Interrupts and Timers
|
|
|
- Anna Pitts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Indian Institute of Technology Bombay CS684/CS308 Embedded Systems Interrupts and Timers E.R.T.S. Lab 1 Lab Objective This lab will introduce you to the use of Timers and Interrupts on the TM4C123GH6PM. 2 Pre-requisite 1. Lab 1: Interface led and both the switches. 2. Reference material: Please go through student guide and lab manual (Chapter 4) given in the resource section before you proceed further. 3 Problem Statement 1. Use sw1 to change the color of the led (R G B R....) where you should press the switch just once instead of long press in Lab 1. Use switch debouncing mentioned below in the procedure to differentiate between switch bounce and actual key press. 2. Use sw2 to increment a global variable once for each button press. Check if the variable always increments by one (adjust the time interval of 10 ms if you wish to) 1
2 Figure 1: Button Bounce Waveform 4 Relevant Theory This lab will use a timer to generate interrupts and we will write a timer interrupt service routine (ISR) that implements a state machine to perform software button debouncing. Button Bounce:From the above diagram it is clear that when you press the switch the signal bounces for a finite amount of time before settling down to its final logic state. This is due to the tendency of any two metal contacts in an electronic device to generate multiple signals as the contacts close or open. The bounce period is 10 to 20 ms. Solution: There are several ways to do button debouncing which includes modifications in both hardware and software. In this lab we will explore software debouncing. In software debouncing too, there are a couple of ways to solve this problem viz. 1. Polling the switch plus introducing finite delays: In polling method the controller is busy polling the switch hence it will not be able to perform any other tasks. 2. Using interrupts and timers: If we want to use this time to do other tasks, then we can use interrupts and timers. Switch debouncing using interrupts and timers: We will check for the status of the switch at finite intervals (say 10 ms). This time interval will be generated using timers. When the 10 ms interval is over the timer should generate an interrupt and the code in the interrupt service routine (ISR) will be executed. In the interrupt service routine, we 2
3 will implement a state machine. Here the idea is that if we find the switch pressed for two successive intervals (of 10 ms) then we confirm that the switch is pressed and we will detect the next key press only if we confirm that the switch is released. This will ensure that if a switch press is only detected once. A state machine is described below for implementing software debouncing. In this state machine there are three states viz. Idle, Press and Release for a switch. There are two transition paths in each state. Any state transition condition is checked after a fixed interval of time which is set by a timer (in this case it is 10 ms). Note: As the bounce period is 10 ms to 20 ms you can change this time interval based on your experimental trials. It is possible that different switches have different bounce periods. IDLE If the key is pressed, enter press state else remain in IDLE state PRESS If key is still pressed, then enter release state and make flag 1 indicating that key was pressed. else return to idle state (de-bouncing period) RELEASE If the key is released, then enter an idle state else remain in release state until key is released. 3
4 Figure 2: Switch debouncing state diagram 4
5 5 Procedure 1. Configure and initialize Timer 0 and set the time interval to 10ms. Use the lab exercise in student guide and lab manual (Chapter 4) as a starting point. 2. Make a user defined function called detectkeypress() and call this in the interrupt handler. This function will return 1 only if a key press is detected according to the state machine. The prototype of the function is given below. unsigned char detectkeypress() { return flag; } 3. Describe the state machinefigure:2 in this function and each time the function is called from the interrupt handler the machine should make a transition to the next stage. Make sure that the previous state (Scope of variables) of the system is maintained each time the function is called. 4. Write a code for debouncing both sw1 and sw2. 5. Verify that both the switches are de-bounced. Note: The action associated with the switches should be performed exactly once for each switch press. Long press of the switch should not lead to multiple triggers. 6 Demo and Submissions Show the output to your TA and explain if this approach helps in debouncing the switches. Document your code. You will be asked to upload your codes on GitHub. It is recommended that you make your code modular and use this debouncing method in upcoming labs. 5
Interfacing Graphics LCD (GLCD)
 Indian Institute of Technology Bombay CS684/CS308 Embedded Systems Interfacing Graphics LCD (GLCD) E.R.T.S. Lab 1 Lab Objective The objective of this lab is to introduce you to interfacing 128x64 Graphics
Indian Institute of Technology Bombay CS684/CS308 Embedded Systems Interfacing Graphics LCD (GLCD) E.R.T.S. Lab 1 Lab Objective The objective of this lab is to introduce you to interfacing 128x64 Graphics
Scheduling in TI-RTOS
 Indian Institute of Technology Bombay CS684/CS308 Embedded Systems Lab Scheduling in TI-RTOS E.R.T.S. Lab 1 Lab Objective Analysis of time driven scheduling using the game console and TI-RTOS. Identifying
Indian Institute of Technology Bombay CS684/CS308 Embedded Systems Lab Scheduling in TI-RTOS E.R.T.S. Lab 1 Lab Objective Analysis of time driven scheduling using the game console and TI-RTOS. Identifying
Embedded Systems and Software
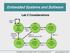 Embedded Systems and Software Lab 5 Considerations Lab 5 Considerations Slide 1 Big Picture Keypad Mag-Stripe Card Reader User PINs are stored in μμμμ FLASH memory Swipe Card LCD Lab 5 Considerations Slide
