XRT94L43 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER GENERAL DESCRIPTION
|
|
|
- Mitchell Lester Watts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER NOVEMBER 2006 REV GENERAL The XRT94L43 is an SDH to PDH physical layer processor with integrated SONET OC-12 and 12 DS3/E3 framing controller. The XRT94L43 contains an integral SONET framer which provides framing and error accumulation in accordance with ANSI/ITU- T specifications. For a multiple channel DS3/E3 feature, each channel contains identical elements. The configuration of this device is through internal registers accessible via an 8-bit parallel, memory mapped, microprocessor interface. The SONET/SDH transmit and receive blocks are used to transmit/receive an STS-12/STM-4 signals or compose and decompose 12, STS-1/DS3/E3 signals. The blocks operate at a peak internal clock speed of 77 MHz and support 8-bit internal data paths. The transmit and receive blocks are compliant with both SONET and SDH standards. The XRT94L43 performs all SONET transport and path overhead processing for use in broadband data transport applications. FEATURES Single Chip solution for 12 DS3/E3 to SONET/SDH Mapping Generates and terminates SONET section, line and path layers. Provides SONET frame scrambling and descrambling. Differential Line Interfaces 8-bit microprocessor interface Requires +2.5 and +3.3V power supplies with +5V input tolerance -40 C to +85 C Operating Temperature Range Available in a 516 Ball PBGA package APPLICATIONS Network switches Concentrators Frame Relay Switches SONET Customer Premises Multiplexers Network Access Equipment Test/Monitoring Equipment Exar Corporation Kato Road, Fremont CA, (510) FAX (510)
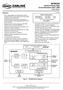
2 REV XRT94L43 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER FIGURE 1. BLOCK DIAGRAM OF THE XRT94L43 WHEN CONFIGURED IN SONET MODE Tx STM -4 Tx STM -4 SOH Processor SOH Processor Block Block Tx AU -4 Tx AU -4 Mapper/VC -4 Mapper/VC -4 POH POH Processor Processor Block Block Tx TUG -3 Tx TUG -3 Mapper / Mapper / VC - Tx 3 POH VC - Tx 3 VC POH-3 VC -3 Processor Processor POH POH Block Processor Block Processor Block Block Rx STM - 4 SOH Rx STM - 4 SOH Processor Processor Block Block STM -4 STM -4 Telecom Bus Telecom Bus Block Block SERDES SERDES Block Block (Primary) (Primary) Rx AU -4 Rx AU -4 Mapper/VC -4 Mapper/VC -4 POH POH Processor Processor Block Block AUG # 1 DS3/E3 DS3/E3 DS3/E3 Mapper DS3/E3 Mapper Mapper DS3/E3 Block Mapper Block Block Mapper Block Block Rx TUG -3 Rx TUG -3 Mapper / Mapper / VC - 3 POH VC - 3 POH Processor Processor Block Block DS3/E3 DS3/E3 Jitter Jitter Attenuator Attenuator Block Block DS3/E3 DS3/E3 Framer DS3/E3 Framer DS3/E3 DS3/E3 Block Framer Block Framer Framer DS3/E3 Block Block Framer Block Block SERDES SERDES Block Block (APS) (APS) To AUG # 2-4 From AUG # 2-4 Clock Clock Synthesizer Synthesizer Block Block Microprocessor Microprocessor Interface Interface JTAG Test JTAG Test Port Port 2
3 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER REV FIGURE 2. BLOCK DIAGRAM OF THE XRT94L43 WHEN CONFIGURED IN SDH/TUG-3 MODE Tx STM-4 Tx STM-4 SOH Processor SOH Processor Block Block Tx AU-3 Tx AU-3 Mapper/VC-3 Mapper/VC-3 POH POH Processor Processor Block Block Rx VC-3 Rx VC-3 Pointer Pointer Justification Justification Block Block Rx STM-0 Rx STM-0 VC-3 POH VC-3 POH Block Block Rx STM-0 Rx STM-0 SOH SOH Block Block Rx STM-4 SOH Rx STM-4 SOH Processor Processor Block Block STM-4 STM-4 Telecom Bus Telecom Bus Block Block SERDES SERDES Block Block (Primary) (Primary) Rx AU-3 Rx AU-3 Mapper/VC-3 Mapper/VC-3 POH POH Processor Processor Block Block Channel 1 Tx VC-3 Tx VC-3 Pointer Pointer Justification Justification Block Block DS3/E3 DS3/E3 Mapper Mapper Block Block Tx STM-0 Tx STM-0 VC-3 POH VC-3 POH Block Block DS3/E3 DS3/E3 Jitter Jitter Attenuator Attenuator Block Block Tx STM-0 Tx STM-0 SOH SOH Block Block DS3/E3 DS3/E3 Framer Framer Block Block SERDES SERDES Block Block (APS) (APS) To Channels 2 12 From Channels 2 12 Clock Synthesizer Clock Synthesizer Block Block Microprocessor Microprocessor Interface Interface JTAG Test JTAG Test Port Port FIGURE 3. BLOCK DIAGRAM OF THE XRT94L43 WHEN CONFIGURED IN SDH/AU-3 MODE Tx STS-12 Tx STS-12 TOH Processor TOH Processor Block Block Tx SONET Tx SONET POH POH Processor Processor Block Block Rx STS-1 Rx STS-1 Pointer Pointer Justification Justification Block Block Rx STS-1 Rx STS-1 POH POH Block Block Rx STS-1 Rx STS-1 TOH TOH Block Block Rx STS-12 TOH Rx STS-12 TOH Processor Processor Block Block STS-12 STS-12 Telecom Bus Telecom Bus Block Block SERDES SERDES Block Block (Primary) (Primary) Rx SONET Rx SONET POH POH Processor Processor Block Block Channel 1 Tx STS-1 Tx STS-1 Pointer Pointer Justification Justification Block Block DS3/E3 DS3/E3 Mapper Mapper Block Block Tx STS-1 Tx STS-1 POH POH Block Block DS3/E3 DS3/E3 Jitter Jitter Attenuator Attenuator Block Block Tx STS-1 Tx STS-1 TOH TOH Block Block DS3/E3 DS3/E3 Framer Framer Block Block SERDES SERDES Block Block (APS) (APS) To Channels 2 12 From Channels 2 12 Clock Synthesizer Clock Synthesizer Block Block Microprocessor Microprocessor Interface Interface JTAG Test JTAG Test Port Port 3
4 REV PRODUCT FEATURES SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER SONET TRANSMITTER Generates and Transmits Standard STS-12/STM-4 data Generates and Transmits either an STM-4/TUG-3 or STM-4/AU-3 signals for SDH applications Conforms to ITU-T 1.432, ANSI T1.105 and Bellcore GR-253 Standards Performs SONET frame insertion and accepts external frame synchronization Performs Optional Transmit Data Scrambling Permits the user to externally insert their own values for the POH and TOH into the outbound STS-12/STM-4 traffic Generates transmit payload pointer (H1,H2) (fixed at 522) with NDF insertion Inserts A1/A2 with optional error mask Computes and inserts BIP-8 (B1,B2) with optional error mask Generates and transmits REI-L and RDI-L either upon Software Command or automatically based upon errors and defects that are detected/declared by the SONET Receiver. Permits the user to transmit the LOS pattern via Software Command. Generates and transmits RDI-P and REI-P either upon Software Command or automatically based upon errors and defects that are detected/declared by the SONET Receiver. Inserts the fixed-stuff columns, calculates and inserts the B3 byte value into each outbound STS-1 SPE/VC- 3 or STS-3c SPE/VC-4 SONET RECEIVER Receives and processes standard STS-12/STM-4 signals Receives and processes either an STM-4/TUG-3 or STM-4/AU-3 signal for SDH Applications Permits the user to fully program the B2 Byte Error-rate thresholds for declaration and clearance of the SD and SF defect conditions Provides section trace buffer with mismatch detection and invalid message detection Performs SONET Frame Synchronization Supports NDF, positive stuff and negative stuff for pointer processor Performs receive data de-scrambling Performs POH and TOH interpretation/extraction Interprets payload pointer (H1,H2) Extracts data communication channels from D1-D3 and D4-D12 Declares and Clears the SEF (Severely Erred Frame), LOF (Loss of Frame) and LOS (Loss of Signal) defect conditions Declares and clears the Line AIS (AIS-L) and the Line Remote Defect Indicator (RDI-L) defect conditions Declares and Clears the Path - AIS (AIS-P), Loss of Pointer (LOP-P) and Path - Unequipped (UNEQ-P) defect conditions. Supports either the Single-Bit or Extended form of RDI-P Monitors the Path Signal Label and declares/clears the PLM-P defect condition 4
5 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER REV Contains 12 on-chip 64 byte Expected Receive Path Trace Message Buffer, in which the user will load in an expected Path Trace Message Contains 12 on-chip 64 byte Actual" Receive Path Trace Message Buffers, that will contain the actual Received Path Trace Message The SONET Receiver will use the contents within both the Expected and Actual Receive Path Trace Message Buffers to either declare or clear the TIM-P defect condition Computes and verifies the B3 bytes within each incoming STS-1 SPE/VC-3 or STS-3c SPE/VC-4 and increments on-chip Performance Monitoring registers each time it detects B3 byte errors. Detects and Flags Line - Remote Error Indicator (REI-L) and Path - Remote Error Indicator (REI-P) events, and increments on-chip Performance Monitoring registers each time it detects REI-L or REI-P events Computes and verifies both the B1 and B2 bytes within the incoming STS-12/STM-4 data-stream and increments on-chip Performance Monitoring registers each time it detects B1 or B2 byte errors MAPPER Maps DS3 data into/de-maps DS3 data from an STS-1 SPE per the requirements in Telcordia GR-253- CORE Maps DS3/E3 data into/de-maps DS3/E3 data from a VC-3 per ITU-T G.707 Implements AU-3 to VC-3 multiplexing and de-multiplexing DS3 RECEIVE FRAMER Offers off-line framing algorithm Complies with the standards as: Bellcore TR-NWT and TR-NWT Supports overhead extraction Detects and flags LCV (Line Code Violations) and EXZ (Excessive Zero Events). Reports and counts FEBE HDLC controller complies with ITU-T Q.921 LAPD protocol Provides Line and Local Loop-backs Supports either the M13 or the C-bit Parity Framing formats Supports B3ZS line decoding which can be user enabled.replaces valid B0V or 00V with 3 zeros Synchronizes to incoming frame based upon 10 valid F bits followed by 3 consecutive valid M frames, Offers optional AIC-bit or parity verification before declaration of sync Detects Out of Frame (OOF) upon 3 or 6 F bits out of 15 F bits in error or 1 or more M bits in 3 of 4 consecutive frames in error Detects Loss of Signal (LOS) upon encountering 180 consecutive 0 s and clears on at least 60 of successive received 1 s.offers optional disable Detects idle state by checking C-bit in subframe 3 are all zero, X-bits are one and repeating payloads. Declaration occurs when all the above conditions persist for 63 M-frames. Clears the condition when 63 valid M-frames are received Detects AIS with different algorithm Computes and verifies P and CP-Bits Validate FERF bits, sets to one when both X-bits are zero and clears when they are One Detects and validates FEAC codes upon 8 out of 10 last identical received codes.invalidates on 3 in 10 mismatch 5
6 REV SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER Provides 15-bit PRBS lock DS3 TRANSMIT FRAMER Offers following frame generation mechanism: Asynchronous operation, using receive side clock, external framing Supports either C-bit operation or M13 operation: optional all C bits set to "1" or C-bit parity ID bit (C11) toggled in each frame for M13 operation Provides start of frame control with external pin Inserts frame overhead bits via External serial port or Internal generation Generates and checks parity Automatically transmits the DS3 FERF/REI indicator whenever the DS3 Receiver declares either the DS3 LOS, DS3 AIS or DS3 OOF defect conditions. Permits the user to control the DS3 FEBE/REI bit-fields via Software Control, or to automatically transmit the FEBE/REI indicator whenever the DS3 Receiver detects CP-Bit or Framing (F or M) bit errors Provides FEAC channel processing including generation of valid FEAC patterns and transmissions of all 1 s upon programming of idle code Inserts path maintenance data link through HDLC transmitter which contains the following features: AM for storage of entire LAPD message Selection of message length to 82 or 76 bytes Optional frame header generation Generation of flag sequences Computation and insertion of CRC Zero stuffing Register bits for communication with microprocessor Interrupt generation upon transmission of message LOS Insertion enabled by register bit AIS Insertion enabled by register bit or pin Idle signal insertion enabled by register bit Supports B3ZS encoding Generates AIS, Idle and Yellow force alarms Inserts errors optionally in the P, F, FEBE and M bits Provides 15-bit PRBS generator E3 RECEIVE FRAMER Offers off-line framing algorithm Complies with standards as: ITU-T G.751 and G.832 Provides line code violation detection and excess zero count LAPD controller complies with ITU Q.921 LAPD protocol Provides local loop-back Supports G.751 and G.832 framing formats Supports HDB3 line decoding which can be user enabled. Replaces valid B00V or 000V with 4 zero s 6
