Chapter 7. Basic Wireless Concepts and Configuration. Part I
|
|
|
- Lindsey Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 7 Basic Wireless Concepts and Configuration Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 7-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks must go out to Rick Graziani of Cabrillo College. His material and additional information was used as a reference in their creation. If anyone finds any errors or omissions, please let me know at: tdame@stclaircollege.ca. CCNA3-2 Chapter 7-1
2 Basic Wireless Concepts and Configuration The Wireless LAN CCNA3-3 Chapter 7-1 Why Use Wireless? Business networks today are evolving to support people who are on the move. Productivity is no longer restricted to a fixed work location or a defined time period. People now expect to be connected at any time and place,, from the office to the airport or even the home. Now employees can check , voice mail, and the status of products on personal digital assistants (PDAs) while at many temporary locations. At home, the method of accessing the Internet has quickly moved from temporary modem dialup service to dedicated DSL or cable service. CCNA3-4 Chapter 7-1
3 Why Use Wireless? Early communication relied on face-to to-face conversations. The telephone was used for voice and the post office delivered most of the written communications. Video communication was one-way using the television. CCNA3-5 Chapter 7-1 Why Use Wireless? Early networks were limited to character based information. Communications between computers was not easy and required a host (no pun intended) of resources to accomplish the simplest data transfer. CCNA3-6 Chapter 7-1
4 Why Use Wireless? Silver and Diamond Cell Phone $1.3Million Today s s networks Wind carry Energy multiple Cell Phone types of Charger information through many types of devices - SIMULTANEOUSLY. People expect immediate response wherever they are located. CCNA3-7 Chapter 7-1 Introducing Inter-VLAN Routing In addition to the flexibility that WLANs offer, another important benefit is reduced costs. Moving persons Wired Network within a building with a Wireless wireless Network Component infrastructure. Qty Cost Total Qty Cost Total Switches, Moving into a new building with no wired infrastructure. cabinets, etc , , , ,100 Cabling 7, , ,920 Network Adapters 2, ,500 2, ,500 Wireless Access Points 250 1, ,500 POE Adapters ,680 Total 1,039, ,520 Note: Values are estimates and do not reflect actual pricing. CCNA3-8 Chapter 7-1
5 Wireless LANs Most current business networks rely on switch-based LANs for day-to to-day operation inside the office. Workers are becoming more mobile and want to maintain access to their business LAN resources from locations other than their desks. CCNA3-9 Chapter 7-1 Wireless LANs The Wireless LAN, then, is an extension of the Ethernet LAN. CCNA3-10 Chapter 7-1
6 Comparing a WLAN to a LAN Network Architecture Standards Physical Media CCNA3-11 Chapter 7-1 Comparing a WLAN to a LAN Privacy Issues Wireless Access Points (AP) instead of a switch. CCNA3-12 Chapter 7-1
7 Wireless LAN Components Additional components and protocols are used for wireless connections to extend the Ethernet LAN. Wireless Access Point (AP) CCNA3-13 Chapter 7-1 Wireless LAN Standards wireless LAN: An IEEE standard that defines how radio frequency (RF) in the unlicensed industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) frequency bands is used for the Physical layer and the MAC sub-layer of wireless links. Final ratification Typically, the choice of which standard expected to use is in based on data rate. November, 2009 CCNA3-14 Chapter 7-1
8 Wireless LAN Standards Data Rates are affected by modulation technique: Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS): Simpler of the two methods. Less expensive to implement b and g. Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM): Faster data rates than DSSS a, g, n. CCNA3-15 Chapter 7-1 Wireless LAN Standards a Standard: OFDM modulation and uses the 5 GHz band. Less likely to experience interference than devices that operate in the 2.4 GHz band because there are fewer consumer devices that use the 5 GHz band. CCNA3-16 Chapter 7-1
9 Wireless LAN Standards a Standard: Disadvantages to using the 5GHz band. More easily absorbed by walls (obstructions). Slightly poorer range than g. Some countries prohibit use. CCNA3-17 Chapter 7-1 Wireless LAN Standards b and g Standard: Both use the 2.4 GHz band b: Up to 11 Mb/s using DSSS g: Up to 54 Mb/s using OFDM. Backward compatible. CCNA3-18 Chapter 7-1
10 Wireless LAN Standards 2.4 GHz band: Advantage: Better range than the 5GHz band since devices are not as easily obstructed. Disadvantage: Many other devices use this band so it is prone to interference (microwave ovens, baby monitors, Bluetooth,, cordless phones). CCNA3-19 Chapter 7-1 Wireless LAN Standards n: (November 2009) Intended to improve WLAN data rates and range without requiring additional power or RF band allocation. Uses multiple radios and antennae at endpoints,, each broadcasting on the same frequency to establish multiple streams. Multiple Input / Multiple Output (MIMO) and OFDM. Theoretical maximum of 248 Mb/s. CCNA3-20 Chapter 7-1
11 WI-FI Certification Wi-Fi Alliance: March, A global, nonprofit, industry trade association devoted to promoting the growth and acceptance of WLANs. The Wi-Fi Alliance s s testing and certification programs help ensure the interoperability of WLAN products based on the IEEE specification. More than 4,000 products certified. CCNA3-21 Chapter 7-1 WI-FI Certification Three key organizations that influence WLAN standards: International Telecommunications Union Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) R): Regulates the allocation of the RF spectrum. Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE): Specifies how RF is modulated to carry the information. (802.3 Ethernet, Wireless LAN). Wi-Fi Alliance: Ensures that devices are inter-operable. CCNA3-22 Chapter 7-1
12 Wireless Infrastructure Components Wireless NICs: The device that makes a client station capable of sending and receiving RF signals is the wireless NIC. Like an Ethernet NIC, the wireless NIC, using the modulation technique it is configured to use, encodes a data stream onto an RF signal. Wireless NICs are most often associated with mobile devices, such as laptop computers. CCNA3-23 Chapter 7-1 Wireless Infrastructure Components Wireless Access Points: An access point is a Layer 2 device that functions like an Ethernet hub. Connects wireless clients (or stations) to the wired LAN. Client devices communicate with the AP not each other. Converts the TCP/IP data packets from their frame encapsulation to the Ethernet frame format. Clients must associate with an access point to obtain network services. Association: The process by which a client joins an network. It is similar to plugging into a wired LAN. CCNA3-24 Chapter 7-1
13 Wireless Infrastructure Components CSMA/CA: Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance. This simply means that devices on a WLAN must sense the medium for energy (RF stimulation above a certain threshold) and wait until the medium is free before sending. If an access point receives data from a client station, it sends an acknowledgement to the client that the data has been received. This acknowledgement keeps the client from assuming that a collision occurred and prevents a data retransmission by the client. CCNA3-25 Chapter 7-1 Wireless Infrastructure Components CSMA/CA: RF signals attenuate. That means that they lose their energy as they move away from their point of origin. Hidden Node/Station Problem: Two client stations that both connect to the access point, but are at opposite sides of its reach. If they are at the maximum range to reach the access point, they will not be able to reach each other. Neither of those stations sense the other on the medium, and they may end up transmitting simultaneously. CCNA3-26 Chapter 7-1
