Router Configuration. Router Fundamentals Connecting to the Console Port Router Modes -- User EXEC Router Modes -- Privileged EXEC Lab #9 Goals
|
|
|
- Antonia Warren
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Router Configuration Router Fundamentals Connecting to the Console Port Router Modes -- User EXEC Router Modes -- Privileged EXEC Lab #9 Goals
2 Router Fundamentals Here, we will examine two types of networks: flat vs routed. Devices in a local area network (LAN) tend to be connected at Layers 1 (Physical) and 2 (Data Link), by devices like hubs and switches. Smaller LANs can be interconnected into a larger LAN, with the aid of an additional switch. o If the number of networked hosts is not too large, then it should not be problematic. o However, as the number of hosts increases, it can become a problem because all the hosts will be part of a common broadcast domain.
3 Router Fundamentals A broadcast domain is the set of hosts that will receive a broadcast sent out on a network. o Layer 2 switches create a common broadcast domain. o If there are many hosts, slowdowns can happen because every computer will have to look at a broadcast to decide whether or not to respond When smaller LANs are combined into a larger LAN -- where all have the same broadcast domain -- you have a flat network. These should usually be avoided because of the increased network delays.
4 Router Fundamentals A better option is a routed network, where Layer 3 addresses are used to determine where data packets should be sent. o For this reason, it is also known as a Layer 3 network. o One such example is Figure 7-2. (Where have you seen this figure before?) Figure 7-2 depicts a routed network, consisting of o Four LANs:A, B, C, and D o Three routers:a, B, and C
5 Router Fundamentals Each LAN has a switch that interconnects o The local hosts o...and one of the routers The network is divided into segments, such that a segment is indicated by a connection o From a router to a switch (one of the LANs) o From a router to another router Each segment has an address, so it may also be called a NET or a subnet.
6 Router Fundamentals Unlike a flat network -- where the switches do not separate broadcast domains -- the routers partition a Layer 3 network into separate broadcast domains. The router has multiple Ethernet ports, each of which is connected to one of the segments/subnets. o Each LAN is its own subnet, where hosts IPs start at X.X.X.1, and IP for router/gateway is X.X.X.250 LAN A: LAN B: LAN C: LAN D:
7 Router Fundamentals o Each router-to-router connection is its own subnet, where router local IPs start at X.X.X.1 A-to-B: B-to-C: C-to-A: Within each LAN, the local router connection serves as the default gateway o This is where hosts send data packets addressed outside of the LAN. o The router will have a local IP (i.e., the same subnet) that will be the default gateway address. o Network traffic to a destination outside of the LAN -- or into the LAN from the outside -- will pass through the gateway.
8 Router Fundamentals To determine if the destination IP is within the same subnet, the source host will need to apply the subnet mask to it. o If so, then it can simply be forwarded by the switch at Layer 2 o Otherwise, the data must be sent to the default gateway -- here, the router. Once the router received the outward-bound data, it will choose the next hop The next hop address is the IP of the next networking device that can send the packet, to its eventual destination.
9 Router Fundamentals This information is determined by consulting a routing table, which may contain multiple paths, in case one path is not functional. Each router or other internetworking device -- through which the data must pass, on its way to its destination -- is a "hop". o All other things being equal, the preferred "next hop" is to the shortest path to the destination. o In many cases, "shortest" will simply mean the least hops.
10 Connecting to the Console Port When configuring a router, you will often form a serial connection between the RS-232 serial communications ports of your computer and the router. o On the router, this connection will take place at an RJ-45 jack. (Looks like an Ethernet port but has a different function) o On your computer, this will be a DB-9 or DB-25 connector, with the latter being less common. See Figure 7-6 This linkage will be made over a console cable, which runs between a computer's serial port and a router's console port.
11 Connecting to the Console Port This console cable make take a number of forms: o An RJ-45 plug on one end and a DB-9 plug on the other o Or, something with an adapter -- such as DB-9 to RJ-45. Once the physical connection is formed, you can console into the router with a software program like o HyperTerminal oputty ozterm (Mac)
12 Router Modes -- User EXEC Here, we will be speaking in the context of Cisco routers, specifically. o A Cisco router will run Cisco IOS - the Cisco Internet Operating System o You will interact with the OS via a command line interface (CLI) When you console into a Cisco router, you will see a command prompt consisting of two parts: o Your router's hostname -- the name by which it is known on the network o A symbol, such as # or >
13 Router Modes -- User EXEC For example, when starting the GNS3 labs, your router's hostname is probably "R1", so you may get a prompt that looks like this: R1> This is a clue that you are connected in user EXEC mode -- also known as user mode. o (If you have a ">" instead of a "#", then you are already in a different mode, which we will cover below...) User EXEC mode will not allow you to configure the router, but you can get some basic information about your device.