7 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER REV Synchronizes to incoming frame based upon occurrence of two sets of FA1, FA2 with expected separation - G.832 or detection of three consecutive frame alignment signals (FAS) - G.751 Detects Out of Frame (OOF) upon 4 consecutive invalid frames Detects Loss of Signal (LOS) upon encountering 32 consecutive 0 s and clears on occurrence of 32 bits without a string of 4 0s Detects AIS if 7 or less 0s detected in each of 2 consecutive frames and clears if more than seven 0 s detected in each of 2 consecutive frames Calculation and comparison of BIP-8 (G.832) or BIP-4 (G.751). BIP-4 calculation can be disabled Supports overhead extraction Microprocessor access to TR trail trace message - 16 TTB registers (G.832) or service (Alarm and Nation) bits (G.751) Detects MA FERF if 3 or 5 consecutive MA MSBs are 1and clears if 3 or 5 consecutive MA MSBs are 0 (only E3 G.832) Indicates last validated FERF value and interrupt upon a change in validated FERF value Extracts payload type (MA) bits and stores in a register (Only E3 G.832) Extracts Timing Marker bit and checks for consistency over 3 or 5 consecutive frames (only E3 G.832) Extracts Synchronous Status Message bits and stores it in register bits when enabled (only G.832) Overhead output on synchronous serial interface E3 TRANSMIT FRAMER Offers following frame generation mechanism: Asynchronous operation, using receive side clock, external framing Supports either G.751 or G.832 framing format Generates and checks parity BIP-8 (G.832), BIP-4 (G.751) BIP-4 computation can be disabled Inserts data link message through E3 data line channel which contains the following features: Insertion into NR or GC byte (programmable through register bit) (E3 G.832 only) Insertion into Nation bit in case of E3 G.751 when LAPD is enabled RAM storage of entire LAPD message Selection of message length to 82 or 76 bytes Generation of flag sequences Computation and insertion of CRC-16 Zero stuffing Register bits for communication with microprocessors Interrupt generation upon complete transmission of message LOS insertion enabled by register bit to force all 0s in the transmit stream AIS insertion enabled by register bit and/or pin to force all 1 s in the transmit stream Supports HDB3 encoding enabled by register bit Inserts frame overhead bits via External serial/nibble port (except for FA1,FA2 and EM bytes in case of E3 G.832 and FAS and BIP-4 in case of G.751) or through external overhead interface or from configuration register or internal generation Inserts FA1, FA2, EM, TR, MA and GC bytes into G.832 stream or FAS service bits and BIP4 (if enabled) into G.751 stream 7
8 REV XRT94L43 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER Inserts MA,NR,GC and TR (TTB) from microprocessor accessible registers (service bit for G.751) Inserts FEBE in MA upon receipt of EM byte errors.programmable through register bit (G.832) Asserts FERF upon any combination of LOS,OOF or AIS received from receiver (G.832) Inserts synchronous status message from microprocessor accessible registers, when enabled (G.832) Error masks for framing bytes, and computed parity (BIP-8 in case of G.832 and BIP-4 in case of G.751) Optionally accepts overhead bits (except FA bytes for G.832 and FAS bits for G.751) from input interface E3/DS3/STS-1 DE-JITTERING/DE-SYNC CIRCUIT Meets the E3/DS3/STS-1 jitter requirements Compliant with jitter transfer template outlined in ITU G.751,G.752,G.755 and GR-499-CORE Meets output jitter requirement as specified by ETSI TBR24 Meets the jitter and wander specifications described in T b,GR-253 and GR-499 standards Performs the De-synchronizer function and pointer adjustments for STS-1 to DS3 mapping PERFORMANCE MONITORING Supports line and path performance monitoring Provides 32-bit saturating counter of OOF errors Provides 32-bit saturating counter LOF errors Provides 32-bit saturating counter of LOS errors Provides 32-bit saturating counter of SD errors Provides 32-bit saturating counter of SF errors Provides 32-bit saturating counter B3 errors Provides 32-bit saturating counter of the line RDI, path AIS,REI-L errors, REI-P errors and BIP-8(B1,B2),B3 errors and loss of pointer Provides 16-bit saturating counter of DS3 framing bit errors, DS3 frame parity errors, line code violations, frame parity (BIP) errors, DS3 frame CP bit errors and DS3 Far-End Block errors One second statistics 1. Bipolar violations 2. Frames with parity errors 3. Frames with CP bit errors 4. Errored second indication 5. Severely errored second indication INTERRUPT, STATUS AND TEST Provides individually maskable interrupts Provides one second interrupt generations Generates interrupts from the following causes: DS3 OOF status change, LOS status change, DS3 AIS status, LAPD message received, DS3 parity error,ds3 FEAC validation, DS3 FEAC removal, DS3 IDLE status change, FEBE (E3) change, DS3 FERF change, DS3 format change (AIC), LAPD end of message transmission and DS3 FEAC end of message transmission, DS3 Framing alignment change, SONET OOF status change and COFA Provides local and remote line loopback 8
9 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER REV Provides SONET remote loopback 9
10 REV ORDERING INFORMATION XRT94L43 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER PART NUMBER PACKAGE OPERATING TEMPERATURE RANGE XRT94L43IB 516 Ball BGA -40 C to +85 C FIGURE 4. PIN OUT OF THE XRT94L43 (See pin list for pin names and function) TOP VIEW AF AF 26 AF 1 AE AE 1 AD AD 1 AC AC 26 AC 23 AC 4 AC 1 AB AB 1 AA AA 1 Y Y1 W W1 V V1 U U1 T Y 26 T2 25 T 24 T 23 T 22 T 21 G G G G G G T6 T5 T4 T3 T2 T1 R V2 V2 G G V1 V1 R1 P V2 V2 G G V1 V1 P1 N V2 V2 G G V1 V1 N1 M V2 V2 G G V1 V1 M1 L L 26 L 25 L 24 L 23 L 22 L 21 V3 V3 V3 V3 V3 V3 L6 L5 L4 L3 L2 L1 K J XRT94L43 K1 J1 H H1 G G1 F F1 E E1 D D 26 D 23 D4 D1 C C1 B B1 A A 26 A
11 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER REV TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL... 1 FEATURES... 1 APPLICATIONS... 1 FIGURE 1. BLOCK DIAGRAM OF THE XRT94L43 WHEN CONFIGURED IN SONET MODE... 2 FIGURE 2. BLOCK DIAGRAM OF THE XRT94L43 WHEN CONFIGURED IN SDH/TUG-3 MODE... 3 FIGURE 3. BLOCK DIAGRAM OF THE XRT94L43 WHEN CONFIGURED IN SDH/AU-3 MODE... 3 PRODUCT FEATURES... 4 SONET TRANSMITTER... 4 SONET RECEIVER... 4 MAPPER... 5 DS3 RECEIVE FRAMER... 5 DS3 TRANSMIT FRAMER... 6 E3 RECEIVE FRAMER... 6 E3 TRANSMIT FRAMER... 7 E3/DS3/STS-1 DE-JITTERING/DE-SYNC CIRCUIT... 8 PERFORMANCE MONITORING... 8 INTERRUPT, STATUS AND TEST... 8 ORDERING INFORMATION FIGURE 4. PIN OUT OF THE XRT94L TABLE OF CONTENTS... I PIN S - DIRECT ADDRESSING... 8 MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE... 8 SONET/SDH SERIAL LINE INTERFACE PINS STS-12/STM-4 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE - TRANSMIT DIRECTION STS-12/STM-4 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE - RECEIVE DIRECTION SONET/SDH OVERHEAD INTERFACE - TRANSMIT DIRECTION STS-3/STM-1 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE - TRANSMIT DIRECTION RXSTS-1 TOH/POH INTERFACE STS-3/STM-1 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE - RECEIVE DIRECTION RECEIVE TRANSPORT OVERHEAD INTERFACE GENERAL PURPOSE INPUT/OUTPUT CLOCK INPUTS BOUNDARY SCAN MISCELLANEOUS PINS POWER SUPPLY PINS VDD = 3.3V VDD (2.5V) GROUND NO CONNECTS PIN S - INDIRECT ADDRESSING MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE SONET/SDH SERIAL LINE INTERFACE PINS STS-12/STM-4 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE - TRANSMIT DIRECTION STS-12/STM-4 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE - RECEIVE DIRECTION SONET/SDH OVERHEAD INTERFACE - TRANSMIT DIRECTION STS-3/STM-1 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE - TRANSMIT DIRECTION RXSTS-1 TOH/POH INTERFACE STS-3/STM-1 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE - RECEIVE DIRECTION RECEIVE TRANSPORT OVERHEAD INTERFACE GENERAL PURPOSE INPUT/OUTPUT CLOCK INPUTS BOUNDARY SCAN MISCELLANEOUS PINS I
12 REV XRT94L43 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER POWER SUPPLY PINS VDD = 3.3V VDD (2.5V) GROUND NO CONNECTS DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS DC CHARACTERISTICS FOR TTL INPUT/CMOS OUTPUT DC CHARACTERISTICS FOR LVPECL I/O AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE TIMING FOR REVISION D SILICON MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE TIMING - ASYNCHRONOUS INTEL MODE FIGURE 5. ASYNCHRONOUS MODE 1 - INTEL PROGRAMMED I/O TIMING (WRITE CYCLE) FIGURE 6. ASYNCHRONOUS MODE 1 - INTEL PROGRAMMED I/O TIMING (READ CYCLE) TABLE 1: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE, WHEN CONFIGURED TO OPERATE IN THE INTEL ASYNCHRONOUS MODE MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE TIMING - ASYNCHRONOUS MOTOROLA (68K) MODE FIGURE 7. ASYNCHRONOUS MODE 2 - MOTOROLA 68K PROGRAMMED I/O TIMING (WRITE CYCLE) FIGURE 8. ASYNCHRONOUS MODE 2 - MOTOROLA 68K PROGRAMMED I/O TIMING (READ CYCLE) TABLE 2: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE WHEN CONFIGURED TO OPERATE IN THE MOTOROLA (68K) ASYN- CHRONOUS MODE MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE TIMING - POWER PC 403 SYNCHRONOUS MODE FIGURE 9. SYNCHRONOUS MODE 3 - IBM POWERPC 403 INTERFACE TIMING (WRITE CYCLE) FIGURE 10. SYNCHRONOUS MODE 3 - IBM POWERPC 403 INTERFACE TIMING (READ CYCLE) TABLE 3: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE, WHEN CONFIGURED TO OPERATE IN THE IBM POWER PC403 MODE MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE TIMING - IDT3051/52 MODE FIGURE 11. SYNCHRONOUS MODE 4 - IDT3051/52 INTERFACE TIMING (WRITE CYCLE) FIGURE 12. SYNCHRONOUS MODE 4 - IDT3051/52 INTERFACE TIMING (READ CYCLE) TABLE 4: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE, WHEN CONFIGURED TO OPERATE IN THE IDT3051/52 MODE STS-12/STM-4 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE TIMING INFORMATION STS-12/STM-4 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE TIMING INFORMATION THE TRANSMIT STS-12/STM-4 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE TIMING FIGURE 13. WAVEFORMS OF THE S THAT ARE OUTPUT VIA THE TRANSMIT STS-12/STM-4 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE FIGURE 14. TIMING RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN THE TXSBFP INPUT PIN AND THE TXA_CLK OUTPUT PIN WITHIN THE TRANSMIT STS-12/STM- 4 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE TABLE 5: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE TRANSMIT STS-12/STM-4 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE THE RECEIVE STS-12/STM-4 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE TIMING FIGURE 15. WAVEFORMS OF THE S THAT ARE INPUT VIA THE RECEIVE STS-12/STM-4 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE TABLE 6: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE RECEIVE STS-12/STM-4 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE STS-12/STM-4 PECL INTERFACE TIMING INFORMATION THE RECEIVE STS-12/STM-4 PECL INTERFACE TIMING FIGURE 16. WAVEFORMS OF THE S THAT ARE INPUT VIA THE RECEIVE STS-12/STM-4 PECL INTERFACE TABLE 7: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE RECEIVE STS-12/STM-4 PECL INTERFACE THE TRANSMIT STS-12/STM-4 PECL INTERFACE BLOCK FIGURE 17. WAVEFORMS OF THE TRANSMIT STS-12/STM-4 PECL INTERFACE S TABLE 8: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE TRANSMIT STS-12/STM-4 PECL INTERFACE DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU INTERFACE TIMING INFORMATION INGRESS DS3/E3/STS-1 INTERFACE TIMING FIGURE 18. WAVEFORMS OF THE DS3/E3/STS-1 S THAT ARE INPUT TO THE DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU INTERFACE IN THE INGRESS DIREC- TION INGRESS TIMING FOR DS3/E3 APPLICATIONS TABLE 9: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE INGRESS DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU INTERFACE FOR DS3/E3 APPLICATIONS WHEN THE DS3/E3 FRAMER BLOCK HAS BEEN CONFIGURED TO SAMPLE THE DS3/E3/STS_1_DATA_IN AND DS3/E3/STS_1_NEG_IN INPUT PINS UPON THE RISING EDGE OF DS3/E3/STS_1_CLOCK_IN TABLE 10: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE INGRESS DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU INTERFACE FOR DS3/E3 APPLICATIONS AND WHEN THE DS3/E3 FRAMER BLOCK HAS BEEN CONFIGURED TO SAMPLE THE DS3/E3/STS_1_DATA_IN AND DS3/E3/STS_1_NEG_IN INPUT PINS UPON THE FALLING EDGE OF DS3/E3/STS_1_CLOCK_IN INGRESS TIMING FOR STS-1/STM-0 APPLICATIONS TABLE 11: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE INGRESS DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU INTERFACE FOR STS-1/STM-0 APPLICATIONS THE EGRESS DS3/E3/STS-1 INTERFACE TIMING FIGURE 19. WAVEFORMS OF THE DS3/E3/STS-1 S THAT ARE OUTPUT FROM THE DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU INTERFACE (IN THE RECEIVE/ EGRESS DIRECTION) II