Embedded Systems and Software Lab 5 Considerations Lab 5 Considerations Slide 1 Big Picture Keypad Mag-Stripe Card Reader User PINs are stored in μμμμ FLASH memory Swipe Card LCD Lab 5 Considerations Slide
e-pg Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Interrupt Programming in Embedded C Module No: CS/ES/20 Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Interrupt Programming in Embedded C Module No: CS/ES/20 Quadrant 1 e-text In this lecture embedded C program for interrupt handling
e-pg Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Embedded System Module: Interrupt Programming in Embedded C Module No: CS/ES/20 Quadrant 1 e-text In this lecture embedded C program for interrupt handling
Microcontrollers and Interfacing week 8 exercises
 2 HARDWARE DEBOUNCING Microcontrollers and Interfacing week 8 exercises 1 More digital input When using a switch for digital input we always need a pull-up resistor. For convenience, the microcontroller
2 HARDWARE DEBOUNCING Microcontrollers and Interfacing week 8 exercises 1 More digital input When using a switch for digital input we always need a pull-up resistor. For convenience, the microcontroller
ENGR 40M Project 3c: Switch debouncing
 ENGR 40M Project 3c: Switch debouncing For due dates, see the overview handout 1 Introduction This week, you will build on the previous two labs and program the Arduino to respond to an input from the
ENGR 40M Project 3c: Switch debouncing For due dates, see the overview handout 1 Introduction This week, you will build on the previous two labs and program the Arduino to respond to an input from the
Chapter 11: Interrupt On Change
 Chapter 11: Interrupt On Change The last two chapters included examples that used the external interrupt on Port C, pin 1 to determine when a button had been pressed. This approach works very well on most
Chapter 11: Interrupt On Change The last two chapters included examples that used the external interrupt on Port C, pin 1 to determine when a button had been pressed. This approach works very well on most
BASICS OF THE RENESAS SYNERGY PLATFORM
 BASICS OF THE RENESAS SYNERGY PLATFORM TM Richard Oed 2017.12 02 CHAPTER 9 INCLUDING A REAL-TIME OPERATING SYSTEM CONTENTS 9 INCLUDING A REAL-TIME OPERATING SYSTEM 03 9.1 Threads, Semaphores and Queues
BASICS OF THE RENESAS SYNERGY PLATFORM TM Richard Oed 2017.12 02 CHAPTER 9 INCLUDING A REAL-TIME OPERATING SYSTEM CONTENTS 9 INCLUDING A REAL-TIME OPERATING SYSTEM 03 9.1 Threads, Semaphores and Queues
ELEC 3040/3050 Lab 5. Matrix Keypad Interface Using Parallel I/O
 ELEC 3040/3050 Lab 5 Matrix Keypad Interface Using Parallel I/O Goals of this lab exercise Control a real device with the microcontroller Coordinate parallel I/O ports to control and access a device Implement
ELEC 3040/3050 Lab 5 Matrix Keypad Interface Using Parallel I/O Goals of this lab exercise Control a real device with the microcontroller Coordinate parallel I/O ports to control and access a device Implement
UNIVERSITY OF CONNECTICUT. ECE 3411 Microprocessor Application Lab: Fall Quiz IV
 Department of Electrical and Computing Engineering UNIVERSITY OF CONNECTICUT ECE 3411 Microprocessor Application Lab: Fall 2015 Quiz IV There is 1 questions in this quiz. There are 15 pages in this quiz
Department of Electrical and Computing Engineering UNIVERSITY OF CONNECTICUT ECE 3411 Microprocessor Application Lab: Fall 2015 Quiz IV There is 1 questions in this quiz. There are 15 pages in this quiz
ELEC 3040/3050 Lab 5. Matrix Keypad Interface Using Parallel I/O
 ELEC 3040/3050 Lab 5 Matrix Keypad Interface Using Parallel I/O Goals of this lab exercise Control a real device with the microcontroller Coordinate parallel I/O ports to control and access a device Implement
ELEC 3040/3050 Lab 5 Matrix Keypad Interface Using Parallel I/O Goals of this lab exercise Control a real device with the microcontroller Coordinate parallel I/O ports to control and access a device Implement
ECE PRACTICE EXAM #2 Clocks, Timers, and Digital I/O
 ECE2049 -- PRACTICE EXAM #2 Clocks, Timers, and Digital I/O Study HW3, Class Notes, Davies Ch 2.6, 5.8, 8, 9.2-3, 9.7, MSP43F5529 User's Guide Ch 5, 17, 28 Work all problems with your note sheet first
ECE2049 -- PRACTICE EXAM #2 Clocks, Timers, and Digital I/O Study HW3, Class Notes, Davies Ch 2.6, 5.8, 8, 9.2-3, 9.7, MSP43F5529 User's Guide Ch 5, 17, 28 Work all problems with your note sheet first
Variations on a Theme
 Variations on a Theme Shlomo Engelberg December 27, 2013 1 Chapter 6 of ADuC841 Microcontroller Design Manual: From Microcontroller Theory to Design Projects No variations in this chapter are planned for
Variations on a Theme Shlomo Engelberg December 27, 2013 1 Chapter 6 of ADuC841 Microcontroller Design Manual: From Microcontroller Theory to Design Projects No variations in this chapter are planned for
Unit 13 Timers and Counters
 Unit 13 Timers and Counters 1 2 Review of some key concepts from the first half of the semester A BRIEF SUMMARY 3 A Few Big Ideas 1 Setting and clearing bits in a register tells the hardware what do and
Unit 13 Timers and Counters 1 2 Review of some key concepts from the first half of the semester A BRIEF SUMMARY 3 A Few Big Ideas 1 Setting and clearing bits in a register tells the hardware what do and
BASICS OF THE RENESAS SYNERGY TM
 BASICS OF THE RENESAS SYNERGY TM PLATFORM Richard Oed 2018.11 02 CHAPTER 9 INCLUDING A REAL-TIME OPERATING SYSTEM CONTENTS 9 INCLUDING A REAL-TIME OPERATING SYSTEM 03 9.1 Threads, Semaphores and Queues
BASICS OF THE RENESAS SYNERGY TM PLATFORM Richard Oed 2018.11 02 CHAPTER 9 INCLUDING A REAL-TIME OPERATING SYSTEM CONTENTS 9 INCLUDING A REAL-TIME OPERATING SYSTEM 03 9.1 Threads, Semaphores and Queues
ARM: Microcontroller Touch-switch Design & Test (Part 1)
 ARM: Microcontroller Touch-switch Design & Test (Part 1) 2 nd Year Electronics Lab IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON v2.00 Table of Contents Equipment... 2 Aims... 2 Objectives... 2 Recommended Timetable... 2 Introduction
