CS589: Advanced Computer Networks
|
|
|
- Francis Wilkerson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS589: Advanced Computer Networks Instructor - Z. Morley Mao (zmao@umich.edu, 4629 CSE) Lecture time: TuTh, 10:30-12:30 PM Location: 1018 DOW Office hour: - TuTh 1-2PM - for appointment Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 1
2 Topics Covered Internet design philosophies and principles Internet routing characterization, Internet AS relationships Routing security ISP traffic engineering Critical network infrastructure services Network security: IDS, worms, and honeypots CDNs, Peer to peer and overlay networks, DHTs Wireless networking, meshed networks, mobile systems Sensor networking Network measurements Network security Network models Network algorithmics: building fast networks Networking in challenging environments Data center networking Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 2
3 Interesting new/hot topics A research agenda for Web 2.0 Architectural support for security or availability Computing in the cloud: what role for networking research? Ensuring correctness for distributed protocols Evolution of storage area networks Lessons drawn from failed research, and controversial or disruptive topics Measurement and management of metro-area WiFi networks Network coding: hype or reality? Power as a first-class design property; "green" protocols/implementations Protocol design for optical switching The future role of network processors Third-world networking challenges Understanding the economics of operational costs Unique challenges of massive multi-player game systems Validation of measurement-based research: what are our standards? Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 3
4 Lecture Overview Administrative trivia Course overview Self introduction, student introduction Overview and history of the Internet A Taxonomy of Communication Networks Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 4
5 Administrative Trivia Course Web page: Linked from my home page: - Check it periodically to get the latest information Please come prepared for each class - Reading summaries are due before each class - Attendance is important Assignments are done individually, unless otherwise noted Research project are encouraged to be done in groups (at most 3 people) Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 5
6 Goals of this Course Critical examination of current topics of computer networks - What assumptions are no longer valid - What are the new research problems to look at Understand solutions in context - Goals - Assumptions Learning how to do research in systems - Paper review, writing, and presentation Appreciate what is good research - Problem selection - Solution & research methodology - Presentation Apply what you learned in a class project Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 6
7 What Do You Need To Do? A research-oriented class project Paper readings, selective book chapters Lead at least one class discussion 2-3 assignments Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 7
8 Research Project Investigate new ideas and solutions in a class research project - Define the problem - Execute the research - Work with your partner - Write up and present your research Ideally, best projects will become conference papers (e.g., SIGCOMM, INFOCOM, MOBICOM, Sensys, Mobisys, IMC) Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 8
9 Research Project: Steps I ll distribute a list of projects - You can either choose one of these projects or come up with your own Pick your project, partner, and submit a one page proposal describing: - The problem you are solving - Your plan of attack with milestones and dates - Any special resources you may need A midterm presentation of your progress (>10 minutes) Final project presentation (>30 minutes) Submit project papers Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 9
10 Paper Reviews Goal: synthesize main ideas and concepts in the papers Number: about two papers per class Length: no more than half page per paper Content - Main points intended by the author - Points you particularly liked/disliked - Other comments (writing, conclusions ) Submission: - Submit each review via on lecture day in class - See class web page for details Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 10
11 Grading Term project 50% Assignments 20% Paper presentation 10% Reading summaries 10% Class discussion 10% This is a graduate networking class: more important is what you realize/learn than the grade Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 11
12 Self Introduction Faculty in the software lab Past and ongoing research: - Internet routing, BGP How to protect the Internet routing systems better? - Network measurement How do we know how well networks are doing? - Content distribution networks - Intrusion detection systems - Network troubleshooting, debugging - Network configuration management, provisioning - Denial of service attacks - General interest: Internet networks, routing systems, network security. Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 12
13 Example research project 1: dark DNS Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 13
14 Dark DNS Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 14
15 Example research project 2: Testing the reachability of (new) address space x Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 15
16 Testing reachability We can identify regions in the Internet that do not have reachability It is possible to achieve a reasonable coverage of the Internet We don t only check reachability: we also detect places where there is "non-optimal" connectivity Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 16
17 Example research project 3: On the Impact of Route Monitor Selection Use of route monitoring - Dynamic properties: Routing instability monitoring IP prefix hijacking detection - Static properties: AS topologies Prefix to origin AS mappings - Inference of important network properties AS relationships Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 17
18 Student introduction Please introduce yourself: name, standing, research area (for grad students) Say a few words about what you think you would like to learn about computer networks And what you think are unsolved problems in computer networks Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 18
19 Some unsolved problems QoS - Networks are not fast enough - Networks do not satisfy application requirements - Networks are not robust, highly available Security - There are attacks every where on the Internet - Hosts are easily compromised We still don t have ubiquitous access New technologies: can networks take advantage of them? - Dual core, new algorithms (machine learning, statistical techniques, optimization) Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 19
20 Overview Administrative trivia Overview and history of the Internet A Taxonomy of Communication Networks Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 20
21 What is a Communication Network? (End system view) Network offers a service: move information - Bird, fire, messenger, truck, telegraph, telephone, Internet - Another example, transportation service: move objects horse, train, truck, airplane... What distinguish different types of networks? - The services they provide What distinguish the services? - Latency - Bandwidth - Loss rate - Number of end systems - Service interface (how to invoke?) - Other details Reliability, unicast vs. multicast, real-time, message vs. byte... - What services are missing from today s Internet? Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 21
22 What is a Communication Network? (Infrastructure Centric View) Electrons and photons as communication medium Links: fiber, copper, satellite, Switches: electronic/optical, crossbar/banyan Protocols: TCP/IP, ATM, MPLS, SONET, Ethernet, PPP, X.25, FrameRelay, AppleTalk, IPX, SNA Functionalities: routing, error control, congestion control, Quality of Service (QoS) Applications: FTP, WEB, X windows,... New infrastructures : - Wireless access points, NATs, firewalls, caches, traffic shapers, or middleboxes - Anything you can think of? Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 22
23 Types of Networks Geographical distance - Local Area Networks (LAN): Ethernet, Token ring, FDDI - Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN): DQDB, SMDS - Wide Area Networks (WAN): X.25, ATM, frame relay - Caveat: LAN, MAN, WAN may mean different things service, network technology, networks Information type - Data networks vs. telecommunication networks Application type - Special purpose networks: airline reservation network, banking network, credit card network, telephony - General purpose network: Internet - Private networks or virtual private networks (VPNs) Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 23