13 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER REV EGRESS TIMING FOR DS3/E3 APPLICATIONS TABLE 12: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE EGRESS DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU INTERFACE FOR DS3/E3 APPLICATIONS AND WHEN THE DS3/E3 FRAMER BLOCK HAS BEEN CONFIGURED TO OUTPUT THE OUTBOUND DS3/E3 DATA (VIA THE DS3/E3/STS_1_DATA_OUT AND DS3/E3/STS_1_NEG_OUT OUTPUT PINS) UPON THE RISING EDGE OF DS3/E3/STS_1_CLOCK_OUT TABLE 13: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE EGRESS DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU INTERFACE FOR DS3/E3 APPLICATIONS AND WHEN THE DS3/E3 FRAMER BLOCK HAS BEEN CONFIGURED TO OUTPUT THE OUTBOUND DS3/E3 DATA (VIA THE DS3/E3/STS_1_DATA_OUT AND DS3/E3/STS_1_NEG_OUT OUTPUT PINS) UPON THE FALLING EDGE OF DS3/E3/STS_1_CLOCK_OUT EGRESS TIMING FOR STS-1/STM-0 APPLICATIONS TABLE 14: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE EGRESS DS3/E3/STS-1 LIU INTERFACE FOR STS-1/STM-0 APPLICATIONS STS-3/STM-1 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE TIMING INFORMATION STS-3/STM-1 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE TIMING INFORMATION THE RECEIVE STS-3/STM-1 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE TIMING FIGURE 20. WAVEFORMS OF THE S THAT ARE OUTPUT VIA THE RECEIVE STS-3/STM-1 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE TABLE 15: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE RECEIVE STS-3/STM-1 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE THE TRANSMIT STS-3/STM-1 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE TIMING FIGURE 21. WAVEFORMS OF THE S THAT ARE INPUT VIA THE TRANSMIT STS-3/STM-1 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE TABLE 16: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE TRANSMIT STS-3/STM-1 TELECOM BUS INTERFACE TRANSMIT TOH OVERHEAD INPUT PORT TRANSMIT TOH OVERHEAD INPUT PORT FIGURE 22. TIMING WAVEFORM OF THE TRANSMIT TOH OVERHEAD INPUT PORT TABLE 17: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE TRANSMIT TOH OVERHEAD INPUT PORT TRANSMIT POH OVERHEAD INPUT PORT TRANSMIT POH OVERHEAD INPUT PORT FIGURE 23. TIMING WAVEFORM OF THE TRANSMIT POH OVERHEAD INPUT PORT TABLE 18: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE TRANSMIT POH OVERHEAD INPUT PORT TRANSMIT ORDERWIRE (E1, F1, E2) BYTE OVERHEAD INPUT PORT TRANSMIT E1, F1, E2 (ORDER-WIRE) BYTE OVERHEAD INPUT PORT FIGURE 24. TIMING WAVEFORM OF THE TRANSMIT ORDER-WIRE BYTE OVERHEAD INPUT PORT TABLE 19: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE TRANSMIT ORDER-WIRE BYTE OVERHEAD INPUT PORT TRANSMIT SECTION DCC INSERTION INPUT PORT TRANSMIT SECTION DCC INSERTION INPUT PORT FIGURE 25. TIMING WAVEFORM OF THE TRANSMIT SECTION DCC OVERHEAD INSERTION PORT TABLE 20: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE TRANSMIT ORDER-WIRE BYTE OVERHEAD INPUT PORT TRANSMIT LINE DCC INSERTION INPUT PORT TRANSMIT LINE DCC INSERTION INPUT PORT FIGURE 26. TIMING WAVEFORM OF THE TRANSMIT LINE DCC INSERTION INPUT PORT TABLE 21: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE TRANSMIT LINE DCC INSERTION INPUT PORT RECEIVE TOH OVERHEAD OUTPUT PORT RECEIVE TOH OVERHEAD OUTPUT PORT FIGURE 27. TIMING WAVEFORM OF THE RECEIVE TOH OVERHEAD OUTPUT PORT TABLE 22: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE RECEIVE TOH OVERHEAD OUTPUT PORT RECEIVE POH OVERHEAD OUTPUT PORT RECEIVE POH OVERHEAD OUTPUT PORT FIGURE 28. TIMING WAVEFORM OF THE RECEIVE POH OVERHEAD OUTPUT PORT TABLE 23: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE RECEIVE POH OVERHEAD OUTPUT PORT RECEIVE ORDERWIRE (E1, F1, E2) BYTES OVERHEAD OUTPUT PORT RECEIVE E1, F1, E2 (ORDER-WIRE) BYTE OVERHEAD OUTPUT PORT FIGURE 29. TIMING WAVEFORM OF THE RECEIVE ORDER-WIRE BYTE OVERHEAD OUTPUT PORT TABLE 24: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE RECEIVE ORDER-WIRE BYTE OVERHEAD OUTPUT PORT RECEIVE SECTION DCC EXTRACTION OUTPUT PORT RECEIVE SECTION DCC OUTPUT PORT FIGURE 30. TIMING WAVEFORM OF THE RECEIVE SECTION DCC OUTPUT PORT TABLE 25: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE RECEIVE SECTION DCC OUTPUT PORT RECEIVE LINE DCC EXTRACTION OUTPUT PORT RECEIVE LINE DCC OUTPUT PORT FIGURE 31. TIMING WAVEFORM OF THE RECEIVE LINE DCC OUTPUT PORT TABLE 26: TIMING INFORMATION FOR THE RECEIVE LINE DCC OUTPUT PORT ORDERING INFORMATION PACKAGE DIMENSIONS REVISION HISTORY III
14 REV PIN S - DIRECT ADDRESSING SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE U22 PCLK I TTL Microprocessor Interface Clock Input: This clock input signal is only used if the Microprocessor Interface has been configured to operate in one of the Synchronous Modes (e.g., Power PC 403 Mode). If the Microprocessor Interface is configured to operate in one of these modes, then it will use this clock signal to do the following. To sample the CS, WR/R/W, A[15:0], D[7:0], RD/DS and DBEN input pins, and To update the state of the D[7:0] and the RDY/DTACK output signals. NOTES: 1. The Microprocessor Interface can work with µpclk frequencies ranging up to 66MHz. 2. This pin is inactive if the user has configured the Microprocessor Interface to operate in either the Intel-Asynchronous or the Motorola-Asynchronous Modes. In this case, the user should tie this pin to GND. L25 L23 L22 A23 F24 W21 AE22 A25 H24 AB23 AD15 V26 R24 P26 M24 T26 M22 M25 L26 P_0 P_1 P_2 PADDR_0 PADDR_1 PADDR_2 PADDR_3 PADDR_4 PADDR_5 PADDR_6 PADDR_7 PADDR_8 PADDR_9 PADDR_10 PADDR_11 PADDR_12 PADDR_13 PADDR_14 PADDR_15 I TTL Microprocessor Type Select input: These three input pins are used to configure the Microprocessor Interface block to readily support a wide variety of Microprocessor Interfaces. The relationship between the settings of these input pins and the corresponding Microprocessor Interface configuration is presented below. P[2:0] Microprocessor Interface Mode 000 Intel - Asynchronous Mode l001 Motorola - Asynchronous Mode (Motorola 68k) 010 Intel X Intel I IDT3051/52 (MIPS) 101 Power PC 403 Mode I TTL Address Bus Input pins (Microprocessor Interface): These pins permit the Microprocessor to identify on-chip registers and Buffer/Memory locations (within the XRT94L43) whenever it performs READ and WRITE operations with the XRT94L43. 8
15 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER REV MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE T22 R22 U24 R21 W26 T25 R25 R26 Y26 PDATA_0 PDATA_1 PDATA_2 PDATA_3 PDATA_4 PDATA_5 PDATA_6 PDATA_7 WR/ R/W I/O TTL Bi-Directional Data Bus Pins (Microprocessor Interface): These pins are used to drive and receive data over the bi-directional data bus,, whenever the Microprocessor performs READ or WRITE operations with the Microprocessor Interface of the XRT94L43. I TTL Write Strobe/Read-Write operation Identifier: The function of this input pin depends upon which mode the Microprocessor Interface has been configured to operate in. Intel-Asynchronous Mode - WR - Write Strobe Input: If the Microprocessor Interface is configured to operate in the Intel-Asynchronous Mode, then this input pin functions as the WR (Active Low WRITE Strobe) input signal from the Microprocessor. Once this active-low signal is asserted, then the input buffers (associated with the Bi-Directional Data Bus pin, D[7:0]) will be enabled. The Microprocessor Interface will latch the contents on the Bi-Directional Data Bus (into the "target" register or address location, within the XRT94L43) upon the rising edge of this input pin. Motorola-Asynchronous Mode - R/W - Read/Write Operation Identification Input Pin: If the Microprocessor Interface is operating in the "Motorola-Asynchronous Mode", then this pin is functionally equivalent to the "R/W" input pin. In the Motorola Mode, a "READ" operation occurs if this pin is held at a logic "1", coincident to a falling edge of the RD/DS (Data Strobe) input pin. Similarly a WRITE operation occurs if this pin is at a logic "0", coincident to a falling edge of the RD/DS (Data Strobe) input pin. Power PC 403 Mode - R/W - Read/Write Operation Identification Input: If the Microprocessor Interface is configured to operate in the Power PC 403 Mode, then this input pin will function as the "Read/Write Operation Identification Input" pin. Anytime the Microprocessor Interface samples this input signal at a logic low (while also sampling the CS input pin "low") upon the rising edge of µpclk, then the Microprocessor Interface will (upon the very same rising edge of µpclk) latch the contents of the Address Bus (A[15:0]) into the Microprocessor Interface circuitry, in preparation for this forthcoming READ operation. At some point (later in this READ operation) the Microprocessor will also assert the DBEN/OE input pin, and the Microprocessor Interface will then place the contents of the "target" register (or address location within the XRT94L43) upon the Bi-Directional Data Bus pins (D[7:0]), where it can be read by the Microprocessor. Anytime the Microprocessor Interface samples this input signal at a logic high (while also sampling the CS input pin a logic "low") upon the rising edge of µpclk, then the Microprocessor Interface will (upon the very same rising edge of µpclk) latch the contents of the Address Bus (A[15:0]) into the Microprocessor Interface circuitry, in preparation for the forthcoming WRITE operation. At some point (later in this WRITE operation) the Microprocessor will also assert the RD/DS/WE input pin, and the Microprocessor Interface will then latch the contents of the Bi-Directional Data Bus (D[7:0]) into the contents of the "target" register or buffer location (within the XRT94L43). 9
16 REV MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE XRT94L43 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER T23 RD/ DS/ WE I TTL READ Strob/Data Strobe: The function of this input pin depends upon which mode the Microprocessor Interface has been configured to operate in. Intel-Asynchronous Mode - RD - READ Strobe Input: If the Microprocessor Interface is operating in the Intel-Asynchronous Mode, then this input pin will function as the RD (Active Low Read Strobe) input signal from the Microprocessor. Once this active-low signal is asserted, then the XRT94L43 will place the contents of the addressed register (or buffer location) on the Microprocessor Interface Bi-directional data bus (D[7:0]). When this signal is negated, then the Data Bus will be tristated. Motorola-Asynchronous (68K) Mode - DS - Data Strobe: If the Microprocessor Interface is operating in the Motorola-Asynchronous Mode, then this input pin will function as the DS (Data Strobe) input signal. Power PC 403 Mode - WE - Write Enable Input: If the Microprocessor Interface is operating in the Power PC 403 Mode, then this input pin will function as the WE (Write Enable) input pin. Anytime the Microprocessor Interface samples this active-low input signal (along with CS and WR/R/W) also being asserted (at a logic low level) upon the rising edge of µpclk, then the Microprocessor Interface will (upon the very same rising edge of µpclk) latch the contents on the Bi-Directional Data Bus (D[7:0]) into the "target" on-chip register or buffer location within the XRT94L43. R23 PALE/PAS_L I TTL Address Latch Enable/Address Strobe: This input pin is used to latch the address (present at the Microprocessor Interface Address Bus pins (A[6:0]) into the Mapper/Framer Microprocessor Interface block and to indicate the start of a READ or WRITE cycle. This input pin is active-high, in the Intel Mode and active-low in the Motorola Mode. V22 PCS_L I TTL Chip Select Input: The user must assert this active low signal in order to select the Microprocessor Interface for READ and WRITE operations between the Microprocessor and the XRT94L43 on-chip registers and buffer locations. 10
17 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER REV MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE Y25 PRDY_L/ DTACK/ RDY O CMOS READY or DTACK Output: The function of this input pin depends upon which mode the Microprocessor Interface has been configured to operate in. Intel-Asynchronous Mode - RDY - Ready Output: If the Microprocessor Interface has been configured to operate in the Intel- Asynchronous Mode, then this output pin will function as the "active-low" READY output. During a READ or WRITE cycle, the Microprocessor Interface block will toggle this output pin to the logic low level, ONLY when it (the Microprocessor Interface) is ready to complete or terminate the current READ or WRITE cycle. Once the Microprocessor has determined that this input pin has toggled to the logic "low" level, then it is now safe for it to move on and execute the next READ or WRITE cycle. If (during a READ or WRITE cycle) the Microprocessor Interface block is holding this output pin at a logic "high" level, then the Microprocessor is expected to extend this READ or WRITE cycle, until it detects this output pin being toggled to the logic low level. Motorola-Asynchronous Mode - DTACK - Data Transfer Acknowledge Output If the Microprocessor Interface has been configured to operate in the Motorola-Asynchronous Mode, then this output pin will function as the "active-low" DTACK output. During a READ or WRITE cycle, the Microprocessor Interface block will toggle this output pin to the logic low level, ONLY when it (the Microprocessor Interface) is ready to complete or terminate the current READ or WRITE cycle. Once the Microprocessor has determined that this input pin has toggled to the logic "low" level, then it is now safe for it to move on and execute the next READ or WRITE cycle. If (during a READ or WRITE cycle) the Microprocessor Interface block is holding this output pin at a logic "high" level, then the Microprocessor is expected to extend this READ or WRITE cycle, until it detects this output pin being toggled to the logic low level. Power PC 403 Mode - RDY - Ready Output: If the Microprocessor Interface has been configured to operate in the Power PC 403 Mode, then this output pin will function as the "active-high" READY output.during a READ or WRITE cycle, the Microprocessor Interface block will toggle this output pin to the logic high level, ONLY when it (the Microprocessor Interface) is ready to complete or terminate the current READ or WRITE cycle. Once the Microprocessor has sampled this signal being at the logic "high" level (upon the rising edge of PCLK), then it is now safe for it to move on and execute the next READ or WRITE cycle. If (during a READ or WRITE cycle) the Microprocessor Interface block is holding this output pin at a logic "low" level, then the Microprocessor is expected to extend this READ or WRITE cycle, until it samples this output pin being at the logic low level. NOTE: The Microprocessor Interface will update the state of this output pin upon the rising edge of µpclk. 11
