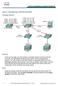 Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller Topology Diagram Scenario Step 1 In the next two labs, you will configure a wireless solution involving a WLAN controller, two lightweight wireless access points,
Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller Topology Diagram Scenario Step 1 In the next two labs, you will configure a wireless solution involving a WLAN controller, two lightweight wireless access points,
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Setup a VTP v2 Domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q Trunking. Setup a VTP v3 Domain.
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Setup a VTP v2 Domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q Trunking. Setup a VTP v3 Domain.
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