24 Types of Networks Right to use - private: enterprise networks - public: telephony network, Internet Ownership of protocols - proprietary: SNA - open: IP Technologies - terrestrial vs. satellite - wired vs. wireless Protocols - IP, AppleTalk, SNA Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 24
25 The Internet Global scale, general purpose, heterogeneoustechnologies, public, computer network Internet Protocol - Open standard: Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as standard body - Technical basis for other types of networks Intranet: enterprise IP network Developed by the research community Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 25
26 History of the Internet 70 s: started as a research project, 56 kbps, < 100 computers 80-83: ARPANET and MILNET split, 85-86: NSF builds NSFNET as backbone, links 6 Supercomputer centers, 1.5 Mbps, 10,000 computers 87-90: link regional networks, NSI (NASA), ESNet(DOE), DARTnet, TWBNet (DARPA), 100,000 computers 90-92: NSFNET moves to 45 Mbps, 16 mid-level networks 94: NSF backbone dismantled, multiple private backbones Today: backbones run at 10 Gbps, 10s millions computers in 150 countries Internet organically evolved! Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 26
27 Time Line of the Internet Source: Internet Society Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 27
28 Growth of the Internet Number of Hosts on the Internet: Aug Oct ,024 Dec ,174 Oct ,000 Oct ,056,000 Apr ,706,000 Jul ,540,000 Jul ,218,000 Jul ,888,197 Jul ,128,493 Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 28
29 Recent Growth ( ) Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 29
30 Who is Who in the Internet? Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF): The IETF is the protocol engineering and development arm of the Internet. Subdivided into many working groups, which specify Request For Comments or RFCs. IRTF (Internet Research Task Force): The Internet Research Task Force is a composed of a number of focused, long-term and small Research Groups. Internet Architecture Board (IAB): The IAB is responsible for defining the overall architecture of the Internet, providing guidance and broad direction to the IETF. The Internet Engineering Steering Group (IESG): The IESG is responsible for technical management of IETF activities and the Internet standards process. Standards. Composed of the Area Directors of the IETF working groups. Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 30
31 Internet Standardization Process All standards of the Internet are published as RFC (Request for Comments). But not all RFCs are Internet Standards! - available: A typical (but not only) way of standardization is: - Internet Drafts - RFC - Proposed Standard - Draft Standard (requires 2 working implementation) - Internet Standard (declared by IAB) David Clark, MIT, 1992: "We reject: kings, presidents, and voting. We believe in: rough consensus and running code. Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 31
32 Services Provided by the Internet Shared access to computing resources - Telnet (1970 s) Shared access to data/files - FTP, NFS, AFS (1980 s) Communication medium over which people interact - (1980 s), on-line chat rooms, instant messaging (1990 s) - Audio, video (1990 s) Replacing telephone network? A medium for information dissemination - USENET (1980 s) - WWW (1990 s) Replacing newspaper, magazine? - Audio, video (2000 s) Replacing radio, CD, TV? Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 32
33 Internet Physical Infrastructure ISP Backbone ISP Residential Access - Modem - DSL - Cable modem - Satellite Enterprise/ISP access, Backbone transmission - T1/T3, DS-1 DS-3 - OC-3, OC-12 - ATM vs. SONET, vs. WDM Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS Campus network - Ethernet, ATM Internet Service Providers - access, regional, backbone - Point of Presence (POP) - Network Access Point (NAP) Where do you think the bottleneck is on today s Internet?
34 Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 34
35 Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 35
36 Is it easy to create network partitions? Where are the shared bottlenecks? How do we guarantee fault isolations? Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 36
37 Overview Administrative trivia Overview and history of the Internet A Taxonomy of Communication Networks Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 37
38 A Taxonomy of Communication Networks Communication networks can be classified based on the way in which the nodes exchange information: Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 38
39 Broadcast vs. Switched Communication Networks Broadcast communication networks - information transmitted by any node is received by every other node in the network examples: usually in LANs (Ethernet, Wavelan) - Problem: coordinate the access of all nodes to the shared communication medium (Multiple Access Problem) Switched communication networks - information is transmitted to a sub-set of designated nodes examples: WANs (Telephony Network, Internet) - Problem: how to forward information to intended node(s) this is done by special nodes (e.g., routers, switches) running routing protocols - New technologies: optical packet switching! Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 39
40 A Taxonomy of Communication Networks Communication networks can be classified based on the way in which the nodes exchange information: Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 40
41 Circuit Switching Three phases 1. circuit establishment 2. data transfer 3. circuit termination If circuit not available: Busy signal Examples - Telephone networks - ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Networks) Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 41
42 Host 1 Host 2 Node 1 Node 2 processing delay at Node 1 DATA propagation delay between Host 1 and Node 1 propagation delay between Host 2 and Node 1 Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 42
43 Circuit Switching A node (switch) in a circuit switching network incoming links Node outgoing links Switches and routers are very complicated! -new requirements for today s routers: ability to filter traffic at line speed graceful degradation under attacks, anything else? Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 43
44 Circuit Switching: Multiplexing/ Demultiplexing Time divided in frames and frames divided in slots Relative slot position inside a frame determines which conversation the data belongs to Needs synchronization between sender and receiver In case of non-permanent conversations - Needs to dynamic bind a slot to a conservation Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 44
45 A Taxonomy of Communication Networks Communication networks can be classified based on the way in which the nodes exchange information: Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 45
46 Packet Switching Data are sent as formatted bit-sequences, so-called packets. Packets have the following structure: Header Data Trailer Header and Trailer carry control information (e.g., destination address, check sum) Each packet is passed through the network from node to node along some path (Routing) At each node the entire packet is received, stored briefly, and then forwarded to the next node - (Store-and-Forward Networks) Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 46
47 Packet Switching A node in a packet switching network incoming links Node Memory outgoing links Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 47
48 Packet Switching: Multiplexing/ Demultiplexing Data from any conversation can be transmitted at any given time How to tell them apart? - use meta-data (header) to describe data Research issues: defense against DDoS attacks, malicious traffic behavior. Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 48
49 A Taxonomy of Communication Networks Communication networks can be classified based on the way in which the nodes exchange information: Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 49
50 Datagram Packet Switching Each packet is independently switched - each packet header contains destination address No resources are pre-allocated (reserved) in advance Example: IP networks Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 50
51 Host 1 Host 2 transmission time of Packet 1 at Host 1 Packet 1 Packet 2 Packet 3 propagation delay between Host 1 and Node 2 Packet 1 Packet 2 Packet 3 Packet 1 Packet 2 Packet 3 Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 51
52 Datagram Packet Switching Host C Host A Host D Node 1 Node 2 Node 3 Node 5 Host B Node 4 Node 6 Node 7 Host E Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 52