18 REV MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE XRT94L43 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER T21 PDBEN_L I TTL Bi-directional Data Bus Enable Input Pin: This input pin permits the user to either enable or tri-state the Bi-Directional Data Bus pins (D[7:0]), as described below. Setting this input pin "low" enables the Bi-directional Data bus. Setting this input "high" tri-states the Bi-directional Data Bus. U25 PBLAST_L I TTL Last Burst Transfer Indicator input Pin: If the Microprocessor Interface is operating in the Intel-I960 Mode, then this input pin is used to indicate (to the Microprocessor Interface block) that the current data transfer is the last data transfer within the current burst operation. The Microprocessor should assert this input pin (by toggling it "Low") in order to denote that the current READ or WRITE operation (within a BURST operation) is the last operation of this BURST operation. NOTE: If the user has configured the Microprocessor Interface to operate in the Intel-Asynchronous, the Motorola-Asynchronous or the Power PC 403 Mode, then he/she should tie this input pin to GND. AC26 PINT_L O CMOS Interrupt Request Output: This active-low, active-low output signal will be asserted when the XRT94L43 is requesting interrupt service from the Microprocessor. This output pin should typically be connected to the Interrupt Request input of the Microprocessor. L24 RESET_L I TTL Reset Input: When this active-low signal is asserted, the XRT94L43 will be asynchronously reset. When this occurs, all outputs will be tri-stated and all on-chip registers will be reset to their default values. M26 M23 FULL_ADDR_ SEL DIRECT_ADD _SEL I TTL Full Address Select input pin:this input pin, along with "DIRECT_ADD_SEL" (pin M23) must both be pulled "HIGH" in order to configure the Microprocessor Interface block to operate in the "Full Address" Mode.If the Microprocessor Interface is configured to operate in the "Full Address" Mode, then it will then provide a 16-bit Address Bus (which is sufficient to "Directly Address" all of the on-chip registers. I TTL Direct Address Select input pin:this input pin, along with "FULL_ADDR_SEL" (pin M26) must both be pulled "HIGH" in order to configure the Microprocessor Interface block to operate in the "Full Address" Mode.If the Microprocessor Interface is configured to operate in the "Full Address" Mode, then it will then provide a 16-bit Address Bus (which is sufficient to "Directly Address" all of the on-chip registers. 12
19 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER REV SONET/SDH SERIAL LINE INTERFACE PINS M5 RXL_CLKL_P I LVPECL Receive STS-12/STM-4 Clock - Positive Polarity PECL Input: This input pin, along with RXL_CLKL_N functions as the Recovered Clock Input, from a System back-plane or an Optical Transceiver. The Receive STS-12/STM-4 Interface Block will sample the data, applied at the RXLDATA_P/RXLDATA_N input pins, upon the rising edge of this signal. NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this input pin, along with RXL_CLKL_N functions as the Primary Receive Clock Input port. L5 RXL_CLKL_N I LVPECL Receive STS-12/STM-4 Clock - Negative Polarity PECL Input: This input pin, along with RXL_CLKL_P functions as the Recovered Clock Input, from a System back-plane or an Optical Transceiver. The Receiver STS-12/STM-4 Interface Block will sample the data applied at the RXLDATA_P/RXLDATA_N input pins, upon the falling edge of this signal. NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this input pin, along with RXL_CLKL_P functions as the Primary Receive Clock Input Port. K2 RXL_CLKL_R_P I LVPECL Receive STS-12/STM-4 Clock - Positive Polarity PECL Input - Redundant Port: This input pin, along with RXL_CLKL_R_N functions as the Recovered Clock Input, from a System back-plane or an Optical Transceiver. The Receive STS-12/STM-4 Interface Block will sample the data, applied at the RXLDATA_P/RXLDATA_N input pins, upon the rising edge of this signal. NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this input pin, along with RXL_CLKL_R_N functions as the Redundant Receive Clock Input Port. K1 RXL_CLKL_R_N I LVPECL Receive STS-12/STM-4 Clock - Negative Polarity PECL Input - Redundant Port: This input pin, along with RXL_CLKL_P functions as the Recovered Clock Input, from a System back-plane or an Optical Transceiver. The Receiver STS-12/STM-4 Interface Block will sample the data applied at the RXLDATA_P/RXLDATA_N input pins, upon the falling edge of this signal. NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this input pin, along with RXL_CLKL_R_ P functions as the Redundant Receive Clock Input Port. K4 RXL_DATA_P I LVPECL Receive STS-12/STM-4 Data - Positive Polarity PECL Input: This input pin, along with RXL_DATA_N functions as the Recovered Data Input, from a System back-plane or an Optical Transceiver. The Receive STS-12/STM-4 Interface block will sample the data applied to these input pins, upon the rising edge of the RXL_CLKL_P (and the falling edge of the RXL_CLKL_N) signals. NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this input pin, along with RXL_DATA_N functions as the Primary Receive Data Input Port. 13
20 REV SONET/SDH SERIAL LINE INTERFACE PINS XRT94L43 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER L4 RXL_DATA_N I LVPECL Receive STS-12/STM-4 Data - Negative Polarity PECL Input: This input pin, along with RXL_DATA_P functions as the Recovered Data Input, from a System back-plane or an Optical Transceiver. The Receive STS-12/STM-4 Interface block will sample the data applied to these input pins, upon the rising edge of the RXL_CLKL_P (and the falling edge of the RXL_CLKL_N) signals. NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this input pin, along with RXL_DATA_P functions as the Primary Receive Data Input Port. K3 RXL_DATA_R_P I LVPECL Receive STS-12/STM-4 Data - Positive Polarity PECL Input - Redundant Port: This input pin, along with RXL_DATA_R_N functions as the Recovered Data Input, from a System back-plane or an Optical Transceiver. The Receive STS-12/STM-4 Interface block will sample the data applied to these input pins, upon the rising edge of the RXL_CLKL_R_P (and the falling edge of the RXL_CLKL_R_N) signals. NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this input pin, along with RXL_DATA_R_N functions as the Redundant Receive Data Input Port. L3 RXL_DATA_R_N I LVPECL Receive STS-12/STM-4 Data - Negative Polarity PECL Input - Redundant Port: This input pin, along with RXL_DATA_R_P functions as the Recovered Data Input, from a System back-plane or an Optical Transceiver. The Receive STS-12/STM-4 Interface block will sample the data applied to these input pins, upon the rising edge of the RXL_CLKL_R_P (and the falling edge of the RXL_CLKL_R_N) signals. NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this input pin, along with RXL_DATA_R_N functions as the Redundant Receive Data Input Port. T3 TXL_CLKI_P I LVPECL Transmit Reference Clock - Positive Polarity PECL Input: This input pin, along with TxL_CLKI_N can be configured to function as the timing source for the STS-12/STM-4 Transmit Interface Block. If these two input pins are configured to function as the timing source, then a MHz clock signal must be applied to these input pins in the form of a PECL signal. These two inputs can be configured to function as the timing source by writing the appropriate data into the Interface Control Register - Byte 2 (Indirect Address = 0x00, 0x31), (Direct Address = 0x0131). 14
21 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER REV SONET/SDH SERIAL LINE INTERFACE PINS T4 TXL_CLKI_N I LVPECL Transmit Reference Clock - Negative Polarity PECL Input: This input pin, along with TxL_CLKI_P can be configured to function as the timing source for the STS-12/STM-4 Transmit Interface Block. If these two input pins are configured to function as the timing source, then a MHz clock signal must be applied to these input pins in the form of a PECL signal. These two inputs can be configured to function as the timing source by writing the appropriate data into the Interface Control Register - Byte 2 (Indirect Address = 0x00, 0x31), (Direct Address = 0x0131). N1 TXL_DATA_P O LVPECL Transmit STS-12/STM-4 Data - Positive Polarity PECL Output: This output pin, along with TXL_DATA_N functions as the Transmit Data Output, to the System back-plane (for transmission to some other System Board) or an Optical Transceiver (for transmission to remote terminal equipment). For High-Speed Back-Plane Applications, it should noted that data is output from these output pins upon the rising/falling edge of TXL_CLKO_P/TXL_CLKO_N). NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this output pin, along with TXL_DATA_N functions as the Primary Transmit Data Output Port. N2 TXL_DATA_N O LVPECL Transmit STS-12/STM-4 Data - Negative Polarity PECL Output: This output pin, along with TXL_DATA_P functions as the Transmit Data Output, to the System back-plane (for transmission to some other System Board) or an Optical Transceiver (for transmission to remote terminal equipment). For High-Speed Back-Plane Applications, it should noted that data is output from these output pins upon the rising/falling edge of TXL_CLKO_P/TXL_CLKO_N). NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this output pin, along with TXL_DATA_P functions as the Primary Transmit Data Output Port. P1 TXL_DATA_R_P O LVPECL Transmit STS-12/STM-4 Data - Positive Polarity PECL Output - Redundant Port: This output pin, along with TXL_DATA_R_N functions as the Transmit Data Output, to the System back-plane (for transmission to some other System Board) or an Optical Transceiver (for transmission to remote terminal equipment). For High-Speed Back-Plane Applications, it should noted that data is output from these output pins upon the rising/falling edge of TXL_CLKO_R_P/TXL_CLKO_R_N). NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this output pin, along with TXL_DATA_N functions as the Redundant Transmit Data Output Port. 15
22 REV SONET/SDH SERIAL LINE INTERFACE PINS XRT94L43 SONET/SDH OC-12 TO 12XDS3/E3 MAPPER P2 TXL_DATA_R_N O LVPECL Transmit STS-12/STM-4 Data - Negative Polarity PECL Output - Redundant Port: This output pin, along with TXL_DATA_R_P functions as the Transmit Data Output, to the System back-plane (for transmission to some other System Board) or an Optical Transceiver (for transmission to remote terminal equipment). For High-Speed Back-Plane Applications, it should noted that data is output from these output pins upon the rising/falling edge of TXL_CLKO_R_P/TXL_CLKO_R_N). NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this output pin, along with TXL_DATA_R_P functions as the Redundant Transmit Data Output Port. M1 TXL_CLKO_P O LVPECL Transmit STS-12/STM-4 Clock - Positive Polarity PECL Output: This output pin, along with TXL_CLKO_N functions as the Transmit Clock Output signal. These output pins are typically used in High- Speed Back-Plane Applications. In this case, outbound STS-12/ STM-4 data is output via the TXL_DATA_P/TXL_DATA_N output pins upon the rising edge of this clock signal. NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this output pin, along with TXL_CLKO_N functions as the Primary Transmit Output Clock signal. M2 TXL_CLKO_N O LVPECL Transmit STS-12/STM-4 Clock - Negative Polarity PECL Output: This output pin, along with TXLCLKO_P functions as the Transmit Clock Output signal. These output pins are typically used in High- Speed Back-Plane Applications. In this case, outbound STS-12/ STM-4 data is output via the TXL_DATA_P/TXL_DATA_N output pins upon the falling edge of this clock signal. NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this output pin, along with TXL_CLKO_N functions as the Primary Transmit Output Clock signal. R1 TXL_CLKO_R_P O LVPECL Transmit STS-12/STM-4 Clock - Positive Polarity PECL Output - Redundant Port: This output pin, along with TXL_CLKO_R_N functions as the Transmit Clock Output signal. These output pins are typically used in High-Speed Back-Plane Applications. In this case, outbound STS-12/STM-4 data is output via the TXL_DATA_R_P/ TXL_DATA_R_N output pins upon the rising edge of this clock signal. NOTE: For APS (Automatic Protection Switching) purposes, this output pin, along with TXL_CLKO_R_N functions as the Redundant Transmit Output Clock signal. 16