ARM: Microcontroller Touch-switch Design & Test (Part 1) 2 nd Year Electronics Lab IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON v2.00 Table of Contents Equipment... 2 Aims... 2 Objectives... 2 Recommended Timetable... 2 Introduction
Interrupt handling. Purpose. Interrupts. Computer Organization
 Namn: Laborationen godkänd: Computer Organization Interrupt handling Purpose The purpose of this lab assignment is to give an introduction to interrupts, i.e. asynchronous events caused by external devices
Namn: Laborationen godkänd: Computer Organization Interrupt handling Purpose The purpose of this lab assignment is to give an introduction to interrupts, i.e. asynchronous events caused by external devices
Program Modeling Concepts:
 Program Modeling Concepts: Lesson-6: FSM STATE TABLE AND ITS APPLICATIONS 1 FSM State Table A state table can then be designed for representation of every state in its rows. The following six columns are
Program Modeling Concepts: Lesson-6: FSM STATE TABLE AND ITS APPLICATIONS 1 FSM State Table A state table can then be designed for representation of every state in its rows. The following six columns are
Introduction to Embedded Systems
 Stefan Kowalewski, 4. November 25 Introduction to Embedded Systems Part 2: Microcontrollers. Basics 2. Structure/elements 3. Digital I/O 4. Interrupts 5. Timers/Counters Introduction to Embedded Systems
Stefan Kowalewski, 4. November 25 Introduction to Embedded Systems Part 2: Microcontrollers. Basics 2. Structure/elements 3. Digital I/O 4. Interrupts 5. Timers/Counters Introduction to Embedded Systems
Laboratory 10. Programming a PIC Microcontroller - Part II
 Laboratory 10 Programming a PIC Microcontroller - Part II Required Components: 1 PIC16F88 18P-DIP microcontroller 1 0.1 F capacitor 3 SPST microswitches or NO buttons 4 1k resistors 1 MAN 6910 or LTD-482EC
Laboratory 10 Programming a PIC Microcontroller - Part II Required Components: 1 PIC16F88 18P-DIP microcontroller 1 0.1 F capacitor 3 SPST microswitches or NO buttons 4 1k resistors 1 MAN 6910 or LTD-482EC
CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems (Timers/Input Capture) Instructors: Dr. Phillip Jones
 CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems (Timers/Input Capture) Instructors: Dr. Phillip Jones 1 Announcements HW 4, Due Wed 6/13 Quiz 5 (15 min): Wed 6/13, Textbook reading: Section 9.1, 9.2 (your one-side
CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems (Timers/Input Capture) Instructors: Dr. Phillip Jones 1 Announcements HW 4, Due Wed 6/13 Quiz 5 (15 min): Wed 6/13, Textbook reading: Section 9.1, 9.2 (your one-side
Laboratory Exercise 7
 Laboratory Exercise 7 Using Interrupts with C code The purpose of this exercise is to investigate the use of interrupts for the Nios II processor, using C code. To do this exercise you need to have a good
Laboratory Exercise 7 Using Interrupts with C code The purpose of this exercise is to investigate the use of interrupts for the Nios II processor, using C code. To do this exercise you need to have a good
ECE2049: Embedded Systems in Engineering Design Lab Exercise #3 C Term Making a Time and Temperature Display
 ECE2049: Embedded Systems in Engineering Design Lab Exercise #3 C Term 2019 Making a Time and Temperature Display In this laboratory you will use the MSP430 and several of its peripherals to implement
ECE2049: Embedded Systems in Engineering Design Lab Exercise #3 C Term 2019 Making a Time and Temperature Display In this laboratory you will use the MSP430 and several of its peripherals to implement
F²MC-16FX FAMILY MB96340 KEY MATRIX INTERFACE USING I/O PORT 16-BIT MICROCONTROLLER APPLICATION NOTE. Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe Application Note
 Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe Application ote MCU-A-300238-E-V12 F²MC-16FX FAMIL 16-BIT MICROCOTROLLER MB96340 KE MATRIX ITERFACE APPLICATIO OTE Revision History Revision History Date Issue 2007-04-16
Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe Application ote MCU-A-300238-E-V12 F²MC-16FX FAMIL 16-BIT MICROCOTROLLER MB96340 KE MATRIX ITERFACE APPLICATIO OTE Revision History Revision History Date Issue 2007-04-16
Interrupts, timers and counters
 Interrupts, timers and counters Posted on May 10, 2008, by Ibrahim KAMAL, in Micro-controllers, tagged Most microcontrollers come with a set of ADD-ONs called peripherals, to enhance the functioning of
Interrupts, timers and counters Posted on May 10, 2008, by Ibrahim KAMAL, in Micro-controllers, tagged Most microcontrollers come with a set of ADD-ONs called peripherals, to enhance the functioning of
EE 109 Unit 15 State Machines 15.1
 EE 109 Unit 15 State Machines 15.1 15.2 What is state? You see delicious looking potato salad in the cafeteria? Do you eat it? Ate potato salad as a kid As a teen, ate potato salad at a picnic after a
EE 109 Unit 15 State Machines 15.1 15.2 What is state? You see delicious looking potato salad in the cafeteria? Do you eat it? Ate potato salad as a kid As a teen, ate potato salad at a picnic after a
Lab 3a: Scheduling Tasks with uvision and RTX
 COE718: Embedded Systems Design Lab 3a: Scheduling Tasks with uvision and RTX 1. Objectives The purpose of this lab is to lab is to introduce students to uvision and ARM Cortex-M3's various RTX based Real-Time
COE718: Embedded Systems Design Lab 3a: Scheduling Tasks with uvision and RTX 1. Objectives The purpose of this lab is to lab is to introduce students to uvision and ARM Cortex-M3's various RTX based Real-Time
CSE3215 Embedded Systems Laboratory
 CSE3215 Embedded Systems Laboratory Lab3 Reaction Time Measurement Introduction Human reaction time is a parameter of interest in many psychological and physiological studies of the effects of drugs, stress,
CSE3215 Embedded Systems Laboratory Lab3 Reaction Time Measurement Introduction Human reaction time is a parameter of interest in many psychological and physiological studies of the effects of drugs, stress,
Using programmed I/O on the M16C; and Writing an Interrupt Service Routine (ISR)