14 Wireless Infrastructure Components Remember, stations actually CSMA/CA: communicate through the Access One means Point. of resolving The access the point has a hidden node single problem channel is a for all traffic. feature called request to send/clear to send (RTS/CTS). When RTS/CTS is enabled in a network, access points allocate the medium to the requesting station for as long as is required to complete the transmission. When the transmission is complete, other stations can request the channel in a similar fashion. CCNA3-27 Chapter 7-1 Wireless Infrastructure Components Wireless Routers: Wireless routers perform the role of access point, Ethernet switch, and router. The Linksys WRT54GL is most commonly used as a small business or residential wireless access device. The expected load on the device is low enough that it should be able to manage the provision of WLAN, Ethernet, and connect to an ISP. CCNA3-28 Chapter 7-1
15 Wireless Operation Configurable Wireless Parameters: g is backward compatible with b. Mixed mode supports both. CCNA3-29 Chapter 7-1 Wireless Operation Configurable Wireless Parameters: Several access points can share an SSID. A shared service set identifier (SSID) is a unique identifier that client devices use to distinguish between multiple wireless networks in the same vicinity. Alphanumeric, case-sensitive, sensitive, from 2 to 32 characters. CCNA3-30 Chapter 7-1
16 Wireless Operation Configurable Wireless Parameters: The IEEE standard MHz overlap establishes the channelization scheme for the use of the unlicensed ISM RF bands in WLANs. 3 Access Many access points can automatically select Points a channel based on adjacent channel use. The 2.4 GHz band is broken down into Some products continuously monitor the radio space 11 channels for North America to adjust the channel settings dynamically in response and 13 channels for Europe. to environmental changes. Best practices Each for arc WLANs represents that require 1 channel. multiple access points are set to use non-overlapping overlapping channels. CCNA3-31 Chapter 7-1 Wireless Topologies WLANs can accommodate various network topologies. When describing these topologies, the fundamental building block of the IEEE WLAN architecture is the basic service set (BSS). BSS: A group of stations that communicate with each other. Three Types: Ad Hoc (Independent Basic Service Set IBSS) Basic Service Set (BSS( BSS) Extended Service Set (ESS( ESS) CCNA3-32 Chapter 7-1
17 Wireless Topologies Ad Hoc: Wireless networks can operate without access points. Client stations which are configured to operate in ad hoc mode configure the wireless parameters between themselves. CCNA3-33 Chapter 7-1 Wireless Topologies Basic Service Sets (BSS): Access points provide an infrastructure that adds services and improves the range for clients. A single Basic access Service point Area in infrastructure mode manages the wireless parameters and the topology is simply a BSS. The coverage area for both an IBSS or a BSS is the basic service area (BSA). CCNA3-34 Chapter 7-1
18 Wireless Topologies Extended Service Sets (ESS): When a single BSS provides insufficient RF coverage, one or more can Different be joined MAC through Addresses a common distribution system into an extended = different service BSSIDs. set (ESS). One BSS is differentiated from another by the BSS identifier (BSSID). The MAC address of the access point. The coverage area is the extended service area (ESA). CCNA3-35 Chapter 7-1 Wireless Topologies Common Distribution System: Allows multiple access points in an ESS to appear to be a single BSS. An ESS generally includes a common SSID to allow a user to roam from access point to access point. Cells represent the coverage area provided by a single channel. An ESS should have 10 to 15 percent overlap between cells. Roaming capability created by using non-overlapping overlapping channels (e.g. one cell on channel 1 and the other on channel 6). CCNA3-36 Chapter 7-1
19 Wireless Association Key part of the process is discovering a WLAN and connecting to it. The primary components: Beacons: Frames used by the WLAN network to advertise its presence. Probes: Frames used by WLAN clients to find their networks. Authentication: Left over from the original standard, but still required. Association: Establishing the data link between an access point and a WLAN client. CCNA3-37 Chapter 7-1 Wireless Association Beacons: Frames used by the WLAN network to advertise its presence. The only part of the process that may be broadcast on a regular basis. Not necessarily enabled. CCNA3-38 Chapter 7-1
20 Wireless Association Before an client can send data over a WLAN network, it goes through the following three-stage process: Step 1: Probing. Step 2: Authentication. Step 3: Association. CCNA3-39 Chapter 7-1 Wireless Association Step 1: Probing specific network by: Clients search for a specific Sending a probe request out on multiple channels. Specifies the network name (SSID) and bit rates. A typical WLAN client is configured with a desired SSID. Client is simply trying to discover available WLANs: Sends out a probe request with no SSID. All access points that are configured to respond to this type of query respond. WLANs with the broadcast SSID feature disabled do not respond. CCNA3-40 Chapter 7-1
21 Wireless Association Step 2: Authentication was originally developed with two authentication mechanisms. Open Authentication: A NULL authentication The client says "authenticate me. The access point responds with "yes. This is the mechanism used in almost all deployments. CCNA3-41 Chapter 7-1 Wireless Association Step 2: Authentication was originally developed with two authentication mechanisms. Shared Key Authentication: Based on a key that is shared between the client station and the access point called the Wired Equivalency Protection (WEP) key. The idea of the shared WEP key is that it gives a wireless link the equivalent privacy of a wired link, but the original implementation was flawed. WEP needs to be included in client and access point implementations for standards compliance but it is not used or recommended. CCNA3-42 Chapter 7-1
22 Wireless Association Step 3: Association Finalizes the security and bit rate options. Establishes the data link between the WLAN client and the access point. The client learns the BSSID (MAC Address) of the access point. Access point maps a logical port known as the association identifier (AID) to the WLAN client. AID is equivalent to a port on a switch. Association allows the infrastructure switch to keep track of frames destined for the WLAN client so that they can be forwarded. CCNA3-43 Chapter 7-1 Wireless Association CCNA3-44 Chapter 7-1
23 Planning the Wireless LAN There needs to be a well-documented plan before a wireless network can be implemented. Number of Users: Not a straightforward calculation. Depends on the geographical layout of your facility (how many bodies and devices fit in a space), Data Rates: RF is a shared medium and the more users there are the greater the contention for RF. Use non-overlapping overlapping channels in an ESS. You will have sufficient wireless support for your clients if you plan your network for proper RF coverage in an ESS. CCNA3-45 Chapter 7-1 Planning the Wireless LAN Location of Access Points: You may not be able to simply draw coverage area circles and drop them over a plan. Do access points use existing wiring? Position access points: Above obstructions. Vertically near the ceiling in the center of each coverage area, if possible. In locations where users are expected to work. For example, conference rooms are typically a better location for access points than a hallway. CCNA3-46 Chapter 7-1