53 A Taxonomy of Communication Networks Communication networks can be classified based on the way in which the nodes exchange information: Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 53
54 Virtual-Circuit Packet Switching Hybrid of circuit switching and packet switching - data is transmitted as packets - all packets from one packet stream are sent along a preestablished path (=virtual circuit) Guarantees in-sequence delivery of packets However: Packets from different virtual circuits may be interleaved Example: ATM networks Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 54
55 Virtual-Circuit Packet Switching Communication with virtual circuits takes place in three phases 1. VC establishment 2. data transfer 3. VC disconnect Note: packet headers don t need to contain the full destination address of the packet Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 55
56 Host 1 Host 2 VC establishment propagation delay between Host 1 and Node 1 Packet 1 Data transfer Packet 2 Packet 3 Packet 1 Packet 2 Packet 3 Packet 1 Packet 2 Packet 3 VC termination Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 56
57 Datagram Packet Switching Host C Host A Host D Node 1 Node 2 Node 3 Node 5 Host B Node 4 Node 6 Node 7 Host E Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 57
58 Packet-Switching vs. Circuit-Switching Most important advantage of packet-switching over circuit switching: Ability to exploit statistical multiplexing: - efficient bandwidth usage; ratio between peak and average rate is 3:1 for audio, and 15:1 for data traffic However, packet-switching needs to deal with congestion: - more complex routers - harder to provide good network services (e.g., delay and bandwidth guarantees) In practice they are combined: - IP over SONET, IP over Frame Relay Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 58
59 What s in the news that s relevant? Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 59
60 Flash crowd effect Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 60
61 Real DDoS attacks Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 61
62 Summary Course administrative trivia Internet history and trivia Rest of the course a lot more technical and (hopefully) exciting Z. Morley Mao, Fall 2009, CS589 62
CS 268: Graduate Computer Networks Spring Overview
 CS 268: Graduate Computer s Spring 2006 Instructor: Ion Stoica (istoica@cs.berkeley.edu, 645 Soda Hall) Lecture time: MW, 1:00-2:30pm Place: 320 Soda Hall Office hour: W 2:30-4pm 1 Overview Administrative
CS 268: Graduate Computer s Spring 2006 Instructor: Ion Stoica (istoica@cs.berkeley.edu, 645 Soda Hall) Lecture time: MW, 1:00-2:30pm Place: 320 Soda Hall Office hour: W 2:30-4pm 1 Overview Administrative
EE 122: Introduction to Computer Networks Fall 2002
 EE 122: Introduction to Computer Networks Fall 2002 Instructors - Ion Stoica (istoica@cs.berkeley.edu, 645 Soda Hall) - Kevin Lai (laik@cs.berkeley.edu, 445 Soda Hall) Lecture time - Monday/Wednesday,
EE 122: Introduction to Computer Networks Fall 2002 Instructors - Ion Stoica (istoica@cs.berkeley.edu, 645 Soda Hall) - Kevin Lai (laik@cs.berkeley.edu, 445 Soda Hall) Lecture time - Monday/Wednesday,
Page # Course Description. CS 552 Computer Networks. Overview. Administrative
 Course Description CS 552 Computer s Fall 2004 Rich Martin Graduate course on computer networking Undergraduate knowledge of networking assumed Packets,routing (DV,link-state), layering and encapsulation,
Course Description CS 552 Computer s Fall 2004 Rich Martin Graduate course on computer networking Undergraduate knowledge of networking assumed Packets,routing (DV,link-state), layering and encapsulation,
Computer Networks
 15-441 Computer s Lecture 3 Professor Hui Zhang Wean Hall 7126 hzhang@cs.cmu.edu 1 Review of Lecture 1 How long does it take to move 1GB data from campus to your home? 56Kbps modem 2Mbps DSL Other possibilities?
15-441 Computer s Lecture 3 Professor Hui Zhang Wean Hall 7126 hzhang@cs.cmu.edu 1 Review of Lecture 1 How long does it take to move 1GB data from campus to your home? 56Kbps modem 2Mbps DSL Other possibilities?
CS 552 Computer Networks. Fall 2008 Rich Martin
 CS 552 Computer Networks Fall 2008 Rich Martin Course Description Graduate course on computer networking Undergraduate knowledge of networking assumed Packets,routing (DV,link-state), layering and encapsulation,
CS 552 Computer Networks Fall 2008 Rich Martin Course Description Graduate course on computer networking Undergraduate knowledge of networking assumed Packets,routing (DV,link-state), layering and encapsulation,
Course goals and overview
 Course goals and overview EECS 489 Computer Networks http://www.eecs.umich.edu/~zmao/eecs489 Z. Morley Mao Tuesday Sept 7, 2004 Acknowledgement: Some slides taken from Kurose&Ross and Katz&Stoica 1 Instructors
Course goals and overview EECS 489 Computer Networks http://www.eecs.umich.edu/~zmao/eecs489 Z. Morley Mao Tuesday Sept 7, 2004 Acknowledgement: Some slides taken from Kurose&Ross and Katz&Stoica 1 Instructors
Welcome to CS 340 Introduction to Computer Networking
 Welcome to CS 340 Introduction to Computer ing Overview Course Administrative Trivia Internet Architecture Protocols Edge A taxonomy of communication networks Some slides are in courtesy of J. Kurose and
Welcome to CS 340 Introduction to Computer ing Overview Course Administrative Trivia Internet Architecture Protocols Edge A taxonomy of communication networks Some slides are in courtesy of J. Kurose and
Lecture 3 Protocol Stacks and Layering
 Lecture 3 Protocol Stacks and ing Hui Zhang School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University 15-441 Networking, Fall 2007 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~srini/15-441/f07/ 1 What is a Communication Network?
Lecture 3 Protocol Stacks and ing Hui Zhang School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University 15-441 Networking, Fall 2007 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~srini/15-441/f07/ 1 What is a Communication Network?
EECS 122: Introduction to Computer Networks Course Goals and Overview. Instructors
 EECS 122: Introduction to Computer Networks Course Goals and Overview Computer Science Division Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Berkeley, CA
EECS 122: Introduction to Computer Networks Course Goals and Overview Computer Science Division Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Berkeley, CA
CS4700/CS5700 Fundaments of Computer Networks
 CS4700/CS5700 Fundaments of Computer Networks Lecture 4: Fundamental network design issues Slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica, Hui Zhang Alan Mislove amislove
CS4700/CS5700 Fundaments of Computer Networks Lecture 4: Fundamental network design issues Slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica, Hui Zhang Alan Mislove amislove
INTRODUCTORY COMPUTER
 INTRODUCTORY COMPUTER NETWORKS TYPES OF NETWORKS Faramarz Hendessi Introductory Computer Networks Lecture 4 Fall 2010 Isfahan University of technology Dr. Faramarz Hendessi 2 Types of Networks Circuit
INTRODUCTORY COMPUTER NETWORKS TYPES OF NETWORKS Faramarz Hendessi Introductory Computer Networks Lecture 4 Fall 2010 Isfahan University of technology Dr. Faramarz Hendessi 2 Types of Networks Circuit
CS 268: Computing Networking
 CS 268: Computing Networking Scott Shenker and Ion Stoica (Fall, 2010) 1 People Scott Shenker (shenker@eecs.berkeley.edu) 465 Soda Hall Office Hours: TBA Ion Stoica (istoica@eecs.berkeley.edu) 465 Soda
CS 268: Computing Networking Scott Shenker and Ion Stoica (Fall, 2010) 1 People Scott Shenker (shenker@eecs.berkeley.edu) 465 Soda Hall Office Hours: TBA Ion Stoica (istoica@eecs.berkeley.edu) 465 Soda
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
 CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 15: Networking overview Prof. (amislove@ccs.neu.edu) What is a network? 2 What is a network? Wikipedia: A telecommunications network is a network
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 15: Networking overview Prof. (amislove@ccs.neu.edu) What is a network? 2 What is a network? Wikipedia: A telecommunications network is a network
Goals for Today s Class. EE 122: Networks & Protocols. What Global (non-digital) Communication Network Do You Use Every Day?
 Goals for Today s Class EE 122: & Protocols Ion Stoica TAs: Junda Liu, DK Moon, David Zats http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee122/fa09 (Materials with thanks to Vern Paxson, Jennifer Rexford, and colleagues
Goals for Today s Class EE 122: & Protocols Ion Stoica TAs: Junda Liu, DK Moon, David Zats http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee122/fa09 (Materials with thanks to Vern Paxson, Jennifer Rexford, and colleagues
EECS 122 Communications Networks
 EECS 122 Communications Networks Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Table of Contents 1. Course Organization 2. Introduction 3. Applications/Design 4. Architecture 1 5. Models 6.