 Tutorial 2 Basic M16C Programming 1 Introduction The goal for Tutorial 2 is to take a more in-depth look at the sample program from the previous tutorial, and make use of it as a foundation for writing
Tutorial 2 Basic M16C Programming 1 Introduction The goal for Tutorial 2 is to take a more in-depth look at the sample program from the previous tutorial, and make use of it as a foundation for writing
CHAPTER 11 INTERRUPTS PROGRAMMING
 CHAPTER 11 INTERRUPTS PROGRAMMING Interrupts vs. Polling An interrupt is an external or internal event that interrupts the microcontroller To inform it that a device needs its service A single microcontroller
CHAPTER 11 INTERRUPTS PROGRAMMING Interrupts vs. Polling An interrupt is an external or internal event that interrupts the microcontroller To inform it that a device needs its service A single microcontroller
Investigating IO Interrupts
 Introduction Investigating IO s At the of this lab you should be able to: Describe what interrupt vectors are and explain how they are used Describe two main methods of IO interrupt handling Explain the
Introduction Investigating IO s At the of this lab you should be able to: Describe what interrupt vectors are and explain how they are used Describe two main methods of IO interrupt handling Explain the
Timers and Pulse Accumulator
 7 7.1 Objectives: Tiva is equipped with six General Purpose Timer Modules named TIMERn. Additionally, each TIMERn consists of two 16 bit timers (A and B). Most GPIO pins can be assigned a TIMERn as an
7 7.1 Objectives: Tiva is equipped with six General Purpose Timer Modules named TIMERn. Additionally, each TIMERn consists of two 16 bit timers (A and B). Most GPIO pins can be assigned a TIMERn as an
16.317: Microprocessor Systems Design I Fall Exam 3 December 15, Name: ID #:
 16.317: Microprocessor Systems Design I Fall 2014 Exam 3 December 15, 2014 Name: ID #: For this exam, you may use a calculator and one 8.5 x 11 double-sided page of notes. All other electronic devices
16.317: Microprocessor Systems Design I Fall 2014 Exam 3 December 15, 2014 Name: ID #: For this exam, you may use a calculator and one 8.5 x 11 double-sided page of notes. All other electronic devices
Software debouncing of buttons
 Software debouncing of buttons snigelen February 5, 2015 1 Introduction Connecting a button as an input to a micro-controller is a relatively easy task, but there are some problems. The main problem is
Software debouncing of buttons snigelen February 5, 2015 1 Introduction Connecting a button as an input to a micro-controller is a relatively easy task, but there are some problems. The main problem is
CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems Exam 1 Review. 1
 CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems Exam 1 Review http://class.ece.iastate.edu/cpre288 1 Overview of Today s Lecture Announcements Exam 1 Review http://class.ece.iastate.edu/cpre288 2 Announcements
CprE 288 Introduction to Embedded Systems Exam 1 Review http://class.ece.iastate.edu/cpre288 1 Overview of Today s Lecture Announcements Exam 1 Review http://class.ece.iastate.edu/cpre288 2 Announcements
Embedded Systems Programming
 Embedded Systems Programming Introduction (Module 1) Yann-Hang Lee Arizona State University yhlee@asu.edu (480) 727-7507 Summer 2014 Course Syllabus Course Goals: fundamental issues as well as practical
Embedded Systems Programming Introduction (Module 1) Yann-Hang Lee Arizona State University yhlee@asu.edu (480) 727-7507 Summer 2014 Course Syllabus Course Goals: fundamental issues as well as practical
Lab 9: On-Board Time Generation and Interrupts
 Lab 9: On-Board Time Generation and Interrupts Summary: Develop a program and hardware interface that will utilize externally triggered interrupts and the onboard timer functions of the 68HC12. Learning
Lab 9: On-Board Time Generation and Interrupts Summary: Develop a program and hardware interface that will utilize externally triggered interrupts and the onboard timer functions of the 68HC12. Learning
ECE 362 Experiment 4: Interrupts
 ECE 362 Experiment 4: Interrupts 1.0 Introduction Microprocessors consistently follow a straight sequence of instructions, and you have likely only worked with this kind of programming until now. In this
ECE 362 Experiment 4: Interrupts 1.0 Introduction Microprocessors consistently follow a straight sequence of instructions, and you have likely only worked with this kind of programming until now. In this
Interrupts L33-1. Interrupts
 L33-1 Interrupts Interrupts Interrupts are like receiving a telephone call while you are in a face-to-face meeting: The phone rings (ie, an interrupt is sent) Tell the person you are meeting with to please
L33-1 Interrupts Interrupts Interrupts are like receiving a telephone call while you are in a face-to-face meeting: The phone rings (ie, an interrupt is sent) Tell the person you are meeting with to please
Design and Implementation of Embedded Serial Communication Based on Finite State Machine
 , pp.25-32 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijhit.2015.8.9.03 Design and Implementation of Embedded Serial Communication Based on Finite State Machine Jian Feng and Yuanyuan Ding College of Computer Science
, pp.25-32 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijhit.2015.8.9.03 Design and Implementation of Embedded Serial Communication Based on Finite State Machine Jian Feng and Yuanyuan Ding College of Computer Science
By the end of Class. Outline. Homework 5. C8051F020 Block Diagram (pg 18) Pseudo-code for Lab 1-2 due as part of prelab
 By the end of Class Pseudo-code for Lab 1-2 due as part of prelab Homework #5 on website due before next class Outline Introduce Lab 1-2 Counting Timers on C8051 Interrupts Laboratory Worksheet #05 Copy
By the end of Class Pseudo-code for Lab 1-2 due as part of prelab Homework #5 on website due before next class Outline Introduce Lab 1-2 Counting Timers on C8051 Interrupts Laboratory Worksheet #05 Copy
University of Texas at El Paso Electrical and Computer Engineering Department. EE 3176 Laboratory for Microprocessors I.