14 Router Modes -- User EXEC In this mode, there are some basic commands, such as: o? (The help command) On its own, the help command will give you a list of commands and their descriptions After another command, it will give you possible options and arguments to that command. o show Can display various pieces of information about the system, according to the arguments supplied show flash - Information about router's flash memory show version - The version of Cisco IOS on your router.
15 Router Modes -- User EXEC o ping - Testing whether a host is reachable over the network o traceroute - Display route between your current host and some endpoint o enable -- Brings you to privileged EXEC mode o disable -- Opposite of enable
16 Router Modes -- Privileged EXEC If you want to configure your Cisco router's ports and other features, then you will need to be in privileged mode. o If you are currently only in user EXEC mode, then you can use the enable command to enter the privileged mode. o You will know you are there when your command is the router's hostname, followed by a "#" symbol. For example: R1# o Once you make your router password protected, you will need the password to get in o Be careful in this mode, as any mistakes could adversely affect your network.
17 Router Modes -- Privileged EXEC In privileged mode, a very useful command is show ip interface brief, which will display basic information for the various network interfaces on your router. To see more commands, type? and press Enter For actual configuration tasks, you will need to enter configuration mode, using the command configure terminal o A shorthand version of this command is conf t o Many commands have shorthand versions, which you can look up in the textbook and online o If shorthand does not work, then just use the full command
18 Router Modes -- Privileged EXEC When you enter configuration mode, your prompt will have (config) between the hostname and "#" symbol. For example: R1(config)# In configuration mode, you can... o Changing the router's hostname: Enter the command hostname, followed by the router's new name Example: hostname itvm29-6b o Password protection for privileged mode: Enter the command enable, followed by the option secret and the password you chose Example: enable secret itvm29-6b
19 Router Modes -- Privileged EXEC o Configuring FastEthernet and serial interfaces: Enter the command interface, followed by the name of the interface you want to configure Examples: interface FastEthernet0/0 interface Serial0/0 In interface configuration mode, your prompt will replace (config) with (configif). Example: R1(config-if)# o Setting a domain name server, if you want your router to be able to resolve URLs into IP addresses Enter the command ip, followed by name-server and the IP address for your server of choice. Example:ip name-server After name-server, you can enter up to 6 IP addresses, if you want multiple domain name servers
20 Router Modes -- Privileged EXEC o To see more commands available to you in this mode, type? and press Enter o Leaving configuration mode: Type exit and press Enter When you are in interface configuration mode, some important tasks you can do are... o Setting the network address for the interface: Enter the command ip, followed by address and arguments Static IP example: ip address Dynamic IP example: ip address dhcp
21 Router Modes -- Privileged EXEC o Starting up the interface: Enter the command no shutdown o Stopping the interface: Enter the command shutdown o To see more commands available to you in this mode, type? and press Enter o Leaving interface configuration mode: Type exit and press Enter As before, many of these commands have shorthand forms that can save you some typing o sh ip int br for show ip interface brief o no shut for no shutdown
22 Lab #9 Goals In the 9th lab, we are setting up simulated LANs in GNS3 -- each consisting of three PCs and a router, all interconnected by a switch in the middle. The simulated LAN has the subnet address of x.0/24, where 2x is the number (21-28) of your physical machine. o The host computers' IP addresses start at x.101, which you configure accordingly. o The router is connected to the switch on its FastEthernet0/1 interface, which is configured with the IP address x.1 o Therefore, for the hosts, the default gateway address is x.1
23 Lab #9 Goals On your router's other network interface, FastEthernet0/0, it will be connected to the IT Lab LAN, with an IP address in the /24 subnet. o This is the same subnet on which the physical machines in the lab are connected. o Therefore, your router forms a gateway between your simulated LAN ( x.0/24) and the IT Lab LAN ( /24). You do not manually configure the FastEthernet0/0 interface on your router -- at least not the specifics.
24 Lab #9 Goals Instead, you will "configure" the FastEthernet0/0 interface to obtain its configuration information (IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, etc.) automatically -- via DHCP. o DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. o The network interface will obtain its information from a source -- a DHCP server -- that allocates this information according to its own settings. At this point, hosts on your simulated LAN should be able to: o Send and receive data among themselves o Send data to a destination outside the LAN
25 Lab #9 Goals However, they will not be able to: o Receive traffic from a source outside the LAN o Interact with hosts in other groups' simulated LANs With a combination of NAT and static routing, though, we can do both of these...