EECS 122 Communications Networks Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Table of Contents 1. Course Organization 2. Introduction 3. Applications/Design 4. Architecture 1 5. Models 6.
Communication Networks - 3 general areas: data communications, networking, protocols
 Communication Networks - Overview CSE 3213 Fall 2011 1 7 September 2011 Course Content 3 general areas: data communications, networking, protocols 1. Data communications: basic concepts of digital communications
Communication Networks - Overview CSE 3213 Fall 2011 1 7 September 2011 Course Content 3 general areas: data communications, networking, protocols 1. Data communications: basic concepts of digital communications
PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU START
 Page 1 of 11 MIDTERM EXAMINATION #1 OCT. 16, 2013 COMPUTER NETWORKS : 03-60-367-01 U N I V E R S I T Y O F W I N D S O R S C H O O L O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E Fall 2013-75 minutes This examination
Page 1 of 11 MIDTERM EXAMINATION #1 OCT. 16, 2013 COMPUTER NETWORKS : 03-60-367-01 U N I V E R S I T Y O F W I N D S O R S C H O O L O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E Fall 2013-75 minutes This examination
Chapter 2 Communicating Over the Network
 Chapter 2 Communicating Over the Network Elements of Communication Communicating the Messages Continuous stream of bits 00101010100101010101010101010101010 I have to wait Single communications (e.g. video,
Chapter 2 Communicating Over the Network Elements of Communication Communicating the Messages Continuous stream of bits 00101010100101010101010101010101010 I have to wait Single communications (e.g. video,
Study Guide. Module Three
 Exam Three will draw questions four content areas: our textbook, our assignments, the Rackspace Web Hosting Tutorial, and our class lectures. The purpose of this guide is to help you focus your exam preparations.
Exam Three will draw questions four content areas: our textbook, our assignments, the Rackspace Web Hosting Tutorial, and our class lectures. The purpose of this guide is to help you focus your exam preparations.
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
 CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 17: Internet architecture Prof. Alan Mislove (amislove@ccs.neu.edu) Slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 17: Internet architecture Prof. Alan Mislove (amislove@ccs.neu.edu) Slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion
Data Networks. Lecture 1: Introduction. September 4, 2008
 Data Networks Lecture 1: Introduction September 4, 2008 Slide 1 Learning Objectives Fundamental aspects of network Design and Analysis: Architecture: layering, topology design, switching mechanisms Protocols:
Data Networks Lecture 1: Introduction September 4, 2008 Slide 1 Learning Objectives Fundamental aspects of network Design and Analysis: Architecture: layering, topology design, switching mechanisms Protocols:
Digital Communication Networks
 Digital Communication Networks MIT PROFESSIONAL INSTITUTE, 6.20s July 25-29, 2005 Professor Muriel Medard, MIT Professor, MIT Slide 1 Digital Communication Networks Introduction Slide 2 Course syllabus
Digital Communication Networks MIT PROFESSIONAL INSTITUTE, 6.20s July 25-29, 2005 Professor Muriel Medard, MIT Professor, MIT Slide 1 Digital Communication Networks Introduction Slide 2 Course syllabus
What Global (non-digital) Communication Network Do You Use Every Day?"
 Goals for Today" CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 13 Communication network taxonomy! Circuit switching! Packet switching! Statistical multiplexing! Packet Switching" March 7, 2011!
Goals for Today" CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 13 Communication network taxonomy! Circuit switching! Packet switching! Statistical multiplexing! Packet Switching" March 7, 2011!
Fundamental Issues. System Models and Networking Chapter 2,3. System Models. Architectural Model. Middleware. Bina Ramamurthy
 System Models and Networking Chapter 2,3 Bina Ramamurthy Fundamental Issues There is no global time. All communications are by means of messages. Message communication may be affected by network delays
System Models and Networking Chapter 2,3 Bina Ramamurthy Fundamental Issues There is no global time. All communications are by means of messages. Message communication may be affected by network delays
Lecture 1 Overview - Data Communications, Data Networks, and the Internet
 DATA AND COMPUTER COMMUNICATIONS Lecture 1 Overview - Data Communications, Data Networks, and the Internet Mei Yang Based on Lecture slides by William Stallings 1 OUTLINE Data Communications and Networking
DATA AND COMPUTER COMMUNICATIONS Lecture 1 Overview - Data Communications, Data Networks, and the Internet Mei Yang Based on Lecture slides by William Stallings 1 OUTLINE Data Communications and Networking
PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU START
 Page 1 of 11 MIDTERM EXAMINATION #1 OCT. 13, 2011 COMPUTER NETWORKS : 03-60-367-01 U N I V E R S I T Y O F W I N D S O R S C H O O L O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E Fall 2011-75 minutes This examination
Page 1 of 11 MIDTERM EXAMINATION #1 OCT. 13, 2011 COMPUTER NETWORKS : 03-60-367-01 U N I V E R S I T Y O F W I N D S O R S C H O O L O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E Fall 2011-75 minutes This examination
EECS 228a Lecture 1 Overview: Networks. Jean Walrand
 EECS 228a Lecture 1 Overview: Networks Jean Walrand www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~wlr Fall 2002 Course Information Instructor: Jean Walrand n Office Hours: M-Tu 1:00-2:00 Time/Place: MW 2:00-3:30 in 285 Cory
EECS 228a Lecture 1 Overview: Networks Jean Walrand www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~wlr Fall 2002 Course Information Instructor: Jean Walrand n Office Hours: M-Tu 1:00-2:00 Time/Place: MW 2:00-3:30 in 285 Cory
IT114 NETWORK+ Learning Unit 1 Objectives: 1, 2 Time In-Class Time Out-Of-Class Hours 2-3. Lectures: Course Introduction and Overview
 IT114 NETWORK+ Course Objectives Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Identify the devices and elements of computer networks; 2. Diagram network models using the appropriate
IT114 NETWORK+ Course Objectives Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Identify the devices and elements of computer networks; 2. Diagram network models using the appropriate
What Global (non-digital) Communication Network Do You Use Every Day?"
 CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 8 Introduction to Networking, Packet Switching" September 26, 2011! Anthony D. Joseph and Ion Stoica! http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Review:
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 8 Introduction to Networking, Packet Switching" September 26, 2011! Anthony D. Joseph and Ion Stoica! http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Review:
Virtual Link Layer : Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace
 Virtual Link Layer 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia 3 Lectures left HW #2
Virtual Link Layer 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia 3 Lectures left HW #2
Virtual Link Layer : Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace
 Virtual Link Layer 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia 3 Lectures left HW #2
Virtual Link Layer 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia 3 Lectures left HW #2
Overview of Networks
 CMPT765/408 08-1 Overview of Networks Qianping Gu 1 Overview of Networks This note is mainly based on Chapters 1-2 of High Performance of Communication Networks by J. Walrand and P. Pravin, 2nd ed, and
CMPT765/408 08-1 Overview of Networks Qianping Gu 1 Overview of Networks This note is mainly based on Chapters 1-2 of High Performance of Communication Networks by J. Walrand and P. Pravin, 2nd ed, and
Navpreet Singh INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKS. Computer Centre Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Kanpur INDIA
 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKS Navpreet Singh Computer Centre Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Kanpur INDIA (Ph : 2597371, Email : navi@iitk.ac.in) About Myself About Myself I am Network Manager
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKS Navpreet Singh Computer Centre Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Kanpur INDIA (Ph : 2597371, Email : navi@iitk.ac.in) About Myself About Myself I am Network Manager
BLM6196 COMPUTER NETWORKS AND COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS
 BLM6196 COMPUTER NETWORKS AND COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (1 st Week) Outline Course Information and Policies Course Syllabus 1. Data Communications, Data Networks, and the Internet
BLM6196 COMPUTER NETWORKS AND COMMUNICATION PROTOCOLS Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (1 st Week) Outline Course Information and Policies Course Syllabus 1. Data Communications, Data Networks, and the Internet
Chapter 1. Uses of Computer Networks Network Hardware Network Software Reference Models Example Networks Network Standardization. Revised: August 2011
 Introduction ti Chapter 1 Uses of Computer Networks Network Hardware Network Software Reference Models Example Networks Network Standardization Metric Units Revised: August 2011 Uses of Computer Networks
Introduction ti Chapter 1 Uses of Computer Networks Network Hardware Network Software Reference Models Example Networks Network Standardization Metric Units Revised: August 2011 Uses of Computer Networks
Network Connectivity and Mobility
 Network Connectivity and Mobility BSAD 141 Dave Novak Topics Covered Lecture is structured based on the five elements of creating a connected world from the text book (with additional content) 1. Network
Network Connectivity and Mobility BSAD 141 Dave Novak Topics Covered Lecture is structured based on the five elements of creating a connected world from the text book (with additional content) 1. Network
Announcements. CS 5565 Network Architecture and Protocols. Outline for today. The Internet: nuts and bolts view. The Internet: nuts and bolts view
 Announcements CS 5565 Network Architecture and Protocols Lecture 2 Godmar Back Created Lectures Page Created CS5565 Forum Use this to find a project partner All projects will be done in groups of up to
Announcements CS 5565 Network Architecture and Protocols Lecture 2 Godmar Back Created Lectures Page Created CS5565 Forum Use this to find a project partner All projects will be done in groups of up to
CS 268: Internet Architecture & E2E Arguments. Today s Agenda. Scott Shenker and Ion Stoica (Fall, 2010) Design goals.
 CS 268: Internet Architecture & E2E Arguments Scott Shenker and Ion Stoica (Fall, 2010) 1 Today s Agenda Design goals Layering (review) End-to-end arguments (review) 2 1 Internet Design Goals Goals 0 Connect
CS 268: Internet Architecture & E2E Arguments Scott Shenker and Ion Stoica (Fall, 2010) 1 Today s Agenda Design goals Layering (review) End-to-end arguments (review) 2 1 Internet Design Goals Goals 0 Connect
Introduction to Network Technologies & Layered Architecture BUPT/QMUL
 Introduction to Network Technologies & Layered Architecture BUPT/QMUL 2015-3-5 Review What is the Internet? How does it work? When & how did it come about? Who controls it? Where is it going? 2 Agenda
Introduction to Network Technologies & Layered Architecture BUPT/QMUL 2015-3-5 Review What is the Internet? How does it work? When & how did it come about? Who controls it? Where is it going? 2 Agenda
Defining the Internet
 Defining the Internet Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Communications and Networking Brigham Young University What is the Internet? 2/23 Internet Map, courtesy Barrett Lyon, 2003 What is the Internet? 3/23
Defining the Internet Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Communications and Networking Brigham Young University What is the Internet? 2/23 Internet Map, courtesy Barrett Lyon, 2003 What is the Internet? 3/23
IP Packet Switching. Goals of Todayʼs Lecture. Simple Network: Nodes and a Link. Connectivity Links and nodes Circuit switching Packet switching
 IP Packet Switching CS 375: Computer Networks Dr. Thomas C. Bressoud Goals of Todayʼs Lecture Connectivity Links and nodes Circuit switching Packet switching IP service model Best-effort packet delivery
IP Packet Switching CS 375: Computer Networks Dr. Thomas C. Bressoud Goals of Todayʼs Lecture Connectivity Links and nodes Circuit switching Packet switching IP service model Best-effort packet delivery
Gigabit Networks, VLANs & Wireless LANs
 Hands-On Gigabit Networks, VLANs & Wireless LANs ( Advanced Local Area Networks ) Course Description This Hands-On course will discuss traditional Ethernet as it is evolving today and its future. Ethernet
Hands-On Gigabit Networks, VLANs & Wireless LANs ( Advanced Local Area Networks ) Course Description This Hands-On course will discuss traditional Ethernet as it is evolving today and its future. Ethernet
INTRODUCTION DATA COMMUNICATION TELECOMMUNICATIONS SYSTEM COMPONENTS 1/28/2015. Satish Chandra satish0402.weebly.com
 INTRODUCTION DATA COMMUNICATION Satish Chandra satish0402.weebly.com The term telecommunication means communication at a distance. The word data refers to information presented in whatever form is agreed
INTRODUCTION DATA COMMUNICATION Satish Chandra satish0402.weebly.com The term telecommunication means communication at a distance. The word data refers to information presented in whatever form is agreed
BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS
 BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS INTRODUCTION TO DATA COMMUNICATION NETWORKS Data communications are the exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission medium such as a wire cable.
BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS INTRODUCTION TO DATA COMMUNICATION NETWORKS Data communications are the exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission medium such as a wire cable.