24 Planning the Wireless LAN Coverage Area of Access Points: Estimate the expected coverage area of an access point. This value varies depending on: The WLAN standard or mix of standards that you are deploying. The nature of the facility. The transmit power that the access point. Based on your plan, place access points on the floor plan so that coverage circles are overlapping. CCNA3-47 Chapter ,000 Sq. Ft. (1860 Sq. Meters) Planning the Wireless LAN Number of Access Points Minimum of 6 Mbps b throughput for each Basic Service Area (BSA) 20,000 Sq. Ft. with a coverage of 5,000 Sq. Ft. results in 4 Access Points. Can be achieved with a coverage area of 5,000 Sq. Ft. (465 Sq. Meters) CCNA3-48 Chapter 7-1
25 Planning the Wireless LAN Dimension of Coverage Area 50 foot (15 Meter) Radius 71 foot (22 Meter) Square CCNA3-49 Chapter 7-1 Planning the Wireless LAN Location of Access Points CCNA3-50 Chapter 7-1
Wireless technology Principles of Security
 Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
IT220 Network Standards & Protocols. Unit 6: Chapter 6 Wireless LANs
 IT220 Network Standards & Protocols Unit 6: Chapter 6 Wireless LANs 2 Objectives Identify the major needs and stakeholders for computer networks and network applications. Identify the classifications of
IT220 Network Standards & Protocols Unit 6: Chapter 6 Wireless LANs 2 Objectives Identify the major needs and stakeholders for computer networks and network applications. Identify the classifications of
NT1210 Introduction to Networking. Unit 6: Chapter 6, Wireless LANs
 NT1210 Introduction to Networking Unit 6: Chapter 6, Wireless LANs Objectives Identify the major needs and stakeholders for computer networks and network applications. Identify the classifications of networks
NT1210 Introduction to Networking Unit 6: Chapter 6, Wireless LANs Objectives Identify the major needs and stakeholders for computer networks and network applications. Identify the classifications of networks
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs
 Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks Wireless Transmission for LAN Radio Frequency Transmission (RF) Infrared Transmission 2 1
Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks Wireless Transmission for LAN Radio Frequency Transmission (RF) Infrared Transmission 2 1
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Wireless Technologies
 Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
Wireless Networking. Chapter The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 Wireless Networking Chapter 23 Overview In this chapter, you will learn how to Discuss wireless networking components Analyze and explain wireless networking standards Install and configure wireless networks
Wireless Networking Chapter 23 Overview In this chapter, you will learn how to Discuss wireless networking components Analyze and explain wireless networking standards Install and configure wireless networks
04/11/2011. Wireless LANs. CSE 3213 Fall November Overview
 Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
Wireless Networks. Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas. Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov.
 Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
WiFi Networks: IEEE b Wireless LANs. Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018
 WiFi Networks: IEEE 802.11b Wireless LANs Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018 Background (1 of 2) In many respects, the IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN (WLAN) standard
WiFi Networks: IEEE 802.11b Wireless LANs Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Winter 2018 Background (1 of 2) In many respects, the IEEE 802.11b wireless LAN (WLAN) standard
WNC-0300USB. 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL
 WNC-0300USB 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL Contents 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Product Feature...3 1.2 System Requirement...3 2. Getting Start...3 2.1 LED Indicators...3 2.2 Install the 54Mbps Wireless
WNC-0300USB 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL Contents 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Product Feature...3 1.2 System Requirement...3 2. Getting Start...3 2.1 LED Indicators...3 2.2 Install the 54Mbps Wireless
1. INTRODUCTION. Wi-Fi 1
 Wi-Fi 1 1. INTRODUCTION Wi-Fi, or Wireless Fidelity, is freedom: it allows you to connect to the Internet from your home, a bed in a hotel room or at a conference room at work without wires. How? Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi 1 1. INTRODUCTION Wi-Fi, or Wireless Fidelity, is freedom: it allows you to connect to the Internet from your home, a bed in a hotel room or at a conference room at work without wires. How? Wi-Fi
Mobile and Sensor Systems
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Protocols and Wireless Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo In this lecture We will describe medium access control protocols and wireless systems
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Protocols and Wireless Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo In this lecture We will describe medium access control protocols and wireless systems
Wireless Networking based on Chapter 15 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers
 Wireless Networking 802.11 based on Chapter 15 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers topics Standards Technical Concepts Implementation Troubleshooting 802.11 timeline source: Anandtech
Wireless Networking 802.11 based on Chapter 15 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers topics Standards Technical Concepts Implementation Troubleshooting 802.11 timeline source: Anandtech
Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment:
 Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment: This material is based on the slides formatted by Dr Sunilkumar S. manvi and Dr Mahabaleshwar S. Kakkasageri, the authors of the textbook: Wireless and Mobile Networks, concepts
Chapter 3.1 Acknowledgment: This material is based on the slides formatted by Dr Sunilkumar S. manvi and Dr Mahabaleshwar S. Kakkasageri, the authors of the textbook: Wireless and Mobile Networks, concepts
Outdoor High Power b/g/n Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL 4.0
 Outdoor High Power 802.11b/g/n Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL 4.0 2012 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Hardware Installation... 4 3 Driver Installation... 6 3.1 Windows XP... 6 3.2 Windows Vista... 9
Outdoor High Power 802.11b/g/n Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL 4.0 2012 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Hardware Installation... 4 3 Driver Installation... 6 3.1 Windows XP... 6 3.2 Windows Vista... 9
Feature. What exactly is WLAN? More reading:
 The WLAN Roadmap Wireless Local Area Networking (WLAN) is a simple concept, but one that entails a wide, sometimes confusing, variety of standards, implementations, and future plans for development. This
The WLAN Roadmap Wireless Local Area Networking (WLAN) is a simple concept, but one that entails a wide, sometimes confusing, variety of standards, implementations, and future plans for development. This
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks
 Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach Featuring the Internet, 3 rd edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, July 2004. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach Featuring the Internet, 3 rd edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley, July 2004. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks 6
Learning Objectives. Introduction. Advantages of WLAN. Information Technology. Mobile Computing. Module: Wireless Local Area Network: IEEE 802.