XRT94L33 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 3-CHANNEL DS3/E3/STS-1 TO STS-3/STM-1 MAPPER IC DATA SHEET
 N0VEMBER 2006 REV.1.2.0. GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a highly integrated SONET/SDH terminator designed for E3/DS3/STS-1 mapping/de-mapping functions from either the STS-3 or STM-1 data stream. The interfaces
N0VEMBER 2006 REV.1.2.0. GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a highly integrated SONET/SDH terminator designed for E3/DS3/STS-1 mapping/de-mapping functions from either the STS-3 or STM-1 data stream. The interfaces
XRT94L33 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
 33- -CCHHAANNNNEELL DDSS33/ //EE33/ //SSTTSS- -11 TTOO SSTTSS- -33/ //SSTTM- -11 MAAPPPPEERR SSOONNEETT AATTM/ //PPPPPP HHAARRWAARREE MAANNUUAALL March 2007 Rev 2.0.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a highly
33- -CCHHAANNNNEELL DDSS33/ //EE33/ //SSTTSS- -11 TTOO SSTTSS- -33/ //SSTTM- -11 MAAPPPPEERR SSOONNEETT AATTM/ //PPPPPP HHAARRWAARREE MAANNUUAALL March 2007 Rev 2.0.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a highly
Performance Monitoring
 CHAPTER 15 The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration.
CHAPTER 15 The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration.
SONET. By Sadhish Prabhu. Unit II
 SONET By Sadhish Prabhu History Digital carrier systems The hierarchy of digital signals that the telephone network uses. Trunks and access links organized in DS (digital signal) hierarchy Problem: rates
SONET By Sadhish Prabhu History Digital carrier systems The hierarchy of digital signals that the telephone network uses. Trunks and access links organized in DS (digital signal) hierarchy Problem: rates
CMA 5000 extended Transport Analysis Application
 CMA 5000 extended Transport Analysis Application Applications CMA 5000 The Field Portable Solution for Installation, Commissioning and Maintenance of SONET/SDH Networks (ready for NGN) The compact size
CMA 5000 extended Transport Analysis Application Applications CMA 5000 The Field Portable Solution for Installation, Commissioning and Maintenance of SONET/SDH Networks (ready for NGN) The compact size
SONET Testing and Maintenance
 a step ahead Application Series SONET Testing and Maintenance 302 Enzo Drive San Jose CA 95138 USA ph 1 408 363 8000 fax 1 408 363 8313 info@sunrisetelecom.com www.sunrisetelecom.com Publication Number
a step ahead Application Series SONET Testing and Maintenance 302 Enzo Drive San Jose CA 95138 USA ph 1 408 363 8000 fax 1 408 363 8313 info@sunrisetelecom.com www.sunrisetelecom.com Publication Number
áç PRELIMINARY XRT72L13
 XRT72L13 APRIL 2001 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The XRT72L13 is a fully integrated, low power, Multiplexer/Framer IC which performs Multiplexing/Demutiplexing of 28 DS1or 21 E1 signals into/from a DS3 signal with
XRT72L13 APRIL 2001 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The XRT72L13 is a fully integrated, low power, Multiplexer/Framer IC which performs Multiplexing/Demutiplexing of 28 DS1or 21 E1 signals into/from a DS3 signal with
Performance Monitoring
 CHAPTER 15 Performance monitoring (PM) parameters are used by service providers to gather, store, set thresholds, and report performance data for early detection of problems. In this chapter, PM parameters
CHAPTER 15 Performance monitoring (PM) parameters are used by service providers to gather, store, set thresholds, and report performance data for early detection of problems. In this chapter, PM parameters
áç XRT71D00 GENERAL DESCRIPTION E3/DS3/STS-1 JITTER ATTENUATOR
 SEPTEMBER 2001 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a single channel, single chip Jitter Attenuator, that meets the Jitter transfer characteristic requirements specified in the ETSI TBR-24, Bellcore GR-499-CORE
SEPTEMBER 2001 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a single channel, single chip Jitter Attenuator, that meets the Jitter transfer characteristic requirements specified in the ETSI TBR-24, Bellcore GR-499-CORE
SDH Principle. Copyright 2012 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
 SDH Principle www.huawei.com Objectives Upon completion of this course, you will be able to: Understand the basic of SDH multiplexing standard Know the features, applications and advantages of SDH based
SDH Principle www.huawei.com Objectives Upon completion of this course, you will be able to: Understand the basic of SDH multiplexing standard Know the features, applications and advantages of SDH based
ITU-T G.832. Transport of SDH elements on PDH networks Frame and multiplexing structures
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T G.832 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (10/98) SERIES G: TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS AND MEDIA, DIGITAL SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS Digital transmission systems
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T G.832 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (10/98) SERIES G: TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS AND MEDIA, DIGITAL SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS Digital transmission systems
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION CCITT G.709 THE INTERNATIONAL TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE CONSULTATIVE COMMITTEE (11/1988) SERIES G: TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS AND MEDIA, DIGITAL SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS General
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION CCITT G.709 THE INTERNATIONAL TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE CONSULTATIVE COMMITTEE (11/1988) SERIES G: TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS AND MEDIA, DIGITAL SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS General
TRANSPORT OF SDH ELEMENTS ON PDH NETWORKS: FRAME AND MULTIPLEXING STRUCTURES ITU-T
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T G.832 TELECOMMUNICATION (11/93) STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU DIGITAL NETWORKS TRANSPORT OF SDH ELEMENTS ON PDH NETWORKS: FRAME AND MULTIPLEXING STRUCTURES ITU-T
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T G.832 TELECOMMUNICATION (11/93) STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU DIGITAL NETWORKS TRANSPORT OF SDH ELEMENTS ON PDH NETWORKS: FRAME AND MULTIPLEXING STRUCTURES ITU-T
155 Mb/s Optical Line Interface
 155 Mb/s Optical Line Interface Agilent Technologies Broadband Series Test System Product Features Cell based implementation Operates in both cell mode and SONET/SDH frame mode Provides access to ATM cells
155 Mb/s Optical Line Interface Agilent Technologies Broadband Series Test System Product Features Cell based implementation Operates in both cell mode and SONET/SDH frame mode Provides access to ATM cells
Technical Committee. E3 Public UNI. af-phy
 Technical Committee E3 Public UNI August 1995 1995 The ATM Forum. All Rights Reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means The information in this publication is believed
Technical Committee E3 Public UNI August 1995 1995 The ATM Forum. All Rights Reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means The information in this publication is believed
DS3112 TEMPE T3/E3 Multiplexer 3.3V T3/E3 Framer and M13/E13/G.747 Mux
 TEMPE T3/E3 Multiplexer 3.3V T3/E3 Framer and M13/E13/G.747 Mux www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Operates as M13 or E13 multiplexer or as standalone T3 or E3 framer Flexible multiplexer can be programmed for
TEMPE T3/E3 Multiplexer 3.3V T3/E3 Framer and M13/E13/G.747 Mux www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Operates as M13 or E13 multiplexer or as standalone T3 or E3 framer Flexible multiplexer can be programmed for
T3 Framer MegaCore Function (T3FRM)
 MegaCore Function August 2001; ver. 1.02 Data Sheet Features Achieving optimum performance in the Altera APEX TM 20K device architecture, the multi-featured MegaCore Function meets your innovative design
MegaCore Function August 2001; ver. 1.02 Data Sheet Features Achieving optimum performance in the Altera APEX TM 20K device architecture, the multi-featured MegaCore Function meets your innovative design
VC Look-Up Table. External Memory Controller. TX SAR Local Memory. Local Memory. Figure 1 - MT90528 Block Diagram
 28-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-0078.000) Supports both Unstructured and
28-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-0078.000) Supports both Unstructured and
Network Topologies & Error Performance Monitoring in SDH Technology
 Network Topologies & Error Performance Monitoring in SDH Technology Shiva Sharma Electronics and Communications Department Dronacharya College of Engineering Gurgaon, Haryana Shiva.92@hotmail.com Abstract
Network Topologies & Error Performance Monitoring in SDH Technology Shiva Sharma Electronics and Communications Department Dronacharya College of Engineering Gurgaon, Haryana Shiva.92@hotmail.com Abstract
VC Look-Up Table. Segmentation / Reassembly Circular Buffers. External Memory Controller. TX SAR Local Memory. Local Memory
 8-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-78.) Supports both Unstructured and Structured
8-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-78.) Supports both Unstructured and Structured
JJ TTC STANDARDS. Physical Layer Specifications of kbit/s Optical. Subscriber Line. Version 1. Nov
 TTC STANDARDS JJ-50.30 Physical Layer Specifications of 155520kbit/s Optical Subscriber Line Version 1 Nov 25 1999 THE TELECOMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY COMMITTEE Introduction This document provides the TTC
TTC STANDARDS JJ-50.30 Physical Layer Specifications of 155520kbit/s Optical Subscriber Line Version 1 Nov 25 1999 THE TELECOMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY COMMITTEE Introduction This document provides the TTC
Network Working Group. Category: Standards Track Overture Networks R. Cohen, Ed. Resolute Networks D. Zelig Corrigent Systems April 2007
 Network Working Group Request for Comments: 4842 Category: Standards Track A. Malis Verizon Communications P. Pate Overture Networks R. Cohen, Ed. Resolute Networks D. Zelig Corrigent Systems April 2007
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 4842 Category: Standards Track A. Malis Verizon Communications P. Pate Overture Networks R. Cohen, Ed. Resolute Networks D. Zelig Corrigent Systems April 2007
SONET/SDH STS-12c/STM-4 Framer MegaCore Function (STS12CFRM)
 July 2001; ver. 1.01 SONET/SDH STS-12c/STM-4 Framer MegaCore Function (STS12CFRM) Data Sheet Features Performs synchronous optical network (SONET)/synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) framing and transport
July 2001; ver. 1.01 SONET/SDH STS-12c/STM-4 Framer MegaCore Function (STS12CFRM) Data Sheet Features Performs synchronous optical network (SONET)/synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) framing and transport
áç XRT71D03 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 3 CHANNEL E3/DS3/STS-1 JITTER ATTENUATOR
 áç SEPTEMBER 2001 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a three channel, single chip Jitter Attenuator, that meets the Jitter transfer characteristics requirements specified in the ETSI TBR-24, Bellcore GR-499 and
áç SEPTEMBER 2001 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a three channel, single chip Jitter Attenuator, that meets the Jitter transfer characteristics requirements specified in the ETSI TBR-24, Bellcore GR-499 and
4 CHANNEL E3/DS3/STS-1 JITTER ATTENUATOR, STS-1 TO DS3 DESYNCHRONIZER APRIL 2001 REV Timing Control Block / Phase locked Loop.