Module 2 Overview of Computer Networks
 Module 2 Overview of Computer Networks Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link:
Module 2 Overview of Computer Networks Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link:
Module 2 Overview of. Computer Networks
 Module Overview of Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link: CS454/654 - Issues How
Module Overview of Networks and Communication Give me names of all employees Who earn more than $00,000 ISP intranet backbone satellite link desktop computer: server: network link: CS454/654 - Issues How
Module 1. Introduction. Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 1 Introduction Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur Introduction In this module we shall highlight some of the basic aspects of computer networks in two lessons. In lesson 1.1 we shall start with the historical
Module 1 Introduction Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur Introduction In this module we shall highlight some of the basic aspects of computer networks in two lessons. In lesson 1.1 we shall start with the historical
CS 204: Advanced Computer Networks
 CS 204: Advanced Computer Networks Jiasi Chen Lectures: MWF 12:10-1pm Humanities and Social Sciences 1403 http://www.cs.ucr.edu/~jiasi/teaching/cs204_spring17/ 1 Why Networks? Supports the applications
CS 204: Advanced Computer Networks Jiasi Chen Lectures: MWF 12:10-1pm Humanities and Social Sciences 1403 http://www.cs.ucr.edu/~jiasi/teaching/cs204_spring17/ 1 Why Networks? Supports the applications
A Whirlwind Introduction to the Internet. A Whirlwind Introduction to the Internet Overview
 CPSC 852 Intering A Whirlwind Introduction to the Internet Michele Weigle Department of Computer Science Clemson University mweigle@cs.clemson.edu http://www.cs.clemson.edu/~mweigle/courses/cpsc852 1 A
CPSC 852 Intering A Whirlwind Introduction to the Internet Michele Weigle Department of Computer Science Clemson University mweigle@cs.clemson.edu http://www.cs.clemson.edu/~mweigle/courses/cpsc852 1 A
WAN Technology & Design. Dr. Nawaporn Wisitpongphan
 WAN Technology & Design Dr. Nawaporn Wisitpongphan 1 WAN Connection Modules 2 WAN Comparison 3 Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) All-digital phone line connection Technology since 1980s Allow
WAN Technology & Design Dr. Nawaporn Wisitpongphan 1 WAN Connection Modules 2 WAN Comparison 3 Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) All-digital phone line connection Technology since 1980s Allow
Networking interview questions
 Networking interview questions What is LAN? LAN is a computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected
Networking interview questions What is LAN? LAN is a computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected
CHAPTER -1. Introduction to Computer Networks
 CHAPTER -1 Introduction to Computer Networks PRELIMINARY DEFINITIONS computer network :: [Tanenbaum] a collection of autonomous computers interconnected by a single technology. communications network ::a
CHAPTER -1 Introduction to Computer Networks PRELIMINARY DEFINITIONS computer network :: [Tanenbaum] a collection of autonomous computers interconnected by a single technology. communications network ::a
Typical Network Uses
 Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Innovation and the Internet
 Innovation and the Internet 29 April 2005 Christopher Buja, Deputy Director Academic Research & Technology Initiatives, Cisco cbuja@cisco.com 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda Introduction
Innovation and the Internet 29 April 2005 Christopher Buja, Deputy Director Academic Research & Technology Initiatives, Cisco cbuja@cisco.com 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda Introduction
Reminder: Datalink Functions Computer Networking. Datalink Architectures
 Reminder: Datalink Functions 15-441 15 441 15-641 Computer Networking Lecture 5 Media Access Control Peter Steenkiste Fall 2015 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f15 Framing: encapsulating a network layer datagram
Reminder: Datalink Functions 15-441 15 441 15-641 Computer Networking Lecture 5 Media Access Control Peter Steenkiste Fall 2015 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f15 Framing: encapsulating a network layer datagram
CS 268: Lecture 4 (Internet Architecture & E2E Arguments)
 CS 268: Lecture 4 (Internet Architecture & E2E Arguments) Today s Agenda Course Theme Course overview History of the Internet Design goals Layering (review) Focus on the Internet Other topics covered,
CS 268: Lecture 4 (Internet Architecture & E2E Arguments) Today s Agenda Course Theme Course overview History of the Internet Design goals Layering (review) Focus on the Internet Other topics covered,
Chapter 3. Underlying Technology. TCP/IP Protocol Suite 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 3 Underlying Technology TCP/IP Protocol Suite 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. OBJECTIVES: To briefly discuss the technology of dominant
Chapter 3 Underlying Technology TCP/IP Protocol Suite 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. OBJECTIVES: To briefly discuss the technology of dominant
Part 1: Introduction. Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview
 Part 1: Introduction Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview Get context Get overview, feel of the Internet Application layer protocols and addressing Network layer / Routing Link layer / Example
Part 1: Introduction Goal: Review of how the Internet works Overview Get context Get overview, feel of the Internet Application layer protocols and addressing Network layer / Routing Link layer / Example
0 TCP/IP overview. 0.1 The Internet
 0521841445 - / Essentials: A Lab-Based Approach 0 / overview From these assumptions comes the fundamental structure of the Internet: a packet switched communications facility in which a number of distinguishable
0521841445 - / Essentials: A Lab-Based Approach 0 / overview From these assumptions comes the fundamental structure of the Internet: a packet switched communications facility in which a number of distinguishable
Introduction to Computer Networks INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKS
 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKS Computer Networks Computer network connects two or more autonomous computers. The computers can be geographically located anywhere. LAN, MAN & WAN Network in small geographical
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKS Computer Networks Computer network connects two or more autonomous computers. The computers can be geographically located anywhere. LAN, MAN & WAN Network in small geographical
Part I: Introduction. 1: Introduction 1
 Part I: Introduction Chapter goal: get context, overview, feel of networking more depth, detail later in course approach: descriptive use Internet as example Overview: what s the Internet what s a protocol?
Part I: Introduction Chapter goal: get context, overview, feel of networking more depth, detail later in course approach: descriptive use Internet as example Overview: what s the Internet what s a protocol?
Computer Communication Networks
 Contents ELL 785 Computer Communication Networks Introduction Lecture 1 Taxonomy of communication works Computer Communication Networks Building a work ed work architecture 1-1 Introduction PC server wireless
Contents ELL 785 Computer Communication Networks Introduction Lecture 1 Taxonomy of communication works Computer Communication Networks Building a work ed work architecture 1-1 Introduction PC server wireless
Lecture #25: Networks and Communications. Communication and Networks. What will we learn?