 Information Technology Mobile Computing Module: Wireless Local Area Network: IEEE 802.11 Learning Objectives Introduction to Wireless Local Area Network Advantages of WLAN Types of WLAN IEEE 802.11 standards
Information Technology Mobile Computing Module: Wireless Local Area Network: IEEE 802.11 Learning Objectives Introduction to Wireless Local Area Network Advantages of WLAN Types of WLAN IEEE 802.11 standards
CSNT 180 Wireless Networking. Chapter 7 WLAN Terminology and Technology
 CSNT 180 Wireless Networking Chapter 7 WLAN Terminology and Technology Norman McEntire norman.mcentire@servin.com Founder, Servin Corporation, http://servin.com Technology Training for Technology Professionals
CSNT 180 Wireless Networking Chapter 7 WLAN Terminology and Technology Norman McEntire norman.mcentire@servin.com Founder, Servin Corporation, http://servin.com Technology Training for Technology Professionals
Public Wireless LAN Service.
 Public Wireless LAN Service touch@coe.psu.ac.th Radio Wave Wave Frequency Amplitude Wave Length Radio Wave Band Frequency Wavelength VLF 3-30 khz > 10 km LF 30-300 khz 1-10 km MF 300-3,000 khz 100-1000
Public Wireless LAN Service touch@coe.psu.ac.th Radio Wave Wave Frequency Amplitude Wave Length Radio Wave Band Frequency Wavelength VLF 3-30 khz > 10 km LF 30-300 khz 1-10 km MF 300-3,000 khz 100-1000
Naveen Kumar. 1 Wi-Fi Technology
 Naveen Kumar 1 Contents 2 Introduction Need of Purpose History How a Wi-Fi Network Works Topologies & Configurations Applications Wi-Fi Security Advantages & Limitations Innovations Introduction 3 Wireless
Naveen Kumar 1 Contents 2 Introduction Need of Purpose History How a Wi-Fi Network Works Topologies & Configurations Applications Wi-Fi Security Advantages & Limitations Innovations Introduction 3 Wireless
Everybody s connecting.
 Everybody s connecting. The ABGs of Wireless LAN Technology Overview February 2003 Introduction Wireless LANs (WLANs) using the 802.11 standard offer compelling value in office, public, and home LAN environments.
Everybody s connecting. The ABGs of Wireless LAN Technology Overview February 2003 Introduction Wireless LANs (WLANs) using the 802.11 standard offer compelling value in office, public, and home LAN environments.
802.11g PC Card/USB Wireless Adapter
 802.11g PC Card/USB Wireless Adapter User Guide Regulatory Approvals FCC Statement This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of
802.11g PC Card/USB Wireless Adapter User Guide Regulatory Approvals FCC Statement This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE standards
 HW Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE 802.11 standards WLAN Standard (IEEE 802.11) The IEEE 802.11 is a family of standards that governs the operations and functions of WLANs.
HW Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE 802.11 standards WLAN Standard (IEEE 802.11) The IEEE 802.11 is a family of standards that governs the operations and functions of WLANs.
Wireless LANs. ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications
 Wireless LANs ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications Aim: Aim and Contents Understand how IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs work Understand what influences the performance of wireless LANs Contents: IEEE
Wireless LANs ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications Aim: Aim and Contents Understand how IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs work Understand what influences the performance of wireless LANs Contents: IEEE
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 8 High-Speed WLANs and WLAN Security Objectives Describe how IEEE 802.11a networks function and how they differ from 802.11 networks Outline how 802.11g
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 8 High-Speed WLANs and WLAN Security Objectives Describe how IEEE 802.11a networks function and how they differ from 802.11 networks Outline how 802.11g
Overview of IEEE Networks. Timo Smura
 Overview of IEEE 802.11 Networks Timo Smura 24.03.2004 Outline Introduction IEEE 802.11 standards Protocol model Network topologies 802.11 MAC layer 802.11 PHY layers Interoperability: Wi-Fi Alliance 3GPP
Overview of IEEE 802.11 Networks Timo Smura 24.03.2004 Outline Introduction IEEE 802.11 standards Protocol model Network topologies 802.11 MAC layer 802.11 PHY layers Interoperability: Wi-Fi Alliance 3GPP
Technical Introduction
 802.11 Technical Introduction Tomas Krag t@wire.less.dk Unlicensed Spectrum There was a need for spectrum with fewer regulations The ISM band at 2.4 Ghz & 5.2 GHz The UNII band at 5.8 GHz No need for a
802.11 Technical Introduction Tomas Krag t@wire.less.dk Unlicensed Spectrum There was a need for spectrum with fewer regulations The ISM band at 2.4 Ghz & 5.2 GHz The UNII band at 5.8 GHz No need for a
WIRELESS USB 2.0 ADAPTER. Manual (DN & DN )
 WIRELESS USB 2.0 ADAPTER Manual (DN-7043-4 & DN-7053-2) 1. Introduction... 1 2. Wireless LAN Basics... 3 3. IP ADDRESS... 4 4. Install Driver/Utility... 5 4.1 Windows XP/Vista... 5 5. Wireless Network
WIRELESS USB 2.0 ADAPTER Manual (DN-7043-4 & DN-7053-2) 1. Introduction... 1 2. Wireless LAN Basics... 3 3. IP ADDRESS... 4 4. Install Driver/Utility... 5 4.1 Windows XP/Vista... 5 5. Wireless Network
Overview : Computer Networking. Spectrum Use Comments. Spectrum Allocation in US Link layer challenges and WiFi WiFi
 Overview 15-441 15-441: Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 21: Wireless Justine Sherry Peter Steenkiste Fall 2017 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f17 Link layer challenges and WiFi WiFi Basic WiFi design Some
Overview 15-441 15-441: Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 21: Wireless Justine Sherry Peter Steenkiste Fall 2017 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f17 Link layer challenges and WiFi WiFi Basic WiFi design Some
Wireless LAN. Access Point. Provides network connectivity over wireless media
 LAN Technologies 802.11 Wireless LAN Network connectivity to the legacy wired LAN Access Point Desktop with PCI 802.11 LAN card Laptop with PCMCIA 802.11 LAN card Provides network connectivity over wireless
LAN Technologies 802.11 Wireless LAN Network connectivity to the legacy wired LAN Access Point Desktop with PCI 802.11 LAN card Laptop with PCMCIA 802.11 LAN card Provides network connectivity over wireless
This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to successfully survey, install, and administer enterprise Wi-Fi networks.