NETWORK LAB 2 Configuring Switch Desktop
 Configuring Switch 1. Select the switch tab and then add a switch from the list of switches we have to the workspace, we will choose (2950-24) switch. 2. Add a number of PCs next to the switch in order
Configuring Switch 1. Select the switch tab and then add a switch from the list of switches we have to the workspace, we will choose (2950-24) switch. 2. Add a number of PCs next to the switch in order
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding
 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate the ability
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate the ability
Chapter 4: Routing Concepts. Routing & Switching
 Chapter 4: Routing Concepts Routing & Switching Routers are Computers Routers are specialized computers containing the following required components to operate: Central processing unit (CPU) Operating
Chapter 4: Routing Concepts Routing & Switching Routers are Computers Routers are specialized computers containing the following required components to operate: Central processing unit (CPU) Operating
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers %
 CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 100% 1. Which two features are characteristics of flash memory? (Choose two.) Flash provides nonvolatile storage. Flash receives a copy of the IOS from RAM when
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 100% 1. Which two features are characteristics of flash memory? (Choose two.) Flash provides nonvolatile storage. Flash receives a copy of the IOS from RAM when
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 1 Planning and Cabling a Network V 4.0
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 1 Planning and Cabling a Network V 4.0 135 points 1.1.1 What are the common components between a router and other computers? CPU RAM ROM Operating System 1.1.1.2 What does a router connect?
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 1 Planning and Cabling a Network V 4.0 135 points 1.1.1 What are the common components between a router and other computers? CPU RAM ROM Operating System 1.1.1.2 What does a router connect?
Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE3080F tutor to get assigned to your routers.
 EEE00F Lab Basics of the Network Lab Student Lab Manual Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE00F tutor to get assigned to your routers. Contents. Resources used in the labs...
EEE00F Lab Basics of the Network Lab Student Lab Manual Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE00F tutor to get assigned to your routers. Contents. Resources used in the labs...
Static Routing. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine directly
Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine directly
CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers UPDATE 2012 eg.1
 CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers UPDATE 2012 eg.1 January 12th, 2012AdminLeave a commentgo to comments Which of the following are the address ranges of the private IP addresses? (Choose three.) 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers UPDATE 2012 eg.1 January 12th, 2012AdminLeave a commentgo to comments Which of the following are the address ranges of the private IP addresses? (Choose three.) 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI
 Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013
 CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1. Refer to the exhibit. A switch was configured as shown. A ping to the default gateway was issued, but the ping was not successful. Other switches in the same
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1. Refer to the exhibit. A switch was configured as shown. A ping to the default gateway was issued, but the ping was not successful. Other switches in the same
~ 1 ~ Ankara University Department of Computer Engineering COM LAB 1 Part 1
 ~ 1 ~ Ankara University Department of Computer Engineering COM332 2017 LAB 1 Part 1 SECTION 1 PC Network TCP/IP Configuration Objective Identify tools used to discover a computer network configuration
~ 1 ~ Ankara University Department of Computer Engineering COM332 2017 LAB 1 Part 1 SECTION 1 PC Network TCP/IP Configuration Objective Identify tools used to discover a computer network configuration
Lab Troubleshooting RIP
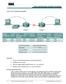 Lab 7.2.6 Troubleshooting RIP Objective Set up an IP addressing scheme using class B networks. Configure RIP on routers. Observe routing activity using the debug ip rip command. Examine routes using the
Lab 7.2.6 Troubleshooting RIP Objective Set up an IP addressing scheme using class B networks. Configure RIP on routers. Observe routing activity using the debug ip rip command. Examine routes using the
Lab Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Smart Serial. Show interfaces. Shut down. logging synchronous
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 2 Static Networking V 4.0 2.1.1 What are the primary responsibilities of the router? 2.1.3 What is the first serial connector described called at the router end? What is the first serial
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 2 Static Networking V 4.0 2.1.1 What are the primary responsibilities of the router? 2.1.3 What is the first serial connector described called at the router end? What is the first serial
Lab Command Line Fundamentals Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 2.2.9 Command Line Fundamentals Instructor Version 2500 Objective Log into a router and go to the user and privileged modes. Use several basic router commands to determine how the router is configured.
Lab 2.2.9 Command Line Fundamentals Instructor Version 2500 Objective Log into a router and go to the user and privileged modes. Use several basic router commands to determine how the router is configured.
CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers UPDATE 2012 eg.2
 CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers UPDATE 2012 eg.2 January 12th, 2012AdminLeave a commentgo to comments 1. When must a router serial interface be configured with the clock rate command? when the interface is functioning
CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers UPDATE 2012 eg.2 January 12th, 2012AdminLeave a commentgo to comments 1. When must a router serial interface be configured with the clock rate command? when the interface is functioning
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals. Configuration of Routers and Establishing Routed Networks
 King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Electrical Engineering Department EE 400, Experiment # 7 Objectives: Configuration of Routers and Establishing Routed Networks The objective of this experiment
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Electrical Engineering Department EE 400, Experiment # 7 Objectives: Configuration of Routers and Establishing Routed Networks The objective of this experiment
Lab 1. CLI Navigation. Scenario. Initial Configuration for R1
 Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services?
 CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam Answers v4.0 100% 1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services? application presentation session transport network 2. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam Answers v4.0 100% 1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services? application presentation session transport network 2. Refer to the exhibit.
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM
 Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
CS356 Lab NIL (Lam) In this lab you will learn: Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 20 min Access Control Lists PartC 30 min Explore!
 CS356 Lab NIL (Lam) In this lab you will learn: PartA Time: 2 hrs 40 min Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 20 min Access Control Lists PartC 30 min Explore! Components used: 2 computers
CS356 Lab NIL (Lam) In this lab you will learn: PartA Time: 2 hrs 40 min Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 20 min Access Control Lists PartC 30 min Explore! Components used: 2 computers
Lab 2.8.2: Challenge Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 Web Server Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 209.165.200.225
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 Web Server Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 209.165.200.225
CS 326e Lab 2, Edmondson-Yurkanan, Spring 2004 Router Configuration, Routing and Access Lists
 CS 326e Lab 2, Edmondson-Yurkanan, Spring 2004 Router Configuration, Routing and Access Lists Name: In this lab you will learn: PartA Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 20 min Dynamic
CS 326e Lab 2, Edmondson-Yurkanan, Spring 2004 Router Configuration, Routing and Access Lists Name: In this lab you will learn: PartA Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 20 min Dynamic
PreLab for CS356 Lab NIL (Lam) (To be submitted when you come for the lab)
 PreLab for CS356 Lab NIL (Lam) (To be submitted when you come for the lab) Name: UT EID: 1. Differentiate between Routers, Switches, and Hubs. 2. Explain subnet masks. 3. For this lab, where is subnet
PreLab for CS356 Lab NIL (Lam) (To be submitted when you come for the lab) Name: UT EID: 1. Differentiate between Routers, Switches, and Hubs. 2. Explain subnet masks. 3. For this lab, where is subnet
CHAPTER 2 ACTIVITY
 CHAPTER 2 ACTIVITY 2.1.1.1 1. CLI stands for 2. GUI stands for 3. Write the step you used to go to CLI interface on Windows 4. The OS, normally loads from a disk drive, into RAM. 5. The portion of the
CHAPTER 2 ACTIVITY 2.1.1.1 1. CLI stands for 2. GUI stands for 3. Write the step you used to go to CLI interface on Windows 4. The OS, normally loads from a disk drive, into RAM. 5. The portion of the
Lab Using the CLI to Gather Network Device Information Topology
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
Lab : Challenge OSPF Configuration Lab. Topology Diagram. Addressing Table. Default Gateway. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
CS 386M Lab 1 Router Configuration and Routing
 CS 386M Lab 1 Router Configuration and Routing In this lab you will learn: PartA Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 30 min Dynamic Routing PartC 40 min Explore! Components used in this
CS 386M Lab 1 Router Configuration and Routing In this lab you will learn: PartA Cisco 2600 Router Configuration Static Routing PartB 30 min Dynamic Routing PartC 40 min Explore! Components used in this
Q&As. Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1. Pass Cisco Exam with 100% Guarantee
 640-822 Q&As Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Pass Cisco 640-822 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee 100% Money
640-822 Q&As Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Pass Cisco 640-822 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee 100% Money
Lab 1.4.6B Implementing Port Security
 Lab 1.4.6B Implementing Port Security Device Designation Device Name VLAN 1 Address Subnet mask S1 FC-ASW-1 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 PC1 Host 1 10.0.0.254 255.255.255.0 PC2 Host 2 10.0.0.253 255.255.255.0
Lab 1.4.6B Implementing Port Security Device Designation Device Name VLAN 1 Address Subnet mask S1 FC-ASW-1 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 PC1 Host 1 10.0.0.254 255.255.255.0 PC2 Host 2 10.0.0.253 255.255.255.0
Lab Configuring DHCP
 Lab 1.2.6 Configuring DHCP Objective Configure a router for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to dynamically assign addresses to attached hosts. Background/Preparation Routing between the ISP
Lab 1.2.6 Configuring DHCP Objective Configure a router for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to dynamically assign addresses to attached hosts. Background/Preparation Routing between the ISP
Powering On the Cisco VG224 Voice Gateway
 CHAPTER 4 To power on your Cisco VG224 voice gateway, perform the following tasks in the order listed, as required: Checklist for Power-On, page 4-1 Power-On Procedure, page 4-1 Initial Configuration Procedures,
CHAPTER 4 To power on your Cisco VG224 voice gateway, perform the following tasks in the order listed, as required: Checklist for Power-On, page 4-1 Power-On Procedure, page 4-1 Initial Configuration Procedures,
CCNA2 Chapter 1 Practice
 CCNA2 Chapter 1 Practice Where should a crossover UTP cable be used? (Choose 2) To connect two PCs together directly. To connect a router to an Ethernet switch. To connect a PC to an Ethernet switch. To
CCNA2 Chapter 1 Practice Where should a crossover UTP cable be used? (Choose 2) To connect two PCs together directly. To connect a router to an Ethernet switch. To connect a PC to an Ethernet switch. To
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces.