 áç APRIL 2001 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a four channel, single chip Jitter Attenuator, that meets the Jitter transfer characteristic requirements specified in the ETSI TBR-24, Bellcore GR-499 and GR-253
áç APRIL 2001 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a four channel, single chip Jitter Attenuator, that meets the Jitter transfer characteristic requirements specified in the ETSI TBR-24, Bellcore GR-499 and GR-253
Final draft ETSI EN V1.4.1 ( )
 Final draft EN 300 147 V1.4.1 (2001-05) European Standard (Telecommunications series) Transmission and Multiplexing (TM); Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH); Multiplexing structure 2 Final draft EN 300
Final draft EN 300 147 V1.4.1 (2001-05) European Standard (Telecommunications series) Transmission and Multiplexing (TM); Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH); Multiplexing structure 2 Final draft EN 300
DS33M30/DS33M31/DS33M33 Ethernet Over SONET/SDH Mapper
 Rev 1; 010809 DS33M30/DS33M31/DS33M33 Ethernet Over SONET/SDH Mapper General Description The DS33M30 family of products provides a compact and efficient solution for transporting Gigabit Ethernet traffic
Rev 1; 010809 DS33M30/DS33M31/DS33M33 Ethernet Over SONET/SDH Mapper General Description The DS33M30 family of products provides a compact and efficient solution for transporting Gigabit Ethernet traffic
CMA extended Transport Analysis Application. Applications
 CMA 5000 extended Transport Analysis Application Applications CMA 5000 The Field Portable Solution for Installation, Commissioning and Maintenance of SONET/SDH Networks (ready for NGN) The compact size
CMA 5000 extended Transport Analysis Application Applications CMA 5000 The Field Portable Solution for Installation, Commissioning and Maintenance of SONET/SDH Networks (ready for NGN) The compact size
XRT91L30. Network & Transmission Products. STS-12/STM-4 or STS-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH TRANSCEIVER JUNE Rev
 JUNE 2007 Rev. 1.0.2 STS-12/STM-4 or STS-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH TRANSCEIVER Network & Transmission Products STS-12/STM-4 OR STS-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH TRANSCEIVER REV. 1.0.2 NOTES: II REV. 1.0.2 STS-12/STM-4 OR
JUNE 2007 Rev. 1.0.2 STS-12/STM-4 or STS-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH TRANSCEIVER Network & Transmission Products STS-12/STM-4 OR STS-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH TRANSCEIVER REV. 1.0.2 NOTES: II REV. 1.0.2 STS-12/STM-4 OR
Troubleshooting Physical Layer Alarms on SONET and SDH Links
 Troubleshooting Physical Layer Alarms on SONET and SDH Links Document ID: 16154 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Alarms at SONET's Layers Alarm Indicators Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Physical Layer Alarms on SONET and SDH Links Document ID: 16154 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Alarms at SONET's Layers Alarm Indicators Troubleshooting
EUROPEAN ETS TELECOMMUNICATION April 1997 STANDARD
 EUROPEAN ETS 300 147 TELECOMMUNICATION April 1997 STANDARD Third Edition Source: ETSI TC-TM Reference: RE/TM-03045 ICS: 33.020 Key words: Transmission, mux, SDH Transmission and Multiplexing (TM); Synchronous
EUROPEAN ETS 300 147 TELECOMMUNICATION April 1997 STANDARD Third Edition Source: ETSI TC-TM Reference: RE/TM-03045 ICS: 33.020 Key words: Transmission, mux, SDH Transmission and Multiplexing (TM); Synchronous
ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 DESIGN OF A FAMILY OF VLSI CIRCUIT FOR PROCESSING RSOH OVERHEAD OF THE STS-1/STM-0 and STS-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH SIGNALS J. Aguirre, D. Torres and M. Guzmán sonet@gdl.cinvestav.mx, dtorres@gdl.cinvestav.mx
DESIGN OF A FAMILY OF VLSI CIRCUIT FOR PROCESSING RSOH OVERHEAD OF THE STS-1/STM-0 and STS-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH SIGNALS J. Aguirre, D. Torres and M. Guzmán sonet@gdl.cinvestav.mx, dtorres@gdl.cinvestav.mx
XRT91L31 STS-12/STM-4 OR STS-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH TRANSCEIVER
 STS-12/STM-4 OR STS-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH TRANSCEIVER JULY 2008 REV. 1.0.2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a fully integrated SONET/SDH transceiver for SONET/SDH 622.08 Mbps STS-12/ STM-4 or 155.52 Mbps STS-3/STM-1
STS-12/STM-4 OR STS-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH TRANSCEIVER JULY 2008 REV. 1.0.2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a fully integrated SONET/SDH transceiver for SONET/SDH 622.08 Mbps STS-12/ STM-4 or 155.52 Mbps STS-3/STM-1
Forward Error Correction in Optical Networks
 Forward Error Correction in Optical Networks P. Michael Henderson michael.henderson@cox.net P. Michael Henderson, michael.henderson@cox.net 1 Agenda Why FEC? In-band SONET/SDH FEC Digital wrapper Frame
Forward Error Correction in Optical Networks P. Michael Henderson michael.henderson@cox.net P. Michael Henderson, michael.henderson@cox.net 1 Agenda Why FEC? In-band SONET/SDH FEC Digital wrapper Frame
DS3112 TEMPE T3/E3 Multiplexer 3.3V T3/E3 Framer and M13/E13/G.747 Mux
 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Operates as M13 or E13 Multiplexer or as Stand-Alone T3 or E3 Framer Flexible Multiplexer can be Programmed for Multiple Configurations Including: M13 Multiplexing (28 T1 Lines
www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Operates as M13 or E13 Multiplexer or as Stand-Alone T3 or E3 Framer Flexible Multiplexer can be Programmed for Multiple Configurations Including: M13 Multiplexing (28 T1 Lines
JUNE 2007 REV XRT91L32. STS-12/STM-4 or STS-3/STM-1 TRANSCEIVER. PISO (Parallel Input Serial Output) Div by 8 CMU RLOOPS DLOOP MUX CDR MUX
 STS-12/STM-4 OR STS-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH TRANSCEIVER JUNE 2007 REV. 1.0.3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a fully integrated SONET/SDH transceiver for SONET/SDH 622.08 Mbps STS-12/ STM-4 or 155.52 Mbps STS-3/STM-1
STS-12/STM-4 OR STS-3/STM-1 SONET/SDH TRANSCEIVER JUNE 2007 REV. 1.0.3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a fully integrated SONET/SDH transceiver for SONET/SDH 622.08 Mbps STS-12/ STM-4 or 155.52 Mbps STS-3/STM-1
SONET/SDH Compiler. Introduction. SONET/SDH Compiler v2.3.0 Issues
 January 2005, Compiler Version 2.3.0 Errata Sheet Introduction This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for version 2.3.0 of the SONET/SDH Compiler. Errata are design functional defects
January 2005, Compiler Version 2.3.0 Errata Sheet Introduction This document addresses known errata and documentation changes for version 2.3.0 of the SONET/SDH Compiler. Errata are design functional defects
ANT-20, ANT-20E Advanced Network Tester Extended Overhead Analysis
 1 ANT-20, ANT-20E Advanced Network Tester Extended Overhead Analysis BN 3035/90.15 Software Version 7.20 Operating Manual BN 3035/98.34 Please direct all enquiries to your local Wavetek Wandel Goltermann
1 ANT-20, ANT-20E Advanced Network Tester Extended Overhead Analysis BN 3035/90.15 Software Version 7.20 Operating Manual BN 3035/98.34 Please direct all enquiries to your local Wavetek Wandel Goltermann
Table of Contents 1 E-CPOS Interface Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 E-CPOS Interface Configuration 1-1 Overview 1-1 SONET 1-1 SDH 1-1 E-CPOS 1-5 Configuring an E-CPOS Interface 1-6 Configuring an E-CPOS Interface 1-6 Configuring the Operating Mode of
Table of Contents 1 E-CPOS Interface Configuration 1-1 Overview 1-1 SONET 1-1 SDH 1-1 E-CPOS 1-5 Configuring an E-CPOS Interface 1-6 Configuring an E-CPOS Interface 1-6 Configuring the Operating Mode of
Displaying Overhead Bytes
 Victoria Combo enables you to view Overhead Bytes of STM-16/OC-48 and STM-64/OC-192 traffic. This is particularly useful in fault-finding on a network. This Application Note describes how to display overhead
Victoria Combo enables you to view Overhead Bytes of STM-16/OC-48 and STM-64/OC-192 traffic. This is particularly useful in fault-finding on a network. This Application Note describes how to display overhead
Configuring SDH on 1-Port OC-192/STM-64 or 8-Port OC-3/12/48/STM-1/-4/-16 Module
 Configuring SDH on 1-Port OC-192/STM-64 or 8-Port OC-3/12/48/STM-1/-4/-16 Module SDH is a standard that defines optical signals as well as a synchronous frame structure for multiplexed digital traffic.
Configuring SDH on 1-Port OC-192/STM-64 or 8-Port OC-3/12/48/STM-1/-4/-16 Module SDH is a standard that defines optical signals as well as a synchronous frame structure for multiplexed digital traffic.
Be the First without uncertainties! Tandem Connection Monitoring. The principle of TCM TCM analysis. White Paper. July 99
 Be the First without uncertainties! Tandem Connection Monitoring Tandem Connection Monitoring The principle of TCM TCM analysis White Paper July 99 1 Where do the errors come from? Provider 1 BIP? BIP?
Be the First without uncertainties! Tandem Connection Monitoring Tandem Connection Monitoring The principle of TCM TCM analysis White Paper July 99 1 Where do the errors come from? Provider 1 BIP? BIP?
Technical Committee. Interoperability Abstract Test Suites for the Physical Layer. af-test
 Technical Committee Interoperability Abstract Test Suites af-test-0036.000 April, 1995 af-test-0036.000 Interoperability Abstract Test Suites Interoperability Abstract Test Suites Version 1.0 April, 1995
Technical Committee Interoperability Abstract Test Suites af-test-0036.000 April, 1995 af-test-0036.000 Interoperability Abstract Test Suites Interoperability Abstract Test Suites Version 1.0 April, 1995
DIGITAL TRANSMISSION MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
 SDH/SONET ANALYZER ME3520A/3620A PTA OPTION GPIB The ME3520A/3620A can access the Network Node Interface (NNI) of Synchronous Multiplexer/Demultiplexer systems in the world at 52, 156, 622, and 2488 Mb/s.
SDH/SONET ANALYZER ME3520A/3620A PTA OPTION GPIB The ME3520A/3620A can access the Network Node Interface (NNI) of Synchronous Multiplexer/Demultiplexer systems in the world at 52, 156, 622, and 2488 Mb/s.