 Certified Wireless Network Administrator (CWNA) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to successfully survey, install, and administer enterprise Wi-Fi networks. Course
Certified Wireless Network Administrator (CWNA) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to successfully survey, install, and administer enterprise Wi-Fi networks. Course
Wireless Networks
 802.11 Wireless Networks Presentation for North Central Regional Meeting October 19, 2010 Tom Jones, PE, RCDD / NTS Field Sales Engineer, D-Link Agenda Brief History of Wireless Networks 802.11b, 802.11g
802.11 Wireless Networks Presentation for North Central Regional Meeting October 19, 2010 Tom Jones, PE, RCDD / NTS Field Sales Engineer, D-Link Agenda Brief History of Wireless Networks 802.11b, 802.11g
CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networking
 CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networking Lecture 6 Wireless LAN Components and Characteristics Winter 2017 Some Material in these slides from J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross All material copyright 1996-2007 1 Introduction
CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networking Lecture 6 Wireless LAN Components and Characteristics Winter 2017 Some Material in these slides from J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross All material copyright 1996-2007 1 Introduction
Wireless LAN Access Point
 Wireless LAN Access Point IEEE 802.11b 11Mbps User s Manual Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Package Contents... 2 1.2 Features... 2 1.3 Specifications... 2 1.4 Physical Description...
Wireless LAN Access Point IEEE 802.11b 11Mbps User s Manual Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Package Contents... 2 1.2 Features... 2 1.3 Specifications... 2 1.4 Physical Description...
U S E R M A N U A L b/g PC CARD
 U S E R M A N U A L 802.11b/g PC CARD Table of Content CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 WIRELESS LAN FEATURE FUNCTIONS... 1 1.2 REGULATORY NOTICE... 1 1.2.1 FCC Class B Statement...1 1.2.2 Canadian Regulatory
U S E R M A N U A L 802.11b/g PC CARD Table of Content CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 WIRELESS LAN FEATURE FUNCTIONS... 1 1.2 REGULATORY NOTICE... 1 1.2.1 FCC Class B Statement...1 1.2.2 Canadian Regulatory
Wireless Terms. Uses a Chipping Sequence to Provide Reliable Higher Speed Data Communications Than FHSS
 How to Set Up a Secure Home Wireless Network What you don t know about setting up a home wireless network can hurt you. 2008 APCUG Convention Session Tom Jones, P.E., RCDD-NTS CQS-CWLSS AGENDA Some Terms
How to Set Up a Secure Home Wireless Network What you don t know about setting up a home wireless network can hurt you. 2008 APCUG Convention Session Tom Jones, P.E., RCDD-NTS CQS-CWLSS AGENDA Some Terms
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition. Chapter 8 Wireless Networking
 Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 8 Wireless Networking Objectives Explain how nodes exchange wireless signals Identify potential obstacles to successful wireless transmission and their repercussions,
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 8 Wireless Networking Objectives Explain how nodes exchange wireless signals Identify potential obstacles to successful wireless transmission and their repercussions,
Wednesday, May 16, 2018
 Wednesday, May 16, 2018 8:00 AM - 5:00 PM Wi Fi/WLAN Fundamentals Training by Tessco; Day Two of a Two Day Training. (Attendees must bring laptop computers for this training. Attendees should bring available
Wednesday, May 16, 2018 8:00 AM - 5:00 PM Wi Fi/WLAN Fundamentals Training by Tessco; Day Two of a Two Day Training. (Attendees must bring laptop computers for this training. Attendees should bring available
Architecture. Copyright :I1996 IEEE. All rights reserved. This contains parts from an unapproved draft, subject to change
 802.11 Architecture Copyright :I1996 IEEE. All rights reserved. This contains parts from an unapproved draft, subject to change What is unique about wireless? Difficult media - interference and noise -
802.11 Architecture Copyright :I1996 IEEE. All rights reserved. This contains parts from an unapproved draft, subject to change What is unique about wireless? Difficult media - interference and noise -
Wireless Local Area Networks. Networks: Wireless LANs 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
IEEE Romel Rudyard J. Lucentales, ECE 5
 IEEE 802.11 Romel Rudyard J. Lucentales, ECE 5 IEEE 802.11 a set of standards for wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication developed by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee (IEEE 802)
IEEE 802.11 Romel Rudyard J. Lucentales, ECE 5 IEEE 802.11 a set of standards for wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication developed by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee (IEEE 802)
WLAN TRENDS. Dong Wang. Prof. Dr. Eduard Heindl 05/27/2009. E-Business Technologies
 WLAN TRENDS Dong Wang 232495 Prof. Dr. Eduard Heindl E-Business Technologies 05/27/2009 1 Declaration I, Dong Wang, hereby declare that this paper is my own work and all the related work cites are shown
WLAN TRENDS Dong Wang 232495 Prof. Dr. Eduard Heindl E-Business Technologies 05/27/2009 1 Declaration I, Dong Wang, hereby declare that this paper is my own work and all the related work cites are shown
CWTS Exam Objectives (Exam PW0-070)
 Introduction The Certified Wireless Technology Specialist (CWTS) certification, covering the current objectives, will certify that successful candidates know the fundamentals of RF behavior, can explain
Introduction The Certified Wireless Technology Specialist (CWTS) certification, covering the current objectives, will certify that successful candidates know the fundamentals of RF behavior, can explain
Introduction to Networking Devices
 Introduction to Networking Devices Objectives Explain the uses, advantages, and disadvantages of repeaters, hubs, wireless access points, bridges, switches, and routers Define the standards associated
Introduction to Networking Devices Objectives Explain the uses, advantages, and disadvantages of repeaters, hubs, wireless access points, bridges, switches, and routers Define the standards associated
SEMESTRAL PROJECT 37MK
 SEMESTRAL PROJECT 37MK WIRELESS TOPOLOGIES Jméno : Onofre Arce Juan Pablo Introduction.- The most common devices used on WLANs (Wireless Lans) are workstations, which include both laptop and desktop models.