 Lecture #25: Networks and Communications Communication and Networks What will we learn? How a communications system works What a network is What networks used for What network operating systems do What
Lecture #25: Networks and Communications Communication and Networks What will we learn? How a communications system works What a network is What networks used for What network operating systems do What
Introduction and Layered Network Architecture. EEE 538 Dr. Nail Akar Bilkent University Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department
 Introduction and Layered Network Architecture EEE 538 Dr. Nail Akar Bilkent University Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department 1 Fundamental Aspects of Network Analysis Architecture Layering
Introduction and Layered Network Architecture EEE 538 Dr. Nail Akar Bilkent University Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department 1 Fundamental Aspects of Network Analysis Architecture Layering
Network Architecture
 Unit 7 Network Architecture Acknowledgments: These slides were originally developed by Prof. Jean Walrand for EE122. The past and current EE122 instructors including Kevin Fall, Abhay Parekh, Shyam Parekh,
Unit 7 Network Architecture Acknowledgments: These slides were originally developed by Prof. Jean Walrand for EE122. The past and current EE122 instructors including Kevin Fall, Abhay Parekh, Shyam Parekh,
ECPE / COMP 177 Fall Some slides from Kurose and Ross, Computer Networking, 5 th Edition
 ECPE / COMP 177 Fall 2014 Some slides from Kurose and Ross, Computer Networking, 5 th Edition Instructor: Dr. Jeff Shafer Email: jshafer at pacific dot edu Office: Anderson 205 Office hours (posted on
ECPE / COMP 177 Fall 2014 Some slides from Kurose and Ross, Computer Networking, 5 th Edition Instructor: Dr. Jeff Shafer Email: jshafer at pacific dot edu Office: Anderson 205 Office hours (posted on
Introductions. Computer Networking Lecture 01. January 16, HKU SPACE Community College. HKU SPACE CC CN Lecture 01 1/36
 Introductions Computer Networking Lecture 01 HKU SPACE Community College January 16, 2012 HKU SPACE CC CN Lecture 01 1/36 Outline What is a Computer Network? Basic Requirements of Building a Computer Network
Introductions Computer Networking Lecture 01 HKU SPACE Community College January 16, 2012 HKU SPACE CC CN Lecture 01 1/36 Outline What is a Computer Network? Basic Requirements of Building a Computer Network
Data & Computer Communication
 Basic Networking Concepts A network is a system of computers and other devices (such as printers and modems) that are connected in such a way that they can exchange data. A bridge is a device that connects
Basic Networking Concepts A network is a system of computers and other devices (such as printers and modems) that are connected in such a way that they can exchange data. A bridge is a device that connects
Introduction to Networking
 Introduction to Networking The fundamental purpose of data communications is to exchange information between user's computers, terminals and applications programs. Simplified Communications System Block
Introduction to Networking The fundamental purpose of data communications is to exchange information between user's computers, terminals and applications programs. Simplified Communications System Block
Introduction COURSE BACKGROUND. Lecture Notes. Today s Lecture. Your Instructor. Syllabus and Calendar Are Online
 Lecture Notes Introduction Will be online by noon of the preceding day (today was an exception) Internet Protocols CSC / ECE 573 Fall, 2005 N. C. State University copyright 2005 Douglas S. Reeves 2 Today
Lecture Notes Introduction Will be online by noon of the preceding day (today was an exception) Internet Protocols CSC / ECE 573 Fall, 2005 N. C. State University copyright 2005 Douglas S. Reeves 2 Today
EEC-484/584 Computer Networks
 EEC-484/584 Computer Networks Lecture 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cleveland State University wenbing@ieee.org (Lecture nodes are based on materials supplied by Dr. Louise Moser
EEC-484/584 Computer Networks Lecture 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cleveland State University wenbing@ieee.org (Lecture nodes are based on materials supplied by Dr. Louise Moser
CSc 450/550 Computer Networks Introduction. Jianping Pan Summer 2007
 Computer Networks Introduction Jianping Pan Summer 2007 1 About the course Computer Communications and Networks lectures: MR 11:30am - 1pm, MAC D116 http://www.csc.uvic.ca/~csc450 lectures, labs, discussion
Computer Networks Introduction Jianping Pan Summer 2007 1 About the course Computer Communications and Networks lectures: MR 11:30am - 1pm, MAC D116 http://www.csc.uvic.ca/~csc450 lectures, labs, discussion
Contents. Introduction to Networking. Preface...i. Introduction... xix
 Contents Introduction to Networking Introduction to Networking Preface...i Key Topics...i Course Objectives...ii Pedagogical Features...ii Learning Objectives, Unit Summaries, Discussion Questions, and
Contents Introduction to Networking Introduction to Networking Preface...i Key Topics...i Course Objectives...ii Pedagogical Features...ii Learning Objectives, Unit Summaries, Discussion Questions, and
Computer Communications and Network Basics p. 1 Overview of Computer Communications and Networking p. 2 What Does Computer Communications and
 Computer Communications and Network Basics p. 1 Overview of Computer Communications and Networking p. 2 What Does Computer Communications and Networking Technologies Mean? p. 3 What Is a Computer Network?
Computer Communications and Network Basics p. 1 Overview of Computer Communications and Networking p. 2 What Does Computer Communications and Networking Technologies Mean? p. 3 What Is a Computer Network?
31270 Networking Essentials Focus, Pre-Quiz, and Sample Exam Answers
 31270 Networking Essentials Focus, Pre-Quiz, and Sample Exam Answers CONTENTS Focus Questions... 2 Chapter 1: Explore the Network... 2 Chapter 2: Configure a Network Operating System... 5 Chapter 3: Network
31270 Networking Essentials Focus, Pre-Quiz, and Sample Exam Answers CONTENTS Focus Questions... 2 Chapter 1: Explore the Network... 2 Chapter 2: Configure a Network Operating System... 5 Chapter 3: Network
Lecture 2: Internet Structure
 Lecture 2: Internet Structure COMP 332, Spring 2018 Victoria Manfredi Acknowledgements: materials adapted from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition: 1996-2016, J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross,
Lecture 2: Internet Structure COMP 332, Spring 2018 Victoria Manfredi Acknowledgements: materials adapted from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition: 1996-2016, J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross,
Computer Networks. 9/29/2017 Vasile Dadarlat --Computer Networks 1
 Computer Networks Lecturer: Prof. Vasile Dadarlat, PhD Grading Type: normal, Credits:5 No prerequisite modules required Basic knowledge in Physics, Mathematics, Computer Architecture feel free to ask questions
Computer Networks Lecturer: Prof. Vasile Dadarlat, PhD Grading Type: normal, Credits:5 No prerequisite modules required Basic knowledge in Physics, Mathematics, Computer Architecture feel free to ask questions
Communications and Networking 1
 Communications and Networking 1 ET4254 CS4225 CS5222 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Murphy kevin.murphy@ul.ie Electronic & Computer Engineering Department, University of Limerick, Limerick 1 ET4254 - Communications
Communications and Networking 1 ET4254 CS4225 CS5222 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Murphy kevin.murphy@ul.ie Electronic & Computer Engineering Department, University of Limerick, Limerick 1 ET4254 - Communications
ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies. Networks
 ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies Networks A First Look Under the Hood 2 3 Communication Channels Mediums for transporting data from one system to another Physical Twisted Pair (CAT-3, CAT-5/6)
ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies Networks A First Look Under the Hood 2 3 Communication Channels Mediums for transporting data from one system to another Physical Twisted Pair (CAT-3, CAT-5/6)
WAN Technologies CCNA 4
 WAN Technologies CCNA 4 Overview Note: Most of this will be described in more detail in later chapters. Differentiate between a LAN and WAN Identify the devices used in a WAN List WAN standards Describe
WAN Technologies CCNA 4 Overview Note: Most of this will be described in more detail in later chapters. Differentiate between a LAN and WAN Identify the devices used in a WAN List WAN standards Describe
ECE 333: Introduction to Communication Networks Fall Lecture 1: Introduction
 ECE 333: Introduction to Communication Networks Fall 2001 Lecture 1: Introduction Examples of communication networks/uses Course Goals History Classification of networks Related courses 1 Notes: This is
ECE 333: Introduction to Communication Networks Fall 2001 Lecture 1: Introduction Examples of communication networks/uses Course Goals History Classification of networks Related courses 1 Notes: This is
6 Computer Networks 6.1. Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning
 6 Computer Networks 6.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: 6.2 Describe network criteria, physical structures and categories
6 Computer Networks 6.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: 6.2 Describe network criteria, physical structures and categories
EE 122: Introduction To Communication Networks. Some Questions & Answers
 EE 122: Introduction To Communication Networks Fall 2007 (WF 4-5:30 in Cory 277) Vern Paxson TAs: Lisa Fowler, Daniel Killebrew & Jorge Ortiz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee122/ Materials with thanks
EE 122: Introduction To Communication Networks Fall 2007 (WF 4-5:30 in Cory 277) Vern Paxson TAs: Lisa Fowler, Daniel Killebrew & Jorge Ortiz http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee122/ Materials with thanks
Design Principles : Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace
 Design Principles 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia No Paper Review for today
Design Principles 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia No Paper Review for today
Lecture 1: Introduction
 Int ernet w orking Lecture 1: Introduction The Internet, underlying link layer, and IP addressing Literature: Forouzan: TCP/IP Protocol Suite: Ch 1-5 The Internet today 250 million hosts 580 million users
Int ernet w orking Lecture 1: Introduction The Internet, underlying link layer, and IP addressing Literature: Forouzan: TCP/IP Protocol Suite: Ch 1-5 The Internet today 250 million hosts 580 million users
Goals and topics. Verkkomedian perusteet Fundamentals of Network Media T Circuit switching networks. Topics. Packet-switching networks
 Verkkomedian perusteet Fundamentals of Media T-110.250 19.2.2002 Antti Ylä-Jääski 19.2.2002 / AYJ lide 1 Goals and topics protocols Discuss how packet-switching networks differ from circuit switching networks.