JANUARY 2007 REV GENERAL DESCRIPTION. Re-Timer CMU DLOOP CDR. Hardware Control LOOPTM_NOJA LOOPBW POLARITY LOSDET TEST SDEXT DLOOP RLOOPP
 xr XRT91L80 2.488/2.666 GBPS STS-48/STM-16 SONET/SDH TRANSCEIVER JANUARY 2007 REV. 1.0.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The XRT91L80 is a fully integrated SONET/SDH transceiver for SONET OC-48/STM-16 applications
xr XRT91L80 2.488/2.666 GBPS STS-48/STM-16 SONET/SDH TRANSCEIVER JANUARY 2007 REV. 1.0.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The XRT91L80 is a fully integrated SONET/SDH transceiver for SONET OC-48/STM-16 applications
DIGITAL TRANSMISSION MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
 SDH/SONET ANALYZER ME3620A For Evaluating Transmission Characteristics of Synchronous MUX/DEMUX Equipment Worldwide PTA OPTION GPIB The ME3620A can access the Network Node Interface (NNI) of Synchronous
SDH/SONET ANALYZER ME3620A For Evaluating Transmission Characteristics of Synchronous MUX/DEMUX Equipment Worldwide PTA OPTION GPIB The ME3620A can access the Network Node Interface (NNI) of Synchronous
CMA 3000, all-in-one field tester SDH test options
 CMA 3000, all-in-one field tester SDH test options KEY FEATURES Simultaneous bidirectional monitoring of SDH lines Powerful testing of SDH systems and embedded PDH systems Mapping and demapping Comprehensive
CMA 3000, all-in-one field tester SDH test options KEY FEATURES Simultaneous bidirectional monitoring of SDH lines Powerful testing of SDH systems and embedded PDH systems Mapping and demapping Comprehensive
OTM2515/2516/ M/622M/2.5GSDH/SONET Test Module
 www.opwill.com OTM2515/2516/2517 155M/622M/2.5GSDH/SONET Test Module OTM2515 (155M), OTM2516 (622M), and OTM2517 (2.5G)SDH/SONET Module is a battery-operated handheld test solution for testing legacy PDH/DSn,
www.opwill.com OTM2515/2516/2517 155M/622M/2.5GSDH/SONET Test Module OTM2515 (155M), OTM2516 (622M), and OTM2517 (2.5G)SDH/SONET Module is a battery-operated handheld test solution for testing legacy PDH/DSn,
CE Ethernet Operation
 25 CHAPTER Note The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring
25 CHAPTER Note The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring
LIM Configuration Menu
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter deals with configura tion of LIM devices. It is organized as follows:, page 7-1 LIM Maintenance, page 7-4 LIM Alarms, page 7-7 SONET/SDH, page 7-7 SONET Maintenance, page 7-13 DSX1,
CHAPTER 7 This chapter deals with configura tion of LIM devices. It is organized as follows:, page 7-1 LIM Maintenance, page 7-4 LIM Alarms, page 7-7 SONET/SDH, page 7-7 SONET Maintenance, page 7-13 DSX1,
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION. SERIES G: TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS AND MEDIA, DIGITAL SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS Digital networks General aspects
 INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T G.804 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (06/2004) SERIES G: TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS AND MEDIA, DIGITAL SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS Digital networks General
INTERNATIONAL TELECOMMUNICATION UNION ITU-T G.804 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (06/2004) SERIES G: TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS AND MEDIA, DIGITAL SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS Digital networks General
PIN DIAGRAM. Richa Upadhyay Prabhu. NMIMS s MPSTME January 19, 2016
 PIN DIAGRAM Richa Upadhyay Prabhu NMIMS s MPSTME richa.upadhyay@nmims.edu January 19, 2016 Richa Upadhyay Prabhu (MPSTME) 8080 Microprocessor January 19, 2016 1 / 51 Pin Diagram of 8086 Richa Upadhyay
PIN DIAGRAM Richa Upadhyay Prabhu NMIMS s MPSTME richa.upadhyay@nmims.edu January 19, 2016 Richa Upadhyay Prabhu (MPSTME) 8080 Microprocessor January 19, 2016 1 / 51 Pin Diagram of 8086 Richa Upadhyay
VePAL UX400 Universal Test Platform
 UX400-2.5G Module OTN/SDH/SONET/PDH/DSn Testing VePAL UX400 Universal Test Platform Next Generation Modular Platform for Transport, Carrier Ethernet, Mobile Backhaul, and Legacy Testing VeEX UX400 is the
UX400-2.5G Module OTN/SDH/SONET/PDH/DSn Testing VePAL UX400 Universal Test Platform Next Generation Modular Platform for Transport, Carrier Ethernet, Mobile Backhaul, and Legacy Testing VeEX UX400 is the
LightSpeed1000 (w/ GigE and USB 2.0) OC-3/STM-1, OC-12/STM-4 Analysis and Emulation Card
 Wirespeed Record/Playback/ Processing of ATM, PoS, RAW, and Ethernet Traffic LightSpeed1000 (w/ GigE and USB 2.0) OC-3/STM-1, OC-12/STM-4 Analysis and Emulation Card x4 PCIExpress, USB 2.0, and Gigabit
Wirespeed Record/Playback/ Processing of ATM, PoS, RAW, and Ethernet Traffic LightSpeed1000 (w/ GigE and USB 2.0) OC-3/STM-1, OC-12/STM-4 Analysis and Emulation Card x4 PCIExpress, USB 2.0, and Gigabit
SONET network testing simplified. Key Features
 2008 Global Test & Measurement Emerging Company of the Year Award VePAL TX150 Handheld SONET Test Set SONET network testing simplified VeEX VePAL TX150 is a next generation test solution for SONET networks
2008 Global Test & Measurement Emerging Company of the Year Award VePAL TX150 Handheld SONET Test Set SONET network testing simplified VeEX VePAL TX150 is a next generation test solution for SONET networks
Technical Committee. 2.4 Gbps Physical Layer Specification AF-PHY
 Technical Committee 2.4 Gbps Physical Layer Specification AF-PHY-0133.000 October, 1999 1999 by The ATM Forum. This specification/document may be reproduced and distributed in whole, but (except as provided
Technical Committee 2.4 Gbps Physical Layer Specification AF-PHY-0133.000 October, 1999 1999 by The ATM Forum. This specification/document may be reproduced and distributed in whole, but (except as provided
INTERFACING THE ISCC TO THE AND 8086
 APPLICATION NOTE INTERFACING THE ISCC TO THE 68 AND 886 INTRODUCTION The ISCC uses its flexible bus to interface with a variety of microprocessors and microcontrollers; included are the 68 and 886. The
APPLICATION NOTE INTERFACING THE ISCC TO THE 68 AND 886 INTRODUCTION The ISCC uses its flexible bus to interface with a variety of microprocessors and microcontrollers; included are the 68 and 886. The
This specification this document to get an official version of this User Network Interface Specification
 This specification describes the situation of the Proximus network and services. It will be subject to modifications for corrections or when the network or the services will be modified. Please take into
This specification describes the situation of the Proximus network and services. It will be subject to modifications for corrections or when the network or the services will be modified. Please take into
extended Transport Analysis Application Jitter and Wander Option
 CMA 5000 extended Transport Analysis Application Jitter and Wander Option The compact size of the XTA Application module with its jitter and wander option, conveniently fits into the CMA 5000 Multi-Layer
CMA 5000 extended Transport Analysis Application Jitter and Wander Option The compact size of the XTA Application module with its jitter and wander option, conveniently fits into the CMA 5000 Multi-Layer
RADview-EMS/TDM. Element Management System for TDM Applications Optimux RAD Data Communications Publication 03/06
 RADview-EMS/TDM Element Management System for TDM Applications Optimux-1551 1994 2006 RAD Data Communications Publication 03/06 Contents Chapter 1. Introduction 1.1 OP-1551 Hardware Overview... 1-1 1.2
RADview-EMS/TDM Element Management System for TDM Applications Optimux-1551 1994 2006 RAD Data Communications Publication 03/06 Contents Chapter 1. Introduction 1.1 OP-1551 Hardware Overview... 1-1 1.2
ANT Advanced Network Tester Family ANT-20, ANT-20se, ANT-10G
 COMMUNICATIONS TEST & MEASUREMENT SOLUTIONS ANT Advanced Network Tester Family ANT-20, ANT-20se, ANT-10G Key Features Easy-to-use, portable, compact and comprehensive test kit for SDH/SONET bit rates up
COMMUNICATIONS TEST & MEASUREMENT SOLUTIONS ANT Advanced Network Tester Family ANT-20, ANT-20se, ANT-10G Key Features Easy-to-use, portable, compact and comprehensive test kit for SDH/SONET bit rates up
extended Transport Analysis Application Next Generation SONET/SDH Option
 CMA 5000 extended Transport Analysis Application Next Generation SONET/SDH Option Key Features Ideal tool for Next- Generation SONET/SDH measurement in a field environment LCAS source and sink state machines
CMA 5000 extended Transport Analysis Application Next Generation SONET/SDH Option Key Features Ideal tool for Next- Generation SONET/SDH measurement in a field environment LCAS source and sink state machines
CPE/EE 421/521 Fall 2004 Chapter 4 The CPU Hardware Model. Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH. The CPU Hardware Model - Overview
 CPE/EE 421/521 Fall 2004 Chapter 4 The 68000 CPU Hardware Model Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH Fall 2004 1 The 68000 CPU Hardware Model - Overview 68000 interface Timing diagram Minimal configuration using the
CPE/EE 421/521 Fall 2004 Chapter 4 The 68000 CPU Hardware Model Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH Fall 2004 1 The 68000 CPU Hardware Model - Overview 68000 interface Timing diagram Minimal configuration using the
Differences Between SONET and SDH Framing in Optical Networks
 Differences Between SONET and SDH Framing in Optical Networks Document ID: 16180 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions SONET and SDH Framing ATM Over SONET Packet
Differences Between SONET and SDH Framing in Optical Networks Document ID: 16180 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions SONET and SDH Framing ATM Over SONET Packet
1. Internal Architecture of 8085 Microprocessor
 1. Internal Architecture of 8085 Microprocessor Control Unit Generates signals within up to carry out the instruction, which has been decoded. In reality causes certain connections between blocks of the
1. Internal Architecture of 8085 Microprocessor Control Unit Generates signals within up to carry out the instruction, which has been decoded. In reality causes certain connections between blocks of the
Section 2: Physical Layer Interfaces Specification
 Section 2: Physical Layer Interfaces Specification 11 ATM USER-NETWORK INTERFACE SPECIFICATION (V3.1) 2 Physical Layer Interfaces Specification This section provides specifications for physical layer ATM
Section 2: Physical Layer Interfaces Specification 11 ATM USER-NETWORK INTERFACE SPECIFICATION (V3.1) 2 Physical Layer Interfaces Specification This section provides specifications for physical layer ATM
Transmission Technology Ses SDH
 Transmission Technology Ses SDH ALTTC/TX1/SDH/CONCEPTS 1 CONTENTS SDH PROTECTION PLANNING SYNCHRONISATION ALTTC/TX1/SDH/CONCEPTS 2 SDH: DISCUSSION AREA WHAT IS SDH? EVOLUTION DRIVING FORCES LIMITATIONS
Transmission Technology Ses SDH ALTTC/TX1/SDH/CONCEPTS 1 CONTENTS SDH PROTECTION PLANNING SYNCHRONISATION ALTTC/TX1/SDH/CONCEPTS 2 SDH: DISCUSSION AREA WHAT IS SDH? EVOLUTION DRIVING FORCES LIMITATIONS
XRT75VL00D E3/DS3/STS-1 LINE INTERFACE UNIT WITH SONET
 E3/DS3/STS-1 LINE INTERFACE UNIT WITH SONET SEPTEMBER 28 REV. 1..4 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a single-channel fully integrated Line Interface Unit (LIU) with Sonet Desynchronizer for E3/DS3/STS-1 applications.
E3/DS3/STS-1 LINE INTERFACE UNIT WITH SONET SEPTEMBER 28 REV. 1..4 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a single-channel fully integrated Line Interface Unit (LIU) with Sonet Desynchronizer for E3/DS3/STS-1 applications.
DS2155 T1/E1/J1 Single-Chip Transceiver
 ERRATA SHEET DS2155 T1/E1/J1 Single-Chip Transceiver www.maxim-ic.com REVISION B1 ERRATA The errata listed below describe situations where DS2155 revision B1 components perform differently than expected
ERRATA SHEET DS2155 T1/E1/J1 Single-Chip Transceiver www.maxim-ic.com REVISION B1 ERRATA The errata listed below describe situations where DS2155 revision B1 components perform differently than expected
learntelecoms interactive e-learning suite of courses: SyncNet v6 SDH-based broadband networks SyncNet
 Tel: 0845 0949 120 Email: info@ptt.co.uk Web site: www.ptt.co.uk SyncNet SyncNet v6 SDH-based broadband networks SyncNet is a suite of interactive, multimedia e-learning courses. provides training in the
Tel: 0845 0949 120 Email: info@ptt.co.uk Web site: www.ptt.co.uk SyncNet SyncNet v6 SDH-based broadband networks SyncNet is a suite of interactive, multimedia e-learning courses. provides training in the
SDH-1620A SDH/PDH Transmission Analyzer. DADI Telecom. Professional Communication Tester Manufacturer from China
 SDH-1620A SDH/PDH Transmission Analyzer DADI Telecom Professional Communication Tester Manufacturer from China SDH-1620A is an advanced SDH and PDH transmission analyzer. Basic configuration can support
SDH-1620A SDH/PDH Transmission Analyzer DADI Telecom Professional Communication Tester Manufacturer from China SDH-1620A is an advanced SDH and PDH transmission analyzer. Basic configuration can support
M13FX M13 Multiplexer and DS3 Framer PEB 3445 E V1.1
 Data Sheet, DS1, Sep. 2000 M13FX M13 Multiplexer and DS3 Framer PEB 3445 E V1.1 Datacom Never stop thinking. Edition 2000-09-27 Published by Infineon Technologies AG, St.-Martin-Strasse 53, D-81541 München,
Data Sheet, DS1, Sep. 2000 M13FX M13 Multiplexer and DS3 Framer PEB 3445 E V1.1 Datacom Never stop thinking. Edition 2000-09-27 Published by Infineon Technologies AG, St.-Martin-Strasse 53, D-81541 München,
SoC / ASIC / FPGA / IP
 Top Notch Solution Providers in design & Verification for SoC / ASIC / FPGA / IP Delivering high quality services with technical excellence, continuous innovation, passion and unyielding integrity. KACPER
Top Notch Solution Providers in design & Verification for SoC / ASIC / FPGA / IP Delivering high quality services with technical excellence, continuous innovation, passion and unyielding integrity. KACPER
DS3/ATM Physical Layer Interface Specification
 Technical Committee DS3 Physical Layer Interface Specification January, 1996 (C) 1996 The ATM Forum. All Rights Reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means. The
Technical Committee DS3 Physical Layer Interface Specification January, 1996 (C) 1996 The ATM Forum. All Rights Reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means. The
Configuring Automatic Protection Switching
 Application Note Configuring Automatic Protection Switching Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94089 USA 408 745 2000 or 888 JUNIPER www.juniper.net Part Number : 350021-001
Application Note Configuring Automatic Protection Switching Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94089 USA 408 745 2000 or 888 JUNIPER www.juniper.net Part Number : 350021-001
Configuring Clear Channel SONET Controllers on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router
 Configuring Clear Channel SONET Controllers on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the configuration of clear channel SONET controllers on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. SONET controller
Configuring Clear Channel SONET Controllers on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the configuration of clear channel SONET controllers on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. SONET controller
Table of Contents. Preface. 1 Introduction. 2 Network Compatibility. 3 Rates and Formats
 Issue 5, October 2009 SONET Transport Systems: Common Criteria Preface 1 Introduction 1.1 Requirements Terminology............................. 1 1 1.2 Requirement Labeling Conventions.........................