SEMESTRAL PROJECT 37MK WIRELESS TOPOLOGIES Jméno : Onofre Arce Juan Pablo Introduction.- The most common devices used on WLANs (Wireless Lans) are workstations, which include both laptop and desktop models.
Announcements / Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 9: Wireless LANs Wireless. Regular Ethernet CSMA/CD.
 Announcements 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 9: Wireless LANs 802.11 Wireless Peter Steenkiste Homework 1 should be out by tomorrow Project 1 by Friday Schedule:» Thursday lecture
Announcements 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 9: Wireless LANs 802.11 Wireless Peter Steenkiste Homework 1 should be out by tomorrow Project 1 by Friday Schedule:» Thursday lecture
Chapter 7. OSI Data Link Layer
 Chapter 7 OSI Data Link Layer CCNA1-1 Chapter 7 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks must go
Chapter 7 OSI Data Link Layer CCNA1-1 Chapter 7 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks must go
Chapter 7. OSI Data Link Layer. CCNA1-1 Chapter 7
 Chapter 7 OSI Data Link Layer CCNA1-1 Chapter 7 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks must go
Chapter 7 OSI Data Link Layer CCNA1-1 Chapter 7 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks must go
02/21/08 TDC Branch Offices. Headquarters SOHO. Hot Spots. Home. Wireless LAN. Customer Sites. Convention Centers. Hotel
 TDC 363 Introductions to LANs Lecture 7 Wireless LAN 1 Outline WLAN Markets and Business Cases WLAN Standards WLAN Physical Layer WLAN MAC Layer WLAN Security WLAN Design and Deployment 2 The Mobile Environment
TDC 363 Introductions to LANs Lecture 7 Wireless LAN 1 Outline WLAN Markets and Business Cases WLAN Standards WLAN Physical Layer WLAN MAC Layer WLAN Security WLAN Design and Deployment 2 The Mobile Environment
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks
 CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: Wireless Networks Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Last Time Mobile applications are taking off! What about current platforms is fueling this? How are an application s permission
Wireless Security Protocol Analysis and Design. Artoré & Bizollon : Wireless Security Protocol Analysis and Design
 Protocol Analysis and Design 1 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 2 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 1.1 WiFi 802.11 3 Networks OSI Structure 4 Networks Infrastructure Networks BSS : Basic Set Service ESS : Extended
Protocol Analysis and Design 1 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 2 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 1.1 WiFi 802.11 3 Networks OSI Structure 4 Networks Infrastructure Networks BSS : Basic Set Service ESS : Extended
CWNP PW Certified Wireless Analysis Professional. Download Full Version :
 CWNP PW0-270 Certified Wireless Analysis Professional Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/pw0-270 QUESTION: 50 ABC Company is having VoWiFi latency problems on their 802.11g
CWNP PW0-270 Certified Wireless Analysis Professional Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/pw0-270 QUESTION: 50 ABC Company is having VoWiFi latency problems on their 802.11g
WLAN a-z 2010/02/15. (C) Herbert Haas
 WLAN 802.11a-z (C) Herbert Haas 2010/02/15 Wireless Products WLAN is integrated E. g. Intel Centrino chipsets Increasing data rates Towards Fast Ethernet speeds and more Today strong native security solutions
WLAN 802.11a-z (C) Herbert Haas 2010/02/15 Wireless Products WLAN is integrated E. g. Intel Centrino chipsets Increasing data rates Towards Fast Ethernet speeds and more Today strong native security solutions
 Wireless Networking WiFi Standards 802.11a 5GHz 54MB 802.11b 2.4 GHz 11MB 802.11g 2.4GHz 52MB 802.11n 2.4/5GHz 108MB 802.11b The 802.11b standard has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s, and uses
Wireless Networking WiFi Standards 802.11a 5GHz 54MB 802.11b 2.4 GHz 11MB 802.11g 2.4GHz 52MB 802.11n 2.4/5GHz 108MB 802.11b The 802.11b standard has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s, and uses
Tuesday, May :00 AM - 5:00 PM
 Tuesday, May 15 2018 8:00 AM - 5:00 PM Wi Fi/WLAN Fundamentals Training by Tessco; Day One of a Two Day Training. (Attendees must bring laptop computers for this training. Attendees should bring available
Tuesday, May 15 2018 8:00 AM - 5:00 PM Wi Fi/WLAN Fundamentals Training by Tessco; Day One of a Two Day Training. (Attendees must bring laptop computers for this training. Attendees should bring available
IP network that supports DHCP or manual assignment of IP address, gateway, and subnet mask
 Network Requirements, page 1 Wireless LAN, page 2 Wi-Fi Network Components, page 3 802.11 Standards for WLAN Communications, page 6 Security for Communications in WLANs, page 9 WLANs and Roaming, page
Network Requirements, page 1 Wireless LAN, page 2 Wi-Fi Network Components, page 3 802.11 Standards for WLAN Communications, page 6 Security for Communications in WLANs, page 9 WLANs and Roaming, page
Troubleshooting Microsoft Windows XP-based Wireless Networks in the Small Office or Home Office
 Operating System Troubleshooting Microsoft Windows XP-based Wireless Networks in the Small Office or Home Office Microsoft Corporation Published: December 2004 Update: May 2005 Abstract Because small office/home
Operating System Troubleshooting Microsoft Windows XP-based Wireless Networks in the Small Office or Home Office Microsoft Corporation Published: December 2004 Update: May 2005 Abstract Because small office/home
Wireless Networks. CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: , Kurose and Ross
 Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Last Lecture: Data Link Layer
 Last Lecture: Data Link Layer 1. Design goals and issues 2. (More on) Error Control and Detection 3. Multiple Access Control (MAC) 4. Ethernet, LAN Addresses and ARP 5. Hubs, Bridges, Switches 6. Wireless
Last Lecture: Data Link Layer 1. Design goals and issues 2. (More on) Error Control and Detection 3. Multiple Access Control (MAC) 4. Ethernet, LAN Addresses and ARP 5. Hubs, Bridges, Switches 6. Wireless
Chapter 6 Medium Access Control Protocols and Local Area Networks
 Chapter 6 Medium Access Control Protocols and Local Area Networks 802.11 Wireless LAN CSE 3213, Winter 2010 Instructor: Foroohar Foroozan Wireless Data Communications Wireless communications compelling