 University of Texas at El Paso Electrical and Computer Engineering Department EE 3176 Laboratory for Microprocessors I Fall 2016 LAB 04 Timer Interrupts Goals: Learn about Timer Interrupts. Learn how to
University of Texas at El Paso Electrical and Computer Engineering Department EE 3176 Laboratory for Microprocessors I Fall 2016 LAB 04 Timer Interrupts Goals: Learn about Timer Interrupts. Learn how to
Magic 8 Ball. Student's name & ID (1): Partner's name & ID (2): Your Section number & TA's name
 MPS Magic 8 Ball Lab Exercise Magic 8 Ball Student's name & ID (1): Partner's name & ID (2): Your Section number & TA's name Notes: You must work on this assignment with your partner. Hand in a printer
MPS Magic 8 Ball Lab Exercise Magic 8 Ball Student's name & ID (1): Partner's name & ID (2): Your Section number & TA's name Notes: You must work on this assignment with your partner. Hand in a printer
Unit B - Rotary Encoders B.1
 Unit B - Rotary Encoders B.1 B.2 Rotary Encoders Electromechanical devices used to measure the angular position or rotation of a shaft. Two types: Absolute: Output a binary number for the current angular
Unit B - Rotary Encoders B.1 B.2 Rotary Encoders Electromechanical devices used to measure the angular position or rotation of a shaft. Two types: Absolute: Output a binary number for the current angular
EE475 Lab #3 Fall Memory Placement and Interrupts
 EE475 Lab #3 Fall 2005 Memory Placement and Interrupts In this lab you will investigate the way in which the CodeWarrior compiler and linker interact to place your compiled code and data in the memory
EE475 Lab #3 Fall 2005 Memory Placement and Interrupts In this lab you will investigate the way in which the CodeWarrior compiler and linker interact to place your compiled code and data in the memory
Accelerometer-Based Musical Instrument
 Accelerometer Music Instrument University of Texas at Austin TI Innovation Challenge 2015 Project Report Team Leader: Team Members: Advising Professor: Video Texas Instruments Mentor (if applicable): Date:12/13/2014
Accelerometer Music Instrument University of Texas at Austin TI Innovation Challenge 2015 Project Report Team Leader: Team Members: Advising Professor: Video Texas Instruments Mentor (if applicable): Date:12/13/2014
ECG (EKG) Primer Jingxi Zhang ABSTRACT
 ECG (EKG) Primer Jingxi Zhang ABSTRACT This project is for detecting human ECG (Electrocardiogram, or EKG). A tiny amplifier is embedded (
ECG (EKG) Primer Jingxi Zhang ABSTRACT This project is for detecting human ECG (Electrocardiogram, or EKG). A tiny amplifier is embedded (
Rapid Prototyping System for Teaching Real-Time Digital Signal Processing
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON EDUCATION, VOL. 43, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2000 19 Rapid Prototyping System for Teaching Real-Time Digital Signal Processing Woon-Seng Gan, Member, IEEE, Yong-Kim Chong, Wilson Gong, and
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON EDUCATION, VOL. 43, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2000 19 Rapid Prototyping System for Teaching Real-Time Digital Signal Processing Woon-Seng Gan, Member, IEEE, Yong-Kim Chong, Wilson Gong, and
8051 Peripherals. On-Chip Memory Timers Serial Port Interrupts. Computer Engineering Timers
 8051 Peripherals On-Chip Memory Timers Serial Port Interrupts Computer Engineering 2 2-1 8051 Timers 8051 Timers The 8051 has 2 internal 16-bit timers named Timer 0 and Timer 1 Each timer is a 16-bit counter
8051 Peripherals On-Chip Memory Timers Serial Port Interrupts Computer Engineering 2 2-1 8051 Timers 8051 Timers The 8051 has 2 internal 16-bit timers named Timer 0 and Timer 1 Each timer is a 16-bit counter
Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics, and Computer Science Delft University of Technology
 Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics, and Computer Science Delft University of Technology exam Embedded Software TI2726-B January 28, 2019 13.30-15.00 This exam (6 pages) consists of 60 True/False
Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics, and Computer Science Delft University of Technology exam Embedded Software TI2726-B January 28, 2019 13.30-15.00 This exam (6 pages) consists of 60 True/False
MICROPROCESSORS A (17.383) Fall Lecture Outline
 MICROPROCESSORS A (17.383) Fall 2010 Lecture Outline Class # 03 September 21, 2010 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Syllabus review Microcontroller Hardware and/or Interface Programming/Software Lab Homework
MICROPROCESSORS A (17.383) Fall 2010 Lecture Outline Class # 03 September 21, 2010 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Syllabus review Microcontroller Hardware and/or Interface Programming/Software Lab Homework
Lab 6 Using PicoBlaze. Fast Sorting.
 Lab 6 Using PicoBlaze. Fast Sorting. Design, implement, and verify experimentally a circuit shown in the block diagram below, composed of the following major components: PicoBlaze-6 microcontroller with
Lab 6 Using PicoBlaze. Fast Sorting. Design, implement, and verify experimentally a circuit shown in the block diagram below, composed of the following major components: PicoBlaze-6 microcontroller with
Viewing the tm4c123gh6pm_startup_ccs.c file, the first piece of code we see after the comments is shown in Figure 1.
 Viewing the tm4c123gh6pm_startup_ccs.c file, the first piece of code we see after the comments is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 Forward declaration for the default handlers These are the forward declarations,
Viewing the tm4c123gh6pm_startup_ccs.c file, the first piece of code we see after the comments is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 Forward declaration for the default handlers These are the forward declarations,
WATCHDOG TIMER ISR DEVELOPMENT TDD APPROACH
 WATCHDOG TIMER ISR DEVELOPMENT TDD APPROACH Through the use of user stories You can use a very similar approach when testing your CORE_TIMER ISR during Assignment 2 When developing the coffeepot Water
WATCHDOG TIMER ISR DEVELOPMENT TDD APPROACH Through the use of user stories You can use a very similar approach when testing your CORE_TIMER ISR during Assignment 2 When developing the coffeepot Water
AC OB S. Multi-threaded FW framework (OS) for embedded ARM systems Torsten Jaekel, June 2014
 AC OB S Multi-threaded FW framework (OS) for embedded ARM systems Torsten Jaekel, June 2014 ACOBS ACtive OBject (operating) System Simplified FW System for Multi-Threading on ARM embedded systems ACOBS
AC OB S Multi-threaded FW framework (OS) for embedded ARM systems Torsten Jaekel, June 2014 ACOBS ACtive OBject (operating) System Simplified FW System for Multi-Threading on ARM embedded systems ACOBS
Input/Output Modes Chapter 8
 Input/Output Modes Chapter 8 Microcomputers can communicate with a variety of I/O devices This information can be either data or control Data is usually encoded in numeric or alphanumeric forms such as
Input/Output Modes Chapter 8 Microcomputers can communicate with a variety of I/O devices This information can be either data or control Data is usually encoded in numeric or alphanumeric forms such as
4) In response to the the 8259A sets the highest priority ISR, bit and reset the corresponding IRR bit. The 8259A also places
 Lecture-52 Interrupt sequence: The powerful features of the 8259A in a system are its programmability and the interrupt routine address capability. It allows direct or indirect jumping to the specific
Lecture-52 Interrupt sequence: The powerful features of the 8259A in a system are its programmability and the interrupt routine address capability. It allows direct or indirect jumping to the specific
Lab 3c Performance Debugging Page 3c.1
 Lab 3c Performance Debugging Page 3c.1 Lab 3c Performance Debugging This laboratory assignment accompanies the book, Embedded Microcomputer Systems: Real Time Interfacing, by, published by Brooks-Cole,
Lab 3c Performance Debugging Page 3c.1 Lab 3c Performance Debugging This laboratory assignment accompanies the book, Embedded Microcomputer Systems: Real Time Interfacing, by, published by Brooks-Cole,
The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL
 The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Comp 541 Digital Logic and Computer Design Prof. Montek Singh Fall 2016 Lab #6: A Multidigit Display and a Stop Watch Issued Wed 9/28/16; Due Fri 10/7/16
The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Comp 541 Digital Logic and Computer Design Prof. Montek Singh Fall 2016 Lab #6: A Multidigit Display and a Stop Watch Issued Wed 9/28/16; Due Fri 10/7/16
Interrupt Basics Karl-Ragmar Riemschneider
 Interrupt Basics Exceptions and Interrupts Interrupts Handlers vs. Subroutines Accept or hold Pending: Priority control Exception vector table Example Karl-Ragmar Riemschneider Exceptions
Interrupt Basics Exceptions and Interrupts Interrupts Handlers vs. Subroutines Accept or hold Pending: Priority control Exception vector table Example Karl-Ragmar Riemschneider Exceptions
CSC227: Operating Systems Fall Chapter 1 INTERRUPTS. Dr. Soha S. Zaghloul
 CSC227: Operating Systems Fall 2016 Chapter 1 INTERRUPTS Dr. Soha S. Zaghloul LAYOUT 1.3 Devices Controlling Techniques 1.3.1 Polling 1.3.2 Interrupts H/W Interrupts Interrupt Controller Process State
CSC227: Operating Systems Fall 2016 Chapter 1 INTERRUPTS Dr. Soha S. Zaghloul LAYOUT 1.3 Devices Controlling Techniques 1.3.1 Polling 1.3.2 Interrupts H/W Interrupts Interrupt Controller Process State
Registers Format. 4.1 I/O Port Address
 4 Registers Format The detailed descriptions of the register format and structure of the ACL- 8112 are specified in this chapter. This information is quite useful for the programmer who wish to handle
4 Registers Format The detailed descriptions of the register format and structure of the ACL- 8112 are specified in this chapter. This information is quite useful for the programmer who wish to handle
SRI VENKATESWARA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
 COURSE DELIVERY PLAN - THEORY Page 1 of 6 Department of Computer Science & Engineering / Information Technology B.E/B.Tech/M.E/M.Tech : B.E - CSE / B.Tech - IT Regulation: 2013 PG Specialisation : - Sub.