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces.
Vendor: Cisco. Exam Code: Exam Name: Cisco Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1 v3.0) Version: Demo
 Vendor: Cisco Exam Code: 100-105 Exam Name: Cisco Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1 v3.0) Version: Demo DEMO QUESTION 1 If the resume command is entered after the sequence that is
Vendor: Cisco Exam Code: 100-105 Exam Name: Cisco Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1 v3.0) Version: Demo DEMO QUESTION 1 If the resume command is entered after the sequence that is
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces. 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces. 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All
Packet Tracer - Connect a Router to a LAN (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default
TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS
 QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping
 Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
MiPDF.COM. 3. Which procedure is used to access a Cisco 2960 switch when performing an initial configuration in a secure environment?
 CCNA1 v6.0 Chapter 2 Exam Answers 2017 (100%) MiPDF.COM 1. What is the function of the kernel of an operating software? It provides a user interface that allows users to request a specific task. The kernel
CCNA1 v6.0 Chapter 2 Exam Answers 2017 (100%) MiPDF.COM 1. What is the function of the kernel of an operating software? It provides a user interface that allows users to request a specific task. The kernel
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS. Cisco Lab Øvelse Af Kim Donnerborg / RTS. Side 0 af 8
 KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
Lab 2.8.1: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Lab Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity
 Lab 9.2.4 Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fast Ethernet 0/2 S1 S1 VLAN
Lab 9.2.4 Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fast Ethernet 0/2 S1 S1 VLAN
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Lab Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 2.2.1 Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the System Configuration dialog (setup). Establish some basic router configurations. Background/Preparation A new router
Lab 2.2.1 Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the System Configuration dialog (setup). Establish some basic router configurations. Background/Preparation A new router
Lab Spanning-Tree Recalculation
 Lab 7.2.6 Spanning-Tree Recalculation Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Observe the behavior of spanning-tree algorithm in presence of switched network topology changes. Background/Preparation
Lab 7.2.6 Spanning-Tree Recalculation Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Observe the behavior of spanning-tree algorithm in presence of switched network topology changes. Background/Preparation
Exam E1 Copyright 2010 Thaar AL_Taiey
 Exam E1 2 Exam E1 E1-1. Which of the following statements is true regarding the internetwork shown in Figure E1-1? (Select all that apply) Figure E1-1 A Sample Internetwork A. The link number 15 uses a
Exam E1 2 Exam E1 E1-1. Which of the following statements is true regarding the internetwork shown in Figure E1-1? (Select all that apply) Figure E1-1 A Sample Internetwork A. The link number 15 uses a
CCNA 1 Chapter 6 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013
 CCNA 1 Chapter 6 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1 After troubleshooting a router, the network administrator wants to save the router configuration so that it will be used automatically the next time that the router
CCNA 1 Chapter 6 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1 After troubleshooting a router, the network administrator wants to save the router configuration so that it will be used automatically the next time that the router
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Chapter 6: Network Layer
 Chapter 6: Network Layer CCNA Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0 Chapter 6 - Sections & Objectives 6.1 Network Layer Protocols Explain how network layer protocols and services support
Chapter 6: Network Layer CCNA Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0 Chapter 6 - Sections & Objectives 6.1 Network Layer Protocols Explain how network layer protocols and services support
Lab b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.1b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500 Objective Scenario Plan, configure, and apply a standard ACL to permit or deny specific traffic and test the ACL to determine if the desired results were
Lab 11.2.1b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500 Objective Scenario Plan, configure, and apply a standard ACL to permit or deny specific traffic and test the ACL to determine if the desired results were
Lab Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems
 Lab 9.4.2 Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems e Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 BRANCH1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.16.0.1
Lab 9.4.2 Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems e Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 BRANCH1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.16.0.1
Packet Tracer Mini-Lab 08: Supplement Configuring 2 LANs/2 Routers using Config, CLI, & RIPv2
 Packet Tracer Mini-Lab 08: Supplement Configuring 2 LANs/2 Routers using Config, CLI, & RIPv2 CAVEAT: THE LABS IN CC2-180 MAY NOT WORK ENTIRELY AS PLANNED. WE WILL BE UTILIZING BOTH A SERVER 2012 R2 HOST