Chapter 6 Medium Access Control Protocols and Local Area Networks 802.11 Wireless LAN CSE 3213, Winter 2010 Instructor: Foroohar Foroozan Wireless Data Communications Wireless communications compelling
MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8
 MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8 Michael L. Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University November 2017 The Multiple Access Problem How can multiple mobiles access (communicate with) the same
MSIT 413: Wireless Technologies Week 8 Michael L. Honig Department of EECS Northwestern University November 2017 The Multiple Access Problem How can multiple mobiles access (communicate with) the same
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing. Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology
 CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part II WiFi vs 802.11 IEEE 802.11 Features Hidden Node
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part II WiFi vs 802.11 IEEE 802.11 Features Hidden Node
Mobile Computing IEEE Standard 9/11/12. CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2012
 Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2012 IEEE IEEE (Ins4tute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) established the 802.11 Group in 1990. Specifica4ons for standard ra4fied in 1997. Ini4al speeds were
Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2012 IEEE IEEE (Ins4tute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) established the 802.11 Group in 1990. Specifica4ons for standard ra4fied in 1997. Ini4al speeds were
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer. Computer Networks: Wireless LANs
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer 1 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones)
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer 1 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones)
Data Communication & Networks G Session 5 - Main Theme Wireless Networks. Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti
 Data Communication & Networks G22.2262-001 Session 5 - Main Theme Wireless Networks Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science Department Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences
Data Communication & Networks G22.2262-001 Session 5 - Main Theme Wireless Networks Dr. Jean-Claude Franchitti New York University Computer Science Department Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences
based on Chapter 15 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers
 Wireless Networking 802.11 based on Chapter 15 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers topics History Standards Technical Concepts Implementation Troubleshooting 1 HISTORY AND STANDARDS History
Wireless Networking 802.11 based on Chapter 15 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers topics History Standards Technical Concepts Implementation Troubleshooting 1 HISTORY AND STANDARDS History
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-2
 Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
University of Würzburg Institute of Computer Science Research Report Series. Performance Comparison of Handover Mechanisms in Wireless LAN Networks
 University of Würzburg Institute of Computer Science Research Report Series Performance Comparison of Handover Mechanisms in Wireless LAN Networks Rastin Pries and Klaus Heck Report No. 339 September 2004
University of Würzburg Institute of Computer Science Research Report Series Performance Comparison of Handover Mechanisms in Wireless LAN Networks Rastin Pries and Klaus Heck Report No. 339 September 2004
Wireless Router at Home
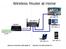 Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
CCNA 1 Capítulo 8 OSI Physical Layer. 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 CCNA 1 Capítulo 8 OSI Physical Layer 1 Physical Layer Protocols & Services There are three basic forms of network media on which data is represented: Copper cable Fiber Wireless 2 Physical Layer Protocols
CCNA 1 Capítulo 8 OSI Physical Layer 1 Physical Layer Protocols & Services There are three basic forms of network media on which data is represented: Copper cable Fiber Wireless 2 Physical Layer Protocols
Wireless Networking Basics. Ed Crowley
 Wireless Networking Basics Ed Crowley 2014 Today s Topics Wireless Networking Economic drivers and Vulnerabilities IEEE 802.11 Family WLAN Operational Modes Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) WPA and WPA2
Wireless Networking Basics Ed Crowley 2014 Today s Topics Wireless Networking Economic drivers and Vulnerabilities IEEE 802.11 Family WLAN Operational Modes Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) WPA and WPA2
Module 6: Wireless Mobile Networks
 Module 6: Wireless Mobile Networks SMD123 Computer Communications Kaustubh Phanse Department of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Luleå University of Technology Lecture Objectives Wireless links
Module 6: Wireless Mobile Networks SMD123 Computer Communications Kaustubh Phanse Department of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Luleå University of Technology Lecture Objectives Wireless links
Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371
 Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371 Wireless Systems: AM, FM Radio TV Broadcast Satellite Broadcast 2-way Radios Cordless Phones Satellite Links Mobile Telephony Systems Wireless Local Loop
Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371 Wireless Systems: AM, FM Radio TV Broadcast Satellite Broadcast 2-way Radios Cordless Phones Satellite Links Mobile Telephony Systems Wireless Local Loop
Module Three SG. Study Guide. Exam Three Content Areas. Module Three. Chapter Seven, Backbone Networks
 SG Exam Three will draw questions from multiple content areas including: our networking textbook, our wireless electronic textbook, our assignments and our class lectures. The purpose of this guide is
SG Exam Three will draw questions from multiple content areas including: our networking textbook, our wireless electronic textbook, our assignments and our class lectures. The purpose of this guide is
Deploying WLANs: This section lists a set of generic steps for installing small WLANs, with no product-specific details.