COURSE DELIVERY PLAN - THEORY Page 1 of 6 Department of Computer Science & Engineering / Information Technology B.E/B.Tech/M.E/M.Tech : B.E - CSE / B.Tech - IT Regulation: 2013 PG Specialisation : - Sub.
Page 1. Logistics. Introduction to Embedded Systems. Last Time. ES Software Design. Labs start Wed CS/ECE 6780/5780. Al Davis
 Logistics Introduction to Embedded Systems CS/ECE 6780/5780 Al Davis Today s topics: logistics - minor synopsis of last lecture software desig finite state machine based control Labs start Wed make sure
Logistics Introduction to Embedded Systems CS/ECE 6780/5780 Al Davis Today s topics: logistics - minor synopsis of last lecture software desig finite state machine based control Labs start Wed make sure
ECGR 4101/5101, Fall 2011: Lab 4 A pseudo physics simulator with remote communication.
 Learning Objectives: ECGR 4101/5101, Fall 2011: Lab 4 A pseudo physics simulator with remote communication. This lab will test your ability to apply the knowledge you have obtained from the last three
Learning Objectives: ECGR 4101/5101, Fall 2011: Lab 4 A pseudo physics simulator with remote communication. This lab will test your ability to apply the knowledge you have obtained from the last three
Computer Labs: I/O and Interrupts
 Computer Labs: I/O and Interrupts 2 o MIEIC Pedro F. Souto (pfs@fe.up.pt) October 3, 2010 I/O Operation I/O devices are the interface between the computer and its environment Most of the time, the processor
Computer Labs: I/O and Interrupts 2 o MIEIC Pedro F. Souto (pfs@fe.up.pt) October 3, 2010 I/O Operation I/O devices are the interface between the computer and its environment Most of the time, the processor
Human Response Timer
 Human Response Timer Matthew Beckler beck0778@umn.edu EE2361 Lab Section 007 March 29, 2006 Abstract In this lab, we create a very useful application, a human response timer. The user s reaction time is
Human Response Timer Matthew Beckler beck0778@umn.edu EE2361 Lab Section 007 March 29, 2006 Abstract In this lab, we create a very useful application, a human response timer. The user s reaction time is
Module 3. Embedded Systems I/O. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 3 Embedded Systems I/O Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 15 Interrupts Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would learn Interrupts
Module 3 Embedded Systems I/O Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 15 Interrupts Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would learn Interrupts
Lecture 9. Timer Operations and Programming
 Lecture 9 Timer Operations and Programming Timer Operations and Programming Introduction Summary of timers Timer programming sequence Summary of timer SFRs Timer 0-1: 8-bit auto-reload mode (mode 2) Programming
Lecture 9 Timer Operations and Programming Timer Operations and Programming Introduction Summary of timers Timer programming sequence Summary of timer SFRs Timer 0-1: 8-bit auto-reload mode (mode 2) Programming
I/O handling. Purpose. Seven-segment displays. Digital Systems 15 hp
 Namn: Laborationen godkänd: Digital Systems 15 hp I/O handling Purpose The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to demonstrate how to write programs that interact with the different I/O devices available
Namn: Laborationen godkänd: Digital Systems 15 hp I/O handling Purpose The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to demonstrate how to write programs that interact with the different I/O devices available
Lesson 5: Software for embedding in System- Part 2
 Lesson 5: Software for embedding in System- Part 2 Device drivers, Device manager, OS, RTOS and Software tools 1 Outline Device drivers Device manager Multitasking using an operating system (OS) and Real
Lesson 5: Software for embedding in System- Part 2 Device drivers, Device manager, OS, RTOS and Software tools 1 Outline Device drivers Device manager Multitasking using an operating system (OS) and Real
LPC4088 Timer Interrupts CM0506 Small Embedded Systems
 LPC4088 Timer Interrupts CM0506 Small Embedded Systems Dr Alun Moon Seminar 5 Here the module begins to separate from EN0572. The programming structure will make extensive use of interrupts to handle events,
LPC4088 Timer Interrupts CM0506 Small Embedded Systems Dr Alun Moon Seminar 5 Here the module begins to separate from EN0572. The programming structure will make extensive use of interrupts to handle events,
CSC 2405: Computer Systems II
 CSC 2405: Computer Systems II Dr. Mirela Damian http://www.csc.villanova.edu/~mdamian/csc2405/ Spring 2016 Course Goals: Look under the hood Help you learn what happens under the hood of computer systems
CSC 2405: Computer Systems II Dr. Mirela Damian http://www.csc.villanova.edu/~mdamian/csc2405/ Spring 2016 Course Goals: Look under the hood Help you learn what happens under the hood of computer systems
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SANTA CRUZ BOARD OF STUDIES IN COMPUTER ENGINEERING CMPE13/L: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING IN C SPRING 2013
 Introduction Reading Concepts UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SANTA CRUZ BOARD OF STUDIES IN COMPUTER ENGINEERING CMPE13/L: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING IN C SPRING 2013 Lab 2 Bouncing LEDs In this lab, you will
Introduction Reading Concepts UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SANTA CRUZ BOARD OF STUDIES IN COMPUTER ENGINEERING CMPE13/L: INTRODUCTION TO PROGRAMMING IN C SPRING 2013 Lab 2 Bouncing LEDs In this lab, you will
Exceptions in H8S/2357. Exercise Interrupts "Traffic Light Controller"
 Exceptions in H8S/2357 Exercise Interrupts "Traffic Light Controller" - Principles Time Based Event Handling - Implementation H8S/2357 as Internal TPU Controlled Interrupts - Recapitulation - Handling
Exceptions in H8S/2357 Exercise Interrupts "Traffic Light Controller" - Principles Time Based Event Handling - Implementation H8S/2357 as Internal TPU Controlled Interrupts - Recapitulation - Handling
EE345L Spring 2004 Quiz 1 Page 1 of 5. Last Name: First Name:
 EE345L Spring 2004 Quiz 1 Page 1 of 5 Last Name: First Name: Jonathan W. Valvano February 25, 2004, 1:00pm-1:50pm This is a closed book exam. No notes or calculators are allowed, just a pencil and eraser.