Packet Tracer Mini-Lab 08: Supplement Configuring 2 LANs/2 Routers using Config, CLI, & RIPv2 CAVEAT: THE LABS IN CC2-180 MAY NOT WORK ENTIRELY AS PLANNED. WE WILL BE UTILIZING BOTH A SERVER 2012 R2 HOST
Lab Configuring the OSPF Routing Process
 Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area 0. Configure and verify Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing. Background/Preparation Cable a network
Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area 0. Configure and verify Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing. Background/Preparation Cable a network
IOS and Configuration Basics
 APPENDIX C This appendix contains basic information about the Cisco Internet Operating System (IOS) software and includes the following sections: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation Getting Context-Sensitive
APPENDIX C This appendix contains basic information about the Cisco Internet Operating System (IOS) software and includes the following sections: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation Getting Context-Sensitive
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program
 Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program Accessing the CLI Through Express Setup, page 1 Accessing the CLI Through the Console Port, page 1 Entering the Initial Configuration Information,
Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program Accessing the CLI Through Express Setup, page 1 Accessing the CLI Through the Console Port, page 1 Entering the Initial Configuration Information,
Lab Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 6.1.6 Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure static routes between routers to allow data transfer between routers without the use of dynamic routing protocols. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.1.6 Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure static routes between routers to allow data transfer between routers without the use of dynamic routing protocols. Background/Preparation
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 ( )
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (100-101) Exam Description: The 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1) is a 1.5- hour exam with 50 60 questions. The 100-101 Interconnecting
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (100-101) Exam Description: The 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND1) is a 1.5- hour exam with 50 60 questions. The 100-101 Interconnecting
Lab - Building a Switch and Router Network
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.0.1 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.1 PC-B NIC 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 R1 Objectives
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.0.1 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.1 PC-B NIC 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 R1 Objectives
Enter your answers to the questions in this lab using Canvas Quiz Ch.5 Global Unicast Address + Lab. Additional questions are included in the quiz.
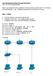 Lab: Introducing Global Unicast Addresses CIS 116 IPv6 Fundamentals Enter your answers to the questions in this lab using Canvas Quiz Ch.5 Global Unicast Address + Lab. Additional questions are included
Lab: Introducing Global Unicast Addresses CIS 116 IPv6 Fundamentals Enter your answers to the questions in this lab using Canvas Quiz Ch.5 Global Unicast Address + Lab. Additional questions are included
CCNA 1 Chapter 11 V4.0 Answers
 CCNA 1 Chapter 11 V4.0 Answers 1. Refer to the exhibit. What command will place the router into the correct mode to configure an appropriate interface to connect to a LAN? UBAMA# configure terminal UBAMA(config)#
CCNA 1 Chapter 11 V4.0 Answers 1. Refer to the exhibit. What command will place the router into the correct mode to configure an appropriate interface to connect to a LAN? UBAMA# configure terminal UBAMA(config)#
Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program
 Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix contains these topics: Accessing the CLI Through Express Setup, page 1 Accessing the CLI Through the Console Port, page 1 Entering
Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix contains these topics: Accessing the CLI Through Express Setup, page 1 Accessing the CLI Through the Console Port, page 1 Entering
CCENT Practice Certification Exam # 2 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing the WAN (Version 4.0)
 CCENT Practice Certification Exam # 2 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing the WAN (Version 4.0) 1. Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function
CCENT Practice Certification Exam # 2 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing the WAN (Version 4.0) 1. Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function
FPG Endpoint Agnostic Port Allocation
 When the Endpoint Agnostic Port Allocation feature is configured, an entry is added to the Symmetric Port Database. If the entry is already available, the port listed in the Symmetric Port Database is
When the Endpoint Agnostic Port Allocation feature is configured, an entry is added to the Symmetric Port Database. If the entry is already available, the port listed in the Symmetric Port Database is
Chapter 2: Configure a Network Operating System. Every computer requires an operating system to function, including computerbased
 2.0.1.1 Chapter 2: Configure a Network Operating System Every computer requires an operating system to function, including computerbased network devices such as switches, routers, access points, and firewalls.