 This chapter covers the following subjects: Wireless LAN Concepts: This section explains the basic theory behind transmitting data with radio waves using wireless LAN standards. Deploying WLANs: This section
This chapter covers the following subjects: Wireless LAN Concepts: This section explains the basic theory behind transmitting data with radio waves using wireless LAN standards. Deploying WLANs: This section
Wireless LAN -Architecture
 Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
Wireless Protocols. Training materials for wireless trainers
 Wireless Protocols Training materials for wireless trainers Goals The goal of this lecture is to introduce: IEEE wireless protocols coverage 802.11 radio protocols terminology WiFi modes of operation details
Wireless Protocols Training materials for wireless trainers Goals The goal of this lecture is to introduce: IEEE wireless protocols coverage 802.11 radio protocols terminology WiFi modes of operation details
Chapter 5. RIP Version 1 (RIPv1)
 Chapter 5 RIP Version 1 (RIPv1) CCNA2-1 Chapter 5 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks must
Chapter 5 RIP Version 1 (RIPv1) CCNA2-1 Chapter 5 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario. Thanks must
The Wi-Fi Boom. Dr. Malik Audeh Tropos Networks March 13, 2004
 1 The Wi-Fi Boom Dr. Malik Audeh Tropos Networks March 13, 2004 Outline 2 Wi-Fi has gone mainstream Background of Wi-Fi/802.11 Technical Details of Wi-Fi Physical Layer(s) MAC Layer Security Wi-Fi in different
1 The Wi-Fi Boom Dr. Malik Audeh Tropos Networks March 13, 2004 Outline 2 Wi-Fi has gone mainstream Background of Wi-Fi/802.11 Technical Details of Wi-Fi Physical Layer(s) MAC Layer Security Wi-Fi in different
Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit. Manual
 Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit Manual Dear Customer, Thanks for choosing Hamlet. Please carefully follow the instructions for its use and maintenance and, once this item has run its life span, we kindly
Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit Manual Dear Customer, Thanks for choosing Hamlet. Please carefully follow the instructions for its use and maintenance and, once this item has run its life span, we kindly
Data and Computer Communications. Chapter 13 Wireless LANs
 Data and Computer Communications Chapter 13 Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topology Infrastructure LAN Connect to stations on wired LAN and in other cells May do automatic handoff Ad hoc LAN No hub Peer-to-peer
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 13 Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topology Infrastructure LAN Connect to stations on wired LAN and in other cells May do automatic handoff Ad hoc LAN No hub Peer-to-peer
Fieldbus Foundation India Marketing Committee. Fieldbus Foundation End Users Council Conference Wireless LANs in Industrial Environments
 Fieldbus Foundation India Marketing Committee Fieldbus Foundation End Users Council Conference-2009 Date : 19 th June, 2009 ( Friday ) Time : from 09:00 am to 06:00 pm. Venue : The Maratha, Sahar Road,
Fieldbus Foundation India Marketing Committee Fieldbus Foundation End Users Council Conference-2009 Date : 19 th June, 2009 ( Friday ) Time : from 09:00 am to 06:00 pm. Venue : The Maratha, Sahar Road,
EnGenius Quick Start Guide
 T he operates seamlessly in the 2.4 GHz frequency spectrum supporting the 802.11b (2.4GHz, 11Mbps) and the newer, faster 802.11g (2.4GHz, 54Mbpswireless standard. High output power and high sensitivity
T he operates seamlessly in the 2.4 GHz frequency spectrum supporting the 802.11b (2.4GHz, 11Mbps) and the newer, faster 802.11g (2.4GHz, 54Mbpswireless standard. High output power and high sensitivity
CWNP PW Certified Wireless Network Administrator (CWNA) Download Full Version :
 CWNP PW0-105 Certified Wireless Network Administrator (CWNA) Download Full Version : https://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/pw0-105 Answer: E QUESTION: 109 In an infrastructure Basic Service Set (BSS),
CWNP PW0-105 Certified Wireless Network Administrator (CWNA) Download Full Version : https://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/pw0-105 Answer: E QUESTION: 109 In an infrastructure Basic Service Set (BSS),
Lecture 23 Overview. Last Lecture. This Lecture. Next Lecture ADSL, ATM. Wireless Technologies (1) Source: chapters 6.2, 15
 Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Lecture 23 Overview Last Lecture ADSL, ATM This Lecture Wireless Technologies (1) Wireless LAN, CSMA/CA, Bluetooth Source: chapters 6.2, 15 Next Lecture Wireless Technologies (2) Source: chapter 16, 19.3
Chapter 2. Switch Concepts and Configuration. Part I
 Chapter 2 Switch Concepts and Configuration Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 2-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor,
Chapter 2 Switch Concepts and Configuration Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 2-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor,
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560. Wireless Technologies. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth 7/3/2014.
 Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Wireless 300N Access Point 300 Mbps, MIMO, Bridge, Repeater, Multiple SSIDs and VLANs Part No.:
 Wireless 300N Access Point 300 Mbps, MIMO, Bridge, Repeater, Multiple SSIDs and VLANs Part No.: 524728 Wireless networking with three times the speed and five times the flexibility. The INTELLINET NETWORK
Wireless 300N Access Point 300 Mbps, MIMO, Bridge, Repeater, Multiple SSIDs and VLANs Part No.: 524728 Wireless networking with three times the speed and five times the flexibility. The INTELLINET NETWORK
Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures
 Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures Wireless Network Technology Wireless network refers to any type of computer network which is wireless, and is commonly associated with a network whose interconnections
Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures Wireless Network Technology Wireless network refers to any type of computer network which is wireless, and is commonly associated with a network whose interconnections
6.9 Summary. 11/20/2013 Wireless and Mobile Networks (SSL) 6-1. Characteristics of selected wireless link standards a, g point-to-point
 Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Wireless and Mobile Networks
 Wireless and Mobile Networks Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse473-11/
Wireless and Mobile Networks Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse473-11/
Topic 2b Wireless MAC. Chapter 7. Wireless and Mobile Networks. Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach
 Topic 2b Wireless MAC Chapter 7 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 7-1 Ch. 7: Background: # wireless
Topic 2b Wireless MAC Chapter 7 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 7-1 Ch. 7: Background: # wireless
Table of Contents. Chapter 1Introduction Package Contents Features Specifications Physical Description...
 Table of Contents Chapter 1Introduction... 3 1.1 Package Contents... 3 1.2 Features... 3 1.3 Specifications... 3 1.4 Physical Description... 4 Chapter 2Wireless LAN Access Point Connection... 5 Chapter
Table of Contents Chapter 1Introduction... 3 1.1 Package Contents... 3 1.2 Features... 3 1.3 Specifications... 3 1.4 Physical Description... 4 Chapter 2Wireless LAN Access Point Connection... 5 Chapter
Attack & Defense in Wireless Networks
 Attack & Defense in Wireless Networks John M. Shea April 22, 2008 Overview Wireless networks fundamentals vulnerabilities WING testbed Demonstration of Denial-of-Service Attack and Defense Classification:
Attack & Defense in Wireless Networks John M. Shea April 22, 2008 Overview Wireless networks fundamentals vulnerabilities WING testbed Demonstration of Denial-of-Service Attack and Defense Classification:
Shared Access Networks Wireless. 1/27/14 CS mywireless 1
 Shared Access Networks Wireless 1 Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected devices equals
Shared Access Networks Wireless 1 Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected devices equals