EE345L Spring 2004 Quiz 1 Page 1 of 5 Last Name: First Name: Jonathan W. Valvano February 25, 2004, 1:00pm-1:50pm This is a closed book exam. No notes or calculators are allowed, just a pencil and eraser.
UNIVERSITY OF CONNECTICUT. ECE 3411 Microprocessor Application Lab: Fall Quiz V
 Department of Electrical and Computing Engineering UNIVERSITY OF CONNECTICUT ECE 3411 Microprocessor Application Lab: Fall 2015 Quiz V There are 3 questions in this quiz. There are 10 pages in this quiz
Department of Electrical and Computing Engineering UNIVERSITY OF CONNECTICUT ECE 3411 Microprocessor Application Lab: Fall 2015 Quiz V There are 3 questions in this quiz. There are 10 pages in this quiz
Interrupt and Timer ISRs. Student's name & ID: Partner's name(s) & ID(s): Your Section number & TA's name
 MPS Interrupt Lab Exercise Interrupt and Timer ISRs Student's name & ID: Partner's name(s) & ID(s): Your Section number & TA's name Notes: You must work on this assignment with your partner. Hand in a
MPS Interrupt Lab Exercise Interrupt and Timer ISRs Student's name & ID: Partner's name(s) & ID(s): Your Section number & TA's name Notes: You must work on this assignment with your partner. Hand in a
Application Note One Wire Digital Output. 1 Introduction. 2 Electrical Parameters for One Wire Interface. 3 Start and Data Transmission
 Application Note One Wire Digital Output 1 Introduction The pressure transmitter automatically outputs pressure data, and when appropriate temperature data, in a fixed interval. The host simply waits for
Application Note One Wire Digital Output 1 Introduction The pressure transmitter automatically outputs pressure data, and when appropriate temperature data, in a fixed interval. The host simply waits for
Interrupts Peter Rounce - room 6.18
 Interrupts Peter Rounce - room 6.18 P.Rounce@cs.ucl.ac.uk 20/11/2006 1001 Interrupts 1 INTERRUPTS An interrupt is a signal to the CPU from hardware external to the CPU that indicates than some event has
Interrupts Peter Rounce - room 6.18 P.Rounce@cs.ucl.ac.uk 20/11/2006 1001 Interrupts 1 INTERRUPTS An interrupt is a signal to the CPU from hardware external to the CPU that indicates than some event has
Embedded systems. Exercise session 3. Microcontroller Programming Lab Preparation
 Embedded systems Exercise session 3 Microcontroller Programming Lab Preparation Communications Contact Mail : michael.fonder@ulg.ac.be Office : 1.82a, Montefiore Website for the exercise sessions and the
Embedded systems Exercise session 3 Microcontroller Programming Lab Preparation Communications Contact Mail : michael.fonder@ulg.ac.be Office : 1.82a, Montefiore Website for the exercise sessions and the
 UNIT II SYSTEM BUS STRUCTURE 1. Differentiate between minimum and maximum mode 2. Give any four pin definitions for the minimum mode. 3. What are the pins that are used to indicate the type of transfer
UNIT II SYSTEM BUS STRUCTURE 1. Differentiate between minimum and maximum mode 2. Give any four pin definitions for the minimum mode. 3. What are the pins that are used to indicate the type of transfer
Digital Input and Output
 Digital Input and Output Topics: Parallel Digital I/O Simple Input (example) Parallel I/O I/O Scheduling Techniques Programmed Interrupt Driven Direct Memory Access Serial I/O Asynchronous Synchronous
Digital Input and Output Topics: Parallel Digital I/O Simple Input (example) Parallel I/O I/O Scheduling Techniques Programmed Interrupt Driven Direct Memory Access Serial I/O Asynchronous Synchronous
Using the KD30 Debugger
 ELEC3730 Embedded Systems Tutorial 3 Using the KD30 Debugger 1 Introduction Overview The KD30 debugger is a powerful software tool that can greatly reduce the time it takes to develop complex programs
ELEC3730 Embedded Systems Tutorial 3 Using the KD30 Debugger 1 Introduction Overview The KD30 debugger is a powerful software tool that can greatly reduce the time it takes to develop complex programs
Parallel I/O and Keyboard Scanning
 4 4.1 Objectives: Microprocessors can monitor the outside world using input ports. They can also control it using output ports. The TM4C123G (Tiva) performs I/O using 6 ports. Computer keyboards are typically
4 4.1 Objectives: Microprocessors can monitor the outside world using input ports. They can also control it using output ports. The TM4C123G (Tiva) performs I/O using 6 ports. Computer keyboards are typically
5.1. Unit 5. State Machines
 5.1 Unit 5 State Machines 5.2 What is state? You see a DPS officer approaching you. Are you happy? It's late at night and your car broke down. It's late at night and you've been partying a little too hard.
5.1 Unit 5 State Machines 5.2 What is state? You see a DPS officer approaching you. Are you happy? It's late at night and your car broke down. It's late at night and you've been partying a little too hard.