2.0.1.1 Chapter 2: Configure a Network Operating System Every computer requires an operating system to function, including computerbased network devices such as switches, routers, access points, and firewalls.
Smart Install Concepts
 CHAPTER 1 Smart Install is a plug-and-play configuration and image-management feature that provides zero-touch deployment for new switches. This means that a customer can ship a switch to a location, place
CHAPTER 1 Smart Install is a plug-and-play configuration and image-management feature that provides zero-touch deployment for new switches. This means that a customer can ship a switch to a location, place
Lab Selecting the Root Bridge
 Lab 7.2.4 Selecting the Root Bridge Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other
Lab 7.2.4 Selecting the Root Bridge Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other
8.9.2 Lab: Configure an Ethernet NIC to use DHCP in Windows Vista
 8.9.2 Lab: Configure an Ethernet NIC to use DHCP in Windows Vista Introduction If Vista is not available in your classroom, you may complete this lab by viewing the figures in this document. Print and
8.9.2 Lab: Configure an Ethernet NIC to use DHCP in Windows Vista Introduction If Vista is not available in your classroom, you may complete this lab by viewing the figures in this document. Print and
Lab Troubleshooting VTP Configuration
 Lab 4.4.3 Troubleshooting VTP Configuration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Lab 4.4.3 Troubleshooting VTP Configuration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP Fa0/0 172.20.1.129 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.20.1.1 255.255.255.128 N/A Fa0/0 172.20.0.129 255.255.255.128
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP Fa0/0 172.20.1.129 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.20.1.1 255.255.255.128 N/A Fa0/0 172.20.0.129 255.255.255.128
Manual. bintec-elmeg. Proxy ARP. bintec-dm 734-I. Copyright Version bintec-elmeg
 Manual bintec-dm 734-I Copyright Version 11.05 1 Manual Legal Notice Warranty This publication is subject to change. bintec offers no warranty whatsoever for information contained in this manual. bintec
Manual bintec-dm 734-I Copyright Version 11.05 1 Manual Legal Notice Warranty This publication is subject to change. bintec offers no warranty whatsoever for information contained in this manual. bintec
Lab 1.3.2: Review of Concepts from Exploration 1 - Challenge
 Lab 1.3.2: Review of Concepts from Exploration 1 - Challenge Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Create a logical topology given network requirements
Lab 1.3.2: Review of Concepts from Exploration 1 - Challenge Topology Diagram Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Create a logical topology given network requirements
Lab: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Lab: Basic Static Route onfiguration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab: Basic Static Route onfiguration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab Verifying RIP v2 Configuration
 Lab 1.2.5 Verifying RIP v2 Configuration Objective Configure RIP v1 and v2 on routers. Use show commands to verify RIP v2 operation. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the
Lab 1.2.5 Verifying RIP v2 Configuration Objective Configure RIP v1 and v2 on routers. Use show commands to verify RIP v2 operation. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the
Lab10- Configuring EIGRP
 Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Topology Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Page 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup
Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Topology Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Page 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup
Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT
 Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Background/Preparation
Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Background/Preparation
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses
 Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Initial Configuration on ML-Series Card
 CHAPTER 3 This chapter describes the initial configuration of the ML-Series card and contains the following major sections: Hardware Installation, page 3-1 Cisco IOS on the ML-Series Card, page 3-2 Startup
CHAPTER 3 This chapter describes the initial configuration of the ML-Series card and contains the following major sections: Hardware Installation, page 3-1 Cisco IOS on the ML-Series Card, page 3-2 Startup
Antonio Cianfrani. Fundamentals of IP Networking
 Antonio Cianfrani Fundamentals of IP Networking The Internet network routers networks Hosts Network devices TCP/IP protocol stack Application Transport (TCP/UDP) Network (IP) Data Link Applications (HTTP,
Antonio Cianfrani Fundamentals of IP Networking The Internet network routers networks Hosts Network devices TCP/IP protocol stack Application Transport (TCP/UDP) Network (IP) Data Link Applications (HTTP,
Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab Topology Diagram Address Table 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase
Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab Topology Diagram Address Table 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase
Troubleshooting Network analysis Software communication tests and development Education. Protocols used for communication (10 seconds capture)
 Lab 1 Wireshark Wireshark is an open source and free packet analyser used for many purposes, such as: Troubleshooting Network analysis Software communication tests and development Education This reports