Verkkomedian perusteet Fundamentals of Media T-110.250 19.2.2002 Antti Ylä-Jääski 19.2.2002 / AYJ lide 1 Goals and topics protocols Discuss how packet-switching networks differ from circuit switching networks.
CMSC 332 Computer Networks Network Layer
 CMSC 332 Computer Networks Network Layer Professor Szajda CMSC 332: Computer Networks Where in the Stack... CMSC 332: Computer Network 2 Where in the Stack... Application CMSC 332: Computer Network 2 Where
CMSC 332 Computer Networks Network Layer Professor Szajda CMSC 332: Computer Networks Where in the Stack... CMSC 332: Computer Network 2 Where in the Stack... Application CMSC 332: Computer Network 2 Where
Network Architecture. TOC Architecture
 Network Architecture Introduction Layering Example Internet Layers First Look Layering Step by Step Downside of Layering Interconnecting Networks The Internet TOC Architecture Introduction Issues: Inter-operability
Network Architecture Introduction Layering Example Internet Layers First Look Layering Step by Step Downside of Layering Interconnecting Networks The Internet TOC Architecture Introduction Issues: Inter-operability
5105: BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE NATTARMPALLI UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS AND LINK LAYER PART A
 5105: BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE NATTARMPALLI 635 854. NAME OF THE STAFF : R.ANBARASAN DESIGNATION & DEPARTMENT : AP/CSE SUBJECT CODE : CS 6551 SUBJECT NAME : COMPUTER NETWORKS UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS
5105: BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE NATTARMPALLI 635 854. NAME OF THE STAFF : R.ANBARASAN DESIGNATION & DEPARTMENT : AP/CSE SUBJECT CODE : CS 6551 SUBJECT NAME : COMPUTER NETWORKS UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS
ITEC 3800 Data Communication and Network. Introducing Networks
 ITEC 3800 Data Communication and Network Introducing Networks Introduction to Networking Computer network, or simply network Refers to the connection of two or more computers by some type of medium You
ITEC 3800 Data Communication and Network Introducing Networks Introduction to Networking Computer network, or simply network Refers to the connection of two or more computers by some type of medium You
Internet Architecture & Performance. What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view
 Internet Architecture & Performance Internet, Connection, Protocols, Performance measurements What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end systems pc s workstations,
Internet Architecture & Performance Internet, Connection, Protocols, Performance measurements What s the Internet: nuts and bolts view millions of connected computing devices: hosts, end systems pc s workstations,
Parts of a Network. app. router. link. host. Computer Networks 2
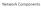 Network Components Parts of a Network app host router link Computer Networks 2 Parts of a Network app host router link Computer Networks 3 Component Names Component Function Example Application, or app,
Network Components Parts of a Network app host router link Computer Networks 2 Parts of a Network app host router link Computer Networks 3 Component Names Component Function Example Application, or app,
Computer Networks. Introduction to Network. Dr. Adel Gaafar Abd Elrahim
 Computer Networks Introduction to Network Dr. Adel Gaafar Abd Elrahim A Communications Model Source generates data to be transmitted Transmitter Converts data into transmittable signals Transmission System
Computer Networks Introduction to Network Dr. Adel Gaafar Abd Elrahim A Communications Model Source generates data to be transmitted Transmitter Converts data into transmittable signals Transmission System
Class Overview. CSE 123b Communications Software. Some hints. Some hints (2) Administrativa. Course material. Winter 2002
 CSE 123b Communications Software Winter 2002 Lecture1: I ntroducti on & Re vi e w Stefan Savage Class Overview Course Material Class lectures, textbook readings, and handouts Course Assignments Homework
CSE 123b Communications Software Winter 2002 Lecture1: I ntroducti on & Re vi e w Stefan Savage Class Overview Course Material Class lectures, textbook readings, and handouts Course Assignments Homework
SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR
 SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & APPLICATIONS QUESTION BANK (2017-2018) Course / Branch : BCA Semester /Year : EVEN / III Subject Name : Data
SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & APPLICATIONS QUESTION BANK (2017-2018) Course / Branch : BCA Semester /Year : EVEN / III Subject Name : Data
Special expressions, phrases, abbreviations and terms of Computer Networks
 access access point adapter Adderssing Realm ADSL (Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line) algorithm amplify amplitude analog antenna application architecture ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) AS (Autonomous
access access point adapter Adderssing Realm ADSL (Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line) algorithm amplify amplitude analog antenna application architecture ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) AS (Autonomous
Computer Networks. Lecture 1: Introduction. Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach. Dr. Yaoqing Liu
 Computer Networks Lecture 1: Introduction Dr. Yaoqing Liu liu@clarkson.edu Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 Based on slides by J. F.
Computer Networks Lecture 1: Introduction Dr. Yaoqing Liu liu@clarkson.edu Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 Based on slides by J. F.
IT 4504 Section 4.0. Network Architectures. 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 1
 IT 4504 Section 4.0 Network Architectures 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 1 Section 4.1 Introduction to Computer Networks 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 2 Introduction
IT 4504 Section 4.0 Network Architectures 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 1 Section 4.1 Introduction to Computer Networks 2008, University of Colombo School of Computing 2 Introduction
PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU START
 Page 1 of 20 MIDTERM EXAMINATION #1 - B COMPUTER NETWORKS : 03-60-367-01 U N I V E R S I T Y O F W I N D S O R S C H O O L O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E Fall 2008-75 minutes This examination document
Page 1 of 20 MIDTERM EXAMINATION #1 - B COMPUTER NETWORKS : 03-60-367-01 U N I V E R S I T Y O F W I N D S O R S C H O O L O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E Fall 2008-75 minutes This examination document
PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU START
 Page 1 of 20 MIDTERM EXAMINATION #1 - A COMPUTER NETWORKS : 03-60-367-01 U N I V E R S I T Y O F W I N D S O R S C H O O L O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E Fall 2008-75 minutes This examination document
Page 1 of 20 MIDTERM EXAMINATION #1 - A COMPUTER NETWORKS : 03-60-367-01 U N I V E R S I T Y O F W I N D S O R S C H O O L O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E Fall 2008-75 minutes This examination document