How to Properly Manage Tabor s AWG Arbitrary Memory
 How to Properly Manage Tabor s AWG Arbitrary Memory In this tutorial, we will give a quick start guide on how you can manage the Tabor AWG s arbitrary memory using a specific set of Standard Commands for
How to Properly Manage Tabor s AWG Arbitrary Memory In this tutorial, we will give a quick start guide on how you can manage the Tabor AWG s arbitrary memory using a specific set of Standard Commands for
CprE 288 Translating C Control Statements and Function Calls, Loops, Interrupt Processing. Instructors: Dr. Phillip Jones Dr.
 CprE 288 Translating C Control Statements and Function Calls, Loops, Interrupt Processing Instructors: Dr. Phillip Jones Dr. Zhao Zhang 1 Announcements Final Projects Projects: Mandatory Demos Deadweek
CprE 288 Translating C Control Statements and Function Calls, Loops, Interrupt Processing Instructors: Dr. Phillip Jones Dr. Zhao Zhang 1 Announcements Final Projects Projects: Mandatory Demos Deadweek
Interrupts & Interrupt Service Routines (ISRs)
 ECE3411 Fall 2015 Lecture 2c. Interrupts & Interrupt Service Routines (ISRs) Marten van Dijk, Syed Kamran Haider Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut Email: vandijk,
ECE3411 Fall 2015 Lecture 2c. Interrupts & Interrupt Service Routines (ISRs) Marten van Dijk, Syed Kamran Haider Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut Email: vandijk,
This resource describes how to program the myrio in C to perform timer interrupts.
 Resource 07 Timer interrupts This resource describes how to program the myrio in C to perform timer interrupts. C.07.1 Main thread: background Initializing the timer interrupt is similar to initializing
Resource 07 Timer interrupts This resource describes how to program the myrio in C to perform timer interrupts. C.07.1 Main thread: background Initializing the timer interrupt is similar to initializing
MEDIS Module 2. Microcontroller based systems for controlling industrial processes. Chapter 4: Timer and interrupts. M. Seyfarth, Version 0.
 MEDIS Module 2 Microcontroller based systems for controlling industrial processes Chapter 4: Timer and interrupts M. Seyfarth, Version 0.1 Steuerungstechnik 1: Speicherprogrammierbare Steuerungstechnik
MEDIS Module 2 Microcontroller based systems for controlling industrial processes Chapter 4: Timer and interrupts M. Seyfarth, Version 0.1 Steuerungstechnik 1: Speicherprogrammierbare Steuerungstechnik
Chapter 6 PROGRAMMING THE TIMERS
 Chapter 6 PROGRAMMING THE TIMERS Lesson 3 Real Time Clocked Interrupts and Software Timers 2 Real Time Clock Interrupt 3 Real Time interrupts Prescaling Pre-scaling by RT1-RT0 bits for 4 or 8 or 16 2 13
Chapter 6 PROGRAMMING THE TIMERS Lesson 3 Real Time Clocked Interrupts and Software Timers 2 Real Time Clock Interrupt 3 Real Time interrupts Prescaling Pre-scaling by RT1-RT0 bits for 4 or 8 or 16 2 13
Mechatronics Laboratory Assignment 2 Serial Communication DSP Time-Keeping, Visual Basic, LCD Screens, and Wireless Networks
 Mechatronics Laboratory Assignment 2 Serial Communication DSP Time-Keeping, Visual Basic, LCD Screens, and Wireless Networks Goals for this Lab Assignment: 1. Introduce the VB environment for PC-based
Mechatronics Laboratory Assignment 2 Serial Communication DSP Time-Keeping, Visual Basic, LCD Screens, and Wireless Networks Goals for this Lab Assignment: 1. Introduce the VB environment for PC-based
Task Based Programming Revisited Real Time Operating Systems
 ECE3411 Fall 2016 Lecture 6a. Task Based Programming Revisited Real Time Operating Systems Marten van Dijk, Syed Kamran Haider Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
ECE3411 Fall 2016 Lecture 6a. Task Based Programming Revisited Real Time Operating Systems Marten van Dijk, Syed Kamran Haider Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
Programmed I/O (busy( wait) ) method for ports and devices, and the need for interrupt driven IOs
 DEVICE DRIVERS AND INTERRUPTS SERVICE MECHANISM Lesson-1: Programmed I/O (busy( and wait) ) method for ports and devices, and the need for interrupt driven IOs 1 Programmed IOs approach from ports and
DEVICE DRIVERS AND INTERRUPTS SERVICE MECHANISM Lesson-1: Programmed I/O (busy( and wait) ) method for ports and devices, and the need for interrupt driven IOs 1 Programmed IOs approach from ports and
Microprocessors B (17.384) Spring Lecture Outline
 Microprocessors B (17.384) Spring 2013 Lecture Outline Class # 04 February 12, 2013 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Administrative Microcontroller Hardware and/or Interface Programming/Software Lab Homework
Microprocessors B (17.384) Spring 2013 Lecture Outline Class # 04 February 12, 2013 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Administrative Microcontroller Hardware and/or Interface Programming/Software Lab Homework
Laboratory Exercise 7
 Laboratory Exercise 7 Finite State Machines This is an exercise in using finite state machines. Part I We wish to implement a finite state machine (FSM) that recognizes two specific sequences of applied
Laboratory Exercise 7 Finite State Machines This is an exercise in using finite state machines. Part I We wish to implement a finite state machine (FSM) that recognizes two specific sequences of applied
Events! Event Driven Embedded Software and UML State Charts. Matthew Eshleman covemountainsoftware.com
 Events! Event Driven Embedded Software and UML State Charts Matthew Eshleman covemountainsoftware.com Background - Matthew Eshleman Nearly 20 years of embedded software engineering, architecture, and project
Events! Event Driven Embedded Software and UML State Charts Matthew Eshleman covemountainsoftware.com Background - Matthew Eshleman Nearly 20 years of embedded software engineering, architecture, and project
These three counters can be programmed for either binary or BCD count.
 S5 KTU 1 PROGRAMMABLE TIMER 8254/8253 The Intel 8253 and 8254 are Programmable Interval Timers (PTIs) designed for microprocessors to perform timing and counting functions using three 16-bit registers.
S5 KTU 1 PROGRAMMABLE TIMER 8254/8253 The Intel 8253 and 8254 are Programmable Interval Timers (PTIs) designed for microprocessors to perform timing and counting functions using three 16-bit registers.