Issue 5, October 2009 SONET Transport Systems: Common Criteria Preface 1 Introduction 1.1 Requirements Terminology............................. 1 1 1.2 Requirement Labeling Conventions.........................
MULTISERVICE INTERFACE MICS FOR MX SERIES
 DATASHEET MULTISERVICE INTERFACE MICS FOR MX SERIES Product Overview Juniper Networks MX Series 3D Universal Edge Routers provide industry-leading intelligence, flexibility and efficiency, and they are
DATASHEET MULTISERVICE INTERFACE MICS FOR MX SERIES Product Overview Juniper Networks MX Series 3D Universal Edge Routers provide industry-leading intelligence, flexibility and efficiency, and they are
Configuring POS interfaces
 Contents Configuring POS interfaces 1 Overview 1 SONET 1 SDH 1 POS 1 Configuration procedure 1 Displaying and maintaining POS interfaces 3 POS interface configuration examples 4 Directly connecting switches
Contents Configuring POS interfaces 1 Overview 1 SONET 1 SDH 1 POS 1 Configuration procedure 1 Displaying and maintaining POS interfaces 3 POS interface configuration examples 4 Directly connecting switches
OmniBER OTN 10 Gb/s communications performance analyzer. Product note. The key to (10G) line card testing G.709
 OmniBER OTN 10 Gb/s communications performance analyzer Product note The key to (10G) line card testing G.709 The growing demand for bandwidth in the network has encouraged service providers to install
OmniBER OTN 10 Gb/s communications performance analyzer Product note The key to (10G) line card testing G.709 The growing demand for bandwidth in the network has encouraged service providers to install
What is SDH? Telecommunications Standards Primer. Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy (PDH) Limitations of PDH Network
 Página 1 de 7 Telecommunications Standards Primer What is SDH? This document is intended as an introductory guide to the Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) standard. The following is a representative
Página 1 de 7 Telecommunications Standards Primer What is SDH? This document is intended as an introductory guide to the Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) standard. The following is a representative
CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers
 CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers THE 68000 CPU HARDWARE MODEL Instructor: Dr Aleksandar Milenkovic Lecture Notes Lecture 19 CPE/EE 421/521 Microcomputers 1 THE 68000 CPU HARDWARE MODEL Chapter 4 68000 interface
CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers THE 68000 CPU HARDWARE MODEL Instructor: Dr Aleksandar Milenkovic Lecture Notes Lecture 19 CPE/EE 421/521 Microcomputers 1 THE 68000 CPU HARDWARE MODEL Chapter 4 68000 interface
Configuring SDH on 1-Port OC192/STM-64 or 8-Port OC3/12/48/STM-1/-4/-16 Module
 Configuring SDH on 1-Port OC192/STM-64 or 8-Port OC3/12/48/STM-1/-4/-16 Module SDH is a standard that defines optical signals as well as a synchronous frame structure for multiplexed digital traffic. It
Configuring SDH on 1-Port OC192/STM-64 or 8-Port OC3/12/48/STM-1/-4/-16 Module SDH is a standard that defines optical signals as well as a synchronous frame structure for multiplexed digital traffic. It
PIC Guide. End-of-Life PICs. M20 Internet Router. Juniper Networks, Inc.
 M20 Internet Router PIC Guide End-of-Life PICs Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net Part Number: 530-010561-01, Revision 7 M20
M20 Internet Router PIC Guide End-of-Life PICs Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net Part Number: 530-010561-01, Revision 7 M20
Tunable OTN XFP MSA Compliant DWDM 11.1Gb/s Transceiver with Integrated G.709 and FEC
 Tunable OTN XFP MSA Compliant DWDM 11.1Gb/s Transceiver with Integrated G.709 and FEC Management XFI Electrical Interface Description Menara Networks Tunable OTN XFP DWDM transceiver combines carrier grade
Tunable OTN XFP MSA Compliant DWDM 11.1Gb/s Transceiver with Integrated G.709 and FEC Management XFI Electrical Interface Description Menara Networks Tunable OTN XFP DWDM transceiver combines carrier grade
Single Channel HDLC Core V1.3. LogiCORE Facts. Features. General Description. Applications
 Sept 8, 2000 Product Specification R Powered by Xilinx Inc. 2100 Logic Drive San Jose, CA 95124 Phone: +1 408-559-7778 Fax: +1 408-559-7114 E-mail: logicore@xilinx.com URL: www.xilinx.com/ipcenter Support:
Sept 8, 2000 Product Specification R Powered by Xilinx Inc. 2100 Logic Drive San Jose, CA 95124 Phone: +1 408-559-7778 Fax: +1 408-559-7114 E-mail: logicore@xilinx.com URL: www.xilinx.com/ipcenter Support:
32 Channel HDLC Core V1.2. Applications. LogiCORE Facts. Features. General Description. X.25 Frame Relay B-channel and D-channel
 May 3, 2000 Xilinx Inc. 2100 Logic Drive San Jose, CA 95124 Phone: +1 408-559-7778 Fax: +1 408-559-7114 E-mail: logicore@xilinx.com URL: www.xilinx.com/ipcenter Support: www.support.xilinx.com Features
May 3, 2000 Xilinx Inc. 2100 Logic Drive San Jose, CA 95124 Phone: +1 408-559-7778 Fax: +1 408-559-7114 E-mail: logicore@xilinx.com URL: www.xilinx.com/ipcenter Support: www.support.xilinx.com Features
High-Speed Jitter Testing of XFP Transceivers
 White Paper High-Speed Jitter Testing of XFP Transceivers By Andreas Alpert Abstract Jitter is a key performance factor in high-speed digital transmission systems, such as synchronous optical networks/synchronous
White Paper High-Speed Jitter Testing of XFP Transceivers By Andreas Alpert Abstract Jitter is a key performance factor in high-speed digital transmission systems, such as synchronous optical networks/synchronous
Tandem Connection Monitoring: Fundamentals, Operation, Test Solutions
 Application Note Tandem Connection Monitoring: Fundamentals, Operation, Test Solutions Application: Qualification of a TCM link section The Advanced Network Tester is designed for mobile testing of digital
Application Note Tandem Connection Monitoring: Fundamentals, Operation, Test Solutions Application: Qualification of a TCM link section The Advanced Network Tester is designed for mobile testing of digital
M40e Multiservice Edge Router End-of-Life PIC Guide
 M40e Multiservice Edge Router End-of-Life PIC Guide August 2010 This guide provides an overview and description of the PICs supported by the Juniper Networks M40e Multiservice Edge Router that are end-of-life
M40e Multiservice Edge Router End-of-Life PIC Guide August 2010 This guide provides an overview and description of the PICs supported by the Juniper Networks M40e Multiservice Edge Router that are end-of-life
Architecture of 8085 microprocessor
 Architecture of 8085 microprocessor 8085 consists of various units and each unit performs its own functions. The various units of a microprocessor are listed below Accumulator Arithmetic and logic Unit
Architecture of 8085 microprocessor 8085 consists of various units and each unit performs its own functions. The various units of a microprocessor are listed below Accumulator Arithmetic and logic Unit
1 MALP ( ) Unit-1. (1) Draw and explain the internal architecture of 8085.
 (1) Draw and explain the internal architecture of 8085. The architecture of 8085 Microprocessor is shown in figure given below. The internal architecture of 8085 includes following section ALU-Arithmetic
(1) Draw and explain the internal architecture of 8085. The architecture of 8085 Microprocessor is shown in figure given below. The internal architecture of 8085 includes following section ALU-Arithmetic
Acknowledgements. No part of this guide may be reproduced in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of EXFO.
 Acknowledgements This guide would not have been possible without the valuable input and teamwork of the EXFO team; particularly Mr. Claudio Mazzuca, B.Eng., M.B.A, Senior Product Manager; Ms. Mai Abou-Shaban,
Acknowledgements This guide would not have been possible without the valuable input and teamwork of the EXFO team; particularly Mr. Claudio Mazzuca, B.Eng., M.B.A, Senior Product Manager; Ms. Mai Abou-Shaban,
a step ahead SunSet 10G SONET and SDH Testing in a Single Handheld Unit
 a step ahead SunSet 10G SONET and SDH Testing in a Single Handheld Unit Advanced SONET and SDH Transmission Testing & Analysis in a Handheld Set It's not magic; it's Sunrise Telecom technology. Revolutionizing
a step ahead SunSet 10G SONET and SDH Testing in a Single Handheld Unit Advanced SONET and SDH Transmission Testing & Analysis in a Handheld Set It's not magic; it's Sunrise Telecom technology. Revolutionizing
VePAL TX150+ Handheld SONET Test Set
 VePAL TX150+ Handheld SONET Test Set SONET network testing simplified VeEX VePAL TX150+ is a next generation test solution for SONET, DS3/DS1 networks transporting legacy and next generation services.
VePAL TX150+ Handheld SONET Test Set SONET network testing simplified VeEX VePAL TX150+ is a next generation test solution for SONET, DS3/DS1 networks transporting legacy and next generation services.
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL INTRODUCTION TO OPTICAL TRANSPORT CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO OPTICAL TRANSPORT This chapter covers the history of the development of SDH, SONET, and OTN. For consistency in the terminology used in this book I have included a list of conventions.
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO OPTICAL TRANSPORT This chapter covers the history of the development of SDH, SONET, and OTN. For consistency in the terminology used in this book I have included a list of conventions.
Installing ONS SDH OC3 IR 4/STM1 SH 1310 Cards
 Installing ONS 15454 SDH OC3 IR 4/STM1 SH 1310 Cards Product Name: 15454E-S1.1-4= This document contains a description of OC3 IR 4/STM1 SH 1310 card features, installation procedures, removal instructions,
Installing ONS 15454 SDH OC3 IR 4/STM1 SH 1310 Cards Product Name: 15454E-S1.1-4= This document contains a description of OC3 IR 4/STM1 SH 1310 card features, installation procedures, removal instructions,
STANDARD T1.PP Pre-published American National Standard for Telecommunications -
 PE E-PUBLISHED STANDAD T1.PP.105-2001 Pre-published American National Standard for Telecommunications - Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) - Basic Description including Multiplex Structure, ates and Formats
PE E-PUBLISHED STANDAD T1.PP.105-2001 Pre-published American National Standard for Telecommunications - Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) - Basic Description including Multiplex Structure, ates and Formats
8086 Hardware Specification
 Content: Segment 5 8086 Hardware Specification 8086 Modes of operation. Pin diagram and pin function of 8086. 8284A Clock generator operation and pin functions. Prepared By: Mohammed Abdul Kader Lecturer,
Content: Segment 5 8086 Hardware Specification 8086 Modes of operation. Pin diagram and pin function of 8086. 8284A Clock generator operation and pin functions. Prepared By: Mohammed Abdul Kader Lecturer,
Optical Network Tester (ONT)
 Module-E 10 G/2.5 G Jitter Module 10 G E Jitter Module 2.5 G D Optical Network Tester (ONT) Module-E and Jitter Modules Today s market is facing tremendous new packet-based services growth such as VoIP
Module-E 10 G/2.5 G Jitter Module 10 G E Jitter Module 2.5 G D Optical Network Tester (ONT) Module-E and Jitter Modules Today s market is facing tremendous new packet-based services growth such as VoIP