Lab 1 Wireshark Wireshark is an open source and free packet analyser used for many purposes, such as: Troubleshooting Network analysis Software communication tests and development Education This reports
OSI Model with Protocols. Layer Name PDU Address Protocols Device
 NetEss Name: Networking Essentials Prof. CHIN OSI Model with Protocols Layer Name PDU Address Protocols Device 7 Application Data FTP, SSH, Telnet, SMTP, DNS TFTP,HTTP, POP3, IMAP, HTTPS 6 Presentation
NetEss Name: Networking Essentials Prof. CHIN OSI Model with Protocols Layer Name PDU Address Protocols Device 7 Application Data FTP, SSH, Telnet, SMTP, DNS TFTP,HTTP, POP3, IMAP, HTTPS 6 Presentation
Classful Address Subnet Mask Number of Hosts per Subnet (2 x 2)
 LAB 1 Exercise 1- Subnetting exercises. Write the subnet, broadcast address, and valid host range for question 1 through question 6: 1. 192.168.100.25/30 2. 192.168.100.37/28 3. 192.168.100.66/27 4. 192.168.100.17/29
LAB 1 Exercise 1- Subnetting exercises. Write the subnet, broadcast address, and valid host range for question 1 through question 6: 1. 192.168.100.25/30 2. 192.168.100.37/28 3. 192.168.100.66/27 4. 192.168.100.17/29
Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM
 Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 Lo1 S0/0/0 Lo1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 S/0/0/1 Learning Objectives
Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 Lo1 S0/0/0 Lo1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 S/0/0/1 Learning Objectives
Switch configuration. By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch.
 By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch. 4 SESSION OVERVIEW... 2 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS... 3 WHY CONFIGURE SWITCHES?... 4 CONSOLE PORT...
By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch. 4 SESSION OVERVIEW... 2 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS... 3 WHY CONFIGURE SWITCHES?... 4 CONSOLE PORT...
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
NAT Routemaps Outside-to-Inside Support
 The feature enables you to configure a NAT routemap configuration that allows IP sessions to be initiated from outside the network to inside the network. This module explains how to configure the feature.
The feature enables you to configure a NAT routemap configuration that allows IP sessions to be initiated from outside the network to inside the network. This module explains how to configure the feature.
Lab Configuring Switch Security Features Topology
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 172.16.99.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 99 172.16.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.16.99.1 PC-A NIC 172.16.99.3
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 172.16.99.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 99 172.16.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.16.99.1 PC-A NIC 172.16.99.3
Module 1 Basic Topology and Router Setup
 Module 1 Basic Topology and Router Setup Objective: Create a basic physical lab with IP addressing and essential router configuration. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working
Module 1 Basic Topology and Router Setup Objective: Create a basic physical lab with IP addressing and essential router configuration. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working
Initial Configuration
 3 CHAPTER This chapter describes the initial configuration of the ML-Series card and contains the following major sections: Hardware Installation, page 3-1 Cisco IOS on the ML-Series Card, page 3-2 Startup
3 CHAPTER This chapter describes the initial configuration of the ML-Series card and contains the following major sections: Hardware Installation, page 3-1 Cisco IOS on the ML-Series Card, page 3-2 Startup
Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Using Packet Tracer to Build a Network
 Using Packet Tracer to Build a Network We will be using Packet Tracer today to create the following network. This topology requires one 2811 router two 2960 switches and three workstations. Launch Packet
Using Packet Tracer to Build a Network We will be using Packet Tracer today to create the following network. This topology requires one 2811 router two 2960 switches and three workstations. Launch Packet
Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing
 Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN
Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN
Lab Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
 Lab 9.3.6 Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create a basic configuration
Lab 9.3.6 Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create a basic configuration
Department Of Computer Science
 Department Of Computer Science Laboratory Manual Prepared By: Muhammad Nouman Farooq Lecturer and Course Coordinator Course: Computer Communication and Networks (CS-205) Page 1 of 43 Table of Contents
Department Of Computer Science Laboratory Manual Prepared By: Muhammad Nouman Farooq Lecturer and Course Coordinator Course: Computer Communication and Networks (CS-205) Page 1 of 43 Table of Contents
Hochschule Bremen Networking Lab
 Hochschule Bremen Networking Lab User Manual Welcome to the Hochschule Bremen networking lab. This manual will give you a brief introduction on how to use the PCs and networking hardware in the lab. The
Hochschule Bremen Networking Lab User Manual Welcome to the Hochschule Bremen networking lab. This manual will give you a brief introduction on how to use the PCs and networking hardware in the lab. The
